
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7


Change Management Case Study Examples: Lessons from Industry Giants
Explore some transformative journeys with efficient Change Management Case Study examples. Delve into case studies from Coca-Cola, Heinz, Intuit, and many more. Dive in to unearth the strategic wisdom and pivotal lessons gleaned from the experiences of these titans in the industry. Read to learn about and grasp the Change Management art!

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Certified Professional Change Management CPCM
- Risk Management for Change Training
- Managing Change with Agile Methodology Training
- Complete Change Management Assessments Training
- Managing Organisational Change Effectively

In the fast-paced world of business, staying ahead means being able to adapt. Have you ever wondered how some brands manage to thrive despite huge challenges? This blog dives into a collection of Change Management Case Studies, sharing wisdom from top companies that have faced and conquered adversity through effective Change Management Activities. These aren’t just stories; they’re success strategies.
Each Change Management Case Study reveals the smart choices and creative fixes that helped companies navigate rough waters. How did they turn crises into chances to grow? What can we take away from their successes and mistakes? Keep reading to discover these inspiring stories and learn how they can reshape your approach to change in your own business.
Table of Contents
1) What is Change Management in Business?
2) Top Examples of Case Studies on Change Management
a) Coca-Cola
b) Adobe
c) Heinz
d) Intuit
e) Kodak
f) Barclays Bank
3) Conclusion
What is Change Management in Business?
Change management in business refers to the structured process of planning, implementing, and managing changes within an organisation. It involves anticipating, navigating, and adapting to shifts in strategy, technology, processes, or culture to achieve desired outcomes and sustain competitiveness.
Effective Change Management entails identifying the need for change, engaging stakeholders, communicating effectively, and mitigating resistance to ensure smooth transitions. By embracing Change Management principles and utilizing change management tools , businesses can enhance agility, resilience, and innovation, driving growth and success in dynamic environments.

Top Examples of Case Studies on Change Management
Let's explore some transformative journeys of industry leaders through compelling case studies on Change Management:
1) Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, the beverage titan, acknowledged the necessity to evolve with consumer tastes, market shifts, and regulatory changes. The rise of health-conscious consumers prompted Coca-Cola to revamp its offerings and business approach. The company’s proactive Change Management centred on innovation and diversification, leading to the launch of healthier options like Coca-Cola Zero Sugar.

Strategic alliances and acquisitions broadened Coca-Cola’s market reach and variety. Notably, Coca-Cola introduced eco-friendly packaging like the PlantBottle and championed sustainability in its marketing, bolstering its brand image.
Acquire the expertise to facilitate smooth changes and propel your success forward – join our Change Management Practitioner Course now!
2) Adobe
Adobe, with its global workforce and significant revenue, faced a shift due to technological advancements and competitive pressures. In 2011, Adobe transitioned from physical software sales to cloud-based services, offering free downloads or subscriptions.
This shift necessitated a transformation in Adobe’s HR practices, moving from traditional roles to a more human-centric approach, aligning with the company’s innovative and millennial-driven culture.
Discover the Impact of Change Management Salaries on Career Growth and Organizational Success!
3) Heinz
Berkshire Hathaway and 3G Capital’s acquisition of Heinz led to immediate, sweeping changes. The new management implemented cost-cutting measures and altered executive perks.

Additionally, it introduced a more insular leadership style, contrasting with 3G’s young, mobile, and bonus-driven executive team.
Commence on a journey of transformative leadership and achieve measurable outcomes by joining our Change Management Foundation Course today!
4) Intuit
Steve Bennett’s leadership at Intuit marked a significant shift. Adopting the McKinsey 7S Model, he restructured the organisation to enhance decision-making, align rewards with strategy, and foster a performance-driven culture. His changes resulted in a notable increase in operating profits.
Discover the Best Change Management Books ! Read our top picks and transform your organization today!
5) Kodak
Kodak, the pioneer of the first digital and megapixel cameras in 1975 and 1986, faced bankruptcy in 2012. Initially, digital technology was costly and had subpar image quality, leading Kodak to predict a decade before it threatened their traditional business. Despite this accurate forecast, Kodak focused on enhancing film quality rather than digital innovation.
Dominating the market in 1976 and peaking with £12,52,16 billion in sales in 1999, Kodak’s reluctance to adopt new technology led to a decline, with revenues falling to £4,85,11,90 billion in 2011.
Get ready for your interview with our top Change Management Interview Questions .

In contrast, Fuji, Kodak’s competitor, embraced digital transformation and diversified into new ventures.
Empower your team to manage change effectively through our Managing Change With Agile Methodology Training – sign up now!
6) Barclays Bank
The financial sector, particularly hit by the 2008 mortgage crisis, saw Barclays Capital aiming for global leadership under Bob Diamond. However, the London Inter-bank Offered Rate (LIBOR) scandal led to fines and resignations, prompting a strategic overhaul by new CEO Antony Jenkins in 2012.
Changes included rebranding, refocusing on core markets, altering the business model away from high-risk lending, fostering a customer-centric culture, downsizing, and embracing technology for efficiency. These reforms aimed to strengthen Barclays, improve shareholder returns, and restore trust.
Dive into the detailed Case Study on Change Management
Conclusion
The discussed Change Management Case Study examples serve as a testament to the transformative power of adept Change Management. Let these insights from industry leaders motivate and direct you as you navigate your organisation towards a path of continuous innovation and enduring prosperity.
Enhance your team’s ability to manage uncertainty and achieve impactful results – sign up for our comprehensive Risk Management For Change Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
The five key elements of Change Management typically include communication, leadership, stakeholder engagement, training and development, and measurement and evaluation. These elements form the foundation for successfully navigating organisational change and ensuring its effectiveness.
The seven steps of Change Management involve identifying the need for change, developing a Change Management plan, communicating the change vision, empowering employees, implementing change initiatives, celebrating milestones, and sustaining change through ongoing evaluation and adaptation.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Change Management Courses , including the Change Management Practitioner Course, Change Management Foundation Training, and Risk Management for Change Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Change Management Metrics .
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Change Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Mon 7th Oct 2024
Sat 12th Oct 2024, Sun 13th Oct 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Mon 4th Nov 2024
Sat 9th Nov 2024, Sun 10th Nov 2024
Mon 11th Nov 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Sat 7th Dec 2024, Sun 8th Dec 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
- go to walkme.com
Amazon: The Ultimate Change Management Case Study

Amazon’s innovations have helped it become extremely successful, making it an excellent change management case study.
Since it was formed, Amazon has innovated across countless areas and industries, including:
- Warehouse automation
- The web server industry
- Streaming video and on-demand media
- Electronic books
Considering that Amazon started as an online bookstore, these accomplishments are quite impressive.
Examining Amazon as a change management highlights a few important business lessons:
- Innovation fuels success, especially in today’s digital economy
- Speed is the ultimate weapon
- Those who resist organizational change can easily get left behind
Below, we’ll examine some of Amazon’s changes … and hopefully discover a few reasons why it has become so successful.

Below are 10 ways Amazon has changed its business, transforming itself far beyond a mere online bookseller.
In no particular order…
1. Amazon Web Services
When Amazon Web Services (AWS) started out, most developers didn’t take it seriously.
A decade later, it was the go-to cloud server company in the world.
In fact, Bezos has even said that AWS was the biggest part of the company.
Since it has more capacity than its nearest 14 competitors combined, this shouldn’t come as a surprise.
2. Whole Foods
After acquiring Whole Foods , Amazon began making changes to the grocery store chain.
A few of these include:
- Adding Amazon products to the shelves
- Integrating Whole Foods and Amazon Prime
- Internal restructuring
Other programs include food delivery from Whole Foods, rewards for customers using Amazon credit cards, and discounts for Prime members.
3. Delivery
Amazon has drastically innovated product delivery.
For instance, customers with Prime memberships can enjoy free two-day delivery.
In certain cities , Prime members can also get free same-day or one-day delivery.
And with its drone delivery program on the horizon, customers may be able to receive orders in 30 minutes or less .
4. Warehouse Automation
Amazon warehouses have undergone major technological transformations.
Currently, Amazon warehouses uses robots to collect and transport many of its products.
In coming years, though, even more of the company’s 200,000+ warehouse workers could be replaced by robots .
In 2016 alone, it increased robot workers by 50% .
5. TV and Prime Video
Another innovation of the former bookseller is its foray into TV, movies, and video.
Amazon began by selling videos and DVDs. Now it streams, rents, and sells digital copies of videos.
On top of that, the company has joined YouTube, Netflix, and other tech giants by producing its own movies and TV shows.
6. Amazon in Other Countries
Change managers would also be interested in how Amazon adapts itself to other countries’ economies.
In India, for instance, Amazon has been forced to adopt unique measures.
These include:
- Using mom-n-pop stores as delivery locations
- Hiring bicycle or motorcycle couriers for last-mile deliveries
- Creating mobile tea carts that serve tea and teach business owners about e-commerce
These types of innovations are necessary to succeed in other countries.
Failure to adapt to these changes often proves disastrous, which is a major reason why Google China failed .
7. Amazon Go
Amazon isn’t just an online retailer … it has now opened up physical grocery stores.
However, as with all of its business ventures, it aims to disrupt, transform, and dominate retail grocery stores.
In this case, Amazon wants to create grocery stores with zero clerks .
Amazon Go is a venture that promises no checkout lines, no hassle, and ultra-convenience.
8. Kindle and E-Books
Everyone knows that Kindle has been one of Amazon’s biggest innovations.
This product has single-handedly revolutionized the book publishing industry.
For better or for worse, Kindle has changed the way books are read, sold, and distributed.
Some estimates have placed Kindle e-book revenue at over half a billion dollars per year.
9. Affiliate Marketing
Early on in Amazon’s career, it opened its doors to online sales associates.
Members of Amazon Associates can earn revenue by sending web visitors to the sales giant.
According to Amazon, there are over 900,000 global members – all working to promote the company’s products and online presence.
10. Blue Origin
Technically speaking, Blue Origin is a different company from Amazon.
However, it’s worth noting that Amazon and Jeff Bezos can hardly be separated.
Without the famous founder’s extreme drive and vision, Amazon wouldn’t be what it is today.
And without his willingness to innovate, he never would have founded Blue Origin.
Like Elon Musk’s SpaceX, Blue Origin literally aims for the stars.
Its mission and goal – “millions of people living and working in space.”
Conclusion: Amazon Proves that Change Drives Success
It’s safe to say that Amazon’s defining trait has been its willingness to change.
What started as an online bookstore has become a multi-industry behemoth.
It has crushed companies that don’t innovate … it has revolutionized several industries … and it shows no signs of slowing.
The biggest lesson from this change management case study? Innovation and strategic change drive success.

Like what you are reading?
Sign up for our weekly digest of the latest digital trends and insights delivered straight to your inbox.
By clicking the button, you agree to the Terms and Conditions . Click Here to Read WalkMe's Privacy Policy
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Thanks for subscribing to WalkMe’s newsletter!
Matt Garris
Above the Fray & Beneath the Surface
- Mar 12, 2021
- 11 min read
Case Studies in Change Leadership

The following post is adapted from my personal academic coursework.
At its essence, leadership is a change-focused enterprise. Leaders influence others to change. While this influence takes place at various levels and through diverse means, change is always the common denominator. Change is the distinguishing feature of leadership. History contains accounts of strong leaders, both good and bad, and weak leaders. The chronicles of the exploits of these leaders fill archives and libraries—those who have made changes that drastically improved the human condition, those who caused others to suffer, and those who history remembers only for the opportunities they squandered. These types of leaders existed throughout human history, from ancient times through the present day. For instance, World War II had good leaders like Eisenhower and Nimitz, bad leaders like Hitler and Mussolini, and weak leaders like Neville Chamberlain. The Bible tells numerous stories of good leaders like Joseph, bad leaders like Nebuchadnezzer, and weak leaders like Adam. Merida also recounted stories of all these leadership types, including the weak leadership of King Ahab, the bad leadership of Queen Jezebel, and the good leadership of King Josiah.
If the adage is true that history repeats itself, then it is vital for modern leaders to learn from the legacies of those who have preceded them. They must be able to identify those characteristics that distinguish good leaders from bad ones and strong leaders from weak ones. Aspiring leaders must know how to replicate good leadership traits and avoid evil ones. Because leaders are constantly effecting transformation, they operate within a moral imperative of making sure they are making the right changes. These changes should maximize the good they achieve while minimizing any negative impacts. This paper serves the goal of learning from others’ leadership through the identification of current best practices in leading organizational change and studying the examples of other organizational leaders from various contexts.
Best Practices
Experts have written countless volumes on the best practices of leadership. Ecclesiastes 12:12 (NKJV) admonishes readers that “Of making many books there is no end, and much study is wearisome to the flesh.” While it is therefore impossible to exhaustively catalogue the best practices of organizational change leadership, the following four main tactics will serve all leaders well: implement necessary changes, begin with the end in mind, rally the troops, and anchor the changes.
Implement Necessary Changes
Kotter stated that establishing a sense of urgency was the first step in achieving significant organizational change. He added that “establishing a sense of urgency is crucial to gaining needed cooperation.” Unfortunately, many leaders struggle to generate the urgency their initiatives require because they either implement changes that are not necessary or fail to implement those changes that are. Thus, a good starting point for any leader is to determine which changes are necessary. This is important because it is nearly impossible to establish a sense of urgency around an unnecessary change.
While applying Kotter’s eight steps to manage change in the United Kingdom’s Integrated Offender Management program, King et al. found that “not all partners had ‘bought into’ the philosophy and objectives of the schemes” because the initiatives did not seem necessary to multiple different agencies in the criminal justice community. This belief highlights how important it is for leaders to choose to implement necessary changes. Kotter stated that “People will find a thousand ingenious ways to withhold cooperation from a process they think is unnecessary or wrongheaded.
Graamans et al. presented another example of this withheld cooperation in their study of a failed attempt to change the brand of suture in a Dutch hospital. They found that cardiothoracic surgeons “adamantly refused to work with the suture…, …stockpil[ed] their own supplies of surgical suture…, …[and threatened to hold] managers accountable for patient deaths that could arise from use of the new suture.” Why were the surgeons so opposed to new suture? They believed that it presented a danger to patient health outcomes. In other words, what was a dollars and cents issue to the hospital management was a life and death issue to the surgeons. The hospital management tried to make this unnecessary change and it ultimately failed. Leaders must make those changes which are necessary and avoid making those which are not.
Begin with the End in Mind
Covey famously articulated this next best practice for change leaders as the second of his seven steps, “Begin with the end in mind.” Covey further explained, “To begin with the end in mind means to start with a clear understanding of your destination. It means to know where you’re going… …so that the steps you take are always in the right direction.” Covey suggested that leaders ask themselves, “What are the things I want to accomplish?” Kotter echoed this sentiment in the third stage of his eight-step process, “Develop a vision and strategy.” Essentially, leaders must know where they are leading the organization. They must have a clear vision of the desired outcome and know the paths that will lead to it. Watts explained, “Defining specific outcomes is an effective way to create actionable goals that… …focus on those whom the initiative is intended to support.” Watts added that “defining outcomes can assist in… …solidifying group buy-in to help move the project forward.” Watts understood the importance of having a clearly defined destination. Effective leaders must begin with the end in mind.
Rally the Troops
Another best practice of change leaders is to get people united around the leader’s vision for the organization. Two of Kotter’s steps—creating the guiding coalition and communicating the change vision—are in keeping with this best practice. Grenny et al. suggested that those who want to lead others should “engage all six sources of influence.” These sources of influence include personal motivation, personal ability, social motivation, social ability, structural motivation, and structural ability. While there are many ways which leaders may employ to draw people to their causes, most of them involve some form of communication. In Habakkuk 2:2 (NKJV), God says to “Write the vision and make it plain on tablets, that he may run who reads it.” Clearly articulating the change vision is critical to the leader’s success.
Watts stated that “If the team knows where they are headed, all the members can steer in the same direction.” Similarly, Muthusamy made the following recommendation: “Managers and leaders should employ collaborative and consensus-building socio-linguistic jargons… [because] …sharing positive communication is central to the creation, sustenance and achieving organizational transformation. Thus, the process of creating, acquiring, articulating, sharing inspiration and knowledge through positive maxims and metaphors is a core organizational capability for modern management. If managers and leaders enact the words they articulate, organizations can realize the mission and goals that seem impossible.” Hemme et al. also emphasized the importance of language in communicating the vision: “We argue for more deliberately crafted change messages that emphasize some aspects over others under consideration of change recipients’ specific change concerns and context. Whereas some readiness beliefs need to be addressed clearly and deliberately early on, others can be affected more easily at later points during the change initiative. Specifically, change recipients need to be convinced that the proposed changes are in fact suitable to engender significant organizational benefits – otherwise all other efforts to affect other change-related attitudes appear to be moot.”
Anchor the Change
A final best practice is for leaders to anchor the change. Kotter recommended that leaders “anchor new approaches in the culture.” Atkins et al. related the story of a failed change effort which relied too heavily upon a single person and dissolved upon that individual’s retirement: “The most significant barrier [to continuing the change effort]… …was the retirement of and failure to replace the director of sustainability. This… …affected virtually all aspects of empowerment through authority. The long-established director position was eliminated… It had created a point person…, but after the person who had held the job retired, support from the Academic Affairs Office declined in awareness, structural support, and resources. With no one assigned to report to the university president about sustainability or lead university-wide efforts, the academic branch… …met with significant setbacks that jeopardized its upward trajectory in gaining participation of both faculty and students on its campuses. The vital role… …was placed at risk.”
Wei and Clegg also addressed anchoring approaches in the culture through their research on the dominance of organizational cultures during acquisition. They found that several trends related to the acquiring company’s culture, the target company’s culture, the power differential between these organizations, and how those impacted the post-acquisition culture of the organization. They found that organizations in the acquisition process pass through three phases—resistance, conformity, and integration. These phases also may be present in other change efforts. Finally, Jeong and Shin found that “when high-performance work practices are paired with organizational change, organizations have a much better chance of survival and prosperity.”
Case Studies
The following case studies offer valuable insights into the organizational change process.
Talent Culture
Li discussed his own experiences building a talent culture at HKBN, a leading Hong Kong news agency.
The Change Process
Li developed a blended approach to organizational change drawing from Kotter’s eight-step model and Yu’s 3H (heart-head-hand) model.. Li spread his blended approach across three super-steps for change: creating the climate for change, engaging and enabling the organization, and implementing and sustaining for change, and explained how he implemented these super-steps at HKBN.
In creating the climate for change, Li created urgency, formed a coalition, and created a vision; in engaging and enabling the organization, he communicated the vision, empowered action, and created the quick win; and in implementing and sustaining for change, he built on the change and made it stick.
The Outcome
Li was successful in creating the talent culture he envisioned. He attributed his success in part to how he balanced the 3H model with Kotter’s eight steps.
Suture Situation
Graamans et al. explained how one Dutch hospital’s effort to reduce expenses by purchasing a different brand of suture backfired.
Although the hospital management thought this was a “relatively small-scale change initiative,” they still utilized some change-management principles. These included building a guiding coalition, consulting department heads, and communicating the change to the surgeons. In fact, this change was believed to be so simple that it would have been one of the guiding coalition’s early wins as they had more cost-cutting measures planned for the future. One manager even stated it, “This appeared to us as an easy win.”
Unfortunately, appearances are sometimes misleading, and this was not an easy win. The surgeons refused to use the new suture, citing patient safety, and the management abandoned the mew suture. One reason for this outcome is that the management team tried to make a change that was not necessary. Another reason the initiative failed is because the hospital management team did not effectively rally the troops.
Integrated Offender Management
King et al. examined the limited success of the United Kingdom’s Integrated Offender Management system, a multi-agency approach to criminal justice and rehabilitation. This program coordinated the efforts of police officers, probation officers, drug addiction counselors, and other stakeholders within the system.
After seeing the system fail to maximize its potential, King et al. retroactively evaluated the implementation of the system using Kotter’s eight-step change model to identify its shortcomings. They found significant issues at several stages. While the police and probation officers saw the urgent need for change, some of the supporting agencies did not and this hindered the entire process. The system had no guiding coalition and no strategic plan to implement its vision. King et al. also found issues with communicating the vision to adjacent law enforcement and probation units and empowering others to act.
Kotter stated that “successful change of any magnitude goes through all eight stages.” King et al. found that the lack of a strategic plan led to later difficulty creating short-term wins, consolidating gains and producing more change, and institutionalizing the new approaches.
King et al. made numerous recommendations for improvement to the system implementation at every stage of Kotter’s process. They acknowledged the difficulty of public-sector inter-agency cooperation, but stated that “the possible tensions between occupational cultures could be mitigated through some of the early phases of Kotter’s model.”
Self-Directed Teams
Vito addressed a failed case of implementing self-directed teams at a large mental health and development services agency.
Two new, inexperienced directors at this agency implemented a rapid-fire change to the organization’s vision, mission, values, strategic direction and structure. The changes all happened in a matter of months with poor preparation, minimal communication, and inadequate support systems.
For many reasons, this change initiative ultimately failed. While the reasons for the failure are varied, they have much more to do with the change process than the change’s intended outcome. Every organization has a limit to the amount of change it may withstand before it reaches critical mass. This study demonstrates precisely why managing change is so vitally important to an organization’s health.
Leading Librarian
Watts described his experience establishing the Department of Knowledge Production at the University of Nevada at Las Vegas.
Watts began with what he knew from experience. As he considered his plans, which consisted of “practical and cutting-edge technologies, furniture ideas, and job descriptions that were applicable to the UNLV campus context.” Watts realized that he was still missing some necessary information: “However, understanding and communicating how learners and researchers would make use of the new services and spaces did not easily unfold. A list of topics and technologies and a sheaf of carpet samples will not help a librarian or project team identify the behaviors that indicate learning or the evidence to demonstrate that a space or service meets an instructional or research need. Further exploration was required. The objectives for the initiative had to be further clarified.” In addition to Watts (2019) explaining how he developed a better plan, he also provided guidance for how to handle what he termed “side-eye” and fear when leading organizational change. Watts succeeded in launching the department.
Case studies contain a wealth of information for aspiring leaders. The case studies in this paper highlighted four best practices—implementing necessary changes, beginning with the end in mind, rallying the team, and anchoring the changes in the organization’s culture. Additionally, the case studies tell the stories of leadership successes, like those of Li and Watts; of leadership failures, such as Graamans et al. and Vito; and of reflective leaders, like King et al. Their experiences help develop the next generation of organizational change leaders.
Akins, E. E., Giddens, E., Glassmeyer, D., Gruss, A., Kalamas Hedden, M., Slinger-Friedman, V., & Weand, M. (2019). Sustainability education and organizational change: A critical case study of barriers and change drivers at a higher education institution. Sustainability, 11 (2), 501-517. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020501
Covey, S. R. (1989). The seven habits of highly effective people: Restoring the character ethic. Simon & Schuster.
Graamans, E., Aij, K., Vonk, A., & Ten Have, W. (2020). Case study: Examining failure in change management. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 33 (2), 319-330. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-06-2019-0204
Grenny, J., Patterson, L., Maxfield, D., McMillian, R., & Switzler, A. (2013). Influencer: The new science of leading change. McGraw-Hill Education.
Hemme, F., Bowers, M. T., & Todd, J. S. (2018). Change readiness as fluid trajectories: A longitudinal multiple-case study. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 31 (5), 1153-1175. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-07-2017-0824
Jeong, I. & Shin, S. J. (2019). High-performance work practices and organizational creativity during organizational change: A collective learning perspective. Journal of Management, 45 (3), 909-925. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206316685156
King, S., Hopkins, M., & Cornish, N. (2018). Can models of organizational change help to understand ‘success’ and ‘failure’ in community sentences? Appling Kotter’s model of organizational change to an integrated offender management case study. Criminology & Criminal Justice, 18 (3), 273-290. https://doi.org/10.1177/1748895817721274
Kotter, J. P. (2012). Leading change. Harvard Business Review Press.
Li, E. (2018). A case study of the critical success factors for organizational change of a public listed corporation. Public Administration and Policy, 21 (2), 152-165. https://doi.org/10.1109/PAP-10-2018-010
Muthusamy, S. K. (2019). Power of positive words: Communication, cognition, and organizational transformation. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 32 (1), 103-122. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-05-2018-0140
Merida, T. (2015). Christ-centered exposition commentary: Exalting Jesus in 1 & 2 Kings. B & H Publishing Group.
The Holy Bible, New King James Version (1982). Thomas Nelson, Inc.
Vito, R. (2019). Self-directed teams as an organizational change strategy to empower staff: A teaching/learning case study. Human Service Organizations, Management, Leadership & Governance, 43(2), 146-151. https://doi.org/10.1080/23303131.2019.1614852
Watts, J. (2019). Navigating the new: A case study on leading organizational change. Portal: Libraries and the Academy, 19 (2), 223-232. https://doi.org/10.1353/pla.2019.0013
Wei, T. & Clegg, J. (2018). Effect of organizational identity change on integration approaches in acquisitions: Role of organizational dominance. British Journal of Management, 29 (2), 337-355. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.12226
Recent Posts
Technology and Expansion
Organizations as Open Systems
Changes of Organizations
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Hello! You are viewing this site in English language. Is this correct?
Explore the Levels of Change Management
9 Successful Change Management Examples For Inspiration

Updated: September 6, 2024
Published: January 3, 2024
Welcome to our guide on change management examples, which are pivotal for steering through today's dynamic business terrain. Immerse yourself in the transformative power of change management, a tool for resilience, growth, innovation, and employee morale enhancement.
This guide equips you with strategies to promote an innovative, adaptable work environment and boost employee morale for lasting organizational success.
Uncover diverse types of change management with Prosci's established methodology and explore real-world examples that illustrate these principles in action.
What is Change Management?
Change management is a strategy for guiding an organization and its people through change. It goes beyond top-down orders, involving employees at all levels. This people-focused approach encourages everyone to participate actively, helping them adapt and use changes in their everyday work.
Effective change management aligns closely with a company's culture, values, and beliefs.
When change fits well with these cultural aspects, it feels more natural and is easier for employees to adopt. This contributes to smoother transitions and leads to more successful and lasting organizational changes.
Why is Change Management Important?
Change management is pivotal in guiding organizations through transitions, ensuring impactful and long-lasting results.
For example, a $28B electronic components and services company with 18,000 employees realized the importance of enhancing its processes. They knew to adopt more streamlined, efficient approaches, known as Lean initiatives .
However, they encountered challenges because they needed a more structured method for effectively managing the human aspects of these changes.
The company formed a specialized group focused on change to address their challenges and initiate key projects. These projects aligned with their culture of innovation and precision, which helped ensure that the changes were well-received and effectively implemented within the organization.
Matching change management to an organization's unique style and structure contributes to more effective transformations and strengthens the business for future challenges.
What Are the Main Types of Change Management?
Discover Prosci's change management models: from individual application and organizational strategies to enterprise-wide integration and effective portfolio management, all are vital for transformative success.
Individual change management
At Prosci, we understand that change begins with the individual.
The Prosci ADKAR ® Model ( Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability and Reinforcement ) is expertly designed to equip change leaders with tools and strategies to engage your team.
This model is a framework that will guide and support you in confidently navigating and adapting to new changes.
Organizational change management
In organizational change management , we focus on the core elements of your company to fully understand and address each aspect of the change.
Our approach involves creating tailored strategies and detailed plans that benefit you and manage you to manage challenges effectively, which include:
- Clear communication
- Strong leadership support
- Personalized coaching
- Practical training
Our strategies are specifically aimed at meeting the diverse needs within your organization, ensuring a smooth and well-supported transition for everyone involved.
Enterprise change management capability
At the enterprise level, change management becomes an embedded practice, a core competency woven throughout the organization.
When you implement change capabilities:
- Employees know what to ask during change to reach success
- Leaders and managers have the training and skills to guide their teams during change
- Organizations consistently apply change management to initiatives
- Organizations embed change management in roles, structures, processes, projects and leadership competencies
It's a tactical effort to integrate change management into the very DNA of an organization—nurturing a culture that's ready and able to adapt to any change.
Change portfolio management
While distinct from project-level change management, managing a change portfolio is vital for an organization to stay flexible and responsive.

9 Dynamic Change Management Success Stories to Revolutionize Your Business
Prosci case studies reveal how diverse organizations spanning different sectors address and manage change. These cases illustrate how change management can provide transformative solutions from healthcare to finance:
1. Hospital system
A major healthcare organization implemented an extensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) system and adapted to healthcare reform. This case study highlights overcoming significant challenges through strategic change management:
Industry: Healthcare Revenue: $3.7 billion Employees: 24,000 Facilities: 11 hospitals
Major changes:
- Implemented a new ERP system across all hospitals
- Prepared for healthcare reform
Challenges:
- Managing significant, disruptive changes
- Difficulty in gaining buy-in for change management
- Align with culture: Strategically implemented change management to support staff, reflecting the hospital's core value of caring for people
- Focus on a key initiative: Applied change management in the electronic health record system implementation
- Integrate with existing competencies: Recognized change leadership as crucial at various leadership levels
This example shows that when change management matches a healthcare organization's values, it can lead to successful and smooth transitions.
2. Transportation department
A state government transportation department leveraged change management to effectively manage business process improvements amid funding and population challenges. This highlights the value of comprehensive change management in a public sector setting:
Industry: State Government Transportation Revenue: $1.3 billion Employees: 3,000 Challenges:
- Reduced funding
- Growing population
- Increasing transportation needs
Initiative:
- Major business process improvement
Hurdles encountered:
- Change fatigue
- Need for widespread employee adoption
- Focus on internal growth
- Implemented change management in process improvement
This department's experience teaches us the vital role of change management in successfully navigating government projects with multiple challenges.
3. Pharmaceuticals
A global pharmaceutical company navigated post-merger integration challenges. Using a proactive change management approach, they addressed resistance and streamlined operations in a competitive industry:
Industry: Pharma (Global Biopharmaceutical Company) Revenue: $6 billion Number of employees: 5,000
Recent activities: Experienced significant merger and acquisition activity
- Encountered resistance post-implementation of SAP (Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing)
- They found themselves operating in a purely reactive mode
- Align with your culture: In this Lean Six Sigma-focused environment, where measurement is paramount, the ADKAR Model's metrics were utilized as the foundational entry point for initiating change management processes.
This company's journey highlights the need for flexible and responsive change management.
4. Home fixtures
A home fixtures manufacturing company’s response to the recession offers valuable insights on effectively managing change. They focused on aligning change management with their disciplined culture, emphasizing operational efficiency:
Industry: Home Fixtures Manufacturing Revenue: $600 million Number of employees: 3,000
Context: Facing the lingering effects of the recession
Necessity: Need to introduce substantial changes for more efficient operations
Challenge: Change management was considered a low priority within the company
- Align with your culture: The company's culture, characterized by discipline in projects and processes, ensured that change management was implemented systematically and disciplined.
This company’s experience during the recession proves that aligning change with company culture is key to overcoming tough times.

5. Web services
A web services software company transformed its culture and workspace. They integrated change management into their IT strategy to overcome resistance and foster innovation:
Industry : Web Services Software Revenue : $3.3 billion Number of employees : 10,000
Initiatives : Cultural transformation; applying an unassigned seating model
Challenges : Resistance in IT project management
- Focus on a key initiative: Applied change management in workspace transformation
- Go where the energy is: Establishing a change management practice within its IT department, developing self-service change management tools, and forming thoughtful partnerships
- I ntegrate with existing competencies: "Leading change" was essential to the organization's newly developed leadership competency model.
This case demonstrates the importance of weaving change management into the fabric of tech companies, especially for cultural shifts.
6. Security systems
A high-tech security company effectively managed a major restructuring. They created a change network that shifted change management from HR to business processes:
Industry : High-Tech (Security Systems) Revenue : $10 billion Number of employees: 57,000
Major changes : Company separation; division into three segments
Challenge : No unified change management approach
- Formed a network of leaders from transformation projects
- Go where the energy is: Shifted change management from HR to business processes
- Integrate with existing competencies: Included principles of change management in the training curriculum for the project management boot camp.
- Treat growing your capability like a change: Executive roadshow launch to gain support for enterprise-wide change management
This company’s innovative approach to restructuring shows h ow reimagining change management can lead to successful outcomes.
7. Clothing store
A major clothing retailer’s journey to unify its brand model. They overcame siloed change management through collaborative efforts and a community-driven approach:
Industry : Retail (Clothing Store) Revenue : $16 billion Number of employees : 141,000
Major change initiative : Strategic unification of the brand operating model
Historical challenge : Traditional management of change in siloes
- Build a change network : This retailer established a community of practice for change management, involving representatives from autonomous units to foster consensus on change initiatives.
The story of this retailer illustrates how collaborative efforts in change management can unify and strengthen a brand in the retail world.
A major Canadian bank initiative to standardize change management across its organization. They established a Center of Excellence and tailored communities of practice for effective change:
Industry : Financial Services (Canadian Bank) Revenue : $38 billion Number of employees : 78,000
Current state : Absence of enterprise-wide change management standards
Challenge :
- Employees, contractors, and consultants using individual methods for change management
- Reliance on personal knowledge and experience to deploy change management strategies
- Build a change network: The bank established a Center of Excellence and created federated communities of practice within each business unit, aiming to localize and tailor change management efforts.
This bank’s journey in standardizing change management offers valuable insights for large organizations looking to streamline their processes.
9. Municipality
You can learn from a Canadian municipality’s significant shift to enhance client satisfaction. They integrated change management across all levels to achieve profound organizational change and improved public service:
Industry : Municipal Government (Canadian Municipality) Revenue : $1.9 billion Number of employees : 3,000
New mandate:
- Implementing a new deliberate vision focusing on each individual’s role in driving client satisfaction
Nature of shift :
- A fundamental change within the public institution
Scope of impact :
- It affected all levels, from leadership to front-line staff
Solution :
- Treat growing your capability like a change: Change leaders promoted awareness and cultivated a desire to adopt change management as a standard enterprise-wide practice.
The municipality's strategy shows us how effective change management can significantly improve public services and organizational efficiency.

6 Tactics for Growing Enterprise Change Management Capability
Prosci's exploration with 10 industry leaders uncovered six primary tactics for enterprise change growth , demonstrating a "universal theme, unique application" approach.
This framework goes beyond standard procedures, focusing on developing a deep understanding and skill in managing change. It offers transformative tactics, guiding organizations towards excelling in adapting to change. Here, we uncover these transformative tactics, guiding organizations toward mastery of change.
1. Align with Your culture
Organizational culture profoundly influences how change management should be deployed.
Recognizing whether your organization leans towards traditional practices or innovative approaches is vital. This understanding isn't just about alignment; it's an opportunity to enhance and sometimes shift your cultural environment.
When effectively combined with an organization's unique culture, change management can greatly enhance key initiatives. This leads to widespread benefits beyond individual projects and promotes overall growth and development within the organization.
Embrace this as a fundamental tool to strengthen and transform your company's cultural fabric.
2. Focus on key initiatives
In the early phase of developing change management capabilities, selecting noticeable projects with executive backing is important.
This helps demonstrate the real-world impact of change management, making it easier for employees and leadership to understand its benefits. This strategy helps build support and maintain the momentum of change management initiatives within your organization.
Focus on capturing and sharing these successes to encourage buy-in further and underscore the importance of change management in achieving organizational goals.
3. Build a change network
Building change capability isn't just about a few advocates but creating a network of change champions across your organization.
This network, essential in spreading the message and benefits of change management, varies in composition but is universally crucial. It could include departmental practitioners, business unit leaders, or a mix of roles working together to enhance awareness, credibility, and a shared purpose.
Our Best Practices in Change Management study shows that 45% of organizations leverage such networks. These groups boost the effectiveness of change management and keep it moving forward.
4. Go where the energy is
To build change capabilities throughout an organization effectively, the focus should be on matching the organization's current readiness rather than just pushing new methods.
Identify and focus on parts of your organization that are ready for change. Align your change initiatives with these sectors. Involve senior leaders and those enthusiastic about change to naturally generate demand for these transformations.
Showcasing successful initiatives encourages a collaborative culture of change, making it an organic part of your organization's growth.
5. Integrate with existing competencies
Change management is a vital skill across various organizational roles.
Integrating it into competency models and job profiles is increasingly common, yet often lacks the necessary training and tools.
When change management skills expand beyond the experts, they become an integral part of the organization's culture—nurturing a solid foundation of effective change leadership.
This approach embeds change management deeper within the company and cultivates leaders who can support and sustain this essential practice.
6. Treat growing your capability like a change
Growing change capability is a transformative journey for your business and your employees. It demands a structured, strategic approach beyond telling your network that change is coming.
Applying the ADKAR Model universally and focusing on your organization's unique needs is pivotal. It's about building awareness, sparking a desire for change across the enterprise, and equipping employees with the knowledge and skills for effective, lasting change.
Treating capability-building like a change ensures that change management becomes a core part of your organization's fabric, benefitting every team member.
These six tactics are powerful tools for enhancing your organization's ability to adapt and remain resilient in a rapidly changing business environment.
Comprehensive Insights From Change Management Examples
These diverse change management examples provide field-tested savvy and offer a window into how varied organizations successfully manage change.
Case studies , from healthcare reform to innovative corporate restructuring, exemplify how aligning with organizational culture, building strong change networks, and focusing on tactical initiatives can significantly impact change management outcomes.
This guide, enriched with real-world applications, enhances understanding and execution of effective change management, setting a benchmark for future transformations.
To learn more about partnering with Prosci for your next change initiative, discover Prosci's Advisory services and enterprise training options and consider practitioner certification .

Founded in 1994, Prosci is a global leader in change management. We enable organizations around the world to achieve change outcomes and grow change capability through change management solutions based on holistic, research-based, easy-to-use tools, methodologies and services.
See all posts from Prosci
You Might Also Like
Enterprise - 8 Mins

3 Essential Change Management Strategies in Healthcare

What Is Change Management in Healthcare?
Subscribe here.

Transformational change: Theory and practice
A look at how transformational change themes apply in practice, with case studies providing practical examples
Explores how the themes on transformational change apply in practice
Our report, Landing transformational change: Closing the gap between theory and practice explores how the themes identified in earlier research apply in practice. Case studies from four organisations provide practical examples of how organisations have approached transformational change.
The report also includes recommendations that HR, OD and L&D professionals should consider for their organisations and their own skill set, if they are to be successful expert initiators and facilitators of transformational change.
Whilst these findings and case studies are UK-based, the broader trends and implications should be of interest wherever you are based.
Download the report and individual case studies below
Landing transformational change
This earlier report covers some of the thinking and innovative ideas in the field of change management that can help to land transformational change. Drawing on a comprehensive literature review on change management the report develops ten themes on transformational change practice to provide a platform of knowledge on designing, managing and embedding change essential for OD, L&D and HR professionals.
Tackling barriers to work today whilst creating inclusive workplaces of tomorrow.
Bullying and harassment
Discover our practice guidance and recommendations to tackle bullying and harassment in the workplace.

How can people teams balance line managers’ need for operational people management support while growing their team’s strategic influence through the HRBP role?

We look at how investing in digital technologies, HR skills and culture drive success in restructured people functions

A case study of an HR function shifting from an Ulrich+ model towards an employee experience-driven model

A case study of a people function shifting to a four-pillar model to deliver a more consistent employee experience throughout the organisation
More reports

Trend analysis and benchmarking data on recruitment, retention and talent management to inform HR and employers on practice considerations and decision-making

Read our latest Labour Market Outlook report for analysis on employers’ recruitment, redundancy and pay intentions

A Northern Ireland summary of the CIPD Good Work Index 2024 survey report

A Wales summary of the CIPD Good Work Index 2024 survey report
Purdue Polytechnic Institute
Global mobile menu.
- Departments
- Statewide Locations
Managing Change in Uncertain Times: A Case Study
Change management, defined as the methods and processes by which a company effects and adapts to change, has long been vital to the functioning of successful organizations. As John C. Maxwell said , “change is inevitable, growth is optional.” All organizations undergo changes during their lifespans, but not all organizations are able to effectively respond to change or harness it for success.
This fact was made painfully apparent during the COVID-19 pandemic. After businesses were forced to shut down in-person operations, many suffered catastrophic losses. The airline industry, travel and leisure industry, oil and gas industry, and restaurant industry were among the hardest hit . Thousands of businesses were forced to close for good, and thousands more suffered through significant profit loss, layoffs and downsizing. Still, some businesses made vital adaptations that carried them through the worst of the pandemic. Many restaurants, for example, shifted from traditional, in-person service and poured resources into curbside, takeout and delivery services, using technology to communicate with their customers and remain up and running. These adaptations built on services that the restaurants already offered, making the changes easier to implement and accept.
A Case Study in Change: Delta Airlines
Unlike restaurants, airlines did not have much existing infrastructure to carry them through a global pandemic. Airlines profit based on the tickets they book, and if nobody is willing to fly, airlines can’t just pivot to a “take-out” travel option. After the pandemic hit, airlines were faced with a crucial ultimatum: find an innovative solution or suffer catastrophic losses. Delta Airlines, one of the oldest and largest airlines in the country, decided to tackle the change head-on and immediately started working on a change management plan.

Delta structured changes to its operations around what would make customers more comfortable and ultimately found that customers were willing to pay for some extra peace of mind. Implementing the change was made easier by quick and effective communication across all levels of operation. Flight attendants, gate staffers and corporate communications professionals were given the tools they needed to communicate the company’s safety plan to prospective passengers and execute the new seating rules. As the immediate changes took effect and began yielding results, Delta worked on making the changes more efficient and seamless, refining its process every step of the way.
The Science of Change Management
Delta’s quick and effective response to a major change in business operations helped usher it through the worst of the pandemic without suffering bigger losses. Innovative research on best practices in change management is poised to help other businesses do the same. According to the Change Management Review , using technological and organizational tools to manage “the human side of change” is particularly important. Consider, many businesses were forced to move their operations online after the start of COVID-19, and this change affected employees most of all. The businesses who fared best after moving online were the ones who assisted their employees in adapting to the change by providing opportunities for virtual team building, socialization, and mental wellness checkups, for instance. By considering the effects of change on their employees, these businesses took a proactive approach to getting their teams through a daunting and sudden transition.
David Michels and Kevin Murphy, two industry experts who research change management, have helped quantify what exactly makes some organizations excel at handling change. According to their study , there are nine organizational elements that contribute to an organization’s ability to manage change:
- Purpose and direction – the qualities that help organizations lead change.
- Connection, capacity, and choreography – the qualities that help organizations accelerate change.
- And scaling, development, action, and flexibility – the qualities that help organizations organize change.
Michels and Murphy also developed categories identifying the challenges many organizations face when dealing with change. They determined that organizations struggling with change were either:
- In search of focus, meaning they struggle to lead change, identify ambitions and map agendas.
- Stuck and skeptical, meaning they struggle to move beyond small-level changes and avoid big decision making.
- Aligned but constrained, meaning they struggle with change because of organizational barriers.
- And struggling to keep up, meaning they struggle with organizational fatigue and burnout.
This kind of change management research gives organizations the opportunity to critically evaluate their responses to change and map effective plans for dealing with change in the future. Even without the pandemic factor, being able to change and grow is of primary importance in a world of fast-paced technological advancement and global communication. Change management specialists are in high demand in every industry, with 12% projected job growth (U.S Bureau of Labor Statistics) and a median salary of $128,992 (Salary.com).
Purdue Prepares Project Managers to Master Change
Purdue University’s 100% online Master of Science in IT Project Management prepares students for project management careers in the fast-growing information technology field. Students develop mastery of project management processes and procedures using program materials included in the Body of Knowledge developed by the Project Management Institute (PMI®). Courses are taught by industry experts in high-demand specialization areas such as change management, risk management and security management.
Since the program is entirely online, working professionals can arrange their plan of study around their busy schedules and take classes from anywhere. The program is specifically tailored to industry-experienced go-getters who want to break into the IT field or advance their careers by developing project management expertise.
Professionals who want to grow their expertise without committing to a master’s degree can choose to complete a four-course graduate certificate in Managing Information Technology Projects. The credits from the graduate certificate can be applied towards the master’s degree if a student chooses to pursue the master’s after completing the certificate.
Learn more about the program and graduate certificate on the course’s website .
About the author.

Rachel (RM) Barton
Change Management: Results With and Without. A Case Study.
22 February 2022 Same change, same time, two different approaches, widely different outcomes. Article written by Nelly Tire and Vincent Piedboeuf
Prosci Europe's case studies offer practical insights for organisations wishing to make changes that stick.
Executive Summary
Why should I read? To get a real-life example of what can happen without a structured approach to managing the change. We uncover the difference in outcome between two organisations seeking to deploy the same technological solution to a recurrent and common issue in the personal care service sector.
Highlights:
- In one case, the implementation phase proved much longer than expected. Only half of the staff was or stayed on board. The gulf between the target set and the number of people proficiently using the change kept widening every day.
- The second case shows adoption and utilisation rates close to 88%. A clear CM plan with actionable strategies delivered expected results on time.
- For a complete overview of what a successful CM plan looks like, please see Keys to application.
Background
Year – 2021.
Sector – Personal Care Services.
Who – Two non-profit organisations offering social services such as childcare, home nursing, special assistance to vulnerable people, heavy-duty housework, etc.
What – In a nutshell, outdated paper-based management and monitoring systems generate errors, poor responsiveness, and late payments while also causing the organisations and the sector to miss out on new opportunities. The new "Mobile Teleprocessing System" attempts to leverage technology to optimise the provision of existing and future services.
Type of change – See below.
The challenge (why the change?)
Baseline. Managing and controlling provided services happens through a two-fold mechanism of phone check-in used by staff members in the home of users (elderly, physically- challenged people, etc.) and paper-form shift sheets subsequently signed by users (date of the month, number of hours).
Internal reasons to change. Both entities sought to provide practical solutions to recurrent problems reported by frontline employees/account services. Climbing on the train of digitisation was also expected to raise the sector's attractiveness. More specifically, both associations faced the following issues:
- The excessive shift sheet volume led to repeated data processing and validation delays, pushing back invoicing and wage payments to 15 days the following month.
- Frontline employees (caretakers) found it challenging to check-in using the user's phone landline .
- There were problems managing shift sheets/forms , sometimes signed by disabled or vulnerable people (users), by staff members themselves, when not simply lost.
External reasons to change. The availability of game-changing technological solutions, which could also respond to concerns related to funding, turned the change into a pressing issue. The mix of specific requirements and opportunities included:
- system loopholes – the phone clocking in/out mechanism could only be used for some services.
- technological developments and new apps designed to smooth out the problems of bureaucracy and speed up data exchange.
- requests from funders to better control the use of resources allocated to the associations and allow real-time communication with home care services.
The solution
This set of external and internal drivers led to "Mobile Teleprocessing" project. The overarching element of the action plan was the switch from the aforementioned "point system" (fixed phone system and shift sheets) to the use of a particular app running on a professional smartphone and connected in real-time with the all-in-one software for planning/accountancy . This advanced solution could also help manage instant alerts in case of a change in the internal working schedule. Sending off invoices would be just one click away. Other apps responding to specific health and care issues were also under consideration.
Expected benefits ranged from shortening processing times and reducing errors when logging data to improving communication with frontline employees and funders.
Keys to application – 1st case
Highlight: The first organisation implemented the solution within one month, impacting 500 employees. The plan was based upon Prosci's best practices and ADKAR model for individual change. Here is an overview of the main items:
a. Sponsorship, the face of change.
Active and visible sponsorship throughout the whole duration of the project is the number-one success factor of any change initiative. In this case, the Director-General was designated as the primary sponsor. Beyond its involvement in the early phases, he was provided with data fresh from the field to remind people of the rules and communicate results.
b. Bringing in Change Management resources.
The association allocated resources to CM, setting up a dedicated team with a change practitioner and a network of change agents.
c. Evaluating impact.
The organisation identified the groups impacted by the change (frontline employees, team leaders, accounting services) to prepare targeted training sessions.
d. Creating Awareness and Desire.
Before moving any further along the change journey, the association communicated extensively around the project and the strategic reasons underpinning it. They proceeded to:
- Convene and conduct a meeting to introduce the project and CM plan to team leaders and super-users.
- Get executives and team leaders actively involved with CM and fully committed to the process.
- Circulate a promotional film featuring the change and its rationale, along with footage of an employee using the new tool.
- Disseminating information on the intranet to communicate with frontline staff (caretakers operating in users' homes)
- Send mail communications to present the "Mobile Teleprocessing" project to users and employees.
e. Building Knowledge and Ability.
After completing the impact analysis and conducting preliminary campaigns to raise awareness and desire, the organisation started to prepare the people for the change. They did so by:
- Delivering 21 training sessions to 500 collaborators
- Choosing instructors among expert users
- Designing high-quality training materials, with a strong focus on user-friendliness (practical exercises, quizzes, appropriate evaluation forms, ….)
- Systematically collecting and analysing feedback to improve materials
- Creating FAQs on the intranet
- Uploading Video tutorials on the association website
- Developing memos for teams on specific topics
- At the end of the project, team leaders took over the role of instructors for new employees entering the application.
f. Reinforcing.
To ensure long-lasting results and effective use of the phone and app, the association proceeded to:
- Collect info on clocking in/out processes and the remaining volume of shift sheets.
- Hold a special briefing on results, including a quick review/reminder of the rules (main sponsor).
- Diffuse reminders on the intranet.
- Issue warning letters to people tricking the system by logging incorrect data, holding multiple broken phones, or repeatedly losing them.
Keys to application – 2 nd case
Highlight : The size of the change was even more significant in the second case, impacting about 800 employees. The expected time for completion was one month and a half. But unlike its counterpart, this association did not implement any structured Change Management plan. Team leaders viewed the technical solution as an easy fix.
Items : Team leaders were tasked with demonstrating how the application worked, with the following consequences:
- Employees complained that they received poor guidance and struggled to use the phone or the application.
- Employees perceived the new tool as a "policing instrument."
- The roll-out proved difficult, triggering resistance among staff and causing the training modules to be delivered late.
Results and Takeaways
Clear differences in outcomes show the importance of adopting a structured approach to managing the change. The implementation lasted one month without any significant setback in the first case . Not only did this association meet the deadline. Adoption and utilisation rates after four months were close to 88% . In contrast , implementation suffered from major delays in the second case . While leaders had planned on a one-month and a half roll-out, deployment was only complete after six months. Moreover, adoption and utilisation rates proved grossly insufficient , with a more modest 50%.
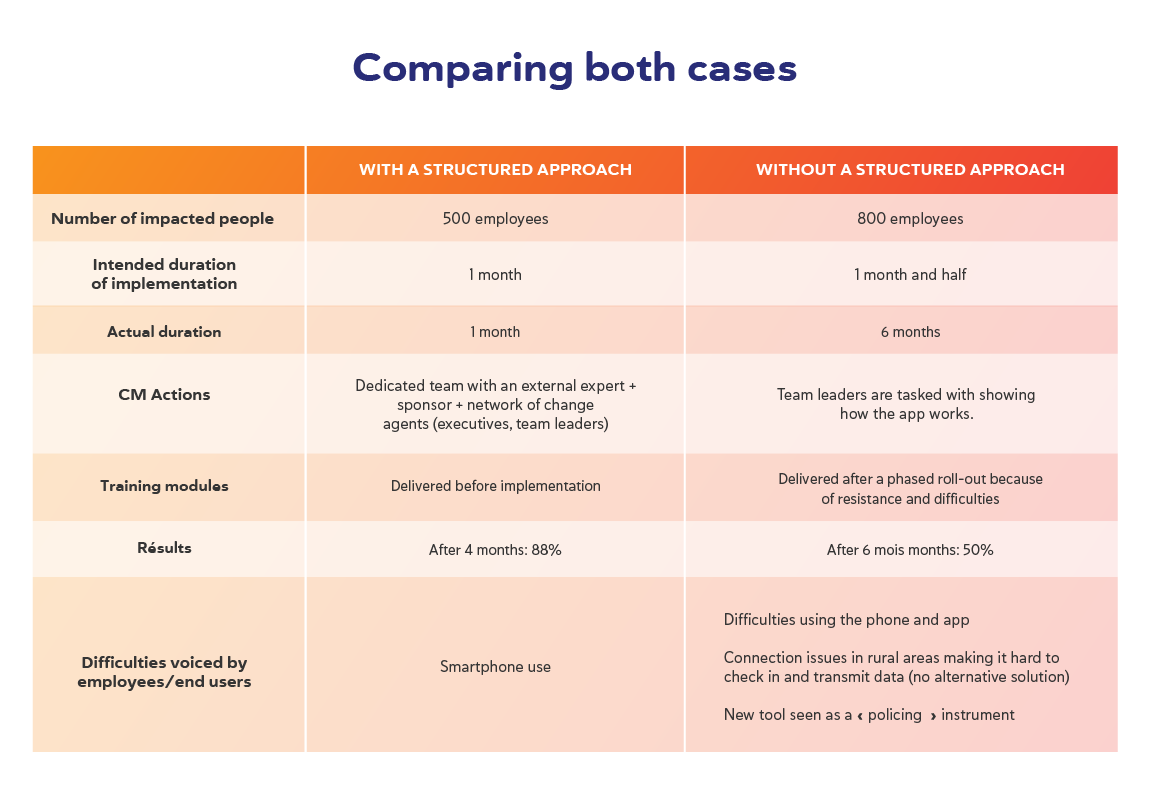
If all the above-described Change Management items account for what did go well in the first case, what went wrong in the second one?
A common mistake is to jump right into equipping the people without raising A wareness and creating D esire. This second case study clearly illustrates the consequences of not laying the foundations for the change. Omitting this part led to early resistances, crystallizing without any strategy or capacity to mitigate them. The new system was seen as a policing maneuver of sorts.
Furthermore, there was no attempt to create engaging training materials, leaving team leaders without a clear roadmap or tools to deliver K nowledge. Frontline employees lamented the lack of information or guidance. Issues with the phone connection in some rural regions also meant that employees were unable ( A bility) to use the solution. The new system, first seen as a quick fix, created distrust, and with nothing being done, the snowball effect sat in.
Change cannot be left to chance.
Check out our resources to learn more about Change Management and stay updated!
PROSCI Methodology in action
PROSCI's impact analysis provides a very accurate overview of the kind of change involved. The following "radar graphs" identify how the project "Mobile Teleprocessing" affects the three main target groups: Area Managers, Domestic Helpers, and Accounting Services. Most dimensions are self-explanatory [1] , but let's point out that processes , systems , tools, and critical behaviours – heavily emphasised in this case study – refer to:
- the "action steps to achieve a defined outcome" ( processes ), or how the provision of care services will be managed and monitored from this point on.
- the "combination of people and automated application" necessary to meet a set of goals ( systems ), in this case, all stakeholders and what is expected from them in terms of promoting, showcasing, and or being able to use the new "Mobile Teleprocessing" system.
- "an item used for a specific purpose" ( tools ), that is, a professional phone and related app to clock out, report, or log other relevant information.
- "a specific response to a stimulus" ( critical behaviours ), in this example, the consistent and proficient use of the professional phone and app.
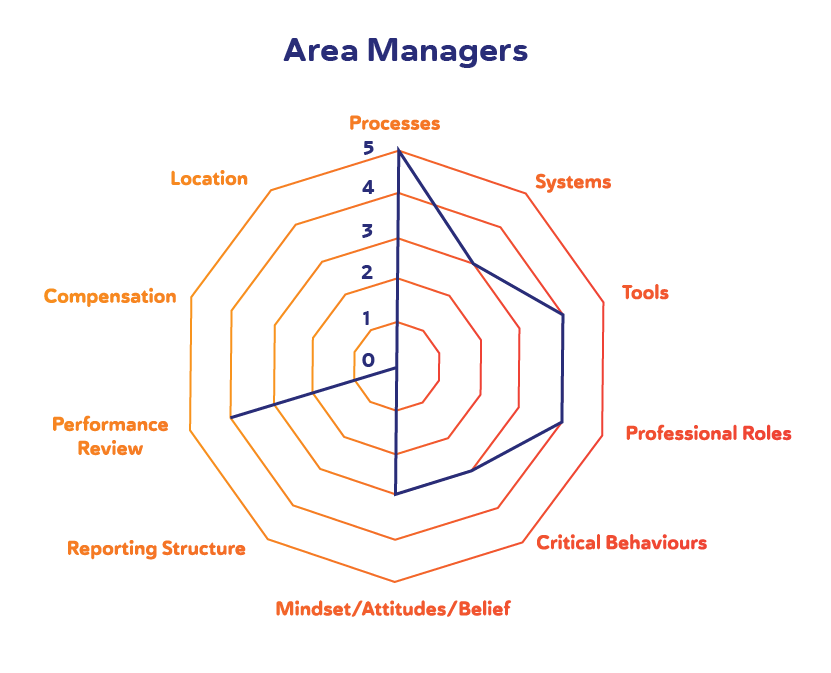
[1] PROSCI's change impact model offers a robust framework to define the change along 10 dimensions that may impact people involved. These dimensions or areas typically include Processes (1), Systems (2), Tools (3), Professional Roles (4), Critical Behaviours (5), Mindset/Attitudes/Belief (6), Reporting Structure (7), Performance Review (8), Compensation (9), Location (10). To learn more: https://www.prosci.com/blog/defining-change-impact
After having managed a large number of changes in a wide range of business sectors, Vincent Piedboeuf dedicates his time helping managers to optimise their return on investment through effective integration of the people side in their change projects. He is one of the most active Change Management instructors and certifies hundreds of people in Prosci methodology every year.

Nelly Tire and Vincent Piedboeuf
Do you want to learn more?

Know more about Change Management

Learn the foundations of Change Management

Replay our Webinars
Be in the know.
Join the community to receive the latest articles on Change Management, upcoming events and exclusive newsletter.
We guarantee 100% privacy. Your personal details will not be shared to third party partners.
Join the community to receive the latest thought change management articles, upcoming events and exclusive newsletter
By completing and submitting this form, I authorize the use of my data for being informed of Prosci Europe upcoming events, and gaining access to useful materials tailored to my specific needs. For further information regarding the processing of your personal data or your rights on your personal data, please refer to our Privacy Policy .
Don't ask me anymore
We’ll get back to you soon.