

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principal tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question
- Log in
- Site search
How to write an essay
Essay writing is an inevitable part of the student experience. To achieve top grades on these assignments, discover how to compose a well-written essay
You might think you know how to write a good essay from your time at school but writing an essay at undergraduate level is a whole new ball game. Taking the time to properly plan your work can lead to higher marks, with lecturers welcoming a logical structure that clearly demonstrates your understanding of the subject.
However, knowing where to begin and how to go about completing the assignment is not always easy - especially if you're still adjusting to university life and you haven't written at undergraduate level before.
'There is an art (and a bit of a science) to every type of writing,' says Dr Rushana Khusainova, lecturer in marketing at the University of Bristol. 'By mastering the art of academic essay writing, you'll also be mastering the skill for writing general and business emails, reports, etc. Overall, it's a vital skill to have.'
Katherine Cox, professor and head of department for humanities and law at Bournemouth University agrees. 'Getting feedback on your development is a key part of developing as a student. Essay writing is an excellent opportunity for formal feedback on your progress, and like any skill it needs practice and polish.'
Here we'll cover the seven main points of planning and executing a well-written essay:
- understanding the question
- researching and gathering helpful resources
- putting together an essay plan
- writing the essay
- tackling the introduction and conclusion
- reviewing what you’ve written.
Mastering how to write an essay early on will also help you prepare for writing your dissertation in your final year.
Understand the question
The first step in tackling an essay is to make sure that you understand what is being asked of you.
'I recommend that you read and re-read the essay question,' advises Dr Khusainova. 'With each time, the question will feel clearer.' Break it down into its component parts and pay particular attention to instruction words, for example, 'explain', 'discuss', 'outline' - what do these mean in practice? What are you being asked to do? Be aware that essays take several different forms and a 'compare and contrast' essay requires a different approach to an analytical ('analyse') or argumentative ('critically examine') essay.
For example, the question, 'Compare and contrast the representation of masculinity in two James Bond films from the 1960s and 2000s', can be classified like this:
- instruction (i.e. compare and contrast)
- topic (i.e. the representation of masculinity)
- focus (i.e. in two James Bond films)
- further information (i.e. from the 1960s and 2000s).
'Take coloured pens and highlight each sub-question or sub-task within the essay brief,' explains Dr Khusainova. 'Write bullet points for all sub-questions of the essay. I would recommend using pen and paper. Research suggests that when we use pen and paper to write down our thoughts, our brain structures information in a more efficient way.'
Ask yourself:
- What is significant about the question and its topic?
- What existing knowledge do you have that will help you answer this question?
- What do you need to find out?
- How are you going to successfully address this question?
- What logical sequence will your ideas appear in?
If you still don't understand the question or the complexity of the response expected from you, don't be afraid to ask for clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you need it. If you have questions, speak up when the essay is set rather than leaving it too late.
Gather resources
With so much information available, it's vital that you only look for directly relevant material when researching. Decide where the gaps in your knowledge and understanding are, and identify the areas where you need more supporting evidence. Make a list of keywords that describe the topic and use them to search with.
Useful resources include:
- course material
- lecture notes
- library books
- journal articles
Engage in active reading and keep organised with effective note-taking. Once you've done your research, create a mind map. Carefully note the key theories, information and quotes that will help you to answer all components of the question. Consider grouping these into three or four main themes, including only the most significant points. You must be ruthless and exclude ideas that don't fit in seamlessly with your essay's focus.
Create an essay plan
'You can write an essay without planning, but I'm not sure you can write a good essay without planning,' says Katherine.
When you have an idea of the points you're going to address in your essay, and a rough idea of the order in which these will appear, you're ready to start planning. There are two main ways to do this:
- Linear plans - useful for essays requiring a rigid structure. They provide a chronological breakdown of the key points you're going to address.
- Tabular plans - best for comparative assignments. You'll be able to better visualise how the points you're contrasting differ across several aspects.
Scrutinise the notes you've already made - including those from your evaluation of relevant materials from your literature search - and ensure they're placed into a logical order.
There are different approaches to planning an essay. Some students might prefer a step-by-step, structured approach, while others might find it helpful to begin in a more fluid way - jotting down keywords and ideas that they later develop into a more structured working plan. Essay planning can take several forms, 'for example, you might try a mind map, a collage, or use headings. You might prefer to plan in written form or online. You'll also turn ideas over in your head - just remember to jot down these insights,' adds Katherine.
'In my experience most students find it helpful to start by writing an essay skeleton - a bullet pointed structure of the essay,' says Dr Khusainova.
'I also advise taking an inverted pyramid approach to the storyline. This is where you start broad and slowly narrow down your focus to the specific essay question.'
Write clearly and concisely
Most university essays are set with a word count and deadline in place. It's therefore important that you don't waste time or words on waffle. You need to write clearly and concisely and ensure that every sentence and paragraph works towards answering the essay question.
Aim to write a first draft where you cover everything in your plan. You can then refine and edit this in your second draft.
'A successful essay is one that answers all parts of the essay question,' explains Dr Khusainova. 'Also consider elements such as the level of critical thinking and whether it's written in a suitable style.
'One of the most important (and coincidentally, the most challenging) elements of essay writing is ensuring your assignment has a logical storyline. Make sure no idea is coming out of the blue and that the discussion flows logically.'
Also consider your method of referencing. Some institutions specify a preferred citation style such as The Harvard System. Whatever referencing system you're using ensure that you're doing so correctly to avoid plagiarism. It should go without saying that your writing needs to be your own.
If you need help Katherine points out 'you can turn to your tutors and your peers. Perhaps you can you organise a study group and discuss one another's ideas? It's tempting with new and emerging artificial intelligence technology to turn to these resources but they are in their infancy and not particularly reliable. A number of universities advise you to avoid these resources altogether.'
Carefully consider the introduction and conclusion
Starting an essay and writing an impactful conclusion are often the trickiest parts.
It can be useful to outline your introduction during the early stages of writing your essay. You can then use this as a frame of reference for your writing. If you adopt this approach be aware that your ideas will likely develop or change as you write, so remember to revisit and review your introduction in later stages to ensure it reflects the content of your final essay.
While the conclusion may not be the first thing you write, it's still helpful to consider the end point of your essay early on, so that you develop a clear and consistent argument. The conclusion needs to do justice to your essay, as it will leave the greatest impression on your reader.
On the other hand, if you're unsure what shape your argument may take, it's best to leave both your introduction and conclusion until last.
Evaluate what you've written
Once you've written and edited your essay, leave it alone for a couple of days if possible. Return to it with fresh eyes and give it a final check.
'Reading an essay out loud works well for some students,' says Dr Khusainova. 'Swapping drafts with a classmate could also work on some modules.'
Don't skip this step, final checks are important. This is when you can pick up on formatting and spelling errors and correct any referencing mistakes.
- Check that your introduction provides a clear purpose for your essay.
- Ensure that the conclusion provides a clear response to the essay question, summarising your key findings/argument.
- Check the structure of your paragraphs for clear topic and link sentences. Are the paragraphs in a logical order with a clear and consistent line of argument that a reader can follow?
- Read your essay slowly and carefully. Writing has a rhythm - does your writing flow and is it correctly punctuated?
- Remove unnecessary repetition.
- Review the examples and evidence you've used. Is there enough to support your argument?
'Receiving feedback can be an emotional experience - so be honest with yourself,' advises Katherine. 'What is the feedback telling you - what are your strengths? What areas could you improve?'
Find out more
- Struggling with your workload? Here are 5 ways to manage student stress .
- Discover how to revise for exams .
- Take a look at 7 time management tips for students .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Write a Great College Essay, Step-by-Step
College Admissions , College Essays

Writing your personal statement for your college application is an undeniably overwhelming project. Your essay is your big shot to show colleges who you are—it's totally reasonable to get stressed out. But don't let that stress paralyze you.
This guide will walk you through each step of the essay writing process to help you understand exactly what you need to do to write the best possible personal statement . I'm also going to follow an imaginary student named Eva as she plans and writes her college essay, from her initial organization and brainstorming to her final edits. By the end of this article, you'll have all the tools you need to create a fantastic, effective college essay.
So how do you write a good college essay? The process starts with finding the best possible topic , which means understanding what the prompt is asking for and taking the time to brainstorm a variety of options. Next, you'll determine how to create an interesting essay that shows off your unique perspective and write multiple drafts in order to hone your structure and language. Once your writing is as effective and engaging as possible, you'll do a final sweep to make sure everything is correct .
This guide covers the following steps:
#1: Organizing #2: Brainstorming #3: Picking a topic #4: Making a plan #5: Writing a draft #6: Editing your draft #7: Finalizing your draft #8: Repeating the process
Step 1: Get Organized
The first step in how to write a college essay is figuring out what you actually need to do. Although many schools are now on the Common App, some very popular colleges, including Rutgers and University of California, still have their own applications and writing requirements. Even for Common App schools, you may need to write a supplemental essay or provide short answers to questions.
Before you get started, you should know exactly what essays you need to write. Having this information allows you to plan the best approach to each essay and helps you cut down on work by determining whether you can use an essay for more than one prompt.
Start Early
Writing good college essays involves a lot of work: you need dozens of hours to get just one personal statement properly polished , and that's before you even start to consider any supplemental essays.
In order to make sure you have plenty of time to brainstorm, write, and edit your essay (or essays), I recommend starting at least two months before your first deadline . The last thing you want is to end up with a low-quality essay you aren't proud of because you ran out of time and had to submit something unfinished.
Determine What You Need to Do
As I touched on above, each college has its own essay requirements, so you'll need to go through and determine what exactly you need to submit for each school . This process is simple if you're only using the Common App, since you can easily view the requirements for each school under the "My Colleges" tab. Watch out, though, because some schools have a dedicated "Writing Supplement" section, while others (even those that want a full essay) will put their prompts in the "Questions" section.
It gets trickier if you're applying to any schools that aren't on the Common App. You'll need to look up the essay requirements for each college—what's required should be clear on the application itself, or you can look under the "how to apply" section of the school's website.
Once you've determined the requirements for each school, I recommend making yourself a chart with the school name, word limit, and application deadline on one side and the prompt or prompts you need to respond to on the other . That way you'll be able to see exactly what you need to do and when you need to do it by.

The hardest part about writing your college essays is getting started.
Decide Where to Start
If you have one essay that's due earlier than the others, start there. Otherwise, start with the essay for your top choice school.
I would also recommend starting with a longer personal statement before moving on to shorter supplementary essays , since the 500-700 word essays tend to take quite a bit longer than 100-250 word short responses. The brainstorming you do for the long essay may help you come up with ideas you like for the shorter ones as well.
Also consider whether some of the prompts are similar enough that you could submit the same essay to multiple schools . Doing so can save you some time and let you focus on a few really great essays rather than a lot of mediocre ones.
However, don't reuse essays for dissimilar or very school-specific prompts, especially "why us" essays . If a college asks you to write about why you're excited to go there, admissions officers want to see evidence that you're genuinely interested. Reusing an essay about another school and swapping out the names is the fastest way to prove you aren't.
Example: Eva's College List
Eva is applying early to Emory University and regular decision to University of Washington, UCLA, and Reed College. Emory, the University of Washington, and Reed both use the Common App, while University of Washington, Emory, and Reed all use the Coalition App.
| 1. Describe an example of your leadership experience in which you have positively influenced others, helped resolve disputes, or contributed to group efforts over time. | |
| 7. Share an essay on any topic of your choice. It can be one you've already written, one that responds to a different prompt, or one of your own design. | |
| What academic areas are you interested in exploring in college? | |
| after the Greek term signifying "education"—the complete education of mind, body and spirit. What would you teach that would contribute to the Reed community? |
Even though she's only applying to four schools, Eva has a lot to do: two essays for UW, four for the UCLA application, one for the Common App (or the Coalition App), and two essays for Emory. Many students will have fewer requirements to complete, but those who are applying to very selective schools or a number of schools on different applications will have as many or even more responses to write.
Eva's first deadline is early decision for Emory, she'll start by writing the Common App essay, and then work on the Emory supplements. (For the purposes of this post, we'll focus on the Common App essay.)
Pro tip: If this sounds like a lot of work, that's because it is. Writing essays for your college applications is demanding and takes a lot of time and thought. You don't have to do it alone, though. PrepScholar has helped students like you get into top-tier colleges like Stanford, Yale, Harvard, and Brown. Our essay experts can help you craft amazing essays that boost your chances of getting into your dream school .

Step 2: Brainstorm
Next up in how to write a college essay: brainstorming essay ideas. There are tons of ways to come up with ideas for your essay topic: I've outlined three below. I recommend trying all of them and compiling a list of possible topics, then narrowing it down to the very best one or, if you're writing multiple essays, the best few.
Keep in mind as you brainstorm that there's no best college essay topic, just the best topic for you . Don't feel obligated to write about something because you think you should—those types of essays tend to be boring and uninspired. Similarly, don't simply write about the first idea that crosses your mind because you don't want to bother trying to think of something more interesting. Take the time to come up with a topic you're really excited about and that you can write about in detail.
Analyze the Prompts
One way to find possible topics is to think deeply about the college's essay prompt. What are they asking you for? Break them down and analyze every angle.
Does the question include more than one part ? Are there multiple tasks you need to complete?
What do you think the admissions officers are hoping to learn about you ?
In cases where you have more than one choice of prompt, does one especially appeal to you ? Why?
Let's dissect one of the University of Washington prompts as an example:
"Our families and communities often define us and our individual worlds. Community might refer to your cultural group, extended family, religious group, neighborhood or school, sports team or club, co-workers, etc. Describe the world you come from and how you, as a product of it, might add to the diversity of the UW. "
This question is basically asking how your personal history, such as your childhood, family, groups you identify with etc. helped you become the person you are now. It offers a number of possible angles.
You can talk about the effects of either your family life (like your relationship with your parents or what your household was like growing up) or your cultural history (like your Jewish faith or your Venezuelan heritage). You can also choose between focusing on positive or negative effects of your family or culture. No matter what however, the readers definitely want to hear about your educational goals (i.e. what you hope to get out of college) and how they're related to your personal experience.
As you try to think of answers for a prompt, imagine about what you would say if you were asked the question by a friend or during a get-to-know-you icebreaker. After all, admissions officers are basically just people who you want to get to know you.
The essay questions can make a great jumping off point, but don't feel married to them. Most prompts are general enough that you can come up with an idea and then fit it to the question.
Consider Important Experiences, Events, and Ideas in Your Life
What experience, talent, interest or other quirk do you have that you might want to share with colleges? In other words, what makes you you? Possible topics include hobbies, extracurriculars, intellectual interests, jobs, significant one-time events, pieces of family history, or anything else that has shaped your perspective on life.
Unexpected or slightly unusual topics are often the best : your passionate love of Korean dramas or your yearly family road trip to an important historical site. You want your essay to add something to your application, so if you're an All-American soccer player and want to write about the role soccer has played in your life, you'll have a higher bar to clear.
Of course if you have a more serious part of your personal history—the death of a parent, serious illness, or challenging upbringing—you can write about that. But make sure you feel comfortable sharing details of the experience with the admissions committee and that you can separate yourself from it enough to take constructive criticism on your essay.

Think About How You See Yourself
The last brainstorming method is to consider whether there are particular personality traits you want to highlight . This approach can feel rather silly, but it can also be very effective.
If you were trying to sell yourself to an employer, or maybe even a potential date, how would you do it? Try to think about specific qualities that make you stand out. What are some situations in which you exhibited this trait?
Example: Eva's Ideas
Looking at the Common App prompts, Eva wasn't immediately drawn to any of them, but after a bit of consideration she thought it might be nice to write about her love of literature for the first one, which asks about something "so meaningful your application would be incomplete without it." Alternatively, she liked the specificity of the failure prompt and thought she might write about a bad job interview she had had.
In terms of important events, Eva's parents got divorced when she was three and she's been going back and forth between their houses for as long as she can remember, so that's a big part of her personal story. She's also played piano for all four years of high school, although she's not particularly good.
As for personal traits, Eva is really proud of her curiosity—if she doesn't know something, she immediately looks it up, and often ends up discovering new topics she's interested in. It's a trait that's definitely come in handy as a reporter for her school paper.
Step 3: Narrow Down Your List
Now you have a list of potential topics, but probably no idea where to start. The next step is to go through your ideas and determine which one will make for the strongest essay . You'll then begin thinking about how best to approach it.
What to Look for in a College Essay Topic
There's no single answer to the question of what makes a great college essay topic, but there are some key factors you should keep in mind. The best essays are focused, detailed, revealing and insightful, and finding the right topic is vital to writing a killer essay with all of those qualities.
As you go through your ideas, be discriminating—really think about how each topic could work as an essay. But don't be too hard on yourself ; even if an idea may not work exactly the way you first thought, there may be another way to approach it. Pay attention to what you're really excited about and look for ways to make those ideas work.

Consideration 1: Does It Matter to You?
If you don't care about your topic, it will be hard to convince your readers to care about it either. You can't write a revealing essay about yourself unless you write about a topic that is truly important to you.
But don't confuse important to you with important to the world: a college essay is not a persuasive argument. The point is to give the reader a sense of who you are , not to make a political or intellectual point. The essay needs to be personal.
Similarly, a lot of students feel like they have to write about a major life event or their most impressive achievement. But the purpose of a personal statement isn't to serve as a resume or a brag sheet—there are plenty of other places in the application for you to list that information. Many of the best essays are about something small because your approach to a common experience generally reveals a lot about your perspective on the world.
Mostly, your topic needs to have had a genuine effect on your outlook , whether it taught you something about yourself or significantly shifted your view on something else.
Consideration 2: Does It Tell the Reader Something Different About You?
Your essay should add something to your application that isn't obvious elsewhere. Again, there are sections for all of your extracurriculars and awards; the point of the essay is to reveal something more personal that isn't clear just from numbers and lists.
You also want to make sure that if you're sending more than one essay to a school—like a Common App personal statement and a school-specific supplement—the two essays take on different topics.
Consideration 3: Is It Specific?
Your essay should ultimately have a very narrow focus. 650 words may seem like a lot, but you can fill it up very quickly. This means you either need to have a very specific topic from the beginning or find a specific aspect of a broader topic to focus on.
If you try to take on a very broad topic, you'll end up with a bunch of general statements and boring lists of your accomplishments. Instead, you want to find a short anecdote or single idea to explore in depth .
Consideration 4: Can You Discuss It in Detail?
A vague essay is a boring essay— specific details are what imbue your essay with your personality . For example, if I tell my friend that I had a great dessert yesterday, she probably won't be that interested. But if I explain that I ate an amazing piece of peach raspberry pie with flaky, buttery crust and filling that was both sweet and tart, she will probably demand to know where I obtained it (at least she will if she appreciates the joys of pie). She'll also learn more about me: I love pie and I analyze desserts with great seriousness.
Given the importance of details, writing about something that happened a long time ago or that you don't remember well isn't usually a wise choice . If you can't describe something in depth, it will be challenging to write a compelling essay about it.
You also shouldn't pick a topic you aren't actually comfortable talking about . Some students are excited to write essays about very personal topics, like their mother's bipolar disorder or their family's financial struggles, but others dislike sharing details about these kinds of experiences. If you're a member of the latter group, that's totally okay, just don't write about one of these sensitive topics.
Still, don't worry that every single detail has to be perfectly correct. Definitely don't make anything up, but if you remember a wall as green and it was really blue, your readers won't notice or care.

Consideration 5: Can It Be Related to the Prompt?
As long as you're talking about yourself, there are very few ideas that you can't tie back to one of the Common App or Coalition App prompts. But if you're applying to a school with its own more specific prompt, or working on supplemental essays, making sure to address the question will be a greater concern.
Deciding on a Topic
Once you've gone through the questions above, you should have a good sense of what you want to write about. Hopefully, it's also gotten you started thinking about how you can best approach that topic, but we'll cover how to plan your essay more fully in the next step.
If after going through the narrowing process, you've eliminated all your topics, first look back over them: are you being too hard on yourself? Are there any that you really like, but just aren't totally sure what angle to take on? If so, try looking at the next section and seeing if you can't find a different way to approach it.
If you just don't have an idea you're happy with, that's okay! Give yourself a week to think about it. Sometimes you'll end up having a genius idea in the car on the way to school or while studying for your U.S. history test. Otherwise, try the brainstorming process again when you've had a break.
If, on the other hand, you have more than one idea you really like, consider whether any of them can be used for other essays you need to write.
Example: Picking Eva's Topic
- Love of books
- Failed job interview
- Parents' divorce
Eva immediately rules out writing about playing piano, because it sounds super boring to her, and it's not something she is particularly passionate about. She also decides not to write about splitting time between her parents because she just isn't comfortable sharing her feelings about it with an admissions committee.
She feels more positive about the other three, so she decides to think about them for a couple of days. She ends up ruling out the job interview because she just can't come up with that many details she could include.
She's excited about both of her last two ideas, but sees issues with both of them: the books idea is very broad and the reporting idea doesn't seem to apply to any of the prompts. Then she realizes that she can address the solving a problem prompt by talking about a time she was trying to research a story about the closing of a local movie theater, so she decides to go with that topic.
Step 4: Figure Out Your Approach
You've decided on a topic, but now you need to turn that topic into an essay. To do so, you need to determine what specifically you're focusing on and how you'll structure your essay.
If you're struggling or uncertain, try taking a look at some examples of successful college essays . It can be helpful to dissect how other personal statements are structured to get ideas for your own , but don't fall into the trap of trying to copy someone else's approach. Your essay is your story—never forget that.
Let's go through the key steps that will help you turn a great topic into a great essay.
Choose a Focal Point
As I touched on above, the narrower your focus, the easier it will be to write a unique, engaging personal statement. The simplest way to restrict the scope of your essay is to recount an anecdote , i.e. a short personal story that illustrates your larger point.
For example, say a student was planning to write about her Outward Bound trip in Yosemite. If she tries to tell the entire story of her trip, her essay will either be far too long or very vague. Instead, she decides to focus in on a specific incident that exemplifies what mattered to her about the experience: her failed attempt to climb Half Dome. She described the moment she decided to turn back without reaching the top in detail, while touching on other parts of the climb and trip where appropriate. This approach lets her create a dramatic arc in just 600 words, while fully answering the question posed in the prompt (Common App prompt 2).
Of course, concentrating on an anecdote isn't the only way to narrow your focus. Depending on your topic, it might make more sense to build your essay around an especially meaningful object, relationship, or idea.
Another approach our example student from above could take to the same general topic would be to write about the generosity of fellow hikers (in response to Common App prompt 4). Rather than discussing a single incident, she could tell the story of her trip through times she was supported by other hikers: them giving tips on the trails, sharing snacks, encouraging her when she was tired, etc. A structure like this one can be trickier than the more straightforward anecdote approach , but it can also make for an engaging and different essay.
When deciding what part of your topic to focus on, try to find whatever it is about the topic that is most meaningful and unique to you . Once you've figured that part out, it will guide how you structure the essay.

Decide What You Want to Show About Yourself
Remember that the point of the college essay isn't just to tell a story, it's to show something about yourself. It's vital that you have a specific point you want to make about what kind of person you are , what kind of college student you'd make, or what the experience you're describing taught you.
Since the papers you write for school are mostly analytical, you probably aren't used to writing about your own feelings. As such, it can be easy to neglect the reflection part of the personal statement in favor of just telling a story. Yet explaining what the event or idea you discuss meant to you is the most important essay —knowing how you want to tie your experiences back to your personal growth from the beginning will help you make sure to include it.
Develop a Structure
It's not enough to just know what you want to write about—you also need to have a sense of how you're going to write about it. You could have the most exciting topic of all time, but without a clear structure your essay will end up as incomprehensible gibberish that doesn't tell the reader anything meaningful about your personality.
There are a lot of different possible essay structures, but a simple and effective one is the compressed narrative, which builds on a specific anecdote (like the Half Dome example above):
Start in the middle of the action. Don't spend a lot of time at the beginning of your essay outlining background info—it doesn't tend to draw the reader in and you usually need less of it than you think you do. Instead start right where your story starts to get interesting. (I'll go into how to craft an intriguing opener in more depth below.)
Briefly explain what the situation is. Now that you've got the reader's attention, go back and explain anything they need to know about how you got into this situation. Don't feel compelled to fit everything in—only include the background details that are necessary to either understand what happened or illuminate your feelings about the situation in some way.
Finish the story. Once you've clarified exactly what's going on, explain how you resolved the conflict or concluded the experience.
Explain what you learned. The last step is to tie everything together and bring home the main point of your story: how this experience affected you.
The key to this type of structure is to create narrative tension—you want your reader to be wondering what happens next.
A second approach is the thematic structure, which is based on returning to a key idea or object again and again (like the boots example above):
Establish the focus. If you're going to structure your essay around a single theme or object, you need to begin the essay by introducing that key thing. You can do so with a relevant anecdote or a detailed description.
Touch on 3-5 times the focus was important. The body of your essay will consist of stringing together a few important moments related to the topic. Make sure to use sensory details to bring the reader into those points in time and keep her engaged in the essay. Also remember to elucidate why these moments were important to you.
Revisit the main idea. At the end, you want to tie everything together by revisiting the main idea or object and showing how your relationship to it has shaped or affected you. Ideally, you'll also hint at how this thing will be important to you going forward.
To make this structure work you need a very specific focus. Your love of travel, for example, is much too broad—you would need to hone in on a specific aspect of that interest, like how traveling has taught you to adapt to event the most unusual situations. Whatever you do, don't use this structure to create a glorified resume or brag sheet .
However you structure your essay, you want to make sure that it clearly lays out both the events or ideas you're describing and establishes the stakes (i.e. what it all means for you). Many students become so focused on telling a story or recounting details that they forget to explain what it all meant to them.

Example: Eva's Essay Plan
For her essay, Eva decides to use the compressed narrative structure to tell the story of how she tried and failed to report on the closing of a historic movie theater:
- Open with the part of her story where she finally gave up after calling the theater and city hall a dozen times.
- Explain that although she started researching the story out of journalistic curiosity, it was important to her because she'd grown up going to movies at that theater.
- Recount how defeated she felt when she couldn't get ahold of anyone, and then even more so when she saw a story about the theater's closing in the local paper.
- Describer her decision to write an op-ed instead and interview other students about what the theater meant to them.
- Finish by explaining that although she wasn't able to get the story (or stop the destruction of the theater), she learned that sometimes the emotional angle can be just as interesting as the investigative one.
Step 5: Write a First Draft
The key to writing your first draft is not to worry about whether it's any good—just get something on paper and go from there. You will have to rewrite, so trying to get everything perfect is both frustrating and futile.
Everyone has their own writing process. Maybe you feel more comfortable sitting down and writing the whole draft from beginning to end in one go. Maybe you jump around, writing a little bit here and a little there. It's okay to have sections you know won't work or to skip over things you think you'll need to include later.
Whatever your approach, there are a few tips everyone can benefit from.
Don't Aim for Perfection
I mentioned this idea above, but I can't emphasize it enough: no one writes a perfect first draft . Extensive editing and rewriting is vital to crafting an effective personal statement. Don't get too attached to any part of your draft, because you may need to change anything (or everything) about your essay later .
Also keep in mind that, at this point in the process, the goal is just to get your ideas down. Wonky phrasings and misplaced commas can easily be fixed when you edit, so don't worry about them as you write. Instead, focus on including lots of specific details and emphasizing how your topic has affected you, since these aspects are vital to a compelling essay.

Write an Engaging Introduction
One part of the essay you do want to pay special attention to is the introduction. Your intro is your essay's first impression: you only get one. It's much harder to regain your reader's attention once you've lost it, so you want to draw the reader in with an immediately engaging hook that sets up a compelling story .
There are two possible approaches I would recommend.
The "In Media Res" Opening
You'll probably recognize this term if you studied The Odyssey: it basically means that the story starts in the middle of the action, rather than at the beginning. A good intro of this type makes the reader wonder both how you got to the point you're starting at and where you'll go from there . These openers provide a solid, intriguing beginning for narrative essays (though they can certainly for thematic structures as well).
But how do you craft one? Try to determine the most interesting point in your story and start there. If you're not sure where that is, try writing out the entire story and then crossing out each sentence in order until you get to one that immediately grabs your attention.
Here's an example from a real student's college essay:
"I strode in front of 400 frenzied eighth graders with my arm slung over my Fender Stratocaster guitar—it actually belonged to my mother—and launched into the first few chords of Nirvana's 'Lithium.'"
Anonymous , University of Virginia
This intro throws the reader right into the middle of the action. The author jumps right into the action: the performance. You can imagine how much less exciting it would be if the essay opened with an explanation of what the event was and why the author was performing.
The Specific Generalization
Sounds like an oxymoron, right? This type of intro sets up what the essay is going to talk about in a slightly unexpected way . These are a bit trickier than the "in media res" variety, but they can work really well for the right essay—generally one with a thematic structure.
The key to this type of intro is detail . Contrary to what you may have learned in elementary school, sweeping statements don't make very strong hooks. If you want to start your essay with a more overall description of what you'll be discussing, you still need to make it specific and unique enough to stand out.
Once again, let's look at some examples from real students' essays:
Neha, Johns Hopkins University
Brontë, Johns Hopkins University
Both of these intros set up the general topic of the essay (the first writer's bookshelf and and the second's love of Jane Eyre ) in an intriguing way. The first intro works because it mixes specific descriptions ("pushed against the left wall in my room") with more general commentary ("a curious piece of furniture"). The second draws the reader in by adopting a conversational and irreverent tone with asides like "if you ask me" and "This may or may not be a coincidence."

Don't Worry Too Much About the Length
When you start writing, don't worry about your essay's length. Instead, focus on trying to include all of the details you can think of about your topic , which will make it easier to decide what you really need to include when you edit.
However, if your first draft is more than twice the word limit and you don't have a clear idea of what needs to be cut out, you may need to reconsider your focus—your topic is likely too broad. You may also need to reconsider your topic or approach if you find yourself struggling to fill space, since this usually indicates a topic that lacks a specific focus.
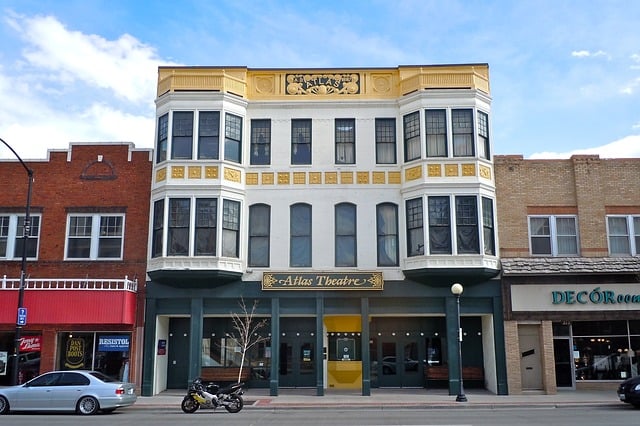
Eva's First Paragraph
I dialed the phone number for the fourth time that week. "Hello? This is Eva Smith, and I'm a reporter with Tiny Town High's newspaper The Falcon. I was hoping to ask you some questions about—" I heard the distinctive click of the person on the other end of the line hanging up, followed by dial tone. I was about ready to give up: I'd been trying to get the skinny on whether the Atlas Theater was actually closing to make way for a big AMC multiplex or if it was just a rumor for weeks, but no one would return my calls.
Step 6: Edit Aggressively
No one writes a perfect first draft. No matter how much you might want to be done after writing a first draft—you must take the time to edit. Thinking critically about your essay and rewriting as needed is a vital part of writing a great college essay.
Before you start editing, put your essay aside for a week or so . It will be easier to approach it objectively if you haven't seen it in a while. Then, take an initial pass to identify any big picture issues with your essay. Once you've fixed those, ask for feedback from other readers—they'll often notice gaps in logic that don't appear to you, because you're automatically filling in your intimate knowledge of the situation. Finally, take another, more detailed look at your essay to fine tune the language.
I've explained each of these steps in more depth below.
First Editing Pass
You should start the editing process by looking for any structural or thematic issues with your essay . If you see sentences that don't make sense or glaring typos of course fix them, but at this point, you're really focused on the major issues since those require the most extensive rewrites. You don't want to get your sentences beautifully structured only to realize you need to remove the entire paragraph.
This phase is really about honing your structure and your voice . As you read through your essay, think about whether it effectively draws the reader along, engages him with specific details, and shows why the topic matters to you. Try asking yourself the following questions:
- Does the intro make you want to read more?
- Is the progression of events and/or ideas clear?
- Does the essay show something specific about you? What is it and can you clearly identify it in the essay?
- Are there places where you could replace vague statements with more specific ones?
- Do you have too many irrelevant or uninteresting details clogging up the narrative?
- Is it too long? What can you cut out or condense without losing any important ideas or details?
Give yourself credit for what you've done well, but don't hesitate to change things that aren't working. It can be tempting to hang on to what you've already written —you took the time and thought to craft it in the first place, so it can be hard to let it go. Taking this approach is doing yourself a disservice, however. No matter how much work you put into a paragraph or much you like a phrase, if they aren't adding to your essay, they need to be cut or altered.
If there's a really big structural problem, or the topic is just not working, you may have to chuck this draft out and start from scratch . Don't panic! I know starting over is frustrating, but it's often the best way to fix major issues.

Consulting Other Readers
Once you've fixed the problems you found on the first pass and have a second (or third) draft you're basically happy with, ask some other people to read it. Check with people whose judgment you trust : parents, teachers, and friends can all be great resources, but how helpful someone will be depends on the individual and how willing you are to take criticism from her.
Also, keep in mind that many people, even teachers, may not be familiar with what colleges look for in an essay. Your mom, for example, may have never written a personal statement, and even if she did, it was most likely decades ago. Give your readers a sense of what you'd like them to read for , or print out the questions I listed above and include them at the end of your essay.
Second Pass
After incorporating any helpful feedback you got from others, you should now have a nearly complete draft with a clear arc.
At this point you want to look for issues with word choice and sentence structure:
- Are there parts that seem stilted or overly formal?
- Do you have any vague or boring descriptors that could be replaced with something more interesting and specific?
- Are there any obvious redundancies or repetitiveness?
- Have you misused any words?
- Are your sentences of varied length and structure?
A good way to check for weirdness in language is to read the essay out loud. If something sounds weird when you say it, it will almost certainly seem off when someone else reads it.
Example: Editing Eva's First Paragraph
In general, Eva feels like her first paragraph isn't as engaging as it could be and doesn't introduce the main point of the essay that well: although it sets up the narrative, it doesn't show off her personality that well. She decides to break it down sentence by sentence:
I dialed the phone number for the fourth time that week.
Problem: For a hook, this sentence is a little too expository. It doesn't add any real excitement or important information (other than that this call isn't the first, which can be incorporate elsewhere.
Solution: Cut this sentence and start with the line of dialogue.
"Hello? This is Eva Smith, and I'm a reporter with Tiny Town High's newspaper The Falcon. I was hoping to ask you some questions about—"
Problem: No major issues with this sentence. It's engaging and sets the scene effectively.
Solution: None needed, but Eva does tweak it slightly to include the fact that this call wasn't her first.
I heard the distinctive click of the person on the other end of the line hanging up, followed by dial tone.
Problem: This is a long-winded way of making a point that's not that important.
Solution: Replace it with a shorter, more evocative description: " Click. Bzzzzzzz. Whoever was on the other end of the line had hung up."
I was about ready to give up: I'd been trying to get the skinny on whether the Atlas Theater was actually closing to make way for a big AMC multiplex or if it was just a rumor for weeks, but no one would return my calls.
Problem: This sentence is kind of long. Some of the phrases ("about ready to give up," "get the skinny") are cliche.
Solution: Eva decides to try to stick more closely to her own perspective: "I'd heard rumors that Atlas Theater was going to be replaced with an AMC multiplex, and I was worried." She also puts a paragraph break before this sentence to emphasize that she's now moving on to the background info rather than describing her call.

Step 7: Double Check Everything
Once you have a final draft, give yourself another week and then go through your essay again. Read it carefully to make sure nothing seems off and there are no obvious typos or errors. Confirm that you are at or under the word limit.
Then, go over the essay again, line by line , checking every word to make sure that it's correct. Double check common errors that spell check may not catch, like mixing up affect and effect or misplacing commas.
Finally, have two other readers check it as well . Oftentimes a fresh set of eyes will catch an issue you've glossed over simply because you've been looking at the essay for so long. Give your readers instructions to only look for typos and errors, since you don't want to be making any major content changes at this point in the process.
This level of thoroughness may seem like overkill, but it's worth taking the time to ensure that you don't have any errors. The last thing you want is for an admissions officer to be put off by a typo or error.
Example: Eva's Final Draft (Paragraphs 1 and 2)
"Hello? This is Eva Smith again. I'm a reporter with Tiny Town High's newspaper The Falcon , and I was hoping to ask you some questions about —" Click. Bzzzzzzz. Whoever was on the other end of the line had hung up.
I'd heard rumors that the historic Atlas Theater was going to be replaced with an AMC multiplex, and I was worried. I'd grown up with the Atlas: my dad taking me to see every Pixar movie on opening night and buying me Red Vines to keep me distracted during the sad parts. Unfortunately my personal history with the place didn't seem to carry much weight with anyone official, and my calls to both the theater and city hall had thus far gone unanswered.
Once you've finished the final check, you're done, and ready to submit! There's one last step, however.
Step 8: Do It All Again
Remember back in step one, when we talked about making a chart to keep track of all the different essays you need to write? Well, now you need to go back to that list and determine which essays you still need to write . Keep in mind your deadlines and don't forget that some schools may require more than one essay or ask for short paragraphs in addition to the main personal statement.
Reusing Essays
In some cases, you may be able to reuse the essay you've already written for other prompts. You can use the same essay for two prompts if:
Both of them are asking the same basic question (e.g. "how do you interact with people who are different from you?" or "what was an important experience and why?"), or
One prompt is relatively specific and the other is very general (e.g. "tell us about how your family shaped your education" and "tell us something about your background"), and
Neither asks about your interest in a specific school or program.
If you choose to reuse an essay you wrote for a different prompt, make sure that it addresses every part of question and that it fits the word limit. If you have to tweak a few things or cut out 50-odd words, it will probably still work. But if the essay would require major changes to fit the criteria, you're probably better off starting from scratch (even if you use the same basic topic).
Crafting Supplemental Essays
The key to keep in mind in when brainstorming for supplemental essays is that you want them to add something new to your application . You shouldn't write about the same topic you used for your personal statement, although it's okay to talk about something similar, as long as you adopt a clearly different angle.
For example, if you're planning to be pre-med in college and your main essay is about how volunteering at the hospital taught you not to judge people on their appearance, you might write your secondary essay on your intellectual interest in biology (which could touch on your volunteering). There's some overlap, but the two topics are clearly distinct.
And now, you're really, truly, finally done. Congrats!

What's Next?
Now that you know how to write a college essay, we have a lot more specific resources for you to excel.
Are you working on the Common App essay ? Read our breakdown of the Common App prompts and our guide to picking the best prompt for you.
Or maybe you're interested in the University of California ? Check out our complete guide to the UC personal statements .
In case you haven't finished the rest of the application process , take a look at our guides to asking for recommendations , writing about extracurriculars , and researching colleges .
Finally, if you're planning to take the SAT or ACT one last time , try out some of our famous test prep guides, like "How to Get a Perfect Score on the SAT" and "15 Key ACT Test Day Tips."

Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Alex is an experienced tutor and writer. Over the past five years, she has worked with almost a hundred students and written about pop culture for a wide range of publications. She graduated with honors from University of Chicago, receiving a BA in English and Anthropology, and then went on to earn an MA at NYU in Cultural Reporting and Criticism. In high school, she was a National Merit Scholar, took 12 AP tests and scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and ACT.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Tips for Writing an Effective Application Essay
Find the right college for you.
Writing an essay for college admission gives you a chance to use your authentic voice and show your personality. It's an excellent opportunity to personalize your application beyond your academic credentials, and a well-written essay can have a positive influence come decision time.
Want to know how to draft an essay for your college application ? Here are some tips to keep in mind when writing.
Tips for Essay Writing
A typical college application essay, also known as a personal statement, is 400-600 words. Although that may seem short, writing about yourself can be challenging. It's not something you want to rush or put off at the last moment. Think of it as a critical piece of the application process. Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor.
1. Start Early.
Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school. That way, you have ample time to think about the prompt and craft the best personal statement possible.
You don't have to work on your essay every day, but you'll want to give yourself time to revise and edit. You may discover that you want to change your topic or think of a better way to frame it. Either way, the sooner you start, the better.
2. Understand the Prompt and Instructions.
Before you begin the writing process, take time to understand what the college wants from you. The worst thing you can do is skim through the instructions and submit a piece that doesn't even fit the bare minimum requirements or address the essay topic. Look at the prompt, consider the required word count, and note any unique details each school wants.
3. Create a Strong Opener.
Students seeking help for their application essays often have trouble getting things started. It's a challenging writing process. Finding the right words to start can be the hardest part.
Spending more time working on your opener is always a good idea. The opening sentence sets the stage for the rest of your piece. The introductory paragraph is what piques the interest of the reader, and it can immediately set your essay apart from the others.
4. Stay on Topic.
One of the most important things to remember is to keep to the essay topic. If you're applying to 10 or more colleges, it's easy to veer off course with so many application essays.
A common mistake many students make is trying to fit previously written essays into the mold of another college's requirements. This seems like a time-saving way to avoid writing new pieces entirely, but it often backfires. The result is usually a final piece that's generic, unfocused, or confusing. Always write a new essay for every application, no matter how long it takes.
5. Think About Your Response.
Don't try to guess what the admissions officials want to read. Your essay will be easier to write─and more exciting to read─if you’re genuinely enthusiastic about your subject. Here’s an example: If all your friends are writing application essays about covid-19, it may be a good idea to avoid that topic, unless during the pandemic you had a vivid, life-changing experience you're burning to share. Whatever topic you choose, avoid canned responses. Be creative.
6. Focus on You.
Essay prompts typically give you plenty of latitude, but panel members expect you to focus on a subject that is personal (although not overly intimate) and particular to you. Admissions counselors say the best essays help them learn something about the candidate that they would never know from reading the rest of the application.
7. Stay True to Your Voice.
Use your usual vocabulary. Avoid fancy language you wouldn't use in real life. Imagine yourself reading this essay aloud to a classroom full of people who have never met you. Keep a confident tone. Be wary of words and phrases that undercut that tone.
8. Be Specific and Factual.
Capitalize on real-life experiences. Your essay may give you the time and space to explain why a particular achievement meant so much to you. But resist the urge to exaggerate and embellish. Admissions counselors read thousands of essays each year. They can easily spot a fake.
9. Edit and Proofread.
When you finish the final draft, run it through the spell checker on your computer. Then don’t read your essay for a few days. You'll be more apt to spot typos and awkward grammar when you reread it. After that, ask a teacher, parent, or college student (preferably an English or communications major) to give it a quick read. While you're at it, double-check your word count.
Writing essays for college admission can be daunting, but it doesn't have to be. A well-crafted essay could be the deciding factor─in your favor. Keep these tips in mind, and you'll have no problem creating memorable pieces for every application.
What is the format of a college application essay?
Generally, essays for college admission follow a simple format that includes an opening paragraph, a lengthier body section, and a closing paragraph. You don't need to include a title, which will only take up extra space. Keep in mind that the exact format can vary from one college application to the next. Read the instructions and prompt for more guidance.
Most online applications will include a text box for your essay. If you're attaching it as a document, however, be sure to use a standard, 12-point font and use 1.5-spaced or double-spaced lines, unless the application specifies different font and spacing.
How do you start an essay?
The goal here is to use an attention grabber. Think of it as a way to reel the reader in and interest an admissions officer in what you have to say. There's no trick on how to start a college application essay. The best way you can approach this task is to flex your creative muscles and think outside the box.
You can start with openers such as relevant quotes, exciting anecdotes, or questions. Either way, the first sentence should be unique and intrigue the reader.
What should an essay include?
Every application essay you write should include details about yourself and past experiences. It's another opportunity to make yourself look like a fantastic applicant. Leverage your experiences. Tell a riveting story that fulfills the prompt.

What shouldn’t be included in an essay?
When writing a college application essay, it's usually best to avoid overly personal details and controversial topics. Although these topics might make for an intriguing essay, they can be tricky to express well. If you’re unsure if a topic is appropriate for your essay, check with your school counselor. An essay for college admission shouldn't include a list of achievements or academic accolades either. Your essay isn’t meant to be a rehashing of information the admissions panel can find elsewhere in your application.
How can you make your essay personal and interesting?
The best way to make your essay interesting is to write about something genuinely important to you. That could be an experience that changed your life or a valuable lesson that had an enormous impact on you. Whatever the case, speak from the heart, and be honest.
Is it OK to discuss mental health in an essay?
Mental health struggles can create challenges you must overcome during your education and could be an opportunity for you to show how you’ve handled challenges and overcome obstacles. If you’re considering writing your essay for college admission on this topic, consider talking to your school counselor or with an English teacher on how to frame the essay.
Related Articles
Related topics.

English for Uni
Essay Writing
Ms parrot: essay chef.
View the video, then try the essay exercises to test your knowledge! Watch the whole story, or see sections of the story below. All the videos have captions that you can view on YouTube.
View the video on the Chinese site youku .
View the individual video chapters
To view the individual chapters of the above video, you can either click the 'PLAYLIST' menu item in the above YouTube video and select the chapter from there, or, you can click one of the links below and view the individual video on YouTube.
- Essay Chef - Introduction
- Essay Chef - The cooking show
- Essay Chef - Teaching
- Exercise 1: Introductions
- Exercise 2: Conclusions
- Exercise 3: Voice
- Exercise 4: Paraphrasing
- Exercise 5: Referencing
- Exercise 6: Academic Integrity
Download the transcript of the video or download the exercises in PDF format or as a Word document .
Essays in different academic cultures Teachers' notes
Essay structure
Essays help you discover more about a topic and write a reasoned analysis of the issues in question, using a range of external sources to support your position.
An essay is a highly structured piece of writing with follow a typical pattern:
| Section | Explanation of section contents |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | ackground statement — where you set the context for your essay ssue(s) — where you outline the specific issues that are relevant to your essay. hesis — where you state your position in relation to the issues. cope — where you outline what exactly is going to be covered in relation to your argument. |
| 2. Main body | Each paragraph should focus on one idea only. The idea can then be developed in a number of ways, such as through explanation, evaluation, exemplification or incorporation of research data. Your paragraphs should be balanced — keep to the rule of no less than 3 sentences per paragraph. Your paragraphs should link together — use connective words, both within and between paragraphs, to keep a sense of cohesion and linkage. |
| 3. Conclusion | Begin with a link to the preceding paragraph. Restate your thesis and summarise your principal points. End with a broad statement relating to the significance of your argument. |
Writing a good essay can be compared to baking a cake—if you do not mix the right ingredients in the right quantities or order, and do not follow the required processes, then the end result will not be what you hoped for! There is no set model for an essay, but the English for Uni website presents one popular way to do it. The following example is based around a 1000 word discussion essay. To read about essays in greater detail, download this PDF or Word document .
Topic/title
It is important for you to analyse your topic and title very carefully in order to understand the specific aim of the question. To do this, you need to break down the question. Most essay questions will contain these three elements:
Content/Topic words give the subject of the essay. Limiting/Focus words provide a narrower scope for the essay. Directive or Instructional words tell you how to approach the essay. Look at these sample essay titles from A) Economics and B) Nutrition:
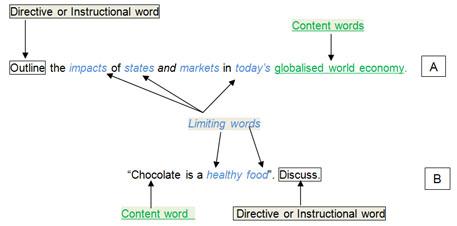
In example B, answering the question fully involves looking closely at the directive word Discuss and analysing its exact meaning.
Discuss: Present various points and consider the different sides. A discussion is usually longer than an explanation, as you need to present evidence and state which argument is more persuasive.
So, in your essay entitled:
“Chocolate is a healthy food”. Discuss.”
you would need to:
- consider a number of points in relation to the title
- balance your points between supporting and opposing positions
- consider which of the positions is the most persuasive and explain why
You also need to consider the length of your essay. In a 2000 word essay you can cover more points than in a 1000 word one! This example is based on a 1000 word essay.
In relation to Content words your focus is clear: chocolate!
In relation to Limiting words, you need to consider what healthy food actually means. A good way to expand your vocabulary is to look at the Academic Word List (developed by Averil Coxhead at Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand). The uefap website also has very useful lists of words found in particular subjects, such as mathematics, business and health science.
Directive or Instructional words
There are a number of directive words, or instructional words as they are sometimes called, which tell you what to do in your essay. Some common directive words include:
| Look at something in depth, examining the details. | |
| Give reasons for why you agree or disagree with something and show that you understand different points of view. | |
| Compare different points and see if the argument or information is true or persuasive. | |
| Show the similarities between two sets of information or arguments. ‘Compare’ often appears with ‘contrast’ in essay questions. | |
| Show the differences between two sets of information or arguments. ‘Contrast’ often appears with ‘compare’ in essay questions. | |
| Evaluate an argument or a text to see if it is good. ‘Criticise’ does not mean you have to be negative. | |
| Evaluate an argument or a text to see if it is good. ‘Critique’ does not mean you have to be negative. | |
| Explain the meaning of a word or a term, especially in the context of your essay. You can use a dictionary definition if it’s helpful, but remember that the word might be used in a particular way in the subject you are studying. | |
| Give details about something. | |
| Look at the different sides of an argument and say which is more convincing. Help your reader to understand more about something by giving relevant details. | |
| Look at the strengths and weaknesses of the material and give your final opinion of it. | |
| Look at the strengths and weaknesses of the material and give your final opinion of it. | |
| Help your reader to understand more about something by giving relevant details. | |
| Give examples to make something clearer. | |
| Help your reader to understand more about something and provide your own perspective if necessary. | |
| Give reasons to explain what you think about a subject. | |
| Give a broad explanation of something without too many details. | |
| Show if something is true and demonstrate how you reached that conclusion. | |
| Look at something in detail and give your perspective on it. | |
| Put your ideas or arguments clearly. | |
| Pull everything together and present it clearly without using too much detail. |
Brainstorming
Brainstorming means producing ideas related to a theme. You can write the ideas down in any order.
Here is a possible brainstorm for the chocolate essay, done in the form of a mind map:
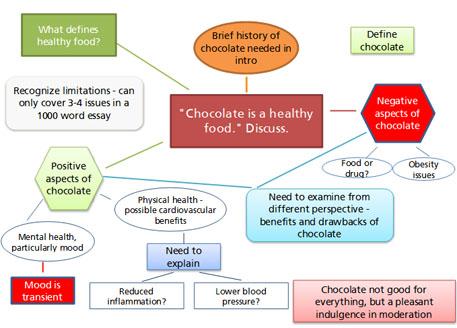
Text description of the above image.
Note that the central focus (the essay question) has several boxes linked to it which represent the writer’s first ideas. Other boxes area then added. A brainstorm like this is organic; it does not necessarily stop growing. You can add, remove or reorganise it as you wish. If you like to put more system into your brainstorm, use a step-based model such as the following:
Step 1 Time yourself for the first draft of your mind map Set a fixed time for this drafting from your base topic/question and stick to it.
Step 2 Look critically at your draft Which ideas could you develop or remove? Is there a balance of ideas?
Step 3 Think about ordering Which issues might you tackle first in your essay and why?
Step 4 Anticipate readers’ needs Are there any words and/or phrases that might need explaining? If so, when is the best time in the essay to do this?
Step 5 Move Reflect upon your brainstorming. Once you are happy with your brainstorm you can use it to plan your essay.
Researching for your essay
Once you have done some brainstorming, it’s time to get researching!
Remember that an academic essay requires academic sources.
Finding what you want takes time and effort. The best place to start (assuming you haven’t already been given a prescribed reading list!) is by using an academic database. If you are not sure how to use a database, then book an appointment with your subject librarian at your institution.
Another option is to use an internet academic search engine such as Google Scholar. N.B. Make sure you are logged in to the library at your educational institution, so that you can use the full database capacities linked to Google Scholar.
You need to enter keywords to begin with. For the chocolate essay, one of the first associations we thought of was chocolate and mood. If we enter these words into Google Scholar it will look like this:

This will take you to a webpage which lists a number of relevant articles, like this:
The first two articles have been cited 90 times and 103 times respectively, suggesting that they might be good sources for your essay. The links to the right indicate that you can access the articles through your university website.
If you think an article looks promising, click on the link and look at the abstract:
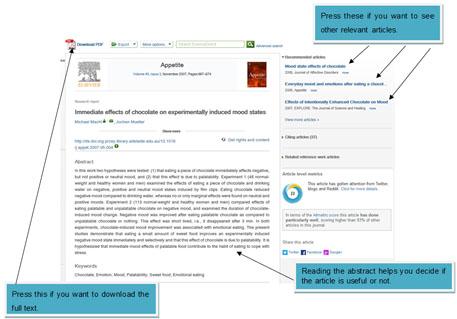
Read the abstract and ask yourself if the content of the article is likely to be relevant to your essay.
a) If yes, click on the PDF. This will take you to the full article which you can then skim read quickly to decide if it is relevant. b) If no, then you have a choice. Either click on the links to other related articles or go back to Google Scholar and then choose another article to skim read.
If you do not find what you are looking for, then you need to change your keywords search.
When you have found what you think might be useful, make a note in your plan at the appropriate place.
Do the same thing for all the points that need academic references to support them.
Remember that during your research you might discover new issues and perspectives that you hadn’t considered before, so your original plan might be quite different from the final one!
Planning your essay
Once you have brainstormed your ideas and done some initial research, start putting them into a logical order as part of the essay planning process. Brainstorming helps you to see what you know about the topic. Researching will give you more depth. Brainstorming, researching and planning are cyclical, which means that each process helps the other processes and you might want to do each process more than once.
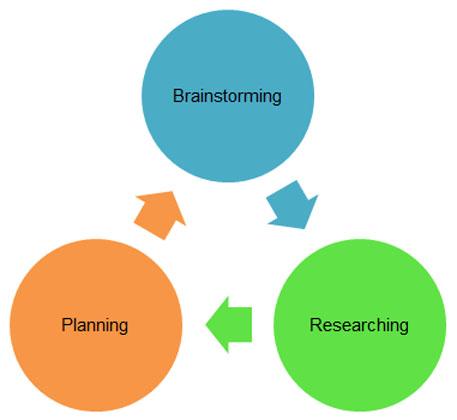
Here is the brainstorm for the chocolate essay again, which you can use to develop the planning process:
Read the text version of the brainstorming mind map .
Planning or a plan?
In the first instance, it is important to distinguish between planning and a plan . Planning is an ongoing process, from when you receive the essay title to when you submit your final draft. A plan is a physical outline of the way you intend to conceptualise, structure and present your ideas.
Plans can be structured/restructured at any time during the planning process.
At this point it is time to write your first plan. However, do not stop doing research yet. Why not?
| A plan helps you to put your ideas into a form which gives you a for your . | Once you have written your ideas up into a plan, you are beginning to in . | You might surprise yourself by discovering . This can help . |

Remember that a plan is just that—a plan. It can be modified after you do more research; you might discover some different perspectives or issues you hadn’t previously anticipated.
Example: Developing an essay plan after research (linear style)
Title: “Chocolate is a healthy food.” Discuss.
Introduction Context for paper – popularity of chocolate. Issue – whether chocolate is a healthy food is questionable. Thesis – chocolate may be enjoyable but not healthy. Scope – (only 4 aspects are covered here to keep the example short)
| Positive: | Can positively impact on mood |
|---|---|
| Positive: | Possible health benefits for cardiovascular system |
| Negative: | Chocolate can be seen as a drug rather than a food |
| Negative: | Potential correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity |
Main body Paragraph 1 with possible sources Ways in which chocolate can impact positively on mood. ‘Feel good effect’ - Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006), Scholey and Owen (2013), Macht and Dettmer (2006) and Macht and Mueller (2007).
Is the chocolate and improved mood scenario measurable/transient? Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006) – chocolate mood effects do not last. Macht and Dettmer (2006) – anticipation effect and more studies needed.
Paragraph 2 Possible benefits of chocolate on cardiovascular health – how much/what type(s) of chocolate have benefit? (Sources needed to help answer these questions.) Problems with measuring correlation between chocolate consumption and cardiovascular health. (Sources needed to help answer this.)
Paragraph 3 Chocolate best viewed as a food or a drug? Indulgence or addiction – are the boundaries unclear? (See what external sources have to say on this) Medication elements of chocolate? (Readings needed around this issue.)
Paragraph 4 The correlation between chocolate and obesity. (Definition of obesity needed.) What does the literature say in relation to other causal factors?
Conclusion Summary of four arguments presented. Chocolate is not a healthy food, but it is enjoyable nevertheless.
Example: Developed essay plan (linear style)
Main body Paragraph 1 Ways in which chocolate can impact positively on mood. ‘Feel good effect’-Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006), Scholey and Owen (2013), Macht and Dettmer (2006) and Macht and Mueller (2007)
Is the chocolate and improved mood scenario measurable/transient? Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006) chocolate mood effects do not last. Macht and Dettmer (2006) – anticipation effect and more studies needed.
Paragraph 2 Possible benefits of chocolate on cardiovascular health – how much/what type(s) of chocolate have benefit? Can provide heart-friendly flavanols (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002) – helps with blood clotting and is anti-inflammatory (Schramm et al., 2001) Maximising benefits of chocolate lies in minimising fat levels (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002). Current processes destroy flavanols (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002). Note the change of focus from the original idea (correlation between chocolate consumption and cardiovascular health) due to the lack of research data available.
Paragraph 3 Chocolate best viewed as a food or a drug? Indulgence or addiction – are the boundaries unclear? Chocolate contains some biologically active ingredients, but in small amounts (Bruinsma & Taren, 1999). ‘Chocolate addicts’ – negative correlation: chocolate consumption and mood (Macdiramid & Hetherington, 1995) but chocolate cravings sensory rather than addictive (Bruinsma & Taren,1999). Medication elements of chocolate? Used in relation to magnesium deficiency in women (Pennington, 2000 in Steinberg et al., 2003). Findings concur with Abraham and Lubran (1981) who found a correlation between magnesium deficiency and nervous tension in women. Note the narrow focus of medical benefits (i.e. only considering magnesium) due to the short length of the essay.
Paragraph 4 The correlation between chocolate and obesity. No specific correlation found in literature (Beckett, 2008; Lambert, 2009). Note the findings show that there is no clear relationship between chocolate and obesity – an issue flagged in the introduction. Typified by Mellor’s (2013) findings – adults showed no weight increase after chocolate controlled diet. Lambert (2009) exemplified that chocolate consumption alone unlikely to precipitate obesity. ‘Chocoholic’ more likely to consume other sweet foods and less likely to exercise as much as others. Chocolate consumption thus marginal in causes of obesity.
Conclusion Summary of four arguments presented Chocolate is not a healthy food, but it is enjoyable nevertheless.
Writing your conclusion
It might seem strange to think about writing your conclusion before you write the body of your essay, but unless you know where you are going you can easily lose direction. Also, the conclusion is the last thing the reader actually reads, so it needs to be memorable.
There are a number of questions you should ask yourself, such as:
How will everything finish? What are you aiming for? What final impression do you want your readers to have?
Your conclusion ties your essay together. It should normally:
- Begin with a link to the preceding paragraph.
- Restate your thesis and summarise your principal points.
- End with a broad statement relating to the significance of your argument.
So, our chocolate essay conclusion should mirror this pattern.
The conclusion should not just repeat the ideas from the introduction. The introduction includes the background to the essay, the important issues and a thesis statement. The introduction leads your reader into the essay. The conclusion reminds your reader of the main points made in your essay and leaves your reader with a final impression and ideas to think about later.
Chocolate essay conclusion
The following conclusion has three parts.
(A) The first sentence links the conclusion to the discussion in the previous paragraph. (B) The following sentences restate the main points and reaffirm the thesis. (C) The last sentence is a broad statement relating to the significance of the argument.
(A) Obesity and chocolate consumption seemingly have no proven correlations. (B) Yet, in this essay, many chocolate focused arguments have been presented, including the transient effect of chocolate on mood and evidence that it is as likely to create feelings of guilt as of well-being. Another possible positive dimension to chocolate is a correlation with cardiovascular health. Yet the potential benefits of flavanols in chocolate are currently offset by the high fat/carbohydrate content of most forms of chocolate. Whether chocolate is a food or a drug is also unclear. The literature outlines the chemical properties of chocolate which could help explain some addictive type behaviour, particularly in regards to nervous tension in women, but also there is a strong research focus on chocolate as a sensory-based indulgence. (C) It can therefore be said that chocolate is not a healthy food, but can be enjoyed as part of a healthy and balanced diet and lifestyle.
Writing the body paragraphs
At the heart of your essay lie your body paragraphs. Typically, a body paragraph will follow the format below.
| The topic sentence can function as a sentence of transition from the previous paragraph. The Topic Sentence should unambiguously express the topic of the paragraph and be linked with the overall thesis of the essay. | |
| Elaboration of the main point should add more detailed information in relation to the topic sentence. Examples and Evidence should support your main point using paraphrases, summaries or direct quotations, all of which need to be appropriately referenced. | |
| The Concluding Sentence should echo the main point of the paragraph and function as a bridge to the next paragraph. |
N.B. Paragraphs should be balanced – keep to the ‘no less than 3 sentences per paragraph’ rule.
Remember to link all the points in your paragraph to the idea in the topic sentence. One way to check if you have done this is to write keywords in the margin for each sentence. If your keywords are related to the topic sentence, your paragraph is good. If there are ideas that are not related, you should remove them.
In the following example, the unrelated ideas are highlighted in red:
| Paragraph | Sentence keywords |
|---|---|
| It has been claimed that chocolate is a healthy food, but in fact it contains a lot of sugar, which can be unhealthy. For example, sugar can cause tooth decay, which can lead to dental problems in later life. Too much sugar can also lead to obesity, which is a serious health risk. In addition, sugar contains a high amount of fructose, which is bad for the liver. The amount of sugar contained in chocolate means, therefore, that chocolate, particularly milk and white chocolate, may not be healthy. | Topic sentence – sugar and health sugar and tooth decay (health)
obesity (health)
|
These unrelated ideas can be removed to make a more coherent paragraph:
It has been claimed that chocolate is a healthy food, but in fact it contains a lot of sugar, which can be unhealthy. For example, sugar can cause tooth decay, which can lead to dental problems in later life. Too much sugar can also lead to obesity, which is a serious health risk. In addition, sugar contains a high amount of fructose, which is bad for the liver. The amount of sugar contained in chocolate means, therefore, that chocolate, particularly milk and white chocolate, may not be healthy.
You can then add examples and references to make your paragraph stronger.
Here is an example:
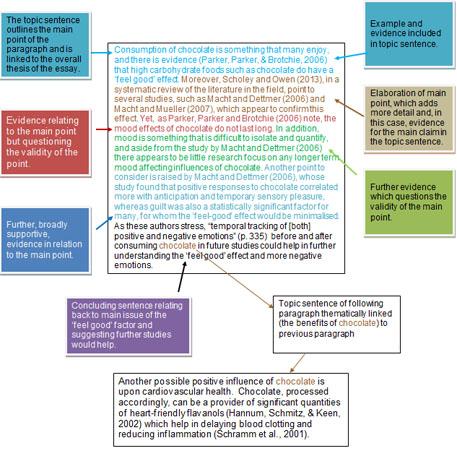
View the text description of the above body paragraph example .
Writing your introduction
Once you have drafted your main body paragraphs and your conclusion, it is time to draft your introduction.
Writing your introduction last means you are more likely to have a tighter fit between the introduction, main body and conclusion because you already know what your essay will be about.
Let us have another look at the functions of an introduction:
B ackground statement — where you set the context for your essay I ssue(s) — where you outline the specific issues that are relevant to your essay. T hesis — where you state your position in relation to the issues. S cope — where you outline what exactly is going to be covered in relation to your argument.
The thesis and scope are sometimes combined to form one or more sentences known as a thesis statement . The thesis statement often comes at the end of the introduction, although it can be written earlier.
Sometimes an essay will begin with a direct quote to draw readers into the essay.
Sometimes, particularly in very short essays, the essay will begin with an issue rather than a background statement.
Essays also sometimes begin with an issue, outline the scope and then move on to end the introduction with the thesis statement.
It is important to remember that there is not a fixed ordering for the introduction, though the BITS/BIST patterning is a very common one, which is why it is modelled for you as an example.
Example introduction
“Chocolate is a healthy food”. Discuss.
| Explanation | Sentence(s) in order |
|---|---|
| Background statement which draws the reader into the issue | Since Spanish explorers brought back chocolate from the new world, chocolate consumption has become a worldwide phenomenon. |
| Additional information to the background statement | At first, chocolate, a derivative of the cacao bean, was consumed as a drink, only later achieving mass popularity in tablet or bar form. |
| The issue that is suggested by the title | However, chocolate's inherent popularity does not equate to it possessing healthy properties, as suggested by the title. |
| Scope of the essay | The realities of chocolate are more down to earth; a number of these realities will be addressed in this essay. Chocolate has chemical properties that can influence mood and there is possible evidence for some positive impacts of chocolate on cardiovascular health. Yet, such positive attributes are counterbalanced somewhat by the argument that, in some instances, chocolate can be viewed as a drug rather than a food. Moreover, there is the possibility of some correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity. |
| Thesis statement | Thus, it will be argued that despite chocolate's positive effect in some cases on mood and the cardiovascular system it has also been linked to addiction and obesity. |
Writing references for your essay
When you are writing an essay you will need to include references to external academic sources.
Why do you need to reference?
- To show respect for other people's ideas and work
- To clearly identify information coming from another source
- To distinguish an external source from your interpretation or your own findings
- To support your own arguments, thus giving you more credibility
- To show evidence of wide (and understood) reading
- To avoid being accused of plagiarism, which includes copying another’s work, paraphrasing or summarising without acknowledgement, colluding with others and presenting either identical or very similar essays
What does referencing include?
A. In-text citations, which can take three forms:
- Paraphrasing, where you keep the original author’s ideas intact, but just change the wording
- Summarising, where you summarise the whole of the author’s work, rather than one particular aspect
- Direct quoting, where you take a word-for-word copy of a short extract from the original author’s work, and include it in your essay, making use of quotation marks and page number
- All of these need a reference in the text.
B. A reference list at the end of your essay, which includes details such as:
- Date of publication
- Publisher and place of publication (for books)
- Journal name, volume and issue (for journals)
- Internet address or doi (digital object identifier) for electronic sources
Referencing is integral to academic essay writing and shouldn’t be viewed as an ‘add-on’. When you are referencing, always use a referencing guide to help you ensure 100% accuracy.
Normally, when writing an essay at university you will be expected to use only academic sources. The following learning guide on source credibility will help you to determine whether an external source is academic or not.
The chocolate essay uses the American Psychological Association (APA) style of referencing, which is easy to distinguish from the Harvard Author-Date System, as the format is different:
| Harvard | APA |
|---|---|
When you are writing an essay and including external sources, more often than not you want the reader to focus on what is said rather than who is saying it. In that case the information comes before the author. For example:
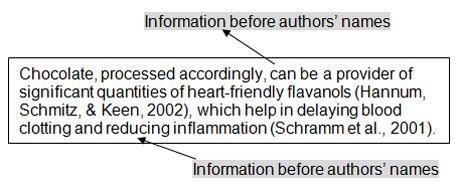
Such citations are called information-centred citations.
When the focus is more on who is saying it then the citation is written like this:

Such citations are called author-centred citations.
Try and achieve a balance between both types of in text-references in your essay writing.
Reference list
In the APA style of referencing, the reference list has certain conventions that you must also follow. Here are some examples from the chocolate essay:

Text description of the APA style of referencing example above.
Don’t make referencing something you do just as an editing or proofreading activity. Include your in-text citations and reference list as part of your first draft.
An excellent website to help with your APA referencing is the APA Interactive tool at Massey University.
Redrafting your essay
Leave yourself enough time to look at your essay more than once. For a 1000 word essay you need at least three days to redraft your essay.
Always save each draft as a separate file; then you can see how your essay develops and improves.
Here are the sorts of questions you should ask yourself:
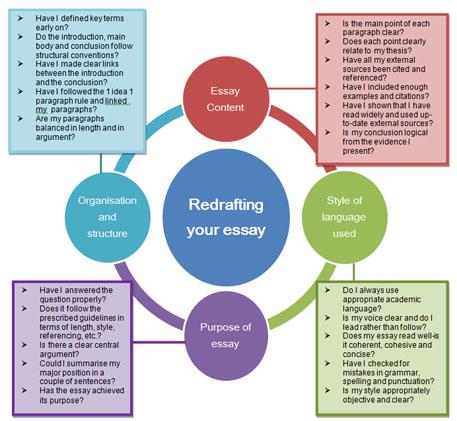
View a text version of the redrafting your essay diagram above.
You can also look at other checklists such as this one on editing your own work .
Let’s see how the writer of the chocolate essay redrafted their original introduction:

View the text version of the redrafted essay .
Now compare the above with the final draft:
Since Spanish explorers brought back chocolate from the new world, chocolate consumption has become a worldwide phenomenon. At first, chocolate, a derivative of the cacao bean, was consumed as a drink, only later achieving mass popularity in tablet or bar form. However, chocolate’s inherent popularity does not equate to it possessing healthy properties, as suggested by the title. The realities of chocolate are more down to earth; a number of these realities will be addressed in this essay. Chocolate has chemical properties that can influence mood and there is possible evidence for some positive impacts of chocolate on cardiovascular health. Yet, such positive attributes are counterbalanced somewhat by the argument that, in some instances, chocolate can be viewed as a drug rather than a food. Moreover, there is the possibility of some correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity. Thus, it will be argued that despite chocolate’s positive effect in some cases on mood and the cardiovascular system it has also been linked to addiction and obesity.
Take your time and be careful when redrafting—it will be worth it!
Incorporating your own voice
How do you write in an academic way?
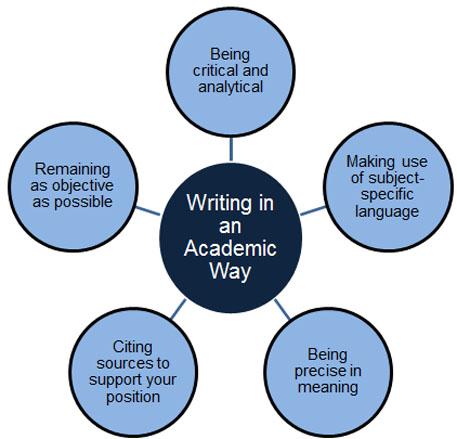
Your lecturers will want to hear your ‘voice’ as they read your essay.
Imagine your essay as a kind of story. You are the principal storyteller, the internal voice of the writer, leading the reader through to your conclusion.
During the story, there are different voices that appear from time to time. These are the external voices (citations) that add substance to your story, providing detail and support for what you are saying and sometimes even giving an alternative perspective. The external voices can be divided into two categories in your essay: the direct external voice of an author (through a direct quote) and the indirect external voice of an author (through a paraphrase).
The reader needs to know at all times whose voice they are hearing. Is it your internal voice or the external voice of other authors?
You might wonder how you can include your own voice and still sound academic when you are writing about a subject area in which you have little (or no) knowledge. Including your voice does not mean that you should say ‘I think’ or ‘in my opinion’.
Here are some examples of the critical/analytical language that you can use as your own internal voice when you present other people’s ideas:
| Phrase | How your voice is included |
|---|---|
| It has been argued (Smith & Jones, 2010) that… | Pointing out what has been said by an external source |
| As Smith and Jones (2010) note… | Showing your agreement with the external source |
| However, Smith and Jones (2010) fail to address… | Showing that you recognise the limitations of the source |
| Seemingly, Smith and Jones (2010) have… | Showing you have tentative support for the external source |
| On the other hand, Smith and Jones (2010) argue that… | Showing that there is a contrast with a previous argument you have included |
| Smith and Jones (2010) assert that… | Showing that the position of the external source is strong but you are likely to have doubts about it |
| It has been suggested that… (Smith & Jones, 2010; Brown & Culbertson, 2005; Lloyd & Giggs, 2004) | Showing that you recognise a number of authors have reached a similar conclusion, and you might/might not agree with it |
| One advantage of the work of Smith and Jones (2010)… | Showing that you are positively engaging with an external source |
Let’s look at one of the paragraphs from the chocolate essay to see how the text is an interplay of the internal voice of the writer and the external voices of other authors. The internal voice of the writer is colour-coded in yellow; the indirect external voices of other authors (i.e. paraphrases) are coded in grey; and the direct external voices of other authors (i.e. quotations) are coded in blue.

View a text version of the voice explanation above.
This is a balanced paragraph. The writer sets the scene at the beginning of the topic sentence and also links together all of the sentences, using their own voice to lead into content which is provided by the external voices.
Look at the same paragraph re-written, with the amount of the writer’s voice substantially reduced:
View a text version of the above re-written paragraph .
Here the writer is not ‘in charge’ of the paragraph, and it reads a little like a list. That is something your lecturers do not want to see.
When you are drafting your paragraphs, use a colour-coding system like the one used here. It will help you ensure your academic voice is clear!
When you get more confident in using external sources, you will gradually expand the language of your critical internal voice. The Phrasebank website at Manchester University provides examples of some more expressions to use when assessing external sources.
Proofreading and editing your essay
Editing focuses on the big picture elements such as overall structure, appropriate paragraphing and whether the question has been answered.
Proofreading has a micro-focus on the details of your essay, such as formatting, grammar and punctuation.
Everybody has their own personal style of editing and proofreading. You need to focus on the types of errors you commonly make by looking at the marker’s comments on your previous work.
Some people proofread alone; some get other people involved. Having others involved is a really good idea.
Fresh eyes can help you find things you might not otherwise have seen.
Here are some things to consider when proofreading and editing:
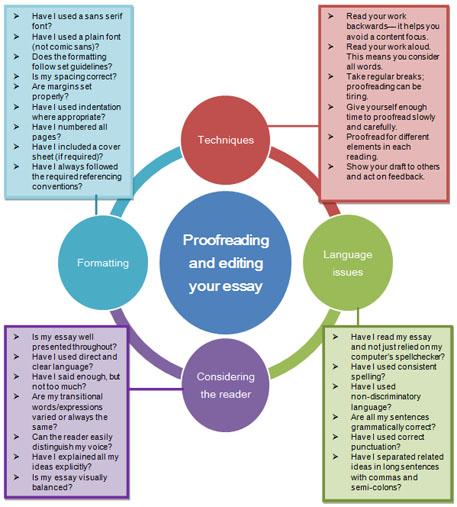
View a text version of the above proofreading and editing your essay considerations.
The Purdue OWL website has even more detail on the proofreading process.
Submitting on time
Students regularly underestimate the time it takes to write an essay, in particular the planning and researching stages.
Before you begin your essay, have a look at the Massey University assignment planning calculator . You might be surprised how long the whole process takes!
As you can see from the assignment planning calculator, if you only start your essay a few days before the due date, you will have to do things too quickly.
If you think of the essay/cake analogy, you need time to mix all the ingredients properly, or the end result will not be what you want to share with others!
To write a 1000 word essay, ideally you should allow yourself about 3 weeks.
Let’s have a look at how an essay time management ‘cake’ could be divided into slices:

View a text description of the writing an essay time management 'cake' .
You can see that the biggest part of your time is spent on the planning/research elements and redrafting/editing/proofreading elements, which together should comprise around 60% of your time.
Have a look at another model to see what you also need to consider:
Essay example
Here is the final version of the chocolate essay. You can also download a PDF version of the chocolate essay .
“Chocolate is a healthy food.” Discuss.
Since Spanish explorers brought back chocolate from the new world, chocolate consumption has become a worldwide phenomenon. At first, chocolate, a derivative of the cacao bean, was consumed as a drink, only later achieving mass popularity in tablet or bar form. However, chocolate’s inherent popularity does not equate to it possessing healthy properties, as suggested by the title. The realities of chocolate are more down to earth; a number of these realities will be addressed in this essay. Chocolate has chemical properties that can influence mood and there is possible evidence for some positive impacts of chocolate on cardiovascular health. Yet, such positive attributes are counterbalanced somewhat by the argument that, in some instances, chocolate can be viewed as a drug rather than a food. Moreover, there is the possibility of some correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity. Thus, it will be argued that despite chocolate’s positive effect in some cases on mood and the cardiovascular system it has also been linked to addiction and obesity.
Consumption of chocolate is something that many enjoy, and there is evidence (Parker, Parker, & Brotchie, 2006) that high carbohydrate foods such as chocolate do have a ‘feel good’ effect. Moreover, Scholey and Owen (2013) in a systematic review of the literature in the field point to several studies, such as Macht and Dettmer (2006) and Macht and Mueller (2007), which appear to confirm this effect. Yet, as Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006, p. 150) note, the mood effects of chocolate "are as ephemeral as holding a chocolate in one’s mouth". In addition, mood is something that is difficult to isolate and quantify, and aside from the study by Macht and Dettmer (2006) there appears to be little research on any longer term mood affecting influences of chocolate. Another point is raised by Macht and Dettmer (2006), whose study found that positive responses to chocolate correlated more with anticipation and temporary sensory pleasure, whereas guilt was also a statistically significant factor for many, for whom the ‘feel-good’ effect would be minimalised. As these authors stress, “temporal tracking of [both] positive and negative emotions” (p.335) before and after consuming chocolate in future studies could help in further understanding the ‘feel good’ effect and more negative emotions.
Another possible positive influence of chocolate is upon cardiovascular health. Chocolate, processed accordingly, can be a provider of significant quantities of heart-friendly flavanols (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002) which help in delaying blood clotting and reducing inflammation (Schramm et al., 2001). Such attributes of flavanols in chocolate need to be considered in the context of chocolate’s other components – approximately 30% fat, 61% carbohydrate, 6% protein and 3% liquid and minerals (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002). The key to maximising the benefits of flavanols in chocolate appears to lie in the level of fats present. Cocoa, which is simply chocolate minus the fat, is the most obvious candidate for maximising heart health, but as Hannum, Schmitz and Keen (2002) note, most cocoa products are made through an alkali process which destroys many flavanols. Optimal maximisation of the flavanols involves such compounds being present in cocoa and chocolate products at levels where they are biologically active (Ariefdjohan & Savaiano, 2005).
The biological makeup of chocolate is also relevant in determining whether chocolate is better viewed as a food or a drug, but the boundaries between indulgence and addictive behaviour are unclear. Chocolate contains some biologically active elements including methylxanthines, and cannabinoid-like unsaturated fatty acids (Bruinsma & Taren, 1999) which could represent a neurochemical dependency potential for chocolate, yet are present in exceedingly small amounts. Interestingly, and linked to chocolate and mood, Macdiarmid and Hetherington (1995) claim their study found that “self-identified chocolate ‘addicts’” reported a negative correlation between chocolate consumption and mood. This is perhaps indicative of addictive or compulsive type behaviour. However, as Bruinsma and Taren (1999) note, eating chocolate can represent a sensory reward based, luxurious indulgence, based around texture, aroma and flavour anticipation, rather than a neurochemically induced craving. Yet, it has been argued that chocolate is sometimes used as a form of self-medication, particularly in relation to magnesium deficiency. A study by Pennington (2000 in Steinberg, Bearden, & Keen 2003) noted that women do not generally meet US guidelines for trace elements, including magnesium. This correlates with earlier studies by Abraham and Lubran (1981), who found a high correlation between magnesium deficiency and nervous tension in women. Thus, tension-related chocolate cravings could be a biological entity fuelled by magnesium deficiency. Overall, however, it would appear that the proportion of people using chocolate as a drug rather than a food based sensory indulgence is small, though further research might prove enlightening.
A final point to consider in relation to chocolate is the perception that chocolate is linked to obesity. A person is defined as being obese when their Body Mass Index is greater than 30. The literature on chocolate and obesity has clearly demonstrated that there are no specific correlations between the two variables (Beckett, 2008; Lambert, 2009). This is typified by the findings of Mellor (2013), who found that, over a period of eight weeks of eating 45 grams of chocolate per day, a group of adults demonstrated no significant weight increase. As Lambert (2009) notes, chocolate consumption alone is not likely to cause obesity, unless large amounts of other calorie dense foods are consumed and this calorie dense intake is greater than needed for bodily function, bearing in mind levels of activity. The stereotypical ‘chocoholic’ seems more likely to consume many other sweet foods and be less likely to take exercise than other people, so chocolate consumption is only one possible variable when considering the causes of obesity.
Obesity and chocolate consumption seemingly have no proven correlations. Yet, in this essay, many chocolate focused arguments have been presented, including the transient effect of chocolate on mood and the fact that it is as likely to create feelings of guilt as of well-being. Another possible positive dimension to chocolate is a correlation with cardiovascular health. Yet the potential benefits of flavanols in chocolate are currently offset by the high fat/carbohydrate content of most forms of chocolate. Whether chocolate is a food or a drug is also unclear. The literature outlines the chemical properties of chocolate which could help explain some addictive type behaviour, particularly in regards to nervous tension in women, but there is also a strong research focus on chocolate as a sensory-based indulgence. It can therefore be said that chocolate is not a healthy food, but can be enjoyed as part of a healthy and balanced diet and lifestyle.
(Word count: 1087. This is within 10% of the word limit, which is usually acceptable. Check this with your lecturer if you are in any doubt.)
Abraham, G. E., & Lubran, M. M. (1981). Serum and red cell magnesium levels in patients with premenstrual tension. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition , 34 (11), 2364-2366. Retrieved from http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/34/11/2364.short
Ariefdjohan, M. W., & Savaiano, D. A. (2005). Chocolate and cardiovascular health: Is it too good to be true? Nutrition Reviews , 63 (12), 427-430. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2005.tb00118.x
Beckett, S. T. (2000). The science of chocolate . Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry.
Bruinsma, K., & Taren, D. L. (1999). Chocolate: Food or drug? Journal of the American Dietetic Association , 99 (10), 1249-12. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8223(99)00307-7
Hannum, S. M., Schmitz, H. H., & Keen, C. L. (2002). Chocolate: A heart-healthy food? Show me the science! Nutrition Today , 37 (3), 103-109. Retrieved from http://journals.lww.com/nutritiontodayonline/Abstract/2002/05000/Chocol…
Lambert, J. P. (2009). Nutrition and health aspects of chocolate. In S. Beckett (Ed.), Industrial chocolate manufacture and use , (4th ed., pp. 623-635). London: Wiley Blackwell. Retrieved from http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781444301588.ch27/pdf
Macht, M., & Dettmer, D. (2006). Everyday mood and emotions after eating a chocolate bar or an apple. Appetite , 46 (3), 332-336. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2006.01.014
Macht, M., & Mueller, J. (2007). Immediate effects of chocolate on experimentally induced mood states. Appetite , 49 (3), 667-674. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2007.05.004
Macdiarmid, J. I., & Hetherington, M. M. (1995). Mood modulation by food: An exploration of affect and cravings in ‘chocolate addicts’. British Journal of Clinical Psychology , 34 (1), 129-138. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1995.tb01445.x
Mellor, D. D. (2013). The effects of polyphenol rich chocolate on cardiovascular risk and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus (Doctoral dissertation, University of Hull, UK). Retrieved from https://hydra.hull.ac.uk/resources/hull:7109
Parker, G., Parker, I., & Brotchie, H. (2006). Mood state effects of chocolate. Journal of Affective Disorders , 92 (2), 149-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2006.02.007
Scholey, A., & Owen, L. (2013). Effects of chocolate on cognitive function and mood: a systematic review. Nutrition reviews , 71 (10), 665-681. doi:10.1111/nure.12065
Schramm, D. D., Wang, J. F., Holt, R. R., Ensunsa, J. L., Gonsalves, J. L., Lazarus, S. A., Schmitz, H. H., German, J. Bruce, & Keen, C. L. (2001). Chocolate procyanidins decrease the leukotriene-prostacyclin ratio in humans and human aortic endothelial cells. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition , 73 (1), 36-40. Retrieved from http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/73/1/36.full
Steinberg, F. M., Bearden, M. M., & Keen, C. L. (2003). Cocoa and chocolate flavonoids: Implications for cardiovascular health. Journal of the American Dietetic Association , 103 (2), 215-223. doi: 10.1053/jada.2003.50028
Academic integrity and plagiarism
‘Integrity’ relates to ‘honesty’, and academic integrity involves writing in an honest way, so that no one will think you are claiming that words or ideas from someone else are your own. This is very important in academic writing in western countries, and if you do not do this you might be accused of plagiarism, which is a serious offence at university.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words, ideas or diagrams without acknowledgement.
Of course, when we write an essay we need to refer to other people’s ideas. We gave some of the reasons for this before:
Being a good writer involves using other people’s ideas to support your work. However, you should never forget to say where these ideas come from, even if you don’t quote the person’s exact words.
Include a reference in the text, where the words or ideas appear, and in a reference list at the end of the essay.
All the references in the text must appear in the reference list, and all the references in the list must also appear in the text.
There is a short video clip on plagiarism here and a wonderful Plagiarism Carol video here (click on ‘captions’ to get subtitles in English).
Another word connected to academic integrity is collusion .
Collusion means that you work with someone else and submit the same or very similar assignments without your lecturer’s permission.
For example, if you and a friend work together on an essay and then submit identical or very similar versions of the essay, one under your name and one under your friend’s name, that is collusion . However, if you are doing a group work assignment and your lecturer has asked you to work together and submit the assignment jointly, that is not collusion . Collusion, like plagiarism, has an element of dishonesty in it. People who collude do so secretly, as they know that the lecturer would not be happy.
People make genuine mistakes, so lecturers are usually very happy to advise you if you ask them.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The On-Campus and Online versions of Purdue OWL assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue OWL serves the Purdue West Lafayette and Indianapolis campuses and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
Message from the assistant director of content development
At the Purdue OWL, we are dedicated to supporting students, instructors, and writers through our comprehensive range of resources. We are constantly working on developing and revising these materials, keeping the users’ needs in mind.
Our team is continuously exploring possibilities for a better design, prioritizing accessibility and user experience. As the OWL undergoes these changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
Thank you for being a part of the Purdue OWL community and for helping us continue being a leading resource for writers worldwide.
Wishing you all the very best!
Kritika Sharma
Social Media
Facebook Twitter

College Writing
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you figure out what your college instructors expect when they give you a writing assignment. It will tell you how and why to move beyond the five-paragraph essays you learned to write in high school and start writing essays that are more analytical and more flexible.
What is a five-paragraph essay?
High school students are often taught to write essays using some variation of the five-paragraph model. A five-paragraph essay is hourglass-shaped: it begins with something general, narrows down in the middle to discuss specifics, and then branches out to more general comments at the end. In a classic five-paragraph essay, the first paragraph starts with a general statement and ends with a thesis statement containing three “points”; each body paragraph discusses one of those “points” in turn; and the final paragraph sums up what the student has written.
Why do high schools teach the five-paragraph model?
The five-paragraph model is a good way to learn how to write an academic essay. It’s a simplified version of academic writing that requires you to state an idea and support it with evidence. Setting a limit of five paragraphs narrows your options and forces you to master the basics of organization. Furthermore—and for many high school teachers, this is the crucial issue—many mandatory end-of-grade writing tests and college admissions exams like the SAT II writing test reward writers who follow the five-paragraph essay format.
Writing a five-paragraph essay is like riding a bicycle with training wheels; it’s a device that helps you learn. That doesn’t mean you should use it forever. Once you can write well without it, you can cast it off and never look back.
Why don’t five-paragraph essays work well for college writing?
The way college instructors teach is probably different from what you experienced in high school, and so is what they expect from you.
While high school courses tend to focus on the who, what, when, and where of the things you study—”just the facts”—college courses ask you to think about the how and the why. You can do very well in high school by studying hard and memorizing a lot of facts. Although college instructors still expect you to know the facts, they really care about how you analyze and interpret those facts and why you think those facts matter. Once you know what college instructors are looking for, you can see some of the reasons why five-paragraph essays don’t work so well for college writing:
- Five-paragraph essays often do a poor job of setting up a framework, or context, that helps the reader understand what the author is trying to say. Students learn in high school that their introduction should begin with something general. College instructors call these “dawn of time” introductions. For example, a student asked to discuss the causes of the Hundred Years War might begin, “Since the dawn of time, humankind has been plagued by war.” In a college course, the student would fare better with a more concrete sentence directly related to what he or she is going to say in the rest of the paper—for example, a sentence such as “In the early 14th century, a civil war broke out in Flanders that would soon threaten Western Europe’s balance of power.” If you are accustomed to writing vague opening lines and need them to get started, go ahead and write them, but delete them before you turn in the final draft. For more on this subject, see our handout on introductions .
- Five-paragraph essays often lack an argument. Because college courses focus on analyzing and interpreting rather than on memorizing, college instructors expect writers not only to know the facts but also to make an argument about the facts. The best five-paragraph essays may do this. However, the typical five-paragraph essay has a “listing” thesis, for example, “I will show how the Romans lost their empire in Britain and Gaul by examining military technology, religion, and politics,” rather than an argumentative one, for example, “The Romans lost their empire in Britain and Gaul because their opponents’ military technology caught up with their own at the same time as religious upheaval and political conflict were weakening the sense of common purpose on the home front.” For more on this subject, see our handout on argument .
- Five-paragraph essays are often repetitive. Writers who follow the five-paragraph model tend to repeat sentences or phrases from the introduction in topic sentences for paragraphs, rather than writing topic sentences that tie their three “points” together into a coherent argument. Repetitive writing doesn’t help to move an argument along, and it’s no fun to read.
- Five-paragraph essays often lack “flow.” Five-paragraph essays often don’t make smooth transitions from one thought to the next. The “listing” thesis statement encourages writers to treat each paragraph and its main idea as a separate entity, rather than to draw connections between paragraphs and ideas in order to develop an argument.
- Five-paragraph essays often have weak conclusions that merely summarize what’s gone before and don’t say anything new or interesting. In our handout on conclusions , we call these “that’s my story and I’m sticking to it” conclusions: they do nothing to engage readers and make them glad they read the essay. Most of us can remember an introduction and three body paragraphs without a repetitive summary at the end to help us out.
- Five-paragraph essays don’t have any counterpart in the real world. Read your favorite newspaper or magazine; look through the readings your professors assign you; listen to political speeches or sermons. Can you find anything that looks or sounds like a five-paragraph essay? One of the important skills that college can teach you, above and beyond the subject matter of any particular course, is how to communicate persuasively in any situation that comes your way. The five-paragraph essay is too rigid and simplified to fit most real-world situations.
- Perhaps most important of all: in a five-paragraph essay, form controls content, when it should be the other way around. Students begin with a plan for organization, and they force their ideas to fit it. Along the way, their perfectly good ideas get mangled or lost.
How do I break out of writing five-paragraph essays?
Let’s take an example based on our handout on thesis statements . Suppose you’re taking a course on contemporary communication, and the professor asks you to write a paper on this topic:
Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.
Thanks to your familiarity with the five paragraph essay structure and with the themes of your course, you are able to quickly write an introductory paragraph:
Social media allows the sharing of information through online networks among social connections. Everyone uses social media in our modern world for a variety of purposes: to learn about the news, keep up with friends, and even network for jobs. Social media cannot help but affect public awareness. In this essay, I will discuss the impact of social media on public awareness of political campaigns, public health initiatives, and current events.
Now you have something on paper. But you realize that this introduction sticks too close to the five-paragraph essay structure. The introduction starts too broadly by taking a step back and defining social media in general terms. Then it moves on to restate the prompt without quite addressing it: while it’s reasserted that there is an impact, the impact is not actually discussed. And the final sentence, instead of presenting an argument, only lists topics in sequence. You are prepared to write a paragraph on political campaigns, a paragraph on public health initiatives, and a paragraph on current events, but you aren’t sure what your point will be.
So you start again. Instead of trying to come up with something to say about each of three points, you brainstorm until you come up with a main argument, or thesis, about the impact of social media on public awareness. You think about how easy it is to share information on social media, as well as about how difficult it can be to discern more from less reliable information. As you brainstorm the effects of social media on public awareness in connection to political campaigns specifically, you realize you have enough to say about this topic without discussing two additional topics. You draft your thesis statement:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
Next you think about your argument’s parts and how they fit together. You read the Writing Center’s handout on organization . You decide that you’ll begin by addressing the counterargument that misinformation on social media has led to a less informed public. Addressing the counterargument point-by-point helps you articulate your evidence. You find it ends up taking more than one paragraph to discuss the strategies people use to compare and evaluate information as well as the evidence that people end up more informed as a result.
You notice that you now have four body paragraphs. You might have had three or two or seven; what’s important is that you allowed your argument to determine how many paragraphs would be needed and how they should fit together. Furthermore, your body paragraphs don’t each discuss separate topics, like “political campaigns” and “public health.” Instead they support different points in your argument. This is also a good moment to return to your introduction and revise it to focus more narrowly on introducing the argument presented in the body paragraphs in your paper.
Finally, after sketching your outline and writing your paper, you turn to writing a conclusion. From the Writing Center handout on conclusions , you learn that a “that’s my story and I’m sticking to it” conclusion doesn’t move your ideas forward. Applying the strategies you find in the handout, you may decide that you can use your conclusion to explain why the paper you’ve just written really matters.
Is it ever OK to write a five-paragraph essay?
Yes. Have you ever found yourself in a situation where somebody expects you to make sense of a large body of information on the spot and write a well-organized, persuasive essay—in fifty minutes or less? Sounds like an essay exam situation, right? When time is short and the pressure is on, falling back on the good old five-paragraph essay can save you time and give you confidence. A five-paragraph essay might also work as the framework for a short speech. Try not to fall into the trap, however, of creating a “listing” thesis statement when your instructor expects an argument; when planning your body paragraphs, think about three components of an argument, rather than three “points” to discuss. On the other hand, most professors recognize the constraints of writing blue-book essays, and a “listing” thesis is probably better than no thesis at all.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Blue, Tina. 2001. “AP English Blather.” Essay, I Say (blog), January 26, 2001. http://essayisay.homestead.com/blather.html .
Blue, Tina. 2001. “A Partial Defense of the Five-Paragraph Theme as a Model for Student Writing.” Essay, I Say (blog), January 13, 2001. http://essayisay.homestead.com/fiveparagraphs.html .
Denecker, Christine. 2013. “Transitioning Writers across the Composition Threshold: What We Can Learn from Dual Enrollment Partnerships.” Composition Studies 41 (1): 27-50.
Fanetti, Susan et al. 2010. “Closing the Gap between High School Writing Instruction and College Writing Expectations.” The English Journal 99 (4): 77-83.
Hillocks, George. 2002. The Testing Trap: How State Assessments Control Learning . New York and London: Teachers College Press.
Hjortshoj, Keith. 2009. The Transition to College Writing , 2nd ed. New York: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Shen, Andrea. 2000. “Study Looks at Role of Writing in Learning.” Harvard Gazette (blog). October 26, 2000. https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2000/10/study-looks-at-role-of-writing-in-learning/ .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Summer 2025 application is coming soon!
College essay writing.
Nurture your unique voice and articulate your thoughts with clarity and precision to write a top-notch essay for your college application.
Instructor: Pending

Course Description
This course is designed to equip students with the tools needed to elevate their writing to be persuasive, informative, and impactful to stand out among the crowd. Through a blend of guided instruction, hands-on exercises, and personalized feedback, students will tap into their creative and critical thinking skills to craft standout personal statements and polished essays. You will explore the basics of essay construction, composition, editing, grammar, spelling, and punctuation and learn what makes a compelling college application essay topic. With this foundation, you will develop an engaging personal narrative and refine your writing to persuasively showcase your unique experiences, talents, and aspirations. This workshop will focus on preparing you to write college application essays, but more importantly, you’ll leave the program armed with the tools, techniques, and confidence essential for successful writing in college and the future.
Admissions Criteria
- Completed Summer Discovery application
- Students must have a proficiency in English as this class is not intended as a study or practice of the English language.
Program Outcomes
- Successful Course Completion Certificate
- Letter of Recognition
- Capstone Project for Student Portfolio (where applicable)
Information subject to change as program updates come in for 2025!

Summer Discovery Certificate of Completion
After successfully finishing this course, you will be awarded a certification completion for your accomplishment.
*This is a preview, not what you will receive
Sign Up for Our Newsletter!
Find out more about what's happening at Summer Discovery!

Postgraduate Advanced Clinical Education (PACE) study support guide: 6.1 Academic writing
- 1. University jargon-buster
- 2. Library resources
- 3. Literature searching
- 4. Plagiarism
- 5.1 Using EndNote
- 6.1 Academic writing
- 6.2 Reflective practice & writing
- 6.3 Understanding feedback
- 6.4 Presentations
- 6.5 Preparing for exams and OSCEs
Academic vs professional writing
- Similarities
- Differences

Things to avoid in academic writing
- Writing in bullet points
- Having paragraphs of only one or two lines
- Forgetting to reference fully
- Making statements that are not backed by evidence
- Selecting the first piece of evidence that seems roughly related, thinking ‘that will do’
- Including irrelevant information or wandering from the point
- Neglecting to redraft and proof-read carefully
Academic writing shares some commonality with professional writing, they both:
- follow specific criteria
- have their own layout and formatting conventions
- are written in a formal style
- are need to be well presented and should be thoroughly proof-read
- must meet stated deadlines
It can be helpful to think of academic writing as a different genre with different conventions, style and expectations. Being aware of these differences can help you adapt your writing for an academic audience:
| Writing for an academic audience | Writing for a professional audience | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Written to demonstrate your learning and meet marking criteria | Written with a specific purpose and audience in mind (e.g. patients, healthcare professionals, managers) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Written in continuous prose with complete paragraphs and full sentences | Can be written using bullet points and very short paragraphs of a few lines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Explores ideas |
Developing your ideas and arguments
Developing a coherent argument and position in academic writing is often done in the stages before and after you start writing. Planning helps prevent your ideas from wandering, and redrafting can help identify and sharpen up your argument, so it is good to allow enough time for these stages in longer pieces of work. If you are finding it difficult to work out what you think in the midst of all the views of other people, try asking yourself questions about the validity of the evidence that others are basing their views upon: Do you agree or disagree with their standpoint and, importantly, what is making you agree or disagree? A questioning attitude is the basis of critical thinking…and critical thinking is not just something we do when writing academically. The Critical analysis guide produced by the University's Study Advice Team gives tips on critical thinking, reading and writing:
Good assignment planning starts with ideas generation and identifying what you know and what you want to find out. Before readin gThis is a really valuable stage which many people miss out, but it makes your reading and planning much easier. Before rushing into your reading, note down your initial thoughts about the question/topic - an essay plan, spider diagram or mind map are all good techniques for this.  The kinds of things to note briefly are:
This helps you start formulating your argument and direction for answering the question. It also helps you focus your reading, as you can pinpoint what you need to find out and go straight to the parts of books, chapters, articles that will be most relevant. After readingAfter your reading, it is often good to summarise all your findings on a page – again, a spider diagram or mind map can help with this. Bringing together the key points from your reading helps clarify what you have found out, and helps you find a pathway through all the ideas and issues you have encountered. If you include brief details of authors and page nos. for key information, it can act as a quick at-a-glance guide for finding the evidence you need to support your points later. It also helps you see how your initial response to the question might have changed or become more sophisticated in light of the reading you've done. It leads into planning your essay structure which can be done in any way that suits you best: A bullet point list, spider diagram, short summary. It does not matter as long as you have a ‘road map’ to keep you on track when writing. If you are finding it hard to get started, or there are certain aspects of your academic writing you’d like to develop, try some of these quick writing strategies:
Your argument/positionYou can think of the argument running through a piece of academic writing like a river. Sometimes it is only possible to identify your argument clearly once you have written your first draft, as the act of writing helps clarify your thoughts. We often do not know what our position is on an issue until we have expressed what we think. The redrafting stage is a good time to identify that argument and draw it out fully. You can do this by making sure that there is a consistent message (or river) running from your introduction to your conclusion, and that every paragraph has a role to play in advancing this message Skip to 45 seconds in on this short video for an explanation of the idea of an argument as a river, or feel free to watch the whole video for more on Structuring your Essay. If you are unable to view this video on YouTube it is also available on YuJa - view the Structuring your essay video on YuJa (University username and password required) Try this writing strategyWhat's my argument? Can you summarise your overall answer to your assignment question in a paragraph? Try writing a short summary of your argument and refer to it to help ensure you are bringing this out clearly throughout your writing. For more writing strategies to help develop your academic writing see the ‘Writing strategies’ page in this guide. Structuring your work and paragraphing
Structure is important in academic writing because it helps to make your ideas clear, guides the reader's comprehension and can strengthen your arguments. Some academic writing, such as scientific reports, have a given structure or template. In this case, you should find out what is required under each heading and adhere to this; it is most likely mapped to the marking criteria so you will lose marks for not following a stated structure. Other writing might require you to select and organise the material you are writing yourself and so develop a structure from scratch. Usually, in the introduction you should set out the structure so that the reader knows what to expect and the order in which it will be presented. The order in which information is presented should be logical so that the reader can follow your ideas and research, ideally write your structure with just one point/argument/idea per paragraph. In addition, the ideas should flow or be linked so that the reader is drawn through an explanation or argument, rather than stopping and starting at each new point. The conclusion to the piece should draw together all the points or ideas and come to a conclusion. Whether you are following a template or devising your own structure, paragraphs in academic writing can be thought of like a ‘mini-essay’ with an introduction, main body and conclusion. The first line introduces the point being made, the main body presents and discusses the evidence to support the point and the final line concludes the point and links it back to the assignment title. Other useful guides
When presenting a point of view, such as a line of argument for an essay, decide on the main points that you want to communicate. A paragraph can be planned (like a mini-essay) using the PEEL format:
Like any model, not all your paragraphs will fit neatly into this framework, but it is a useful guide to check the balance of your paragraphs: Do you have a clear point? Does the end of the paragraph link to the beginning? Have you interpreted your evidence not just left it there to ‘speak for itself’? Also it is helpful to think of the length of your paragraphs. If they are only a few lines long, it is unlikely you are interpreting your evidence fully. If they are over a page in length, it is likely you have more than one main point and need to separate them out. Skip to 5 minutes in on this video tutorial for an explanation and example of the model paragraph or feel free to watch the whole video for more on Targeted Reading and Use of Evidence. If you are unable to view this video on YouTube it is also available on YuJa - view the Targeted reading and use of evidence video on YuJa (University username and password required) You do not have to refer to each piece of evidence in the same depth. Sometimes you need to show that you understand the wider context of the issue, and a short summary of the key issues and key researchers is all that is needed. For example: Many studies have investigated household accidents caused by cheese. These studies disagree about the most significant reasons for cheese-based injury with some arguing that choking on cheese poses the highest risk (1-3). Other studies claim that burns from melted cheese are more hazardous (4,5), whilst a minority of recent studies have identified slipping on cheese as a growing danger (6). A significant amount of reading and in-depth understanding of the field is demonstrated in those sentences above even though the individual mentions of the evidence are quite short. The summary maps out the state of current research and the positions taken by the key researchers, and despite being short it has taken careful reading, grouping, identification, and understanding of the issues. Sometimes you need to go into greater depth and refer to some sources in more detail in order to interrogate the methods and standpoints expressed by these researchers. For example: A recent study introduces a new model for assessing the relative dangers of cheese related-injuries, identifying the overall total damage done as more important than the frequency of injuries (1). However, this model does not adequately take into account the theory of 'Under-reporting' which states that people are less likely to report frequently occurring small accidents until a critical mass of injuries are reached (2). Even in this more analytical piece of writing, only the relevant points of the study and the theory are mentioned briefly - but you need a confident and thorough understanding to refer to them so concisely. If you find it challenging to integrate evidence into your paragraphs, have a look at:
See also this video from the University's Study Advice Team on effective paraphrasing for postgraduates: If you are unable to view this video on YouTube it is also available on YuJa - view the Effective paraphrasing for postgraduates video on YuJa (University username and password required) Do not be tempted to use complex language or expressions that are not your own, just to make your writing appear "academic". Use straightforward language. Your reader needs to understand the information or ideas that you are conveying. Communicate succinctly without losing vital information or meaning. It is often easier to write fluently and then to edit out unnecessary words and phrases. Some academic writing, such as scientific informatoin, needs to be especially precise. A reader may need to have all the information required to understand exact conditions of a scientific study and to replicate it. Using simple sentences can be helpful. Avoid using non-quantifiable descriptions, such as: The company's production rate was high <--replace with--> The company produced 16,00 units per week. The wind was strong <--replace with--> The wind measured 6 on the Beaufort scale. Editing tips to reduce word count
Your written work may be interesting, well structured and informed. Yet it may still make a bad impression because of poor proof reading. Part of your assessment will usually relate to the standard of your written English. It's important to pay attention to things like tenses, gender, plurals and the structure of your sentences, especially if you have rewritten or moved sections of your work. It's easy to lose marks - but it's also easy to make sure you don't. Below are ten brief tips to help you to proof read your work as effectively as possible.
Top tips for effective proof reading
Writing at level 7
When at studying level 7 (Masters Level), your academic writing must reflect the level of critical analysis, synthesis and application to practice commensurate with this level of study. Studying at level 7 means developing your studying practices from those suited to being an independent learner to those suited to being an independent practitioner . You will be working at a more complex and sophisticated level, with a need for broader and more independently sourced resources. You will need not only to evaluate what other people have found but also to put your own knowledge and research into context. You will be expected to be meticulous and professional and show higher standards of scholarship. The advice on this page aims to explain some of the differences between undergraduate and Masters level study. The full marking criteria for taught postgraduate study can be found at the link below, the information in this section of the guide interprets this information to the context in which you are doing your studies.
Guidance on the requirements for assessments are included in the individual module handbooks. Some overarching principles will apply across all the assessments for all practitioners:
Key concepts of level 7 writingAchievement of level 7 study includes:
Accurate and appropriate use of language in your writing is one way of demonstrating academic rigour. You will need to be more thoughtful about the way you use language. Remember that the best writing style is clear and accurate, not unnecessarily complicated. If English is not your first language, there is more specialised support and advice available from the University's International Study and Language Institute website (link below). At level 7 you cannot get away with writing about something that you only vaguely understand, or squeezing in a theory in the hope it will gain extra marks - your markers will be able to tell, and this does not demonstrate the accuracy or professionalism of a researcher. Imagine you write the sentence: "Freudian psychoanalysis demonstrates how our personalities are developed from our childhood experiences." At level 7, the word 'demonstrates' becomes very loaded and potentially inaccurate. This is because you are expected to interrogate the assumptions, boundaries, and way in which knowledge is constructed in your subject. With this in mind, the sentence above raises a lot of contextual questions: To what extent could Freud's theory of psychoanalysis really be said to 'demonstrate' the origins of our personalities? What part of Freud's many theories are you referring to when you write 'psychoanalysis'? What about the developments in psychoanalysis that have happened since Freud, and the many arguments against his theories? Your writing needs to take these questions into account, and at least be aware of them, even if you don't address all of them. Do not just stop at discussing the pros and cons of a debate; academics rarely agree on interpretations of theories or ideas, so academic knowledge is more like a complex network of views than two clear sides.
Writing at level 6
When studying at level 6 (Bachelor's level) you will be aware that you need to develop your academic writing for higher education - but how? Will you need to use a lot of long words and complicated sentences? Will you be expected to include some original idea that no-one else has ever written about to get good marks? Actually neither of these are what good academic writing is about. Rather you will need to be able to communicate complicated ideas clearly, know how to support the things you say with evidence, and explain your thinking. Academic rigour means checking and testing information to assess whether it is free of errors and is backed by accurate and appropriate evidence. It needs to be strong so that it can support your arguments - like making sure foundations will hold a building up. Whether you are writing about someone else's ideas or your own, you will be expected to support the points you wish to make with evidence, perhaps from your own primary research or observations, or from your reading. When this evidence is taken from someone else's work (a book, journal article or website, for instance), you need to provide a reference or citation to show the source. The full marking criteria for bachelor's study can be found at the link below, the information in this section of the guide interprets this information to the context in which you are doing your studies.
In higher education, you are going to be asked to think about, explain and discuss a complex range of ideas and arguments. You may be bringing together ideas from a number of different scholars that you have read, for instance: or showing what the results of your own primary research mean in the context of a particular problem. In either case, it's important to write clearly so that your reader can be certain that they understand what you're saying, and that you understand what you're writing about. How is this different from your previous study?
Avoid long, complex sentences... You are less likely to lose track of what you are trying to say if you write in shorter sentences. If you need to link a number of ideas together in a sentence, make sure you separate them with appropriate punctuation: commas, semi-colons, colons and parentheses. More on how to use punctuation. Longer words don't make your writing more academic... A good piece of advice is to 'write to express, not to impress'. You are looking for words that will best communicate your ideas. Sometimes these will be long complicated words and sometimes they will be shorter. What you need is the most appropriate words for the job they have to do. Give your reader signposts... If you tell your reader what you are going to say, they will know what to look out for. Include a few sentences in your introduction on how you are going to answer the question: something like, "This essay will discuss the proposition that Brown's thesis is flawed. The proposition will be examined by first considering x, then looking at y, and finally z. Conclusions will then be drawn about the validity of Brown's thesis." Then start each of your sections with a topic sentence (or sub-heading, in a report) that shows what it is you are going to be discussing. Watch out for informality and vagueness... You are trying to reduce any possibility of your reader misunderstanding what you are trying to say, so aim to avoid the kind of language that might be interpreted differently by different readers. More on writing formally:
It is confusing when you are told you need to be original in your thinking - but then you are told that you need more references to other people's work too. In higher education, being original is rarely about having a brilliant idea that no-one has ever had before. Rather it means that you will be expected to take different sources of information and think about how they fit (or do not fit) together so that you can work out your own interpretation and understanding of the topic. Always start from your own ideas… so that you are less likely to fall into the trap of uncritically believing the first scholar you read. Before you start doing detailed research, take what you know already about the topic, and use it to make an educated guess about the answer to the question or main message about the topic you are researching. Then test that idea against your reading or research. Your conclusion is for summing up… not for adding speculative ideas with no evidence to support them. If you have a brilliant original idea and can show how you worked it out and how it fits into the evidence you have, then include it in the main body of your work. Do not worry!... your work will naturally be original if you always think critically and have a bit of confidence in your own interpretations and evaluations. If you and your best friend both read the same books and articles, attended the same lectures, and wrote an answer to the same question, they would still both be different and original, provided you do your own thinking and don't uncritically believe other people's ideas.
Analytical Essay Guide: Primary Document Analysis & Writing Tips Creative WritingThe Department of English offers creative writing instruction in multiple formats and offers several degrees and qualifications. UndergraduateAt the undergraduate level, students who are enrolled in a B.A. program at UT Austin can pursue the Creative Writing Certificate . For graduate students, there are two degree options in creative writing:
We invite you to visit the center's pages for information on their programs. Have a language expert improve your writingRun a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
What Is Academic Writing? | Dos and Don’ts for StudentsAcademic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You’ll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you’ll be expected to write your essays , research papers , and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but it has specific conventions in terms of content, structure and style.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your textUpload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes  Table of contentsTypes of academic writing, academic writing is…, academic writing is not…, useful tools for academic writing, academic writing checklist. Academics mostly write texts intended for publication, such as journal articles, reports, books, and chapters in edited collections. For students, the most common types of academic writing assignments are listed below.
Different fields of study have different priorities in terms of the writing they produce. For example, in scientific writing it’s crucial to clearly and accurately report methods and results; in the humanities, the focus is on constructing convincing arguments through the use of textual evidence. However, most academic writing shares certain key principles intended to help convey information as effectively as possible. Whether your goal is to pass your degree, apply to graduate school , or build an academic career, effective writing is an essential skill. Check for common mistakesUse the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text. Fix mistakes for free Formal and unbiasedAcademic writing aims to convey information in an impartial way. The goal is to base arguments on the evidence under consideration, not the author’s preconceptions. All claims should be supported with relevant evidence, not just asserted. To avoid bias, it’s important to represent the work of other researchers and the results of your own research fairly and accurately. This means clearly outlining your methodology and being honest about the limitations of your research. The formal style used in academic writing ensures that research is presented consistently across different texts, so that studies can be objectively assessed and compared with other research. Because of this, it’s important to strike the right tone with your language choices. Avoid informal language , including slang, contractions , clichés, and conversational phrases:
Clear and preciseIt’s important to use clear and precise language to ensure that your reader knows exactly what you mean. This means being as specific as possible and avoiding vague language :
Avoid hedging your claims with words like “perhaps,” as this can give the impression that you lack confidence in your arguments. Reflect on your word choice to ensure it accurately and directly conveys your meaning:
Specialist language or jargon is common and often necessary in academic writing, which generally targets an audience of other academics in related fields. However, jargon should be used to make your writing more concise and accurate, not to make it more complicated. A specialist term should be used when:
The best way to familiarize yourself with the kind of jargon used in your field is to read papers by other researchers and pay attention to their language. Focused and well structuredAn academic text is not just a collection of ideas about a topic—it needs to have a clear purpose. Start with a relevant research question or thesis statement , and use it to develop a focused argument. Only include information that is relevant to your overall purpose. A coherent structure is crucial to organize your ideas. Pay attention to structure at three levels: the structure of the whole text, paragraph structure, and sentence structure.
Well sourcedAcademic writing uses sources to support its claims. Sources are other texts (or media objects like photographs or films) that the author analyzes or uses as evidence. Many of your sources will be written by other academics; academic writing is collaborative and builds on previous research. It’s important to consider which sources are credible and appropriate to use in academic writing. For example, citing Wikipedia is typically discouraged. Don’t rely on websites for information; instead, use academic databases and your university library to find credible sources. You must always cite your sources in academic writing. This means acknowledging whenever you quote or paraphrase someone else’s work by including a citation in the text and a reference list at the end.
There are many different citation styles with different rules. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago . Make sure to consistently follow whatever style your institution requires. If you don’t cite correctly, you may get in trouble for plagiarism . A good plagiarism checker can help you catch any issues before it’s too late. You can easily create accurate citations in APA or MLA style using our Citation Generators. APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator Correct and consistentAs well as following the rules of grammar, punctuation, and citation, it’s important to consistently apply stylistic conventions regarding:
In some cases there are several acceptable approaches that you can choose between—the most important thing is to apply the same rules consistently and to carefully proofread your text before you submit. If you don’t feel confident in your own proofreading abilities, you can get help from Scribbr’s professional proofreading services or Grammar Checker . Academic writing generally tries to avoid being too personal. Information about the author may come in at some points—for example in the acknowledgements or in a personal reflection—but for the most part the text should focus on the research itself. Always avoid addressing the reader directly with the second-person pronoun “you.” Use the impersonal pronoun “one” or an alternate phrasing instead for generalizations:
The use of the first-person pronoun “I” used to be similarly discouraged in academic writing, but it is increasingly accepted in many fields. If you’re unsure whether to use the first person, pay attention to conventions in your field or ask your instructor. When you refer to yourself, it should be for good reason. You can position yourself and describe what you did during the research, but avoid arbitrarily inserting your personal thoughts and feelings:
Long-windedMany students think their writing isn’t academic unless it’s over-complicated and long-winded. This isn’t a good approach—instead, aim to be as concise and direct as possible. If a term can be cut or replaced with a more straightforward one without affecting your meaning, it should be. Avoid redundant phrasings in your text, and try replacing phrasal verbs with their one-word equivalents where possible:
Repetition is a part of academic writing—for example, summarizing earlier information in the conclusion—but it’s important to avoid unnecessary repetition. Make sure that none of your sentences are repeating a point you’ve already made in different words. Emotive and grandioseAn academic text is not the same thing as a literary, journalistic, or marketing text. Though you’re still trying to be persuasive, a lot of techniques from these styles are not appropriate in an academic context. Specifically, you should avoid appeals to emotion and inflated claims. Though you may be writing about a topic that’s sensitive or important to you, the point of academic writing is to clearly communicate ideas, information, and arguments, not to inspire an emotional response. Avoid using emotive or subjective language :
Students are sometimes tempted to make the case for their topic with exaggerated , unsupported claims and flowery language. Stick to specific, grounded arguments that you can support with evidence, and don’t overstate your point:
There are a a lot of writing tools that will make your writing process faster and easier. We’ll highlight three of them below. Paraphrasing toolAI writing tools like ChatGPT and a paraphrasing tool can help you rewrite text so that your ideas are clearer, you don’t repeat yourself, and your writing has a consistent tone. They can also help you write more clearly about sources without having to quote them directly. Be warned, though: it’s still crucial to give credit to all sources in the right way to prevent plagiarism . Grammar checkerWriting tools that scan your text for punctuation, spelling, and grammar mistakes. When it detects a mistake the grammar checke r will give instant feedback and suggest corrections. Helping you write clearly and avoid common mistakes . You can use a summarizer if you want to condense text into its most important and useful ideas. With a summarizer tool, you can make it easier to understand complicated sources. You can also use the tool to make your research question clearer and summarize your main argument. Receive feedback on language, structure, and formattingProfessional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
See an example  Use the checklist below to assess whether you have followed the rules of effective academic writing.
I avoid informal terms and contractions . I avoid second-person pronouns (“you”). I avoid emotive or exaggerated language. I avoid redundant words and phrases. I avoid unnecessary jargon and define terms where needed. I present information as precisely and accurately as possible. I use appropriate transitions to show the connections between my ideas. My text is logically organized using paragraphs . Each paragraph is focused on a single idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence . Every part of the text relates to my central thesis or research question . I support my claims with evidence. I use the appropriate verb tenses in each section. I consistently use either UK or US English . I format numbers consistently. I cite my sources using a consistent citation style . Your text follows the most important rules of academic style. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor! Is this article helpful?Other students also liked.
More interesting articles
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes” After hiding the tool, if you would like to re-enable it, just press CTRL+U to open this window. Or, move your cursor near the tool to display it.  College Prep 101 Virtual SeriesOffice of Admission
Contact InformationPhone: 253-535-7151 Fax: 253-536-5136 Email: [email protected] Pacific Lutheran University 12180 Park Ave S Tacoma, WA 98447-0003 Social Media
 College Prep 101: Expert Tips on Search, Applications & EssaysFeeling a little overwhelmed about how to find (and then successfully apply to) colleges. This College Prep 101 webinar series – led by our admission counselor experts – is designed for you to feel confident going into your college search and make sure you’re putting your best self forward in the application process. Watch one, two, or all of them to learn how to navigate this exciting (and sometimes stressful) next step in your education! FYI: We’re using Zoom Webinar – no Zoom account, microphone, or camera is needed, but you will be able to ask live questions in the Q&A section. Just plan to access the webinar from a device of some kind (phone, laptop, chrome book, etc). The College Search Process: Where do I start?Tuesday, september 17, 6:30-7:00pm pt. How do you choose a college? How do you pick the right type of school? What questions should you be asking to narrow down your search and how do you decide where to apply? These questions are common ones we hear at the beginning of the college search process. It can feel overwhelming, but after this webinar, you’ll know how to make a solid start. College Applications: How to Land in the 'Yes' PileWednesday, september 18, 6:30-7:00pm pt. Have you wondered what the college application process is really like? How does an admission counselor at a 4-year university review your application? What classes should you be taking in high school? What experiences are important? Will a bad grade in one class ruin your chances of getting into your dream college? And what helps you as an applicant stand out from the crowd? If you are curious how to land in the ‘yes’ pile, then this webinar is for you! The College Essay: Writing with ConfidenceThursday, september 19, 6:30-7:00pm pt. Does a college essay really make a difference? Absolutely! But the hardest part is often deciding where to start and what to write about. We will cover how to pick a topic, how to sound authentic, and how to engage a reader (while also staying within the word count)! You’ll leave this webinar equipped with tips to make writing your admissions essay a breeze. EXPLORE MORESchedule visit, meet your counselor, student videos.  |
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
Step 2: Pick one of the things you wrote down, flip your paper over, and write it at the top of your paper, like this: This is your thread, or a potential thread. Step 3: Underneath what you wrote down, name 5-6 values you could connect to this. These will serve as the beads of your essay.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Use your essays to empower your chances of acceptance, merit money, and scholarships.". This college essay tip is by Dr. Rebecca Joseph, professor at California State University and founder of All College Application Essays, develops tools for making the college essay process faster and easier. 15. Get personal.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Here we'll cover the seven main points of planning and executing a well-written essay: understanding the question. researching and gathering helpful resources. putting together an essay plan. writing the essay. tackling the introduction and conclusion. reviewing what you've written.
The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details. Review your essay for typos, mistakes, and any other problems.
Sample College Essay 2 with Feedback. This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org. College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay.
What to Look for in a College Essay Topic. There's no single answer to the question of what makes a great college essay topic, but there are some key factors you should keep in mind. The best essays are focused, detailed, revealing and insightful, and finding the right topic is vital to writing a killer essay with all of those qualities.
Essays are shorter pieces of writing that often require the student to hone a number of skills such as close reading, analysis, comparison and contrast, persuasion, conciseness, clarity, and exposition. As is evidenced by this list of attributes, there is much to be gained by the student who strives to succeed at essay writing.
College Essay Guy - Personal statement and college essay tips, guides, resources, consulting, and webinars for students, parents and counselors. ... Essay Writing Curriculum. Two private, live training sessions with your team; A schedule of daily assignments with interactive exercises that help foster moments of self-discovery;
2. Define your argument. As you plan and prepare to write the essay, you must consider what your argument is going to be. This means taking an informed position or point of view on the topic presented in the question, then defining and presenting a specific argument. Consider these two argument statements:
Conclusion. You are ready to write an essay after you have done these steps: Identified all the components that you must cover so that you address the essay question or prompt. Conducted your initial research and decided on your tentative position and line of argument. Created a preliminary outline for your essay that presents the information ...
Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor. 1. Start Early. Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school.
Making an all-state team → outstanding achievement. Making an all-state team → counting the cost of saying "no" to other interests. Making a friend out of an enemy → finding common ground, forgiveness. Making a friend out of an enemy → confront toxic thinking and behavior in yourself.
Normally, when writing an essay at university you will be expected to use only academic sources. The following learning guide on source credibility will help you to determine whether an external source is academic or not. The chocolate essay uses the American Psychological Association (APA) style of referencing, which is easy to distinguish ...
In summary, here are 10 of our most popular essay writing courses. Getting Started with Essay Writing: University of California, Irvine. Academic English: Writing: University of California, Irvine. Writing in English at University: Lund University. Writing in the Sciences: Stanford University.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...
The five-paragraph model is a good way to learn how to write an academic essay. It's a simplified version of academic writing that requires you to state an idea and support it with evidence. Setting a limit of five paragraphs narrows your options and forces you to master the basics of organization. Furthermore—and for many high school ...
This college essay tip is by Abigail McFee, Admissions Counselor for Tufts University and Tufts '17 graduate. 2. Write like a journalist. "Don't bury the lede!" The first few sentences must capture the reader's attention, provide a gist of the story, and give a sense of where the essay is heading.
You will explore the basics of essay construction, composition, editing, grammar, spelling, and punctuation and learn what makes a compelling college application essay topic. With this foundation, you will develop an engaging personal narrative and refine your writing to persuasively showcase your unique experiences, talents, and aspirations.
Writing a great college essay introduction can make or break your application. Learn how to craft a distinctive and specific opening that hooks your reader and showcases your personality. Find examples and tips from Scribbr, the expert in academic writing.
Whether you are following a template or devising your own structure, paragraphs in academic writing can be thought of like a 'mini-essay' with an introduction, main body and conclusion. The first line introduces the point being made, the main body presents and discusses the evidence to support the point and the final line concludes the ...
English document from University of Miami, 2 pages, Using a selected primary document students will present a concise, coherent 4-5 page essay based on the assignment overview identified in Task 1 of Week 13. Students will upload their completed essay directly to BlackBoard. There is a primary document ana
The Department of English offers creative writing instruction in multiple formats and offers several degrees and qualifications. Undergraduate. At the undergraduate level, students who are enrolled in a B.A. program at UT Austin can pursue the Creative Writing Certificate. Graduate. For graduate students, there are two degree options in ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
The College Essay: Writing with Confidence Thursday, September 19, 6:30-7:00pm PT. Does a college essay really make a difference? Absolutely! But the hardest part is often deciding where to start and what to write about. We will cover how to pick a topic, how to sound authentic, and how to engage a reader (while also staying within the word count)!