
- Dissertation Coaching
- Qualitative Data Analysis
- Statistical Consulting
- Dissertation Editing
- On-Demand Courses

How To Write the Findings Chapter for Qualitative Studies
Writing the findings chapter for qualitative studies is a critical step in the research process. This chapter allows researchers to present their findings, analyze the data collected, and draw conclusions based on the study’s objectives. In this blog post, I’lll explore the purpose, key elements, preparation, writing, and presentation of the findings chapter in qualitative studies.
Introduction: Contextualizing Your Findings
The introductory section serves as the gateway to your qualitative findings chapter. Begin by reiterating your problem statement and research questions, setting the stage for the data that will be presented. Highlighting the purpose of your research is crucial at this point to give context to the reader.
Example: The primary aim of this case study is to explore how educators perceive the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) tools in K-12 education settings. This research seeks to understand the perceptions and experiences of educators who have implemented AI technologies in their classrooms, framed within the context of Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK). In this chapter, data are systematically organized into three overarching themes, each comprising sub-themes that provide a nuanced understanding of the participants’ perspectives. The research questions guiding this investigation were: (1) What are educators’ perceptions of the role of AI tools in K-12 classrooms? (2) How do educators navigate the challenges of integrating AI tools into their teaching practices? The answers to these questions are integral to understanding the complex dynamics of AI implementation in educational contexts.
Overview of Findings
Following this, offer a brief overview of your main findings. While you should not delve into the details here, giving the reader an idea of what to expect can be helpful. Explain the overall structure of your results chapter and how you’ve organized it to maintain coherence and logical flow.
The Heart of the Matter: The Body of Your Chapter
Presentation.
The body of the chapter is where you lay out your data for the reader. In qualitative research, this usually means dividing your data into themes or categories, which should be clearly described and substantiated with quotes and examples from your dataset. These themes provide the skeletal framework upon which your narrative is built.
Structure and Flow
When planning your qualitative findings chapter, carefully outline the sections and subsections to maintain the flow of the writing and improve readability. You can structure your chapter based on themes, which is often the case in qualitative research, but other formats like chronological or framework-based structures may be more appropriate depending on your specific research design.
✅ Consistency is Key: Make sure each portion of findings adheres to a standardized structure. This enhances consistency and enables the reader to follow your line of reasoning.
Objective and Descriptive Language
While your narrative might touch upon individual experiences and perspectives, remember to maintain an objective tone. Your task is to describe, not interpret—that comes later, in the Discussion chapter. Thus, avoid phrases that suggest interpretation, such as “suggests” or “implies.”
Visual Aids
Tables, figures, and other visual aids can add another layer of comprehension and break up the text, but make sure they can be understood independently of your body text. Label them clearly and use color coding judiciously to indicate differences or hierarchy.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
As you delve into the data, aim to narrate a coherent story. Interpret your findings in light of the literature in the field and your theoretical framework, but remember to clearly differentiate between your descriptions and your interpretations.
✅ References and Appendices: When using quotes or data excerpts, reference them appropriately. Use appendices to present additional data and ensure that you cite them according to the referencing style prescribed by your institution (e.g., APA, Harvard).
Bringing It All Together: The Concluding Summary
This is the section where you summarize your key findings in a concise manner, reiterating points that directly relate to your research questions. It serves as a stepping stone to the Discussion chapter, providing the reader with the essential takeaways. As a rule of thumb, this section should contain no new information.
Additional Tips and Tricks
– Write in the past tense, as you present findings that have already been gathered.
– Review your work multiple times, ensuring each theme or finding is backed by sufficient data.
– Use Microsoft Word’s “heading styles” for consistency.
Final Thoughts
With the right approach, writing the Findings chapter can be an enriching experience that showcases your research and prepares you for discussions and conclusions that follow. The tips and guidelines presented here are meant to make this crucial chapter as clear and impactful as possible, helping you make a valuable contribution to your field of study.
Need Further Assistance?
Dissertation by Design is here to support you every step of the way. Our team of experienced academic coaches and methodologists are dedicated to helping you confidently navigate through each stage of your dissertation journey. Book a free, 30-minute consult today.
Happy writing!
Author: Jessica Parker, EdD
Related posts.

Download our free guide on how to overcome the top 10 challenges common to doctoral candidates and graduate sooner.
Thank You 🙌
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 27 October 2016 by Bas Swaen . Revised on 25 October 2022 by Tegan George.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean – any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs discussion vs conclusion, checklist: research results, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analysed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like ‘appears’ or ‘implies’.
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe shop: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the trainers, boots, sandals, etc.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualise trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarise or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
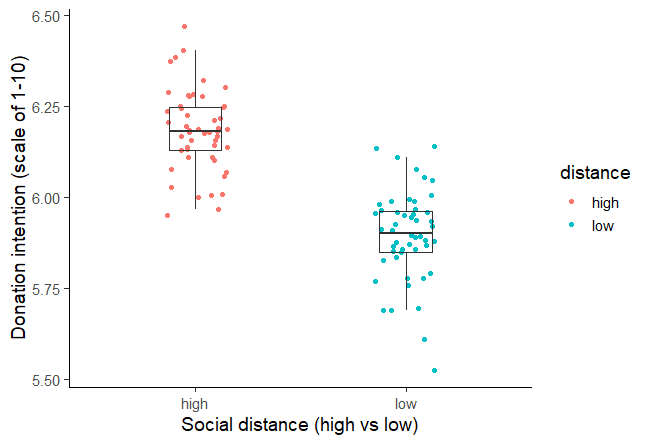
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organisations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
‘I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.’
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Swaen, B. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/results-section/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
What is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion.
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- Where to Find Images for Presentations
- What Is an Internship? Everything You Should Know
- How Long Should a Thesis Statement Be?
- How to Write a Character Analysis Essay
- Best Colours for Your PowerPoint Presentation: Top Colour Combinations
- How to Write a Nursing Essay
- Top 5 Essential Skills You Should Build As An International Student
- How Professional Editing Services Can Take Your Writing to the Next Level
- How to Write an Effective Essay Outline
- How to Write a Law Essay: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

Dissertation findings and discussion sections
(Last updated: 2 March 2020)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
Granted that at some point in the discussion you are going to have to link back to this previous research. But you still have the opportunity to demonstrate how you have met that coveted gap in the research and generally made a useful contribution to knowledge.
There are many ways to write up both your findings and discussion. In shorter dissertations, it might make sense to have both of these comprise one section. In longer pieces of work, these chapters are usually separate.
Preparing to write
We also assume that you have used some sort of software program to help you with the organisation of your findings. If you have not completed this process, you must do so before beginning to write. If not, your findings chapter may end up a confusing and unorganised mess of random information. If you need help in this area, make sure to seek it out before beginning to put your findings down on paper.
One of the main issues that students tend to encounter when writing up their findings is the amount of data to include. By the end of the research process, you've probably collected very large amounts of data . Not all of this can possibly appear in your dissertation without completely overwhelming the reader. As a result, you need to be able to make smart decisions about what to include and what to leave out.
One of the easiest ways to approach this task is to create an outline. In approaching the outline, it is in your best interest to focus on two key points. Firstly, you need to focus on answering your research questions. Secondly, you must include any particularly interesting findings that have cropped up as you completed your research.
An outline will give you the structure you need, and should make the whole process of presenting your findings easier. We realise that it is going to be a difficult process to pick and choose pieces of data to include. But you must be diligent in the work that you cut out. A findings chapter that is long and confusing is going to put the reader off reading the rest of your work.
Introducing your findings
It can be up to 40% of the total word count within your dissertation writing . This is a huge chunk of information, so it's essential that it is clearly organised and that the reader knows what is supposed to be happening. One of the ways you can achieve this is through a logical and organised introduction.
There are four main components that your introduction should include:
Reminding the reader of what you set out to do
A brief description of how you intend approaching the write up of the results
Placing the research in context
Letting the reader know where they can find the research instruments (i.e. the Appendix)
With a findings chapter, there should be no suspense for the reader. You need to tell them what they need to know right from the beginning. This way, they'll have a clear idea about what is still to come. A good introduction will start by telling the reader where you have come from in the research process and what the outcome was (in a couple of paragraphs or less).
You need to highlight the structure of the chapter (as you generally will do with all chapters) and where the reader might find any further information (e.g. in the appendices).
Organisation of data
This is really going to depend on the type of project you have created .
For example, if you have completed a qualitative research project, you might have identified some key themes within the software program you used to organise your data. In this case, highlighting these themes in your findings chapter may be the most appropriate way to proceed. Not only are you using information that you have already documented, you are telling a story in each of your sections (which can be useful in qualitative research).
But what if you undertook a more quantitative type study? You might be better off structuring your findings chapter in relation to your research questions or your hypotheses. This assumes, of course, that you have more than one research question or hypothesis. Otherwise you would end up just having one really long section.
This brings us to our next student mistake – trying to do too much within one section.
Subheadings are ultimately going to be your friend throughout your dissertation writing . Not only do they organise your information into logical pieces, they give the reader guidelines for where your research might be going. This is also a break for the reader. Looking at pages and pages of text without any breaks can be daunting and overwhelming for a reader. You don't want to overwhelm someone who is going to mark your work and who is responsible for your success (or failure).
When writing your introduction, be clear, organised and methodical. Tell the reader what they need to know and try to organise the information in a way that makes the most sense to you and your project. If in doubt, discuss this with your supervisor before you start writing.
Presentation of qualitative data
If you have conducted things like interviews or observations, you are likely to have transcripts that encompass pages and pages of work.
Putting this all together cohesively within one chapter can be particularly challenging. This is true for two reasons. First, it is always difficult to determine what you are going to cut and/or include. Secondly, unlike quantitative data, it can often be difficult to represent qualitative data through figures and tables, so condensing the information into a visual representation is simply not possible. As a writer, it is important to address both these challenges.
When considering how to present your qualitative data, it may be helpful to begin with the initial outline you have created (and the one described above). Within each of your subsections, you are going to have themes or headings that represent impactful talking points that you want to focus on.
Once you have these headings, it might be helpful to go back to your data and highlight specific lines that can/might be used as examples in your writing. If you have used multiple different instruments to collect data (e.g. interviews and observations), you are going to want to ensure that you are using both examples within each section (if possible). This is so that you can demonstrate to more well-rounded perspective of the points you are trying to make. Once you have identified some key examples for each section, you might still have to do some further cutting/editing.
Once you have your examples firmly selected for each subsection, you want to ensure that you are including enough information. This way, the reader will understand the context and circumstances around what you are trying to ‘prove’. You must set up the examples you have chosen in a clear and coherent way.
Students often make the mistake of including quotations without any other information. It is important that you embed your quotes/examples within your own thoughts. Usually this means writing about the example both before and after. So you might say something like, “One of the main topics that my participants highlighted was the need for more teachers in elementary schools. This was a focal point for 7 of my 12 participants, and examples of their responses included: [insert example] by participant 3 and [insert example] by participant 9. The reoccurring focus by participants on the need for more teachers demonstrates [insert critical thought here]. By embedding your examples in the context, you are essentially highlighting to the reader what you want them to remember.
Aside from determining what to include, the presentation of such data is also essential. Participants, when speaking in an interview might not do so in a linear way. Instead they might jump from one thought to another and might go off topic here and there.
It is your job to present the reader with information on your theme/heading without including all the extra information. So the quotes need to be paired down to incorporate enough information for the reader to be able to understand, while removing the excess.
Finding this balance can be challenging. You have likely worked with the data for a long time and so it might make sense to you. Try to see your writing through the eyes of someone else, which should help you write more clearly.
Presentation of quantitative data
Something to consider first with numeric data is that presentation style depends what department you are submitting to. In the hard sciences, there is likely an expectation of heavy numeric input and corresponding statistics to accompany the findings. In the arts and humanities, however, such a detailed analysis might not be as common. Therefore as you write out your quantitative findings, take your audience into consideration.
Just like with the qualitative data, you must ensure that your data is appropriately organised. Again, you've likely used a software program to run your statistical analysis, and you have an outline and subheadings where you can focus your findings. There are many software programs available and it is important that you have used one that is most relevant to your field of study.
For some, Microsoft Excel may be sufficient for basic analysis. Others may rely on SPSS, Stata, R, or any of the other programs available through your institution or online. Whatever program you have used, make sure that you document what you have done and the variables that have affected your analysis.
One common mistake found in student writing is the presentation of the statistical analysis. During your analysis of the data, you are likely to have run multiple different analyses from regressions to correlations. Often, we see students presenting multiple different statistical analyses without any real understanding of what the tests mean.
Presentation of quantitative data is more than just about numbers and tables. You must explain your findings and justify why you have run/presented the tests that you have. You could also explain how they relate to the research question. However, depending on how you have organised your work, this might end up in the discussion section.
Students who are not confident with statistical analysis often have a tendency to revert back to their secondary school mathematics skills. They commonly document the mean, median, and mode for all of their results. Now, these three outcomes can be important. But having a good understanding of why you are proceeding with this strategy of analysis is going to be essential in a primarily quantitative study.
That noted, there are different expectations for an undergraduate dissertation and a PhD thesis, so knowing what these expectations are can be really helpful before you begin.
Presentation of graphs, tables, and figures
The first is the use of colour and/or variables. Depending on the presentation of your dissertation, you may be required to print out a final copy for the marker(s). In many cases, this final copy must be printed in black and white. This means that any figures or graphs that you create must be readable in a black and white (or greyscale) format.
This can be challenging because there are only so many distinct shades of grey. In a pie chart, you might show one section as purple and the other as green. Yet when printed, both the purple and the green translate to approximately the same shade of grey, making your graph suddenly unreadable.
Another common error is overwhelming the reader with graphs and tables. Let's think about your outline and subheadings. If you're including a table under each subheadings, it needs to be relevant to the information that is being discussed in that chapter. There is no correct or incorrect number of graphs that should exist within the section, but you should use your judgement about what looks appropriate.
The final mistake we see is the duplication of writing (or absence of writing) when presenting a graph. Some students will present their findings in a graph or table and then write out this information again below the graph. This defeats the entire purpose of using the graph in the first place. So avoid this at all times.
Conversely, other students sometimes include a graph or figure but nothing else. Doing this denies the reader of context or purpose of said graph or figure. At some point, a balance needs to be struck where the reader has the information they require to really understand the point being made within the section.
Analysis and synthesis in a discussion
The purpose of a discussion chapter.
The structure of your discussion chapter is really going to depend on what you are trying to do and how you have structured your findings. If you chose to structure your findings by theme, it might make sense to continue this into the analysis chapter.
Other people might structure it according to the research questions. This clearly indicates to the reader how you have addressed your study. Marking a dissertation usually requires the marker to comment on the extent to which the research questions have been addressed. So by structuring a dissertation that lays out each research question for the marker, you are making their job easier. Needless to say, this a great thing.
Like any other chapter in your thesis, an introduction is an essential component of your discussion. By this point, the reader has gone through your findings and is now looking for your interpretation. Therefore, at the end of your discussion introduction you should highlight the content that each of the subsections will cover.
A conclusion to your discussion section (or a chapter summary) is also going to be beneficial. The length of the analysis chapter is usually quite long, so a wrap up of the key points at the end can help the reader digest your work. It can also help ensure that the reader actually understands the points you are trying to highlight within your project.
Critical thinking
Without any critical thinking, you are really doing yourself a disservice. It will affect the mark that you obtain on your overall dissertation. This is why the analysis chapter is usually weighted quite heavily on the marking rubric.
We tell students about critical thinking and the importance of it on a daily basis. And yet, there does seem to be a general confusion about what critical thinking entails, i.e. what constitutes critical thinking versus what is a simple description.
Critical thinking asks you to provide your own opinion on your topic, which can be daunting at first. For much of your academic career, you've likely been asked to use research to justify a position that has already been set. Unlike critical thinking, this requires you to use other people’s ideas. But even if you're new to it, try and get to grips with what critical thinking entails and use it in your work.
Creating sub-sections
Subheadings need to be informative but not too long. It is possible to layer your subheadings, so you might have a Chapter 2, a Section 2.1 and then a 2.1.1 and 2.2.2. Usually anything after 3 numerical points does not get a number and would not appear in your table of contents.
When creating titles for your subheadings, consider how they are going to look in the table of contents. They need to fit on one line, ideally, so putting your research question as the subheading might end up being too long. Conversely, one- or two-word subheadings usually doesn't give enough information about the purpose of the section.
Finding this balance is important. But remember you can always edit your subheadings retrospectively.
Linking to previous chapters
Ideally, you will be able to concisely and effectively link your research to what has been researched previously. But this can be a challenge. You don't want to repeat what has been said in your literature review or the findings . But you need to pull examples from both of these sections in order to make the points that you need to.
So, how do you tackle this?
One way is by referring the reader back to previous chapters, sections, or subsections. This process can generally be done at the end. You can put in a place holder until you know how your sections will be numbered. For example you might write: “In Section XYZ, the theme of … was discussed. Findings from this study indicate…. (see Section XYZ for details)”. While ‘XYZ’ is obviously not going to be the same section, by using the same abbreviation, you can then search ‘XYZ’ after you have completed writing and replace each term with the appropriate number. This also makes the proofreading process easier.
If you are submitting an electronic version of this document, you may also consider hyperlinks to take the reader to the different sections. But be aware that this can be considerably more work, so you should allow for this in your timescale if it's something you wish to implement.
Let's outline the main takeaway points:
It is essential that you keep in mind the ‘describe, analyse, synthesise’ model.
The findings chapter is essentially the describe part. You need to ensure that you have clearly identified data that relates to your research questions, hypotheses, or themes of your study.
For the ‘describe’ component, you are not looking to support your work with other research, but rather to present your contribution. It is also important to consider your data in the ‘describe’ section. If you have qualitative data, ensure that you have edited the quotes and examples to a reasonable length. Pick quotes that accurately represent your theme. Try not to focus solely on one or two participants (if possible). Ensure that you are demonstrating links between multiple instruments, if you used them.
If you are using quantitative data, be careful about how many statistical tests you run. Make sure you can justify why you chose one particular test over another. When presenting graphs, use a colour scheme that's appropriate for the reader when printing in black and white. Ensure that graphs and tables are appropriately explained, but that the information provided is not duplicated.
From the ‘describe’ element, you move into the 'analysis' and 'synthesis'. These parts usually appear in the discussion and ask you to employ your critical thinking skills to demonstrate how your research fits into the bigger picture. It is often the case that your analysis holds the most weight in the marking scheme. So you should spend considerable time ensuring this section is appropriate. It needs to demonstrate how you have attempted to answer your research questions.
Finally, create an outline before you begin. While this might seem tedious at first, filling in the sections with the appropriate information will mean that you are not writing things over and over again. It'll also make sure you do not go wildly off topic. It is always beneficial to have a second set of eyes assess your work for any errors or omissions. Many students choose to contact professional editors to help with this as they hold the relevant expertise to guide you on the correct path to creating a perfect discussion section that is ready for submission.
In terms of presentation, both the findings and discussion chapters will benefit from a clear and logical introduction and chapter summary. Remember that both of these chapters are meant to inform. You are leading the reader on a journey, so make sure they stay on the path and arrive at the final destination with you!

Writing your dissertation methodology

10 tips on writing a dissertation literature review

Dissertation introduction, conclusion and abstract
- dissertation chapters
- dissertation discussion
- dissertation findings
- dissertation help
- dissertation writing service
- study skills
- writing tips
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 21, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 18, 2023.

The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results .
It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review and paper or dissertation topic , and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion. It should not be a second results section.
There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your writing around these key elements:
- Summary : A brief recap of your key results
- Interpretations: What do your results mean?
- Implications: Why do your results matter?
- Limitations: What can’t your results tell us?
- Recommendations: Avenues for further studies or analyses
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What not to include in your discussion section, step 1: summarize your key findings, step 2: give your interpretations, step 3: discuss the implications, step 4: acknowledge the limitations, step 5: share your recommendations, discussion section example, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about discussion sections.
There are a few common mistakes to avoid when writing the discussion section of your paper.
- Don’t introduce new results: You should only discuss the data that you have already reported in your results section .
- Don’t make inflated claims: Avoid overinterpretation and speculation that isn’t directly supported by your data.
- Don’t undermine your research: The discussion of limitations should aim to strengthen your credibility, not emphasize weaknesses or failures.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarizing your major findings. To speed up the process you can use a summarizer to quickly get an overview of all important findings. Don’t just repeat all the data you have already reported—aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research question . This should be no more than one paragraph.
Many students struggle with the differences between a discussion section and a results section . The crux of the matter is that your results sections should present your results, and your discussion section should subjectively evaluate them. Try not to blend elements of these two sections, in order to keep your paper sharp.
- The results indicate that…
- The study demonstrates a correlation between…
- This analysis supports the theory that…
- The data suggest that…
The meaning of your results may seem obvious to you, but it’s important to spell out their significance for your reader, showing exactly how they answer your research question.
The form of your interpretations will depend on the type of research, but some typical approaches to interpreting the data include:
- Identifying correlations , patterns, and relationships among the data
- Discussing whether the results met your expectations or supported your hypotheses
- Contextualizing your findings within previous research and theory
- Explaining unexpected results and evaluating their significance
- Considering possible alternative explanations and making an argument for your position
You can organize your discussion around key themes, hypotheses, or research questions, following the same structure as your results section. Alternatively, you can also begin by highlighting the most significant or unexpected results.
- In line with the hypothesis…
- Contrary to the hypothesized association…
- The results contradict the claims of Smith (2022) that…
- The results might suggest that x . However, based on the findings of similar studies, a more plausible explanation is y .
As well as giving your own interpretations, make sure to relate your results back to the scholarly work that you surveyed in the literature review . The discussion should show how your findings fit with existing knowledge, what new insights they contribute, and what consequences they have for theory or practice.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support existing theories, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge existing theories, why do you think that is?
- Are there any practical implications?
Your overall aim is to show the reader exactly what your research has contributed, and why they should care.
- These results build on existing evidence of…
- The results do not fit with the theory that…
- The experiment provides a new insight into the relationship between…
- These results should be taken into account when considering how to…
- The data contribute a clearer understanding of…
- While previous research has focused on x , these results demonstrate that y .
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Even the best research has its limitations. Acknowledging these is important to demonstrate your credibility. Limitations aren’t about listing your errors, but about providing an accurate picture of what can and cannot be concluded from your study.
Limitations might be due to your overall research design, specific methodological choices , or unanticipated obstacles that emerged during your research process.
Here are a few common possibilities:
- If your sample size was small or limited to a specific group of people, explain how generalizability is limited.
- If you encountered problems when gathering or analyzing data, explain how these influenced the results.
- If there are potential confounding variables that you were unable to control, acknowledge the effect these may have had.
After noting the limitations, you can reiterate why the results are nonetheless valid for the purpose of answering your research question.
- The generalizability of the results is limited by…
- The reliability of these data is impacted by…
- Due to the lack of data on x , the results cannot confirm…
- The methodological choices were constrained by…
- It is beyond the scope of this study to…
Based on the discussion of your results, you can make recommendations for practical implementation or further research. Sometimes, the recommendations are saved for the conclusion .
Suggestions for further research can lead directly from the limitations. Don’t just state that more studies should be done—give concrete ideas for how future work can build on areas that your own research was unable to address.
- Further research is needed to establish…
- Future studies should take into account…
- Avenues for future research include…

If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
In the discussion , you explore the meaning and relevance of your research results , explaining how they fit with existing research and theory. Discuss:
- Your interpretations : what do the results tell us?
- The implications : why do the results matter?
- The limitation s : what can’t the results tell us?
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/discussion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?
Reflecting on and Comparing Your Data, Recognising the Strengths and Limitations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
756 Accesses
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with subsections and paragraphs. We also present a list of points to do and avoid when writing the discussion together with a Discussion chapter checklist.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Braun V, Clarke V (2013) Successful qualitative research: a practical guide for beginners. SAGE Publications, London
Google Scholar
McGregor SLT (2018) Understanding and evaluating research: a critical guide. SAGE Publications, Los Angeles, CA
Book Google Scholar
PLOS (2023) Author resources. How to write discussions and conclusions. Accessed Mar 3, 2023, from https://plos.org/resource/how-to-write-conclusions/ . Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Cottrell S (2017) Critical thinking skills: effective analysis, argument and reflection, 3rd edn. Palgrave, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
blog @ precision
Presenting your qualitative analysis findings: tables to include in chapter 4.
The earliest stages of developing a doctoral dissertation—most specifically the topic development and literature review stages—require that you immerse yourself in a ton of existing research related to your potential topic. If you have begun writing your dissertation proposal, you have undoubtedly reviewed countless results and findings sections of studies in order to help gain an understanding of what is currently known about your topic.

In this process, we’re guessing that you observed a distinct pattern: Results sections are full of tables. Indeed, the results chapter for your own dissertation will need to be similarly packed with tables. So, if you’re preparing to write up the results of your statistical analysis or qualitative analysis, it will probably help to review your APA editing manual to brush up on your table formatting skills. But, aside from formatting, how should you develop the tables in your results chapter?
In quantitative studies, tables are a handy way of presenting the variety of statistical analysis results in a form that readers can easily process. You’ve probably noticed that quantitative studies present descriptive results like mean, mode, range, standard deviation, etc., as well the inferential results that indicate whether significant relationships or differences were found through the statistical analysis . These are pretty standard tables that you probably learned about in your pre-dissertation statistics courses.
But, what if you are conducting qualitative analysis? What tables are appropriate for this type of study? This is a question we hear often from our dissertation assistance clients, and with good reason. University guidelines for results chapters often contain vague instructions that guide you to include “appropriate tables” without specifying what exactly those are. To help clarify on this point, we asked our qualitative analysis experts to share their recommendations for tables to include in your Chapter 4.
Demographics Tables
As with studies using quantitative methods , presenting an overview of your sample demographics is useful in studies that use qualitative research methods. The standard demographics table in a quantitative study provides aggregate information for what are often large samples. In other words, such tables present totals and percentages for demographic categories within the sample that are relevant to the study (e.g., age, gender, job title).

If conducting qualitative research for your dissertation, however, you will use a smaller sample and obtain richer data from each participant than in quantitative studies. To enhance thick description—a dimension of trustworthiness—it will help to present sample demographics in a table that includes information on each participant. Remember that ethical standards of research require that all participant information be deidentified, so use participant identification numbers or pseudonyms for each participant, and do not present any personal information that would allow others to identify the participant (Blignault & Ritchie, 2009). Table 1 provides participant demographics for a hypothetical qualitative research study exploring the perspectives of persons who were formerly homeless regarding their experiences of transitioning into stable housing and obtaining employment.
Participant Demographics
| Participant ID | Gender | Age | Current Living Situation |
| P1 | Female | 34 | Alone |
| P2 | Male | 27 | With Family |
| P3 | Male | 44 | Alone |
| P4 | Female | 46 | With Roommates |
| P5 | Female | 25 | With Family |
| P6 | Male | 30 | With Roommates |
| P7 | Male | 38 | With Roommates |
| P8 | Male | 51 | Alone |
Tables to Illustrate Initial Codes
Most of our dissertation consulting clients who are conducting qualitative research choose a form of thematic analysis . Qualitative analysis to identify themes in the data typically involves a progression from (a) identifying surface-level codes to (b) developing themes by combining codes based on shared similarities. As this process is inherently subjective, it is important that readers be able to evaluate the correspondence between the data and your findings (Anfara et al., 2002). This supports confirmability, another dimension of trustworthiness .
A great way to illustrate the trustworthiness of your qualitative analysis is to create a table that displays quotes from the data that exemplify each of your initial codes. Providing a sample quote for each of your codes can help the reader to assess whether your coding was faithful to the meanings in the data, and it can also help to create clarity about each code’s meaning and bring the voices of your participants into your work (Blignault & Ritchie, 2009).

Table 2 is an example of how you might present information regarding initial codes. Depending on your preference or your dissertation committee’s preference, you might also present percentages of the sample that expressed each code. Another common piece of information to include is which actual participants expressed each code. Note that if your qualitative analysis yields a high volume of codes, it may be appropriate to present the table as an appendix.
Initial Codes
| Initial code | of participants contributing ( =8) | of transcript excerpts assigned | Sample quote |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily routine of going to work enhanced sense of identity | 7 | 12 | “It’s just that good feeling of getting up every day like everyone else and going to work, of having that pattern that’s responsible. It makes you feel good about yourself again.” (P3) |
| Experienced discrimination due to previous homelessness | 2 | 3 | “At my last job, I told a couple other people on my shift I used to be homeless, and then, just like that, I get put into a worse job with less pay. The boss made some excuse why they did that, but they didn’t want me handling the money is why. They put me in a lower level job two days after I talk to people about being homeless in my past. That’s no coincidence if you ask me.” (P6) |
| Friends offered shared housing | 3 | 3 | “My friend from way back had a spare room after her kid moved out. She let me stay there until I got back on my feet.” (P4) |
| Mental health services essential in getting into housing | 5 | 7 | “Getting my addiction treated was key. That was a must. My family wasn’t gonna let me stay around their place without it. So that was a big help for getting back into a place.” (P2) |
Tables to Present the Groups of Codes That Form Each Theme
As noted previously, most of our dissertation assistance clients use a thematic analysis approach, which involves multiple phases of qualitative analysis that eventually result in themes that answer the dissertation’s research questions. After initial coding is completed, the analysis process involves (a) examining what different codes have in common and then (b) grouping similar codes together in ways that are meaningful given your research questions. In other words, the common threads that you identify across multiple codes become the theme that holds them all together—and that theme answers one of your research questions.
As with initial coding, grouping codes together into themes involves your own subjective interpretations, even when aided by qualitative analysis software such as NVivo or MAXQDA. In fact, our dissertation assistance clients are often surprised to learn that qualitative analysis software does not complete the analysis in the same ways that statistical analysis software such as SPSS does. While statistical analysis software completes the computations for you, qualitative analysis software does not have such analysis capabilities. Software such as NVivo provides a set of organizational tools that make the qualitative analysis far more convenient, but the analysis itself is still a very human process (Burnard et al., 2008).

Because of the subjective nature of qualitative analysis, it is important to show the underlying logic behind your thematic analysis in tables—such tables help readers to assess the trustworthiness of your analysis. Table 3 provides an example of how to present the codes that were grouped together to create themes, and you can modify the specifics of the table based on your preferences or your dissertation committee’s requirements. For example, this type of table might be presented to illustrate the codes associated with themes that answer each research question.
Grouping of Initial Codes to Form Themes
| Theme Initial codes grouped to form theme | of participants contributing ( =8) | of transcript excerpts assigned |
| Assistance from friends, family, or strangers was instrumental in getting back into stable housing | 6 | 10 |
| Family member assisted them to get into housing | ||
| Friends offered shared housing | ||
| Stranger offered shared housing | ||
| Obtaining professional support was essential for overcoming the cascading effects of poverty and homelessness | 7 | 19 |
| Financial benefits made obtaining housing possible | ||
| Mental health services essential in getting into housing | ||
| Social services helped navigate housing process | ||
| Stigma and concerns about discrimination caused them to feel uncomfortable socializing with coworkers | 6 | 9 |
| Experienced discrimination due to previous homelessness | ||
| Feared negative judgment if others learned of their pasts | ||
| Routine productivity and sense of making a contribution helped to restore self-concept and positive social identity | 8 | 21 |
| Daily routine of going to work enhanced sense of identity | ||
| Feels good to contribute to society/organization | ||
| Seeing products of their efforts was rewarding |
Tables to Illustrate the Themes That Answer Each Research Question
Creating alignment throughout your dissertation is an important objective, and to maintain alignment in your results chapter, the themes you present must clearly answer your research questions. Conducting qualitative analysis is an in-depth process of immersion in the data, and many of our dissertation consulting clients have shared that it’s easy to lose your direction during the process. So, it is important to stay focused on your research questions during the qualitative analysis and also to show the reader exactly which themes—and subthemes, as applicable—answered each of the research questions.

Below, Table 4 provides an example of how to display the thematic findings of your study in table form. Depending on your dissertation committee’s preference or your own, you might present all research questions and all themes and subthemes in a single table. Or, you might provide separate tables to introduce the themes for each research question as you progress through your presentation of the findings in the chapter.
Emergent Themes and Research Questions
| Research question
| Themes that address question
|
| RQ1. How do adults who have previously experienced homelessness describe their transitions to stable housing?
| Theme 1: Assistance from friends, family, or strangers was instrumental in getting back into stable housing Theme 2: Obtaining professional support was essential for overcoming the cascading effects of poverty and homelessness
|
| RQ2. How do adults who have previously experienced homelessness describe returning to paid employment?
| Theme 3: Self-perceived stigma caused them to feel uncomfortable socializing with coworkers Theme 4: Routine productivity and sense of making a contribution helped to restore self-concept and positive social identity |
Bonus Tip! Figures to Spice Up Your Results
Although dissertation committees most often wish to see tables such as the above in qualitative results chapters, some also like to see figures that illustrate the data. Qualitative software packages such as NVivo offer many options for visualizing your data, such as mind maps, concept maps, charts, and cluster diagrams. A common choice for this type of figure among our dissertation assistance clients is a tree diagram, which shows the connections between specified words and the words or phrases that participants shared most often in the same context. Another common choice of figure is the word cloud, as depicted in Figure 1. The word cloud simply reflects frequencies of words in the data, which may provide an indication of the importance of related concepts for the participants.

As you move forward with your qualitative analysis and development of your results chapter, we hope that this brief overview of useful tables and figures helps you to decide on an ideal presentation to showcase the trustworthiness your findings. Completing a rigorous qualitative analysis for your dissertation requires many hours of careful interpretation of your data, and your end product should be a rich and detailed results presentation that you can be proud of. Reach out if we can help in any way, as our dissertation coaches would be thrilled to assist as you move through this exciting stage of your dissertation journey!
Anfara Jr., V. A., Brown, K. M., & Mangione, T. L. (2002). Qualitative analysis on stage: Making the research process more public. Educational Researcher , 31 (7), 28-38. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X031007028
Blignault, I., & Ritchie, J. (2009). Revealing the wood and the trees: Reporting qualitative research. Health Promotion Journal of Australia , 20 (2), 140-145. https://doi.org/10.1071/HE09140
Burnard, P., Gill, P., Stewart, K., Treasure, E., & Chadwick, B. (2008). Analysing and presenting qualitative data. British Dental Journal , 204 (8), 429-432. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2008.292

Home > Blog >
Data analysis in qualitative research, theertha raj, august 30, 2024.
While numbers tell us "what" and "how much," qualitative data reveals the crucial "why" and "how." But let's face it - turning mountains of text, images, and observations into meaningful insights can be daunting.
This guide dives deep into the art and science of how to analyze qualitative data. We'll explore cutting-edge techniques, free qualitative data analysis software, and strategies to make your analysis more rigorous and insightful. Expect practical, actionable advice on qualitative data analysis methods, whether you're a seasoned researcher looking to refine your skills or a team leader aiming to extract more value from your qualitative data.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data is non-numerical information that describes qualities or characteristics. It includes text, images, audio, and video.
This data type captures complex human experiences, behaviors, and opinions that numbers alone can't express.
A qualitative data example can include interview transcripts, open-ended survey responses, field notes from observations, social media posts and customer reviews
Importance of qualitative data
Qualitative data is vital for several reasons:
- It provides a deep, nuanced understanding of complex phenomena.
- It captures the 'why' behind behaviors and opinions.
- It allows for unexpected discoveries and new research directions.
- It puts people's experiences and perspectives at the forefront.
- It enhances quantitative findings with depth and detail.
What is data analysis in qualitative research?
Data analysis in qualitative research is the process of examining and interpreting non-numerical data to uncover patterns, themes, and insights. It aims to make sense of rich, detailed information gathered through methods like interviews, focus groups, or observations.
This analysis moves beyond simple description. It seeks to understand the underlying meanings, contexts, and relationships within the data. The goal is to create a coherent narrative that answers research questions and generates new knowledge.
How is qualitative data analysis different from quantitative data analysis?
Qualitative and quantitative data analyses differ in several key ways:
- Data type: Qualitative analysis uses non-numerical data (text, images), while quantitative analysis uses numerical data.
- Approach: Qualitative analysis is inductive and exploratory. Quantitative analysis is deductive and confirmatory.
- Sample size: Qualitative studies often use smaller samples. Quantitative studies typically need larger samples for statistical validity.
- Depth vs. breadth: Qualitative analysis provides in-depth insights about a few cases. Quantitative analysis offers broader insights across many cases.
- Subjectivity: Qualitative analysis involves more subjective interpretation. Quantitative analysis aims for objective, statistical measures.
What are the 3 main components of qualitative data analysis?
The three main components of qualitative data analysis are:
- Data reduction: Simplifying and focusing the raw data through coding and categorization.
- Data display: Organizing the reduced data into visual formats like matrices, charts, or networks.
- Conclusion drawing/verification: Interpreting the displayed data and verifying the conclusions.
These components aren't linear steps. Instead, they form an iterative process where researchers move back and forth between them throughout the analysis.
How do you write a qualitative analysis?
Step 1: organize your data.
Start with bringing all your qualitative research data in one place. A repository can be of immense help here. Transcribe interviews , compile field notes, and gather all relevant materials.
Immerse yourself in the data. Read through everything multiple times.
Step 2: Code & identify themes
Identify and label key concepts, themes, or patterns. Group related codes into broader themes or categories. Try to connect themes to tell a coherent story that answers your research questions.
Pick out direct quotes from your data to illustrate key points.
Step 3: Interpret and reflect
Explain what your results mean in the context of your research and existing literature.
Als discuss, identify and try to eliminate potential biases or limitations in your analysis.
Summarize main insights and their implications.
What are the 5 qualitative data analysis methods?
Thematic Analysis Identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (themes) within data.
Content Analysis Systematically categorizing and counting the occurrence of specific elements in text.
Grounded Theory Developing theory from data through iterative coding and analysis.
Discourse Analysis Examining language use and meaning in social contexts.
Narrative Analysis Interpreting stories and personal accounts to understand experiences and meanings.
Each method suits different research goals and data types. Researchers often combine methods for comprehensive analysis.
What are the 4 data collection methods in qualitative research?
When it comes to collecting qualitative data, researchers primarily rely on four methods.
- Interviews : One-on-one conversations to gather in-depth information.
- Focus Groups : Group discussions to explore collective opinions and experiences.
- Observations : Watching and recording behaviors in natural settings.
- Document Analysis : Examining existing texts, images, or artifacts.
Researchers often use multiple methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of their topic.
How is qualitative data analysis measured?
Unlike quantitative data, qualitative data analysis isn't measured in traditional numerical terms. Instead, its quality is evaluated based on several criteria.
Trustworthiness is key, encompassing the credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability of the findings. The rigor of the analysis - the thoroughness and care taken in data collection and analysis - is another crucial factor.
Transparency in documenting the analysis process and decision-making is essential, as is reflexivity - acknowledging and examining the researcher's own biases and influences.
Employing techniques like member checking and triangulation all contribute to the strength of qualitative analysis.
Benefits of qualitative data analysis
The benefits of qualitative data analysis are numerous. It uncovers rich, nuanced understanding of complex phenomena and allows for unexpected discoveries and new research directions.
By capturing the 'why' behind behaviors and opinions, qualitative data analysis methods provide crucial context.
Qualitative analysis can also lead to new theoretical frameworks or hypotheses and enhances quantitative findings with depth and detail. It's particularly adept at capturing cultural nuances that might be missed in quantitative studies.
Challenges of Qualitative Data Analysis
Researchers face several challenges when conducting qualitative data analysis.
Managing and making sense of large volumes of rich, complex data can lead to data overload. Maintaining consistent coding across large datasets or between multiple coders can be difficult.
There's a delicate balance to strike between providing enough context and maintaining focus on analysis. Recognizing and mitigating researcher biases in data interpretation is an ongoing challenge.
The learning curve for qualitative data analysis software can be steep and time-consuming. Ethical considerations, particularly around protecting participant anonymity while presenting rich, detailed data, require careful navigation. Integrating different types of data from various sources can be complex. Time management is crucial, as researchers must balance the depth of analysis with project timelines and resources. Finally, communicating complex qualitative insights in clear, compelling ways can be challenging.
Best Software to Analyze Qualitative Data
G2 rating: 4.6/5
Pricing: Starts at $30 monthly.
Looppanel is an AI-powered research assistant and repository platform that can make it 5x faster to get to insights, by automating all the manual, tedious parts of your job.
Here’s how Looppanel’s features can help with qualitative data analysis:
- Automatic Transcription: Quickly turn speech into accurate text; it works across 8 languages and even heavy accents, with over 90% accuracy.
- AI Note-Taking: The research assistant can join you on calls and take notes, as well as automatically sort your notes based on your interview questions.
- Automatic Tagging: Easily tag and organize your data with free AI tools.
- Insight Generation: Create shareable insights that fit right into your other tools.
- Repository Search: Run Google-like searches within your projects and calls to find a data snippet/quote in seconds
- Smart Summary: Ask the AI a question on your research, and it will give you an answer, using extracts from your data as citations.
Looppanel’s focus on automating research tasks makes it perfect for researchers who want to save time and work smarter.
G2 rating: 4.7/5
Pricing: Free version available, with the Plus version costing $20 monthly.
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, offers a range of capabilities for qualitative data analysis including:
- Document analysis : It can easily extract and analyze text from various file formats.
- Summarization : GPT can condense lengthy documents into concise summaries.
- Advanced Data Analysis (ADA) : For paid users, Chat-GPT offers quantitative analysis of data documents.
- Sentiment analysis: Although not Chat-GPT’s specialty, it can still perform basic sentiment analysis on text data.
ChatGPT's versatility makes it valuable for researchers who need quick insights from diverse text sources.
How to use ChatGPT for qualitative data analysis
ChatGPT can be a handy sidekick in your qualitative analysis, if you do the following:
- Use it to summarize long documents or transcripts
- Ask it to identify key themes in your data
- Use it for basic sentiment analysis
- Have it generate potential codes based on your research questions
- Use it to brainstorm interpretations of your findings
G2 rating: 4.7/5 Pricing: Custom
Atlas.ti is a powerful platform built for detailed qualitative and mixed-methods research, offering a lot of capabilities for running both quantitative and qualitative research.
It’s key data analysis features include:
- Multi-format Support: Analyze text, PDFs, images, audio, video, and geo data all within one platform.
- AI-Powered Coding: Uses AI to suggest codes and summarize documents.
- Collaboration Tools: Ideal for teams working on complex research projects.
- Data Visualization: Create network views and other visualizations to showcase relationships in your data.
G2 rating: 4.1/5 Pricing: Custom
NVivo is another powerful platform for qualitative and mixed-methods research. It’s analysis features include:
- Data Import and Organization: Easily manage different data types, including text, audio, and video.
- AI-Powered Coding: Speeds up the coding process with machine learning.
- Visualization Tools: Create charts, graphs, and diagrams to represent your findings.
- Collaboration Features: Suitable for team-based research projects.
NVivo combines AI capabilities with traditional qualitative analysis tools, making it versatile for various research needs.
Can Excel do qualitative data analysis?
Excel can be a handy tool for qualitative data analysis, especially if you're just starting out or working on a smaller project. While it's not specialized qualitative data analysis software, you can use it to organize your data, maybe putting different themes in different columns. It's good for basic coding, where you label bits of text with keywords. You can use its filter feature to focus on specific themes. Excel can also create simple charts to visualize your findings. But for bigger or more complex projects, you might want to look into software designed specifically for qualitative data analysis. These tools often have more advanced features that can save you time and help you dig deeper into your data.
How do you show qualitative analysis?
Showing qualitative data analysis is about telling the story of your data. In qualitative data analysis methods, we use quotes from interviews or documents to back up our points. Create charts or mind maps to show how different ideas connect, which is a common practice in data analysis in qualitative research. Group your findings into themes that make sense. Then, write it all up in a way that flows, explaining what you found and why it matters.
What is the best way to analyze qualitative data?
There's no one-size-fits-all approach to how to analyze qualitative data, but there are some tried-and-true steps.
Start by getting your data in order. Then, read through it a few times to get familiar with it. As you go, start marking important bits with codes - this is a fundamental qualitative data analysis method. Group similar codes into bigger themes. Look for patterns in these themes - how do they connect?
Finally, think about what it all means in the bigger picture of your research. Remember, it's okay to go back and forth between these steps as you dig deeper into your data. Qualitative data analysis software can be a big help in this process, especially for managing large amounts of data.
In qualitative methods of test analysis, what do test developers do to generate data?
Test developers in qualitative research might sit down with people for in-depth chats or run group discussions, which are key qualitative data analysis methods. They often use surveys with open-ended questions that let people express themselves freely. Sometimes, they'll observe people in their natural environment, taking notes on what they see. They might also dig into existing documents or artifacts that relate to their topic. The goal is to gather rich, detailed information that helps them understand the full picture, which is crucial in data analysis in qualitative research.
Which is not a purpose of reflexivity during qualitative data analysis?
Reflexivity in qualitative data analysis isn't about proving you're completely objective. That's not the goal. Instead, it's about being honest about who you are as a researcher. It's recognizing that your own experiences and views might influence how you see the data. By being upfront about this, you actually make your research more trustworthy. It's also a way to dig deeper into your data, seeing things you might have missed at first glance. This self-awareness is a crucial part of qualitative data analysis methods.
What is a qualitative data analysis example?
A simple example is analyzing customer feedback for a new product. You might collect feedback, read through responses, create codes like "ease of use" or "design," and group similar codes into themes. You'd then identify patterns and support findings with specific quotes. This process helps transform raw feedback into actionable insights.
How to analyze qualitative data from a survey?
First, gather all your responses in one place. Read through them to get a feel for what people are saying. Then, start labeling responses with codes - short descriptions of what each bit is about. This coding process is a fundamental qualitative data analysis method. Group similar codes into bigger themes. Look for patterns in these themes. Are certain ideas coming up a lot? Do different groups of people have different views? Use actual quotes from your survey to back up what you're seeing. Think about how your findings relate to your original research questions.
Which one is better, NVivo or Atlas.ti?
NVivo is known for being user-friendly and great for team projects. Atlas.ti shines when it comes to visual mapping of concepts and handling geographic data. Both can handle a variety of data types and have powerful tools for qualitative data analysis. The best way to decide is to try out both if you can.
While these are powerful tools, the core of qualitative data analysis still relies on your analytical skills and understanding of qualitative data analysis methods.
Do I need to use NVivo for qualitative data analysis?
You don't necessarily need NVivo for qualitative data analysis, but it can definitely make your life easier, especially for bigger projects. Think of it like using a power tool versus a hand tool - you can get the job done either way, but the power tool might save you time and effort. For smaller projects or if you're just starting out, you might be fine with simpler tools or even free qualitative data analysis software. But if you're dealing with lots of data, or if you need to collaborate with a team, or if you want to do more complex analysis, then specialized qualitative data analysis software like NVivo can be a big help. It's all about finding the right tool for your specific research needs and the qualitative data analysis methods you're using.
Here’s a guide that can help you decide.
How to use NVivo for qualitative data analysis
First, you import all your data - interviews, documents, videos, whatever you've got. Then you start creating "nodes," which are like folders for different themes or ideas in your data. As you read through your material, you highlight bits that relate to these themes and file them under the right nodes. NVivo lets you easily search through all this organized data, find connections between different themes, and even create visual maps of how everything relates.
How much does NVivo cost?
NVivo's pricing isn't one-size-fits-all. They offer different plans for individuals, teams, and large organizations, but they don't publish their prices openly. Contact the team here for a custom quote.
What are the four steps of qualitative data analysis?
While qualitative data analysis is often iterative, it generally follows these four main steps:
1. Data Collection: Gathering raw data through interviews, observations, or documents.
2. Data Preparation: Organizing and transcribing the collected data.
3. Data Coding: Identifying and labeling important concepts or themes in the data.
4. Interpretation: Drawing meaning from the coded data and developing insights.
Follow us on
Get the best resources for ux research, in your inbox, related articles.

Resources & Guides
February 15, 2024
How to use AI for Qualitative Data Analysis

August 15, 2024
Transcription in Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Guide for UX Researchers

May 22, 2024
Triangulation in Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Guide [2024]
Looppanel automatically records your calls, transcribes them, and centralizes all your research data in one place
We Trust in Human Precision
20,000+ Professional Language Experts Ready to Help. Expertise in a variety of Niches.
API Solutions
- API Pricing
- Cost estimate
- Customer loyalty program
- Educational Discount
- Non-Profit Discount
- Green Initiative Discount1
Value-Driven Pricing
Unmatched expertise at affordable rates tailored for your needs. Our services empower you to boost your productivity.
- Special Discounts
- Enterprise transcription solutions
- Enterprise translation solutions
- Transcription/Caption API
- AI Transcription Proofreading API
Trusted by Global Leaders
GoTranscript is the chosen service for top media organizations, universities, and Fortune 50 companies.
GoTranscript
One of the Largest Online Transcription and Translation Agencies in the World. Founded in 2005.
Speaker 1: Hello, William Levesque here from the Rehabilitation Teaching and Research Unit, RTRU, at the Wellington campus for the University of Otago. This presentation is a short introduction to how to write a discussion section. I've targeted this at PhD and Master's thesis students, so I'll be talking a bit about how to write a discussion chapter for a thesis, but also it's relevant to writing your first paper for publication in a scientific peer-reviewed journal. So to begin with, here is a broad overview about what to include in your discussion section. You want to cover what you did, what you found, what it means, and these things can be summed up to refer to why your research is important. You want to talk about the strengths and limitations of your research and make recommendations for future research. If your research is to do with health science work, then you should also be talking about the implications from your research in terms of clinical practice. Specific journals do have more explicit requirements in terms of the structure of your discussion section sometimes, so do follow those of course if you're submitting a paper for publication. But in general, these are the things that need to be covered in a discussion chapter. In terms of what you did and found, you need to be declarative, direct, and succinct. You want to cover this in a paragraph or two, or if you're writing for publication, a short journal article, this might need to be only a sentence or two in your paper. You don't want to reproduce your results in entirety in your discussion section. Just concentrate on the major findings, the stuff that is most important from your work. In terms of what your research findings mean, you want to interpret your findings rather than just report them descriptively. Reference to existing theory can be useful here. Your research findings may either expand on existing theory or be used to further substantiate existing theory. You want to talk about why your research findings are important and to link your findings to prior research. Highlight the parts of your research that are new. This may be that you have explored a new research question that other people haven't explored before, or it might be that you have found something new or produced new ideas or perspectives through your research, or it might be that your research findings provide important new evidence for existing theory, strengthening existing ideas on a particular topic. So here's an example of a paper that I published last year with my colleagues on research, reporting on some research, some qualitative research, exploring cultural issues around the barriers and facilitators for Māori people accessing pulmonary rehabilitation, which is an exercise and education programme for people with chronic lung disease. I'm just going to scroll down to the results section here, and you'll see at the beginning of the results section I have a summary of our main research findings which have been linked to the prior research in this area. So our work was about barriers and facilitators of accessing pulmonary rehabilitation, so we talk about the findings that relate to, that have previously been identified in other people's work, and we highlight other findings that arose from our work with Māori individuals where these findings are more specific to that population and present new perspectives. Right at the beginning of this discussion section we make an assertive statement that, to our knowledge, this is the first study that has explored these cultural issues regarding the influence of cultural issues on uptake of pulmonary rehabilitation, so we're highlighting what is new. So what are some of the strategies for you to use in order to identify things that you should be talking about in your discussion section in more detail? One idea is to start early. While you are analysing your results, or even during the process of conducting your studies, start jotting ideas down about what sorts of things might be important arising from your work, and you can refer back to these when you're writing your research section. It's also a really good idea to have a clear picture in your head of who your audience is for your work. Write for your audience. What are the key take-home messages that you want people to take from your research, and who are you writing for? If you're writing to a specific journal, it is useful to know who the readership of that journal is, and who the editorship of that journal is, and you want to write for that for those people as well. Consider alternative interpretations of your data. Try and think what other ways you could interpret your research findings, and either use this to strengthen your own ideas or to adapt your own ideas in terms of how to interpret your research findings. Make sure you justify your ideas either way. Another strategy might be to list all the things that you didn't know when you began your research that you have subsequently discovered for yourself. It's easy, particularly for a three-year PhD process, to forget how far you've come in terms of the development of your knowledge, and so it's useful to reflect on the things you didn't know prior to undertaking a study. Develop each of these points in your list as a discrete section in your PhD or Master's thesis discussion chapter, or as discrete paragraphs in the results section of a published article. It can be also useful to treat the background section of your thesis or your published article as the setup to your discussion, and I'll just illustrate this with this paper that I've been referring to here. So if I go back to the introduction, there is reference in here to what other people have written about barriers and facilitators of access to pulmonary rehabilitation, but how little information exists on cultural factors related to the delivery of pulmonary rehabilitation. So, right at the beginning of this paper, I have foreshadowed this discussion that we would have later on in the discussion section of this paper around the importance of considering these things and the implication they might have. So this highlights what's new, again, for this research that we were undertaking. When discussing the limitations of your research, you want to remember that all research has limitations. Examiners expect PhD and Master's theses to have limitations, they expect graduate students to have faced difficulties and problems with their method, and so examiners of theses are more concerned with how problems were dealt with than whether or not they occurred. So it's important, both in writing a thesis and in presenting research for a published article, to be frank and candid about the limitations of your research, but don't be overly apologetic because limitations are inevitable. You want to discuss the implications of the limitations rather than just highlight them. You've got to talk about why the limitations are relevant in terms of interpreting the results of your work. Some limitations are just errors and others are considerations regarding the scope of the work, but both of these things are worth discussing. Discussion of the limitations also provides you with an opportunity to identify future areas of research. You want to make general statements about future areas of research, but also provide specific recommendations about what needs to happen next, what study is needed next, what methods should be employed, what is needed to do these types of studies. And again, to come back to this paper here in the discussion section, at the end we talk about how research on indigenous healthcare is sorely lacking and there's a great need for it, and make a specific recommendation here drawing on other people's work to put out a call for an urgent need for further cost-effectiveness studies to be conducted involving indigenous healthcare interventions in order to better understand the value and to further develop these models. So you can see we've made a general recommendation and some more specific recommendations in terms of the type of research that needs to be conducted. Things to avoid in the discussion section. Avoid repeating too much of your findings without interpretation. Don't just repeat verbatim. You want to take things a little bit further in your discussion section. Avoid presenting new data in your discussion. If you feel like you want to present data that you didn't present in your results section, you might want to go back and revise your results section rather than add it to your discussion section. Avoid over-inflating the importance of your findings. As a scientist, you need to be appropriately conservative in terms of how far you can develop arguments from the data that you have. And similarly, avoid over-extending your arguments. Don't interpret beyond what can be justifiably inferred from the data. One thing to look out for is long strings of inferences, if this, then this, then this, then this, when you've moved a long way away from your original data to reach some hypothetical conclusion. Avoid raising too many tangential issues. However, this can be okay in a chapter section of a PhD thesis or a master's thesis, and that's one of the luxuries of writing a thesis. You do have a bit more room to expand on some of the more fringe ideas in your work. One more consideration. It's useful to use the discussion section of your work to publish arguments that you might want to cite later. So by cite later, I mean in terms of future research grants. It's useful to have arguments presented in a paper to justify future research ideas. But also, use your discussion section to put messages out there that you want in the world. So these could be messages for clinicians or policy makers or for students. In conclusion, you want to write a conclusion and be conclusive. The conclusion might be a separate section in your thesis or in your journal article, or it might be integrated in your discussion at the end. But regardless, conclusions should be tight and to the point. They should follow clearly from your research question. Don't introduce any new citations in your conclusion statements, but make sure that there's a nice flow of logic from your research question to your methods, to your results, to your discussion, to the things you pull out in your conclusion. Be assertive in your conclusions, but be balanced. So that's it from me on writing a discussion section for your PhD thesis, master's thesis or journal article. If you want to follow my work on a more ongoing basis, you can follow me on Twitter at DrLivac.


How To Write A Dissertation Introduction
A Simple Explainer With Examples + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By Dr Eunice Rautenbach (D. Tech) | March 2020
If you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: Writing An Introduction Chapter
- The purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis
A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.

Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.
#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have .
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
45 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
You explain what moment in life caused you to have a peaked interest in the thesis topic. Personal experiences? Or something that had an impact on your life, or others. Something would have caused your drive of topic. Dig deep inside, the answer is within you!
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
This is great!
Thank you for all this information. I feel very confident to complete my dissertation with all the help given. This is awesome and very helpful; I was studying alone with very little supervision and feedback of my thoughts. feelings. aspirations and experiences, with my topic or Kaupapa. It is a topic that very little or few researchers have written a thesis about (from personal experiences). As John Burke said ” unless you are sitting in the front seat and row, up close and personal, you will not understand the difficulties of growing up and living with hearing loss (caused by swimmer’s ears infection, resulting in burst eardrums, unless one denies having a hearing loss. This is from a Māori woman’s cultural perspective. Nga mihi nui kia koutou.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and ...
Don't make the reader do the analytic work for you. Now, on to some specific ways to structure your findings section. 1). Tables. Tables can be used to give an overview of what you're about to present in your findings, including the themes, some supporting evidence, and the meaning/explanation of the theme.
The introductory section serves as the gateway to your qualitative findings chapter. Begin by reiterating your problem statement and research questions, setting the stage for the data that will be presented. Highlighting the purpose of your research is crucial at this point to give context to the reader. Example: The primary aim of this case ...
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George. Revised on July 18, 2023. A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation. You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order.
Qualitative research presents "best examples" of raw data to demonstrate an analytic point, not simply to display data. Numbers (descriptive statistics) help your reader understand how prevalent or typical a finding is. Numbers are helpful and should not be avoided simply because this is a qualitative dissertation.
The results section is where you report the main findings of your research. Watch this video to learn how to report your results concisely and objectively in...
Qualitative research findings can be difficult to write up in your dissertation results chapter. Here are 7 tips to help you showcase your findings in a conc...
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Published on 27 October 2016 by Bas Swaen. Revised on 25 October 2022 by Tegan George. A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation. You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a ...
Introducing your findings. The findings chapter is likely to comprise the majority of your paper. It can be up to 40% of the total word count within your dissertation writing. This is a huge chunk of information, so it's essential that it is clearly organised and that the reader knows what is supposed to be happening.
Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarizing your major findings. To speed up the process you can use a summarizer to quickly get an overview of all important findings. Don't just repeat all the data you have already reported—aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research ...
Chapter 4. What needs to be included in the chapter? The topics below are typically included in this chapter, and often in this order (check with your Chair): Introduction. Remind the reader what your research questions were. In a qualitative study you will restate the research questions. In a quantitative study you will present the hypotheses.
Chapter 1. A Complete Dissertation 7 purpose, or it does not stand alone as a document. Chapter 2: Literature Review This chapter situates the study in the con-text of previous research and scholarly mate - rial pertaining to the topic, presents a critical synthesis of empirical literature according to relevant themes or variables, justifies how
Many students struggle with turning qualitative research projects into a master's thesis or doctoral dissertation because the research itself is inherently messy. To address this challenge, authors Linda Dale Bloomberg and Marie Volpe have distilled decades of experience into a first-of-its-kind, highly practical reference for graduate students.
Chapter 1: The Nature of Dissertation Research Introduction A dissertation is a systematic investigation of a socially significant research question that makes a contribution to the literature and demonstrates the skill of doctoral students to conduct original research. Dissertation research is a collaborative process primarily involving students
Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations of your study. The fourth step in writing up your discussion chapter is to acknowledge the limitations of the study. These limitations can cover any part of your study, from the scope or theoretical basis to the analysis method (s) or sample.
Whilst this method of writing may appear unstructured, if you are only starting your journey as a qualitative researcher, please remember that it is the interpretation of qualitative findings that brings them into being (Braun and Clarke 2013). Therefore, it is usual to have a "Findings and discussion" chapter in dissertations or theses ...
Writing a Dissertation's Chapter 4 and 5 2 Definition of Chapter Four and Five Chapter four of a dissertation presents the findings from the data gathered by the researcher. The nature of the design determines the presentation of the data. For example, one student's "purpose of this quantitative correlational study was to determine the
of qualitative writing: … the sense of argument develops through the whole process of data collection, analysis and organization. This makes qualitative writing in essence very different from quantitative writing. Qualitative writing becomes very much an unfolding story in which the writer gradually makes sense,
The earliest stages of developing a doctoral dissertation—most specifically the topic development and literature review stages—require that you immerse yourself in a ton of existing research related to your potential topic. If you have begun writing your dissertation proposal, you have undoubtedly reviewed countless results and findings sections of studies in order to help gain an ...
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
Designing and writing a qualitative dissertation methodology chapter can be done! Qualitative Dissertation Methodology: A Guide for Research Design and Metho ... By the end of the book, students will have completed the most challenging chapter of a qualitative dissertation and laid a strong foundation for the rest of their dissertation work ...
How do you write a qualitative analysis? Step 1: Organize your data. ... Create charts or mind maps to show how different ideas connect, which is a common practice in data analysis in qualitative research. Group your findings into themes that make sense. Then, write it all up in a way that flows, explaining what you found and why it matters. ...
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you've found in terms of the quantitative data you've collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts.
Speaker 1: Hello, William Levesque here from the Rehabilitation Teaching and Research Unit, RTRU, at the Wellington campus for the University of Otago. This presentation is a short introduction to how to write a discussion section. I've targeted this at PhD and Master's thesis students, so I'll be talking a bit about how to write a discussion chapter for a thesis, but also it's relevant to ...
Resources to Help Write Your Thesis Paper. While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn't have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier. If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.