

National Anthem
Title: Jana Gana Mana
Music by: Rabindranath Tagore
Lyrics by: Rabindranath Tagore
Raga: Alhiya Bilawal
Written on: December 11, 1911
First sung on: December 27, 1911
Declared as National Anthem on: January 24, 1950
Time to play: 52 seconds
Underlying message: Pluralism/Unity in Diversity

National Anthem refers to a musical composition that has been selected by an authorized government bodyand is meant to represent a country’s patriotic ethos. It generally helps citizens relate to the country’s spiritual and philosophical sentiments, its rich culture and colorful history. The national anthem presents a country’s identity to the world and it acts as an instrument of unity among its citizens.
The National Anthem of India is entitled ‘Jana Gana Mana’. The song was originally composed in Bengali by India’s first Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore on December 11, 1911. The parent song, ‘Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata’ is a Brahmo hymn which has five verses and only the first verse has been adopted as National Anthem. If put forwards succinctly, the National Anthem conveys the spirit of pluralism or in more popular term the concept of ‘Unity in Diversity’, which lies at the core of India’s cultural heritage.
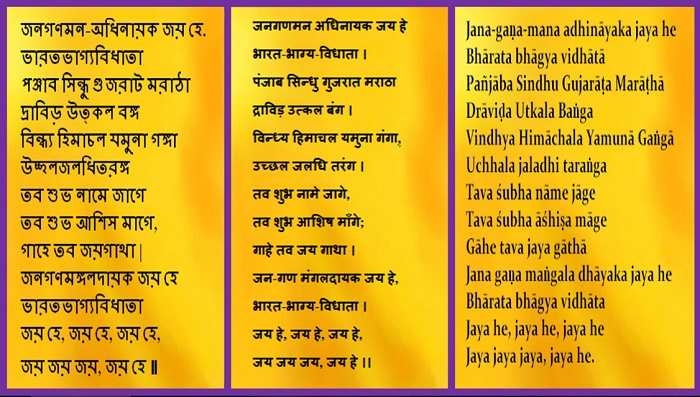
Lyrics and Translation
The original song ‘Jana Gana Mana’ is written in Bengali, but in a Sanskritized dialect known as Sadhu Bhasha. The words are primarily noun but can be used as verbs alternatively. The words again are common in most of the Indian languages and are accepted as such. They remain unchanged in most of them but the pronunciation varies according to the predominant accent of the region. The lyrics of the song are as follows:
Jana-gana-mana-adhinayaka, jaya he
Bharata-bhagya-vidhata.
Punjab-Sindh-Gujarat-Maratha
Dravida-Utkala-Banga
Vindhya-Himachala-Yamuna-Ganga
Uchchala-Jaladhi-taranga.
Tava shubha name jage,
Tava shubha asisa mage,
Gahe tava jaya gatha,
Jana-gana-mangala-dayaka jaya he
Jaya he, jaya he, jaya he, Jaya jaya jaya, jaya he!
The idea of translating the song from Bengali to English came to Tagore while he was visiting the Besant Theosophical College on the invitation of Irish poet James H. Cousins. He penned down the English translation during his stay at Madanapalle, a small town in the Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh. The musical notations for the English version were set down by Margaret Cousin, James Cousin’s wife. The English translation goes as follows:
Thou art the ruler of the minds of all people,
Dispenser of India's destiny.
The name rouses the hearts of Punjab, Sind, Gujarat and Maratha,
Of the Dravid and Orissa and Bengal;
It echoes in the hills of the Vindhyas and Himalayas,
Mingles in the music of the Yamuna and Ganga
And is chanted by the waves of the Indian Sea.
They pray for thy blessings and sing thy praise.
The salvation of all people is in thy hand,
Thou dispenser of India's destiny.
Victory, victory, victory to thee.
A shorter version of the National Anthem is also sung on occasions and it consists of the first and last lines of the verse, like
Jana-gana-mana-adhinayaka jaya he
Jaya he, Jaya he, Jaya he, Jaya Jaya, Jaya, Jaya he.

History of Indian National Anthem
The song ‘Bharat Bhagya Bidhata’ was first sung on the Day 2 of the annual session of the Indian National Congress in Calcutta on December 27, 1911. Song was performed by Sarala Devi Chowdhurani, Tagore’s niece, along with a group of school students, in front of prominent Congress Members like Bishan Narayan Dhar, Indian National Congress President and Ambika Charan Majumdar.
In 1912, the song was published under the title Bharat Bidhata in the Tatwabodhini Patrika, which was the official publication of the Brahmo Samaj and of which Tagore was the Editor.
Outside of Calcutta, the song was first sung by the bard himself at a session in Besant Theosophical College in Madanapalle, Andhra Pradesh on February 28, 1919. The song enthralled the college authorities and they adopted the English version of the song as their prayer song which is sung till today.
On the occasion of India attaining freedom, the Indian Constituent Assembly assembled for the first time as a sovereign body on August 14, 1947, midnight and the session closed with a unanimous performance of Jana Gana Mana.
The members of the Indian Delegation to the General Assembly of the United Nations held at New York in 1947 gave a recording of Jana Gana Mana as the country’s national anthem. The song was played by the house orchestra in front of a gathering consisting of representatives from all over the world.
Jana Gana Mana was officially proclaimed as India’s National Anthem by the Constituent Assembly of India on January 24, 1950.
Occasions for playing the Anthem
The full version of the national anthem requires duration of approximately 52 seconds to be played while the shorter version takes about 20 seconds. The national anthem is a symbol of pride for the citizens of the country and is required to be played on specifically designated occasions which are listed below.
1. The full version of the National Anthem is played on the following occasions:
a. Accompanying the performance of National Salute on ceremonial occasions to the President of India or Governors of States/Union Territories.
b. During parade demonstrations in front of the dignitaries referred in the preceding point
c. before and after the President’s address of the nation
d. Before arrival and departure of the President or Governor from a formal ceremony
e. When the national Flag is hoisted during cultural occasions
f. When the Regimental Colors are presented
2. The National Anthem is not to be played for the Prime Minister generally, except under special circumstances.
3. On the occasion where the National Anthem is performed by a Band, a roll of drums is to precede the actual performance, in order to let the audience know and prepare for paying respect. The roll will be 7 paces of slow march, will start slowly, ascend to a loud volume and should remain audible till the last beat.
National Anthem of India - Code of Conduct
A specific set of rules and regulations have been set by the Government of India to oversee the proper and correct rendition of the National Anthem. The Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971, was penned down by the Government of India to prevent any intentional disrespect or insult towards the National Anthem of the country. Offenders are punishable with up to three years of imprisonment as well as monetary fine.
The following codes of conduct are to be observed by Indian citizens whenever the National Anthem is played:
1. Should stand up to attention.
2. Individual’s head should be held high
3. One should be looking forward.
4. Mass singing of the National Anthem is to accompany the unfurling of the National Flag.
5. No parody/distortion of words or music of the National Anthem is allowed.
Significance
The National Anthem is perhaps one of the most potent declarations of a country’s independent status. India is a nation of multiple languages and dialects therein. Jana Gana Mana is understood unequivocally throughout India and thus brings forth the spirit of unity among these diverse languages. Our National Anthem conveys very aptly the traditions and values that still hold strong as the backbone of the country. It helps reinforce the accepting and assimilating nature of Indian culture along with its tolerance to pluralism. Jana Gana Mana appeals to the country’s patriotic emotions and helps unifying the different races, castes and creeds by solemn singing of the hymn-like verses.
Controversies
A controversy surrounds the song Jana Gana Mana from its inception. A section of congress leaders alleged that Tagore wrote this song in praise of King George V as indicated by the use of the words like “Adhinayaka” and “Bharat Bhagya Bidhata”. The creation of the song coincided with the England Monarch’s first visit to India and his Coronation at Delhi Durbar in 1911. But in a letter to Mr. Pulin Bihari Sen in December 1939, Tagore dismissed the idea. He wrote “A certain high official in His Majesty's service, who was also my friend, had requested that I write a song of felicitation towards the Emperor. The request simply amazed me. It caused a great stir in my heart. In response to that great mental turmoil, I pronounced the victory in Jana Gana Mana of that Bhagya Vidhata [ed. God of Destiny] of India who has from age after age held steadfast the reins of India's chariot through rise and fall, through the straight path and the curved. That Lord of Destiny, that Reader of the Collective Mind of India, that Perennial Guide, could never be George V, George VI, or any other George. Even my official friend understood this about the song. After all, even if his admiration for the crown was excessive, he was not lacking in simple common sense.”

- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
The Star‑Spangled Banner
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 13, 2024 | Original: September 28, 2017

“The Star-Spangled Banner” is the national anthem of the United States. By the time the song officially became the country’s anthem in 1931, it had been one of America’s most popular patriotic tunes for more than a century. The anthem’s history began the morning of September 14, 1814, when an attorney and amateur poet named Francis Scott Key watched U.S. soldiers—who were under bombardment from British naval forces during the War of 1812—raise a large American flag over Fort McHenry in Baltimore, Maryland.
Background: War of 1812
Simmering anger at Britain for interfering in American trade, impressing U.S. sailors into the Royal Navy and standing in the way of westward expansion led the United States to declare war in June 1812.
With British forces distracted by the country’s ongoing war with France, the United States scored some encouraging early victories in the War of 1812 . But in August 1814, British troops invaded Washington, D.C. and set fire to the White House , the Capitol and other government buildings. The Royal Navy then trained its sights on the key seaport of Baltimore, Maryland .
On September 13, U.S. soldiers at Baltimore’s Fort McHenry withstood some 25 hours of British bombardment. Early the next morning, they hoisted a gigantic U.S. flag over the fort, marking a crucial victory and a turning point in what would be considered a second war of American independence.

Why the Star‑Spangled Banner is Played At Sporting Events
The tradition began during a time of national sorrow
10 Things You May Not Know About ‘The Star‑Spangled Banner’
Ten surprising facts about the national anthem and the man who wrote its lyrics.
What Is Flag Day?
Discover the history of the annual holiday and check out 13 facts about the American flag and how to properly display it.
Francis Scott Key
A Maryland-born attorney with a thriving practice in Washington, D.C., Francis Scott Key watched the bombardment of Fort McHenry from a ship anchored in Baltimore’s harbor.
Key had been helping to negotiate the release of an American civilian, Dr. William Beanes, who had been captured in an earlier battle. As a condition of the release, the British ordered the Americans not to return to shore during the attack on Baltimore.
Who Wrote 'The Star-Spangled Banner'?
Francis Scott Key wrote “The Star Spangled Banner” and its initial verse on the back side of a letter while watching the large American flag waving over the fort that morning. Back in Baltimore, he continued working until he had completed four verses (only one of which is commonly known today).
After a local printer issued the song, originally called “Defence of Fort M’Henry,” two Baltimore newspapers printed it, and it spread quickly to various cities along the East Coast.
By November 1814, Key’s composition had appeared in print for the first time under the name “The Star-Spangled Banner.”
From Drinking Song to American Anthem
Ironically, the melody Key assigned to accompany the lyrics of “The Star-Spangled Banner” was a popular English drinking song called “To Anacreon in Heaven.”
Written around 1775 by John Stafford Smith, the song honored the ancient Greek poet Anacreon, a lover of wine. It was originally performed at a London gentleman’s music club called the Anacreontic Society.
The Anacreontic Song, as it was known, had a track record of popularity in the United States by 1814. In one famous case, defenders of the embattled second president, John Adams , used the tune for a song called “Adams and Liberty.”
Key himself had even used the tune before, as accompaniment for verses he wrote in 1805 commemorating American naval victories in the Barbary War .
Key’s Complicated Legacy
After the war of 1812, Key continued his thriving law career. He served as a member of the “Kitchen Cabinet” of President Andrew Jackson and in 1833 was appointed as a U.S. attorney for the District of Columbia.
He composed other verses over the course of his life, but none received anywhere close to the recognition of “The Star-Spangled Banner.” After contracting pleurisy, Key died in 1843 at the age of 63.
Though his celebrated anthem proclaimed the United States “the land of the free,” Key was in fact a slaveholder from an old Maryland plantation family, and as a U.S. attorney argued several prominent cases against the abolitionist movement. He did speak out against the cruelties of the institution of slavery, but did not see abolition as the solution.
Instead, Key became a leader of the colonization movement, which advocated the relocation of black slaves to Africa and eventually resulted in the modern nation of Liberia .
Growing Popularity of 'The Star-Spangled Banner'
At first, “The Star-Spangled Banner” trailed “Yankee Doodle” and “Hail Columbia” in popularity among patriotic 19th-century tunes. But during and immediately after the Civil War , Key’s song gained a deeper meaning, as the American flag became an increasingly powerful symbol of national unity.
By the 1890s, the U.S military had adopted the song for ceremonial purposes, playing it to accompany the raising and lowering of the colors. In 1916, President Woodrow Wilson signed an executive order designating it “the national anthem of the United States.”
In 1931—more than 100 years after it was composed—Congress passed a measure declaring “The Star-Spangled Banner” as the official national anthem.
History of the National Anthem at Sporting Events
“The Star-Spangled Banner” made its sporting-event debut in September 1918, during that year’s first World Series game between the Chicago Cubs and Boston Red Sox.
In addition to the ongoing toll of World War I , a cloud of violence hung over Chicago’s Comiskey Park, as a bomb had torn apart the Chicago Federal Building just the day before. During the seventh-inning stretch, the military band on hand struck up “The Star-Spangled Banner,” and in a moving spectacle, players and fans alike fell silent and saluted the flag.
The practice soon spread across major league baseball, and into other sports, and eventually became a widely accepted pregame tradition.
While many view the playing of “The Star-Spangled Banner” before sporting events as an important patriotic ritual, over the years some athletes have chosen to protest enduring racial injustices in American society by turning their backs on the flag, refusing to stand or taking a knee while the national anthem is performed.
The Star-Spangled Banner, Smithsonian . “Star-Spangled Banner” writer had complex history on race, The Baltimore Sun . “How the national anthem—and subverting it—became a national tradition,” The Washington Post . “How the National Anthem Has Unfurled,” The New York Times . “The Song Remains the Same,” ESPN the Magazine .

HISTORY Vault: America the Story of Us
America The Story of Us is an epic 12-hour television event that tells the extraordinary story of how America was invented.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

Essay on National Symbols of India
Students are often asked to write an essay on National Symbols of India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on National Symbols of India
Introduction.
India, a diverse and culturally rich country, has several national symbols. These symbols represent the country’s identity and heritage.
National Flag
The Indian National Flag, also known as the ‘Tricolor’, has three equal horizontal bands of saffron, white, and green, with a blue Ashoka Chakra in the middle.
National Emblem
The National Emblem of India is derived from the Sarnath Lion Capital of Ashoka. It signifies power, courage, and confidence.
National Anthem and Song
The National Anthem is ‘Jana Gana Mana’ and the National Song is ‘Vande Mataram’. Both songs evoke a sense of patriotism.
National Animal, Bird, and Flower
Also check:
250 Words Essay on National Symbols of India
India, a country with rich cultural heritage and history, is home to numerous national symbols that represent its unique identity. These symbols, ranging from the national flag to the national animal, encapsulate the essence of the nation, reflecting its diversity, values, and aspirations.
The Indian National Flag, often referred to as the ‘Tricolour’, is a horizontal tricolour of saffron, white, and green, with a blue Ashoka Chakra in the center. The saffron signifies courage and sacrifice, white stands for peace and truth, while green represents prosperity. The Ashoka Chakra, a 24-spoke wheel, symbolizes the eternal wheel of law or Dharma.
The National Emblem of India is an adaptation of the Lion Capital of Ashoka at Sarnath. It comprises four Asiatic lions standing back to back, symbolizing power, courage, pride, and confidence. The emblem also features the Ashoka Chakra and a bull, a galloping horse, and a lion separated by intervening wheels.
National Animal and Bird
The Royal Bengal Tiger, known for its strength, agility, and grace, is India’s national animal, symbolizing the country’s rich wildlife and biodiversity. The Indian Peafowl, or Peacock, is the national bird, chosen for its rich religious and legendary involvement in Indian traditions.
In essence, the national symbols of India are not just mere representations but are imbued with profound philosophical and cultural significance. They serve as a reminder of the country’s vibrant history, diverse culture, and commitment to uphold the principles of justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity.
500 Words Essay on National Symbols of India
India, a diverse nation with a rich cultural heritage, is symbolized by several national symbols. These symbols, embodying the essence of India, play a crucial role in representing the country’s identity and unity. They are not merely symbols; they carry a profound meaning and historical significance.
The National Flag
India’s national flag, also known as the Tricolor or ‘Tiranga’, is a symbol of the country’s freedom. It consists of three equal horizontal bands – saffron at the top, signifying courage and sacrifice; white in the middle, representing peace and truth; and green at the bottom, symbolizing fertility, growth, and auspiciousness. The Ashoka Chakra, a 24-spoke wheel in navy blue at the center, represents the eternal wheel of law.
The National Emblem
The National Emblem of India is derived from the Lion Capital of Ashoka at Sarnath. It comprises four Asiatic lions standing back to back, symbolizing power, courage, pride, and confidence. Only three lions are visible from any angle, suggesting the hidden potential within us. The emblem also includes a wheel (Dharma Chakra), a bull, and a galloping horse, symbolizing the dynamic and steadfast spirit of India.
The National Anthem and Song
The national animal, bird, and flower.
The Royal Bengal Tiger, the national animal, symbolizes India’s wildlife wealth. The national bird, the Indian Peacock, known for its grace, joy, beauty, and love, is a representation of India’s rich avian biodiversity. The Lotus, India’s national flower, signifies purity, spirituality, and enlightenment, reflecting the core values of Indian philosophy.
The National Tree and Fruit
The Banyan tree, India’s national tree, symbolizes immortality, epitomizing the country’s strength and longevity. The Mango, the national fruit, represents the tropical climate of India. Both are deeply rooted in Indian culture and folklore, and they signify the country’s lush natural bounty.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Poetry Center

Writing a New National Anthem
This lesson continues with our writing around the election. The announcement has been made that Joe Biden will be the next President of the United States and Kamala Harris will be the next Vice President—and the first woman, Black, and Indian-American person to hold that office. Following with the reading and writing we’ve been doing about America the last few weeks, today we are going to read and consider the poem “A New National Anthem” by poet Ada Limón.
An anthem is defined as: a rousing or uplifting song identified with a particular group, body, or cause. A national anthem is a song identified with a particular country. “The Star-Spangled Banner” was written by Francis Scott Key in 1814 and added to a melody by John Stafford Smith from 1773. It was adopted as the United States national anthem on March 3, 1931.
Today, we’re going to consider what YOU want your national anthem to say. We’re going to look at the national anthem, and Ada Limón’s poem and then do some writing!
Sequence of Activities:
Step 1: Read through the lyrics of our current national anthem and answer the questions after. Also, if there are words you don’t know, circle them and ask your teachers! Write notes on the side if you'd like.
The Star-Spangled Banner
O say can you see, by the dawn’s early light, What so proudly we hail’d at the twilight’s last gleaming, Whose broad stripes and bright stars through the perilous fight O’er the ramparts we watch’d were so gallantly streaming? And the rocket’s red glare, the bombs bursting in air, Gave proof through the night that our flag was still there, O say does that star-spangled banner yet wave O’er the land of the free and the home of the brave?
On the shore dimly seen through the mists of the deep Where the foe’s haughty host in dread silence reposes, What is that which the breeze, o’er the towering steep, As it fitfully blows, half conceals, half discloses? Now it catches the gleam of the morning’s first beam, In full glory reflected now shines in the stream, ’Tis the star-spangled banner - O long may it wave O’er the land of the free and the home of the brave!
And where is that band who so vauntingly swore, That the havoc of war and the battle’s confusion A home and a Country should leave us no more? Their blood has wash’d out their foul footstep’s pollution. No refuge could save the hireling and slave From the terror of flight or the gloom of the grave, And the star-spangled banner in triumph doth wave O’er the land of the free and the home of the brave.
O thus be it ever when freemen shall stand Between their lov’d home and the war’s desolation! Blest with vict’ry and peace may the heav’n rescued land Praise the power that hath made and preserv’d us a nation! Then conquer we must, when our cause it is just, And this be our motto - “In God is our trust,” And the star-spangled banner in triumph shall wave O’er the land of the free and the home of the brave.
Response Questions:
- What are the lines that stand out to you most/why?
- Have you ever heard the other verses here that aren’t usually sung before? What do those verses tell us?
- How is this song trying to portray the United States? What is it trying to say about what the country is and stands for?
- Do you agree with how the country is represented? How or how not?
- Are there things missing about the country that should be in an anthem for the United States? Explain.
Step 2: Watch Whitney Houston singing the national anthem.
Does watching her version add anything to your understanding of or your feeling about the song? Explain/explore.
Step 3: Listen to Ada Limón read her poem “An New National Anthem.” Then print out and read the text of the poem. As you read, underline words that stand out to you and write notes next to the poem on the left about what you think she means. Then answer the questions on the following page.
Vocabulary definitions: * tenacious = not readily relinquishing a position, principle, or course of action; determined. **hireling = a person employed to undertake menial work ***sustenance = nourishment; food and drink regarded as a source of strength
Response questions:
- What is the poet’s opinion of “The Star-Spangled Banner” and how do we know (what are examples of language from her poem that tell us this)?
- What do you think she means by these lines?
"And what of the stanzas we never sing, the third that mentions ‘no refuge could save the hireling and the slave’? Perhaps the truth is that every song of this country has an unsung third stanza, something brutal snaking underneath us as we blindly sing the high notes with a beer sloshing in the stands hoping our team wins.”
- What does she like about the flag? When does she like it most?
- She uses many images throughout the poem to contribute to her meaning. What do these images mean to you?
“something brutal snaking underneath us” =
“until the song in your mouth feels like sustenance” =
“(a song) that sounds like someone’s rough fingers weaving into another’s” =
“(a song) that sounds like a match being lit in an endless cave” =
“the song that says my bones are your bones, and your bones are my bones, and isn’t that enough?” =
- Overall, what do you think she’s trying to say in this poem (there are many possible answers here)?
Step 5: LET’S WRITE! For this prompt, you have a few options. Choose one!
- Write a new national anthem for this country. Write a song that communicates what you want this country to stand for. For this writing exercise, you might try rhyming because this is something that is traditionally done in lyrics. If you want, you could first brainstorm all the things you want the country to stand for before you start writing. OR if you have an idea you can begin.
- Write about how you would approach writing a new national anthem. What would be important for you in writing a new anthem? What would you want to include? Whose voices would you want to be represented? What would it mean to redefine the anthem for the country?
Contributor:
Education level: , genre: , format: , time frame: , required materials: , lesson plan: .

10 Lines on National Anthem
National Anthem of India is sung by the people of India to evoke the history of India’s struggle for freedom. ‘Jan Gana Mana’ is the official national anthem recognized by the government of India which is played and sung on number of occasions including cultural and national events. National Anthem helps in preserving and reinforcing the strong traditional culture by spreading the message of tolerance to pluralism across the world. It also evokes the true sense of patriotism in the heart of the people making them remember the sacrifices of our great freedom fighters and leaders.
10 Lines on National Anthem in English
We are providing 10 lines, 5 lines, 20 lines, few lines and sentences on National Anthem in English for Class 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. After reading these lines you will be able to know everything about National Anthem. You can add these lines in your essays and paragraph writing in your exam as well as in the school competition.
1) “Jan Gan Man” is the National Anthem of India.
2) It was written in 1911 by Rabindra Nath Tagore.
3) It has a total of five paragraphs.
4) The original song was written in the Bengali language.
5) It was translated in Hindi by Captain Abid Ali.
6) It is sung everywhere in the nation in Hindi language.
7) We sing the national anthem in schools in morning prayers.
8) We should stand when the national anthem is sung.
9) It is sung when national flag is hoisted on national festivals.
10) It brings the feeling of patriotism and unity among us.
10 Lines and Sentences on National Anthem
1) Every nation has its own national anthem in the world.
2) The national anthem of any nation depicts its culture and history.
3) The national anthem of India is ‘Jan Gan Man’.
4) Our national anthem is a pride for every Indian.
5) It was created by noble laureate Rabindra Nath Tagore in 1911.
6) It was sung for the first time in Calcutta on 27 December 1911.
7) It was officially accepted as the national anthem of India on 24 January 1950.
8) It is always sung as a token of respect on different occasions.
9) The time taken in singing the complete national anthem is 52 seconds.
10) We must maintain silence and stand when the national anthem is sung.

5 Lines on National Anthem
1) Our National Anthem is ‘Jan Gan Man’.
2) It was written by Ravindra Nath Tagore.
3) It was originally written in Bengali.
4) It consists of 5 stanzas.
5) We sing this at every national event.
20 Lines on National Anthem
1) National Anthem of India is the patriotic musical composition which is ‘’Jana Gana Mana” composed by Rabindranath Tagore.
2) The national anthem of India was originally written in ‘sanskrit tatsama’ Bengali language.
3) “Jan Gana Mana” was officially adopted by Indian constituent assembly as national anthem on 24 th January, 1950.
4) The national anthem consists of five stanzas and the duration of playing its full version is 52 seconds.
5) The national anthem of India is sung on various occasions flag hoisting, school prayers, national festivals etc.
6) The national anthem is often sung across nation in national language which is ‘Hindi’.
7) The proper guidelines have been issued from the government and the Supreme Court of India which should be followed while singing the national anthem.
8) Every citizen of India should stand respectfully while the national anthem is being played or sung on any occasion.
9) The Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971 is the act enacted by the parliament of India to prevent the insult of national anthem.
10) Offence to the act by preventing the singing of the Jana Gana Mana is punishable and may lead to the imprisonment for a year and fine or both.
11) National Anthem of India represents the country’s unique identity to the world.
12) National Anthem acts as a symbol of unity among its citizens as it is sung by people of different communities with the same spirit of patriotism.
13) The five stanzas of ‘Jan Gana Mana’ show the country’s rich, diversified culture and colourful history.
14) The entire lyrics and music of anthem was composed by Rabindranath Tagore in 1911 and was first sung in Calcutta on 27 th December, 2011.
15) Citizens play or sing the national anthem on various occasions like during the prayer in schools, celebration of national events, sports meet etc.
16) ‘Jana Gana Mana’ strengthens the idea of unity in diversity as people from different communities sing the anthem together with full of passion towards nation.
17) In 2016, Supreme Court made the playing of national anthem mandatory in theatres before every movie in order to instil the patriotism among citizens.
18) On cultural occasions, national anthem is played after hoisting ceremony of national flag.
19) National anthem is played before and after the arrival of President or Governor from a formal ceremony.
20) National anthem is also played during the presentation of regimental colours of Indian army.
‘Jana Gana Mana’ appeals greatly to the people from various sections of society by evoking patriotic emotions and bringing a sense of pride and honor. Whenever the national anthem is played live we should stand attentively in honor to pay respect to the freedom fighters who have sacrificed their lives for the nation.
Related Posts
10 lines on mahatma gandhi, 10 lines on patriotism, 10 lines on nationalism, 10 lines on national flag of india, 10 lines on importance of national flag, 10 lines on importance of national festivals of india, 10 lines on national festivals of india, 10 lines on national festivals celebration, 10 lines on a.p.j. abdul kalam, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
The Economic Times daily newspaper is available online now.
‘jana gana mana’: history & significance of india’s national anthem explained.
Here is everything you want to know about India’s national anthem.

Artificial Intelligence(AI)
Java Programming with ChatGPT: Learn using Generative AI
By - Metla Sudha Sekhar, Developer and Lead Instructor

Basics of Generative AI : Unveiling Tomorrow's Innovations

Generative AI for Dynamic Java Web Applications with ChatGPT

Mastering C++ Fundamentals with Generative AI: A Hands-On

Master in Python Language Quickly Using the ChatGPT Open AI

Office Productivity
Zero to Hero in Microsoft Excel: Complete Excel guide 2024

Vastu Shastra Course
By - Sachenkumar Rai, Vastu Shashtri

Data Science
SQL for Data Science along with Data Analytics and Data Visualization

Web Development
A Comprehensive ASP.NET Core MVC 6 Project Guide for 2024

Mastering Microsoft Office: Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and 365

Digital marketing - Wordpress Website Development
By - Shraddha Somani, Digital Marketing Trainer, Consultant, Strategiest and Subject Matter expert

Financial Literacy - TDS, Budget, Income Tax Act, GST, Indirect tax
By - CA Rahul Gupta, CA with 10+ years of domain experience, trainer

Business Storytelling Masterclass
By - Ameen Haque, Founder of Storywallahs
Future of Marketing & Branding Masterclass
By - Dr. David Aaker, Professor at Haas School of Business

HR & People Management
Human Potential and the Future of Employment
By - Lynda Gratton, Co-chair of the World Economic Forum Council on Work, Wages and Job Creation, Professor of Management Practice

ESG and Business Sustainability Strategy
By - Vipul Arora, Partner, ESG & Climate Solutions at Sattva Consulting Author I Speaker I Thought Leader

Financial Reporting and Analytics
By - Dr. C.P. Gupta, Professor: Department of Finance and Business Economics, University of Delhi

India@75: Significance of Tricolour in India's national flag explained

75th Independence Day: The significance of Ashoka Chakra in India's Tricolour

How well do you know India? This Independence Day weekend, here are 10 museums to test your GK
Read More News on
(Catch all the Business News , Breaking News , Budget 2024 Events and Latest News Updates on The Economic Times .)
Subscribe to The Economic Times Prime and read the ET ePaper online.

The hidden truth of SME IPOs, and an inversion you’ve never seen before

Why SIP investing for 20 years may not have a multiplier effect on your wealth

In the GenAI vs. SaaS battle, Klarna fires shots

Why Vodafone Group’s status as the promoter of Indus Towers is in the spotlight

Is Air India like rescue an option to save MTNL?

Indian equities: How OPEC+ output, Fed, and earnings-taper blur returns outlook
Find this comment offensive?
Choose your reason below and click on the Report button. This will alert our moderators to take action
Reason for reporting:
Your Reason has been Reported to the admin.

To post this comment you must
Log In/Connect with:
Fill in your details:
Will be displayed
Will not be displayed
Share this Comment:
Uh-oh this is an exclusive story available for selected readers only..
Worry not. You’re just a step away.

Prime Account Detected!
It seems like you're already an ETPrime member with
Login using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits
Log out of your current logged-in account and log in again using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits.
To read full story, subscribe to ET Prime
₹34 per week
Billed annually at ₹2499 ₹1749
Super Saver Sale - Flat 30% Off
On ET Prime Membership
Unlock this story and enjoy all members-only benefits.
Offer Exclusively For You
Save up to Rs. 700/-
ON ET PRIME MEMBERSHIP
Get 1 Year Free
With 1 and 2-Year ET prime membership
Get Flat 40% Off
Then ₹ 1749 for 1 year
ET Prime at ₹ 49 for 1 month
Freedom Offer
Get flat 20% off on ETPrime
90 Days Prime access worth Rs999 unlocked for you

Exclusive Economic Times Stories, Editorials & Expert opinion across 20+ sectors
Stock analysis. Market Research. Industry Trends on 4000+ Stocks
Get 1 Year Complimentary Subscription of TOI+ worth Rs.799/-
Stories you might be interested in
24/7 writing help on your phone
To install StudyMoose App tap and then “Add to Home Screen”

National Anthem - Free Essay Examples and Topic Ideas
A national anthem is a patriotic song or hymn that represents a country, its people and its values. It is considered as the symbol of the country’s identity and unity. A national anthem is often played during important national events and ceremonies, such as official state functions, sporting events, and military events. The words and the tune of the national anthem often embody the country’s history, culture, and aspirations, and are meant to inspire its citizens to be proud of their country and protect its sovereignty.
- 📘 Free essay examples for your ideas about National Anthem
- 🏆 Best Essay Topics on National Anthem
- ⚡ Simple & National Anthem Easy Topics
- 🎓 Good Research Topics about National Anthem
- ❓ Questions and Answers
Essay examples
Essay topic.
Save to my list
Remove from my list
- Is There a Filipino Identity?
- Julio Nakpil
- Lana Del Rey
- Nothing But the Truth
- What Does It Mean to be Free?
- Lawrence’s Presentation of Elizabeth Bates in Odour of Chrysanthemums
- Reflection on a Book The Chrysanthemum and the Sword
- Poetic Techniques in Kevin Gilbert’s “The New True Anthem”
- Kneeling During the National Anthem: An Opinion Piece
- The ’59 Sound by The Gaslight Anthem
- “Invictus” by William E. Henley and “Anthem“ by Ayn Rand
- Customs and Curtiousies
- The Role of Women in Nation Building
- A Football Match
- What Patriotism means to me?
- The Contradiction in the Japanese National Anthem and Its Influence on Papa in Jeanne Wakatsuki Houston’s Farewell to Manzanar
- Patriotism and National Pride
- National Football League (NFL)
FAQ about National Anthem
👋 Hi! I’m your smart assistant Amy!
Don’t know where to start? Type your requirements and I’ll connect you to an academic expert within 3 minutes.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Essay On Rabindranath Tagore | Essay On My Favourite Poet Rabindranath Tagore in English for Students and Children
February 12, 2024 by Veerendra
Essay on Rabindranath Tagore: The National Anthem that we sing with such pride as written by Rabindranath Tagore, who was one of the most significant men and nationalists in India. He was a poet as well as a writer and had won the Nobel Prize for his piece known as “Gitanjali.” His writings are still studied by students all over the world. We have compiled some long and short essays for the use of the readers.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on Rabindranath Tagore in English Language for Kids and Children
Given below is an extended essay of approximately 400-500 words and is for the students of standards 7-10 and a short piece of nearly 100-150 words for the students of standard 1-6.
Essay On Rabindranath Tagore is for the use of students in classes 7,8,9 and 10.
Long Essay on Rabindranath Tagore in English 500 words
Rabindranath Tagore is the Bard of Bengal and is hailed as one of the most prominent Indian Poets. Tagore’s intense contribution to the world of Literature earned him the prestigious Nobel Prize in Literature. His verses and proses are considered unique in their way that the readers can relate with their day to day lives.
Tagore was born in an elite family of Calcutta and was the youngest of the thirteen siblings. He was not the brightest of student during his school life, but there was always a creative spark in him, which made formal learning difficult for him, and he detested the concept of classroom schooling.
He received great classical music lessons from professional musicians, who were sent by his father. Tagore’s family had an educational bent of mind, which made him stand out of the rest.
His phenomenal talent in portraying the real state of Bengal attracted the mass. In his stories, he tried to reflect what he saw and felt instead of writing farfetched stories. He had used his writings as a weapon to break free from the shackles of the traditional society and helped to construct a modern and logical society. His work is liked and appreciated all over the world and has been translated into innumerable languages.
“Manasi” was one of his best works, which perfectly showcased who genius a writer he was. Many of his poems were a satire to the society and was written t. o raise voice against the dominating British rule. His works portray the humble life and miseries simultaneously. His genuineness was shown by the poignancy and poise writings.
Tagore was quite vocal about his views on different political movements. He was more in support of the intellectual upliftment, and his views often conflicted with Mahatma Gandhi and other eminent political leaders. Tagore was not in favor of the Swadeshi Movement, and Globalisation was something that had a significant impact on him even during the 19th century. He was so patriotic that he had returned the Honorary Knighthood award as a protesting act against the Jallianwala Bagh Tragedy.
You can read more Famous Personalities/People’s Essay writings over here.
Tagore was credited to have written the National Anthem of India. He had also written the National Anthem of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, Aamar Shonar Bangla, and Sri Lanka Matha, respectively. He first wrote the Sri Lanka Matha and then was translated to Sinhala by his student, Ananda Samarakoon.
The dissatisfaction of the traditional education system in England inspired him to start the “Vishwabharati University” in Santiniketan, which was initially a school that offers a friendly environment for the students to study and explore their creativity. The ending of the legend’s life was painful. He was infested by 2 elongated attacks of sickness and was affected by an exhausting disorder.
Read More: Mahatma Gandhi Essay In English 150 Words
Short Essay on Rabindranath Tagore in English 250 words
Students in classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 can use this Essay On Rabindranath Tagore.
Rabindranath Tagore was a great Bengali poet who had upgraded Bengali Literature in commendable ways. He was the youngest son of the leader of Brahmo Samaj, Debendranath Tagore. Rabindranath Tagore wrote the National Anthem of India and two other countries. He had written famous Dramas like Visarjan and Valmiki Pratibha. Rabindranath Tagore’s short stories are the most appreciated ones, out of which The Kabuliwala is very renowned. He received the Nobel Prize for his work “Gitanjali: the song offerings.” He passed away on 8th august 1941 when the world mourned for him.
Read More: Essay On Rabindranath Tagore
10 Lines Essay on Rabindranath Tagore in English 150 words
- Rabindranath Tagore was born in the Tagore family in Mansion of Jorasanko, Calcutta, on 7th May 1861.
- Tagore was an extraordinary writer who was determined to bring concrete changes in society.
- During the freedom struggle, his ideologies did not match with Gandhi and many famous patriots.
- He had first started the ceremony of tying the “yellow thread” to promote the idea of the fraternity during the Partition of Bengal.
- Tagore was a true patriot; he had written poems and songs, which was a powerful weapon to raise voice against the British.
- He was an incredible painter, artist, humanist, nationalist, author, rationalist, writer, philanthropist, and an eminent academician.
- He wrote the National Anthem of India, which is Jana Gana Mana, Bangladesh, which is Aamar Shonar Bangla, and Sri Lanka which is Sri Lanka Matha.
- He won the Nobel Prize in Literature in the year 1913 for his much-celebrated work, “Gitanjali: the Song Offerings.”
- He was deeply disheartened about the traditional education system, which inspired him to build up an institution unlike others, and this is how the world-famous “Viswabharati University” was formed.
- Tagore died on 8th August 1941, leaving behind his dramatic works and ideologies, which are to date studied by students all around the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions Essay On Rabindranath Tagore
Question 1. What was Rabindranath Tagore famous for?
Answer: Rabindranath Tagore was famous for his paintings, short stories, novels, and poems. Tagore was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1913 for Literature.
Question 2. In which year was Rabindranath Tagore born?
Answer: The Bard of Bengal, Rabindranath Tagore, was born on 7th May 1861, Calcutta.
Question 3. What are Rabindranath Tagore’s most famous short stories?
Answer: Some of Tagore’s most celebrated short stories are the Kabuliwala, the postmaster, etc.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
What Does Your Country’s National Anthem Mean to You?
Does the song reflect the beliefs you have about your country? How might it be changed to include more perspectives and experiences?

By Nicole Daniels
Students in U.S. high schools can get free digital access to The New York Times until Sept. 1, 2021.
In the United States, the national anthem, “The Star-Spangled Banner” by Francis Scott Key, is often performed before sporting events, school functions and other important events. Think about the last time you attended or watched an event on TV where the anthem was played. How did you feel hearing the song? Were you moved by the performance and the lyrics? Did you stand or remove your hat? Or did you feel uncomfortable or unaffected by the song?
If you live in another country, when is your national anthem usually played? How do you feel when you hear it?
Recently, after the Dallas Mavericks had stopped playing it through their first 13 preseason and regular-season home games, the N.B.A. began requiring teams to play the national anthem before games. It was an abrupt reversal of an earlier hands-off approach. In “N.B.A. Says Teams Must Play the National Anthem ,” Marc Stein explains:
Cuban told The New York Times on Wednesday that the Mavericks would follow the policy immediately and play the anthem before that night’s nationally televised home game against the Atlanta Hawks at American Airlines Center. “We are good with it,” Cuban said. Most players and coaches regularly knelt during the national anthem to protest social injustice while the league played out the last three months of the 2019-20 season at Walt Disney World near Orlando, Fla., last summer. Adam Silver, the N.B.A. commissioner, said in December that the league did not intend to enforce its rule that players stand for the national anthem. The league’s 29 teams apart from Dallas had mostly played recorded versions of the anthem before games. “I recognize that this is a very emotional issue on both sides of the equation in America right now, and I think it calls for real engagement rather than rule enforcement,” Silver said in December. In a statement released through the Mavericks, Cuban said: “We respect and always have respected the passion people have for the anthem and our country. But we also loudly hear the voices of those who feel that the anthem does not represent them. We feel that their voices need to be respected and heard, because they have not been. “Going forward, our hope is that people will take the same passion they have for this issue and apply the same amount of energy to listen to those who feel differently from them.”
Why do some feel that “The Star-Spangled Banner” does not represent them? In “ African-Americans and the Strains of the National Anthem, ” an Opinion essay from 2018 written in response to the N.F.L. player Colin Kaepernick’s original anthem protest, Brent Staples writes:
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
History | Updated: July 1, 2024 | Originally Published: March 1, 2007
The Real Story Behind the Star-Spangled Banner, the Flag That Inspired the National Anthem
How the flag that flew proudly over Fort McHenry in September 1814 made its way to the Smithsonian
:focal(1000x810:1001x811)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/cb/e8/cbe8de16-fcb4-47aa-9f94-1d061ed3c81c/sia-sia_000095_b31a_f25_002.jpg)
Cate Lineberry ; Updated by Meilan Solly
On a rainy September 13, 1814, British warships sent a downpour of shells and rockets onto Fort McHenry in Baltimore Harbor, relentlessly pounding the American fort for 25 hours. The bombardment, known as the Battle of Baltimore , came only weeks after British forces attacked Washington, D.C., burning the United States Capitol, the Treasury and the White House (then known as the President’s House). It was another chapter in the ongoing War of 1812 .
A week earlier, Francis Scott Key , a 35-year-old American lawyer, had boarded the flagship of the British fleet on the Chesapeake Bay in hopes of persuading the enemy to release the physician William Beanes, a friend who had recently been arrested. Key’s tactics were successful, but because he and his companions had gained knowledge of the impending attack on Baltimore, the British did not yet let them go. Allowed to return to their own vessel, the Americans remained under heavy scrutiny. On September 13, Key and Beanes watched as the barrage of Fort McHenry began some eight miles away.
“It seemed as though mother earth had opened and was vomiting shot and shell in a sheet of fire and brimstone,” Key later wrote . But when darkness arrived, he saw only red erupting in the night sky. Given the scale of the attack, he was certain the British would win. The hours passed slowly, but in the clearing smoke of “the dawn’s early light” on September 14, he saw the American flag —not the British Union Jack—flying over the fort, announcing an American victory.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/3c/f4/3cf47ce4-5f2e-49a7-88a3-8b8192a26b3f/ft_henry_bombardement_1814.jpg)
Key put his thoughts on paper while still on board the ship, setting his words to the tune of a popular English song. His brother-in-law, commander of a militia at Fort McHenry, read Key’s work and had it distributed under the name “Defense of Fort M’Henry.” The Baltimore Patriot newspaper soon published it, and within weeks, Key’s poem, now called “The Star-Spangled Banner,” appeared in print across the country, immortalizing his words and forever naming the flag it celebrated. The song remained popular throughout the 19th century, emerging as a symbol of unity during the Civil War, but only became the U.S.’s official national anthem in 1931.
The flag that inspired Key’s composition still survives today, though it’s fragile and worn by time. First lent to the Smithsonian Institution in 1907, this iconic artifact is now on view in its own state-of-the-art gallery at the National Museum of American History (NMAH).
“The Star-Spangled Banner is a symbol of American history that ranks with the Statue of Liberty and the Charters of Freedom,” said Brent D. Glass , the museum’s then-director, in 2007. “The fact that it [was] entrusted to the National Museum of American History is an honor.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/a5/1a/a51aa79b-1c1c-4470-b1e2-af07014a2938/nmah-ahb2014q000002.jpg)
The flag’s beginnings
The flag’s history starts not with Key, but rather a year earlier, with Major George Armistead , the commander of Fort McHenry. Knowing that his fort was a likely British target, Armistead, in the summer of 1813, told the commander of Baltimore’s defenses that he needed a flag—a big one: “We, sir, are ready at Fort McHenry to defend Baltimore against invading by the enemy … except that we have no suitable ensign to display over the Star Fort, and it is my desire to have a flag so large that the British will have no difficulty seeing it from a distance.”
Armistead soon hired a 37-year-old widow and professional flagmaker, Mary Young Pickersgill , to make a 30-by-42-foot garrison flag with 15 stars and 15 stripes, one for each of the then-15 states. Over the next six or so weeks, Pickersgill, her daughter, two of her nieces, a 13-year-old indentured servant and possibly her mother used 300 yards of English wool bunting to sew the flag. They made the stars, each measuring two feet in diameter, from cotton—a luxury item at the time. Initially, the group worked in Pickersgill’s home (now a private museum known as the Star-Spangled Banner Flag House ), but as their work progressed, they needed more room, so they moved to a brewery across the street. On August 19, 1813, the flag was delivered to Fort McHenry.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/82/a6/82a6b089-7b44-4deb-b8e3-3824fdda3b1d/1280px-fort_mchenry_flag.jpg)
For making the Star-Spangled Banner, Pickersgill was paid $405.90 (almost $8,000 today ). She received another $168.54 (around $3,300 today ) for sewing a smaller, 17-by-25-foot storm flag, likely using the same design. It was this storm flag—not the garrison flag now known as the Star-Spangled Banner—that actually flew during the battle. The garrison flag, according to eyewitness accounts, wasn’t raised until the morning of September 14, 1814.
Armistead remained in command of Fort McHenry for the rest of his short life. Historians are unsure how the Armistead family came into possession of the flag, but upon the military officer’s death in 1818, his wife, Louisa Hughes Armistead, inherited it. She likely sewed a red upside-down “V” (or perhaps the start of the letter “A,” for Armistead) onto the flag. Louisa is also thought to have begun the tradition of giving away pieces of the flag to honor her husband’s memory, as well as the memories of the soldiers who defended the fort under his command.
When Louisa died in 1861, she passed the flag down to her daughter, Georgiana Armistead Appleton , over the legal objections of her son. “Georgiana was the only child born at the fort, and she was named for her father,” said Suzanne Thomassen-Krauss , then a textile conservator at NMAH, in 2007. “Louisa wanted Georgiana to have it.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/69/e2/69e2d4b6-b130-41c3-bdaa-2d71c011dbe2/placing_the_stars.jpg)
The missing pieces
In 1873, Appleton lent the flag to George Preble , a flag historian who had previously thought the artifact was lost. That same year, Preble had the first known photograph of the flag taken at the Boston Navy Yard. He then exhibited it at the New England Historic Genealogical Society, where it remained until 1876.
While the Star-Spangled Banner was under Preble’s care, Appleton allowed him to give away pieces of the flag as he saw fit. She, too, had given away cuttings of the flag to other Armistead descendants, as well as family friends. Appleton once noted , “Had we given all that we have been importuned for, little would be left to show.” This family tradition continued through 1880, when Armistead’s grandson gave away the last documented piece, according to Thomassen-Krauss.
Several of these cuttings from the Star-Spangled Banner have been located over the years, including about a dozen owned by NMAH . “We’re aware of at least a dozen more that exist in other museums and private collections,” said curator Kathleen Kendrick in 2007.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/0d/f3/0df3e15c-e3b0-4e21-859e-28038dfef12d/nmah-jn2014-3216.jpg)
But a missing 15th star has never been found. “There’s a legend that the star was buried with one of the soldiers from Fort McHenry; another says that it was given to Abraham Lincoln,” Kendrick explained. “But no real evidence has surfaced to support these stories, and the true fate of the star remains one of the Smithsonian’s great unsolved mysteries.”
Preserving a national icon at the Smithsonian
After Appleton’s death in 1878, the flag passed to her son Eben Appleton , who lent it to Baltimore for that city’s 1880 sesquicentennial celebration. It remained in a safe deposit vault in New York City until 1907, when Eben lent it to the Smithsonian. Five years later, he made the gift permanent , saying he wanted the flag to belong “to that Institution in the country where it could be conveniently seen by the public and where it would be well cared for.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/33/73/3373c293-9fc5-4dcb-bd70-d5c939f51bd0/repair_work_on_star-spangled_banner.jpg)
When the flag arrived at the Smithsonian, it was smaller, just 30 by 34 feet, damaged from years of use at the fort and the removal of pieces as souvenirs. Recognizing the need for repairs, the Smithsonian hired Amelia Fowler , an embroidery teacher and well-known flag preserver, to replace the canvas backing that had been added in 1873. While working for the United States Naval Academy , Fowler had patented a method of supporting fragile flags with a linen backing that required a honeycomb pattern of stitches. With the help of ten needlewomen, Fowler spent eight weeks in 1914 restoring the flag, receiving $1,243 (around $39,000 today ) for the materials and work.
For the next 50 years, apart from a brief move during World War II, the Star-Spangled Banner was displayed in what is now the Arts and Industries Building . The glass case holding the flag wasn’t long enough to show the entire piece of fabric, so its lower half was folded up.
It was only in 1964 that the public was able to view the flag in its entirety. That year, the flag became the centerpiece of the new National Museum of History and Technology (now NMAH), which had ample space to allow the national treasure to hang freely. The Star-Spangled Banner remained in Flag Hall until 1998, when it taken down to undergo extensive conservation .

Started in 1996, the Star-Spangled Banner preservation project was planned with the help of historians, conservators, curators, engineers and organic scientists. Conservators began working on the flag in 1999, when construction of a conservation lab at the museum was completed. Over the next several years, they clipped 1.7 million stitches from the flag to remove the linen backing that had been added in 1914, lifted debris using dry cosmetic sponges and brushed the flag with an acetone-water mixture to remove soils embedded in fibers. Finally, they added a sheer polyester backing to help support the flag.
“Our goal was to extend [the flag’s] usable lifetime,” said Thomassen-Krauss. The intent was never to make the flag look as it did when it first flew over Fort McHenry. “We didn’t want to change any of the history written on the artifact by stains and soil,” the conservator added. “Those marks tell the flag’s story.”
While the conservators worked, the public looked on. By 2006, when NMAH closed for a two-year renovation , more than 12 million people had peered into the museum’s glass conservation lab to observe the process.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/6d/4f/6d4fb649-b5d3-49af-84a6-6509f99a906e/family_viewing_ssb_in_new_gallery_0.jpg)
NMAH reopened in November 2008, with the Star-Spangled Banner now displayed in its own climate-controlled gallery. As Glass said ahead of the reopening, “The survival of this flag for nearly 200 years is a visible testimony to the strength and perseverance of this nation, and we hope that it will inspire many more generations to come.”
Reflecting on the Star-Spangled Banner’s significance, Kendrick said:
The Star-Spangled Banner resonates with people in different ways, for different reasons. It’s exciting to realize that you’re looking at the very same flag that Francis Scott Key saw on that September morning in 1814. But the Star-Spangled Banner is more than an artifact—it’s also a national symbol. It evokes powerful emotions and ideas about what it means to be an American.
Get the latest History stories in your inbox?
Click to visit our Privacy Statement .
Cate Lineberry | READ MORE
Cate Lineberry was an associate web editor at Smithsonian magazine.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/mellon.png)
Meilan Solly | | READ MORE
Meilan Solly is Smithsonian magazine's senior associate digital editor, history.


National Anthem of India – Jana Gana Mana, Meaning, History and Facts

Table of Contents
National Anthem of India Jana Gana Mana, composed originally in Bengali by Rabindranath Tagore, was adopted in its Hindi version by the Constituent Assembly as the National Anthem of India on 24 January. It is played on occasions of national importance.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
The National Anthem of India is a song sung by the people of India on various national occasions to pay respect to the nation. National Anthem of India starts from “ Jana Gana Mana Adhinayaka Jaya He ” and ends at “ Jaya He, Jaya He, Jaya He, Jaya Jaya Jaya Jaya He ”. The national anthem of India is a very short composition consisting of only fifty-two words. It is very simple and easy to remember. It is sung in the key of E flat major. It has a duration of about fifty-two seconds. The national anthem is very inspiring and it instills a sense of patriotism among the people.

Writer of National Anthem of India
The original national anthem was written by Rabindranath Tagore which was then translated into Hindi and Urdu by Abid Ali. The conversion of original song into the Hindi version by Ali was little different. The full version of the national anthem takes fifty-two seconds to sing whereas the shortened version (having first and last lines) takes 20 seconds to sing.
Translation of Jana Gana Mana into English Version
It was again translated into English version by Tagore. The full version of National Anthem is sung using the orchestral/choral adaptation (made by English composer, Herbert Murrill on request of Nehru). Another song (Amar Sonar Bangla) written by Tagore has been selected as the national anthem of Bangladesh.

History and Importance of Jana Gana Mana
National anthem (Jana-gana-mana) was originally composed by Rabindranath Tagore in Bengali. The Hindi version was adopted in 1950 on 24th of January by the Constituent Assembly. The lyrics and music of the national anthem was given by Rabindranath Tagore in 1911. It was first sung in Calcutta in the meeting of Indian National Congress on 27th of December in 1911.
Full version of national anthem was translated to English from Bengali and music was set in Madanapalle (a city in Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh state).
Importance: National Anthem of a country is the pride of nation and induces a sense of patriotism, courage and nationalism amongst its citizens. It is a way to show respect towards the country and spread the message of unity and harmony. It is also a symbol of freedom, sovereignty and the rich cultural history of the nation. In schools helps to nurture the children with the positive vibes of patriotism since childhood and inculcate the feeling of respect and pride towards their country.
Singing of National Anthem is also a way to pay tribute to our great freedom fighters who fought for the country, and it also binds the whole nation with a single thread of unity and nationalism. The National Anthem of India is the praise of our motherland which helps us to feel proud and hopeful about our country. It showcases a distinct identity of our country’s history, culture, tradition, its people and regions.
National Anthem of India adopted On
The Indian national anthem, Jana Gana Mana, was officially adopted on January 24, 1950. This was the same day that the Constitution of India came into effect, and the country was declared a republic. The national anthem was chosen by the Constituent Assembly of India after considering several songs and ultimately selecting Rabindranath Tagore’s composition.
Lyrics of Jana Gana Mana Of India
The anthem is a poetic representation of India’s diverse heritage and shared destiny. The anthem’s lyrics have a profound and symbolic meaning, celebrating the diverse cultural and geographical aspects of India. Here are the lyrics of National Anthem Of India:
Jana Gana Mana Adhinayaka Jaya Hey, Bharat Bhagya Vidhata Punjab Sindh Gujarat Maratha, Dravida Utkala Banga Vindhya Himachal Yamuna Ganga, Uchchala Jaladhi Taranga Tava Shubha Namey Jage, Tava Shubha Ashish Mage Gahe Tava Jaya Gatha Jana Gana Mangala Dayaka, Jaya Hey Bharat Bhagya Vidhata Jaya Hey Jaya Hey Jaya Hey Jaya Jaya Jaya Jaya Hey.
Also Read Related Articles

Full Version National Anthem of India
Jana-gana-mana-adhinayaka, jaya he Bharata-bhagya-vidhata Panjaba-Sindha-Gujrata-Maharata- Dravida-Utkala-Vanga Vindhya-Himachala-Yamuna-Ganga Uchhala-Jaladhi-taranga Tava shubha name jage
Tava shubha ashisha mage Gave tava jaya-gatha Jana-gana-mangala-dayaka jaya he Bharata-bhagya-vidhata. Jaya he! Jaya he! Jaya he! Jaya jaya jaya, jaya he!
English Translation
Thou art the ruler of the minds of all people, Thou Dispenser of India’s destiny. Thy name rouses the hearts of Punjab, Sind, Gujrat and Maratha, Of Dravid, Orissa and Bengal.
It echoes in the hills of the Vindhyas and Himalayas, Mingles in the music of Jamna and Ganges and is chanted by the waves of the Indian sea. They pray for Thy blessings and sing thy praise. The saving of all people waits in thy hand, Thou Dispenser of India’s destiny, Victory, Victory, Victory to Thee.
Short Version
Short version of the national anthem consists of only first and last lines. It takes approximately 20 seconds to sing. It is sung on various national occasions.
“Jana-gana-mana-adhinayaka jaya he
Bharata-bhagya-vidhata.
Jaya he, Jaya he, Jaya he,
jaya jaya jaya, jaya he.”
Meaning of National Anthem of India
The original version of the national anthem was translated to the English language and edited in 1950 to make some changes. ‘Sindh’ was replaced by ‘Sindhu’ as ‘Sindh’ was allocated to Pakistan after partition. The English meaning of the national anthem is as follows:
“Thou art the ruler of the minds of all people,
Dispenser of India’s destiny.
Thy name rouses the hearts of Punjab, Sindhu,
Gujarat and Maratha,
Of the Dravida and Odisha and Bengal;
It echoes in the hills of the Vindhyas and Himalayas,
mingles in the music of Yamuna and Ganges and is
chanted by the waves of the Indian Sea.
They pray for thy blessings and sing thy praise.
The saving of all people waits in thy hand,
Thou dispenser of India’s destiny.
Victory, victory, victory to thee.”
Also Read: Difference between National Anthem and Song
What is Code of Conduct of National Anthem?
The code of conduct is the set of rules and regulations which should be followed while singing or playing the national anthem. There are some instructions which are issued from time to time by the government of India regarding the correct version of the anthem. The set timing of the national anthem to be sung is 52 seconds. Some of the rules and regulations have been made in order to pay respect and honour to the national anthem.
A law (The Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971) has been implemented by the Indian government to prevent the intentional singing of National Anthem or insulting in any way shall be punished with the imprisonment of term (may be extended to three years) including fine. Following are the rules and regulations which shall be followed while playing or singing full version of the anthem:
It can be sung when National Salute, parade etc., is performed at some ceremonial occasions and formal State functions (organized by the government or public) in the presence of President, Governor, Lieutenant Governor etc. It can be sung before and after President’s addresses to the Nation and arrival of Governor or Lieutenant Governor. When presentation of regimental colours and hoisting of colors in Navy takes place. When special orders are issued by Indian Government on any occasion. Generally it is not played for Prime Minister however at some special occasions it may be played. When it is played by band, it should be preceded by roll of drums or when played to perform National Salute by a guard the drum roll duration must be 7 paces in slow march. First drum roll should be started slowly and go as loud as possible and again decrease to normal. When National Flag hoisting takes place on any cultural occasions. It can be sung in the schools in the morning before starting the day’s work by the students but proper manners should be maintained by the school authorities. All the audience must stand up and give attention while national anthem is sung or played.
Also Read: Republic Day Facts
Why theatres stopped playing the National Anthem in 1975?
Earlier to 1975, there was a custom to play the national anthem in the theatres after the film. However, it was later removed because of the disrespect of National Anthem by the people as they were not standing up and giving proper attention.
Again Supreme Court of India, on 30th November 2016 made it mandatory to play National Anthem in movie theatres before the screening of movies to instill the sense of patriotism among people. However due to many controversies and violent incidents arising after the order, Supreme Court, on 09th January 2018, reversed the order of making it mandatory to play National Anthem in movie theaters.
Related Information:
- Independence Day
- Republic Day
- National Song of India
FAQs on National Anthem of India
What is the full national anthem.
The full National Anthem of India is 'Jana Gana Mana,' consisting of five stanzas.
What is the main purpose of the National Anthem?
The main purpose of the National Anthem is to express unity and pride in the nation.
How many lines are in the National Anthem of India?
The National Anthem of India, 'Jana Gana Mana,' has 5 stanzas with multiple lines in each.
Who wrote the National Anthem in India?
The National Anthem of India, 'Jana Gana Mana,' was written by Rabindranath Tagore.
What is India's national song?
India's national song is 'Vande Mataram,' written by Bankim Chandra Chatterjee.
Is Jana Gana Mana in Sanskrit or Bengali?
'Jana Gana Mana' was originally written in Bengali.
Is the Indian National Anthem written in Sanskrit?
No, the Indian National Anthem is written in Bengali, not Sanskrit.
Who translated the National Anthem to Hindi?
The National Anthem was not translated; it was written in Bengali but adapted to Hindi pronunciation.
Who is the first writer of the National Anthem?
Rabindranath Tagore is the first and only writer of the Indian National Anthem.
Who sang Jana Gana Mana first?
'Jana Gana Mana' was first sung by a group of students in 1911 at the Indian National Congress session.
Which anthem is written by Rabindranath Tagore?
Rabindranath Tagore wrote the Indian National Anthem, 'Jana Gana Mana.'
Related content

Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Select your Course
Please select class.
- Social Sciences
- Secondary School
Essay on national anthem of india in english

New questions in Social Sciences

- About Ayn Rand
- Novels & Works
- Newsletter Sign Up
Anthem Essay Contest
Students > Essay Contests > Anthem
✓ Open to all middle & high school students worldwide, ages 13 and older.
May 31, 2024
Entry Deadline
Book Length
Interested in participating?
Fill out the contact form below, and we’ll email you with more information about this year’s contest—including instructions on how to enter.
Thank you for signing up!
We’ll email you more information about this year’s contest—including instructions on how to enter. In the meantime, please let us know at [email protected] if you have any questions. We’re happy to help.

What is Anthem?
Anthem is Ayn Rand’s classic tale of a dystopian future of the great “We”—a world that deprives individuals of a name or independence.
In all that was left of humanity there was only one man who dared to think, seek, and love. He lived in the dark ages of the future. In a loveless world, he dared to love the woman of his choice. In an age that had lost all trace of science and civilization, he had the courage to seek and find knowledge. But these were not the crimes for which he would be hunted. He was marked for death because he had committed the unpardonable sin: He had stood forth from the mindless human herd. He was a man alone. He had rediscovered the lost and holy word—I.
Improve your ability to write and think effectively. This contest will require you to reflect on philosophic themes, form your own opinion, and argue a thesis with evidence and clarity.
Test yourself against talented students from around the world and the high grading standards of our faculty. On average, only the top 1-3% of essays are awarded prizes each year.
Win cash prizes among five placement categories. This is an excellent way to earn money for college and higher education. We place no restrictions on how the money is spent by recipients.
Choose Your Essay Topic
Select one of the following three prompts about Anthem and write an essay in response to it.
Essays must be written in English only and between 600 and 1,200 words in length, double-spaced.
Questions? Write to us at [email protected] .
Master Our Grading Standards
Essays are judged on whether the student is able to justify and argue for his or her view, not on whether the Institute agrees with the view the student expresses.
Our graders look for writing that is clear, articulate, and logically organized. Essays should stay on topic, address all parts of the selected prompt, and interrelate the ideas and events in the novel.
Winning essays must demonstrate an outstanding grasp of the philosophic meaning of Anthem .
Organization
Understanding, contest timeline, discover the power of anthem.
The main character, Equality 7-2521, tells us he is a sinner and criminal. But what crimes has he committed? Being alone, writing, having personal preferences. He is “cursed” with an active, questioning mind in a society where every institution aims to crush independence and instill obedience to the authority of the collective.
Intelligent and inquisitive, Equality 7-2521 longs to become a scientist and devote his life to discovery and invention. Instead, he is beaten by his teachers and assigned the life work of street sweeper. When, against all odds, he rediscovers the secret power of a lost relic from the ancient past, he must confront the full reality of his society’s ideals.
Learn more and request a free digital copy of the book today.

Learn from Past Winners
Curious to know what makes for a winning essay in the Anthem contest? Check out some of the essays written by our most recent grand-prize winners.
To varying degrees, they all display an excellent grasp of the philosophic meaning of Anthem .
See the full list of winners from our most recent contest here .
Srilekha Mamidala
11th grade student
Garnet Valley High School
Glen Mills, Pennsylvania
United States
9th grade student
Busan Foreign School
South Korea

Jungwoo Yoo
Global Vision Christian School
Mungyeong-Si, Gyeongsangbuk-do

Ashley Yuen
Irvine High School
Irvine, California

Belmont High School
Belmont, Massachusetts

Katrice Wasgatt
10th grade student
Towle Institute
Hockessin, Delaware

Improve Your Writing Skills
Other than endorsing perfect punctuation and grammar in English, the Ayn Rand Institute offers no advice or feedback for essays submitted to its contests. However, we do recommend the following resources as ways to improve the content of your essays.
Writing: A Mini-Course

Sign Up for Contest Updates!
Want to stay up-to-date on any new developments to the contest? Sign up to our email list below.
We’ll send you periodic reminders about the contest deadline, as well as helpful resources to ensure you get the most out of your experience reading and writing about Ayn Rand’s Anthem .
Great! Let's get you a copy of the book.
You're almost there!
Enter your school details below to receive a free digital copy of Anthem .
Let's log you in to your account.
Success! Let's log you in to your account.
We've received your request for a free copy of Anthem and will be emailing you details on how you can access it shortly. In the meantime, are you ready to begin the entry process?
Please enter your password below, either to create a new account or to sign in to your existing account for the contest. Once you're logged in to your account, you'll be able to save your entry progress and return later to complete it.
Hi, . Ready to enter the contest?
Now that you've logged in to your account, let's get you started on your entry for the contest. It's OK if you haven't finished reading the book or writing your essay yet. We'll save your progress for you to continue later.
Then, when you're ready to submit your essay, just return to our platform. Your saved entry will be right where you left off. So, why wait? Take the first step, and start your entry today.

- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Ayn Rand Global
- Ayn Rand Institute eStore
- Ayn Rand University App
Updates From ARI
Copyright © 1985 – 2024 The Ayn Rand Institute (ARI). Reproduction of content and images in whole or in part is prohibited. All rights reserved. ARI is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Contributions to ARI in the United States are tax-exempt to the extent provided by law. Objectivist Conferences (OCON), Ayn Rand Conference (ARC), Ayn Rand University (ARU) and the Ayn Rand Institute eStore are operated by ARI. Payments to OCON, ARC, ARU or the Ayn Rand Institute eStore do not qualify as tax-deductible contributions to the Ayn Rand Institute. AYN RAND, AYN RAND INSTITUTE, ARI, AYN RAND UNIVERSITY and the AYN RAND device are trademarks of the Ayn Rand Institute. All rights reserved.
English Essay on “Our National Symbols” English Essay-Paragraph-Speech for Class 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 CBSE Students and competitive Examination.
Our National Symbols
Like every free country, our country also has many national symbols. The National flag, the National Anthem and the National Emblem are our most important and sacred symbols.
Our National Flag is the symbol of our freedom which has inspired the Indian people during the struggle for freedom. During the freedom struggle, the tricolored flag had a spinning wheel (Charka) in the center. When the tricolor flag was adopted as the National flag, the charka was replaced by the chakra (wheel).
The National flag is a horizontal tri-color. It has three bands of equal proportions. The upper band is of deep saffron color and the lower band is dark green. The middle band is white and has the Chakra in the navy blue in the center.
The Chakra represents the chakra on the high tower with lions built by Asoka in Saranath.
The National flag is hoisted on all important Government buildings in India and on all our Embassies in other countries.
It is our duty to honour and protect the National flag. We salute and respect our National flag.
Our National Anthem is Jana gana mane, an inspiring song composed by Rabindranath Tagore. The National Anthem is the symbol of our unity. It inspires the young and the old. it calls for a strong and United India. We honour and respect our National Anthem. We stand to attention when it is sung or its tune is played.
Every free nation has a National Emblem which represents the authority of the Government. Our National Emblem is found on all coins and currency notes. It appears also on many postal stamps. It can be scan on the documents and publications of the Government.
Our National emblem has also been taken from the Asoka Pillar at Baranath. There_ are three lions standing back to back. Below the lions is the chakra in the center, the same chakra appears on the National flag, To the left of the chakra is a bull and to the right a horse. Below the emblem is engraved the words ‘Satye meva Jayate’ in Devanagari script which means “Truth will triumph.”
Asoka was a lover of peace. We, the Indian people also love peace. Hence our government has adopted the figures horn the pillar at Saranath as our National emblem.
Related Posts

Absolute-Study
Hindi Essay, English Essay, Punjabi Essay, Biography, General Knowledge, Ielts Essay, Social Issues Essay, Letter Writing in Hindi, English and Punjabi, Moral Stories in Hindi, English and Punjabi.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Indian Flag Essay
The Indian National Flag is a symbol of India’s freedom and its integrity. It symbolizes that the nation is governed by its own people, without any foreign interference. Prideful display of the flag demarcates Indian territories and act as a warning to the invaders. National Flag of India is a rectangular Tricolor with three horizontal stripes of saffron, white and green, from top to bottom respectively.
In the middle of the white stripe there is an impression of Ashoka Wheel of Ashoka Chakra printed in blue. The Flag is based on Swaraj Flag designed by Pingali Venkayya. Saffron represents courage and sacrifice, white is a symbol of peace and green represents fertility and prosperity. Tricolor display is governed by the Flag code of India and any act of dishonor to the National Flag is a punishable offence.
Independence Day | Independence Day Essay | Essay on Importance of Independence Day in India | Independence Day Speech | Slogans on Independence Day | Paragraph on Independence Day | Facts about Independence Day of India | Independence Day Quotes
Long and Short Essay on National Flag of India in English
The National flag of India is a symbol of honour and freedom for the country. It is of great significance to us. We should respect and know everything about our national flag.
Here we have provided some simple long and short essay on Indian National Flag. These Indian National Flag Essay are written in simple language so that they could be easily memorized and presented whenever needed.
After going through the essays you would know the history of our National flag as well as its significance in keeping the nation united.
You can select any of the below given essays and present it in speech, debates of essay writing competitions in your school or college.
National Flag of India Essay 1 (100 Words)
India is our country and our National Flag is very important for all of us. Our national flag is the symbol of unity for the people of different religions living here. We should honour and respect our country and its national flag. It is very necessary for every independent country to have a national flag. Our national flag is tricolour so also called as Tiranga. The topmost colour of our national flag is saffron, middle one is white and lowermost color is green colour. The middle strip of white colour contains a navy blue Ashok Chakra having 24 equally divided spokes.

National Flag of India Essay 2 (150 Words)
National flag is our unique identity of being a citizen of an independent nation. Every independent nation has its unique flag. Our national flag is a symbol of unity and freedom. The national flag is hoisted on every national occasion by the government official however Indian citizens are also allowed to fly the national flag on some occasions.
It is hoisted in the government offices, schools and other educational institutions on the occasions of Republic Day , Independence Day and other national events. Indian national flag was first time adopted on July 22 nd in 1947. Our national flag is a beautifully designed tricolour flag, also known as Tiranga. It is made up of hand-made Khadi clothes. It is completely restricted to make the Indian flag using clothes other than the Khadi. The topmost colour of national flag is saffron, middle white and lower deep green. Saffron colour symbolizes sacrifice and selflessness, white colour truth and purity and green youth and energy.
National Flag of India Essay 3 (200 Words)
The national flag of India was adopted on 22 nd of July in 1947 some days after the independence of India on 15 th of August, 1947 from the British rule. The Indian national flag contains three colours and thus also called as the Tiranga. The uppermost saffron colour indicates sacrifice and selflessness, middle white colour indicates truth, peace and purity and lowermost green colour indicates youth and energy. The middle white colour contains a navy blue colour Ashoka Chakra which has 24 equal spokes. Our national flag is a symbol of freedom, pride, unity and honour. Ashok Chakra indicates real victory of honesty and justice.
Our national flag teaches us the lesson of unity, peace and humanity. It helps us to believe in the truth and unity. It is hoisted every year by the Indian prime Minister of India on 15 th of August and by the President of India on 26 th of January. However, it is hoisted by both of them at Red Fort followed by address to people of India. Our national flag is made up of khadi clothe, a hand-made clothe initiated by the Mahatma Gandhi. It is strictly prohibited in our country to fly a national flag made up of clothe other than Khadi.
National Flag of India Essay 4 (250 Words)
India got independence after long years of struggle of more than thousands brave Indian freedom fighters. India got freedom on 15 th of August in 1947 from the British rule. Some days before the independence of India, the national flag of India was adopted on 22 nd of July in 1947 (in the meeting of constituent assembly) as a symbol of unity and great triumph. Our national is tricolour so called Tiranga Zanda. Our national flag is courage and inspiration for us. It makes us remember about the sacrifices of our great Indian freedom fighters. It makes us remember that how tough that moment was for them. Getting freedom was not so easy. We should always respect our flag and never let it go down for our motherland.
Our national flag is horizontally designed using tricolour strips of saffron, white and green. The middle white portion has navy blue Ashok Chakra with 24 spokes. All the three colours, Ashok Chakra and 24 spokes have their own meaning and significance. The uppermost Saffron colour symbolizes the devotion and renunciation. The middle white color indicates the peace and harmony. And the lowermost green colour indicates youth and energy. However, the Ashoka Chakra (means Wheel of Ashoka) symbolizes the peace and courageousness.
Our national flag is made up of khadi clothe which is a special hand-spun cloth initiated by the Mahatma Gandhi. All the manufacturing processes and designing specifications are handled by the Bureau of Indian Standards. It is strictly forbidden in our country to use the flag made up of other clothes instead of Khadi.
National Flag of India Essay 5 (300 Words)
Our national flag is also called as the Tiranga Jhanda as it has three colours. It contains tricolour horizontal stripes of uppermost saffron, middle white and lowermost green. The middle one white strip contains a navy blue Ashoka Chakra (also called Dharma Chakra) in its centre. The present time Indian national flag was first officially adopted in the Constituent Assembly meeting on 22 nd of July in 1947. The ratio of length and width of the Indian flag is 3:2.
Prevention of Improper Use Act, 1950 and Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971 both, governs the use and display of national flag. Flag Code of India was established in 2002 to govern all the laws, practices conventions, and instructions to respect and honour the Indian flag. The Indian national flag was first proposed by the Mahatma Gandhi in 1921 to the Indian National Congress. Our national flag was first designed by the Pingali Venkayya. It is considered that the saffron and green strip was decided to honour both religions like Hindu and Muslim. Later a white strip was added in the middle with a spinning wheel in the centre to symbolize the respect to other religions.
Before the independence of India, various Indian flags were designed to precede the Indian Independence Movement to get freedom from the British rulers. Finally the present design of the national was officially adopted. Earlier the display of national flag was prohibited by the common public and it was only displayed by the government officials during any national event however later it was allowed to the common public to display the national flag to their own premises. It is a symbol of unity and honour to our motherland, so we all should always respect our national flag and never let its honour go down.
National Flag of India Essay 6 (400 Words)
The National Flag of India is also known as the Tiranga Jhanda. It was first officially adopted during the meeting of Constituent Assembly on July 22 nd in 1947. It was adopted 24 days before the independence of India from British rule. It was designed by the Pingali Venkayya. It was so designed in horizontal shape having three colours of saffron, white and green in equivalent proportions. The upper saffron colour, white middle, lower dark green colours. Our national flag contains 2:3 ratio of width and length. In the centre a navy blue wheel having 24 spokes is designed in the middle white strip. Ashoka Chakra was taken from the pillar of the Ashok, Sarnath (Lion Capital of Ashoka).
Our national flag is of great significance to all of us. All the colours, strips, wheel and clothe used in the flag have their special significance. Flag code of India decides the use and display of national flag. Till 52 years after the independence of India, national flag was not allowed to display by the people however later the rule was altered (according to the flag code 26 th January 2002) to use flag at homes, offices and factories on any special occasion. National Flag is hoisted on the national occasions like Republic day, Independence day, etc. It is also displayed in the schools and educational institutions (colleges, universities, sports camps, scout camps, etc) to inspire the students for honouring and respecting the Indian Flag.
Students take an oath and sing national anthem while unfurling the national flag in the schools and colleges. Public and private organization members may also hoist the flag on any occasions, ceremonial event, etc. It is restricted to display the national flag for any communal or personal gains. Nobody is allowed to display the flag made of other clothes otherwise it is a punishment of imprisonment and fine. National Flag can be flown from morning till evening (sunrise to sunset) in any weather. It is prohibited to intentionally dishonour the national flag or touch it to the ground, floor or trail in water. It should not be used to cover the top, bottom, sides or back of any vehicle, like car, boat, trains, or aircraft. On flag other than the Indian should be displayed at higher level.
Essay on Importance of National Flag of India – Essay 7 (600 Words)
Introduction
National Flag of India, fondly known as Tiranga, is the nation’s pride. It is an important and integral part of the Republic of India. It represents the sovereignty of the country and is respected by its citizens. It is flown on all the government buildings in India. It is a ritual to hoist the national flag of India on national festivals such as Independence Day, Republic Day and Gandhi Jayanti.
Importance of the Indian National Flag
The National Flag of India reflects its culture, civilization and history. The flag flowing in the air is a symbol of freedom. It reminds the Indian citizens of the sacrifices made by the freedom fighters to free our country from the tyranny of the British. It also inspires them to be humble and value the freedom and independence they have attained after much struggle.
The Indian national flag is referred to as Tiranga as it consists of three colours -Saffron, White and Green. The saffron colour on the top symbolizes indifference which means our leaders must remain indifferent towards materialistic things. Serving the nation should be on the top of their priority list and they must do their work selflessly. The white colour in the middle represents truth and purity which means we must always follow the path of truth and right conduct. The green colour at the bottom symbolizes soil and nature and reminds us to stay grounded to our roots.
The Ashoka Chakra printed in the middle of the flag on the white portion is a symbol of the law of Dharma. It means that Dharma or virtue must be the main guiding principles of those who serve the nation. It is also a symbol of motion and inspires to keep moving in life irrespective of the challenges and hardships.
History of the Indian National Flag
It was Mahatma Gandhi who came up with the idea of a flag for the Indian National Congress in the year 1921 when the struggle for Indian independence was still going on. The flag had a spinning wheel printed in the middle as it symbolized Bapu’s goal of making the citizens of India self-reliant by spinning and fabricating clothes. The design of the flag evolved and improvised with time. On India’s independence, the flag was modified further and the spinning wheel was replaced by the Ashoka Chakra that is the eternal wheel of law.
Code of Indian National Flag
The citizens of India are expected to respect and keep the honour of the national flag of the country. A set of rules have been put in place against the mistreatment of the national flag. Some of these are as follows:
- Flying the Tiranga made of any material other than Khadi or hand-spun cloth is punishable by law.
- The flag can be carried during processions but must be borne only on the right shoulder of the bearer. Secondly, it must always be carried in front of the procession.
- The flag must always be held high and not lowered before anything.
- No other flag can be placed above the Tri-colour neither can it be placed to its right.
- Whenever the flag is in a moving column, the people present must stand in attention position and pay respect by saluting as it passes them.
- The flag must be flown at half mast to signify mourning. It is flown half mast across the nation in case of death of President, Vice-president and Prime Minister during their duty period.
Our National Flag is our pride. We must uphold its dignity even if it is at the cost of our lives. It must always flow high as it is a symbol of the freedom that was earned after years of struggle and sacrifices.
Related Information:
National Flag Adoption Day
Paragraph on National Flag of India
Slogans on National Flag of India
Speech on National Flag
More Information:
Independence Day
Independence Day Essay
Independence Day Speech
Slogans on Independence Day
Paragraph on Independence Day
Essay on National Festivals of India
Paragraph on National Festivals of India
Essay on Importance of Independence Day in India
Facts about Independence Day of India
Independence Day Quotes
Related Posts
Money essay, music essay, importance of education essay, education essay, newspaper essay, my hobby essay, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- National Flag Essay for Students in English

Essay on National Flag
'The symbol of the nation'
'The symbol of unity of population'
Here I am talking about the thing which is mighty for all Indians, for which every Indian is mad for serving, it is the only thing for which all Indians think about their religious and caste boundaries. So here the thing I am talking about the national flag of India i.e. TIRANGA (Means the combination of three colours). The history of Tiranga was very old. Mahatma Gandhi first spoke about the need for an Indian flag in 1921. He proposed a flag with the charkha or spinning wheel at the center and if we talk about its look it is not always like that as we have seen today. In the nearby time of 1947, it was of three colours in which saffron is at the top, white is at middle and green is at the bottom.
In the middle of which there is a charkha that is known as Ashok Chakra. In it saffron represents sacrifice, white represents peace, green color represents progress and charkha represents the spirit of swadeshi. To represent Gandhi Ji’s fight for freedom but nowadays we are seeing it as in the same colours with the same message but with chakra, in place of charkha as the symbol of the wheel of duty with 24 spokes it is the only reason for what designers have put it in the flag. The designer who designed the modern flag is Pingali Venkayya. The flag has been designed on the bases of swaraj flag or the flag of Indian National Congress.
Importance of National Flag:
It means a lot not only for the officials of the country but also for civilians. But now people are becoming careless day by day as we can easily see on the occasion of any national festival people buy them and move throughout the day with it but the scenario of next day is like that all those flags were lying on the grounds and none of us pick up them but I think it is not our fault it is the fault of being seniors who told us about good jobs, earning, careers but never told us about Saheed Bhagat Singh, Subhash Chandra Bose and many other martyrs who sacrificed their lives to bring independence because if our seniors told us about all of them so then we come to know the value of this flag for raising of which our country had loosed many precious gems.
So now I think that from today we shall take the pledge to respect our national flag and follow all its conveyed messages for the betterment of our country and to raise our national flag at the top of the world and we all know that it is India’s heritage to see all the countries of the world as a family. So that all countries will see India not only as the world leader but also as the father of all countries. As the work of the father is to guide the family members and maintain harmony. India and its flag also get such opportunity and respect and we all know that it is the heritage of India to see the whole world as the family.
Existence Across the World:
The national flag is a symbol of our country, it gives us the same patriotic feeling where we go and make our country proud. Currently in entertainment zones as well whether you watch any movie it is mandatory to stand for the national anthem to show respect for our country, in schools children sing the national anthem every day followed by their regular prayer, any government and private sector of the organization also hoist flags and pay tribute on those special occasions.
No matter where we live it’s our integrity towards our nation to celebrate special days i.e. 15 August or 26th January across the world. This shows the love and integrity of India. Our Indian National flag has made a wide existence across the globe. People are making India proud by achieving a good name and fame in various sectors or industries.
The national flag of any country is not only the symbol of that nation but also the symbol of the unity of its population. The Indian flag is the one emblem that we all look at, and dedicate our lives to serving, in some way or the other; the appearance of the flag makes all caste and religious boundaries disappear.
The national flag of India is known as the ‘Tiranga’ - for the three colors represented in it, saffron, white, and green.
It was Mahatma Gandhi in the year 1921 who first spoke of the need for an Indian flag; he always spoke of the need for the spinning wheel or ‘charkha’ on the flag, although the appearance of the flag has changed many times throughout the years.
Around the year 1947, the flag was mostly finalized - the tricolor, with saffron at the top and green at the bottom, sandwiching the white in the middle with what is known as the Ashoka Chakra upon it. Each element of the flag represents something; the saffron represents sacrifice, white for peace, green for progress, and finally, the charkha represents the spirit of ‘swadeshi’. The main difference made since then is the removal of the charkha and replacing it with the chakra, the wheel of duty with 24 spokes.
The flag as we know it today has been designed by Pingali Venkayya, who based it upon that of the Indian National Congress, or the Swaraj flag.
For every patriot we find today, there was a freedom fighter who helped make it possible for these patriots to shine today. While it is important to focus on our futures, we must remain aware that such a future would not even be possible without the likes of Shaheed Bhagat Singh, Subhas Chandra Bose, and other martyrs who lived and died fighting for the flag and the freedom it represents, and all the opportunities it brings with it for all citizens of India, past, present, and future.
As students, we must take a pledge to respect our national flag with great veneration, and follow all of its prescribed tenets with temerity. It is us as citizens who can bring India up to its true potential, and secure its place on the world stage. It is up to us to share our heritage, and we can only do it once we ourselves are aware of it
Existence Across the world
The national flag exists to give us a united sense of patriotism wherever we go, as it is the foremost symbol of our country; it is emblematic of what India as a country represents.
India as a country has made respect for the flag impossible to avoid, and thereby imbibes in people young and old the importance of this one piece of cloth. It is mandatory to stand for the national anthem accompanied by the flag whenever one goes for any movie or concert; children in school sing the national anthem in praise and respect of the country and its flag; flags are hoisted in both public and private spaces, and tributes are often paid.

FAQs on National Flag Essay for Students in English
1. What Do 3 Colours on the Flag Represent?
The Indian national flag has three colours i.e. saffron, white and green, these all colours signifies courage, sacrifice, peace and faith respectively. And Ashoka Chakra in the centre represents the wheel of the law.
2. Who designed the current Indian National Flag?
Pingali Venkayya was the one who designed the Indian national flag as we know it now, based upon the design of the Swaraj flag, of the Indian National Congress before the time of Independence; this was the design made by Mahatma Gandhi, whose wheel or charkha symbolized the previous Indian goal of becoming self-dependent.
3. What Does Tiranga Symbolize?
The Tiranga, our National Flag was designed as a symbol of freedom, and the ultimate meaning of the Tiranga is to symbolize independence. The colors of our national flag with equal proportions of the deep saffron color on the top, the white color in the middle and the dark green color at the bottom, all have significant meanings. The saffron stands for courage, sacrifice and the spirit of renunciation. The white stands for purity and truth and the green stands for faith and fertility.
4. What is the Indian flag composed of?
The Indian National flag, also known as the Tricolor or the Tiranga, is composed of the three colors of saffron, white, and green, each representing sacrifice, peace, and progress respectively. At the very center of the flag, in the white shade, lies what is known as the Ashoka Chakra, coloured blue - it is the wheel of duty.
5. Where can we get sample essays?
Essay writing is important for all school students, especially for those in the junior classes. It is important to be able to practice some of the sample essays to do well in exams. The online portal, Vedantu.com offers important questions along with answers and samples of essays on various topics, and also on ‘The National Flag’, along with other very helpful study material on essays, that have been formulated in a well structured, well researched, and easy to understand manner. These study materials and solutions are all important and are very easily accessible from Vedantu.com and can be downloaded for free.
6. What is the Importance of the National Flag?
In modernized India, it is easy to get caught up in urbanity and forget the importance of the national flag; the truth is, it isn’t merely officials who ought to have great reverence for the flag, but all ordinary civilians as well.
It is not that we aren’t taught about how important this flag is, but we often tend to forget the very symbol of our freedom while taking our freedom for granted. As citizens of India, our Indian national flag represents our past, our present, and even our future.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Mass singing of the National Anthem is to accompany the unfurling of the National Flag. 5. No parody/distortion of words or music of the National Anthem is allowed. Significance. The National Anthem is perhaps one of the most potent declarations of a country's independent status. India is a nation of multiple languages and dialects therein.
National Anthem History. On the morning of September 14, 1814, the sun rose to reveal a surprising sight to Francis Scott Key. Just a month after the British had burned the White House during the height of the War of 1812, Key was aboard a British vessel negotiating the release of a friend who was being held prisoner.
Ironically, the melody Key assigned to accompany the lyrics of "The Star-Spangled Banner" was a popular English drinking song called "To Anacreon in Heaven.". Written around 1775 by John ...
250 Words Essay on National Symbols of India Introduction. India, a country with rich cultural heritage and history, is home to numerous national symbols that represent its unique identity. These symbols, ranging from the national flag to the national animal, encapsulate the essence of the nation, reflecting its diversity, values, and aspirations.
Explain/explore. Step 3: Listen to Ada Limón read her poem "An New National Anthem.". Then print out and read the text of the poem. As you read, underline words that stand out to you and write notes next to the poem on the left about what you think she means. Then answer the questions on the following page.
In India, it is celebrated on a large scale as well. It is celebrated on the 25th of December, every year and is followed by the New Year. There are other National Festivals that are celebrated in India as well. These include Maha Shivratri, Pongal, Onam, Baisakhi, Rakshabandhan, Gurpurab, and Makar Sankranti.
10 Lines on National Anthem. 1) "Jan Gan Man" is the National Anthem of India. 2) It was written in 1911 by Rabindra Nath Tagore. 3) It has a total of five paragraphs. 4) The original song was written in the Bengali language. 5) It was translated in Hindi by Captain Abid Ali.
Whenever someone plays or sings the national anthem of India, no matter where we are, we all come together, stand at attention, salute, and chant 'Jana Gana Mana'. The national anthem is the pride of India and Indians are proud of it. Composed by Nobel Laureate Rabindranath Tagore, the anthem highlights India's national heritage and demonstrates patriotism and loyalty to one's country.
Paper Type: 1200 Word Essay Examples. Odour of Chrysanthemums is a short story by D. H. Lawrence, written in the autumn of 1909. It is set in Nottinghamshire and tells the tale of a coal miner's wife, a young mother, waiting for her abusive husband Walter to come home. She blames his drinking for his absence.
National anthem (Jana-gana-mana) was originally composed by Rabindranath Tagore in Bengali. The Hindi version of the national anthem was adopted in 1950 on 24 th of January by the Constituent Assembly. The lyrics and music of the national anthem was given by Rabindranath Tagore in 1911. It was first sung in Calcutta in the meeting of Indian ...
Essay on Rabindranath Tagore: The National Anthem that we sing with such pride as written by Rabindranath Tagore, who was one of the most significant men and nationalists in India. He was a poet as well as a writer and had won the Nobel Prize for his piece known as "Gitanjali." His writings are still studied by students all over the world.
In "African-Americans and the Strains of the National Anthem," an Opinion essay from 2018 written in response to the N.F.L ... • Learn more about how to use our free daily writing prompts ...
The National Anthem of India is titled "Jana Gana Mana". The song was originally composed in Bengali by India's first Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore on 11 December 1911. [11] [12] [13] The parent song, 'Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata' is a Brahmo hymn that has five verses and only the first verse has been adopted as the national anthem.If put forward succinctly, the anthem conveys the spirit of ...
"The Star-Spangled Banner" is the national anthem of the United States. The lyrics come from the "Defence of Fort M'Henry", [2] a poem written by American lawyer Francis Scott Key on September 14, 1814, after he witnessed the bombardment of Fort McHenry by the British Royal Navy during the Battle of Baltimore in the War of 1812.Key was inspired by the large U.S. flag, with 15 stars and 15 ...
The song remained popular throughout the 19th century, emerging as a symbol of unity during the Civil War, but only became the U.S.'s official national anthem in 1931.
10 Lines Essay on National Anthem in English. Find here ten easy points on National Anthem for Children and Students of all Classes. These few lines and sent...
National anthem (Jana-gana-mana) was originally composed by Rabindranath Tagore in Bengali. The Hindi version was adopted in 1950 on 24th of January by the Constituent Assembly. The lyrics and music of the national anthem was given by Rabindranath Tagore in 1911. It was first sung in Calcutta in the meeting of Indian National Congress on 27th ...
The 'National Anthem of India' is the song 'Jana-gana-mana'. It composed originally in Bengali by Rabindranath Tagore. 'Jana-gana-mana' was adopted in its Hindi version by the Constituent Assembly as the national anthem of India on 24 January 1950.'Jana-gana-mana' was first sung on 27 December 1911 at the Calcutta Session of the Indian National Congress. The complete song consists of five stanzas.
The British National Anthem in its present form dates back to the eighteenth century. The words and tune are anonymous, and may date back to the seventeenth century. 'God Save The King' was a patriotic song first publicly performed in London in 1745, which came to be known as the National Anthem at the beginning of the nineteenth century.
Choose YourEssay Topic. Select one of the following three prompts about Anthem and write an essay in response to it. Essays must be written in English only and between 600 and 1,200 words in length, double-spaced. Questions? Write to us at [email protected]. Prompt #1. Prompt #2. Prompt #3.
Hindi Essay, English Essay, Punjabi Essay, Biography, General Knowledge, Ielts Essay, Social Issues Essay, Letter Writing in Hindi, English and Punjabi, Moral Stories in Hindi, English and Punjabi. Leave a Reply
National Flag of India Essay 6 (400 Words) The National Flag of India is also known as the Tiranga Jhanda. It was first officially adopted during the meeting of Constituent Assembly on July 22 nd in 1947. It was adopted 24 days before the independence of India from British rule. It was designed by the Pingali Venkayya.
The Tiranga, our National Flag was designed as a symbol of freedom, and the ultimate meaning of the Tiranga is to symbolize independence. The colors of our national flag with equal proportions of the deep saffron color on the top, the white color in the middle and the dark green color at the bottom, all have significant meanings. The saffron stands for courage, sacrifice and the spirit of ...