

Item added to your cart
How to write a business plan for your fruit and vegetable store.

A fruit and vegetable store is a great way to provide healthy, fresh food to local communities while also providing a stable source of income.
Additionally, it's an excellent way to support local farmers and increase access to a variety of fresh produce.
But, first thing first, you need a business plan.
A business plan is essential for any new project, as it lays out the goals, objectives, and strategies for success. It provides a roadmap to guide the project and helps to ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page.
In short, a good business plan will help ensure the profitability of your fruit and vegetable store .
What information should you put into the business plan of a fruit and vegetable store? How can it be effectively planned? What are the essential financial figures to include? How can I outline a comprehensive business plan quickly?
Prepare for a thorough exploration of these questions with detailed answers right here!
Additionally, it's worth noting that you have the option to avoid starting your business plan from scratch.
You can download our comprehensive business plan for a fruit and vegetable store and adjust it to match your preferences.
Formulating a business plan for a fruit and vegetable store
Do you need to develop a business plan for your fruit and vegetable store.
Yes, you need to develop a business plan for your fruit and vegetable store.
Creating an effective business plan will help you to:
- learn about the fruit and vegetable market
- stay current with consumer trends and infuse them into your project
- establish success factors for a fruit and vegetable store
- understand which fruits and vegetables are the most popular
- come up with a winning value proposition for your produce market
- monitor competitor partnerships and alliances
- find competitive advantages for your fruit and vegetable store
- find a business model that creates a path to financial viability
- devise a winning strategy that encompasses both short and long-term goals
- assess the risks associated with operating a fruit and vegetable store, such as inventory spoilage and quality control
Our team has drafted a business plan for a fruit and vegetable store that is designed to make it easier for you to achieve all the elements listed.
How to outline a business plan for a fruit and vegetable store?
Inside a business plan, you'll find a lot of important information and details. There should be a clear structure, so it does not look messy.
When we built and designed our business plan for a fruit and vegetable store , we structured it in a proper way.
You'll find 5 sections (Opportunity, Project, Market Research, Strategy and Finances) here.
1. Market Opportunity
The introductory section has been named "Market Opportunity".
Our team has gathered essential information and metrics about the fruit and vegetable store business, enabling you to make informed business decisions.
This section undergoes updates twice a year for up-to-date data.
2. Project Presentation
The "Project" section provides an opportunity to describe your fruit and vegetable store, highlighting the freshness and variety of produce you offer, locally sourced options, organic selections, customer assistance, seasonal offerings, and the unique value proposition that promotes healthy eating and supports local farmers.
At the end of this section, provide a brief introduction about yourself and your commitment to providing fresh and high-quality produce.
Explain your range of fruits and vegetables, your dedication to supporting local farmers, and how you plan to create a vibrant and inviting shopping experience at your fruit and vegetable store. Highlight your focus on seasonal produce, your knowledgeable staff, and your dedication to promoting healthy eating and sustainable agriculture through your fruit and vegetable store.
We wrote some words in our business plan. Tailor it to match your idea exactly.
3. Market Research
Following that, we have the "Market Research" section.
This section provides a description of the market segments for your fruit and vegetable store.
It includes an analysis of competing grocery stores and highlights your store's focus on fresh produce and competitive advantages. A customized SWOT analysis is also included.
4. Strategy
The "Strategy" section presents a comprehensive 3-year action plan, outlining the initiatives and actions required to make your fruit and vegetable store a highly profitable venture.
Furthermore, this section includes a marketing strategy for a fruit and vegetable store, a risk management approach, and a completed Business Model Canvas.
5. Finances
Finally, you'll arrive at the "Finances" section, which displays the financial metrics and calculations for your project.

How to write the Executive Summary for a fruit and vegetable store?
The Executive Summary is a concise overview of the business plan of your fruit and vegetable store.
Don't exceed 2 pages, including only the critical information.
The goal of this document is to make the reader want to read your business plan.
In the Executive Summary of your fruit and vegetable store, answer these questions: what's the innovation behind your project? what's your audience? do you have competitors? are you better than them? what's your background? what's the budget you need?
How to do the market analysis for a fruit and vegetable store?
Conducting a market study for your fruit and vegetable store allows you to understand external factors like customer preferences, demand patterns, and competition in the market.
By conducting a comprehensive market analysis, a nail bar salon can gain a competitive advantage, enhance its service offerings, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns, ultimately leading to an increased customer base and higher demand for nail care services.
Here's what we've incorporated into the "Market Research" section of our business plan for a fruit and vegetable store :
- market trends and data about the fruit and vegetable industry, including consumer preferences, organic produce demand, and sales growth
- a compilation of potential audiences for a fruit and vegetable store
- the competitive analysis
- the potential competitive advantages for a fruit and vegetable store

The key points of the business plan for a fruit and vegetable store
What's the business model of a fruit and vegetable store, business model of a fruit and vegetable store.
A fruit and vegetable store's business model centers around sourcing and selling fresh produce.
The store procures its inventory from local farmers, wholesalers, and distributors to offer customers a variety of high-quality options. By curating fresh and visually appealing produce, the store provides value to customers seeking nutritious and diverse choices. Revenue is primarily generated through produce sales, with pricing strategies based on procurement costs and market demand. The store may also form partnerships with local suppliers and target specific customer segments to enhance its operations and cater to unique preferences.
Business model ≠ Business plan
Avoid confusing "business plan" with "business model."
A business model describes how a company generates income and operates successfully.
In a business plan, you describe your business model by means of a device known as the Business Model Canvas.
Rest assured, we provide a Business Model Canvas in our business plan for a fruit and vegetable store .
How to identify the market segments of a fruit and vegetable store?
Market segmentation for your fruit and vegetable store involves dividing your potential customers into different groups based on their produce preferences, dietary needs, and demographics.
These categories may include factors such as organic produce, locally sourced options, specialty fruits and vegetables, or customers seeking specific fruit and vegetable varieties or culinary uses.
By segmenting your market, you can offer specialized fruit and vegetable options and shopping experiences that cater to each segment's specific requirements. For example, you might focus on organic produce and provide a wide selection of organic fruits and vegetables for health-conscious customers, offer locally sourced options and support local farmers and sustainable agriculture, specialize in specialty fruits and vegetables that are not commonly found in traditional grocery stores, or focus on specific fruit and vegetable varieties or culinary uses to accommodate customers with specific preferences or cooking styles.
Market segmentation allows you to effectively target your marketing efforts, communicate the freshness and quality of your fruit and vegetable offerings, and provide a convenient and diverse shopping experience that meets the unique needs and preferences of each customer segment.
In the business plan for a fruit and vegetable store , you will find a detailed market segmentation that gives you insights into your potential customers.
How to conduct a competitor analysis for a fruit and vegetable store?
Without surprise, you won't be the only fruit and vegetable store in your market. There will be other retailers offering a wide selection of fresh produce to customers.
Make sure to thoroughly analyze your competitors as part of your business plan by listing their attributes, strengths, and weaknesses.
Take stock of their weaknesses (such as limited produce variety, inadequate freshness control, or poor customer satisfaction).
Why is it important to address these concerns? Because these weaknesses can impact customer satisfaction when shopping at fruit and vegetable stores.
By focusing on these areas, you can offer fresh and high-quality fruits and vegetables, provide a visually appealing and well-organized store layout, and deliver friendly and knowledgeable customer service, positioning your fruit and vegetable store as a preferred choice for healthy and nutritious produce.
It's what we call competitive advantages—cultivate them to make your business shine.
Here are some examples of competitive advantages for a produce market: fresh and locally sourced produce, competitive pricing, friendly and knowledgeable staff.
How to draft a SWOT analysis for a produce market?
A SWOT analysis can help identify potential opportunities and threats to a fruit and vegetable store's success.
As you can guess, there is indeed a completed and editable SWOT matrix in our business plan for a fruit and vegetable store
The strengths for a fruit and vegetable store
S represents Strengths, which are the project's internal factors or attributes that give it a competitive advantage.
For a fruit and vegetable store, four possible strengths could be fresh produce, variety of produce, knowledgeable staff, and competitive pricing.
The weaknesses for a fruit and vegetable store
The "W" represents Weaknesses, indicating the areas or aspects of the project that need enhancement.
For a fruit and vegetable store, potential weaknesses could include limited product variety, lack of convenient locations, short shelf life of products, and inability to compete with larger grocery stores.
The opportunities for a fruit and vegetable store
O stands for Opportunities in SWOT, representing the external factors or circumstances that can benefit the project.
In the case of a fruit and vegetable store, potential opportunities could include offering delivery services, providing a subscription-based ordering option, expanding to offer other organic products, and creating a loyalty program.
The threats for a fruit and vegetable store
The letter "T" denotes Threats in SWOT, signifying the external risks or unfavorable factors that can impact the project's outcomes.
How to develop a marketing plan for a produce market?
A marketing strategy is a necessary component of a business plan as it describes how a business will engage customers and generate sales.
Implementing a targeted marketing plan will attract health-conscious customers in need of fresh and organic fruits and vegetables to your store.
Health-conscious individuals won't shop at your fruit and vegetable store without proper promotion; highlighting the freshness, variety, and health benefits of your products is necessary.
Have you explored marketing approaches to attract customers to your fruit and vegetable store? Consider offering organic or locally sourced produce, running targeted advertising campaigns during health-focused seasons, and partnering with fitness centers or wellness influencers for promotions.
Don't worry if you don't know anything about marketing and communication.
How to build a solid financial plan for a produce market?
A solid business plan must include detailed financial information such as projected income, expenses, cash flow, and balance sheets.
When constructing your business plan, it is crucial to incorporate revenue projections for your fruit and vegetable store.
It's important to create a revenue forecast that is relevant and trustworthy.
Our financial plan for a fruit and vegetable store is easy to use and includes built-in checks to help you identify and correct any assumptions, ensuring you create reliable projections with confidence.
Of course, you'll need to create a preliminary budget for the launch of your fruit and vegetable store . Don't overlook any expense. By the way, we've listed them all in our financial plan!
The break-even analysis is central in the financial plan as it will tell you whether your fruit and vegetable store will be profitable or not.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.

Vegetable Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans » Agriculture Sector

Are you about starting a vegetable farm? If YES, here’s a complete sample vegetable farming business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE to raise money .
Okay, so we have considered all the requirements for starting a vegetable farming business. We also took it further by analyzing and drafting a sample vegetable farming marketing plan template backed up by actionable guerrilla marketing ideas for vegetable farms. So let’s proceed to the business planning section.
Suggested for You
- Marijuana Cultivation Business Plan [Sample Template]
- CBD Hemp Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Lavender Farm Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Soybean Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Rose Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
Why Start a Vegetable Farming Business?
As an aspiring entrepreneur who is interested in starting a business in the agricultural sector of your country, you can be rest assured that there are loads of business opportunities available, and vegetable farming is one of them. Vegetable farming is known to be a profitable business which has over the years evolved from small scale (backyard garden), into a global industry in all countries where it is carried out.
Countries in the Caribbean, South America, North America, Europe, Asia, Australia and Africa are known to be in the forefront when it comes to cultivating varieties of vegetables. If you are considering starting a vegetable farm business, the good news is that you cannot get it wrong.
This is because various types of vegetable are consumed by almost everybody all over the globe. It is important to state that starting a vegetable farming business comes with its own share of challenges, but that does not rule out the fact that it is indeed a profitable business venture.
An aspiring entrepreneur can either choose to start a vegetable farm on a small scale or on a large scale depending on their financial status.
If you have decided to go into vegetable farming, then you should ensure that you carry out thorough feasibility studies and market survey. Business plan is yet another very important business document that you should not take for granted when launching your own vegetable farming business.
Below is a sample vegetable farming business plan template that can help you to successfully write your own with little or no difficulty.
A Sample Vegetable Farming Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Vegetable farmers grow a wide variety of vegetables in open fields and in greenhouses. Some vegetable farmers also grow a variety of fruits and other crops.
If you are a close observer of the vegetable farming industry, you will agree that the industry is anticipated to increase due to increasing consumer health consciousness, which has led to increasing demand for fresh produce. While per capita fruit and vegetable consumption has remained stable in recent time, the price of vegetables has increased as consumers demand premium, fresh vegetables.
So also, the number of both small and large farms has been increasing. Small, local farms are benefiting from the organic, local movement, while large, commercial farms are improving labor efficiency. Going forward, players in the vegetable farming industry will continue to increase revenue generation for their business.
The Vegetable Farming industry is indeed a fast – growing industry that is pretty much active in all countries of the world. As a matter of fact, The Netherlands has some of the largest greenhouses where vegetables are cultivated in the world.
That is the scale of food production in the country so much so that in 2000 alone, greenhouses occupied about 10,526 hectares, or 0.25 percent of the total land area.
The Netherlands has an estimate of 4,000 greenhouse establishments that operate well over 9,000 hectares of greenhouses and employ about 150,000 workers, producing €7.2 billion worth of vegetables, fruit, plants and flowers, some 80% of which are exported.
Statistics has it that in the united states of America alone, there are about 76,459 registered and licensed vegetable farms scattered all across the United States responsible for employing about 317,590 and the industry rakes in a whooping sum of $26 billion annually. The industry is projected to enjoy 2.5 percent annual growth.
One thing is certain when it comes to vegetable farming, if you are able to conduct your market research and feasibility studies before choosing a location for cultivating your vegetable, you are likely not going to struggle to grow the vegetable farming business and also sell your vegetables because there are always food processing companies and consumers out there who are ready to buy from you.
Lastly, with vegetable farming it will pay you not to only cultivate vegetable and sell them for consumption in farm markets to retailers and consumers. You can as well start a complimentary business like vegetable processing plant to package your vegetables to save cost.
The bottom line is that if you have enough farm land (space) and you are interested in maximizing vegetable farming, you are sure going to make huge profits from the business.
2. Executive Summary
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a registered and licensed commercial farm that will be based in the outskirts of Los Angeles, California – United States. We have done our detailed market research and feasibility studies and we were able to secure 25 hectares of land to start our vegetable farm.
We will always leverage on greenhouse farming to cultivate vegetable hence we will construct a structure with walls and roof made essentially of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.
At Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC we will be involved in the cultivation of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress,
Basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries. We will also be involved in greenhouse vegetable production.
In the nearest future, hopefully within the first five years of officially running Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC, we will start our food processing and packaging plant and also start exporting our vegetables to other parts of the world.
This is why aside from the fact that we have secured the required farm land and most of the farming equipment and machines, we have also hired key employees who are currently undergoing training so as to be able to fit into the ideal picture of the 21 st century vegetable farming business workforce that we want to build.
We are in the vegetable farming business because we want to leverage on the vast opportunities available in the agriculture industry to contribute our quota in growing the U.S. economy, in national food production, raw materials production for industries, to export agricultural produce from the United States to other countries and over and above to make profit.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is well positioned to become one of the leading vegetable farms in the United States of America, which is why we have been able to source the best hands and machines to run the business with. We have put process and strategies in place that will help us employ best practices when it comes to vegetable farming in the United States of America.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a Private registered commercial farm that is owned by Johnson Jael and his immediate family members. The company will be fully and single handedly managed by the owner – Johnson Jael and his immediate family members at least for a period of time.
3. Our Products and Services
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a commercial farm that will be cultivating various vegetables via greenhouse farming model and land farming for both the United States’ market and the global market. We are in business to produce both vegetables and fruits in commercial quantities.
We will also ensure that we operate a standard food processing and packaging plant as part of our complimentary services. We are in this line of business to make profit and we will ensure that we do all that is allowed by the law of the United States of America to achieve our business goals and objectives.
These are the areas we will concentrate on in our vegetable farms. If need arises we will definitely add more agriculture produce to our list;
- Cultivation of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
- Vegetable and fruit processing and packaging
- Greenhouse construction, consultancy and advisory services
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our Vision is to become one of the leading vegetable farm brands not just in the United States of America but also on the global stage.
- Our mission statement as a commercial farm is to go into full – time cultivation of vegetables and fruits that will not only be consumed in the United States of America but also exported to other parts of the world.
- We want our processed fruits and vegetable to flood the nooks and crannies of the United States and other countries of the world.
Our Business Structure
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a commercial vegetable farm that intends starting small in Los Angeles – California, but hopes to grow big in order to compete favorably with leading commercial vegetable farms in the commercial farming industry both in the United States and on a global stage.
We are aware of the importance of building a solid business structure that can support the picture of the kind of world class business we want to own, which is why we are committed to only hire the best hands in and around California.
At Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC, we will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, hardworking, dedicated, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all our stakeholders (the owners, workforce, and customers).
In view of the above, Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Operating Officer
General Farm Manager
Administrator/Accountant
- Crop (Vegetable and Fruits) Cultivation Manager/Supervisor
Vegetable and Fruits Processing and Packaging Plant Manager/Supervisor
- Sales and Marketing Executive
- Front Desk Officer
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results; developing incentives; developing a climate for offering information and opinions; providing educational opportunities
- Creating, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Responsible for the planning, management and coordinating all farm activities across the various sections on behalf of the organization
- Supervises other section manager
- Ensures compliance during project executions (especially in the construction of greenhouse and hothouse et al)
- Providing advice on the management of farming activities across all section
- Responsible for carrying out risk assessment
- Using IT systems and software to keep track of people and progress of the growth of crops
- Responsible for overseeing the accounting, costing and sale of farm produce after harvest
- Represent the organization’s interest at various stakeholders’ meetings
- Ensures that farming goals are achieved, the most efficient resources (manpower, equipment, tools and chemicals et al) are utilized and different interests involved are satisfied. Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Handles all financial transactions for the company
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carrying out staff induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily farming activities across the various farming sections
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Serves as internal auditor for the company
Crop (Vegetable and fruits) Cultivation Manager/Supervisor
- Responsible for the cultivation of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
- Supervises other workers within the department
- Work closely with the General Manager to achieve the organizations’ goals and objectives
- Responsible for managing the fruits and vegetable processing and packaging plant section of the business
Sales and Marketing Officer
- Identify, prioritize and reach out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of relevant projects.
- Writing winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with company policy
- Responsible for handling business research, marker surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with customers
- Develop, execute and evaluate new plans for expanding increase sales
- Document all customer contact and information
- Represent the company in strategic meetings
- Help increase sales and growth for the farm
Front Desk/Customer’s Service Officer
- Welcomes guests and clients to the farm by greeting them in person or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the company’s products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to clients
- Receives parcels/documents for Hankins Jordan® Banana Farms, Inc.
- Distribute mails in Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC
- Handles any other duties as assigned by the line manager
6. SWOT Analysis
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC do not intend to launch out with trial and error hence the need to conduct a proper SWOT analysis.
We know that if we get it right from the onset, we would have succeeded in creating the foundation that will help us build a standard vegetable farm that will favorably compete with leading commercial vegetable farms in the United States of America and in other parts of the world.
We are quite aware that there are several large, medium and small scale vegetable farms all over Los Angeles – California and even in the same location where we intend locating ours, which is why we are following the due process of establishing a business.
We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be welled equipped to confront our threats.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in the commercial farming industry to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives.
Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Hankins Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC;
Our strength as a vegetable farm company is in the fact that we have healthy relationships with loads of major players (agriculture merchants) in the agricultural industry; both suppliers and buyers within and outside of the United States.
We have some of the latest vegetable farming machines, tools and equipment that will help us cultivate crops (vegetables and fruits) in commercial quantities with less stress. Asides from our relationship (network) and equipment, we can confidently boast that we have some the most experienced hands in the vegetable cum greenhouse commercial farming line of business.
Our major weakness is that we are a new vegetable farm in the United States and it might take some time for our organization to break into the market and gain acceptance especially from international markets in the already saturated and highly competitive commercial farming industry. Another weakness is that we may not have the required cash to promote our business the way we would want to.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities that are available to us cannot be quantified; we know that everybody on planet earth eats different types of vegetables. So also changes in consumer preferences have led supermarkets and other retail outlets to demand fresh vegetables and fruits all year-round. We are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that is available in the industry.
Both the number of small local farms and the number of larger commercial farms have been growing. Increasing imports of fresh produce will slightly constrain demand for vegetables and fruits. Just like any other business, one of the major threats that we are likely to face is economic downturn.
It is a fact that economic downturn affects purchasing/spending power. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a new vegetable farm or commercial greenhouse farm in the same location where our target market exists and who may want to adopt the same business model like us.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
If you are conversant with rising technology and scientific development in the agriculture industry, you will quite agree that vegetable and fruits farming via greenhouse commercial farming model are at the front burner. Greenhouse commercial farming is rapidly gaining entrance in our world today.
Greenhouse farming gives room for greater control over the growing environment of various crops. Dependent upon the technicality and specification of a greenhouse design, some of the important factors which may be controlled include temperature, levels of light and shade, irrigation, fertilizer application, atmospheric humidity et al.
Basically, greenhouses are used to overcome shortcomings in the growing qualities of a piece of land such as a short growing season or poor light levels. In essence, they are designed to improve food production in marginal environments.
So also, if you are a close observer of the trends in the vegetable farming industry, you will agree that the vegetable farming industry is anticipated to increase due to increasing consumer health consciousness, which has led to increasing demand for fresh produce.
While per capita fruit and vegetable consumption has remained stable in recent time, the price of vegetables has increased as consumers demand premium, fresh vegetables.
So also, the number of both small and large farms has been increasing; small local farms are benefiting from the organic, local movement while large, commercial farms are improving labor efficiency. Going forward, players in the vegetable farming industry will continue to increase revenue generation for their business.
8. Our Target Market
Naturally, the end consumers of vegetable farm produce and those who benefit from the business value chain of the vegetable farm industry is all encompassing. Every household consumes produce from vegetable farms be it vegetables or fruits et al. In essence, a vegetable farmer should be able to sell his or her farm produce to as many people as possible.
We will ensure that we position our business to attract consumers of fresh vegetables and fruits not just in the United States of America alone but other parts of the world which is why we will be exporting some of our vegetables and fruits either in raw or processed form to other countries of the world.
Our competitive advantage
It is easier to find entrepreneurs flocking towards an industry that is known to generate consistent income which is why there are more commercial farmers in the United States of America and of course in most parts of the world.
For example, Statistics has it that there are 2.2 million farms in the United States of America, covering an area of 922 million acres. This goes to show that there is an appreciable number of farmers in the United States of America but that does not mean that there is stiff competition in the industry.
As a matter of fact, entrepreneurs are encouraged by the government to embrace commercial farming. This is so because part of the success of any nation is her ability to cultivate her own food and also export foods to other nations of the world.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is fully aware that there are competitions when it comes to selling vegetables and fruits all over the globe, which is why we decided to carry out thorough research so as to know how to take advantage of the available market in the United States and in other parts of the world.
We have done our homework and we have been able to highlight some factors that will give us competitive advantage in the marketplace; some of the factors are effective and reliable farming processes that can help us sell our produce at competitive prices, good network and excellent relationship management.
Our competitive advantage lies in the power of our team; our workforce. We have a team of hardworking and highly proficient farmers, a team with excellent qualifications and experience in various niche areas in the vegetable farming industry.
Aside from the synergy that exists in our carefully selected team members, we have some of the latest and efficient vegetable and greenhouse farm machines and equipment and we will be guided by best practices in the industry.
Another competitive advantage that we are bringing to the industry is the fact that we have designed our business in such a way that we will operate an all – round standard vegetable farm that will be involved in diverse areas such as vegetable and fruit cultivation, food processing and packaging plant. With this, we will be able to take advantage of all the available opportunities within the industry.
Lastly, all our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry. It will enable them to be more than willing to build the business with us, help deliver our set goals and achieve all our business aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is in the vegetable farming business for the purpose of maximizing profits hence we have decided to explore all the available opportunities within the industry to achieve our corporate goals and objectives.
In essence we are not going to rely only on the sale of our farm produce to generate income for the business. Below are the sources we intend exploring to generate income for Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC;
- Sale of crops such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilis, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
10. Sales Forecast
From the survey conducted, we were able to discover that the sales generated by a vegetable farm depend on the size of the farm and the nature of the vegetable farm.
We have perfected our sales and marketing strategies and we are quite optimistic that we will meet or even surpass our set sales target of generating enough income/profits from the first year of operation and build the business from survival to sustainability.
We have been able to critically examine the vegetable farming industry, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast.
- First Year-: $250,000
- Second Year-: $500,000
- Third Year-: $900,000
N.B : This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters (draughts, epidemics), and unfavorable government policies . Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
We are quite aware that the reason why some vegetable farms hardly make good profits is their inability to sell off their farm produce, especially perishable crops as at when due. In view of that, we decided to set up a standard food processing plant to help us
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to stakeholders in the agriculture industry, companies that rely on the agriculture industry for their raw materials, supermarkets, grocery stores, hotels and restaurants and agriculture produce merchants et al.
- Advertise our business and agriculture produce in agro – allied and food related magazines and websites
- List our vegetable farms on yellow pages ads
- Attend related agriculture and food expos, seminars and business fairs et al
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Engage in direct marketing
- Encourage the use of Word of mouth marketing (referrals)
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Any business that wants to grow beyond the corner of the street or the city they are operating from must be ready and willing to utilize every available means (conventional and non – conventional means) to advertise and promote the business.
We intend growing our business which is why we have perfected plans to build our brand via every available means. Below are the platforms we can leverage on to boost our vegetable farm brand and to promote and advertise our business;
- Place adverts on both print (newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community based events/programs
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; Instagram, Facebook, twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our business
- Install our BillBoards on strategic locations all around Los Angeles – California
- Engage in roadshows from time to time in targeted neighborhoods
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas
- Contact corporate organizations and residents in our target areas by calling them up and informing them of Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC and the farm produce we sell
- List our vegetable farms in local directories/yellow pages
- Advertise our vegetable farms in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site.
- Ensure that all our staff members wear our branded shirts and all our vehicles and trucks are well branded with our company logo et al.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
If you want to get the right pricing for your farm produce, then you should ensure that you choose a good location for vegetable farm, choose a good breed/seed that will guarantee bountiful harvest, cut the cost of running your farm to the barest minimum and of course try as much as possible to attract buyers to your farm as against taking your farm produce to the market to source for buyers; with this, you would have successfully eliminate the cost of transporting the goods to the market and other logistics.
We are quite aware that one of the easiest means of penetrating the market and acquiring loads of customers for all our vegetables and fruits is to sell them at competitive prices hence we will do all we can to ensure that the prices of our farm produce are going to be what other commercial farmers would look towards beating.
One thing is certain, the nature of vegetable farming makes it possible for farmers to place prices for their farm produces based on their discretion without following the benchmark in the industry. The truth is that it is one of the means of avoiding running into a loss. The easier you sell off your harvest the better for your business.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via mobile money transfer
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our clients make payment for farm produces without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials to clients who may want to deposit cash or make online transfers.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
When it comes to calculating the cost of starting a vegetable farm with a standard greenhouse farm, there are some key factors that should serve as a guide. The most important expenses is the construction of the greenhouse or hothouse as the case may be.
As a matter of fact, if you choose to start mechanized crop farming, then you should be willing to raise huge capital base to start the business. This is so because some cultivation machines/equipment can be pretty expensive. Below are some of the basic areas we will spend our start – up capital in setting up our vegetable farm;
- The total fee for incorporating the business in United States of America – $750
- The total cost for payment of insurance policy covers (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) at a total premium – $9,400
- The amount needed to acquire/lease a farm land – $50,000
- The amount required for preparing the farm land – $70,000
- The cost for acquiring the required working tools and equipment/machines/fencing et al – $10,000
- The amount required for the purchase of the first set of vegetables and fruits seedlings et al – $50,000
- The amount required to set up a standard vegetable processing plant within the farm facility – $100,000
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $40,000
- The cost of launching an official website – $600
- The amount required for payment of workers for a period of 3 months – $100,000
- Additional Expenditure (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al) – $2,000
Going by the report from detailed research and feasibility studies conducted, we will need an average of $500,000 to start a standard vegetable farm with a processing plant in the United States of America. Basically, vegetable farms do not require an office space, most people that run vegetable farms operate directly from their farms. But we have decided to open a small liaison office; a place where administrative jobs will be carried out.
Generating Funds/Startup Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC
No matter how fantastic your business idea might be, if you don’t have the required money to finance the business, the business might not become a reality. Finance is a very important factor when it comes to starting a vegetable farm. No doubt raising startup capital for a business might not come cheap, but it is a task that an entrepreneur must go through.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is a family business that will be owned and managed by Johnson Jael and his immediate family members. They are the sole financiers of the firm but may likely welcome other partners later which is why they decided to restrict sourcing of start-up capital for the business to just three major sources.
- Generate part of the start – up capital from personal savings and sale of his stocks
- Generate part of the start – up capital from friends and other extended family members
- Generate a larger chunk of the startup capital from the bank (loan facility).
N.B: We have been able to generate about $100,000 ( Personal savings $80,000 and soft loan from family members $20,000 ) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $400,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been duly signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of their employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running.
We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to sell our farm produce (vegetables and fruits) a little cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are well prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Johnson Jael® Vegetable Farms, LLC will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner of our business strategy.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of three years or more as determined by the board of the organization. We know that if this is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry and they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List / Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts in various banks in the United States: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of All form of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of farm land in Los Angeles – California (preparing the farm land inclusive): Completed
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Start – up Capital generation: Completed
- Writing of Business Plan : Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Graphic Designs and Printing of Packaging, Marketing/Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Building /construction of greenhouse and hothouse facility: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed working tools, machines and equipment: Completed
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business (Business PR): In Progress
- Farm land Treatment, Health and Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Establishing business relationship with key players in the industry (agriculture farm produce merchants, transporters/haulage and suppliers of seeds, fertilizers, pesticides and insecticides): Completed

Vegetable Farming Business Plan

Have you ever pictured yourself doing a farming business or even a vegetable farming business ? When you are given the opportunity to try it out, will you take it or will you think that this business will not come out as successful? Many of us may not be able to picture doing this kind of work or even fathom to do this kind of business. Many of us may not want to do this type of business even if it means it is the easiest and less stressful type compared to other types of businesses. However, this is also quite a rewarding type of business if you know what you are doing. Since there are some things that we need to take into consideration. Things like the place, the kind of vegetables to grow and of course the amount of help, time and expenses that would take for this type of business to flourish. Of course for those who have done this before would surely say it takes patience, time, expenses, luck and of course a business plan.
3+ Vegetable Farming Business Plan Examples
1. vegetable farming business plan template.

- Google Docs

2. Organic Vegetables Farming Business Plan

Size: 369 KB
3. Vegetable Farming Business Plan in PDF

Size: 248 KB
4. Vegetable Farming Business Plan

Size: 18 MB
What Is a Vegetable Farming Business Plan?
We know that a business plan is a specific strategic plan that helps businesses thrive. A vegetable farming business plan is the same except it caters to a very specific type of business. A vegetable farming business plan is a type of strategic plan that caters to the business of vegetable farming. This business plan helps by giving you a variety of ways to help make your vegetable farming business a success. In addition to that, a vegetable farming business plan is a road map to help you avoid any risks that always go along with running a business. The purpose of writing a vegetable farming business plan is to make sure that your business, regardless of how you may want it to go, would not have to go through a ton of risks. That you are also able to see the success and the steps you can take for it to grow. A vegetable farming business plan’s purpose is to make it happen at the best time possible.
How to Make a Vegetable Farming Business Plan
Have you ever wondered what a vegetable farming business plan would have? What the details are and what difference does it have with an ordinary business plan? Just like any other kind of business plan, it has its general details, except this kind is far more specific. With that being said, here are some tips to help you write your vegetable farming business plan.
1. Make an Outline of Your Vegetable Farm Business Plan
Making a business plan may already be stressful enough, so the best thing you can do to ease the problem is to start by making an outline of your vegetable farming business plan. From there, it would be easier for you to know where to begin, how to begin it and how to act out from what you have written.
2. Set Up Simple Steps You Can Follow
When you are in doubt with which foot to use to go forward, this is why you are writing a business plan for your vegetable farming. Apart from doing your research about vegetable farming, you should also do and list some simple steps to get you to start. These steps do not necessarily mean that they are going to be what you would use to carry on. There may be some steps that help, while others not as much. The point here is to set up the steps and see which of them takes you there as well.
3. Plan a Budget Ahead of Time
Plan a financial budget while you plan on making the vegetable farming business plan as well. As the financial part of this is also crucial. The best time is to plan ahead. Do your research on the items that you would need in order to start this kind of business.
4. Set Your Milestones and Goals
For every milestone and achieved goal, write it down. The date, the name of the milestone and the activity that you did that made you achieve it. The milestones help as a stepping stone to achieving the vegetable farming business you are planning on running.
5. Do an Update and Repeat
Updating your business plan helps by maintaining the necessary steps, ideas and information. For every milestone or every changes that has happened whether positive or negative, it is always best to update. Repeat the same steps as necessary.
What is a vegetable farm business plan?
A kind of business plan that helps by giving marketing and strategic steps to ensure that the business goes smoothly. It is also the type of business plan that helps by giving you the opportunity to write down your strategies and find the ones that work for you and to help avoid any risks.
Why is it important to be prepared?
The purpose of the vegetable farming business plan is to prepare yourself for the things that are needed for this type of business. Being prepared means you can be a step ahead of the risks and the issues that you have to find a way to avoid as much as possible.
How long can a business plan be?
The length of your business plan may depend on how many strategies and steps you are planning on writing down. There are of course shorter or a single page long business plan as well as a lengthier kind. This may depend on you.
Starting out a vegetable farming business is not as easy as a lot of people may think. But it is surely not impossible. This type of business would take a lot of time, effort, money, patience and of course a business plan. The business plan helps by acting as a road map to avoid any risks that would go with doing the business.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Organic Food Store Business Plan
Start your own organic food store business plan
Last Frontier Market
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Last Frontier Market will offer customers organic and locally grown produce, chemical- and preservative-free groceries, cruelty-free body care and eco-household products. All of our products are healthy alternatives to the products available at conventional grocery chains. Located in the heart of the growing Willow Creek section of Richmond, the market will serve a community of 25,000 residents. The creation of the market is in response to the growing demand in the community for a local natural food store.
The Last Frontier Market will have the advantage of the foot traffic in the Willow Creek retail area which is the home of the Willow Creek Arts and Craft Fair, as well as the home of numerous art and craft shops. The area has a reputation of supporting progressive causes and businesses. The market will be a comfortable place to meet and shop in the community.
In addition, the market will also be the most convenient in the area. The closest competing natural food store to the Willow Creek area is a twenty minute drive.
The Last Frontier Market will give back to the community. We will participate in community projects and host fund-raisers for local community services.

1.1 Objectives
- Provide our customers with the freshest, organically grown fruits and vegetables.
- Offer foods without artificial colors, flavors, or additives.
- Sell earth-friendly cleansers; pure, natural supplements; and gentle, cruelty-free body care products.
- Support organic farms that keep our earth and water pure.
1.2 Mission
The Last Frontier Market is committed to providing the highest quality, fresh and natural food, health and wellness products. Our staff are friendly, eager to serve and ready to educate.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Last Frontier Market is a vegetarian health food store located in the heart of the Willow Creek section of Richmond. The community of 25,000 residents is made up of students attending the State University and families attracted to the new home construction in the area.
Co-owners, Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens, are opening the Last Frontier Market to capitalize on the growing demand in the community for a local food store that offers organic and locally grown produce, chemical and preservative free groceries, cruelty-free body care and eco-household products.
2.1 Company Ownership
Last Frontier Market is owned by Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens.
2.2 Start-up Summary
The start-up cost of the Last Frontier Market will consist primarily of inventory and display equipment. Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens will invest $80,000. They will also secure a $50,000 SBA loan.

| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $77,800 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $52,200 |
| Total Funding Required | $130,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $10,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $42,200 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $42,200 |
| Total Assets | $52,200 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $50,000 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $50,000 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens | $80,000 |
| Other | $0 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $80,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($77,800) |
| Total Capital | $2,200 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $52,200 |
| Total Funding | $130,000 |
| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $1,000 |
| Insurance | $0 |
| Rent | $1,800 |
| Start-Up Inventory | $40,000 |
| Display Set-Up | $5,000 |
| Cash Reserve for Hiring | $30,000 |
| Advertising | $0 |
| Other | $0 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $77,800 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $42,200 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 |
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 |
| Total Assets | $52,200 |
| Total Requirements | $130,000 |
The Last Frontier Market will offer customers organic and locally grown produce, chemical- and preservative-free groceries, cruelty-free body care and eco-household products. The products are:
- Free of artificial preservatives.
- Free of artificial colors.
- Free of chemical additives.
- Organically grown, whenever possible.
- The least processed or unadulterated version available.
- Non-irradiated.
- Cruelty free.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
In the past ten years, the Willow Creek section of Richmond has grown tremendously. The growing student community combined with the new families in the area are a perfect customer support base for the Last Frontier Market.
Currently, the area is served by two major supermarkets that do not carry any of the product lines available at the Last Frontier Market. The closest natural food store is a twenty minute drive.
Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens believe that a local natural food store in the Willow Creek area would be competitive and offer customers a product selection that will assure repeat business.
4.1 Market Segmentation
The Last Frontier Market will focus two significant customer groups:
- Families : Many of the young families moving into the Willow Creek area are doing so because of its unique community environment. The community is home to a number of artists and craft people that operate the Willow Creek Craft Fair. This creates a festive environment in the Willow Creek central commercial/retail area that attract shoppers each weekend. Its close proximity to the university also attracts young families where one or both parents are students or employees of the university. These families are a strong customer base for the Last Frontier Market.
- Students : A significant number of students prefer to shop at a natural food store. The Last Frontier Market will be within walking distance for most area residents. Our location will make our store a convenient place to shop on the way home from classes.
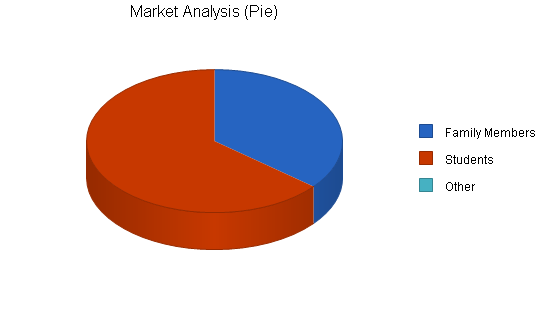
| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Family Members | 15% | 9,000 | 10,350 | 11,903 | 13,688 | 15,741 | 15.00% |
| Students | 10% | 16,000 | 17,600 | 19,360 | 21,296 | 23,426 | 10.00% |
| Other | 0% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00% |
| Total | 11.88% | 25,000 | 27,950 | 31,263 | 34,984 | 39,167 | 11.88% |
Strategy and Implementation Summary
The Last Frontier Market will promote the store opening. We will have live music and food in the store’s parking lot for the opening weekend. The Willow Creek Craft Fair is adjacent to our store and we should have excellent foot traffic for our opening.
We will advertise in the university daily student newspaper as well as the local area advertising flyer. In the advertisements for the market opening, we will have a 20% off coupon for purchases over twenty dollars. We will continue this discount for the first month of operation.
The Last Frontier Market will give back to the community. We will participate in community projects like the area’s food bank and community programs for children. The Last Frontier Market will also hosts a number of community events, such as charity pancake brunches, dog washes benefiting local humane societies and benefit barbecues.
5.1 Competitive Edge
The Last Frontier Market’s competitive edge is:
- Location : The Last Frontier Market is located located in the heart of the Willow Creek section of Richmond. The foot traffic in the Willow Creek retail area is very strong. The closest natural food store to the Willow Creek area is a twenty minute drive.
- Community Support : The Last Frontier Market is a community market that will give back to the community. We will participate in community projects like the area’s food bank and community programs for children. The Last Frontier Market will also host a number of community events, such as charity pancake brunches, dog washes benefiting local humane societies and benefit barbecues.
5.2 Sales Strategy

5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The following is the Last Frontier Market’s sales forecast for three years.

| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Sales | $423,000 | $470,000 | $520,000 |
| Others | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $423,000 | $470,000 | $520,000 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Sales | $128,220 | $150,000 | $175,000 |
| Others | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $128,220 | $150,000 | $175,000 |
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Co-owners, Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens, have fifteen years of experience working in natural food stores.
Mary Stevens was one of the founding members of the Mason Peak Natural Grocery, 4th and Tyler. The grocery was established in 1992 by the non-profit NEDCO, the Neighborhood Economic Development Corporation, and a number of concerned neighbors who wished to save the historic Mason Peak Market from destruction. Mary started as a cashier and advanced to the position of store manager in 1996. The grocery has grown into a community fixture under her management.
Josh Wingard ran the university’s now defunct Natural Food Collective for three years before the program was defunded. The small on-campus store provide natural food products to student customers. Sales increased by 20% each year under his leadership. Unfortunately, the state budget shortfall impacted the continued funding of the program. Prior to this position, Josh worked at Sunburst Natural Foods for four years. His principle responsibilities were product ordering and stocking.
6.1 Management Team
Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens were be the management team for the Last Frontier Market. Mary will be responsible for staffing and daily operations. Josh will be responsible for product ordering, stocking and bookkeeping.
6.2 Personnel Plan
Besides Josh Wingard and Mary Stevens, the last Frontier Market will have a staff of five:
- Three cashiers.
- Two produce staff.
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Mary Stevens | $33,600 | $36,000 | $39,000 |
| Josh Wingard | $33,600 | $36,000 | $39,000 |
| Cashiers | $84,000 | $95,000 | $104,000 |
| Produce Staff | $48,000 | $51,000 | $54,000 |
| Total People | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Total Payroll | $199,200 | $218,000 | $236,000 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following is the Financial Plan for the Last Frontier Market.
7.1 Break-even Analysis
The monthly break-even point is $32,277.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $32,277 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 30% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $22,493 |
7.2 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table and charts highlight the projected profit and loss for three years.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $423,000 | $470,000 | $520,000 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $128,220 | $150,000 | $175,000 |
| Other Production Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $128,220 | $150,000 | $175,000 |
| Gross Margin | $294,780 | $320,000 | $345,000 |
| Gross Margin % | 69.69% | 68.09% | 66.35% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $199,200 | $218,000 | $236,000 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $7,000 | $10,000 | $13,000 |
| Depreciation | $1,440 | $1,440 | $1,440 |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Utilities | $4,800 | $4,800 | $4,800 |
| Insurance | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 |
| Rent | $21,600 | $21,600 | $21,600 |
| Payroll Taxes | $29,880 | $32,700 | $35,400 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $269,920 | $294,540 | $318,240 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $24,860 | $25,460 | $26,760 |
| EBITDA | $26,300 | $26,900 | $28,200 |
| Interest Expense | $4,459 | $3,501 | $2,501 |
| Taxes Incurred | $6,120 | $6,588 | $7,278 |
| Net Profit | $14,281 | $15,372 | $16,981 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 3.38% | 3.27% | 3.27% |
7.3 Projected Cash Flow
The following table and chart highlight the projected cash flow for three years.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $105,750 | $117,500 | $130,000 |
| Cash from Receivables | $251,575 | $345,203 | $382,237 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $357,325 | $462,703 | $512,237 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $4,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $361,325 | $462,703 | $512,237 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $199,200 | $218,000 | $236,000 |
| Bill Payments | $186,715 | $237,222 | $263,081 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $385,915 | $455,222 | $499,081 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $9,996 | $9,996 | $9,996 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $395,911 | $465,218 | $509,077 |
| Net Cash Flow | ($34,586) | ($2,515) | $3,160 |
| Cash Balance | $7,614 | $5,099 | $8,259 |
7.4 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table highlights the projected balance sheet for three years.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $7,614 | $5,099 | $8,259 |
| Accounts Receivable | $65,675 | $72,972 | $80,735 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $73,289 | $78,071 | $88,994 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $1,440 | $2,880 | $4,320 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $8,560 | $7,120 | $5,680 |
| Total Assets | $81,849 | $85,191 | $94,674 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $21,364 | $19,331 | $21,828 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $21,364 | $19,331 | $21,828 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $40,004 | $30,008 | $20,012 |
| Total Liabilities | $61,368 | $49,339 | $41,840 |
| Paid-in Capital | $84,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($77,800) | ($63,519) | ($48,147) |
| Earnings | $14,281 | $15,372 | $16,981 |
| Total Capital | $20,481 | $35,853 | $52,834 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $81,849 | $85,191 | $94,674 |
| Net Worth | $20,481 | $35,853 | $52,834 |
7.5 Business Ratios
Business ratios for the years of this plan are shown below. Industry profile ratios based on the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code 5149, Groceries and Related Products, are shown for comparison.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 11.11% | 10.64% | 4.60% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 80.24% | 85.66% | 85.28% | 33.30% |
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 20.90% |
| Total Current Assets | 89.54% | 91.64% | 94.00% | 80.20% |
| Long-term Assets | 10.46% | 8.36% | 6.00% | 19.80% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 26.10% | 22.69% | 23.06% | 45.20% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 48.88% | 35.22% | 21.14% | 10.00% |
| Total Liabilities | 74.98% | 57.92% | 44.19% | 55.20% |
| Net Worth | 25.02% | 42.08% | 55.81% | 44.80% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 69.69% | 68.09% | 66.35% | 44.10% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 66.31% | 64.81% | 63.08% | 26.70% |
| Advertising Expenses | 1.65% | 2.13% | 2.50% | 0.70% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 5.88% | 5.42% | 5.15% | 0.80% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 3.43 | 4.04 | 4.08 | 1.69 |
| Quick | 3.43 | 4.04 | 4.08 | 1.01 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 74.98% | 57.92% | 44.19% | 55.20% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 99.61% | 61.25% | 45.92% | 3.60% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 24.93% | 25.78% | 25.62% | 8.00% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 3.38% | 3.27% | 3.27% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 69.73% | 42.87% | 32.14% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 4.83 | 4.83 | 4.83 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 57 | 72 | 72 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 9.74 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 32 | 28 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 5.17 | 5.52 | 5.49 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 3.00 | 1.38 | 0.79 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.52 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $51,925 | $58,741 | $67,166 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 5.58 | 7.27 | 10.70 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.18 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 26% | 23% | 23% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.38 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 20.65 | 13.11 | 9.84 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Sales | 0% | $26,000 | $29,000 | $30,000 | $34,000 | $36,000 | $38,000 | $34,000 | $33,000 | $35,000 | $39,000 | $43,000 | $46,000 |
| Others | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $26,000 | $29,000 | $30,000 | $34,000 | $36,000 | $38,000 | $34,000 | $33,000 | $35,000 | $39,000 | $43,000 | $46,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Sales | $9,000 | $9,500 | $9,600 | $10,200 | $10,500 | $11,300 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $11,000 | $12,000 | $12,120 | $13,000 | |
| Others | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $9,000 | $9,500 | $9,600 | $10,200 | $10,500 | $11,300 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $11,000 | $12,000 | $12,120 | $13,000 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Mary Stevens | 0% | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 |
| Josh Wingard | 0% | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 | $2,800 |
| Cashiers | 0% | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 |
| Produce Staff | 0% | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 |
| Total People | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | |
| Total Payroll | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $26,000 | $29,000 | $30,000 | $34,000 | $36,000 | $38,000 | $34,000 | $33,000 | $35,000 | $39,000 | $43,000 | $46,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $9,000 | $9,500 | $9,600 | $10,200 | $10,500 | $11,300 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $11,000 | $12,000 | $12,120 | $13,000 | |
| Other Production Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $9,000 | $9,500 | $9,600 | $10,200 | $10,500 | $11,300 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $11,000 | $12,000 | $12,120 | $13,000 | |
| Gross Margin | $17,000 | $19,500 | $20,400 | $23,800 | $25,500 | $26,700 | $24,000 | $23,000 | $24,000 | $27,000 | $30,880 | $33,000 | |
| Gross Margin % | 65.38% | 67.24% | 68.00% | 70.00% | 70.83% | 70.26% | 70.59% | 69.70% | 68.57% | 69.23% | 71.81% | 71.74% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $1,000 | $1,000 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | |
| Depreciation | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | $120 | |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Utilities | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | |
| Insurance | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | |
| Rent | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 | $2,490 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $22,910 | $22,910 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | $22,410 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($5,910) | ($3,410) | ($2,010) | $1,390 | $3,090 | $4,290 | $1,590 | $590 | $1,590 | $4,590 | $8,470 | $10,590 | |
| EBITDA | ($5,790) | ($3,290) | ($1,890) | $1,510 | $3,210 | $4,410 | $1,710 | $710 | $1,710 | $4,710 | $8,590 | $10,710 | |
| Interest Expense | $410 | $403 | $396 | $389 | $382 | $375 | $368 | $361 | $354 | $347 | $340 | $333 | |
| Taxes Incurred | ($1,896) | ($1,144) | ($722) | $300 | $812 | $1,174 | $367 | $69 | $371 | $1,273 | $2,439 | $3,077 | |
| Net Profit | ($4,424) | ($2,669) | ($1,684) | $701 | $1,896 | $2,740 | $855 | $160 | $865 | $2,970 | $5,691 | $7,180 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | -17.01% | -9.20% | -5.61% | 2.06% | 5.27% | 7.21% | 2.52% | 0.49% | 2.47% | 7.62% | 13.23% | 15.61% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $6,500 | $7,250 | $7,500 | $8,500 | $9,000 | $9,500 | $8,500 | $8,250 | $8,750 | $9,750 | $10,750 | $11,500 | |
| Cash from Receivables | $0 | $650 | $19,575 | $21,775 | $22,600 | $25,550 | $27,050 | $28,400 | $25,475 | $24,800 | $26,350 | $29,350 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $6,500 | $7,900 | $27,075 | $30,275 | $31,600 | $35,050 | $35,550 | $36,650 | $34,225 | $34,550 | $37,100 | $40,850 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $4,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $6,500 | $7,900 | $27,075 | $30,275 | $35,600 | $35,050 | $35,550 | $36,650 | $34,225 | $34,550 | $37,100 | $40,850 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | $16,600 | |
| Bill Payments | $457 | $13,745 | $14,949 | $15,018 | $16,606 | $17,423 | $18,469 | $16,414 | $16,163 | $17,478 | $19,353 | $20,640 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $17,057 | $30,345 | $31,549 | $31,618 | $33,206 | $34,023 | $35,069 | $33,014 | $32,763 | $34,078 | $35,953 | $37,240 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | $833 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $17,890 | $31,178 | $32,382 | $32,451 | $34,039 | $34,856 | $35,902 | $33,847 | $33,596 | $34,911 | $36,786 | $38,073 | |
| Net Cash Flow | ($11,390) | ($23,278) | ($5,307) | ($2,176) | $1,561 | $194 | ($352) | $2,803 | $629 | ($361) | $314 | $2,777 | |
| Cash Balance | $30,810 | $7,532 | $2,224 | $49 | $1,609 | $1,804 | $1,452 | $4,254 | $4,883 | $4,522 | $4,836 | $7,614 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $42,200 | $30,810 | $7,532 | $2,224 | $49 | $1,609 | $1,804 | $1,452 | $4,254 | $4,883 | $4,522 | $4,836 | $7,614 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $19,500 | $40,600 | $43,525 | $47,250 | $51,650 | $54,600 | $53,050 | $49,400 | $50,175 | $54,625 | $60,525 | $65,675 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $42,200 | $50,310 | $48,132 | $45,749 | $47,299 | $53,259 | $56,404 | $54,502 | $53,654 | $55,058 | $59,147 | $65,361 | $73,289 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $120 | $240 | $360 | $480 | $600 | $720 | $840 | $960 | $1,080 | $1,200 | $1,320 | $1,440 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $9,880 | $9,760 | $9,640 | $9,520 | $9,400 | $9,280 | $9,160 | $9,040 | $8,920 | $8,800 | $8,680 | $8,560 |
| Total Assets | $52,200 | $60,190 | $57,892 | $55,389 | $56,819 | $62,659 | $65,684 | $63,662 | $62,694 | $63,978 | $67,947 | $74,041 | $81,849 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $13,247 | $14,451 | $14,465 | $16,027 | $16,805 | $17,922 | $15,877 | $15,582 | $16,834 | $18,666 | $19,903 | $21,364 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $13,247 | $14,451 | $14,465 | $16,027 | $16,805 | $17,922 | $15,877 | $15,582 | $16,834 | $18,666 | $19,903 | $21,364 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $50,000 | $49,167 | $48,334 | $47,501 | $46,668 | $45,835 | $45,002 | $44,169 | $43,336 | $42,503 | $41,670 | $40,837 | $40,004 |
| Total Liabilities | $50,000 | $62,414 | $62,785 | $61,966 | $62,695 | $62,640 | $62,924 | $60,046 | $58,918 | $59,337 | $60,336 | $60,740 | $61,368 |
| Paid-in Capital | $80,000 | $80,000 | $80,000 | $80,000 | $80,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 | $84,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) | ($77,800) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($4,424) | ($7,093) | ($8,777) | ($8,076) | ($6,180) | ($3,440) | ($2,585) | ($2,424) | ($1,559) | $1,411 | $7,101 | $14,281 |
| Total Capital | $2,200 | ($2,224) | ($4,893) | ($6,577) | ($5,876) | $20 | $2,760 | $3,615 | $3,776 | $4,641 | $7,611 | $13,301 | $20,481 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $52,200 | $60,190 | $57,892 | $55,389 | $56,819 | $62,659 | $65,684 | $63,662 | $62,694 | $63,978 | $67,947 | $74,041 | $81,849 |
| Net Worth | $2,200 | ($2,224) | ($4,893) | ($6,577) | ($5,876) | $20 | $2,760 | $3,615 | $3,776 | $4,641 | $7,611 | $13,301 | $20,481 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Business Plan of a Fruits

Related Papers
sangeeta agasty
Vijay Jakkula
Environment and Planning A 42(9), 2043-2057
Anika Trebbin
Since the 1980s power distribution in agrofood networks has changed in many countries in Africa, Latin-America, South Asia, and the postsocialist countries in Europe and Asia. In the course of economic liberalization, retail and wholesale trade as well as the food processing and agroscience sector were opened up to foreign investment. Within the frame of such liberalization many states gradually refrained from directly governing this sector and reregulated the trade in a way that gave private companies the possibility to implement new power structures. We analyze the so-called ‘Food Chain Partnership’ (FCP) program implemented by the transnational company Bayer in India as an example for private governance in agrofood networks. Bayer is advancing and coordinating relations between the food processing and retailing industry and farmers. We explore whether such private activity can substitute for the activities of state institutions in governing agrofood networks. As the case study will show, the FCP model is highly selective in terms of farmers, who can participate (criteria include minimum farm size, irrigation facility, literacy, agricultural practices, and mobile phones), the crops that are covered, and the information passed on to the farmers. This limits the potential of market-driven instruments like the FCP to replace the traditional trade system as they concentrate only on those regions and products which are promising most profit to the companies. The global production network approach builds the analytical framework of this paper.
alex kwalombota
Nitu Bhattacharya
International Food and Agribusiness Management Review
Dr Ravi Nandi
High-value agriculture in India is witnessing a transformation, specifically in fresh fruits and vegetables (FFV). Supply chain stakeholders, mainly small and marginal farmers, receive a very minimal share in consumer rupee due to market uncertainty, high post-harvest losses, information asymmetry, lack of processing facilities and the erratic demand-supply situation. The current study draws from an extensive review to propose a competitive, inclusive, sustainable and scalable supply chain model of primary processing centers connecting farmers directly and efficiently with consumers. The proposed model will connect producers with the rest of the supply chain and streamline the supply chain process to reduce post-harvest losses as much as possible. The integration of a market information system will ensure transparency to help in better decision-making, reduced intermediaries and information asymmetry for producers, as well as the systematic disposal of the produce. The model will in...
Aman Khanna
Mukesh Pandey, Pantnagar (India)
Andrew Shepherd
Dr. Subhendu Dey
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Subhendu Dey
Fabio Musso
Business Intelligence Journal
Kamala Devi
Dr. Somashekhar I C
shubhankar agarwal
Ronnie Susman Natawidjaja
Dr. SRINIVASA REDDY MANDALA
Dhilbar Roshan
Srinivasa Reddy M
Paramjeet kaur Dhindsa
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It serves as a roadmap, outlining the vision, goals, and strategies necessary to establish and grow the business. Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Crop Farming Business Plan Docx. This comprehensive business plan aims to provide Agrolearners.com with a detailed framework for entering the fruit and vegetable industry, addressing key areas such as market ...
For a fruit and vegetable market, it's imperative to detail the range of products you intend to sell. Describe your selection of fruits, vegetables, herbs, and any additional items you plan to offer, and discuss how these choices align with the preferences and needs of your customer base. The operational plan is equally important.
Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580. The cost for hiring business consultant - $2,500.
Financial Summary. Down in the Dirt Farm grossed $66,370 in sales from the 2018 season ($28,675 through their CSA offering whole and half shares, $25,800 through farmers market sales, $8,645 through wholesale, and $3,250 from on-farm pork share sales). The agreed-upon sale price for the new farm is $315,000.
Fresh Fruits & Vegetables Mart is an equal partnership between Muhammad Ismail Habibullah and Muhammad Asghar that will provide home delivery of fresh fruits and vegetables in Shaheed Benazir Abad, Pakistan. The business aims to address the lack of convenient access to quality produce at reasonable prices in the local market. It will require Rs. 700,000 in startup costs and operate through ...
Figure 1. Planning process for a new commercial vegetable business. required, level of care needed, labor time and cost, and capital required and available. Some crops may be more profitable, but they may also be more labor-intensive. If labor is restricted in your area, then these crops may not be the best option.
Belay Tayure Fruit and Vegetables Business Plan - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document provides information about the fruit and vegetable industry in Ethiopia. It discusses key trends in the market such as favorable government policies encouraging private sector investment.
July 14, 2023. A fruit and vegetable store is a great way to provide healthy, fresh food to local communities while also providing a stable source of income. Additionally, it's an excellent way to support local farmers and increase access to a variety of fresh produce. But, first thing first, you need a business plan.
Describe your farming operations in detail, including the types of vegetables you plan to grow, the cultivation methods, and the size of your farm. Discuss the equipment and technology you will use, as well as the labor requirements. Address any environmental considerations, such as sustainable farming practices or organic certification.
Lastly, address any funding needs in the "ask" section of your executive summary. 2. The presentation of the company. In your fruit and vegetable wholesaler business plan, the second section should focus on the structure and ownership, location, and management team of your company.
Gaurav Bansal. Download Free PDF. VEGETABLE AND FRUITS PRODUCTION BUSSINES PLAN 1 fFRUITS AND VEGETABLE PLANTATION LOCATION DODOMA REGION EMAIL ADDRESS, [email protected] PHONE 0714189714/0653385664 PREPARED BY YOUTH FOR BUSINESS 2 f1. BUSINES BACKGROUND Vegetable and Fruit Agriculture is also known as Horticulture Agriculture.
The amount required for the purchase of the first set of vegetables and fruits seedlings et al - $50,000. The amount required to set up a standard vegetable processing plant within the farm facility - $100,000. Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) - $40,000.
NJ_Wholesale_Veg_Industry. Cooperative Extension Martin Hall, Room 309 Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey 88 Lipman Drive New Brunswick, NJ 08901-8525. njaes.rutgers.edu [email protected]. 732-932-5000, Ext. 610 Fax: 732-932-6633.
Vegetable FarmAnalysis Workbook - Financial[PAGE 3] INSTRUCTIONS. Goal: For a one-year period, develop an accrual adjusted income statement. This means preparing the following financial reports: 1. Balance Sheet statement at beginning of year, with both cost and market valuations. 2.
Selling fruits and vegetables. Growing and selling fresh produce can be a profitable and satisfying family business; however, risks are involved. Before investing money, time, and energy into any new business venture, it is advisable to first evaluate personal skills, market conditions, financial resources, and overall project feasibility.
The document provides a business plan for a company called Fresh Mart that will deliver fresh fruits and vegetables directly to customers' homes. Fresh Mart aims to benefit from eliminating limitations in the existing supply chain and provide quality products at reasonable prices. It will initially target 1000 customers in four areas of Ahmedabad city. The business faces risks from high ...
3. Plan a Budget Ahead of Time. Plan a financial budget while you plan on making the vegetable farming business plan as well. As the financial part of this is also crucial. The best time is to plan ahead. Do your research on the items that you would need in order to start this kind of business.
1.1 Objectives. Provide our customers with the freshest, organically grown fruits and vegetables. Offer foods without artificial colors, flavors, or additives. Sell earth-friendly cleansers; pure, natural supplements; and gentle, cruelty-free body care products. Support organic farms that keep our earth and water pure.
Compare price of vegetable supplied to the current market price. Sort vegetable in order to separate bad vegetable from good ones Grade vegetable mix big and small vegetable Washing: vegetable are place in a 60 liter of rubber bowl and water from the tap is use to nicely washed and remove any dirt from the vegetables.
This business plan outlines the steps necessary to achieve this vision, positioning Agrolearners.com as a leading provider of fresh produce in the market. usiness Description: Defining Your Fruit and Vegetable usiness Agrolearners.com is an online platform that acts as an intermediary between farmers and consumers in
Business Plan of a Fruits& Vegetables KIOSK Submitted By: Arvind Kumar Jha(1206) Gaurav Gupta(1211) Pankaj Agarwal(1216) Srijita Dutta(1220) Contents INTRODUCTION In today's highly competitive global market place, the pressure on organizations to find new ways to create and deliver value grows even stronger.
Agriculture Fruit Farm Business Plan - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Farmers Group is being formed through the acquisition of two successful vegetable farms in Alabama. The company plans to provide high quality and nutritious vegetables, fruits, and compost products. It will employ several permanent and temporary employees.
Fruit and Vegetable Canning Business Plan - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document provides a feasibility study for a proposed fruit and vegetable canning unit in Punjab, Pakistan. It analyzes the production and trade of fruits and vegetables in Pakistan, identifying an opportunity for a canning facility.