Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what is the difference between formative and summative assessment, formative assessment.
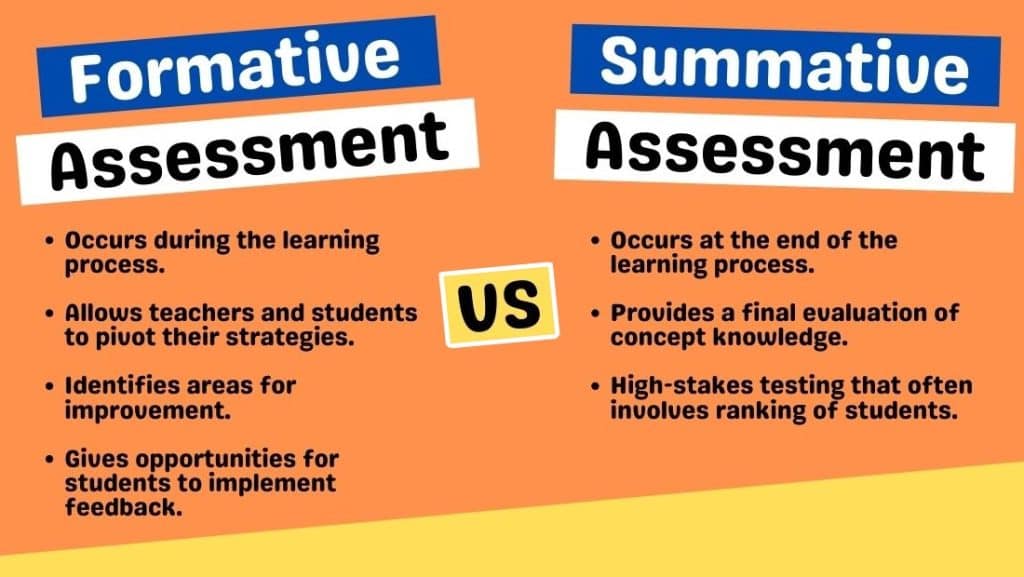
The goal of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can be used by instructors to improve their teaching and by students to improve their learning. More specifically, formative assessments:
- help students identify their strengths and weaknesses and target areas that need work
- help faculty recognize where students are struggling and address problems immediately
Formative assessments are generally low stakes , which means that they have low or no point value. Examples of formative assessments include asking students to:
- draw a concept map in class to represent their understanding of a topic
- submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture
- turn in a research proposal for early feedback

Summative assessment
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark.
Summative assessments are often high stakes , which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include:
- a midterm exam
- a final project
- a senior recital
Information from summative assessments can be used formatively when students or faculty use it to guide their efforts and activities in subsequent courses.
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links
Summative Assessment: Understanding its Definition, Purpose, and Importance in Education
Learn about Summative Assessment in this educational glossary entry.
Summative assessment is a method used in education to evaluate students' learning at the end of an instructional unit or period. It is a formal assessment that typically occurs after a period of learning, such as the completion of a project, a unit of study, or a course. Unlike formative assessment, which aims to provide ongoing feedback to improve learning during the instructional process, summative assessment focuses on measuring the overall learning outcomes and achievement of students.
Summative assessments come in various forms, including standardized tests, final exams, projects, essays, and presentations. These assessments are designed to measure the extent to which students have mastered the learning objectives and standards set by the curriculum. The results of summative assessments are often used to assign grades or scores to students, which are then used to evaluate their academic performance and progress.
Purpose of Summative Assessment
The primary purpose of summative assessment is to evaluate students' understanding of the material covered in a specific period of instruction. By assessing students at the end of a unit or course, educators can determine the extent to which students have achieved the learning objectives and standards set by the curriculum. Summative assessments provide a comprehensive view of students' overall performance and help educators make informed decisions about students' progress and academic success.
Summative assessment also serves as a tool for accountability in education. By measuring students' learning outcomes against established standards, summative assessments help educational institutions, policymakers, and other stakeholders assess the effectiveness of instructional programs and curriculum. These assessments provide valuable data that can be used to identify areas of improvement, make informed decisions about resource allocation, and ensure that students are meeting academic expectations.
Types of Summative Assessment
There are several types of summative assessments commonly used in education, each serving a specific purpose and providing valuable insights into students' learning. Some of the most common types of summative assessment include:
- Standardized Tests: These tests are administered to all students in a standardized format and measure students' knowledge and skills against a set of predetermined criteria. Standardized tests are often used to assess students' proficiency in core subjects such as math, reading, and science.
- Final Exams: Final exams are comprehensive assessments administered at the end of a course or semester to evaluate students' understanding of the material covered throughout the term. These exams typically cover a wide range of topics and require students to demonstrate their knowledge and skills.
- Projects: Project-based assessments require students to apply their knowledge and skills to complete a hands-on project or task. These assessments allow students to demonstrate their creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities in a real-world context.
- Essays: Essay assessments require students to write a structured response to a prompt or question, demonstrating their ability to organize and communicate their ideas effectively. Essays are often used to assess students' writing skills, critical thinking, and analytical abilities.
- Presentations: Presentation assessments require students to deliver a speech or presentation on a specific topic, demonstrating their ability to communicate information clearly and persuasively. Presentations assess students' public speaking skills, research abilities, and presentation techniques.
Importance of Summative Assessment
Summative assessment plays a crucial role in the education system for several reasons:
- Evaluation of Learning: Summative assessments provide educators with a comprehensive view of students' learning outcomes and achievements. By evaluating students' performance at the end of an instructional period, educators can assess the effectiveness of their teaching methods and the extent to which students have mastered the learning objectives.
- Feedback for Improvement: While the primary purpose of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning, the results of these assessments can also provide valuable feedback for improvement. By analyzing students' performance on summative assessments, educators can identify areas of strength and weakness in the curriculum and make necessary adjustments to improve student learning outcomes.
- Accountability and Transparency: Summative assessments help ensure accountability and transparency in education by measuring students' learning outcomes against established standards. These assessments provide objective data that can be used to assess the effectiveness of educational programs, evaluate student performance, and make data-driven decisions to improve educational quality.
- Grading and Reporting: Summative assessments are often used to assign grades or scores to students, which are then used to evaluate their academic performance and progress. These grades provide valuable information to students, parents, and educators about students' achievements, strengths, and areas for improvement.
- Evidence of Learning: Summative assessments serve as evidence of students' learning and achievements, demonstrating the knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout the instructional period. These assessments provide a tangible record of students' progress and can be used to showcase their academic accomplishments to others.
In conclusion, summative assessment is a valuable tool in education that helps evaluate students' learning outcomes, measure their achievements, and ensure accountability in the education system. By providing a comprehensive view of students' performance at the end of an instructional period, summative assessments play a crucial role in assessing student progress, informing instructional decisions, and improving educational quality.
Upgrade Your Account
All paid plans include:, unlimited access to all tools.
Full use of Subject Explorer, Lesson Planner, Worksheets and more
Visual Understanding
Upload and analyze photos with advanced AI capabilities
Upgraded Intelligence
Get smarter, more relevant analysis for better insights
- 3 Subject Explorer analyses per month (non-logged in)
- 5 Subject Explorer analyses per month (with free account)
- Access to basic features
- Manage 1 Student (1 Primary)
- Analysis based on student age
- Unlimited access to all 10 Learning Corner tools
- Add & Manage 2 Students (1 Primary + 1 Additional)
- Add & Manage up to 5 Student Profiles (1 Primary + 4 Additional)
- Priority support
- Add & Manage up to 10 Student Profiles (1 Primary + 9 Additional)
Note: Your primary account is your first student profile. You can update your profile from the "My Account" dropdown in the main menu.
Educational institutions and large organizations: Email [email protected] for tailored pricing.
Got a feature request or is something not working? Let us know here or comment on Facebook .
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Have you gotten your free poster delivered? ✨
Formative, Summative, and More Types of Assessments in Education
All the best ways to evaluate learning before, during, and after it happens.

When you hear the word assessment, do you automatically think “tests”? While it’s true that tests are one kind of assessment, they’re not the only way teachers evaluate student progress. Learn more about the types of assessments used in education, and find out how and when to use them.
Diagnostic Assessments
Formative assessments, summative assessments.
- Criterion-Referenced, Ipsative, and Normative Assessments
What is assessment?
In simplest terms, assessment means gathering data to help understand progress and effectiveness. In education, we gather data about student learning in variety of ways, then use it to assess both their progress and the effectiveness of our teaching programs. This helps educators know what’s working well and where they need to make changes.
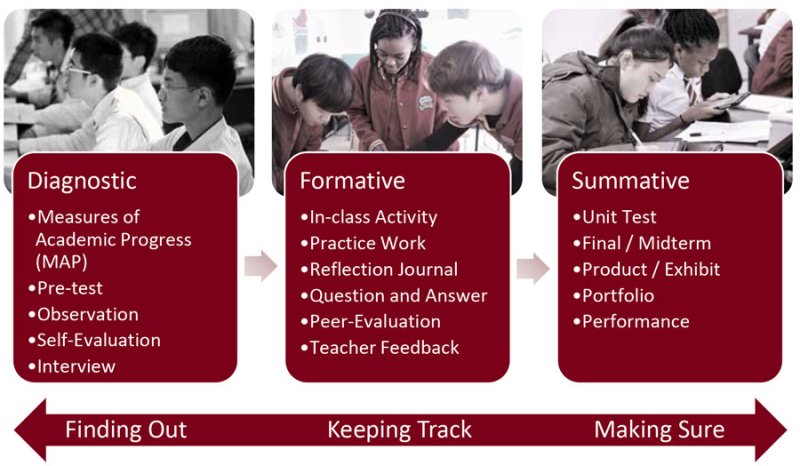
There are three broad types of assessments: diagnostic, formative, and summative. These take place throughout the learning process, helping students and teachers gauge learning. Within those three broad categories, you’ll find other types of assessment, such as ipsative, norm-referenced, and criterion-referenced.
What’s the purpose of assessment in education?
In education, we can group assessments under three main purposes:
- Of learning
- For learning
- As learning
Assessment of learning is student-based and one of the most familiar, encompassing tests, reports, essays, and other ways of determining what students have learned. These are usually summative assessments, and they are used to gauge progress for individuals and groups so educators can determine who has mastered the material and who needs more assistance.
When we talk about assessment for learning, we’re referring to the constant evaluations teachers perform as they teach. These quick assessments—such as in-class discussions or quick pop quizzes—give educators the chance to see if their teaching strategies are working. This allows them to make adjustments in action, tailoring their lessons and activities to student needs. Assessment for learning usually includes the formative and diagnostic types.
Assessment can also be a part of the learning process itself. When students use self-evaluations, flash cards, or rubrics, they’re using assessments to help them learn.
Let’s take a closer look at the various types of assessments used in education.

Diagnostic assessments are used before learning to determine what students already do and do not know. This often refers to pre-tests and other activities students attempt at the beginning of a unit. ADVERTISEMENT
How To Use Diagnostic Assessments
When giving diagnostic assessments, it’s important to remind students these won’t affect their overall grade. Instead, it’s a way for them to find out what they’ll be learning in an upcoming lesson or unit. It can also help them understand their own strengths and weaknesses, so they can ask for help when they need it.
Teachers can use results to understand what students already know and adapt their lesson plans accordingly. There’s no point in over-teaching a concept students have already mastered. On the other hand, a diagnostic assessment can also help highlight expected pre-knowledge that may be missing.
For instance, a teacher might assume students already know certain vocabulary words that are important for an upcoming lesson. If the diagnostic assessment indicates differently, the teacher knows they’ll need to take a step back and do a little pre-teaching before getting to their actual lesson plans.
Examples of Diagnostic Assessments
- Pre-test: This includes the same questions (or types of questions) that will appear on a final test, and it’s an excellent way to compare results.
- Blind Kahoot: Teachers and kids already love using Kahoot for test review, but it’s also the perfect way to introduce a new topic. Learn how Blind Kahoots work here.
- Survey or questionnaire: Ask students to rate their knowledge on a topic with a series of low-stakes questions.
- Checklist: Create a list of skills and knowledge students will build throughout a unit, and have them start by checking off any they already feel they’ve mastered. Revisit the list frequently as part of formative assessment.

Formative assessments take place during instruction. They’re used throughout the learning process and help teachers make on-the-go adjustments to instruction and activities as needed. These assessments aren’t used in calculating student grades, but they are planned as part of a lesson or activity. Learn much more about formative assessments here.
How To Use Formative Assessments
As you’re building a lesson plan, be sure to include formative assessments at logical points. These types of assessments might be used at the end of a class period, after finishing a hands-on activity, or once you’re through with a unit section or learning objective.
Once you have the results, use that feedback to determine student progress, both overall and as individuals. If the majority of a class is struggling with a specific concept, you might need to find different ways to teach it. Or you might discover that one student is especially falling behind and arrange to offer extra assistance to help them out.
While kids may grumble, standard homework review assignments can actually be a pretty valuable type of formative assessment . They give kids a chance to practice, while teachers can evaluate their progress by checking the answers. Just remember that homework review assignments are only one type of formative assessment, and not all kids have access to a safe and dedicated learning space outside of school.
Examples of Formative Assessments
- Exit tickets : At the end of a lesson or class, pose a question for students to answer before they leave. They can answer using a sticky note, online form, or digital tool.
- Kahoot quizzes : Kids enjoy the gamified fun, while teachers appreciate the ability to analyze the data later to see which topics students understand well and which need more time.
- Flip (formerly Flipgrid): We love Flip for helping teachers connect with students who hate speaking up in class. This innovative (and free!) tech tool lets students post selfie videos in response to teacher prompts. Kids can view each other’s videos, commenting and continuing the conversation in a low-key way.
- Self-evaluation: Encourage students to use formative assessments to gauge their own progress too. If they struggle with review questions or example problems, they know they’ll need to spend more time studying. This way, they’re not surprised when they don’t do well on a more formal test.
Find a big list of 25 creative and effective formative assessment options here.

Summative assessments are used at the end of a unit or lesson to determine what students have learned. By comparing diagnostic and summative assessments, teachers and learners can get a clearer picture of how much progress they’ve made. Summative assessments are often tests or exams but also include options like essays, projects, and presentations.
How To Use Summative Assessments
The goal of a summative assessment is to find out what students have learned and if their learning matches the goals for a unit or activity. Ensure you match your test questions or assessment activities with specific learning objectives to make the best use of summative assessments.
When possible, use an array of summative assessment options to give all types of learners a chance to demonstrate their knowledge. For instance, some students suffer from severe test anxiety but may still have mastered the skills and concepts and just need another way to show their achievement. Consider ditching the test paper and having a conversation with the student about the topic instead, covering the same basic objectives but without the high-pressure test environment.
Summative assessments are often used for grades, but they’re really about so much more. Encourage students to revisit their tests and exams, finding the right answers to any they originally missed. Think about allowing retakes for those who show dedication to improving on their learning. Drive home the idea that learning is about more than just a grade on a report card.
Examples of Summative Assessments
- Traditional tests: These might include multiple-choice, matching, and short-answer questions.
- Essays and research papers: This is another traditional form of summative assessment, typically involving drafts (which are really formative assessments in disguise) and edits before a final copy.
- Presentations: From oral book reports to persuasive speeches and beyond, presentations are another time-honored form of summative assessment.
Find 25 of our favorite alternative assessments here.
More Types of Assessments
Now that you know the three basic types of assessments, let’s take a look at some of the more specific and advanced terms you’re likely to hear in professional development books and sessions. These assessments may fit into some or all of the broader categories, depending on how they’re used. Here’s what teachers need to know.
Criterion-Referenced Assessments
In this common type of assessment, a student’s knowledge is compared to a standard learning objective. Most summative assessments are designed to measure student mastery of specific learning objectives. The important thing to remember about this type of assessment is that it only compares a student to the expected learning objectives themselves, not to other students.
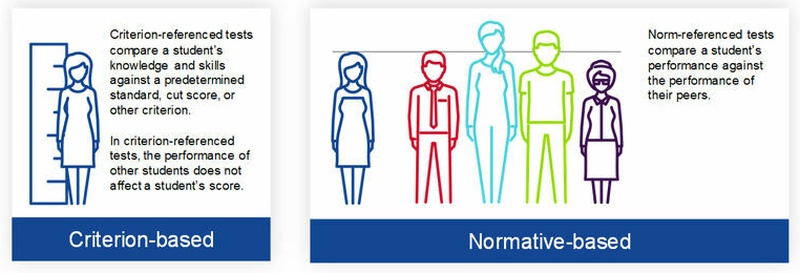
Many standardized tests are criterion-referenced assessments. A governing board determines the learning objectives for a specific group of students. Then, all students take a standardized test to see if they’ve achieved those objectives.
Find out more about criterion-referenced assessments here.
Norm-Referenced Assessments
These types of assessments do compare student achievement with that of their peers. Students receive a ranking based on their score and potentially on other factors as well. Norm-referenced assessments usually rank on a bell curve, establishing an “average” as well as high performers and low performers.
These assessments can be used as screening for those at risk for poor performance (such as those with learning disabilities) or to identify high-level learners who would thrive on additional challenges. They may also help rank students for college entrance or scholarships, or determine whether a student is ready for a new experience like preschool.
Learn more about norm-referenced assessments here.
Ipsative Assessments
In education, ipsative assessments compare a learner’s present performance to their own past performance, to chart achievement over time. Many educators consider ipsative assessment to be the most important of all , since it helps students and parents truly understand what they’ve accomplished—and sometimes, what they haven’t. It’s all about measuring personal growth.
Comparing the results of pre-tests with final exams is one type of ipsative assessment. Some schools use curriculum-based measurement to track ipsative performance. Kids take regular quick assessments (often weekly) to show their current skill/knowledge level in reading, writing, math, and other basics. Their results are charted, showing their progress over time.
Learn more about ipsative assessment in education here.
Have more questions about the best types of assessments to use with your students? Come ask for advice in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out creative ways to check for understanding ..

You Might Also Like

25 Formative Assessment Options Your Students Will Actually Enjoy
Get them excited to show you what they know! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Teaching Commons Autumn Symposium 2024
Get ready for autumn quarter at the Teaching Commons Autumn Symposium. Friday, September 27.
Summative Assessment and Feedback
Main navigation.
Summative assessments are given to students at the end of a course and should measure the skills and knowledge a student has gained over the entire instructional period. Summative feedback is aimed at helping students understand how well they have done in meeting the overall learning goals of the course.
Effective summative assessments
Effective summative assessments provide students a structured way to demonstrate that they have met a range of key learning objectives and to receive useful feedback on their overall learning. They should align with the course learning goals and build upon prior formative assessments. These assessments will address how well the student is able to synthesize and connect the elements of learning from the entirety of the course into a holistic understanding and provide an opportunity to provide rich summative feedback.
The value of summative feedback
Summative feedback is essential for students to understand how far they have come in meeting the learning goals of the course, what they need further work on, and what they should study next. This can affect later choices that students make, particularly in contemplating and pursuing their major fields of study. Summative feedback can also influence how students regard themselves and their academic disciplines after graduation.
Use rubrics to provide consistency and transparency
A rubric is a grading guide for evaluating how well students have met a learning outcome. A rubric consists of performance criteria, a rating scale, and indicators for the different rating levels. They are typically in a chart or table format.
Instructors often use rubrics for both formative and summative feedback to ensure consistency of assessment across different students. Rubrics also can make grading faster and help to create consistency between multiple graders and across assignments.
Students might be given access to the rubric before working on an assignment. No criteria or metric within a summative assessment should come as a surprise to the students. Transparency with students on exactly what is being assessed can help them more effectively demonstrate how much they have learned.
Types of summative assessments
Different summative assessments are better suited to measuring different kinds of learning.
Examinations
Examinations are useful for evaluating student learning in terms of remembering information, and understanding and applying concepts and ideas. However, exams may be less suited to evaluating how well students are able to analyze, evaluate, or create things related to what they've learned.
Presentation
A presentation tasks the student with teaching others what they have learned typically by speaking, presenting visual materials, and interacting with their audience. This can be useful for assessing a student's ability to critically analyze and evaluate a topic or content.
With projects, students will create something, such as a plan, document, artifact, or object, usually over a sustained period of time, that demonstrates skills or understanding of the topic of learning. They are useful for evaluating learning objectives that require high levels of critical thinking, creativity, and coordination. Projects are good opportunities to provide summative feedback because they often build on prior formative assessments and feedback.
With a portfolio, students create and curate a collection of documents, objects, and artifacts that collectively demonstrate their learning over a wide range of learning goals. Portfolios usually include the student's reflections and metacognitive analysis of their own learning. Portfolios are typically completed over a sustained period of time and are usually done by individual students as opposed to groups.
Portfolios are particularly useful for evaluating how students' learning, attitudes, beliefs, and creativity grow over the span of the course. The reflective component of portfolios can be a rich form of self-feedback for students. Generally, portfolios tend to be more holistic and are often now done using ePortfolios .

What is summative assessment? How to further learning with final exams

Grading can be learning, for both students and teachers.
By completing this form, you agree to Turnitin's Privacy Policy . Turnitin uses the information you provide to contact you with relevant information. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time.
Understanding the meaning and function of summative assessment helps clarify its role within education as a critical component of bridging teaching and learning. In this post, we take a closer look at summative assessment’s qualities with the end goal of ensuring that summative assessment supports learning and informs teaching.
Assessment is a term that describes tests, quizzes, exams, and assignments that measure student learning. Each of these methodologies can provide students and teachers with insights. Educators receive data on what students have and have not learned and gain observations into teaching efficacy and exam design. Students, in turn, recognize any learning gaps they might have, and when they receive feedback, understand next steps to further learning.
The most high-stakes type of assessment is called summative assessment. Summative assessment often comes at the endpoint of learning, whether at the end of a unit, course, or curriculum, serving largely as a pure evaluation of knowledge.
It’s easy to consider summative assessments as a final chapter to learning, but summative assessments can also act as a milestone and inform next steps for both educators and students. By examining the definition of summative assessment as well as its capabilities, educators can embrace its strengths, bolster its shortcomings, and foster learning.
Summative assessment is a specific type of assessment that evaluates learning and offers little opportunity for providing student feedback because of its positioning at the end of a learning unit. They are usually high-stakes, contributing to a large portion of a student’s course grade (e.g., final exams) or an exam that has a high impact on a student’s educational outcome. (e.g., standardized exams or entrance exams). Summative assessments include heavily weighted midterm exams, final exams, licensure tests, and standardized exams like A levels in the UK, SATs in the United States, Matriculation Exams in Finland, National Boards in India, or the CSAT in South Korea.
In such a high-stakes context, failing or struggling on summative assessments can negate student effort in other areas of study. On the other hand, summative assessment can be an effective tool to evaluate student knowledge and in the realm of licensure and certification exams, determine qualification for beginning a career.
While we aim to focus discussion on summative assessment, it’s important to describe another type of assessment to provide context; formative assessments not only evaluate learning but provide feedback to students and data to instructors. While formative assessments may or may not be given a grade, they most certainly further learning and occur throughout the course to support student learning needs, and often provide a safe space for failure . Formative assessments include assignments, tests, in-class activities, quizzes, and even midterm exams when they include feedback and opportunities for instructor intervention.
Best practices in formative assessment include providing timely and actionable feedback to students before the next assessment ( Hattie & Timperley, 2007 ).
While formative assessment is the measurement and support of learning as it takes place, summative assessments are evaluations of what a student has learned at the end of a given period (e.g., semester or training course). By assessing students at the end of a module, course, or curriculum, educators gain insight into how well their students have mastered the content and how effective their teaching methods were.
Even though summative assessments are situated at a point where students will find it hard to action results, data from summative assessments can still be used to inform curriculum planning and teaching, as well as any future exam adjustments.
That said, when possible, it’s important to balance formative and summative assessments within a term or curriculum. Fortifying summative assessments with prior formative assessments can support a student’s educational journey. Students who understand what they know and what they need to know in order to move forward are more likely to be prepared for final evaluation. Furthermore, preparing students for final evaluation with frequent opportunities to fail safely and receive feedback reduces stress, increases learning outcomes, and can mitigate academic misconduct .
While every type of assessment has its function to evaluate, every type of assessment, too, can be maximized for learning and teaching. Mid-course exams, for example, have the potential for both summative and formative qualities, serving to evaluate mastery (summative) and provide feedback to promote student learning (formative).
Without feedback, a midterm exam is purely summative. And while a summative component to a mid-course exam is reasonable, there is a lot more potential to them. It is important to provide feedback on mid-course exams so that students understand what they do and do not know and have the tools to bridge learning gaps for the next assessment and ultimately their final exam.
When assessments are provided with timely and actionable feedback, students have the information they need to facilitate their own learning; in this way, even high-stakes midterm exams can pivot towards formative learning opportunities for students. Additionally, summative assessments contain information critical for teacher and curriculum intervention as well as future exam design.
While formative assessments hinge on providing students with immediate feedback to help with the learning process, summative assessments happen after the student learning occurs. However, this doesn’t mean that communicating students’ performance is any less important.
For students to understand what content they have mastered and which topics might need additional study time, they need a detailed breakdown of their performance.
Categorizing summative assessment questions can give instructors the granular performance data they (and their students) need. By tagging exam items to course topics or learning objectives, faculty can provide the detailed feedback students need to be more focused in their study efforts.
Summative assessments are an important part of the assessment process and are incredibly valuable to both students and faculty. By ensuring high-stakes exams are secure, and providing students with performance feedback, educators can gain insight into how well students have learned the content and how well instructors have presented it.
Summative assessments evaluate content mastery. Generally, they are end-of-course or end-of-year exams; however, these are not the only applicable uses of summative assessments. Evaluating student learning could also come at the end of a chapter or learning module with mid-course exams.
Summative exams can also be multi-functional, as they, like all assessments, are rich with data. When item analysis and psychometrics accompany summative assessment, instruction is bolstered. When an assessment occurs at the end of a course or year or curriculum, data insights help educators make adjustments to teaching and curriculum so that future learning can be bolstered. When category-tagging is employed in tools like ExamSoft, educators can pinpoint student preparation for things like licensure exams. And conducting item analysis can inform effective exam design.
Summative assessments are by nature, high-stakes, and very stressful.
Who hasn’t woken from a nightmare in panic about missing or failing a final exam, even decades out from school? The reality that summative assessments can make or break academic success is deeply implanted in our psyche.
While there is little disagreement among educators about the need for or utility of summative assessments, debates and disagreements tend to center on issues of fairness and effectiveness, especially when summative-assessment results are used for high-stakes purposes.
Fair and inclusive assessments uphold accurate assessments. When exams are not fair nor inclusive, they become vulnerable to misconduct, resulting in missed learning opportunities. When exams do not cover what was taught, students may feel stressed and vulnerable. These missed opportunities can compound and widen learning gaps.
Assessments need to contain a variety of formats and question styles to measure different components of learning and include different learning styles. Summative assessments, when poorly designed, reward memorization rather than deep understanding of concepts. Encouraging competition between students, which can happen when grading on a curve, can also increase stress and decrease fairness.
Additionally, when test-takers are not sure how they will be evaluated, summative assessments can be unfair and inaccurate. Providing rubrics to students and graders ensures clarity of expectations and ensuing measurement of learning.
When summative assessments are stressful, do not accurately measure learning, aren’t preceded with learning opportunities beforehand, and/or don’t test what has been taught, they also become more vulnerable to academic misconduct and shortcut solutions like cheating, plagiarism, and AI Writing misuse.
Assessments are a checkpoint for student learning and teaching efficacy; consequently, accurate student responses are critical to increasing learning outcomes.
Most summative assessments are given with the understanding that the student’s score counts toward their final grade. As such, keeping these secure from academic dishonesty is paramount to providing a fair experience for all exam-takers. Though many educational institutions are moving to computer-based testing (CBT), taking exams on laptops or other devices brings a new list of potential security issues, such as access to the internet or other applications during an exam. An effective way to ensure exam integrity is testing software that does not allow use of the internet during an exam and prevents students from accessing other applications on their device.
Preventing academic dishonesty by blocking exam-takers’ information sources isn’t the only point to consider; ensuring students don’t share assessment items is also a concern. Once a test question is compromised, it’s no longer a valid measurement of student learning. Thus, keeping questions secure is vital.
Assessment security is a focus of Professor Phillip Dawson, an authority on assessment security from Deakin University in Australia, who defines assessment security as: “Measures taken to harden assessment against attempts to cheat. This includes approaches to detect and evidence attempts to cheat, as well as measures to make cheating more difficult.”
Dawson suggests a multilayered approach to assessment design, with seven standards for assessment security that institutions ought to consider:
- Coverage across a program - how much of a degree should be secured?
- Authentication - how do we ensure the student is who they say they are?
- Control of circumstances - how can we be sure the task was done in the intended circumstances?
- Difficulty to cheat metrics - we need to know how hard it may be to cheat a task.
- Detection accuracy metrics - we need to know if our detection methods work.
- Proof metrics - we need to be able to prove cases of cheating.
- Prevalence metrics - we need to know approximate rates of undetected, detected, and proven cheating ( Dawson, 2021 ).
According to Professor Roseanna Bourke, Director of Educational Psychology programme and Institute of Education at Massey University, there is a link between student cheating and student understanding and investment in the assigned tasks; when students don’t understand questions and lack confidence, learning itself becomes the barrier ( Bourke, Integrity Matters, n.d. ).
Providing support to students throughout a course or curriculum mitigates academic dishonesty in summative assessments. When students feel seen and supported with formative feedback in their educational journey, they are less likely to cheat. Additionally, rubrics can make clear the purpose of each question.
As stated, summative assessment is useful when the data exchange is maximized and accurate. Not only should it provide information about content mastery to instructors, it can also act as a reservoir of statistics about learning trends, item analysis, and exam effectiveness. Finally, and when possible, summative exams can take on formative qualities when feedback is provided. All of these data points directly benefit student learning.
Because it is a platform to demonstrate a culmination of knowledge, designing summative assessments is particularly critical to make the test accessible and inclusive for all different types of learners, and thus promote accurate measurement and data insights. Exam design principles include:
- Test what has been taught; aligning summative assessment with instruction models and promotes integrity for students.
- Design assessments that focus on measuring both breadth and depth of student knowledge and consider eliminating components that do not inform learning. Offer a variety of assessment formats. Multiple-choice questions can effectively breadth of knowledge in a limited time while short-answer and long-answer formats can evaluate higher-order thinking.
- Offering a variety of formats and questions styles within a summative assessment can also accommodate different learning styles. When diverse formats are offered, a larger spectrum of learning can be assessed. Additionally, diverse formats provide different ways for students to demonstrate their learning.
- And consider eliminating grading on a curve, which can increase competition between students, some of whom may be cheating ( UC Berkeley, 2020 ). Researchers Schinske and Tanner state, “Moving away from curving sets the expectation that all students have the opportunity to achieve the highest possible grade” ( Schinske & Tanner, 2014 ).
- A rubric, too, benefits students by clarifying expectations and acts as added assurance that tests align to previously-communicated learning goals.
Finally, the summative assessment itself is a living document, one that can be continuously optimized.
Analyze student responses to ensure assessments are fair, and to examine answer patterns to see if shortcut solutions have been utilized. Item analysis , or formally examining student responses and patterns, can show whether or not summative assessments are accurately assessing student knowledge. The data (Did every student get one particular question wrong? Did every student get one particular question correct? What kinds of answers are your test questions eliciting? Did you get the answers you expected?) can inform both exam design and teaching. Furthermore, item analysis supports exam robustness by highlighting questions on exams that may need adjustment.
Category tagging , a feature in ExamSoft assessment software, can offer more in-depth insights into future testing. A nursing program, for instance, can evaluate readiness for certification and the strength of curriculum to prepare students for standardized exams. Of course, category tagging can also fortify summative assessment within the curriculum.
In conclusion, summative assessments function largely as a way to evaluate learning at critical learning junctions, whether at the end of a term, end of a curriculum, or for advancement into the next level of schooling or licensure. The nature of summative assessments make them high-stakes, sometimes to the extent that they can negatively impact all prior learning. Moreover, they lack the opportunity for feedback, given their position in the educational journey.
That said, summative assessments are not wholly an endpoint. They are an intersection rich with data for educators to inform teaching, curriculum, and exam design. For students, too, there can be opportunities to learn, either by feedback or via data analysis, their own learning gaps and how to bridge them.
When educators maximize the potential of summative assessment, they can foster learning.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Understanding formative, summative, and interim assessment and their role in student learning

At its core, education is about the teaching and learning process. How do we teach the necessary literacies, content knowledge, critical thinking skills, and habits of mind deemed essential to prepare our children for productive, fulfilling, and engaged lives? How do we know whether students have learned what was taught and to what degree? Formative, summative, and interim assessment strives to answer these questions, providing valuable insights on the degree to which the teaching and learning process succeeded.
That said, there is often confusion as to what types of assessments are administered when, what data they provide, and how they benefit teachers, students, and families. Here’s a quick rundown on the three main assessment types and what they are used for.
Formative assessment guides learning
Formative assessment includes sharing learning goals, modeling what success looks like, and giving clear, actionable feedback to students. By design, formative assessment:
- Has an explicit connection to an instructional unit
- Should never be used for grading
- Consists of many kinds of strategies , and can be as informal as asking a well-crafted question—and using the evidence collected from the question
- Helps educators guide the learning process, rather than measure student performance
- Provides students with data they can use to determine where they are in their learning, set goals, monitor their learning progress, and serve as instructional resources for their peers
Summative assessment certifies learning
Generally, educators administer a summative assessment near the end of an instructional unit to help them answer the question, “What did students learn?” All sorts of different assessment instruments are used for summative assessment, including:
- End-of-unit tests and end-of-course tests
- Performance tasks/simulations
- Oral examinations
- Research reports
- Standardized state summative assessments
Despite the array of possible summative instruments, it’s the state summative assessments that often come to mind. Federal educational policy requires data collected from these tests to be used for accountability purposes; other high stakes are associated with summative assessment, such as selection, promotion, and graduation. Legislators also use state summative assessment data to communicate the state of education to the public.
Since summative assessment happens so late in the instructional process, the most effective use of its test data is more evaluative than instructional. For teachers, data can help guide decisions, such as grades for a course, promotion to the next grade, graduation, credit for courses, and more. Summative assessment data also plays a role at the administrative level, where it can be used for planning curricula, determining professional development needs, and identifying the resources and federal assistance a district needs to flourish.
Interim assessment guides teaching and learning
A wide middle ground exists between teachers’ day-to-day formative assessment of student learning and the formal protocols of state summative assessment. This middle ground offers opportunities—captured under the umbrella term “interim assessment”—to gather information about many things that are relevant to the teaching and learning process, including:
- Individual and collective student growth
- Effectiveness of teaching practices, programs, and initiatives
- Projection of whether a student, class, or school is on track to achieve established proficiency benchmarks
- Instructional needs of individual students
Educators can use interim assessment in a formative way to directly guide instruction. When this happens, data aggregation is considered the key difference between formative and interim assessment. This ability to aggregate data at critical points in the learning cycle allows interim assessment to have a broader set of purposes than both formative and summative assessment. As a result, interim assessment is the only type of assessment that provides educators with data for instructional, predictive, and evaluative purposes.
To understand the value of interim assessment, it’s helpful to understand its variety of purposes. One is to provide educators insight into growth patterns in student learning. Growth can be calculated from student achievement scores taken at logical intervals, such as fall to spring, or fall to fall, or whatever makes the most sense for a district. Many educators use a fall-winter-spring schedule when administering MAP® Growth™ , our interim assessment. The seasonal system permits enough instructional time between test administrations to allow educators to calculate growth in learning with statistical confidence.
Another purpose of interim assessment is to help teachers make decisions around differentiating instruction. If the assessment is adaptive, those decisions can better serve all the students in the class, not only those who are ready to learn at grade level. Within any given classroom, teachers will have students who are ready to go deep with concepts, be challenged, and apply and expand their learning. Conversely, there will be other students who need to learn foundational concepts and skills before they’re prepared for grade-level concepts and skills. Interim assessment can help identify gaps so all students have the opportunity to grow, no matter where they are starting from.
These missing foundational concepts and skills may be from the previous grade, or even further back. The gaps provide an enormous challenge for teachers whose only information on their students relates to specific grade-level content. For the students who are ready to be challenged, what are they ready to be challenged by? And for the students who are not prepared to learn grade-level standards yet, where are they in their learning?
MAP Growth quickly and precisely targets every student’s level of achievement—including students performing at, above, or below grade level. Interim assessment does more than help teachers instructionally. It also supports students in looking at their own growth: where they are and want to go, what their goals should be , and what an action plan for learning looks like. The other purposes of interim assessment are predictive and evaluative. Its data can help educators predict student performance on important markers and evaluate whether teaching strategies, programs, and curricula are effective.
Recommended for you

Sharing assessment data with parents just got simpler

Data in education: Starting small and seeking professional learning

Getting schooled on the MAP Growth Class Profile report
- View all posts

Reading differentiation made easy
MAP Reading Fluency now includes Coach, a virtual tutor designed to help students strengthen reading skills in as little as 30 minutes a week.

Helping students grow
Students continue to rebound from pandemic school closures. NWEA® and Learning Heroes experts talk about how best to support them here on our blog, Teach. Learn. Grow.
See the post

Put the science of reading into action
The science of reading is not a buzzword. It’s the converging evidence of what matters and what works in literacy instruction. We can help you make it part of your practice.
Get the guide

Support teachers with PL
High-quality professional learning can help teachers feel invested—and supported—in their work.
Read the article
Content disclaimer:
Teach. Learn. Grow. includes diverse perspectives that are meant to be a resource to educators and leaders across the country and around the world. The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of NWEA.
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
Summative Assessment And Student Success: A Comprehensive Review
Zoe Benjamin
Are you looking to design summative assessments that accurately measure how much your students have learned and how well they have mastered the content and skills? It may seem like creating a test is a straightforward task – just jot down some questions and select the answers. But if you aspire to create assessments that genuinely reflect your learners’ abilities and enhance their academic achievements, you need to adopt a more considerate approach.
In this article, we’ll delve into the benefits and limitations of summative assessments on student achievement and provide recommendations for teachers to improve the effectiveness of summative assessments for their learners.
What is summative assessment?
Examples of summative assessment, formative vs summative assessments, benefits of summative assessment practices , how can summative assessment impact student achievement, limitations of summative assessment, summative assessment tips for teachers.
An evaluation of students’ current understanding and achievement. It allows teachers to track learners’ progress over a period of time. These types of assessments are typically used to assign grades and determine how well students have mastered the learning objectives at a particular point in time. The findings can be utilized to determine their academic growth and make informed decisions about how to support each student in succeeding.

Common Core Practice Tests Grades 3 to 8
Prepare for your state math test with these Grades 3 to 8 practice assessments for Common Core.
They can take many forms, including standarized tests, exams, projects, or essays, and are often scored to provide a quantifiable measure of students’ performance.
Some examples include:
- Portfolios of work created by students to include samples of their work and projects from different subjects, showcasing their growth and learning over time.
- A final project following a period of group work.
- Midterm exams or classroom assessments at the end of a unit of study.
- Performance assessments that showcase students’ development of new skills.
- Standardized tests that are typically administered at the state or national level and help assess students’ overall proficiency in these subjects.
The difference between formative assessment and summative assessment is their purpose, design, frequency, and outcomes. While summative assessment is an assessment of learning, formative assessment is an assessment for learning . Formative and summative assessments are the two types of assessment that are most prevalent in education literature. The table below shows their main characteristics:
| Summative Assessment | ||
| Purpose | to provide feedback on students’ learning To identify areas where students might be struggling and to offer timely interventions to improve their understanding | To evaluate students’ learning outcomes and achievement at the end of a specific instructional period To determine the overall level of understanding and competence a student has achieved |
| Frequency | Conducted throughout the learning process, at regular intervals They can be ongoing and are often used to inform instructional decisions | End of a unit, semester, course, or year |
| Outcome | Feedback and specific guidance for improvement Identifying areas of weakness and adapting instruction Monitoring learning progress and providing timely interventions | Evaluating overall achievement and learning outcomes Assigning grades or scores to summarize performance Assessing program effectiveness and accountability |
| Examples | Quizzes, in-class discussions, homework assignments, projects, classroom observations | Final exams, standardized tests, end-of-term projects, state assessments |
The benefits of summative assessments may not be as apparent as those of formative assessment, as they are often less immediate and direct than the advantages gained from ongoing assessment strategies that promote learning.
But summative assessments bring many benefits that enhance teaching and learning.
Tracking student progress
Summative assessments offer assessment data that is typically used to track student progress over time. This data indicates whether students are making the expected level of progress based on their age and abilities.
Accountability
The results of summative assessments provide an objective measure of accountability for teachers and students.
Summative assessments provide high-stake conditions for students to showcase their capabilities to themselves and others. These assessments motivate students to prepare and revise more thoroughly than they might for other types of evaluations.
Teachers can use students’ end-of-year or external assessment results in their appraisal meetings to evaluate their teaching approaches. Additionally, students can be held accountable if their results indicate a decrease in effort or underperformance in one or more subjects.
Motivating students
However, lower-ability students and those with exam anxiety may be less motivated by summative assessments, which can lead to a decrease in their effort and motivation as the assessment date approaches.
Preparation for external exams
End-of-year state assessments are external exams that act as summative assessments at the end of a school year. High stakes classroom assessments, such as midterm exams, offer valuable exam practice for time management, meeting assessment objectives, and managing exam anxiety.
Retrieving information from long-term memory during summative assessments strengthens memory for that information and related concepts, which can be beneficial for students during external exams.
Standardization
Summative assessments can provide schools and education systems with objective data to create standardized scores for each learner. This enables individuals and small cohorts to be compared to other students and larger cohorts.
Standardization is often used to determine the grade boundaries in external exams, which are then used by universities to set their entry requirements.
The manner in which summative assessment is carried out can have a considerable impact on the academic progress of students.
Summative assessment helps:
- track student knowledge and progress and identify underachievement, allowing for interventions to be put in place.
- reveal issues with exam technique, which may not be identified through formative assessments.
- hold students and teachers accountable and increase motivation to improve results.
- prepare students for external exams, improving long-term memory retrieval and adjusting revision and exam strategies accordingly.
In all cases above, increased achievement is defined as achieving a higher result in a future summative assessment.
This may not be a reliable or valid measure of achievement, but until education institutions move away from standardized testing and entry requirements that depend on the results of summative assessments, it is an important measure to consider.
Summative assessments are widely used in education to measure student achievement, but they also have limitations every teacher should be aware of:
Provides a limited snapshot of student achievement
Summative assessment is limited in that it provides a snapshot of student achievement at one point in time and uses a limited range of assessment strategies.
Comparing students based on summative grades might be unfair
Using summative grades to compare students to each other or to gain entry into a high school or university, seems unfair when final grades are so dependent on factors outside of students’ control.
Summative assessments emphasize memorization
Summative assessments often require students to memorize material, which is becoming an increasingly redundant skill given how readily information is available online.
Time spent memorizing material ahead of a summative assessment could be better spent deepening students’ understanding or improving their ability to critically interact with new material.
As a teacher, designing and administering effective summative assessments can be challenging. Here are some tips to help you create successful summative assessments for your students.
1. Design a summative assessment based on its purpose
Consider the purpose of the assessment and allow this to determine the most appropriate design for the summative assessment.
If the purpose of the assessment is preparation for an external exam, mimic the format, length, and question style of the external exam paper.
If the purpose of the assessment is to track progress, include questions that relate to knowledge tested on a previous assessment and questions to gain benchmark data for a future assessment.
2. Offer clear instructions throughout the assessment
Ensure the instructions throughout the assessment clearly convey what is required from the student (e.g. show each step of your calculation).
Create a mark scheme or rubric before the assessment is set so that you are clear about what is required from each question and check that the exam instructions accurately explain this to the students.
3. Ensure consistency in summative assessments from year to year
Use the same summative assessments each year so that each cohort of students can be compared to cohorts from previous years. This allows departments to evaluate their own performance and to make adjustments if a cohort’s performance differs significantly from previous years.
Utilize the benefits of retrieval practice and spacing by including a mixture of recent and past topics on each summative assessment.
4. Prepare students in advance
Prepare students for summative assessments and reduce exam anxiety by producing practice papers that match the summative assessment in terms of style and content.
Summative assessment is designed to produce a measure of achievement. It is important because it helps teachers to track their students’ progress and gives students an opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge to external organizations such as employers or universities.
An assessment that has a clear purpose and allows comparisons to be made with the results or past or future assessments.
External exams like end-of-year state assessments End of year or end of topic exams Benchmark or aptitude tests that measure transferable skills and academic potential
Do you have students who need extra support in math? Give your students more opportunities to consolidate learning and practice skills through personalized math tutoring with their own dedicated online math tutor. Each student receives differentiated instruction designed to close their individual learning gaps, and scaffolded learning ensures every student learns at the right pace. Lessons are aligned with your state’s standards and assessments, plus you’ll receive regular reports every step of the way. Personalized one-on-one math tutoring programs are available for: – 2nd grade tutoring – 3rd grade tutoring – 4th grade tutoring – 5th grade tutoring – 6th grade tutoring – 7th grade tutoring – 8th grade tutoring Why not learn more about how it works ?
The content in this article was originally written by secondary maths teacher Zoe Benjamin and has since been revised and adapted for US schools by math curriculum specialist and former elementary math teacher Katie Keeton.
Related articles

6 Types Of Assessments And How To Use Them Effectively To Inform Your Teaching

Progress Monitoring: What It Is And How You Can Use It To Accelerate Math Achievement
![meaning of summative in education 10 Exit Ticket Ideas To Use In The Classroom [Includes Exit Ticket Templates]](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Exit-ticket-1-180x160.jpg)
10 Exit Ticket Ideas To Use In The Classroom [Includes Exit Ticket Templates]

Formative Assessment: Why Is It Still Important For Your Teaching?
3rd to 6th Grade Math Test [FREE]
Always searching for high quality, pedagogically sound, off-the-shelf questions you can trust? Help students prepare for your state’s math tests with these practice assessments carefully created by our math experts to save you time.
Includes 40 multiple choice questions with detailed answers to support test prep, covering a range of topics and aligned to state standards.
Privacy Overview
25 Summative Assessment Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
Summative assessment is a type of achievmeent assessment that occurs at the end of a unit of work. Its goal is to evaluate what students have learned or the skills they have developed. It is compared to a formative assessment that takes place in the middle of the unit of work for feedback to students and learners.
Performance is evaluated according to specific criteria, and usually result in a final grade or percentage achieved.
The scores of individual students are then compared to established benchmarks which can result in significant consequences for the student.
A traditional example of summative evaluation is a standardized test such as the SATs. The SATs help colleges determine which students should be admitted.
However, summative assessment doesn’t have to be in a paper-and-pencil format. Project-based learning, performance-based assessments, and authentic assessments can all be forms of summative assessment.
Summative vs Formative Assessment
Summative assessments are one of two main types of assessment. The other is formative assessment.
Whereas summative assessment occurs at the end of a unit of work, a formative assessment takes place in the middle of the unit so teachers and students can get feedback on progress and make accommodations to stay on track.
Summative assessments tend to be much higher-stakes because they reflect a final judgment about a student’s learning, skills, and knowledge:
“Passing bestows important benefits, such as receiving a high school diploma, a scholarship, or entry into college, and failure can affect a child’s future employment prospects and earning potential as an adult” (States et al, 2018, p. 3).
Summative Assessment Examples
Looking for real-life examples of well-known summative tests? Skip to the next section .
1. Multiple-Choice Exam

Definition: A multiple-choice exam is an assessment where students select the correct answer from several options.
Benefit: This format allows for quick and objective grading of students’ knowledge on a wide range of topics.
Limitation: It can encourage guessing and may not measure deep understanding or the ability to synthesize information.
Design Tip: Craft distractors that are plausible to better assess students’ mastery of the material.
2. Final Essay

Definition: A final essay is a comprehensive writing assessment that requires students to articulate their understanding and analysis of a topic.
Benefit: Essays assess critical thinking, reasoning, and the ability to communicate ideas in writing.
Limitation: Grading can be subjective and time-consuming, potentially leading to inconsistencies.
Design Tip: Provide clear, detailed rubrics that specify criteria for grading to ensure consistency and transparency.
3. Lab Practical Exam

Definition: A lab practical exam tests students’ ability to perform scientific experiments and apply theoretical knowledge practically.
Benefit: It directly assesses practical skills and procedural knowledge in a realistic setting.
Limitation: These exams can be resource-intensive and challenging to standardize across different settings or institutions.
Design Tip: Design scenarios that replicate real-life problems students might encounter in their field.
4. Reflective Journal

Definition: A reflective journal is an assessment where students regularly record learning experiences, personal growth, and emotional responses.
Benefit: Encourages continuous learning and self-assessment, helping students link theory with practice.
Limitation: It’s subjective and heavily dependent on students’ self-reporting and engagement levels.
Design Tip: Provide prompts to guide reflections and ensure they are focused and meaningful.
5. Open-Book Examination

Definition: An open-book examination allows students to refer to their textbooks and notes while answering questions.
Benefit: Tests students’ ability to locate and apply information rather than memorize facts.
Limitation: It may not accurately gauge memorization or the ability to quickly recall information.
Design Tip: Focus questions on problem-solving and application to prevent students from merely copying information.
6. Group Presentation

Definition: A group presentation is an assessment where students collaboratively prepare and deliver a presentation on a given topic.
Benefit: Enhances teamwork skills and the ability to communicate ideas publicly.
Limitation: Individual contributions can be uneven, making it difficult to assess students individually.
Design Tip: Clearly define roles and expectations for all group members to ensure fair participation.
7. Poster Presentation

Definition: A poster presentation requires students to summarize their research or project findings on a poster and often defend their work in a public setting.
Benefit: Develops skills in summarizing complex information and public speaking.
Limitation: Space limitations may restrict the amount of information that can be presented.
Design Tip: Encourage the use of clear visual aids and a logical layout to effectively communicate key points.
8. Infographic

Definition: An infographic is a visual representation of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.
Benefit: Helps develop skills in designing effective and attractive presentations of complex data.
Limitation: Over-simplification might lead to misinterpretation or omission of critical nuances.
Design Tip: Teach principles of visual design and data integrity to enhance the educational value of infographics.
9. Portfolio Assessment

Definition: Portfolio assessment involves collecting a student’s work over time, demonstrating learning, progress, and achievement.
Benefit: Provides a comprehensive view of a student’s abilities and improvements over time.
Limitation: Can be logistically challenging to manage and time-consuming to assess thoroughly.
Design Tip: Use clear guidelines and checklists to help students know what to include and ensure consistency in assessment.
10. Project-Based Assessment

Definition: Project-based assessment evaluates students’ abilities to apply knowledge to real-world challenges through extended projects.
Benefit: Encourages practical application of skills and fosters problem-solving and critical thinking.
Limitation: Time-intensive and may require significant resources to implement effectively.
Design Tip: Align projects with real-world problems relevant to the students’ future careers to increase engagement and applicability.
11. Oral Exams

Definition: Oral exams involve students answering questions spoken by an examiner to assess their knowledge and thinking skills.
Benefit: Allows immediate clarification of answers and assessment of communication skills.
Limitation: Can be stressful for students and result in performance anxiety, affecting their scores.
Design Tip: Create a supportive environment and clear guidelines to help reduce anxiety and improve performance.
12. Capstone Project

Definition: A capstone project is a multifaceted assignment that serves as a culminating academic and intellectual experience for students.
Benefit: Integrates knowledge and skills from various areas, fostering holistic learning and innovation.
Limitation: Requires extensive time and resources to supervise and assess effectively.
Design Tip: Ensure clear objectives and support structures are in place to guide students through complex projects.
Real-Life Summative Assessments
- Final Exams for a College Course: At the end of the semester at university, there is usually a final exam that will determine if you pass. There are also often formative tests mid-way through the course (known in England as ICAs and the USA as midterms).
- SATs: The SATs are the primary United States college admissions tests. They are a summative assessment because they provide a final grade that can determine whether a student gets into college or not.
- AP Exams: The AP Exams take place at the end of Advanced Placement courses to also determine college readiness.
- Piano Exams: The ABRSM administers piano exams to test if a student can move up a grade (from grades 1 to 8), which demonstrates their achievements in piano proficiency.
- Sporting Competitions: A sporting competition such as a swimming race is summative because it leads to a result or ranking that cannot be reneged. However, as there will always be future competitions, they could also be treated as summative – especially if it’s not the ultimate competition in any given sport.
- Drivers License Test: A drivers license test is pass-fail, and represents the culmination of practice in driving skills.
- IELTS: Language tests like IELTS are summative assessments of a person’s ability to speak a language (in the case of IELTS, it’s English).
- Citizenship Test: Citizenship tests are pass-fail, and often high-stakes. There is no room for formative assessment here.
- Dissertation Submission: A final dissertation submission for a postgraduate degree is often sent to an external reviewer who will give it a pass-fail grade.
- CPR Course: Trainees in a 2-day first-aid and CPR course have to perform on a dummy while being observed by a licensed trainer.
- PISA Tests: The PISA test is a standardized test commissioned by the OECD to provide a final score of students’ mathematic, science, and reading literacy across the world, which leads to a league table of nations.
- The MCATs: The MCATs are tests that students conduct to see whether they can get into medical school. They require significant study and preparation before test day.
- The Bar: The Bar exam is an exam prospective lawyers must sit in order to be accepted as lawyers in their jurisdiction.
Summative assessment allows teachers to determine if their students have reached the defined behavioral objectives . It can occur at the end of a unit, an academic term, or academic year.
The assessment usually results in a grade or a percentage that is recorded in the student’s file. These scores are then used in a variety of ways and are meant to provide a snapshot of the student’s progress.
Although the SAT or ACT are common examples of summative assessment, it can actually take many forms. Teachers might ask their students to give an oral presentation, perform a short role-play, or complete a project-based assignment.
Brookhart, S. M. (2004). Assessment theory for college classrooms. New Directions for Teaching and Learning , 100 , 5-14. https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.165
Dixon, D. D., & Worrell, F. C. (2016). Formative and summative assessment in the classroom. Theory into Practice , 55 , 153-159. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405841.2016.1148989
Geiser, S., & Santelices, M. V. (2007). Validity of high-school grades in predicting student success beyond the freshman year: High-school record vs. standardized tests as indicators of four-year college outcomes. Research and Occasional Paper Series. Berkeley, CA: Center for Studies in Higher Education, University of California.
Kibble J. D. (2017). Best practices in summative assessment. Advances in Physiology Education , 41 (1), 110–119. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.00116.2016
Lungu, S., Matafwali, B., & Banja, M. K. (2021). Formative and summative assessment practices by teachers in early childhood education centres in Lusaka, Zambia. European Journal of Education Studies, 8 (2), 44-65.
States, J., Detrich, R., & Keyworth, R. (2018). Summative Assessment (Wing Institute Original Paper). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.16788.19844

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTS: MEANING, EXAMPLES AND TYPES
As an educator, you must have heard of formative and summative evaluations. But, do you know what they are and…

As an educator, you must have heard of formative and summative evaluations . But, do you know what they are and how they differ from one another?
Formative and summative evaluations are two overlapping ways of assessing pupils. Both formative and summative evaluations complement each other while examining a learner’ progress. The end goal of both is to establish the strengths, weaknesses and developmental patterns of students. Formative and summative evaluations are designed so that each type of evaluation gives actionable insights to educationists.
A holistic assessment practice would combine the best features of both formative and summative evaluations , depending on how they can contribute toward the end goal. A combination of the two can improve educational attainment levels and maximize efficacy.
The Meaning Of Summative Assessments
Definition of summative assessment, summative assessment meaning, summative assessment examples, types of summative assessments, benefits of summative assessment, how to use summative assessment, characteristics of summative assessment, assess and evaluate with harappa.
Which are the most effective summative evaluations ? Which formative evaluations are more creative? It appears that summative evaluation has a much greater online presence. Educators are liberally using online tools to track summative evaluations compared to formative evaluations.
Summative assessments are evaluative instead of diagnostic and help ascertain if the stated objectives of the course are being met. They help evaluate the performance of the learner against a predetermined benchmark. The stakes for such assessments are usually very high and have a high value point. These consist of clear instructions and grading rubric to see how much the student has understood and retained. Rubric is a tool that describes the instructor’s performance expectations from an assignment.
Summative assessments can be complemented with materials that help the teacher analyze results and take better actions for strategic learning. This strategy is also now also being incorporated in a number of e-learning modules.
Let’s dive deeper by examining the key differences between summative and formative evaluations , the different types of summative evaluations, the purpose of summative assessments and how summative evaluation is essential to learner development. We’ll gloss over the advantages and disadvantages of summative assessment , and finally review some examples.
A simple definition of summative assessment is that it helps evaluate student learning, knowledge gained and proficiency at the end of an instructional course or learning program. The definition of summative assessment is better understood if we also understand the meaning of formative assessments. When both approaches are combined, chances of success are maximized.
The meaning of summative assessment is that it judges a student’s level of learning and academic prowess at the end of the year or term of learning. This is done by comparing the evaluation against a set, universal standard or benchmark that’s been established in advance.
Now that we’ve outlined the meaning of summative assessment , let’s view some examples.
You can find many examples of summative assessment . Here we’ll list some summative assessment examples that are directly related to student performance. These are:
- Half-yearly, mid-term and end-of-term exams
- Unit tests or chapter tests
- Projects, assignments and creative portfolios
- Tests that are standardized and demonstrate the proficiency of a school. These are often used in admissions. Some of these summative assessment examples are SAT, GCSEs and A-Levels
Summative assessments are indispensable within the learning framework and every individual should acknowledge their profound importance in learning and development of an individual.
There can be several types of summative assessment . Some of these are:
- Teacher-designed quizzes and tests that include short essays, multiple-choice questions, short answers, matching activities and fill in the blanks
- Writing and analytical skills are tested through research papers, media reviews, articles, blogs, pamphlets and brochures
- Descriptive presentations for various audiences can include role play, drama, panel discussions, exhibitions, clay models, debates, musical pieces and dioramas
- Technical creations such as machines, blueprints, spreadsheets, computer programs, podcasts, web pages, collages and channels
- Kinesthetic practices such as aerobics and dance are a unique type of summative assessment
These different types of summative assessment should be designed to align with the goals and outcomes that are needed from these assessments.
There are a host of summative assessment benefits that can help students and teachers reap long-term rewards. These are:
1. Student Motivation
The importance of summative assessment is in its ability to keep students motivated to study throughout the year. Good grades can benefit students and encourage them to put in more effort. For example, SAT practice tests are usually associated with a higher-than-average point increase.
2. Applying Learning
Summative assessments and evaluations are not just about memorizing math multiplication tables. Well-designed assessments can help students apply these skills to the real world. Tests such as multiple-choice questions help students critically analyze what they have learnt and apply that knowledge.
3. Identifying Gaps In Learning
Another importance of summative assessments is that they identify any learning gaps and help bridge them. Most teachers conduct unit tests at the end of each chapter to understand how much students have retained and then progress to the next unit. The students who lag behind can be given extra coaching or encouragement to catch up with the rest of the class.
4. Identifying Teaching Gaps
Another important benefit of summative assessments is that they reveal teaching gaps. Teaching styles may not necessarily be perfect and sometimes teachers miss their mark. One purpose of summative assessment could be making the learning program more student-friendly. If all students are faring poorly, then the grading is probably not related to study time. Some ways by which gaps in teaching can be addressed are:
- Including visual aids in the program
- Excluding or including word problems
- Incorporating interesting and innovative teaching styles that facilitate better student assessment
5. Giving Valuable Insights
Summative assessments benefits also include giving evaluators necessary insights and feedback on student progress and performance. It can highlight what worked and what didn’t. The management can make informed and calculated decisions on which part of the curriculum needs tweaking. This makes it easier on both students and evaluators.The importance of summative assessments can’t be overlooked. Some summative assessments are so well-structured that they give valuable data to academicians at the national and global levels. The entire curriculum can be overhauled if need be. The average test scores of a particular school impact its overall grading. This also determines whether the academic institution will continue to be eligible for further funding or attract the same caliber of student.
The purpose of summative assessment is to enhance learning. The structured and standardized exams that form a part of the curriculum leave little room for innovation or imagination. However, there are other ways by which summative assessments can be made extremely interesting.
We are entering the virtual era where online platforms for student learning abound.Digital literacy can help to re-engage students and divert their attention from the conventional classroom formats. Dragging and dropping answers, MCQs and podcasts are just a few of the tools that can foster learning through summative assessments. Students should be allowed to express themselves comfortably.
Multi-modal summative assessments test the learners’ prowess in different ways. Teachers can get an accurate picture of how much the student has grasped. Final exams can be set in a format that prepares students for job applications and increases their vocational proficiency.
Ideally, a combination of formative and summative assessments is needed to get the best results.
Summative assessments usually have a higher value or stakes compared to formative assessments. Here are some characteristics of summative assessments that you need to know:
- One purpose of a summative assessment is using rubric to lay out the expected criteria of performance for different grade ranges
- Questions have a clear design and meaning, allowing students to creatively express themselves
- Most summative assessments are structured in a way to assess comprehension. These give opportunities to students to consider courses as a holistic element, making broader connections and exhibiting specific skills
- The parameters of summative assessments are usually extremely well-defined. Such parameters include response time, grading method, time and date. This allows students with disabilities to adapt and attempt tests with the right support
- Blind grading techniques are also a part of summative assessments. These give unbiased feedback to students, eliminating the possibility of favoritism
While there are advantages and disadvantages of summative assessments , the pros outnumber the cons. Overall, a comprehensive summative assessment program gives the best insights into where someone stands compared to their peers. It’s a well established way of transforming the classroom environment.
For students and teachers, learning and evaluating is a continuous process. It can be liberating and empowering when you have the chance to build a new skill set. Harappa’s Inspiring faculty program teaches how to learn from experience, get critical insights, reflect on your performance and acquire a new edge.
These insights can be applied to your career and vocation. Assessment tools can open a whole new world of agile learning and adept performance. Our courses offer a strategic path to success. With resilience and diligence, you can take on newer assessment challenges that will prepare you well for the future. Push yourself to learn and grow. Enroll today and unlock expert advice from some of our leading faculty.

- CORE CURRICULUM
- LITERACY > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Literature, 6-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Literature, 6-12" aria-label="Into Literature, 6-12"> Into Literature, 6-12
- LITERACY > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Reading, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Reading, K-6" aria-label="Into Reading, K-6"> Into Reading, K-6
- INTERVENTION
- LITERACY > INTERVENTION > English 3D, 4-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="English 3D, 4-12" aria-label="English 3D, 4-12"> English 3D, 4-12
- LITERACY > INTERVENTION > Read 180, 3-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Read 180, 3-12" aria-label="Read 180, 3-12"> Read 180, 3-12
- SUPPLEMENTAL
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12" aria-label="A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12"> A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Amira Learning, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Amira Learning, K-6" aria-label="Amira Learning, K-6"> Amira Learning, K-6
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Classcraft, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classcraft, K-8" aria-label="Classcraft, K-8"> Classcraft, K-8
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > JillE Literacy, K-3" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="JillE Literacy, K-3" aria-label="JillE Literacy, K-3"> JillE Literacy, K-3
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Waggle, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Waggle, K-8" aria-label="Waggle, K-8"> Waggle, K-8
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Writable, 3-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Writable, 3-12" aria-label="Writable, 3-12"> Writable, 3-12
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > ASSESSMENT" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="ASSESSMENT" aria-label="ASSESSMENT"> ASSESSMENT
- CORE CURRICULUM
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Arriba las Matematicas, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Arriba las Matematicas, K-8" aria-label="Arriba las Matematicas, K-8"> Arriba las Matematicas, K-8
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Go Math!, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Go Math!, K-6" aria-label="Go Math!, K-6"> Go Math!, K-6
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12" aria-label="Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12"> Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Math, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Math, K-8" aria-label="Into Math, K-8"> Into Math, K-8
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Math Expressions, PreK-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math Expressions, PreK-6" aria-label="Math Expressions, PreK-6"> Math Expressions, PreK-6
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Math in Focus, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math in Focus, K-8" aria-label="Math in Focus, K-8"> Math in Focus, K-8
- SUPPLEMENTAL
- MATH > SUPPLEMENTAL > Classcraft, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classcraft, K-8" aria-label="Classcraft, K-8"> Classcraft, K-8
- MATH > SUPPLEMENTAL > Waggle, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Waggle, K-8" aria-label="Waggle, K-8"> Waggle, K-8
- MATH > INTERVENTION > Math 180, 3-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math 180, 3-12" aria-label="Math 180, 3-12"> Math 180, 3-12
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Science, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Science, K-5" aria-label="Into Science, K-5"> Into Science, K-5
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Science, 6-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Science, 6-8" aria-label="Into Science, 6-8"> Into Science, 6-8
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Science Dimensions, K-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science Dimensions, K-12" aria-label="Science Dimensions, K-12"> Science Dimensions, K-12
- SCIENCE > READERS > ScienceSaurus, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="ScienceSaurus, K-8" aria-label="ScienceSaurus, K-8"> ScienceSaurus, K-8
- SOCIAL STUDIES > CORE CURRICULUM > HMH Social Studies, 6-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="HMH Social Studies, 6-12" aria-label="HMH Social Studies, 6-12"> HMH Social Studies, 6-12
- SOCIAL STUDIES > SUPPLEMENTAL > Writable" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Writable" aria-label="Writable"> Writable
- For Teachers
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Coachly" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Coachly" aria-label="Coachly"> Coachly
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Teacher's Corner" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Teacher's Corner" aria-label="Teacher's Corner"> Teacher's Corner
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Live Online Courses" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Live Online Courses" aria-label="Live Online Courses"> Live Online Courses
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Program-Aligned Courses" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Program-Aligned Courses" aria-label="Program-Aligned Courses"> Program-Aligned Courses
- For Leaders
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Leaders > The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" aria-label="The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)"> The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)
- MORE > undefined > Assessment" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Assessment" aria-label="Assessment"> Assessment
- MORE > undefined > Early Learning" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Early Learning" aria-label="Early Learning"> Early Learning
- MORE > undefined > English Language Development" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="English Language Development" aria-label="English Language Development"> English Language Development
- MORE > undefined > Homeschool" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Homeschool" aria-label="Homeschool"> Homeschool
- MORE > undefined > Intervention" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Intervention" aria-label="Intervention"> Intervention
- MORE > undefined > Literacy" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Literacy" aria-label="Literacy"> Literacy
- MORE > undefined > Mathematics" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Mathematics" aria-label="Mathematics"> Mathematics
- MORE > undefined > Professional Development" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Professional Development" aria-label="Professional Development"> Professional Development
- MORE > undefined > Science" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science" aria-label="Science"> Science
- MORE > undefined > undefined" data-element-type="header nav submenu">
- MORE > undefined > Social and Emotional Learning" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social and Emotional Learning" aria-label="Social and Emotional Learning"> Social and Emotional Learning
- MORE > undefined > Social Studies" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social Studies" aria-label="Social Studies"> Social Studies
- MORE > undefined > Special Education" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Special Education" aria-label="Special Education"> Special Education
- MORE > undefined > Summer School" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Summer School" aria-label="Summer School"> Summer School
- BROWSE RESOURCES
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Classroom Activities" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classroom Activities" aria-label="Classroom Activities"> Classroom Activities
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Customer Success Stories" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Customer Success Stories" aria-label="Customer Success Stories"> Customer Success Stories
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Digital Samples" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Digital Samples" aria-label="Digital Samples"> Digital Samples
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Events" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Events" aria-label="Events"> Events
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Grants & Funding" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Grants & Funding" aria-label="Grants & Funding"> Grants & Funding
- BROWSE RESOURCES > International" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="International" aria-label="International"> International
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Research Library" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Research Library" aria-label="Research Library"> Research Library
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Shaped - HMH Blog" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Shaped - HMH Blog" aria-label="Shaped - HMH Blog"> Shaped - HMH Blog
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Webinars" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Webinars" aria-label="Webinars"> Webinars
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Contact Sales" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Contact Sales" aria-label="Contact Sales"> Contact Sales
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Customer Service & Technical Support Portal" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Customer Service & Technical Support Portal" aria-label="Customer Service & Technical Support Portal"> Customer Service & Technical Support Portal
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Platform Login" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Platform Login" aria-label="Platform Login"> Platform Login
- Learn about us
- Learn about us > About" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="About" aria-label="About"> About
- Learn about us > Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion" aria-label="Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion"> Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Learn about us > Environmental, Social, and Governance" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Environmental, Social, and Governance" aria-label="Environmental, Social, and Governance"> Environmental, Social, and Governance
- Learn about us > News Announcements" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="News Announcements" aria-label="News Announcements"> News Announcements
- Learn about us > Our Legacy" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Our Legacy" aria-label="Our Legacy"> Our Legacy
- Learn about us > Social Responsibility" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social Responsibility" aria-label="Social Responsibility"> Social Responsibility
- Learn about us > Supplier Diversity" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Supplier Diversity" aria-label="Supplier Diversity"> Supplier Diversity
- Join Us > Careers" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Careers" aria-label="Careers"> Careers
- Join Us > Educator Input Panel" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Educator Input Panel" aria-label="Educator Input Panel"> Educator Input Panel
- Join Us > Suppliers and Vendors" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Suppliers and Vendors" aria-label="Suppliers and Vendors"> Suppliers and Vendors
- Divisions > Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" aria-label="Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)"> Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)
- Divisions > Heinemann" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Heinemann" aria-label="Heinemann"> Heinemann
- Divisions > NWEA" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="NWEA" aria-label="NWEA"> NWEA
- Platform Login
HMH Support is here to help you get back to school right. Get started
SOCIAL STUDIES
PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT
What Is the Purpose of Summative Assessment in Education?

We’ve covered educational assessment a lot on this blog, but that’s not surprising given its central role in education. There are a wide range of perspectives on assessment, and often disagreement. For our part, we have identified three types of educational assessments: diagnostic , formative , and summative. Here we spotlight what is arguably the more contentious of the three—summative assessment.
Although each assessment differs in its use and intent, at times the differences may seem nuanced as they are often affected by the context in which they are used. An assessment is defined as much by its function as its form, and summative assessment is no different in this regard.
What Is Summative Assessment in Education?
The Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing define summative assessment as an evaluation of a test taker’s knowledge and skills, typically carried out at the completion of a program of learning, such as the end of an instructional unit. This type of assessment tends to be more formal, with time limits and increased content coverage. Examples are final exams, standardized tests, end-of-year projects, or other comprehensive assessments that provide a summary of the learner's performance.
Due to the higher stakes (discussed later) often attributed to summative assessments, item quality is monitored closely and adjusted where appropriate. These assessments are also typically subject to greater scrutiny for test validity and reliability.
What Is the Main Purpose of Summative Assessment?
Simply put, the main purpose of summative assessment is to measure students’ learning outcomes at the completion of an instructional unit, course, or academic program. The key word here is “completion,” indicating the assessing takes place after learning. Diagnostic assessment takes place before instruction and formative assessment takes place during instruction.
The overall purpose of assessment in education is multifaceted, encompassing various goals and objectives that contribute to the overall improvement of the learning process. The different types of assessment—diagnostic, formative and summative—each has its role in helping teachers understand how students are faring in their educational pursuits. Because these assessments are differentiated in nuanced ways, they can often be confusing for administrators, teachers, students, and caregivers. This confusion is probably most prevalent in discussing formative versus summative assessments.
Summative assessment differs from formative assessment in timing, purpose, feedback, and frequency. Another key difference: summative assessment is high-stakes while formative assessment is low-stakes. Below is a comparison of the two types of tests.
|
| |
| Typically occurs at the end of an instructional period, such as the end of a semester, course, or academic year. | Takes place during the learning process, providing ongoing feedback to students and educators to inform and guide instruction. |
| To make a final judgment about a student's achievement. It is often used for advancement, and can be used as a screener for further diagnostic testing, or a baseline to measure growth. | To provide continuous feedback in support of learning and improvement. The main goal is to identify areas of strength and weakness, guide instructional adjustments, and enhance student understanding. |
| Generally less detailed feedback that may not impact the current assessment. The primary feedback is the final grade or score. | Detailed and timely feedback to help students understand their progress and adjust. Often used to address specific learning objectives. Typically not subject to formal scoring. |
| Typically conducted less frequently, often at the beginning or end of a learning period. | Occurs more frequently and can be integrated into the learning process seamlessly, so students are not aware assessment is occurring. |
| Considered high-stakes since results can have significant consequences for students, such as determining eligibility for advancement or remediation. | Generally low-stakes, with a primary focus on supporting student learning rather than making high-stakes decisions. |
All in all, summative assessment serves as a dynamic and integral part of the educational process, contributing to ongoing improvement, accountability, and the overall success of students and educational systems. Different types of assessments, including diagnostic, formative and summative, collectively support a diverse set of purposes by providing a comprehensive view of student learning.

Evaluating the Purpose and Benefits of Summative Assessment in Education
Although it's often dreaded by students and considered controversial by teachers, administrators and advocates, summative assessment does have a place in education . It is important that these assessments are part of a thoughtful system and that an understanding exists with regard to its use and, more importantly, its limitations.
But why use summative assessments at all? Here are eight key benefits. These tests can:
- Measure Learning Outcomes : Summative assessments are used to measure what students have learned and to what extent they have gained specific learning outcomes, knowledge, and skills. They provide a snapshot of student understanding at a specific point in time. This snapshot identifies areas where students have demonstrated skill acquisition and areas where they need further support. In addition, an end-of-year assessment can be used to determine if they have achieved proficiency in a particular domain.
- Track Growth: By comparing current performance to past performance, educators can track individual student progress as well as the aggregated progress of schools and districts. This allows educators to celebrate growth, no matter how small, and understand the degree of progress made toward achieving educational goals.
- Inform Instruction : Assessment results provide valuable information to educators about students' strengths and weaknesses. This information can guide instructional decisions, allowing teachers to tailor their instruction to better meet the needs of individual students or the class as a whole. This may seem similar to the purpose of formative assessment and speaks to the point made earlier in this blog regarding how they are defined. Assessments are often defined by their use as well as function. Summative assessment, like formative assessment, can provide feedback for instruction. The difference is the level of specificity and timing. The feedback provided from summative assessment may occur at a much higher level or granularity and only intermittently throughout the year.
- Guide Curriculum Design : Assessment data allows educators and curriculum designers to evaluate the effectiveness of curriculum materials and instructional strategies. Summative data can be used to explore how well students are learning the standards articulated in the current curriculum, and feedback can be used to make periodic adjustments.
- Promote Accountability : Assessments play a role in ensuring accountability at various levels, including for individual students, educators, schools, and educational systems. They provide evidence of learning outcomes, demonstrating the effectiveness of educational programs. Students can compare their results against set benchmarks, motivating them to strive for improvement. For teachers, assessment offers data to inform their practice and demonstrate the effectiveness of their instruction. For administrators, it provides insights into how well programs are addressing teacher and student needs.
- Facilitate Goal Setting : Assessment results can be used to set goals for individual students, classes, and educational institutions. Involving students in analyzing their results promotes self-reflection. They can identify areas for improvement, set realistic goals, and track their progress over time. This fosters a sense of ownership over learning and empowers students to become active participants in their own growth. Goal setting provides direction for improvement and achievement over the short and long term.
- Support Decision Making : Assessment results are crucial for decision-making processes related to student placement, program modifications, and resource allocation. Educators and administrators rely on assessment data to make informed decisions that impact the educational experience. These evaluations are often used to provide students with the ideal system of supports to address their unique needs or to identify the need for a more thorough diagnostic assessment.
- Provide Feedback to Parents and Caregivers : Assessment results should be communicated to parents, caregivers, and the broader community. This transparency helps everyone understand and support a shared set of educational goals.
A Balanced Assessment Approach
It's important to note that while summative assessments are valuable for making important decisions, a balanced assessment approach often includes diagnostic, formative, and summative assessments to support ongoing learning and improvement. But the crucial role of summative assessment in an integrated system cannot be overstated. Much of the negative perspectives on these end-of-year tests stem not from the simple act of assessing, but the use of the results and how they are framed to students and teachers. Summative assessment results do not have to be demoralizing or threatening. They can be a useful tool in measuring student achievement that can be leveraged to make the beneficial changes needed to improve learning.
F or more on data-driven assessments and instruction, explore HMH assessments that provide educators a complete picture of student achievement.
Get a free guide to choosing the right assessments for your district.
- Professional Learning
Related Reading

Why Is Writing Important for Students?
Shaped Contributor
August 19, 2024

3 Strategies for Redesigning Professional Development
Dr. Amanda Patterson National Director, Academic Planning and Analytics, HMH
August 14, 2024

How to Create a Virtual Field Trip for Students That Engages and Delights
First-Grade Teacher

- Math for Kids
- Parenting Resources
- ELA for Kids
- Teaching Resources

How to Teach Number Recognition to Kids in 8 Easy Steps
How to Teach One to One Correspondence To Kids: 4 Easy Steps
How to Teach Odd and Even Numbers in 4 Easy Steps
How to Teach Long Division to Kids in 6 Easy Steps
15 Famous Mathematicians in History That Kids Should Know
8 Types of Preschool Programs for Kids in 2024
6-year-old Developmental Milestones Checklist
How to Prepare a Schedule for Kindergarten With Examples
How to Prepare a Schedule for Preschoolers With Sample
12 Best Funny Short Stories for Kids to Read in 2024
300+ Halloween Words From A-Z for Kids [Free Downloadable]
17 best guided reading activities for teachers.
190+ Fall Words From A-Z for Kids [Free Downloadable List]
60 Famous Quotes About Reading, Books & Writing for All Ages
What is Reading Assessment? Types & Tools [Full Guide]
11 Best Coloring Apps for Kids [Android & iOS]
12 Best Reading Bulletin Board Ideas for Your Classroom
15 Fun Summer Bulletin Board Ideas for 2024
13 Best Assessment Tools for Teachers in 2024
12 Best STEM Programs for Kids in 2024

What is Summative Assesment? Examples, Importance & More

Teaching is not just an intellectual process anymore. Today, it is also a logical process. Teachers need to assess individual students’ performance with tools like a summative assessment to provide customized classroom learning environments.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun ., you see real learning outcomes ..
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.

Therefore, modern teachers use formative and summative assessments to improve learning standards. Both assessments help educators achieve high learning goals in the classrooms.
But which assessment method is better in today’s education system?
This blog post will help teachers and learners understand summative assessments. We will also share the differences between formative and summative assessments .
What is Summative Assessment?
A summative assessment is an evaluation conducted at the end of a course or academic year. It depends on the grading and scoring system. Some of the common summative assessments are:
- Mid-term tests
- Reports
- Detailed papers
- End-of-class tests, etc.
The main objective of summative assessment is to evaluate the overall progress. This assessment shows how much a student has learned through a course, subject, or project in a particular timeline.
These assessments have high value as they take place in a controlled environment. You can use summative assessments to evaluate the comprehensive performance of the classroom to gain more insight. In a way, summative assessments can help you in two ways:
- Evaluate what your students have learned during the course
- Understand how prepared your students are for the next academic year
Summative Assessment Examples
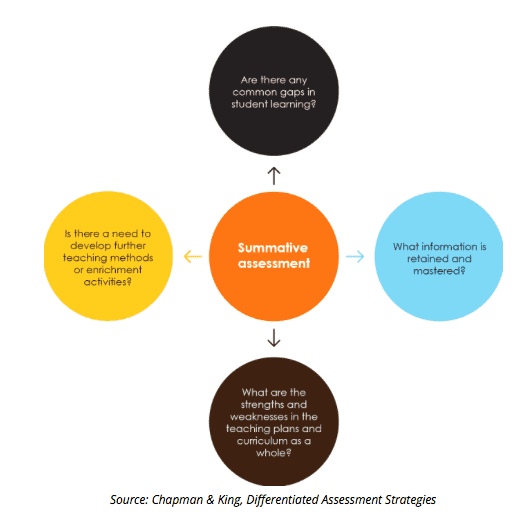
1. In-depth reports
A typical SA example is asking students to pick a topic and write a full report. It helps students research in-depth and use their creativity to write a report. You can evaluate passion, intelligence, and overall student performance through reports.
2. Projects
You can give group or individual projects to your students. This SA will show what your students have learned throughout the year and how they can work together.
3. Personal evaluation papers
This summative assessment example is helpful for financial, business, or other technical subjects. In this, you can understand the in-depth opinions of students. These papers allow students to evaluate topics through different perspectives and build an unbiased view.
Why is Summative Assessment Important?

Today, many scholars are against summative assessments. They think it lacks real-time performance evaluation benefits like formative assessments.
However, we will suggest to teachers that both assessments are equally important to sustain in the modern education system. If formative assessments help monitor progress in real-time , then summative assessments set benchmarks to evaluate performance.
Summative assessments help to improve curriculums. When you note the gap between students’ knowledge and learning targets, this will indicate you want to change your curriculum. You can better plan the curriculum with summative assessments to conduct formative assessments.
Summative Assessment Benefits

Summative assessments can benefit both teachers and students in many ways, such as:
1. Motivates to study
For many students, periodic evaluation is the best motivation to study. Many students can only perform under pressure. So, summative assessment is the perfect motivation for some students to study hard.
2. Implements learning
Summative assessments allow students to implement their learning in a real problem. For example, memorizing the periodic table is one thing. However using the periodic table data in a chemical equation is different.
Thus, summative assessments like multiple-choice tests allow students to test their learning.
3. Finds learning gaps
Summative assessment provides an overview of your class’s performance. This will help you evaluate the weaknesses and strengths of your students.
For example, you have taken a multiplication and factorization test in your class. Most students score high in multiplication tests, and only 50% score higher in factorization. This tells you that you need to improve your class’s teaching factorization.
4. Identifies teaching gaps
Summative assessment helps evaluate learning gaps and teaching gaps. It works as a wake-up call when you grade your student’s tests and the test results are not as expected.
This means your current teaching methods are not up to the mark. You need to adopt a new teaching method or strategy in your classroom, like:
- Use visual learning components
- Provide a stimulating learning environment
- Use different summative assessment methods, etc.
5. Provides insight
Summative assessments provide comprehensive insights to teachers. It shows what worked and what didn’t work in the academic year. Teachers can use this information to tweak their curriculum to raise learning standards for the following year.
6. Controls learning environment
Summative assessment scores provide standards for local, national, and global evaluation. Depending upon the standard scores, the government can fund the schools.
Summative Assessment Limitations

1. Reduces creativity
As strict criteria are set for summative assessment, it reduces creative involvement. Students have little room to showcase their creativity when following a standard assessment method.
2. Reflects on teaching ability
Teachers only have one chance to evaluate students’ performance, which reduces their teaching standards. They can’t make real-time changes in their teaching methods.
3. Can be biased
Summative assessments can be biased. If teachers want, they can favor some students while grading their tests. The success of summative assessments depends upon the integrity and honesty of the teacher.
Creative Ways to Use Summative Assessment in Your Classroom

Indeed, summative assessment has limitations that can impact teaching and learning standards. But if you twist up a standard summative assessment method using your creativity, you can gain immense value from SA. Here are a few creative ways to use summative assessments:
1. Short films
Instead of MCQs or essays, you can ask your students to record their reports on a camera. This way, students can use their creativity to make a unique report. For example, they can use visual charts, stories, or interviews to make their points compelling.
2. Podcasts
You can give a group or individual project to students to create podcasts. It is an interactive way to demonstrate learning and creative skills.
3. Infographics
Creating visual infographics for the final project allows students to show creativity. Students can use attractive visuals to cover different aspects of a topic, like definitions, statistics, etc.
4. Venn diagrams
Venn diagrams are an old yet effective way to visualize learning. This comparison technique helps compare different histories, social studies, and other concepts.
5. Living museum
You can ask students to create a small popup museum in the classrooms. This will help you teach one concept to the entire class excitingly. For teaching history or science concepts, this summative assessment mode is perfect.
Differences Between Summative Assessment and Formative Assessment
Are you confused about using summative or formative assessment in your class? Well, let’s understand what is difference between summative and formative assessment to get a better idea:
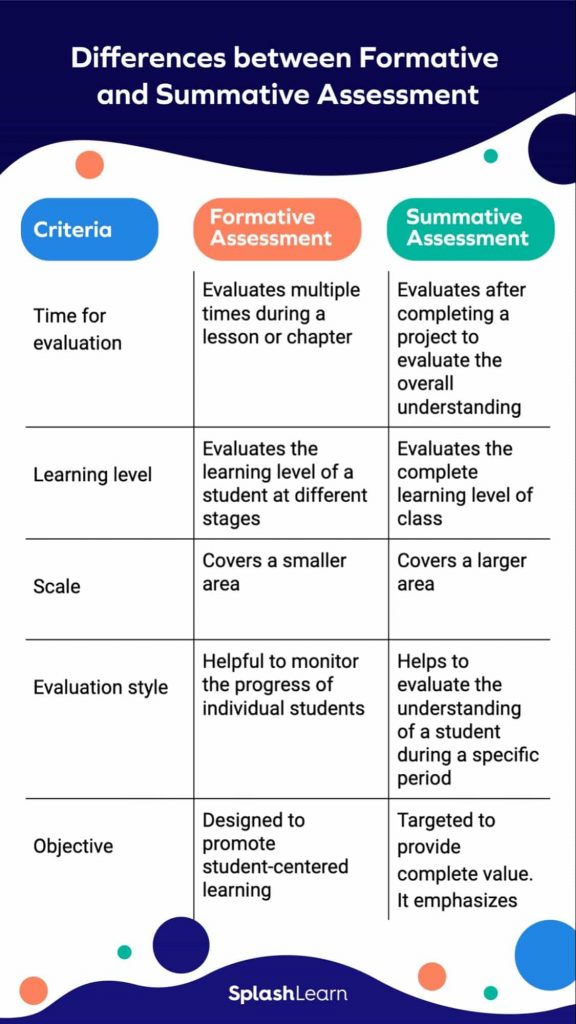
1. Time for evaluation
Teachers use formative assessments multiple times during lessons or chapters to evaluate students’ performance.
The summative assessment comes after completing a project to evaluate a student’s overall understanding.
2. Learning level
Formative assessment means constant monitoring of a student’s performance during a lesson. This allows teachers to evaluate a student’s learning level at different stages. Thus, they make instant decisions to improve the learning standards further.
In contrast, the summative assessment provides a one-time wholesome overview of the student’s performance. This is useful to know the complete learning level of your class.

3. Scale
The summative assessment covers a larger area than the formative assessment. For example, teaching a math chapter and taking a test is a formative assessment. But when you take a test of 5-6 chapters together, that’s a summative assessment.
4. Evaluation style
Formative assessment is helpful to monitor the progress of individual students. It helps teachers to catch problems using the right approach.
Summative assessment is a grading system in which overall performance is graded. It helps to evaluate the understanding of a student during a specific period.
5. Objective
Formative assessment is designed to promote student-centered learning. When teachers evaluate individual students’ performance, they can use personalized teaching methods based on a student’s weaknesses and strengths.
On the flip side, summative assessment is targeted to provide absolute value. It emphasizes a student’s grade at the end of the academic year.
Which Is Better – Formative or Summative Assessment?
Both formative and summative assessments are essential. Teachers need to conduct both assessments in classrooms to improve learning levels.
Using formative assessments , teachers can keep constant tabs on students’ progress and make instant decisions to improve their performance. At the same time, teachers should evaluate the complete performance of students to ensure that they understand the concepts before their next academic year.
So, it would help if you balanced formative and summative assessment strategies to drive maximum results from your students.
SplashLearn’s tool for teachers has elements that cater to both summative and formative assessments. With practice sessions and assignments that can be used after completion of every topic, students will solve their doubts time after time. With end-of-the-year assessments, you can ensure your students are well-prepared for the next academic year!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are examples of formative and summative assessments .
Examples of Formative assessment are homework assignments, quizzes, polls, surveys, entry slips, exit slips, etc. Summative assessment examples are – final projects, reports, presentations, essays, etc.
How do you make a summative assessment?
- Focus on a child’s strengths and make them stand out.
- Draw parents’ attention towards their children’s knowledge level.
- Summative assessment should be free from bias.
- Write in a clean and easy-to-understand manner.
What makes a good summative assessment?
A good summative assessment reflects a wide range of skills of a student. Authenticity and reliability are the two traits of an excellent summative assessment that helps to improve the overall learning level in a classroom.
15 Best Fall Bulletin Board Ideas for the Classroom
30 Best Preschool Graduation Ideas & Activities
13 Best Spring Bulletin Board Ideas: Spring into Creativity
- Pre-Kindergarten
- Kindergarten
Most Popular

76 Best Report Card Comments Samples for Teachers

117 Best Riddles for Kids (With Answers)

40 Best Good Vibes Quotes to Brighten Your Day
Recent posts.
![11 Best Coloring Apps for Kids [Android & iOS] Coloring Apps for Kids](https://www.splashlearn.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/best-coloring-apps-for-kids-100x70.jpg)
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
About SplashLearn
Enter the Splashverse! Inspire lifelong curiosity with this game-based PreK-5 learning experience loved by over 40 million children. SplashLearn is the perfect balance of learning and game-play that your little one needs to build math and reading confidence.
- Games for Kids
- Worksheets for Kids
- Math Worksheets
- ELA Worksheets
- Math Vocabulary
- Number Games
- Addition Games
- Subtraction Games
- Multiplication Games
- Division Games
- Addition Worksheets
- Subtraction Worksheets
- Multiplication Worksheets
- Division Worksheets
- Times Tables Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Writing Games
- Phonics Games
- Sight Words Games
- Letter Tracing Games
- Reading Worksheets
- Writing Worksheets
- Phonics Worksheets
- Sight Words Worksheets
- Letter Tracing Worksheets
- Prime Number
- Order of Operations
- Long multiplication
- Place value
- Parallelogram
- SplashLearn Success Stories
- SplashLearn Apps
© Copyright - SplashLearn

Empower Your Classroom Today!
Engage your students., make learning easy.
Access 14,000+ activities and 450+ lesson plans to engage your students and boost their learning!
Teachers, Use for Free

What Is a Summative Assessment?

Testing & Assessment in Education
Assessments are a part of every child's educational journey and children are not the only people to be tested. Students in college, graduate school and those attaining a doctoral degree are also assessed on their knowledge and its application to a real-world situation. There are two main types of assessments, one of which is a summative assessment.
Description
A summative assessment is a more formal method of testing student knowledge about a previously learned concept or unit of study. This type of evaluation is also commonly given at the end of the quarter, during the middle of the year and as a final, cumulative exam. Summative assessments give the instructor an idea of how much content the students have retained and may use the results to determine effective learning and teaching techniques for the class.
Types of Summative Assessments
End-of-unit tests, final exams, mid-term exams and quarterly tests are considered summative assessments. Many state departments of education devise a state-mandated evaluation and compare the results according to the state standard benchmark to determine the effectiveness of teachers in each district, which is also a summative assessment. Sometimes, these summative assessments determine the amount of funding allotted to the district. For example, the Pennsylvania System of School Assessment is given to students in grades 3 through 12 annually in different subject areas, according to state standards of achievement.
Summative assessments take many forms, including multiple-choice, true-or-false, concept vocabulary matching, fill-in-the-blank and short-answer question tests. One summative assessment may contain a combination of these types of questions or can be comprised exclusively of one type of question. Essay questions or tests are another example of summative assessments, as are performance evaluations. Performance tests may include subject-specific presentations, portfolios, written papers and any other method used to assess student knowledge.
Summative vs. Formative Assessments
Formative assessments are the other main type of assessment that also evaluates student learning but is often more informal. It includes quizzes, projects, answering questions in class and via teacher observation. Summative assessment is a formal method of evaluation and does not take into consideration teacher opinion like some methods of formative assessment. Summative exams end with an exact grade while many student-created projects are more difficult to assess.
Related Articles

High School Assessment & Test Analysis

The Advantages of Exams

Strengths & Weaknesses of the Kaufman Test of Educational Achievement

The Similarities and Difference of Classroom Test and Standardized ...

Achievement Vs. Aptitude Tests

The Difference Between Standardized & Norm Reference Tests

Cognitive Testing Vs. Achievement Testing

Difference Between Criterion-Referenced & Norm-Referenced Tests
- National Middle School Association; "Formative and Summative Assessments in the Classroom"; Catherine Garrison and Michael Ehringhaus; 2007
- Florida Center for Instructional Technology: Formative vs. Summative Assessment
- Learn North Carolina; Summative Assessment; Heather Coffey

- Understanding Summative Evaluation: Definition, Benefits, and Best Practices
- Learning Center

This article provides an overview of summative evaluation, including its definition, benefits, and best practices. Discover how summative evaluation can help you assess the effectiveness of your program or project, identify areas for improvement, and promote evidence-based decision-making. Learn about best practices for conducting summative evaluation and how to address common challenges and limitations.
Table of Contents
What is Summative Evaluation and Why is it Important?
Summative evaluation: purpose, goals, benefits of summative evaluation, types of summative evaluation, best practices for conducting summative evaluation, examples of summative evaluation in practice, examples of summative evaluation questions, challenges and limitations of summative evaluation, ensuring ethical considerations in summative evaluation, future directions for summative evaluation research and practice.
Ready to optimize your resume for a better career? Try Our FREE Resume Scanner!
Optimize your resume for ATS with formatting, keywords, and quantified experience.
- Compare job description keywords with your resume.
- Tailor your resume to match as many keywords as possible.
- Grab the recruiter’s attention with a standout resume.

Summative evaluation is a type of evaluation that is conducted at the end of a program or project, with the goal of assessing its overall effectiveness. The primary focus of summative evaluation is to determine whether the program or project achieved its goals and objectives. Summative evaluation is often used to inform decisions about future program or project development, as well as to determine whether or not to continue funding a particular program or project.
Summative evaluation is important for several reasons. First, it provides a comprehensive assessment of the overall effectiveness of a program or project, which can help to inform decisions about future development and implementation. Second, it can help to identify areas where improvements can be made in program delivery, such as in program design or implementation. Third, it can help to determine whether the program or project is a worthwhile investment, and whether it is meeting the needs of stakeholders.
In addition to these benefits, summative evaluation can also help to promote accountability and transparency in program or project implementation. By conducting a thorough evaluation of the program or project, stakeholders can be assured that their resources are being used effectively and that the program or project is achieving its intended outcomes.
Summative evaluation plays an important role in assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project, and in informing decisions about future development and implementation. It is an essential tool for promoting accountability, transparency, and effectiveness in program or project implementation.
Summative evaluation is an approach to program evaluation that is conducted at the end of a program or project, with the goal of assessing its overall effectiveness. Here are some of the key purposes and goals of summative evaluation.
Purpose of Summative Evaluation
- Assess effectiveness: Summative evaluation is focused on assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project in achieving its intended goals and objectives.
- Determine impact: Summative evaluation is used to determine the impact of a program or project on its intended audience or stakeholders, as well as on the broader community or environment.
- Inform decision-making: Summative evaluation is used to inform decision-making about future program or project development, as well as resource allocation.
Goals of Summative Evaluation
- Measure program outcomes: Summative evaluation is used to measure program outcomes, including the extent to which the program achieved its intended goals and objectives, and the impact of the program on its intended audience or stakeholders.
- Assess program effectiveness: Summative evaluation is used to assess the overall effectiveness of a program, by comparing program outcomes to its intended goals and objectives, as well as to similar programs or initiatives.
- Inform program improvement: Summative evaluation is used to inform program improvement by identifying areas where the program could be modified or improved in order to enhance its effectiveness.
Summative evaluation is a critical tool for assessing the overall effectiveness and impact of programs or projects, and for informing decision-making about future program or project development. By measuring program outcomes, assessing program effectiveness, and identifying areas for program improvement, summative evaluation can help to ensure that programs and projects are meeting their intended goals and making a positive impact on their intended audience or stakeholders.
Summative evaluation is an important tool for assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project. Here are some of the benefits of conducting summative evaluation:
- Provides a Comprehensive Assessment: Summative evaluation provides a comprehensive assessment of the overall effectiveness of a program or project, which can help to inform decisions about future development and implementation.
- Identifies Areas for Improvement : Summative evaluation can help to identify areas where improvements can be made in program delivery, such as in program design or implementation.
- Promotes Accountability and Transparency: Summative evaluation can help to promote accountability and transparency in program or project implementation, by ensuring that resources are being used effectively and that the program or project is achieving its intended outcomes.
- Supports Evidence-Based Decision-Making : Summative evaluation provides evidence-based data and insights that can inform decisions about future development and implementation.
- Demonstrates Impact : Summative evaluation can help to demonstrate the impact of a program or project, which can be useful for securing funding or support for future initiatives.
- Increases Stakeholder Engagement : Summative evaluation can increase stakeholder engagement and ownership of the program or project being evaluated, by involving stakeholders in the evaluation process and soliciting their feedback.
Summative evaluation is an essential tool for assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project, and for informing decisions about future development and implementation. It provides a comprehensive assessment of the program or project, identifies areas for improvement, promotes accountability and transparency, and supports evidence-based decision-making.
There are different types of summative evaluation that can be used to assess the overall effectiveness of a program or project. Here are some of the most common types of summative evaluation:
- Outcome Evaluation: This type of evaluation focuses on the outcomes or results of the program or project, such as changes in behavior, knowledge, or attitudes. Outcome evaluation is often used to determine the effectiveness of an intervention or program in achieving its intended outcomes.
- Impact Evaluation: This type of evaluation focuses on the broader impact of the program or project, such as changes in the community or society. Impact evaluation is often used to assess the overall impact of a program or project on the target population or community.
- Cost-Benefit Evaluation: This type of evaluation focuses on the costs and benefits of the program or project, and is often used to determine whether the program or project is a worthwhile investment. Cost-benefit evaluation can help to determine whether the benefits of the program or project outweigh the costs.
The type of summative evaluation used will depend on the specific goals and objectives of the program or project being evaluated, as well as the resources and data available for evaluation. Each type of summative evaluation serves a specific purpose in assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project, and should be tailored to the specific needs of the program or project being evaluated.
Conducting a successful summative evaluation requires careful planning and attention to best practices. Here are some best practices for conducting summative evaluation:
- Clearly Define Goals and Objectives : Before conducting a summative evaluation, it is important to clearly define the goals and objectives of the program or project being evaluated. This will help to ensure that the evaluation is focused and relevant to the needs of stakeholders.
- Use Valid and Reliable Measures: The measures used in a summative evaluation should be valid and reliable, in order to ensure that the results are accurate and meaningful. This may involve selecting or developing appropriate evaluation tools, such as surveys or assessments, and ensuring that they are properly administered.
- Collect Data from Multiple Sources : Data for a summative evaluation should be collected from multiple sources, in order to ensure that the results are comprehensive and representative. This may involve collecting data from program participants, stakeholders, and other relevant sources.
- Analyze and Interpret Results : Once the data has been collected, it is important to analyze and interpret the results in order to determine the overall effectiveness of the program or project. This may involve using statistical analysis or other techniques to identify patterns or trends in the data.
- Use Results to Inform Future Development : The results of a summative evaluation should be used to inform future program or project development, in order to improve the effectiveness of the program or project. This may involve making changes to program design or delivery, or identifying areas where additional resources or support may be needed.
Conducting a successful summative evaluation requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a commitment to using the results to inform future development and improvement. By following best practices for conducting summative evaluation, stakeholders can ensure that their programs and projects are effective and relevant to the needs of their communities.
Summative evaluation is an important tool for assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project. Here are some examples of summative evaluation in practice:
- Educational Programs : A school district may conduct a summative evaluation of a new educational program, such as a reading intervention program. The evaluation may focus on the program’s outcomes, such as improvements in reading skills, and may involve collecting data from multiple sources, such as teacher assessments, student tests, and parent surveys.
- Health Interventions : A public health agency may conduct a summative evaluation of a health intervention, such as a vaccination campaign. The evaluation may focus on the impact of the intervention on health outcomes, such as reductions in disease incidence, and may involve collecting data from multiple sources, such as healthcare providers, patients, and community members.
- Social Service Programs: A non-profit organization may conduct a summative evaluation of a social service program, such as a job training program for disadvantaged youth. The evaluation may focus on the impact of the program on outcomes such as employment rates and job retention, and may involve collecting data from multiple sources, such as program participants, employers, and community partners.
- Technology Products : A software company may conduct a summative evaluation of a new technology product, such as a mobile app. The evaluation may focus on user satisfaction and effectiveness, and may involve collecting data from multiple sources, such as user surveys, user testing, and usage data.
- Environmental Programs : An environmental organization may conduct a summative evaluation of a conservation program, such as a land protection initiative. The evaluation may focus on the impact of the program on environmental outcomes, such as the protection of natural habitats or the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, and may involve collecting data from multiple sources, such as program participants, community members, and scientific data.
Summative evaluation can be used in a wide range of programs and initiatives to assess their overall effectiveness and inform future development and improvement.
Summative evaluation is an important tool for assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project. Here are some examples of summative evaluation questions that can be used to guide the evaluation process:
- Did the program or project achieve its intended outcomes and goals?
- To what extent did the program or project meet the needs of its intended audience or stakeholders?
- What were the most effective components of the program or project, and what areas could be improved?
- What impact did the program or project have on its intended audience or stakeholders?
- Was the program or project implemented effectively, and were resources used efficiently?
- What unintended consequences or challenges arose during the program or project, and how were they addressed?
- How does the program or project compare to similar initiatives or interventions in terms of effectiveness and impact?
- What were the costs and benefits of the program or project, and were they reasonable given the outcomes achieved?
- What lessons can be learned from the program or project, and how can they inform future development and improvement?
The questions asked during a summative evaluation are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the impact and effectiveness of the program or project. The answers to these questions can inform future programming and resource allocation decisions and help to identify areas for improvement. Overall, summative evaluation is an essential tool for assessing the overall impact and effectiveness of a program or project.
Summative evaluation is an important tool for assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project. However, there are several challenges and limitations that should be considered when conducting summative evaluation. Here are some of the most common challenges and limitations of summative evaluation:
- Timing: Summative evaluation is typically conducted at the end of a program or project, which may limit the ability to make real-time improvements during the implementation phase.
- Resource Constraints: Summative evaluation can be resource-intensive, requiring significant time, effort, and funding to collect and analyze data.
- Bias: The data collected during summative evaluation may be subject to bias, such as social desirability bias, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the evaluation results.
- Difficulty of Measurement: Some outcomes of a program or project may be difficult to measure, which can make it challenging to assess the overall effectiveness of the program or project.
- Difficulty of Generalization: The results of a summative evaluation may not be generalizable to other contexts or settings, which can limit the broader applicability of the evaluation findings.
- Limited Stakeholder Involvement: Summative evaluation may not involve all stakeholders, which can limit the representation of diverse perspectives and lead to incomplete evaluation findings.
- Limited Focus on Process: Summative evaluation typically focuses on outcomes and impact, which may not provide a full understanding of the program or project’s implementation process and effectiveness.
These challenges and limitations of summative evaluation should be considered when planning and conducting evaluations. By understanding these limitations, evaluators can work to mitigate potential biases and limitations and ensure that the evaluation results are accurate, reliable, and useful for program or project improvement.
While conducting summative evaluation, it’s imperative to uphold ethical principles to ensure the integrity and fairness of the evaluation process. Ethical considerations are essential for maintaining trust with stakeholders, respecting the rights of participants, and safeguarding the integrity of evaluation findings. Here are key ethical considerations to integrate into summative evaluation:
Informed Consent: Ensure that participants are fully informed about the purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits of the evaluation before consenting to participate. Provide clear and accessible information, allowing participants to make voluntary and informed decisions about their involvement.
Confidentiality and Privacy: Safeguard the confidentiality and privacy of participants’ information throughout the evaluation process. Implement secure data management practices, anonymize data whenever possible, and only share findings in aggregate or de-identified formats to protect participants’ identities.
Respect for Diversity and Inclusion: Respect and embrace the diversity of participants, acknowledging their unique perspectives, backgrounds, and experiences. Ensure that evaluation methods are culturally sensitive and inclusive, avoiding biases and stereotypes, and accommodating diverse communication styles and preferences.
Avoiding Harm: Take proactive measures to minimize the risk of harm to participants and stakeholders throughout the evaluation process. Anticipate potential risks and vulnerabilities, mitigate them through appropriate safeguards and protocols, and prioritize the well-being and dignity of all involved.
Beneficence and Non-Maleficence: Strive to maximize the benefits of the evaluation while minimizing any potential harm or adverse effects. Ensure that evaluation activities contribute to the improvement of programs or projects, enhance stakeholders’ understanding and decision-making, and do not cause undue stress, discomfort, or harm.
Transparency and Accountability: Maintain transparency and accountability in all aspects of the evaluation, including its design, implementation, analysis, and reporting. Clearly communicate the evaluation’s objectives, methodologies, findings, and limitations, allowing stakeholders to assess its credibility and relevance.
Equitable Participation and Representation: Foster equitable participation and representation of diverse stakeholders throughout the evaluation process. Engage stakeholders in meaningful ways, valuing their input, perspectives, and contributions, and address power differentials to ensure inclusive decision-making and ownership of evaluation outcomes.
Continuous Reflection and Improvement: Continuously reflect on ethical considerations throughout the evaluation process, remaining responsive to emerging issues, challenges, and ethical dilemmas. Seek feedback from stakeholders, engage in dialogue about ethical concerns, and adapt evaluation approaches accordingly to uphold ethical standards.
By integrating these ethical considerations into summative evaluation practices, evaluators can uphold principles of integrity, respect, fairness, and accountability, promoting trust, credibility, and meaningful impact in program assessment and improvement. Ethical evaluation practices not only ensure compliance with professional standards and legal requirements but also uphold fundamental values of respect for human dignity, justice, and social responsibility.
Summative evaluation is an important tool for assessing the overall effectiveness of a program or project. Here are some potential future directions for summative evaluation research and practice:
- Incorporating Technology: Advances in technology have the potential to improve the efficiency and accuracy of summative evaluation. Future research could explore the use of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other technologies to streamline data collection and analysis.
- Enhancing Stakeholder Engagement: Future research could explore ways to enhance stakeholder engagement in summative evaluation, such as by involving stakeholders in the evaluation planning and implementation process.
- Increasing Use of Mixed Methods: Future research could explore the use of mixed methods approaches in summative evaluation, such as combining qualitative and quantitative methods to gain a more comprehensive understanding of program or project effectiveness.
- Addressing Equity and Inclusion: Future research could focus on addressing issues of equity and inclusion in summative evaluation, such as by ensuring that evaluation methods are sensitive to the needs and experiences of diverse stakeholders.
- Addressing Complexity: Many programs and projects operate in complex and dynamic environments. Future research could explore ways to address this complexity in summative evaluation, such as by developing more adaptive and flexible evaluation methods.
- Improving Integration with Formative Evaluation: Summative evaluation is typically conducted after a program or project has been completed, while formative evaluation is conducted during program or project implementation. Future research could explore ways to better integrate summative and formative evaluation, in order to promote continuous program improvement.
These future directions for summative evaluation research and practice have the potential to improve the effectiveness and relevance of summative evaluation, and to enhance its value as a tool for program and project assessment and improvement.
David Ndiyamba
Quite comprehensive Thank you
Fation Luli
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published.
How strong is my Resume?
Only 2% of resumes land interviews.
Land a better, higher-paying career

Jobs for You
College of education: open-rank, evaluation/social research methods — educational psychology.
- Champaign, IL, USA
- University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Deputy Director – Operations and Finance
- United States
Energy/Environment Analyst
Climate finance specialist, call for consultancy: evaluation of dfpa projects in kenya, uganda and ethiopia.
- The Danish Family Planning Association
Project Assistant – Close Out
- United States (Remote)
Global Technical Advisor – Information Management
- Belfast, UK
- Concern Worldwide
Intern- International Project and Proposal Support – ISPI
Budget and billing consultant, manager ii, budget and billing, usaid/lac office of regional sustainable development – program analyst, team leader, senior finance and administrative manager, data scientist.
- New York, NY, USA
- Everytown For Gun Safety
Energy Evaluation Specialist
Services you might be interested in, useful guides ....
How to Create a Strong Resume
Monitoring And Evaluation Specialist Resume
Resume Length for the International Development Sector
Types of Evaluation
Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning (MEAL)
LAND A JOB REFERRAL IN 2 WEEKS (NO ONLINE APPS!)
Sign Up & To Get My Free Referral Toolkit Now:
SAY GOODBYE TO JAMB,GAIN DIRECT ENTRY ÀDMISSION INTO 200LEVEL TO STUDY YOUR DESIRED COURSE IN ANY UNIVERSITY OF YOUR CHOICE.LOW FEES. REGISTRATION IS IN PROGRESS . CALL / WHATSAPP 09059908384.
UNILAG CAMPUS TOUR VIDEO - An Glimpse of Student Life in UNILAG (Like & SUBSCRIBE )
Evaluation in Education: Meaning, Types, Importance, Principles & Characteristics
Let’s start with the definition of evaluation in this article before we delve into evaluation in Education, the meaning as well as types and its importance.
What exactly is evaluation?
Evaluation is a procedure that reviews a program critically. It is a process that involves careful gathering and evaluating of data on the actions, features, and consequences of a program. Its objective is to evaluate programs, improve program effectiveness, and influence programming decisions.
The efficacy of program interventions is assessed through educational evaluation. These often address the learning, such as reading; emotional, behavioral, and social development, such as anti-bullying initiatives; or wider subjects, such as whole-school system improvements such as inclusive education. Within the research community, debates have raged regarding methodology, specifically the use of qualitative approaches in evaluating program efficacy vs quantitative ones. There has also been significant political participation, with certain governments adopting stances on the sort of evidence necessary for assessment studies, with a focus on randomized controlled trials in particular (RCTs).
The initial goal of program assessment is to determine the effectiveness of the intervention. This can be done on a small basis, such as a school studying the implementation of a new reading scheme, but it can also be done on a big scale, at the district, school, state (local authority ), or national level. The availability of national or state data collections, such as those from the United Kingdom. The Government’s National Pupil Database and its student-level School Census provide opportunities for large-scale evaluations of educational interventions, such as curricular reforms or the differential development of types of kids (e.g., the relationship between identification of special educational needs and ethnicity). However, the importance of evaluating both the effectiveness of the program itself and its implementation is becoming increasingly recognized.
Other definitions of Evaluation by other authors;
“The technique of obtaining and assessing information changes in the conduct of all children as they advance through school,” Hanna says.
According to Muffat, “evaluation is a continual process that is concerned with more than the official academic accomplishment of students.” It is viewed in terms of the individual’s growth in terms of desired behavioral change in connection to his feelings, thoughts, and actions.”
Evaluation is a crucial issue in both the first and second years of B.Ed. Every B.Ed. student should comprehend the notion of evaluation and assessment.
Types of Evaluation in Education
- Formative Evaluation
- Summative Evaluation
- Prognostic Evaluation
- Diagnostic Evaluation
- Norm Referenced Evaluation
- Criterion Referenced Evaluation
- Quantitative Evaluation
- Formative evaluation
We would be explaining each of these types of evaluation in education.
1. Formative Evaluation
- This form of evaluation takes place during the instructional process. Its goal is to offer students and teachers with continual feedback.
- This aids in making modifications to the instruction process as needed. It considers smaller and autonomous curricular sections, and pupils are ultimately assessed through assessments.
- It is assessing the kids’ understanding and which part of their work needs more work. A teacher can assess their pupils while educating them on a class or a lesson or after the topic has been completed to see whether or not modifications in teaching approach are required.
- It is really beneficial to make modifications or timely corrections in pupils and teaching style.
2. Summative Evaluation
- Summative evaluation occurs at the end of the school year. It assesses the success of objectives and changes in a student’s general personality at the end of the session.
- Summative evaluations address a wide range of aspects of learning. It considers formative assessment ratings and student tests after course completion to provide final grades and comments to students.
- Summative evaluation is used to grade students.
3. Prognostic Evaluation
- Prognostic evaluations are used to estimate and anticipate a person’s future career.
- A prognostic evaluation adds a new dimension to the discoveries of an assessment with analysis of talents and potentials: the concerned person’s future growth, as well as the necessary circumstances, timeline, and constraints.
4. Diagnostic Evaluation
- As the phrase implies, diagnosis is the process of determining the root cause of a problem. During this examination, a teacher attempts to diagnose each student on many characteristics in order to determine the caliber of pupils.
- A diagnostic assessment is a type of pre-evaluation in which teachers assess students’ strengths, weaknesses, knowledge, and abilities prior to the start of the teaching learning process.
- It necessitates specifically designed diagnostic tests as well as several additional observational procedures.
- It is useful in developing the course and curriculum based on the learner’s ability.
5. Norm Referenced Evaluation
- This type of assessment is centered on evaluating students’ relative performance, either by comparing the outputs of individual learners within the group being evaluated or by juxtaposing their performance to that of others of comparable age, experience, and background.
- It influences the placement of pupils inside the group.
6. Criterion Referenced Evaluation
- Criterion Reference Evaluation explains a person’s performance in relation to a predetermined performance benchmark.
- It describes a student’s performance accuracy, or how well the individual performs in relation to a given standard.
- In other words, it’s like comparing a student’s performance to a predetermined benchmark.
7. Quantitative Evaluation
Quantitative assessments employ scientific instruments and measures. The outcomes can be tallied or measured.
Quantitative Evaluation Techniques or Tools;
- Performance evaluation
8. Formative Evaluation
- Qualitative observations, which are more subjective than qualitative evaluation, are described in science as any observation made utilizing the five senses.
- It entails value assessment.
9. Qualitative Evaluation Techniques or Tools
- Cumulative Records
- The school keeps such statistics to demonstrate pupils’ overall improvement.
10. Anecdotal evidence
These records preserve descriptions of noteworthy events or student efforts.
11. Observation
This is the most popular method of qualitative student assessment. This is the only method for assessing classroom interaction.
12. Checklist
Checklists specify precise criteria and allow instructors and students to collect data and make judgments about what pupils know and can perform in connection to the outcomes. They provide systematic methods for gathering data on certain behaviors, knowledge, and abilities.
Difference Between Evaluation and Assessment
| Improves learning quality | Judges learning level |
| Ungraded | Graded |
| Provides feedback | Shows shortfalls |
| Process-oriented | Product-oriented |
| Ongoing process | Provide closure |
Functions and Importance of Evaluation in Education
The primary goal of the teaching, learning process is to enable the student to obtain the desired learning outcomes. The learning objectives are established during this phase, and then the learning progress is reviewed on a regular basis using tests and other assessment tools.
The evaluation process’s role may be described as follows:
- Evaluation aids in the preparation of instructional objectives: The evaluation results may be used to fix the learning goals expected from the classroom discussion.
- What kind of information and comprehension should the learner gain?
- What skill should they demonstrate?
- What kind of interest and attitude should they cultivate?
Only when we determine the instructional objectives and communicate them clearly in terms of expected learning outcomes will this be achievable. Only a thorough evaluation method allows us to create a set of ideal instructional objectives.
- The evaluation method aids in analyzing the learner’s requirements: It is critical to understand the needs of the learners during the teaching-learning process. The instructor must be aware of the knowledge and abilities that the pupils must learn.
Evaluation aids in delivering feedback to students: An evaluation procedure assists the instructor in determining the students’ learning issues. It contributes to the improvement of many school procedures. It also assures proper follow-up service.
Evaluation aids in the preparation of program materials: A continuous succession of learning sequences is referred to as programmed instruction. First, a limited quantity of teaching content is offered, followed by a test to respond to the instructional material. The following feedback is given based on the accuracy of the response given. Thus, programmed learning is impossible without an adequate evaluation method.
Evaluation aids in curriculum development:
Curriculum creation is an essential component of the educational process. Data from evaluations allow for curriculum creation, determining the efficacy of new methods, and identifying areas that require change. The evaluation also aids in determining the effectiveness of an existing curriculum. Thus, assessment data aids in the development of new curriculum as well as the evaluation of existing curriculum.
- Evaluation aids in communicating the development of students to their parents: A structured evaluation approach gives an objective and complete view of each student’s development. This comprehensive nature of the assessment procedure enables the instructor to report to the parents on the pupil’s overall growth. This sort of objective information about the student serves as the foundation for the most successful collaboration between parents and instructors.
7. Evaluation data are quite valuable in advice and counseling: Educational, vocational, and personal guidance all require evaluation methods. To help students address difficulties in the educational, vocational, and personal domains, the counselor must have an objective understanding of the students’ talents, interests, attitudes, and other personal traits. An successful assessment system aids in the formation of a complete image of the student, which leads to appropriate guiding and counseling.
8 . Evaluation data aids in good school administration: Evaluation data assists administrators in determining the amount to which the school’s objectives are met, determining the strengths and weaknesses of the curriculum, and planning special school programs.
- Evaluation data are useful in school research: Research is required to improve the effectiveness of the school program. Data from evaluations aid in research fields such as comparative studies of different curricula, efficacy of different approaches, effectiveness of different organizational designs, and so on.
Principles of Evaluation
The following concepts guide evaluation:
- Continuity principle: Evaluation is a continual process that continues as long as the student is involved in education. Evaluation is an important part of the teaching-learning process. Whatever the student learns should be examined on a daily basis. Only then will the student have a greater mastery of the language.
- The comprehensiveness principle: states that we must evaluate all parts of the learner’s personality. It is concerned with the child’s whole development.
- The principle of Objectives: states that evaluation should always be based on educational objectives. It should aid in determining where there is a need for revamping and stopping the learner’s behavior.
- Child-Centeredness Principle: The child is at the center of the evaluation process. The child’s conduct is the focal point for evaluation. It assists a teacher in determining a child’s grasping ability and the effectiveness of teaching content.
- The principle of broadness: states that evaluation should be wide enough to encompass all areas of life.
- Principle of Application: The child may learn many things during the teaching and learning process. However, they may be ineffective in his daily life. If he can’t utilize it, it’s pointless to look for it. It can be determined by assessment. The evaluation determines if a student is better able to use his knowledge and understanding in various circumstances in order to thrive in life.
8 Evaluation characteristics in education
- Process what is ongoing: Evaluation is a never-ending process. It co-leads with the teaching-learning process.
- Comprehensive: Evaluation is comprehensive because it encompasses everything that can be reviewed.
- Child-Centered: Evaluation is a child-centered technique that emphasizes the learning process rather than the teaching process.
- Remedial: Although evaluation remarks on the outcome, it is not a remedy. The purpose of an evaluation is to correct problems.
- Cooperative Process: Evaluation is a collaborative process that involves students, instructors, parents, and peer groups.
- Teaching Approaches: The effectiveness of various teaching methods is assessed.
- Common Practice: Evaluation is a typical technique for the optimal mental and physical development of the kid.
- Multiple Aspects: It is concerned with pupils’ whole personalities.
In summary, Evidence of efficacy, often from random controlled trials, and the effectiveness of project planning is required for the evaluation of educational programs. Program evaluations must prove that the program can perform under ideal controlled situations and that it will work when carried out on a broad scale in community settings to order to give valuable data to support policy. To address these many dimensions of effectiveness, evaluation benefits from a combined approaches strategic plan.
Share this:
UNILAG CAMPUS TOUR VIDEO - An Glimpse of Student Life in UNILAG (Like & SUBSCRIBE )
Created by the Great Schools Partnership , the GLOSSARY OF EDUCATION REFORM is a comprehensive online resource that describes widely used school-improvement terms, concepts, and strategies for journalists, parents, and community members. | Learn more »

In education, the term assessment refers to the wide variety of methods or tools that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students.
While assessments are often equated with traditional tests—especially the standardized tests developed by testing companies and administered to large populations of students—educators use a diverse array of assessment tools and methods to measure everything from a four-year-old’s readiness for kindergarten to a twelfth-grade student’s comprehension of advanced physics. Just as academic lessons have different functions, assessments are typically designed to measure specific elements of learning—e.g., the level of knowledge a student already has about the concept or skill the teacher is planning to teach or the ability to comprehend and analyze different types of texts and readings. Assessments also are used to identify individual student weaknesses and strengths so that educators can provide specialized academic support , educational programming, or social services. In addition, assessments are developed by a wide array of groups and individuals, including teachers, district administrators, universities, private companies, state departments of education, and groups that include a combination of these individuals and institutions.
While assessment can take a wide variety of forms in education, the following descriptions provide a representative overview of a few major forms of educational assessment.
Assessments are used for a wide variety of purposes in schools and education systems :
- High-stakes assessments are typically standardized tests used for the purposes of accountability—i.e., any attempt by federal, state, or local government agencies to ensure that students are enrolled in effective schools and being taught by effective teachers. In general, “high stakes” means that important decisions about students, teachers, schools, or districts are based on the scores students achieve on a high-stakes test, and either punishments (sanctions, penalties, reduced funding, negative publicity, not being promoted to the next grade, not being allowed to graduate) or accolades (awards, public celebration, positive publicity, bonuses, grade promotion, diplomas) result from those scores. For a more detailed discussion, see high-stakes test .
- Pre-assessments are administered before students begin a lesson, unit, course, or academic program. Students are not necessarily expected to know most, or even any, of the material evaluated by pre-assessments—they are generally used to (1) establish a baseline against which educators measure learning progress over the duration of a program, course, or instructional period, or (2) determine general academic readiness for a course, program, grade level, or new academic program that student may be transferring into.
- Formative assessments are in-process evaluations of student learning that are typically administered multiple times during a unit, course, or academic program. The general purpose of formative assessment is to give educators in-process feedback about what students are learning or not learning so that instructional approaches, teaching materials, and academic support can be modified accordingly. Formative assessments are usually not scored or graded, and they may take a variety of forms, from more formal quizzes and assignments to informal questioning techniques and in-class discussions with students.
Formative assessments are commonly said to be for learning because educators use the results to modify and improve teaching techniques during an instructional period, while summative assessments are said to be of learning because they evaluate academic achievement at the conclusion of an instructional period. Or as assessment expert Paul Black put it, “When the cook tastes the soup, that’s formative assessment. When the customer tastes the soup, that’s summative assessment.”
- Interim assessments are used to evaluate where students are in their learning progress and determine whether they are on track to performing well on future assessments, such as standardized tests, end-of-course exams, and other forms of “summative” assessment. Interim assessments are usually administered periodically during a course or school year (for example, every six or eight weeks) and separately from the process of instructing students (i.e., unlike formative assessments, which are integrated into the instructional process).
- Placement assessments are used to “place” students into a course, course level, or academic program. For example, an assessment may be used to determine whether a student is ready for Algebra I or a higher-level algebra course, such as an honors-level course. For this reason, placement assessments are administered before a course or program begins, and the basic intent is to match students with appropriate learning experiences that address their distinct learning needs.
- Screening assessments are used to determine whether students may need specialized assistance or services, or whether they are ready to begin a course, grade level, or academic program. Screening assessments may take a wide variety of forms in educational settings, and they may be developmental, physical, cognitive, or academic. A preschool screening test, for example, may be used to determine whether a young child is physically, emotionally, socially, and intellectually ready to begin preschool, while other screening tests may be used to evaluate health, potential learning disabilities, and other student attributes.
Assessments are also designed in a variety of ways for different purposes:
- Standardized assessments are designed, administered, and scored in a standard, or consistent, manner. They often use a multiple-choice format, though some include open-ended, short-answer questions. Historically, standardized tests featured rows of ovals that students filled in with a number-two pencil, but increasingly the tests are computer-based. Standardized tests can be administered to large student populations of the same age or grade level in a state, region, or country, and results can be compared across individuals and groups of students. For a more detailed discussion, see standardized test .
- Standards-referenced or standards-based assessments are designed to measure how well students have mastered the specific knowledge and skills described in local, state, or national learning standards . Standardized tests and high-stakes tests may or may not be based on specific learning standards, and individual schools and teachers may develop their own standards-referenced or standards-based assessments. For a more detailed discussion, see proficiency-based learning .
- Common assessments are used in a school or district to ensure that all teachers are evaluating student performance in a more consistent, reliable, and effective manner. Common assessments are used to encourage greater consistency in teaching and assessment among teachers who are responsible for teaching the same content, e.g. within a grade level, department, or content area . They allow educators to compare performance results across multiple classrooms, courses, schools, and/or learning experiences (which is not possible when educators teach different material and individually develop their own distinct assessments). Common assessments share the same format and are administered in consistent ways—e.g., teachers give students the same instructions and the same amount of time to complete the assessment, or they use the same scoring guides to interpret results. Common assessments may be “formative” or “summative .” For more detailed discussions, see coherent curriculum and rubric .
- Performance assessments typically require students to complete a complex task, such as a writing assignment, science experiment, speech, presentation, performance, or long-term project, for example. Educators will often use collaboratively developed common assessments, scoring guides, rubrics, and other methods to evaluate whether the work produced by students shows that they have learned what they were expected to learn. Performance assessments may also be called “authentic assessments,” since they are considered by some educators to be more accurate and meaningful evaluations of learning achievement than traditional tests. For more detailed discussions, see authentic learning , demonstration of learning , and exhibition .
- Portfolio-based assessments are collections of academic work—for example, assignments, lab results, writing samples, speeches, student-created films, or art projects—that are compiled by students and assessed by teachers in consistent ways. Portfolio-based assessments are often used to evaluate a “body of knowledge”—i.e., the acquisition of diverse knowledge and skills over a period of time. Portfolio materials can be collected in physical or digital formats, and they are often evaluated to determine whether students have met required learning standards . For a more detailed discussion, see portfolio .
The purpose of an assessment generally drives the way it is designed, and there are many ways in which assessments can be used. A standardized assessment can be a high-stakes assessment, for example, but so can other forms of assessment that are not standardized tests. A portfolio of student work can be a used as both a “formative” and “summative” form of assessment. Teacher-created assessments, which may also be created by teams of teachers, are commonly used in a single course or grade level in a school, and these assessments are almost never “high-stakes.” Screening assessments may be produced by universities that have conducted research on a specific area of child development, such as the skills and attributes that a student should have when entering kindergarten to increase the likelihood that he or she will be successful, or the pattern of behaviors, strengths, and challenges that suggest a child has a particular learning disability. In short, assessments are usually created for highly specialized purposes.
While educational assessments and tests have been around since the days of the one-room schoolhouse, they have increasingly assumed a central role in efforts to improve the effectiveness of public schools and teaching. Standardized-test scores, for example, are arguably the dominant measure of educational achievement in the United States, and they are also the most commonly reported indicator of school, teacher, and school-system performance.
As schools become increasingly equipped with computers, tablets, and wireless internet access, a growing proportion of the assessments now administered in schools are either computer-based or online assessments—though paper-based tests and assessments are still common and widely used in schools. New technologies and software applications are also changing the nature and use of assessments in innumerable ways, given that digital-assessment systems typically offer an array of features that traditional paper-based tests and assignments cannot. For example, online-assessment systems may allow students to log in and take assessments during out-of-class time or they may make performance results available to students and teachers immediately after an assessment has been completed (historically, it might have taken hours, days, or weeks for teachers to review, score, and grade all assessments for a class). In addition, digital and online assessments typically include features, or “analytics,” that give educators more detailed information about student performance. For example, teachers may be able to see how long it took students to answer particular questions or how many times a student failed to answer a question correctly before getting the right answer. Many advocates of digital and online assessments tend to argue that such systems, if used properly, could help teachers “ personalize ” instruction—because many digital and online systems can provide far more detailed information about the academic performance of students, educators can use this information to modify educational programs, learning experiences , instructional approaches, and academic-support strategies in ways that address the distinct learning needs, interests, aspirations, or cultural backgrounds of individual students. In addition, many large-scale standardized tests are now administered online, though states typically allow students to take paper-based tests if computers are unavailable, if students prefer the paper-based option, or if students don’t have the technological skills and literacy required to perform well on an online assessment.
Given that assessments come in so many forms and serve so many diverse functions, a thorough discussion of the purpose and use of assessments could fill a lengthy book. The following descriptions, however, provide a brief, illustrative overview of a few of the major ways in which assessments—especially assessment results—are used in an attempt to improve schools and teaching:
- System and school accountability : Assessments, particularly standardized tests, have played an increasingly central role in efforts to hold schools, districts, and state public-school systems “accountable” for improving the academic achievement of students. The most widely discussed and far-reaching example, the 2001 federal law commonly known as the No Child Left Behind Act, strengthened federal expectations from the 1990s and required each state develop learning standards to govern what teachers should teach and students should learn. Under No Child Left Behind, standards are required in every grade level and content area from kindergarten through high school. The law also requires that students be tested annually in grades 3-8 and at least once in grades 10-12 in reading and mathematics. Since the law’s passage, standardized tests have been developed and implemented to measure how well students were meeting the standards, and scores have been reported publicly by state departments of education. The law also required that test results be tracked and reported separately for different “subgroups” of students, such as minority students, students from low-income households, students with special needs, and students with limited proficiency in English . By publicly reporting the test scores achieved by different schools and student groups, and by tying those scores to penalties and funding, the law has aimed to close achievement gaps and improve schools that were deemed to be underperforming. While the No Child Left Behind Act is one of the most controversial and contentious educational policies in recent history, and the technicalities of the legislation are highly complex, it is one example of how assessment results are being used as an accountability measure.
- Teacher evaluation and compensation : In recent years, a growing number of elected officials, policy makers, and education reformers have argued that the best way to improve educational results is to ensure that students have effective teachers, and that one way to ensure effective teaching is to evaluate and compensate educators, at least in part, based on the test scores their students achieve. By basing a teacher’s income and job security on assessment results, the reasoning goes, administrators can identify and reward high-performing teachers or take steps to either help low-performing teachers improve or remove them from schools. Growing political pressure, coupled with the promise of federal grants, prompted many states to begin using student test results in teacher evaluations. This controversial and highly contentious reform strategy generally requires fairly complicated statistical techniques—known as value-added measures or growth measures —to determine how much of a positive or negative effect individual teachers have on the academic achievement of their students, based primarily on student assessment results.
- Instructional improvement : Assessment results are often used as a mechanism for improving instructional quality and student achievement. Because assessments are designed to measure the acquisition of specific knowledge or skills, the design of an assessment can determine or influence what gets taught in the classroom (“teaching to the test” is a common, and often derogatory, phrase used to describe this general phenomenon). Formative assessments, for example, give teachers in-process feedback on student learning, which can help them make instructional adjustments during the teaching process, instead of having to wait until the end of a unit or course to find out how well students are learning the material. Other forms of assessment, such as standards-based assessments or common assessments, encourage educators to teach similar material and evaluate student performance in more consistent, reliable, or comparable ways.
- Learning-needs identification : Educators use a wide range of assessments and assessment methods to identify specific student learning needs, diagnose learning disabilities (such as autism, dyslexia, or nonverbal learning disabilities), evaluate language ability, or determine eligibility for specialized educational services. In recent years, the early identification of specialized learning needs and disabilities, and the proactive provision of educational support services to students, has been a major focus of numerous educational reform strategies. For a related discussion, see academic support .
In education, there is widespread agreement that assessment is an integral part of any effective educational system or program. Educators, parents, elected officials, policy makers, employers, and the public all want to know whether students are learning successfully and progressing academically in school. The debates—many of which are a complex, wide ranging, and frequently contentious—typically center on how assessments are used, including how frequently they are being administered and whether assessments are beneficial or harmful to students and the teaching process. While a comprehensive discussion of these debates is beyond the scope of this resource, the following is a representative selection of a few major issues being debated:
- Is high-stakes testing, as an accountability measure, the best way to improve schools, teaching quality, and student achievement? Or do the potential consequences—such as teachers focusing mainly on test preparation and a narrow range of knowledge at the expense of other important skills, or increased incentives to cheat and manipulate test results—undermine the benefits of using test scores as a way to hold schools and educators more accountable and improve educational results?
- Are standardized assessments truly objective measures of academic achievement? Or do they reflect intrinsic biases—in their design or content—that favor some students over others, such wealthier white students from more-educated households over minority and low-income students from less-educated households? For more detailed discussions, see measurement error and test bias .
- Are “one-size-fits-all” standardized tests a fair way to evaluate the learning achievement of all students, given that some students may be better test-takers than others? Or should students be given a variety of assessment options and multiple opportunities to demonstrate what they have learned?
- Will more challenging and rigorous assessments lead to higher educational achievement for all students? Or will they end up penalizing certain students who come from disadvantaged backgrounds? And, conversely, will less-advantaged students be at an even greater disadvantage if they are not held to the same high educational standards as other students (because lowering educational standards for certain students, such as students of color, will only further disadvantage them and perpetuate the same cycle of low expectations that historically contributed to racial and socioeconomic achievement gaps )?
- Do the costs—in money, time, and human resources—outweigh the benefits of widespread, large-scale testing? Would the funding and resources invested in testing and accountability be better spent on higher-quality educational materials, more training and support for teachers, and other resources that might improve schools and teaching more effectively? And is the pervasive use of tests providing valuable information that educators can use to improve instructional quality and student learning? Or are the tests actually taking up time that might be better spent on teaching students more knowledge and skills?
- Are technological learning applications, including digital and online assessments, improving learning experiences for students, teaching them technological skills and literacy, or generally making learning experiences more interesting and engaging? Or are digital learning applications adding to the cost of education, introducing unwanted distractions in schools, or undermining the value of teachers and the teaching process?

Alphabetical Search
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Formative vs. summative assessment: impacts on academic motivation, attitude toward learning, test anxiety, and self-regulation skill
Seyed m. ismail.
1 College of Humanities and Sciences, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia
D. R. Rahul
2 School of Science and Humanities, Shiv Nadar University Chennai, Chennai, India
Indrajit Patra
3 NIT Durgapur, Durgapur, West Bengal India
Ehsan Rezvani
4 English Department, Isfahan (Khorasgan) Branch, Islamic Azad University, Isfahan, Iran
Associated Data
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
As assessment plays an important role in the process of teaching and learning, this research explored the impacts of formative and summative assessments on academic motivation, attitude toward learning, test anxiety, and self-regulation skill of EFL students in Iran. To fulfill the objectives of this research, 72 Iranian EFL learners were chosen based on the convenience sampling method assigned to two experimental groups (summative group and formative group) and a control group. Then, the groups took the pre-tests of test anxiety, motivation, and self-regulation skill. Then, one experimental group was trained by following the rules of the formative assessment and the other experimental group was taught according to the summative assessment. The control group was instructed without using any preplanned assessment. After a 15-session treatment, the post-tests of the test anxiety, motivation, and self-regulation skill were administered to all groups to assess the impacts of the instruction on their language achievement. Lastly, a questionnaire of attitude was administered to both experimental groups to examine their attitudes towards the impacts of formative and summative assessment on their English learning improvement. The outcomes of one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni tests revealed that both summative and formative assessments were effective but the formative one was more effective on academic motivation, test anxiety, and self-regulation skill. The findings of one sample t -test indicated that the participants had positive attitudes towards summative and formative assessments. Based on the results, it can be concluded that formative assessment is an essential part of teaching that should be used in EFL instructional contexts. The implications of this study can help students to detect their own weaknesses and target areas that need more effort and work.
Introduction
In teaching and learning, assessment is defined as a procedure applied by instructors and students during instruction through which teachers provide necessary feedbacks to modify ongoing learning and teaching to develop learners’ attainment of planned instructional aims (Robinowitz, 2010 ). According to Popham ( 2008 ), assessment is an intended procedure in which evidence of learners’ status is utilized by educators to adjust their ongoing instructional processes or applied by learners to change their present instructional strategies. Assessment intends to improve learning and it is used to reduce the gap between students’ present instructional situation and their target learning objectives (Heritage, 2012 ).
Two types of assessment are formative and summative. According to Glazer ( 2014 ), summative assessment is generally applied to give learners a numerical score with limited feedback. Therefore, summative assessment is commonly used to measure learning and is rarely used for learning. Educators can make the summative assessment more formative by giving learners the opportunity to learn from exams. This would mean supplying pupils with feedback on exams and making use of the teaching potentiality of exams. Wininger ( 2005 ) proposed an amalgamation of assessment techniques between summative assessment and formative assessment. This marriage between summative assessment and formative assessment is referred to as summative-formative assessment. Based on Wininger, summative-formative assessment is used to review the exam with examinees so they can get feedback on comprehension. Formative-summative assessment occurs in two primary forms: using a mock exam before the final or using the final exam before the retake.
Formative assessment allows for feedback which improves learning while summative assessment measures learning. Formative assessment refers to frequent, interactive assessments of students’ development and understanding to recognize their needs and adjust teaching appropriately (Alahmadi et al., 2019 ). According to Glazer ( 2014 ), formative assessment is generally defined as tasks that allow pupils to receive feedback on their performance during the course. In the classroom, teachers use assessments as a diagnostic tool at the termination of lessons or the termination of units. In addition, teachers can use assessments for teaching, by identifying student misconceptions and bridging gaps in learning through meaningful feedback (Dixson & Worrell, 2016 ). Unfortunately, numerous instructors consider formative assessments as a tool to measure students’ learning, while missing out on its teaching potential. Testing and teaching can be one or the same which will be discussed further in this research (Remmi & Hashim, 2021 ).
According to Black et al. ( 2004 ), using formative tests for formative purposes improves classroom practice whereby students can be encouraged in both reflective and active review of course content. In general terms, formative assessment is concerned with helping students to develop their learning (Buyukkarci & Sahinkarakas, 2021 ). Formative assessment can be considered as a pivotal and valid part of the blending of assessment and teaching (Ozan & Kıncal, 2018 ). Formative assessment helps students gain an understanding of the assessment process and provides them with feedback on how to refine their efforts for improvement. However, in practice, assessment for learning is still in its infancy, and many instructors still struggle with providing productive and timely feedback (Clark, 2011 ).
Using the mentioned assessments can positively affect the test anxiety of the students. Test anxiety signifies the extent to which the students experience apprehension, fear, uneasiness, panic tension, and restlessness while even thinking of forthcoming tests or exams (Ahmad, 2012 ). Anxiety can also be regarded as a product of hesitation about imminent events or situations (Craig et al., 2000 ). Test anxiety is the emotional reaction or status of stress that happens before exams and remains throughout the period of the exams (Sepehrian, 2013 ). Anxiety can commonly be connected to coercions to self-efficacy and evaluations of circumstances as threatening or reactions to a resource of stress to continue (Pappamihiel, 2002 ).
The other variable which can influence the consequences of tests or testing sessions in EFL settings is the attitudes of students towards English culture, English language, and English people. Kara ( 2009 ) stated that attitude about learning together with beliefs and opinions have a significant impact on learners’ behaviors and consequently on their performances. Those learners who have desirable beliefs about language learning are willing to rise more positive attitudes toward language learning. On the other hand, having undesirable beliefs can result in negative attitudes, class anxiety, and low cognitive achievements (Chalak & Kassaian, 2010 ; Tella et al., 2010 ). There are both negative and positive attitudes towards learning. Positive attitudes can develop learning and negative attitudes can become barriers to learning because students have these attitudes as they have difficulties in learning or they just feel that what is presented to them is boring. While a negative attitude toward learning can lead to poor performances of students, a positive attitude can result in appropriate and good performances of students (Ellis, 1994 ).
Woods ( 2015 ) says that instructors should regularly utilize formative assessment to advance the learners’ self-regulation skills and boost their motivation. Motivation is referred to the reasons why people have different behaviors in different situations. Motivation is considered as the intensity and direction of the students’ attempts. The intensity of attempt is referred to the extent that students try to reach their objectives and the direction of attempt is referred to the objectives that students intend to reach (Ahmadi et al., 2009 ; Paul & Elder, 2013 ). Motivation is an inborn phenomenon that is influenced by four agents such as aim (the aim of behaviors, purposes, and tendencies), instrument (instruments used to reach objectives), situation (environmental and outer stimulants), and temper (inner state of the organism). To reach their goals, people first should acquire the essential incentives. For instance, academic accomplishment motivation is significant to scholars (Firouznia et al., 2009 ).
Wiliam ( 2014 ) also asserts that self-regulation learning can be a crucial part of a productive formative assessment concerning the techniques of explaining, sharing, and understanding the instructional goals and students’ success and responsibility for their own learning. Self-regulation skill requires learners to dynamically utilize their cognitive skills; try to achieve their learning aims; receive support from their classmates, parents, and instructors when needed; and most significantly, be responsible for their own learning (Ozan & Kıncal, 2018 ). This research aimed to explore the impacts of using summative and formative assessments of Iranian EFL learners’ academic motivation, attitude toward learning, test anxiety, and self-regulation skill. This study is significant as it compared the effects of two kinds of assessments namely formative and summative on academic motivation, attitude toward learning, test anxiety, and self-regulation skill. As this research investigated the effects of the mentioned assessments on four emotional variables simultaneously, it can be considered as a novel study.
Review of the literature
In the field of teaching English as a foreign language, several researchers and experts defined the term “assessment” as a pivotal component of the process of teaching. According to Brown ( 2003 ), assessment is a process of collecting data about learners’ capabilities to conduct learning tasks. That is, assessment is the way instructors use to gather data about their methods and their pupils’ improvement. Furthermore, the assessment process has got an inseparable component from teaching, since it is impossible to think of teaching without assessments. Brown ( 2003 ) defined assessment in relation to testing. The differences between them refer to the fact that the latter occurs at an identified point of time while the former is an ongoing process that occurs regularly (Brown, 2003 ).
Other scholars explained the meaning of assessment by distinguishing it from evaluation. Regarding the difference between the two, Nunan ( 1992 ) asserted that assessment is referred to the procedures and processes whereby teachers determine what students can do in the target language and added evaluation is referred to a wider range of processes that may or may not include assessment data. In this way, then, assessment is process-oriented while evaluation is product-oriented. Palomba and Banta ( 1999 ) defined assessment as “the systematic collection, review, and use of information about educational programs undertaken to improve learning and development” (p.4). All in all, assessing students’ performances means recognizing and gathering information, receiving feedback, and analyzing and modifying the learning processes. The main goal, thus, is to overcome barriers to learning. Assessment is then used to interpret the performances of students, develop learning, and modify teaching (Aouine, 2011 ; Ghahderijani et al., 2021 ).
Two types of assessment are formative and summative. Popham ( 2008 ) said that it is not the nature of the tests to be labeled as summative or formative but the use to which that tests’ outcomes will be put. That is to say, the summative-formative manifestation of assessment does not stop at being a typology but it expands to be purposive due to the nature of assessment. Summative assessment, then, has been referred to as some criteria. Cizek ( 2010 ) suggests that two criteria can define the summative assessment: (1) it is conducted at the termination of some units and (2) its goal is mainly to characterize the performances of the students or systems. Its major goal is to gain measurement of attainment to be utilized in making decisions.
Through Cizek’s definition, a summative assessment seeks to judge the learners’ performances in every single course. Thus, providing diagnostic information is not what this type of assessment is concerned with. Significantly, the judgments made about the students, teachers, or curricula are meant to grade, certificate, evaluate, and research on how effective curricula are, and these are the purposes of summative assessment according to Cizek ( 2010 ).
According to Black and Wiliam ( 2006 ), summative assessment is given occasionally to assess what pupils know and do not know. This type of assessment is done after the learning has been finalized and provides feedback and information that summarize the learning and teaching process. Typically, no more formal learning is occurring at this stage, other than incidental learning that may happen via completing the assignments and projects (Wuest & Fisette, 2012 ). Summative assessment measures what students have learned and mostly is conducted at the end of a course of instruction (Abeywickrama & Brown, 2010 ; Liu et al., 2021 ; Rezai et al., 2022 ).
For Woods ( 2015 ), the summative assessment provides information to judge the general values of the instructional programs, while the outcomes of formative assessment are used to facilitate the instructional programs. Based on Shepard ( 2006 ), a summative assessment must accomplish its major purpose of documenting what learners know and can do but, if carefully created, should also efficaciously fulfill a secondary objective of learning support.
Brown ( 2003 ) claimed that summative assessment aims at measuring or summarizing what students have learned. This means looking back and taking stock of how well that students have fulfilled goals but does not essentially pave the way to future improvement. Furthermore, the summative assessment also known as assessment of learning is clarified by Spolsky and Halt ( 2008 ) who state that assessment of learning is less detailed, and intends to find out the educational programs or students’ outcomes. Thus, summative assessment is applied to evaluating different language skills and learners’ achievements. Even though summative assessment has a main role in the learners’ evaluation, it is not sufficient to know their advancement and to detect the major areas of weaknesses, and this is the essence of formative assessment (Pinchok & Brandt, 2009 ; Vadivel et al., 2021 ).
The term ‘formative assessment’ has been proposed for years and defined by many researchers. A clearer definition is provided by Brown ( 2003 ) in which he claims that formative assessment is referred to the evaluation of learners in the process of “forming” their skills and competencies to help them to keep up that growth process. It is also described as comprising all those activities conducted by instructors or by their learners that supply information to be utilized as feedback to adjust the learning and teaching activities in which they are involved (Fox et al., 2016 ).
Formative assessments aim to gain immediate feedback on students learning through which strengths and weaknesses of students can be diagnosed. Comprehensively, Wiliam ( 2011 ) suggests: Practices in the classrooms are formative to the extent that evidence about students’ accomplishments is elicited, interpreted, and utilized by instructors, students, or their classmates, to decide about the subsequent steps in the education that are probably to be better or better founded, than the decisions they would have taken in the absence of the evidence that was elicited.
Through this definition, formative assessment actively involves both students’ and teachers’ participation as a key component to develop students’ performance. The assessment for learning, which is based on the aim behind using it, is assessing learners’ progress (McCallum & Milner, 2021 ). Therefore, it is all about gathering data about learners’ achievement to recognize their progress in skills, requirements, and capabilities as their weaknesses and strengths before, during, and after the educational courses to develop students’ learning and achievement (Douglas & Wren, 2008 ).
Besides, Popham ( 2008 ) considered the formative assessment as a strategic procedure in which educators or pupils utilize assessment-based evidence to modify what they are presently performing. That describes it as the planned process that is not randomly occurring. Therefore, formative assessment is an ongoing procedure that provides learners with constructive timely feedback, helping them achieve their learning goals and enhancing their achievements (Vogt et al., 2020 ). Formative assessment is a helpful technique that can provide students with formative help by evaluating the interactions between assessment and learning (Chan, 2021 ; Masita & Fitri, 2020 ).
Some criteria related to formative assessment have been presented by Cizek ( 2010 ). In his opinion, formative assessment attempts to identify students’ levels whether high or low, to provide more help for educators to plan subsequent instruction, to make it easier for students to continue their own learning, review their work, and be able to evaluate themselves. To make learners responsible for their learning and do their research Formative assessment, to Cizek, is a sufficient tool and area for learners and teachers to make proficiency in the learning-teaching process. All in all, concerning specific objectives, formative assessment is a goal-oriented process.
Tahir et al. ( 2012 ) stated that formative assessment is a diagnostic use of assessment that can provide feedback to instructors and learners throughout the instructional process. Marsh ( 2007 ) claimed that formative tests are a type of strategy which are prepared to recognize students’ learning problems to provide a remedial procedure to develop the performances of the majority of the learners. The information that is provided for the learners should be utilized for the assessment to be explained as a formative one. The Assessment Reform Group (ARG) ( 2007 ) explains formative assessment as the procedure to look for and interpret the evidence for instructors and their students to make decisions about where the students fit in their learning, where they need to go, and how best to get there. Kathy ( 2013 ) also argued that formative tests aim to analyze the students’ learning problems to develop their academic attainment.
The theory that is behind our study is the sociocultural theory stating that knowledge is generated in a cooperative way within social contexts. It views learning as a condition wherein learners generate their meanings from the materials and content delivered to them, rather than trying to memorize the information (Vygotsky, 1978 ). Based on sociocultural theory, learning can occur successfully when teachers and students have more interactions with each other.
Some empirical studies are reported here. Alahmadi et al. ( 2019 ) aimed to examine whether a formative speaking assessment produced any effect on learners’ performances in the summative test. Besides, they aimed to observe students’ learning and to provide useful feedbacks that can be applied by educators to develop learners’ achievement and assist them to detect their weaknesses and strengths in speaking skills. Their results indicated that formative assessment helped Saudi learners to solve the problems they encounter in speaking tests.
Mahshanian et al. ( 2019 ) highlighted the significance of summative assessment in conjunction with teacher-based (formative) assessments on the learners’ performances. To do this study, 170 EFL students at the advanced level were chosen and grouped based on the kind of assessment they had received. The subjects in this research were administered exams for two main reasons. First, a general proficiency test was given to put the students at different levels of proficiency. Second, for comparing students’ development according to different kinds of assessments within a 4-month learning duration, an achievement test of the course was administered both as the pre-test and the post-test. The data gained via the scores of the participants on the achievement test received analyses and then compared by utilizing ANCOVA, ANOVA, and t- tests. Based on the outcomes of this research, we can conclude that an amalgamation of summative and formative assessments can result in better achievements for EFL students than either summative or formative assessments discretely.
Imen ( 2020 ) attempted to determine the effects of formative assessments on EFL learners’ writing skills. Indeed, the goal of this study was to recognize the effects of formative assessments on developing the writing skills of first-year master’s students at Abdel Elhamid Ibn Badis University, in Mostaganem. This research also attempted to reveal an essential issue that is the lack of the execution of formative assessments in the writing classrooms. To verify the hypotheses, two tools were applied in this study to gather the data, the teachers’ questionnaire and the students’ questionnaire. The findings of the study revealed that the formative assessment was not extensively used in teaching and learning writing skills, at the University of Mostaganem. The results of both questionnaires showed that if the students were evaluated formatively, their writing skills could be highly enhanced.
Ashdale ( 2020 ) attempted to examine the influences of a particular formative assessment named as Progress Trackers, by comparing a control group that did not receive the Progress Tracker with an experimental group that received the formative-based assessment. The research findings revealed that there were no substantial differences between the experimental and control groups based on the results of the pre-test and the post-test scores. While not statistically significant, the experimental group showed a larger increase in the learners with at least a 60% development in achievement. The lack of significant differences between the experimental group and the control group could be created by the uselessness of the formative assessments or the inability to exclude other factors in the class contexts. This could comprise the uses of other formative assessments applied in both groups, delivery of content, and execution of the formative assessments.
Persaud Singh and Ewert ( 2021 ) investigated the effects of quizzes and mock exams as a formative assessment on working adult learners’ achievement using a quasi-experimental quantitative design. One experimental group received both quizzes and mock exams, another group received mock exams only, and a control group received neither. The data gathered received analyses by utilizing t -tests and ANOVA. The findings indicated noticeable differences in the levels of achievement for the groups receiving formative assessments in comparison to the control participants. The “mock exam” group outperformed slightly than the “quizzes and mock exam” group.
Al Tayib Umar and Abdulmlik Ameen ( 2021 ) traced the effects of formative assessment on Saudi EFL students’ achievement in medical English. The research also tried to figure out teachers’ and students’ attitudes toward formative assessment. The participants involved in this research were 98 students selected among the Preparatory Year learners at a Saudi university. They were assigned to an experimental group and a control group. The experimental students were given their English for Specific Purposes (ESP) courses following the formative assessment techniques whereas the control group was trained in their ESP courses by traditional assessment rules. The experimental group teachers were given intensive training courses in Saudi Arabia and abroad on how to use formative assessment principles in the classrooms. At the end of the experiment that continued for 120 days, the control and experimental groups sat for the end of term examination which was designed for all candidates in the Preparatory College. Grades of all participants in the two groups in the final exam were compared. The performance of the experimental group was found to be meaningfully higher than that of the control group. Instructors’ and students’ attitudes towards formative assessment were positive.
Hamedi et al. ( 2022 ) investigated the effects of using formative assessment by Kahoot application on Iranian EFL students’ vocabulary knowledge as well as their burnout levels. This study was conducted on 60 participants who were in two groups of experimental and control. The results indicated that using formative assessment generated significant effects on of Iranian EFL students’ vocabulary knowledge.
In conclusion, the above studies confirmed the positive effects of summative and formative assessment on language learning. Yet, there are a few kinds of research on comparing the effects of the summative and formative assessments on Iranian EFL learners’ academic motivation, attitude toward learning, test anxiety, and self-regulation skill. Most studies in the domain of assessment examined the effects of the summative and formative assessments on the main skills (reading, speaking, writing, and listening) and they did not pay much attention to the psychosocial variables; therefore, this research posed two questions to cover the existing gap.
- RQ1. Does using formative and summative assessments positively affect Iranian EFL learners’ test anxiety, academic motivation, and self-regulation skill?
- RQ2. Do Iranian EFL learners present positive attitudes toward learning through formative and summative assessments?
Methodology
Design of the study, participants.
The participants of this research were 72 Iranian EFL students who have studied English since 2016. The male EFL learners were selected based on the convenience sampling method by administering the Preliminary English Test (PET). They were selected from the Parsian English language institute, located in Ahvaz city, Iran. The participants’ general English proficiency was intermediate and their age average was 21 years old. The participants were divided into two experimental groups (summative and formative) and a control group.
Instrumentations
For homogenizing the subjects in terms of general English proficiency, we gave a version of the PET test, extracted from the book PET Practice Test (Quintana, 2008 ). Because of some limitations, only the sections of reading, grammar, and vocabulary of the test were used in this study. We piloted the test on another similar group and allotted 60 min for answering all its items. Its validity was accepted by some English experts and its reliability was .91.
Britner and Pajares’ ( 2006 ) Science Anxiety Scale (SAS) was used as the other instrument to assess the participants’ test anxiety. Some wordings of the items were changed to make them suitable for measuring test anxiety. There were 12 items in this test that required the participants to consider the items (e.g., I am worried that I will get weak scores in most of the exams) and answer a 6-point scale ranging from certainly false to certainly true. Based on Cronbach’s alpha formula, the reliability index of the anxiety test was .79.
The other tool used in this study was the Self-Regulatory Strategies Scale (SRSS) which was developed by Kadıoğlu et al. ( 2011 ) to assess the self-regulation skills of the participants. The SRSS was a 6-point Likert instrument including never, seldom, occasionally, often, frequently, and constantly. The SRSS consisted of 29 statements in eight dimensions. The results of Cronbach’s alpha formula showed that the reliability of the SRSS was .82.
We used the Attitude/Motivation Test Battery (AMTB) of Gardner ( 2004 ) to evaluate the respondents’ English learning motivation. This measuring instrument had 26 items each with six responses: Highly Disagree, Moderately Disagree, Somewhat Disagree, Somewhat Agree, Moderately Agree, and Highly Agree. We used the Cronbach alpha to measure the reliability of the motivation questionnaire ( r = .87). It should be noted that the motivation questionnaire, the SAS, and the SRSS were used as the pre-tests and post-tests of the research.
The last tool employed in this research was an attitude questionnaire examining the participants’ attitudes towards the effectiveness of summative and formative assessment on their English learning enhancement. The researchers themselves created 17-point Likert- items for this questionnaire and the reliability of this instrument was .80. Likert scale was utilized in the questionnaire to show the amount of disagreement and agreement from 1 to 5 that were highly disagree, disagree, no idea, agree, and highly agree. The validities of all mentioned tools were substantiated by a group of English specialists.
Collecting the needed data
To start the study, first, the PET was administered to 96 EFL learners and 72 intermediate participants were selected among them. As stated previously, the participants were divided into two experimental groups (summative and formative) and one control group. After that, the pretests of test anxiety, motivation, and self-regulation skill were administered to the participants of all groups. After pretesting process, the treatment was conducted on the groups differently; each group received special instruction.
One experimental group was instructed based on the rules of the formative assessment, in the formative group, the teacher (researcher) assisted the students to participate in evaluating their learning via using self and peer assessment. Besides, the teacher’s comprehensive and descriptive elicitation and feedbacks of information about students’ learning were significant in formative class. In fact, there were no tests at the termination of the term and the teacher was flexible concerning the students’ mistakes and provided them with constructive feedback including metalinguistic clues, elicitation, correction, repletion, clarification request, recast, and repletion.
In the summative class, the teacher assessed the students’ learning by giving mid-term and final exams. The teacher did not provide any elaborative feedback, and his feedback was limited to yes/no and true/ false. The control group neither received a formative-based instruction nor a summative-based instruction. The teacher of the control group instructed them without utilizing any preplanned assessments. They finished the course without any formative and summative assessments. After the treatment, the post-tests of the test anxiety, motivation, and self-regulation skill were given to all groups to assess the influences of the intervention on their language achievement. In the final step, the questionnaire of attitude was distributed among both experimental groups to check their opinions about the impacts of summative and formative assessment on their English learning improvement.
The whole study lasted 23 sessions; each took 50 min. In one session, the PET test was administered and in the next three sessions, three pre-tests were conducted. During 15 sessions, the treatment was carried out; in three sessions, three post-tests were given to the participants, and in the last session the attitudinal questionnaire was administered to examine the participants’ attitudes towards the effectiveness of summative and formative assessment of their English learning achievement.
Data analysis
Having prepared all needed data via the procedures mentioned above, some statistical steps were taken to provide answers to the questions raised in this study. First, the data were analyzed descriptively to compute the means of the groups. Second, some one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni tests were used for analyzing the data inferentially. Third, one sample t- test was utilized to analyze the motivation questionnaire data.
Results and discussion
After checking and getting sure about the normality distribution of the data by using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, we used several one-way ANOVA tests and reported their results in the following tables:
As we see in Table Table1, 1 , the mean scores of all groups are almost similar. They got almost equal scores on their anxiety pre-test and the three groups were at the same level of anxiety before conducting the instruction. This claim is verified in the following table with the help of one-way ANOVA.
Descriptive statistics of all groups on the test anxiety pre-tests
| Means | Std. deviations | Std. errors | 95% confidence interval for means | Minimum | Maximum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||||
| Control | 24 | 27.70 | 11.37 | 2.32 | 22.90 | 32.51 | 14.00 | 49.00 |
| Summative | 24 | 28.91 | 11.89 | 2.42 | 23.89 | 33.93 | 13.00 | 50.00 |
| Formative | 24 | 28.41 | 10.93 | 2.23 | 23.79 | 33.03 | 14.00 | 49.00 |
| Total | 72 | 28.34 | 11.25 | 1.32 | 25.70 | 30.99 | 13.00 | 50.00 |
According to the Sig value in Table Table2, 2 , there is not a noticeable difference between the test anxiety of all three groups. They were at the same anxiety level at the outset of the study. The inferential statistics show that all the participants had an equal amount of anxiety before they had received the treatment.
Inferential statistics of all groups on the test anxiety pre-tests
| Sum of squares | df | Mean squares | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 17.69 | 2 | 8.84 | .06 | .93 |
| Within groups | 8980.62 | 69 | 130.15 | ||
| Total | 8998.31 | 71 |
As is seen in Table Table3, 3 , the mean scores of all groups are different on the anxiety post-tests. Based on the descriptive statistics, the groups gained different scores on their anxiety post-test and the experimental groups obtained better scores than the control group. This claim is substantiated in the following table by using a one-way ANOVA test.
Descriptive statistics of all groups on the test anxiety post-tests
| Means | Std. deviations | Std. errors | 95% confidence interval for means | Minimum | Maximum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||||
| Control | 24 | 29.95 | 11.08 | 2.26 | 25.27 | 34.63 | 14.00 | 51.00 |
| Summative | 24 | 37.91 | 10.80 | 2.20 | 33.35 | 42.47 | 19.00 | 60.00 |
| Formative | 24 | 49.50 | 10.37 | 2.11 | 45.11 | 53.88 | 23.00 | 62.00 |
| Total | 72 | 39.12 | 13.33 | 1.57 | 35.99 | 42.25 | 14.00 | 62.00 |
Table Table4 4 depicts that the Sig value is less than .00; accordingly, one can conclude that there is a noticeable difference between the test anxiety post-tests of all three groups. They were at different anxiety levels at the end of the research. It seems that the experimental groups outdid the control group on the post-test.
Inferential statistics of all groups on the test anxiety post-tests
| Sum of squares | Df | Mean squares | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 4635.08 | 2 | 2317.54 | 20.02 | .00 |
| Within groups | 7986.79 | 69 | 115.75 | ||
| Total | 12,621.87 | 71 |
In Table Table5, 5 , the test anxiety level of all groups is compared. This table shows that there are remarkable differences between the anxiety post-tests of the control group and both experimental groups. Also, this table shows that the formative group outdid the control and summative groups. The formative group had the best performance among the three groups of this study.
Multiple comparisons by Bonferroni test (test anxiety)
| (I) groups | (J) groups | Mean differences (I-J) | Std. errors | Sig. | 95% confidence intervals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||
| Control | Summative | −7.95 | 3.10 | .03 | −15.57 | −.33 |
| Formative | −19.54 | 3.10 | .00 | −27.16 | −11.92 | |
| Summative | Control | 7.95 | 3.10 | .03 | .33 | 15.57 |
| Formative | −11.58 | 3.10 | .00 | −19.20 | −3.96 | |
| Formative | Control | 19.54 | 3.10 | .00 | 11.92 | 27.16 |
| Summative | 11.58 | 3.10 | .00 | 3.96 | 19.20 | |
a The mean differences are significant at the 0.05 level
As observed in Table Table6, 6 , all three groups’ performances on the self-regulation pre-tests are almost the same; their mean scores are almost equal. We used a one-way ANOVA to check the groups’ performances on the self-regulation pre-tests.
Descriptive statistics of the three groups on the self-regulation pre-tests
| Means | Std. deviations | Std. errors | 95% confidence interval for means | Minimum | Maximum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||||
| Control | 24 | 77.54 | 17.02 | 3.47 | 70.35 | 84.73 | 39.00 | 99.00 |
| Summative | 24 | 78.20 | 16.22 | 3.31 | 71.35 | 85.06 | 41.00 | 101.00 |
| Formative | 24 | 76.83 | 16.78 | 3.42 | 69.74 | 83.92 | 39.00 | 98.00 |
| Total | 72 | 77.52 | 16.45 | 1.93 | 73.66 | 81.39 | 39.00 | 101.00 |
In Table Table7, 7 , the inferential statistics of all groups on the self-regulation pre-tests are shown. As Sig (.96) is higher than (0.05), the differences between the three groups are not meaningfully significant. Based on this table, all three groups had the same level of self-regulation ability at the outset of the study.
Inferential statistics of the three groups on the self-regulation pre-tests
| Sum of squares | df | Mean squares | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 22.69 | 2 | 11.34 | .04 | .96 |
| Within groups | 19,203.25 | 69 | 278.30 | ||
| Total | 19,225.94 | 71 |
The mean scores of the control group, the summative group, and the formative group are, 80.12, 130.04, and 147.25, respectively (Table (Table8). 8 ). At the first look, we can say that both experimental participants outflank the control participants since their mean scores are very higher than the mean score of the control group.
Descriptive statistics of the three groups on the self-regulation post-tests
| Means | Std. deviations | Std. errors | 95% confidence interval for mean | Minimum | Maximum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||||
| Control | 24 | 80.12 | 17.14 | 3.500 | 72.88 | 87.36 | 47.00 | 114.00 |
| Summative | 24 | 130.04 | 10.44 | 2.13 | 125.62 | 134.45 | 109.00 | 146.00 |
| Formative | 24 | 147.25 | 27.19 | 5.55 | 135.76 | 158.73 | 39.00 | 167.00 |
| Total | 72 | 119.13 | 34.52 | 4.06 | 111.02 | 127.25 | 39.00 | 167.00 |
The results indicate significant differences between the self-regulation post-tests of the groups in favor of the experimental groups (Table (Table9 9 ) . Based on the inferential statistics, the performances of the three groups on the self-regulation post-test are different and the summative group and the formative group outflank the control group.
Inferential statistics of the three groups on the self-regulation post-tests
| Sum of square | Df | Mean squares | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 58,348.52 | 2 | 29,174.26 | 76.60 | .00 |
| Within groups | 26,278.08 | 69 | 380.84 | ||
| Total | 84,626.61 | 71 |
The outcomes in Table Table10 10 indicate that both experimental groups have better performances than the control group on the self-regulation post-tests. Also, the findings show that the formative group performed better than the other two groups. The treatment had the most effect on the formative group.
Multiple comparisons by Bonferroni test (self-regulation)
| (I) groups | (J) groups | Mean differences (I-J) | Std. errors | Sig. | 95% confidence intervals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||
| Control | Summative | −49.91 | 5.63 | .00 | −63.73 | −36.09 |
| Formative | −67.12 | 5.63 | .00 | −80.94 | −53.30 | |
| Summative | Control | 49.91 | 5.63 | .00 | 36.09 | 63.73 |
| Formative | −17.20 | 5.63 | .01 | −31.03 | −3.38 | |
| Formative | Control | 67.12 | 5.63 | .00 | 53.30 | 80.94 |
| Summative | 17.20 | 5.63 | .01 | 3.38 | 31.03 | |
The control group’s mean score is 90.33, the mean score of the summative group is 91.75, and the mean score of the formative group is 92.45 (Table (Table11). 11 ). Accordingly, we can say that the three groups had an equal degree of motivation before conducting the treatment.
Descriptive statistics of the three groups on the motivation pre-tests
| Means | Std. deviations | Std. errors | 95% confidence interval for means | Minimum | Maximum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||||
| Control | 24 | 90.33 | 25.08 | 5.11 | 79.74 | 100.92 | 50.00 | 149.00 |
| Summative | 24 | 91.75 | 22.08 | 4.50 | 82.42 | 101.07 | 55.00 | 128.00 |
| Formative | 24 | 92.45 | 21.69 | 4.42 | 83.29 | 101.62 | 55.00 | 129.00 |
| Total | 72 | 91.51 | 22.69 | 2.67 | 86.18 | 96.84 | 50.00 | 149.00 |
Table Table12 12 presents the inferential statistics of all groups on the motivation pre-tests. One can see that Sig (.94) is larger than 0.50; consequently, no difference is observed among the groups in terms of motivation pre-tests. The inferential statistics show that the students of the three groups had the same amount of motivation before they had received the treatment.
Inferential statistics of the three groups on the motivation pre-tests
| Sum of square | df | Mean squares | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 56.19 | 2 | 28.09 | .05 | .94 |
| Within groups | 36,519.79 | 69 | 529.27 | ||
| Total | 36,575.98 | 71 |
As shown in the Table Table13, 13 , the mean scores of the summative and formative groups are 115.79 and 127.83, respectively, on the motivation post-tests and the mean of the control group is 92.87. It appears that the experimental participants outperform the control participants on the motivation post-tests as their mean scores are higher than the control group.
Descriptive statistics of the three groups on the motivation post-tests
| Means | Std. deviations | Std. errors | 95% confidence interval for means | Minimum | Maximum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||||
| Control | 24 | 92.87 | 20.99 | 4.28 | 84.00 | 101.74 | 60.00 | 129.00 |
| Summative | 24 | 115.79 | 13.50 | 2.75 | 110.09 | 121.49 | 99.00 | 140.00 |
| Formative | 24 | 127.83 | 12.51 | 2.55 | 122.54 | 133.11 | 100.00 | 150.00 |
| Total | 72 | 112.16 | 21.58 | 2.54 | 107.09 | 117.23 | 60.00 | 150.00 |
In Table Table14, 14 , the inferential statistics of all groups on the motivation post-tests are revealed. The Sig value (.00) is less than 0.50; therefore, the differences between the groups are significant. Indeed, the experimental groups outperformed the control group after the instruction and this betterment can be ascribed to the treatment.
Inferential statistics of the three groups on the motivation post-tests
| Sum of square | df | Mean squares | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 15,138.08 | 2 | 7569.04 | 29.12 | .00 |
| Within groups | 17,933.91 | 69 | 259.91 | ||
| Total | 33,072.00 | 71 |
The mean scores of the motivation post-tests are compared in Table Table15. 15 . Accordingly, there are noticeable differences between the post-tests of all groups. The formative participants had better performance than the other two groups. We can say that the formative assessment is more effective than the summative assessment in EFL classes.
Multiple comparisons by Bonferroni test (motivation)
| (I) groups | (J) groups | Mean differences (I-J) | Std. errors | Sig. | 95% confidence intervals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bounds | Upper bounds | |||||
| Control | Summative | −22.91 | 4.65 | .00 | −34.33 | −11.49 |
| Formative | −34.95 | 4.65 | .00 | −46.37 | −23.53 | |
| Summative | Control | 22.91 | 4.65 | .00 | 11.49 | 34.33 |
| Formative | −12.04 | 4.65 | .03 | −23.46 | −.62 | |
| Formative | Control | 34.95 | 4.65 | .00 | 23.53 | 46.37 |
| Summative | 12.04 | 4.65 | .03 | .62 | 23.46 | |
As depicted in Table Table16, 16 , the amount of statistic T -value is 63.72, df =16, and Sig =0.00 which is less than 0.05. This implies that Iranian students held positive attitudes towards the effectiveness of summative and formative assessments on their language learning improvement.
One-sample test of the attitude questionnaire
| Test value = 0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Df | Sig. (2-tailed) | Mean differences | 95% confidence interval of the differences | |||
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Scores | 63.72 | 16 | .000 | 4.52 | 4.37 | 4.67 |
Briefly, the results indicate that both experimental groups had better performances than the control group in their post-tests. The formative group had the best performance among the three groups of this study. Additionally, the results reveal that the participants of the present research had positive attitudes towards the effectiveness of both formative and summative assessments on their language learning development.
After analyzing the data, it was found that all three groups were at the same levels of test anxiety, motivation, and self-regulation skill at the outset of the research. But, the performances of the three groups were different at the end of the investigation. Both experimental groups outdid the control group on their post-tests and the formative group performed better among the three groups. Although both types of assessments (summative and formative) were effective on test the anxiety, motivation, and self-regulation skill of EFL learners, the formative assessment was the most effective one. The findings of the current research also indicated that both experimental groups presented positive attitudes toward the implementation of the summative and formative assessments in EFL classes.
The findings gained in this study are supported by Persaud Singh and Ewert ( 2021 ) who inspected the impacts of formative assessment on adult students’ language improvement. They indicated that there were meaningful differences between the formative participants and the control participants in terms of language achievement in favor of the formative participants. Additionally, our research findings are advocated by Alahmadi et al. ( 2019 ) who explored the effects of formative speaking assessments on EFL learners’ performances in speaking tests. They showed that the formative assessment assisted Saudi EFL learners to solve the problems they encountered in speaking tests.
In addition, our study findings are in accordance with Mahshanian et al. ( 2019 ) who confirmed that the amalgamation of summative and formative assessment can result in better achievement in English language learning. Also, our investigation lends support to the findings of Buyukkarci and Sahinkarakas ( 2021 ) who verified the positive effects of using formative assessment on learners’ language achievement. Additionally, the results of the current research are in agreement with Ounis ( 2017 ) who stated that formative assessment facilitated and supported students’ learning. Our study findings are supported by the sociocultural theory which focuses on the role of social interactions among the students and their teachers in the classroom. Based on this perspective, the learning process is mainly a social process and students’ cognitive functions are made based on their interactions with those around them.
Furthermore, our research results are in agreement with the results of Imen ( 2020 ) who discovered the impacts of formative assessments on EFL students’ writing abilities. His results indicated that using formative assessment develops the participants’ writing skills. Moreover, our research outcomes are supported by the impacts of formative assessments on learners’ academic attainment, opinions about lessons, and self-regulation skills in Ozan and Kıncal ( 2018 ) who performed an investigation on the influences of formative assessments on students’ attitudes toward lessons, academic achievement, and self-regulation skill. They revealed that the experimental class that received the treatment by formative assessment practices had better academic performances and more positive attitudes towards the classes than the control class.
Regarding the positive attitudes of the participants towards formative and summative assessment, our results are in line with Tekin ( 2010 ) who discovered that formative assessment practices meaningfully developed students’ attitudes about mathematics learning. That research indicated that the participants in the treatment group had positive attitudes about mathematics learning. In addition, King ( 2003 ) asserted that the formative assessments enhanced the learners’ attitudes about science classes. Also, Hwang and Chang ( 2011 ) revealed that the formative assessment highly boosted the attitudes and interest of students toward learning in local culture classes.
One explanation for the outperformance of the formative group over the other two groups can be the fact that they received much more input. They were provided with different kinds of feedback and took more exams during the semester. These exams and feedback can be the reasons for their successes in language achievement. This is in line with Krashen’s ( 1981 ) input theory stating that if students are exposed to more input, they can learn more.
The other possible explanations for our results are that formative assessments are not graded so they take the anxiety away from the assessees. They also detach the thinking that they must get everything right. Instead, they serve as a practice for students to get assistance along the way before the final tests. Teachers usually check for understanding if students are struggling during the lesson. Teachers address these issues early on instead of waiting until the end of the unit to assess. Teachers have to do less reteaching at the end because many of the problems with mastery are addressed before final tests. The mentioned advantages can be the reasons for our obtained findings.
In addition, monitoring the students’ learning via using the formative assessment can be the other justification for our results. In fact, monitoring the learning process can provide an opportunity for the teachers to give constructive feedback to their students to improve their language learning. When teachers continuously monitor students’ growth and modify instruction to ensure constant development, they find it easier and more predictable to progress towards meeting the standards on summative assessments. By comprehending precisely what their students know before and during the instruction, teachers have much more power to improve the students’ mastery of the subject matter than if they find out after a lesson or unit is complete.
It is important to point out that when instructors continually evaluate the development of their students and modify their curriculum to assure constant improvement, they find that it is simpler and more predictable to make progress toward fulfilling the requirements on summative assessments. If teachers wait until the end of a session or unit to find out how well their learners have mastered the material, they will have considerably less influence over how well their learners learn the material than if they find out how well their learners have mastered it earlier and during teaching. The value of formative assessment lies in the critical information about student comprehension that it provides throughout the process of learning, as well as the chance it gives educators to provide participants with quick and efficient, and action-oriented feedback, as well as the chance to alter their own behavior so that every respondent has the chance to learn and re-learn the material. Learners whose academic performance falls on the extreme ends of the normal curve, such as those who are struggling and those who excel academically, benefit the most from formative evaluation. These learners have learning requirements that are often one of a kind and highly specialized, and to meet those needs, the instructor needs updated data. In addition, making use of frequent formative evaluation as a means to remediate learning gaps brought up by COVID-19 guarantees that educators can promptly give remediation.
The other justification for our findings can be ascribed to the strength of formative assessments that lies in the formative information they provide about the students’ comprehension throughout the learning process and the opportunities they give to teachers to provide the pupils with action-oriented and timely feedback and to change their own behaviors so that each learner has an opportunity to learn and re-learn. More particularly, using formative assessment can assist the students to detect their own weaknesses and strengths and target areas that need more effort and work. All the positive points enumerated for the formative assessments can be the reasons and explanations for the results gained in the current research.
Moreover, the better performance of assessment groups may be due to numerous reasons. In the first place, consistently evaluating students’ progress helps maintain learning objectives at the forefront of one’s mind. This ensures that learners have a distinct goal to strive towards and that instructors have the opportunity to assist clear up misconceptions before learners get off track. Second, engaging in the process of formative assessment enables instructors to gather the information that reveals the requirements of their students. When instructors have a clear grasp of what it takes for their students to be successful, they are better able to design challenging educational environments that push every learner to their full potential. Thirdly, the primary role of formative assessment that will assist in enhancing academic achievement is to provide both learners and instructors with frequent feedback on the achievement that is being made toward their objectives. Learners can bridge the gap between their existing knowledge and their learning objectives through the use of formative assessment (Greensetin, 2010 ). The fourth benefit of doing the formative assessment is an increase in motivation. Formative assessment entails creating learning objectives and monitoring the progress towards those objectives. When learners have a clear idea of where they want to go, their performance dramatically improves. Fifthly, students must identify a purpose for the work that is assigned to them in the classroom. Connecting the learning objectives with real-world problems and situations draws students into the instructional activities and feeds their natural curiosity about the world. Sixthly, an in-depth examination of the data gathered via formative assessment provides the educator with the opportunity to investigate their own methods of teaching and identify those that are successful and those that are not. It is indeed possible that some of the strategies that work for one group of learners won’t work for another. Lastly, students become self-regulated when they are provided with the tools they need to set, track, and ultimately achieve their own learning objectives. Students may develop into self-reliant thinkers if they are exposed to models of high-quality work and given adequate time to reflect on and refine their own work.
The positive effects of formative and summative assessment on students’ motivation are supported by The Self Determination Theory (SDT) of Motivation which is a motivational theory that provides a way of understanding human motivation in any context (Ryan & Deci, 2000 ). SDT attempts to understand human motivation beyond the simple intrinsic/extrinsic model. It suggests that human motivation varies from fully intrinsic motivation, which is characterized by fully autonomous behavior and “for its own sake” to fully extrinsic motivation, which is characterized by behavior that is fully heteronomous and which is instrumentalized to some other end.
In this study, the self-regulatory skills of the students in the EGs where the formative assessment practices were applied did significantly differ from the ones in the CG where no formative assessment practices were applied. Thus, students’ self-regulation was shown to be improved as a result of formative assessment procedures. Similar findings were observed in the experimental research by Xiao and Yang ( 2019 ) that compared the self-regulation abilities of EG and CG learners in secondary school and discovered a substantial difference in favor of the former group. Research findings based on qualitative data reveal that learners engaged in a variety of cognitive techniques and self-regulatory learning practices. The participants acknowledged that they were an integral part of their own learning and that they accepted personal responsibility for their progress. Teachers reported that learners’ ability to self-regulate improved as a result of formative assessment, which fostered ongoing, meaningful, and learning-effort and performance-focused dialogue between teachers and learners. The students’ progress in the areas of self-regulation and metacognitive abilities, as well as their growth in accordance with educational standards, may be supported by a rise in their success in diagnostic examinations thanks to the use of formative assessment (DeLuca et al., 2015 ). In a study that he conducted in 2015, Woods examined the link between formative assessment and self-regulation. He highlighted that teachers who use formative assessment strategies need to comprehend the participants’ self-regulatory learning processes to make appropriate decisions for their classrooms. Furthermore, Woods ( 2015 ) recommended that educators make regular use of formative assessment to foster the growth of learners’ abilities to self-regulate and to boost the motivation levels of their learners. Wiliam ( 2014 ) also asserted that self-regulatory learning could be an important component of an effective formative assessment in relation to the techniques of explaining, sharing, and comprehending the learning goals and success criteria and students taking the responsibility for their own learning.
It is vital to note that learners who have developed self-regulation skills employ their cognitive abilities; work toward their learning objectives; seek out appropriate support from peers, adults, and authority figures; and, most significantly, accept personal accountability for their academic success. As a result, learners’ abilities to self-regulate have a direct effect on the type of formative assessment based on learning and the applications designed to eliminate learning deficiencies. Self-regulation is an ability that needs time and practice to acquire, but it is possible to do so with the right tools and a continuous strategy. Formative assessment techniques were shown to boost learners’ ability to self-regulate, although this effect was found to be small when the study findings were combined with those found in the literature. This finding may be attributed to the fact that, although formative assessment procedures were implemented for an academic year, they were limited to the context of the social research classroom, and students’ abilities to self-regulate may develop and evolve over time.
The findings of this research can increase the knowledge of the students about two types of assessment. This study can encourage students to want their teachers to assess their performances formatively during the semester. Also, the findings of this study can assist instructors to implement more formative-based assessments and feedback in their classes. This study can highlight the importance of frequent input, feedback, and exam for teachers. An exact analysis of formative assessment data permits the teachers to inspect their instructional practices in order to understand which are producing positive results and which are not. Some that are effective for one group of students may not be effective for another group. The implications of this research can help students try to compensate for their deficiencies by taking responsibility for their own learning instead of just attempting to get good grades. In this respect, formative assessments ensure that students can manage the negative variables such as a high level of examination and grading.
Using formative assessments helps teachers gather the information that reveals the students’ needs. Once teachers have an understanding of what students need to be successful, they can generate a suitable learning setting that will challenge each learner to grow. Providing students and teachers with regular feedback on progress towards their aims is the major function of the formative assessments that will help in increasing academic accomplishment. Formative assessments can help the students close the gap between their present knowledge and their learning objectives. Moreover, using formative assessment gives the students evidence of their present progress to actively monitor and modify their own learning. This also provides the students the ability to track their educational objectives. Also, via using formative assessment, the students have the ability to measure their learning at a metacognitive level. As the students are one of the main agents of the teaching-learning process, instructors must share the learning objectives with them. This sharing can develop the students’ learning in basic knowledge and higher order cognitive processes such as application and transfer (Fulmer, 2017 ). In fact, if learners know that they are expected to learn in that lesson, they will concentrate more on those areas. Formative assessments make the teaching more effective by guiding learners to achieve learning objectives, setting learning needs, modifying teaching accordingly, and increasing teachers’ awareness of efficient teaching methods. Lastly, our findings may aid material developers to implement more formative-based assessment activities in the EFL English books.
In conclusion, this study proved the positive impacts of applying formative assessments on Iranian EFL students’ academic motivation, attitude toward learning, test anxiety, and self-regulation skill. Therefore, teachers are strongly recommended to use formative assessment in their classes to help students improve their language learning. Using formative assessment allows teachers to modify instruction according to the results; consequently, making modifications and improvements can generate immediate benefits for their students’ learning.
One more conclusion is that using formative assessment gives the teacher the ability to provide continuous feedback to their students. This allows the students to be part of the learning environment and to improve self-assessment strategies that will help with the understanding of their own thinking processes. All in all, providing frequent feedback during the learning process is regarded as an efficient technique for motivating and encouraging students to learn a language more successfully. Indeed, by assessing students during the lesson, the teachers can aid them to improve their skills and examine if they are progressing or not. Thus, formative assessment is an essential part of teaching that should be used in EFL instructional contexts.
As we could not include many participants in our study, we recommend that future researchers include a large number of participants to increase the generalizability of their results. We worked on male EFL learners; the next studies are required to work on both genders. We could not gather qualitative data to enrich our results; the upcoming researchers are advised to collect both quantitative and qualitative data to develop the validity of their results. Next researchers are called to examine the effects of the summative and formative assessments on language skills and sub-skills. Also, next researchers are offered to inspect the effects of other types of assessments on language skills and subskills as well as on psychological variables involved in language learning.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
| EFL | English as a foreign language |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| PET | Preliminary English Test |
| SAS | Science Anxiety Scale |
| SRSS | Self-Regulatory Strategies Scale |
| AMTB | Attitude/Motivation Test Battery |
| SDT | Self Determination Theory |
| EG | Experimental group |
| CG | Control group |
Authors’ contributions
All authors had equal contributions. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Seyed M. Ismail is an assistant professor at Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia. His research interests are teaching and learning, testing, and educational strategies. He published many papers in different journals.
D. R. Rahul is an assistant professor School of Science and Humanities, Shiv Nadar University Chennai, Chennai, India. He has published several research papers in national and international language teaching journals.
Indrajit Patra is an Independent Researcher. He got his PhD from NIT Durgapur, West Bengal, India.
Ehsan Rezvani is an assistant professor in Applied Linguistics at Islamic Azad University, Isfahan (Khorasgan) Branch, Isfahan, Iran. He has published many research papers in national and international language teaching journals.
We did not receive any funding at any stage.
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Seyed M. Ismail, Email: [email protected] .
D. R. Rahul, Email: moc.liamg@ttinrdluhar .
Indrajit Patra, Email: moc.liamg@0nortengampi .
Ehsan Rezvani, Email: [email protected] .
- Abeywickrama P, Brown HD. Language assessment: Principles and classroom practices. Pearson Longman; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahmad S. Relationship of academic SE to self-regulated learning, SI, test anxiety and academic achievement. International Journal of Education. 2012; 4 (1):12–25. doi: 10.5296/ije.v4i1.1091. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahmadi S, Namazizadeh M, Abdoli B, Seyedalinejad A. Comparison of achievement motivation of football players between the top and bottom teams of the Football Premier League. Olympic Quarterly. 2009; 17 (3):19–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Al Tayib Umar A, Abdulmlik Ameen A. The effects of formative evaluation on students’ achievement in English for specific purposes. Journal of Educational Research and Reviews. 2021; 9 (7):185–197. doi: 10.33495/jerr_v9i7.21.134. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alahmadi N, Alrahaili M, Alshraideh D. The impact of the formative assessment in speaking test on Saudi students’ performance. Arab World English Journal. 2019; 10 (1):259–270. doi: 10.24093/awej/vol10no1.22. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aouine A. English language assessment in the Algerian middle and secondary schools: A context evaluation . 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashdale M. The effect of formative assessment on achievement and motivation . 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Assessment Reform Group . Assessment for learning. 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Black P, Harrison C, Lee C, Marshall B, Wiliam D. Assessment for learning: Putting it into practice. Open University Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Black P, Wiliam D. Assessment for learning in the classroom. Assessment and Learning. 2006; 5 :9–25. [ Google Scholar ]
- Britner SL, Pajares F. Sources of science SE beliefs of middle school students [Electronic version] Journal of Research in Science and Teaching. 2006; 43 (5):485–499. doi: 10.1002/tea.20131. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown HD. Language assessment principles and classroom practices. Oxford university press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Buyukkarci K, Sahinkarakas S. The impact of formative assessment on students’ assessment preferences. The Reading Matrix: An International Online Journal. 2021; 21 (1):142–161. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chalak A, Kassaian Z. Motivation and attitudes of Iranian undergraduate EFL students towards learning English. GEMA Online Journal of Language Studies. 2010; 10 (2):37–56. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chan KT. Embedding formative assessment in blended learning environment: The case of secondary Chinese language teaching in Singapore. Education Sciences. 2021; 11 (7):360. doi: 10.3390/educsci11070360. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cizek GJ. An introduction to formative assessment: History, characteristics, and challenges. In: Andrade HL, Cizek GJ, editors. Handbook of formative assessment . Routledge; 2010. pp. 3–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark I. Formative assessment: Policy, perspectives and practice. Florida Journal of Educational Administration & Policy. 2011; 4 (2):158–180. [ Google Scholar ]
- Craig KJ, Brown KJ, Baum A. Environmental factors in the etiology of anxiety. 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- DeLuca C, Klinger D, Pyper J, Woods J. Instructional rounds as a professional learning model for systemic implementation of Assessment for Learning. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice. 2015; 22 (1):122–139. doi: 10.1080/0969594X.2014.967168. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dixson DD, Worrell FC. Formative and summative assessment in the classroom. Theory into practice. 2016; 55 (2):153–159. doi: 10.1080/00405841.2016.1148989. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Douglas G, Wren D. Using formative assessment to increase learning . Virginia Beach City Public Schools; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellis R. The study of second language acquisition. Oxford University Press; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Firouznia S, Yousefi A, Ghassemi G. The relationship between academic motivation and academic achievement in medical students of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2009; 9 (1):79–84. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fox J, Haggerty J, Artemeva N. Mitigating risk: The impact of a diagnostic assessment procedure on the first-year experience in engineering. In: Read J, editor. Post-admission language assessment of university students. Springer; 2016. pp. 43–65. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fulmer SM. Should we share learning outcomes / objectives with students at the start of a lesson? 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gardner RC. Attitude/Motivation test battery: International AMTB research project. The University of Western Ontario; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghahderijani BH, Namaziandost E, Tavakoli M, Kumar T, Magizov R. The comparative effect of group dynamic assessment (GDA) and computerized dynamic assessment (C-DA) on Iranian upper-intermediate EFL learners’ speaking complexity, accuracy, and fluency (CAF) Lang Test Asia. 2021; 11 :25. doi: 10.1186/s40468-021-00144-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glazer N. Formative plus summative assessment in large undergraduate courses: Why both? International Journal of Teaching and Learning in Higher Education. 2014; 26 (2):276–286. [ Google Scholar ]
- Greensetin L. What teachers really need to know about formative assessment. ASCD; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamedi A, Fakhraee Faruji L, Amiri Kordestani L. The effectiveness of using formative assessment by Kahoot application on Iranian Intermediate EFL learners’ vocabulary knowledge and burnout level. Journal of new advances in English Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics. 2022; 4 (1):768–786. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heritage M. From formative assessment: Improving teaching and learning . 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hwang HJ, Chang HF. A formative assessment-based mobile learning approach to improving the learning attitudes and achievements of students. Computers and Education. 2011; 56 :1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2010.12.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Imen . The impact of formative assessment on EFL students’ writing skill . 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kadıoğlu C, Uzuntiryaki E, Çapa-Aydın Y. Development of self-regulatory strategies scale (SRSS) Eğitim ve Bilim. 2011; 36 (160):11–23. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kara A. The effect of a ‘learning theories’ unit on students’ attitudes towards learning. Australian Journal of Teacher Education. 2009; 34 (3):100–113. doi: 10.14221/ajte.2009v34n3.5. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kathy D. 22 essay assessment technique for measuring in teaching learning. 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- King MD. The effects of formative assessment on student self-regulation, motivational beliefs, and achievement in elementary science (Doctoral dissertation) 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Krashen S. Second language acquisition and second language learning. Pergamon Press; 1981. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu, F., Vadivel, B., Mazaheri, F., Rezvani, E., & Namaziandost, E. (2021). Using games to promote efl learners’ willingness to communicate (WTC): Potential effects and teachers’ attitude in focus. Frontiers in Psychology , 4526 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mahshanian A, Shoghi R, Bahram M. Investigating the differential effects of formative and summative assessment on EFL learners’ end-of-term achievement. Journal of Language Teaching and Research. 2019; 10 (5):1055–1066. doi: 10.17507/jltr.1005.19. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marsh CJ. A critical analysis of the use of formative assessment in schools. Educational research for policy and practice. 2007; 6 (1):25–29. doi: 10.1007/s10671-007-9024-z. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Masita M, Fitri N. The use of Plickers for formative assessment of vocabulary mastery. Ethical Lingua Journal of Language Teaching and Literature. 2020; 7 (2):311–320. doi: 10.30605/25409190.179. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCallum S, Milner MM. The effectiveness of formative assessment: student views and staff reflections. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education. 2021; 46 (1):1–16. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2020.1754761. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nunan D. Research methods in language learning. CUP; 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ounis A. The assessment of speaking skills at the tertiary level. International Journal of English Linguistics. 2017; 7 (4):95–113. doi: 10.5539/ijel.v7n4p95. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ozan C, Kıncal RY. The effects of formative assessment on academic achievement, attitudes toward the lesson, and self-regulation skills. Educational Sciences: Theory and Practice. 2018; 18 :85–118. [ Google Scholar ]
- Palomba CA, Banta TW. Assessment essentials: Planning, implementing, and improving assessment in higher education. Jossey-Bass Publishers; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pappamihiel NE. English as a second language students and English language anxiety: Issues in the mainstream classroom. ProQuest Education Journal. 2002; 36 (3):327–355. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul R, Elder L. Critical thinking: Tools for taking charge of your professional and personal life. Pearson Education; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Persaud Singh V, Ewert D. The effect of formative assessment on performance in summative assessment: A study on business English students in a language training center . 2021. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinchok N, Brandt WC. Connecting formative assessment research to practice: An introductory guide for educators. Learning point; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Popham WJ. Classroom assessment: What teachers need to know. 5. Prentice Hall; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Quintana J. PET practice tests. Oxford University Press; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Remmi F, Hashim H. Primary school teachers’ usage and perception of online formative assessment tools in language assessment. International Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development. 2021; 10 (1):290–303. doi: 10.6007/IJARPED/v10-i1/8846. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rezai A, Namaziandost E, Miri M, Kumar T. Demographic biases and assessment fairness in classroom: Insights from Iranian university teachers. Language Testing in Asia. 2022; 12 (1):1–20. doi: 10.1186/s40468-022-00157-6. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Robinowitz A. From principles to practice: An embedded assessment system. Applied Measurement in Education. 2010; 13 (2):181–208. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan RM, Deci EL. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist. 2000; 55 (1):68–95. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.55.1.68. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sepehrian A. Self-Efficacy, achievement motivation and academic procrastination as predictors of academic achievement in pre-college students. Proceeding of the Global Summit on Education. 2013; 6 :173–178. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shepard LA. Classroom assessment. In: Brennan RL, editor. Educational measurement. 4. American Council on Education/Praeger; 2006. pp. 623–646. [ Google Scholar ]
- Spolsky B, Halt FM. The handbook of educational linguistics. Blackwell; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tahir, M., Tariq, H., Mubashira, K., & Rabbia, A. (2012). Impact of formative assessment on academic achievement of secondary school students. International Journal of Business and Social Science , 3 (17) http://myflorida.com/apps/vbs/vbs_www.ad.view_ad?advertisement_key_num=107800 .
- Tekin EG. Matematik eğitiminde biçimlendirici değerlendirmenin etkisi [Effect of formative assessment in mathematics education] 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tella J, Indoshi FC, Othuon LA. Relationship between students’ perspectives on the secondary school English curriculum and their academic achievement in Kenya. Research. 2010; 1 (9):390–395. [ Google Scholar ]
- Vadivel B, Namaziandost E, Saeedian A. Progress in English language teaching through continuous professional development—teachers’ self-awareness, perception, and feedback. Frontiers in Education. 2021; 6 :757285. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.757285. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vogt K, Tsagari D, Csépes I, Green A, Sifakis N. Linking learners’ perspectives on language assessment practices to teachers’ assessment literacy enhancement (TALE): Insights from four European countries. Language Assessment Quarterly. 2020; 17 (4):410–433. doi: 10.1080/15434303.2020.1776714. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vygotsky LS. Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Harvard University Press; 1978. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiliam D. Embedded formative assessment. Solution Tree; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiliam D. Formative assessment and contingency in the regulation of learning processes . 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wininger SR. Using your tests to teach: Formative summative assessment. Teaching of Psychology. 2005; 32 (3):164–166. doi: 10.1207/s15328023top3203_7. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Woods, N. (2015). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning. The Journal of Education Retrieved from https://thejournalofeducation.wordpress.com/2015/05/20/formative-assessment-and-self-regulated-learning/ .
- Wuest DA, Fisette JL. Foundations of physical education, exercise science, and sport. 17. McGraw-Hill; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Xiao Y, Yang M. Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: How formative assessment supports students' self-regulation in English language learning. System. 2019; 81 :39–49. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2019.01.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

The PE and sports assessment BLOG
The experiences of an very ordinary pe teacher……, ideas for summative assessment in pe.
Summative Assessment is seen as the assessment of learning, a summary of what has been learnt and is often used for grading and reporting back scores. Often sadly it can be argued that Summative Assessment if not used properly has significantly less impact on the learner than formative assessment. It is therefore crucial that Summative Assessment is used in a way that has impact on the learner – if it does not, then the value of doing it becomes a burden rather than a tool.
The key to making Summative Assessment useful is to assess at the start and at the end. This will allow progress to be clearly measured for each individual student in the group.
Summative Assessment at the start also allows you to construct the correct level of challenge for all learners in the group and allow all to make progress from their own individual starting points.
Using Summative Assessment again at the end will then allow both you as a teacher and more importantly the student’s the opportunity to see how much progress they have made in their learning over a period of time.
Here are four ideas that I use to help assessment of learning with some of my groups;
Keywords and Scenario Cards
One idea is too; at the start of a piece of work give students ‘scenario’ cards which they must either verbally answer or talk about with a partner. With Scenario cards I also put on a traffic light system either side of the statement. At the start they can then indicate their level of confidence in answering the scenario question by ticking;
- red (unsure )
- yellow (some ideas)
- Green (can describe, analyse and evaluate)

The same task can then be used again at the end of the session or block of work. This time though you also give a word cloud with the key words on and ask students to frame their answer using the keyword terminology. They should also tick the traffic light spots on the opposite side of the statement. This gives a good visual of their confidence when answering the question

These can be broken down further if required to help with differentiation;

(Word Cloud 1; Describe Technique, WC 2; Analysing Technique, WC 3; Evaluating)
This should give you a good comparison between the quality and confidence of their answers at the beginning of the lesson and again at the end allowing you to gauge the progress in their learning.
Entry and Exit Worksheets
Another way of gaining a summary of a student’s starting point is to do entry and exit worksheets.

Entry Sheet
At the entry point the promotion of ‘inquiry’ based learning is key; if they cannot fully answer the question what information will they need to gain by the end in order to do so? What questions will they need to ask, what will they need to do to find the answers? I often find that this helps learners really start to take control of their learning and gives them focus within lessons.
I tend to use one worksheet for entry and exit and fold it over for use on entry/exit.

On exit (or at the end of the lesson) the same question can be posed. Often I will also provide visual prompts (much like the excellent cartoon strips idea from @TedfordDanielle) and also some keywords to help them frame a high quality answer.

PDF Version Download here; badminton-summative-sheet
As a teacher and student you can then unfold your worksheet and compare the answer you gave at the start of the lesson with the quality of the answer you have given at the end of the lesson. Students who enjoy seeing a visual of their own learning really buy into this.
Practical; Assessment of Contextual Learning
One of my favourite tools for Summative Assessment is the structure of practical. In the first lesson after completing an open activity I will put them into groups of similar ability and play 3 v 2 modified games. This allows an attacking overload and good passing options for the attacking team and also means that when defending the two defenders must work together to be successful. 3 v 2 also means lots of touches for everyone in the group and also makes decision making and movement an easy visual. I video each small group for around 2-3 minutes normally on an Ipad.

(3 v 2 with one overload player always joining the attacking team)

(3 v 2 Half Court Basketball; when defending one player stands off court, teams switch between defence and attack when possession changes; play always restarts from centre circle)

(4 v 1 attacking end ball game)
Then at the end of our module of work I put them into the same groups and same conditioned games; 3 v 2 and again video them for the same amount of time.
I get students to watch both videos. Using an assessment rubric I then ask them to grade themselves for both the game we did during lesson 1 and then again for the game in our final lesson. I ask them to highlight key areas of progress in their own learning.

It is also an excellent tool for students to develop targets from. The ability to be able to see themselves and watch back decisions they make can lead to rapid improvements.
Progress Report Cards
Another way that you can ensure that your summative assessment has impact is to design and use individual report cards for each student. Whilst the students are playing in their 3 v 2 games as a teacher you can observe and using your assessment rubrics make a judgement on what the students starting point is in that particular area; (Marked in red)

For the report cards I use I then have a quick discussion with them and we create targets for them to focus on which will allow them to make further progress in their learning. We then set that point and call it expected progress (Marked in yellow) ; it is where both we (myself and the student) expect them to be by the end of the module of work. This is really important as it gives us a target for how much learning should take place. I then give a copy to the student that they keep on them. This really helps them focus on their own learning and their own targets.

Then at the end I observe and make a judgement against the assessment rubric and put this on to their report card ( Marked in Green ). This then gives myself and the student the following information;
- What their starting point was
- What we expected to achieve by the end of our work
- Individual targets to help achieve rapid learning
- An end assessment which shows whether expected progress was made or not.

Students find this a very personalised way of doing summative assessment; it gives them guidance for improvement and allows them to see how much progress that they have made.
Due to the progress made by students I actually made this report card method into an app; please do have a visit to the app store or Google Play and have a look; the cards are also supported by assessment rubrics for over 20 different sports and activities. (Please see link below)
Summative Assessment and Formative Assessment have many overlaps but both must have impact on the learner. Summative Grades and scores are important but not as much as the process of the assessment. If within that process we can have maximal impact on learning then our summative assessment is a truly great tool.
I hope you have found the piece interesting and please do share any ideas and thoughts you have. Let me know if you try any out.
By Kevin Peake

Share this:
Published by kpeake2.
Just an ordinary PE Teacher View all posts by kpeake2
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Ending the U.S. Department of Education: What it would mean and why Trump and Project 2025 want it

Sign up for Chalkbeat’s free weekly newsletter to keep up with how education is changing across the U.S.
When Donald Trump told Elon Musk one of his first acts as president would be to “close the Department of Education, move education back to the states,” he was invoking a GOP promise that goes back to President Ronald Reagan and the department’s founding.
Yet through multiple Republican administrations, including Trump’s first term, the U.S. Department of Education has persisted.
That hasn’t stopped Democrats from sounding the alarm that Trump’s views epitomize the GOP’s bad intentions for public schools. The fact that the Republican Party’s platform also calls for closing the department , as does the conservative Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025 , has only intensified Democrats’ distress .
“We are not going to let him eliminate the Department of Education that funds our public schools,” Vice President Kamala Harris said to thunderous applause in her speech at the Democratic National Convention, where she placed the department alongside prized institutions and programs like Social Security, Medicare, and the Affordable Care Act.
The department has become a “kind of trophy” in a larger debate about the meaning of public education, said Rick Hess, director of education policy studies at the American Enterprise Institute.
In fact, he said, “The Department of Education actually has very little to do with that debate. Abolishing it doesn’t advance school choice and keeping it doesn’t do much for traditional district schools. But it’s become a symbol of which side you’re on in that debate.”
So, what exactly does the U.S. Department of Education do? Why do so many conservatives want to see it go away? Why has it survived? And what would it take for that to actually happen?

The U.S. Department of Education: a brief history
The federal government spent money on education and developed education policies going back to the 19th century . But the U.S. Department of Education didn’t become a stand-alone agency until 1980, when it split off from the U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare.
President Jimmy Carter advocated for the creation of the department to fulfill a campaign promise to the National Education Association . Congress passed the Department of Education Organization Act in 1979. Some Democrats and the American Federation of Teachers opposed the idea, due to fears about excessive federal meddling in local education decisions and concerns that it would cater to the NEA’s interests.
Reagan, Carter’s successor, campaigned on abolishing the brand-new department. But Reagan’s first education secretary, Terrel Bell, commissioned the landmark report “A Nation at Risk: The Imperative for Educational Reform,” warning that America was losing its competitive edge. It advocated for a strong federal role to ensure students received a high-quality education.
“If the federal government is coming out with a report that shows all the things that need to be fixed and at the same time, we’re backing out of it, those are not compatible positions,” said Michael Feuer, dean of George Washington University’s Graduate School of Education and Human Development.
The U.S. Department of Education does a lot of things, like monitor school performance and promote evidence-based practices . Its biggest K-12 programs by dollar amount provide money to high-poverty schools and for students with disabilities . Some of its most high-profile and controversial work involves enforcing civil rights protections. The department also plays a major role in distributing financial aid for higher education.
The department is not the primary funder of U.S. schools . Before the infusion of pandemic relief dollars, the federal government only covered about 8% of K-12 educational costs. In recent years, it’s been closer to 11%. But refusing that money to avoid federal rules isn’t necessarily easy.
Why do conservatives want to end the Department of Education?
Some of the dislike is purely ideological.
For conservatives, less government is better. Education is not mentioned directly in the U.S. Constitution. And a new department overseeing functions that remain mostly the purview of local government is low-hanging fruit.
Under Democratic administrations, the department has also sided with more progressive approaches to education and to civil rights enforcement.
The Obama administration, for example, told schools that if they suspended or expelled Black students at much higher rates than other groups, that could be a sign they were illegally discriminating in how they administered student discipline . Critics said the rules pushed schools to adopt laxer disciplinary policies that made schools less safe. Betsy DeVos, Trump’s education secretary, rescinded those rules . (The Biden administration has not reinstated them.)
More recently, the Biden administration issued Title IX rules that provide greater and more explicit protections for LGBTQ students — rules that Republican-led states have sued to block .
Jonathan Butcher, a senior fellow at the Heritage Foundation, said states have been a source of innovation, like charter schools and educational savings accounts. The federal department not only distracts states from efforts to improve education but creates unnecessary bureaucracy.
All the while, achievement gaps based on race and poverty haven’t gone away, Butcher noted, though they have narrowed by some measures .
“We have ample evidence that it is not serving its purpose,” Butcher said of the department. Abolishing it, he added, is “consistent with both the interest in smaller government and the interest in doing what’s right for kids.”
What does Trump say about abolishing the Department of Education?
In his conversation with Musk that aired on X , the social media platform previously known as Twitter, Trump said the U.S. had a “horrible” education ranking at the bottom of developed countries while spending the most.
It’s not totally clear what sources Trump was using. On recent international tests , the U.S. ranked sixth in reading, 10th in science, and 26th in math among 81 countries. Older test results show the U.S. ranked lower , especially in math . The U.S. does spend more per-pupil than most developed nations , including many that score better on key measures.
Trump said some states won’t do well, but many would do a better job on their own while spending less money.
“Of the 50, I would bet that 35 would do great, and 15 of them or 20 of them would be as good as Norway,” Trump told Musk. “You know Norway is considered great.”
He said the federal government could provide “a little monitor. You want to make sure they are teaching English, as an example. Give us a little English, right?”
Trump’s campaign did not respond to a request to elaborate on the candidate’s plans.
How would abolishing the Department of Education work?
Abolishing a federal department would require an act of Congress, just as creating one does. It likely would also require broad bipartisan support , which the idea doesn’t have.
U.S. Rep. Thomas Massie, a Kentucky Republican, has regularly introduced legislation to abolish the department — but the bill has failed to gain traction.
Despite that, Massie said his proposals were serious. “Damn right I want to terminate the Department of Education,” he said in a statement. “Public education in America has gone downhill ever since this bureaucracy was created.”
The Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025, widely seen as a blueprint for a future Trump administration — despite the candidate’s denials — lays out a much more detailed plan that considers necessary steps from Congress and the executive branch.
For example, the plan says civil rights enforcement should move to the Department of Justice, educational data collection to the U.S. Census Bureau, and support for Native American students to the Bureau of Indian Affairs.
Butcher acknowledged that BIA schools don’t have a good track record. But he argued that the agency was better positioned to work on improving educational outcomes.
Meanwhile, Project 2025 says Title I funding for high-poverty schools should be turned into vouchers and then phased out over time, while money from the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act should be given directly to parents.
On a podcast earlier this year, Lindsey Burke, the Heritage Foundation’s director of the Center for Education Policy and author of Project 2025′s education chapter, acknowledged the political difficulty of simply abolishing the department.
But she said the executive branch could take certain actions on its own, such as ending student loan forgiveness programs and not enforcing the new Title IX rules.
Ending the Education Department now ‘part of the conversation’
Hess, of the American Enterprise Institute, said he doesn’t oppose eliminating the department, but the idea has become a kind of “boogie man or quick fix” that’s become a substitute for substantive debate on the federal role in education.
“So much of the culture war that reached a boil during the pandemic focused on schools and colleges, which made the department more contested terrain and made education more contested terrain,” he said.
He’s skeptical that a future Trump administration would get any closer to eliminating the department than the first one did. And a recent U.S. Supreme Court decision limiting the power of administrative agencies could make it even harder to make dramatic changes via executive order, Hess said.
Feuer, of George Washington University, thinks the department has made positive contributions, despite some flaws, and wants to see it stick around. An unfriendly administration could dramatically cut funding or eliminate programs without eliminating the department. That’s the wrong debate to have when students are still recovering from COVID disruptions , he said.
“If we now take this really important moment and get everyone fighting about maintaining the department, instead of keeping our eyes on the kids and the teachers and doing some good work, that would be a really unfortunate distraction,” he said.
Butcher acknowledged that it’s “a big, ambitious idea,” but said it’s also a serious one. Past efforts, he said, lacked willpower and an advocate who prioritized it.
He was encouraged when every candidate in Republican presidential primary debates last year (except Trump, who did not participate) said they supported ending the department .
“We have made it a part of the conversation,” Butcher said.
Erica Meltzer is Chalkbeat’s national editor based in Colorado. Contact Erica at [email protected] .

New Colorado Education Association President Kevin Vick shares how he will approach the job as he replaces Amie Baca-Oehlert.

U.S. officials say the MDE misled districts about what they were entitled to provide for students with disabilities during COVID closures.

Days above 90 degrees on the heat index are expected to quadruple over the next two decades, meaning more closures for Detroit public schools

The superintendent is expected to make school closure recommendations on Nov. 7 and the school board is set to vote on them Nov. 21.
Memphis-Shelby County Schools violated Title IX by not adequately responding to complaints of sexual harassment and assault of students over a three-year period, the U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Civil Rights announced.

The updated application process grew out of a board resolution affirming its desire to collaborate with schools of all kinds, including charters.

- Accelerated Bachelors of Science in Nursing
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) - Executive Nurse Leadership
- Family Nurse Practitioner Track
- Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Track
- Nurse-Midwifery Track
- Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Track
- Adult-Gerontology Acute Care Nurse Practitioner Track
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner Track
- Rankings and Recognition
- Accreditation and Affiliations
- Career Resources
- Clinical Placement Support
- Faculty Profiles
- Message from the Dean
- State Authorization
- Student Services and Support
- Student Testimonials
- Why Baylor University Online?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Baylor In the News
- Become a Student
What is CCNE Accreditation and its Benefits for Aspiring Nurses?

If you’re interested in going back to school to earn a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN), you may be trying to determine the type of nursing program that's best for you.
A nursing program's accreditation status is important to consider because it reflects the quality of education. Graduating from an accredited program will give you the best starting point for your new nursing career.
The Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education (CCNE) is one accrediting agency for nursing programs in the United States. So, what is CCNE accreditation, and what are the benefits of choosing a CCNE-accredited program? Continue reading to find out.
What is CCNE Accreditation?
CCNE accreditation is a voluntary process that evaluates whether nursing programs meet specific quality standards. The process is administered by CCNE, a national accrediting agency recognized by the U.S. Department of Education since 2000.
CCNE accredits the following types of nursing programs :
- Baccalaureate degree
- Master’s degree
- Doctor of Nursing Practice
- Post-graduate advanced practice registered nurse certificate
- Entry-to-practice nurse residency
CCNE standards for accreditation identify nursing programs that prepare nurses for professional practice and foster continuous improvement in nursing education. The standards are the same whether the nursing program delivers coursework online or in-person.
Locating CCNE-Accredited Programs
According to the U.S. Department of Education, the United States is home to more than 1,000 CCNE-accredited nursing programs .
You can search for them using the CCNE database or the U.S. Department of Education Database of Accredited Postsecondary Institutions and Programs (DAPIP).
What is the CCNE Accreditation Process?
The CCNE accreditation process depends on the type of nursing program under evaluation.
For baccalaureate and graduate nursing programs, the process consists of:
- Self-Assessment: The nursing program conducts a self-assessment to identify and explain how it achieves CCNE standards.
- Peer Evaluation: A team of peers appointed by CCNE evaluates the nursing program on-site to validate self-assessment findings.
- Accreditation Decision: The CCNE board reviews the findings and issues an accreditation decision. It can grant, deny, or withdraw accreditation.
CCNE periodically reviews accredited programs to make sure they are complying with CCNE standards and progressing on action plans for quality improvement. The reviews occur every 10 years or less, depending on the program's success.
What Are CCNE Standards for Accreditation?
Accreditation standards are the specific criteria used to assess the quality of nursing programs. CCNE is a nongovernmental, autonomous accrediting agency that develops its own accreditation standards.
There are four CCNE standards, which focus on the governance, curriculum, student support, faculty, and expected outcomes of nursing programs.
1. Program Quality: Mission and Governance
CCNE-accredited programs have missions, goals, and expected outcomes that align with the parent institution, adhere to nursing standards, and cater to the community’s needs. Faculty and students actively participate in program governance and efforts to improve program quality.
2. Program Quality: Institutional Commitment and Resources
Parent institutions of CCNE-accredited programs provide the necessary resources, including faculty and staff, to achieve the program's mission, goals, and expected outcomes.
3. Program Quality: Curriculum and Teaching-Learning Practices
The curriculum of a CCNE-accredited program reflects the program’s mission, goals, and expected outcomes. It also adheres to professional nursing standards and the community’s needs. Accredited programs also use teaching practices that effectively support achieving the expected outcomes.
4. Program Effectiveness: Assessment and Achievement of Program Outcomes
CCNE-accredited programs achieve expected outcomes, including those for students and faculty. The programs collect and use data on program effectiveness to drive continuous improvement.

What Are the Benefits of CCNE Accreditation?
Earning your nursing degree from a CCNE-accredited program will benefit your future nursing career. A program that meets CCNE standards will adequately prepare you for professional licensure, employment, and advanced nursing education.
Professional Licensure
After you graduate from a nursing program, you’ll need to obtain professional licensure from the state where you plan to work as a registered nurse. Twenty-three states and the District of Columbia require nursing graduates to show evidence of graduating from a nationally accredited nursing program.
Attending a CCNE-accredited nursing program will ensure you are eligible for professional licensure.
Some employers require or prefer nurse applicants who’ve graduated from an accredited program. By graduating from a CCNE-accredited program, you can feel confident that you have the educational preparation for nursing employment.
Advanced Nursing Education
If you're interested in advanced nursing education, graduating from an accredited nursing program does matter.
Many advanced practice nursing programs require candidates to have a bachelor’s degree from an accredited nursing school. So, choosing a CCNE-accredited nursing program will allow you to pursue advanced nursing education.
Become a Skilled Nurse with Baylor University’s CCNE-Accredited Distance ABSN Program
Earning your BSN from a CCNE-accredited program will prepare you to thrive in your nursing education and the nursing profession.
If you live in Texas, one option for a CCNE-accredited nursing program is the Distance Accelerated BSN (ABSN) program offered by Baylor University. Professionals with a bachelor's degree in a non-nursing discipline can complete this intensive, full-time program in one year.
As a Baylor Distance ABSN student, you will learn from nationally recognized faculty, benefit from strong academics and a well-earned reputation, gain clinical experience, and study nursing through a Christian worldview.
Take the first step toward fulfilling your calling as a nurse and get your program brochure.
Blog The Education Hub
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2024/08/20/gcse-results-day-2024-number-grading-system/
GCSE results day 2024: Everything you need to know including the number grading system

Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.
Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren’t what you’re expecting.
When is GCSE results day 2024?
GCSE results day will be taking place on Thursday the 22 August.
The results will be made available to schools on Wednesday and available to pick up from your school by 8am on Thursday morning.
Schools will issue their own instructions on how and when to collect your results.
When did we change to a number grading scale?
The shift to the numerical grading system was introduced in England in 2017 firstly in English language, English literature, and maths.
By 2020 all subjects were shifted to number grades. This means anyone with GCSE results from 2017-2020 will have a combination of both letters and numbers.
The numerical grading system was to signal more challenging GCSEs and to better differentiate between students’ abilities - particularly at higher grades between the A *-C grades. There only used to be 4 grades between A* and C, now with the numerical grading scale there are 6.
What do the number grades mean?
The grades are ranked from 1, the lowest, to 9, the highest.
The grades don’t exactly translate, but the two grading scales meet at three points as illustrated below.
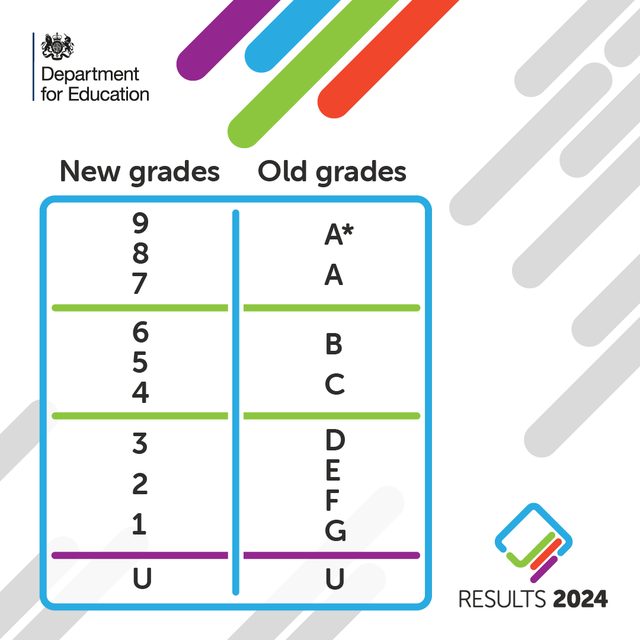
The bottom of grade 7 is aligned with the bottom of grade A, while the bottom of grade 4 is aligned to the bottom of grade C.
Meanwhile, the bottom of grade 1 is aligned to the bottom of grade G.
What to do if your results weren’t what you were expecting?
If your results weren’t what you were expecting, firstly don’t panic. You have options.
First things first, speak to your school or college – they could be flexible on entry requirements if you’ve just missed your grades.
They’ll also be able to give you the best tailored advice on whether re-sitting while studying for your next qualifications is a possibility.
If you’re really unhappy with your results you can enter to resit all GCSE subjects in summer 2025. You can also take autumn exams in GCSE English language and maths.
Speak to your sixth form or college to decide when it’s the best time for you to resit a GCSE exam.
Look for other courses with different grade requirements
Entry requirements vary depending on the college and course. Ask your school for advice, and call your college or another one in your area to see if there’s a space on a course you’re interested in.
Consider an apprenticeship
Apprenticeships combine a practical training job with study too. They’re open to you if you’re 16 or over, living in England, and not in full time education.
As an apprentice you’ll be a paid employee, have the opportunity to work alongside experienced staff, gain job-specific skills, and get time set aside for training and study related to your role.
You can find out more about how to apply here .
Talk to a National Careers Service (NCS) adviser
The National Career Service is a free resource that can help you with your career planning. Give them a call to discuss potential routes into higher education, further education, or the workplace.
Whatever your results, if you want to find out more about all your education and training options, as well as get practical advice about your exam results, visit the National Careers Service page and Skills for Careers to explore your study and work choices.
You may also be interested in:
- Results day 2024: What's next after picking up your A level, T level and VTQ results?
- When is results day 2024? GCSEs, A levels, T Levels and VTQs
Tags: GCSE grade equivalent , gcse number grades , GCSE results , gcse results day 2024 , gsce grades old and new , new gcse grades
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | ||
| 26 | 27 | 29 | 31 | |||
Comments and moderation policy
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Biden-Harris Administration Awards $81.3 Million in Funding to Further Advance the President’s Unity Agenda
Awards including funding to integrate primary and behavioral health care, expand drug treatment court capacity
Today, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), announced $81.3 million in grant awards, including more than $16 million to support the integration of primary and behavioral health care. The integration of primary and behavioral health care is considered the future of health care because it uses systematic, evidence-based approaches to improve the delivery of person-centered comprehensive care; increases access to preventive care and screenings; coordinates care to address mental, physical, social, and substance use related needs; and reduces overall costs of care for patients, providers, and health care systems. The announcement also included more than $24 million to expand capacity of drug treatment courts – a proven model for reducing unnecessary incarceration of individuals with substance use disorder. Previous capacity-expanding awards resulted in increases in abstinence from substance use, in work or educational attainment, and in housing stability.
Additional awards will support Tribal behavioral health, advance prevention science, support communities of recovery, and connect people to care. This funding highlights the Biden-Harris Administration’s continued commitment to address the mental health and overdose crises – two key pillars of the President’s Unity Agenda for the Nation .
“Now, more than ever, we need to make treatment for people with mental health challenges and substance use disorders accessible and affordable. By integrating primary and behavioral health care and utilizing evidence-based approaches, we are helping to ensure that more Americans receive the comprehensive care they need and deserve – while reducing overall costs for patients and providers,” said HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra. “President Biden and Vice President Harris’ Unity Agenda is taking on the biggest challenges facing Americans, including beating the opioid epidemic and tackling the mental health crisis. We will continue to expand our efforts to support Tribal behavioral health, advance prevention science, support communities of recovery, and connect more people to care.”
“Holistic, coordinated behavioral and primary health services gets people the care they need early and minimizes gaps in individuals’ overall health and wellness management,” said Miriam E. Delphin-Rittmon, Ph.D., HHS Assistant Secretary for Mental Health and Substance Use and the leader of SAMHSA. “Integrating these systems will improve the care and delivery experience for both patients and providers, improve the appropriate allocation of resources, and achieve better health outcomes.”
The $81.3 million in awards includes:
- Promoting the Integration of Primary and Behavioral Health Care: States – ($9.2 million) – This program promotes full integration and collaboration in clinical practices between physical and behavioral health care; supports the improvement of integrated care models for physical and behavioral health care to improve overall wellness and physical health status; and promotes the implementation and improvement of bidirectional integrated care services.
- Promoting the Integration of Primary and Behavioral Health Care: Collaborative Care Model – ($7.1 million) – The goal of this program is to support implementation of the Collaborative Care Model, an evidence-based, integrated care approach that addresses mental and substance use conditions in primary care settings.
- Expand Substance Use Disorder Treatment Capacity in Adult and Family Treatment Drug Courts – ($24.6 million) – The goal of this program is to expand substance use disorder (SUD) treatment and recovery support services in existing drug courts.
- Building Communities of Recovery – ($6.7 million) – This program works to mobilize and connect a broad array of community-based resources to increase the availability and quality of long-term recovery support for persons with substance use disorders and co-occurring substance use and mental disorders.
- Tribal Behavioral Health – ($10.2 million) – This program works to prevent and reduce suicidal behavior and substance use/misuse, reduce the impact of trauma, and promote mental health among American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) youth, up to and including age 24, by building a healthy network of systems, services, and partnerships that support youth.
- Screening, Brief Intervention & Referral to Treatment – ($9.4 million) – This program implements the screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment public health model (or SBIRT) for children, adolescents, and/or adults in primary care and community health settings and schools, with a focus on screening for underage drinking, opioid use, and other substance use.
- Prevention Technology Transfer Centers Cooperative Agreements – ($8.1 million) – This program works to maintain and enhance the Prevention Technology Transfer Center Network to provide training and technical assistance services to the substance misuse prevention field, including professionals/pre-professionals, organizations, and others in the prevention community who serve and support children, youth, young adults, families, parents, and other adults.
- First Responders – Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act – ($6 million) – This program provides resources to support first responders with training, administering, and distributing naloxone and other Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved overdose reversal medications or devices.
These grant awards align with SAMHSA’s mission to lead public health and service delivery efforts that promote mental health, prevent substance misuse, and provide treatments and supports to foster recovery while ensuring equitable access and better outcomes.
If you or someone you know is struggling or in crisis, help is available. Call or text 988 or chat at 988lifeline.org . To learn how to get support for mental health, drug or alcohol issues, visit FindSupport.gov . If you are ready to locate a treatment facility or provider, you can go directly to FindTreatment.gov or call 800-662-HELP (4357) .
Reporters with questions should send inquiries to [email protected] .
Sign Up for Email Updates
Receive the latest updates from the Secretary, Blogs, and News Releases
Subscribe to RSS
Receive latest updates

Related News Releases
Biden-harris administration awards over $558 million to improve maternal health, including $440 million to support pregnant and new moms, infants, and children through voluntary home visiting programs proven to improve maternal and child health, child development, and school readiness, hhs launches national public education campaign ahead of respiratory virus season, biden-harris administration awards nearly $9 million to improve access to cancer screening and connections to follow-up treatment in underserved communities to deliver on biden cancer moonshot goals, related blog posts.

Upholding Research Integrity at HHS
Media inquiries.
For general media inquiries, please contact [email protected] .
Disclaimer Policy: Links with this icon ( ) mean that you are leaving the HHS website.
- The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) cannot guarantee the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not mean that HHS or its employees endorse the sponsors, information, or products presented on the website. HHS links outside of itself to provide you with further information.
- You will be bound by the destination website's privacy policy and/or terms of service when you follow the link.
- HHS is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on private websites.
For more information on HHS's web notification policies, see Website Disclaimers .
Watch CBS News
Map shows where RFK Jr. is on the ballot in the 2024 election
By Caitlin Yilek , Allison Novelo
Updated on: August 30, 2024 / 12:08 PM EDT / CBS News
Washington — Unlike the Republican and Democratic presidential nominees, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. faced a costly and time-consuming process to appear on general election ballots as an independent candidate before he suspended his campaign .
Rules vary from state to state , but independent candidates typically have to collect thousands of signatures or be supported by a minor party in order to apply for ballot access.
Kennedy opted to run as an independent last October, abandoning his Democratic primary bid. Democrats and Republicans questioned whether the independent candidate would pull support from their voters.
Seeing no path to victory, Kennedy endorsed former President Donald Trump in a speech in Phoenix on Aug. 23. But he said his name would remain on the ballot in non-battleground states and encouraged voters there to still vote for him.
In battleground states, "where my presence would be a spoiler, I'm going to remove my name, and I've already started that process and urge voters not to vote for me," he said. He added that campaign's polling consistently showed that he would "likely hand the election over to the Democrats" if he was on the ballot in battleground states.

"He's a well-known name," said Dan Mallinson, an associate professor at Pennsylvania State University at Harrisburg. "He's different than a lot of other third-party candidates that run."
Kennedy is currently on the ballot in three tightly contested states — Michigan, North Carolina and Wisconsin. Recent CBS News estimates show Vice President Kamala Harris and Trump are statistically tied in Michigan and North Carolina, with Kennedy attracting 2% support in Michigan and 1% in North Carolina.
Michigan said it's too late for Kennedy to pull his name from the November ballot. Wisconsin rejected Kennedy's request to withdraw — state law requires that candidates remain on the ballot unless they die. North Carolina also rejected his request, saying millions of ballots have already been printed.
"Some of these states are such tight margins that it can matter," Mallinson said before Kennedy made his announcement.
Michigan has nearly 8.4 million registered voters . If Kennedy actually took 2% of the vote, that would be about 167,820 votes. Trump narrowly beat former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton by less than 1 point, or about 10,700 votes, in 2016. President Biden won the state in 2020 by more than 150,000 votes, finishing less than 3 points ahead of Trump.
Democrats saw a bump after swapping their nominee from Mr. Biden to Harris, largely coming from voters who had previously expressed support for Kennedy, according to a Pew Research Center poll .
Polling from Marquette Law School found that when independent candidates were included on the ballot question, Trump had a slightly larger drop in support than Harris. In an Emerson College poll , Harris' and Trump's support evenly decreased by two points with third-party candidates on the ballot. Kennedy's support has dropped in recent months in both polls.
It's typical of third-party candidates to see their poll numbers drop as it gets closer to Election Day, according to Matthew Foster, a professor at American University.
"When you're polling months beforehand, people's choices are a bit mushy," he said. "They're more willing to support a third-party candidate at that moment. But when the election comes down to the wire and it really becomes time for the decision, they tend to go either Republican or Democrat."
Kennedy's campaign said it secured enough signatures in every state and Washington, D.C., except for Mississippi.
In the map below, states where Kennedy's campaign says it has met the threshold to appear on the ballot but are still awaiting official confirmation are light blue.
So far, about half of states — those that are dark blue on the map — have confirmed that he will appear on the November ballot.
Kennedy was officially on the ballot in Arizona and Nevada, both battleground states, Maine, Ohio, South Carolina and Texas, but withdrew his candidacy. He also pulled his name from the ballot in Florida and Pennsylvania after his campaign said he met the states' thresholds.
He failed to qualify in New York and Georgia. In New York, a judge said Kennedy falsely claimed a New York residence on his nominating petitions. A state appellate court upheld the ruling after Kennedy appealed. A Georgia judge recently determined Kennedy was "not qualified" to appear on the ballot in the state, also citing questions about his New York residency. A spokesperson for Georgia's secretary of state confirmed he would not appear on the ballot.
Even if he ends up on a majority of ballots, "he won't make any impact if it's not the battlegrounds," Foster said.

- Alaska
- California
- Colorado
- Delaware
- Hawaii
- Indiana
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Nebraska
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Tennessee
- Vermont
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
Where RFK Jr.'s ballot status is awaiting official confirmation:
- Alabama
- Arkansas
- Connecticut
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Kansas
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Missouri
- Montana
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- North Dakota
- Rhode Island
- South Dakota
- Virginia
- Washington, D.C.
States where he will not be on the ballot:
- Arizona
- Florida
- Georgia
- Maine
- New York
- Pennsylvania
- South Carolina
- Texas
- Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
- 2024 Elections
Caitlin Yilek is a politics reporter at CBSNews.com, based in Washington, D.C. She previously worked for the Washington Examiner and The Hill, and was a member of the 2022 Paul Miller Washington Reporting Fellowship with the National Press Foundation.
More from CBS News

Harris details Biden's phone call about decision to exit 2024 race

GOP-backed Georgia rules risk undermining election certification, critics say

Trump says he wants government or insurance to pay for IVF treatments

Trump says he'll vote to uphold Florida's 6-week abortion ban

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summative assessments are used to evaluate student learning, skill acquisition, and academic achievement at the conclusion of a defined instructional period—typically at the end of a project, unit, course, semester, program, or school year. Generally speaking, summative assessments are defined by three major criteria: The tests, assignments, or projects are used to determine whether students
Summative Assessment Definition. The definition of summative assessment is any method of evaluation performed at the end of a unit that allows a teacher to measure a student's understanding ...
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark. Summative assessments are often high stakes, which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include: a midterm exam. a final project. a paper. a senior recital.
Summative assessment is an evaluation of students' current understanding and achievement. It allows teachers to track learners' progress over a period of time. It is done at the end of teaching unit or several teaching units and can be benchmarked or standardised against other students' work.
Summative assessment plays a crucial role in the education system for several reasons: Evaluation of Learning: Summative assessments provide educators with a comprehensive view of students' learning outcomes and achievements. By evaluating students' performance at the end of an instructional period, educators can assess the effectiveness of ...
St. Paul American School. There are three broad types of assessments: diagnostic, formative, and summative. These take place throughout the learning process, helping students and teachers gauge learning. Within those three broad categories, you'll find other types of assessment, such as ipsative, norm-referenced, and criterion-referenced.
Summative assessment can be used to refer to assessment of educational faculty by their respective supervisor with the aim of measuring all teachers on the same criteria to determine the level of their performance. In this context, summative assessment is meant to meet the school or district's needs for teachers' accountability. The evaluation ...
Summative Assessment and Feedback. Summative assessments are given to students at the end of a course and should measure the skills and knowledge a student has gained over the entire instructional period. Summative feedback is aimed at helping students understand how well they have done in meeting the overall learning goals of the course.
Understanding the meaning and function of summative assessment helps clarify its role within education as a critical component of bridging teaching and learning. In this post, we take a closer look at summative assessment's qualities with the end goal of ensuring that summative assessment supports learning and informs teaching.
Formative, summative, and interim assessment strives to answer these questions, providing valuable insights on the degree to which the teaching and learning process succeeded. That said, there is often confusion as to what types of assessments are administered when, what data they provide, and how they benefit teachers, students, and families.
Here are some tips to help you create successful summative assessments for your students. 1. Design a summative assessment based on its purpose. Consider the purpose of the assessment and allow this to determine the most appropriate design for the summative assessment. If the purpose of the assessment is preparation for an external exam, mimic ...
️ Definition. Summative assessment is a type of achievmeent assessment that occurs at the end of a unit of work. Its goal is to evaluate what students have learned or the skills they have developed. It is compared to a formative assessment that takes place in the middle of the unit of work for feedback to students and learners.. Performance is evaluated according to specific criteria, and ...
The definition of summative assessment is better understood if we also understand the meaning of formative assessments. When both approaches are combined, chances of success are maximized. Summative Assessment Meaning . The meaning of summative assessment is that it judges a student's level of learning and academic prowess at the end of the ...
Simply put, the main purpose of summative assessment is to measure students' learning outcomes at the completion of an instructional unit, course, or academic program. The key word here is "completion," indicating the assessing takes place after learning. Diagnostic assessment takes place before instruction and formative assessment takes ...
Summative assessments can benefit both teachers and students in many ways, such as: 1. Motivates to study. For many students, periodic evaluation is the best motivation to study. Many students can only perform under pressure. So, summative assessment is the perfect motivation for some students to study hard. 2.
Types of Summative Assessments. End-of-unit tests, final exams, mid-term exams and quarterly tests are considered summative assessments. Many state departments of education devise a state-mandated evaluation and compare the results according to the state standard benchmark to determine the effectiveness of teachers in each district, which is also a summative assessment.
There are lots of different kinds of assessments you may hear being spoken about in educational settings. One of these are summative assessments. Summative assessment is sometimes called assessment of learning and is a formal method to evaluate learning by comparing learning to a standard or benchmark This is typically at the end of a unit, module or time period. Summative assessment often ...
Summative evaluation is a type of evaluation that is conducted at the end of a program or project, with the goal of assessing its overall effectiveness. The primary focus of summative evaluation is to determine whether the program or project achieved its goals and objectives. Summative evaluation is often used to inform decisions about future ...
2. Summative Evaluation. Summative evaluation occurs at the end of the school year. It assesses the success of objectives and changes in a student's general personality at the end of the session. Summative evaluations address a wide range of aspects of learning.
In education, the term ... Summative assessments are used to evaluate student learning at the conclusion of a specific instructional period—typically at the end of a unit, course, semester, program, or school year. Summative assessments are typically scored and graded tests, assignments, or projects that are used to determine whether students ...
Assessment in education is an important tool for evaluating student learning and guiding instructional approaches. Two primary assessment types, formative and summative, offer distinct, but ...
Therefore, summative assessment is commonly used to measure learning and is rarely used for learning. Educators can make the summative assessment more formative by giving learners the opportunity to learn from exams. This would mean supplying pupils with feedback on exams and making use of the teaching potentiality of exams.
The key to making Summative Assessment useful is to assess at the start and at the end. This will allow progress to be clearly measured for each individual student in the group. Summative Assessment at the start also allows you to construct the correct level of challenge for all learners in the group and allow all to make progress from their ...
The U.S. Department of Education provides a relatively small share of education funding, but high-needs schools rely on it. (Tierney L. Cross / Getty Images) The U.S. Department of Education: a ...
The U.S. Department of Education (Department) today released the framework for the testing period it will use starting Oct. 1, 2024, ahead of making the 2025-26 Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA®) available to all students and contributors on or before Dec. 1. The Department's top priority remains ensuring the FAFSA form is stable and delivers a smooth and secure experience ...
A nursing program's accreditation status is important to consider because it reflects the quality of education. Graduating from an accredited program will give you the best starting point for your new nursing career. The Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education (CCNE) is one accrediting agency for nursing programs in the United States.
Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.. Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren't what you're expecting.
Awards including funding to integrate primary and behavioral health care, expand drug treatment court capacity. Today, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), announced $81.3 million in grant awards, including more than $16 million to support the integration of primary and behavioral health care.
Seeing no path to victory, Kennedy endorsed former President Donald Trump in a speech in Phoenix on Aug. 23. But he said his name would remain on the ballot in non-battleground states and ...
Dear Colleague: On October 10, 2023, the Secretary published final regulations in the Federal Register (88 FR 70004) that apply to most educational programs that are eligible to participate in the student financial assistance programs authorized under title IV of the Higher Education Act of 1965, as amended (HEA). These Financial Value Transparency and Gainful Employment regulations are ...