The Ultimate Guide to Effective Teacher Presentations: Strategies & Tips

Dianne Adlawan

Teachers, by nature, are considered professional presenters. Their main responsibility is to talk in front of their students to relay educational knowledge, sharpen their minds and skills, and even serve as a second guide alongside their parents. They also speak in front of parents, co-teachers, and school administrators. This just means that preparing for a presentation is already not new to them.
Still, teachers can become so comfortable with their presentation routine that their techniques turn into autopilot. The result of a repetitive task can become tiring and not challenging anymore which may result in students losing interest or attention span in the process.
The tips featured in this article are dedicated to these hard-working professionals. This will help them prepare and perform a better presentation in front of any type of audience.


Why You Should Prepare for a Presentation
- Preparation helps you build to structure your thoughts to create a well-organized presentation. By taking the time to prepare, you can decide what information is most important, plan the flow of the presentation, and make sure that everything is connected and easy to follow.
- Second, it allows you to think ahead of the questions that your audience might ask. Especially if you’re giving a presentation to a group of various audiences, who are curious about the topic at hand. By preparing in advance, you’ll be able to answer any questions they may have, which will not only increase their understanding but also boost your credibility as a teacher.
- Lastly, preparation helps you make the most of your time. Advanced preparation ahead of the presentation can ensure that you’re not wasting time trying to organize your thoughts at the last minute.
Effects of an Organized and Well-Planned Presentation
An audience engages with a speaker who knows their words and poses a confident attitude. While the projector may display clear and concise slides, the presenter is the main ingredient to every presentation.
For teachers, a well-planned lesson presentation helps the teacher maintain the attention and interest of their students, which is crucial for effective learning. Additionally, being organized and prepared will help teachers convey their ideas more effectively and it will help the teacher to feel more confident, which also impacts their teaching and in turn can help to build trust and rapport with their students.
Possible Outcomes of An Unprepared Presentation
Let’s suppose you haven’t allocated enough time to plan and prepare for an important presentation. What could be the potential outcomes?
- Increased Stress and Anxiety: Lack of preparation can lead to increased anxiety and stress, which can not only hinder your ability to deliver a convincing presentation but also hurt your mental health and work balance. It can cause a “mental block,” causing you to lose focus and concentration during your delivery.
- Poor Presentation Delivery: Without proper preparation, your presentation can appear scattered and disjointed. This can lead to an incoherent message that fails to convince your audience.
- Diminished credibility: Delivering an unprepared presentation can harm your reputation as a professional. It can portray you as disorganized and unreliable which could lead your colleagues or students to question your competence and reliability.
Effective Visual and Content Organization Tips
Consider this as the first stage towards an effective teacher presentation. Before moving on to improving your verbal communication cues, let’s enhance first your presentation visuals and content.
Visual Tips
1. add powerpoint animations and different media.
Establishing an attractive slideshow is one of the keys to a successful presentation. This will put a good impression on your audience that you’re prepared just by seeing how well-designed your presentation is. Of course, images add to slideshow attraction, but consider adding another forms of media such as GIFs and videos, as well as animations! Microsoft PowerPoint has a lot of fun & captivating features that you may not be aware of. Check out this example of an easy yet appealing Slide Zoom trick in PowerPoint that you can add to your presentation to wow your audience.
@classpoint.io Did someone say FREE??? Yes, we did. Here are free websites to help you upgrade your next PowerPoint presentation! 😎 #powerpoint #presentation #design #studytok #edutok #tutorial #tipsandtricks #ai ♬ original sound – r & m <33
Read Next: Make Your Presentations POP With This PowerPoint Animation Template
2. Use Readable Font Styles
Make sure to use the best font style that makes your presentation look sleek, readable, and won’t strain your audience’s eyes while reading. We all want to use a fancy font, trust me, I get it. But most of the time, simplicity is beauty, especially if you’re presenting a professional-looking slideshow. Font styles such as Poppins, Tahoma, Verdana, Montserrat, and Helvetica are great examples of font styles that screams simple yet professional to look at.
On the other hand, font styles such as Bradley Hand, Comic Sans, and Chiller are not ideal choices as they are not meant to captivate your audience’s eyes. And another tip is to stick to two or three fonts only!
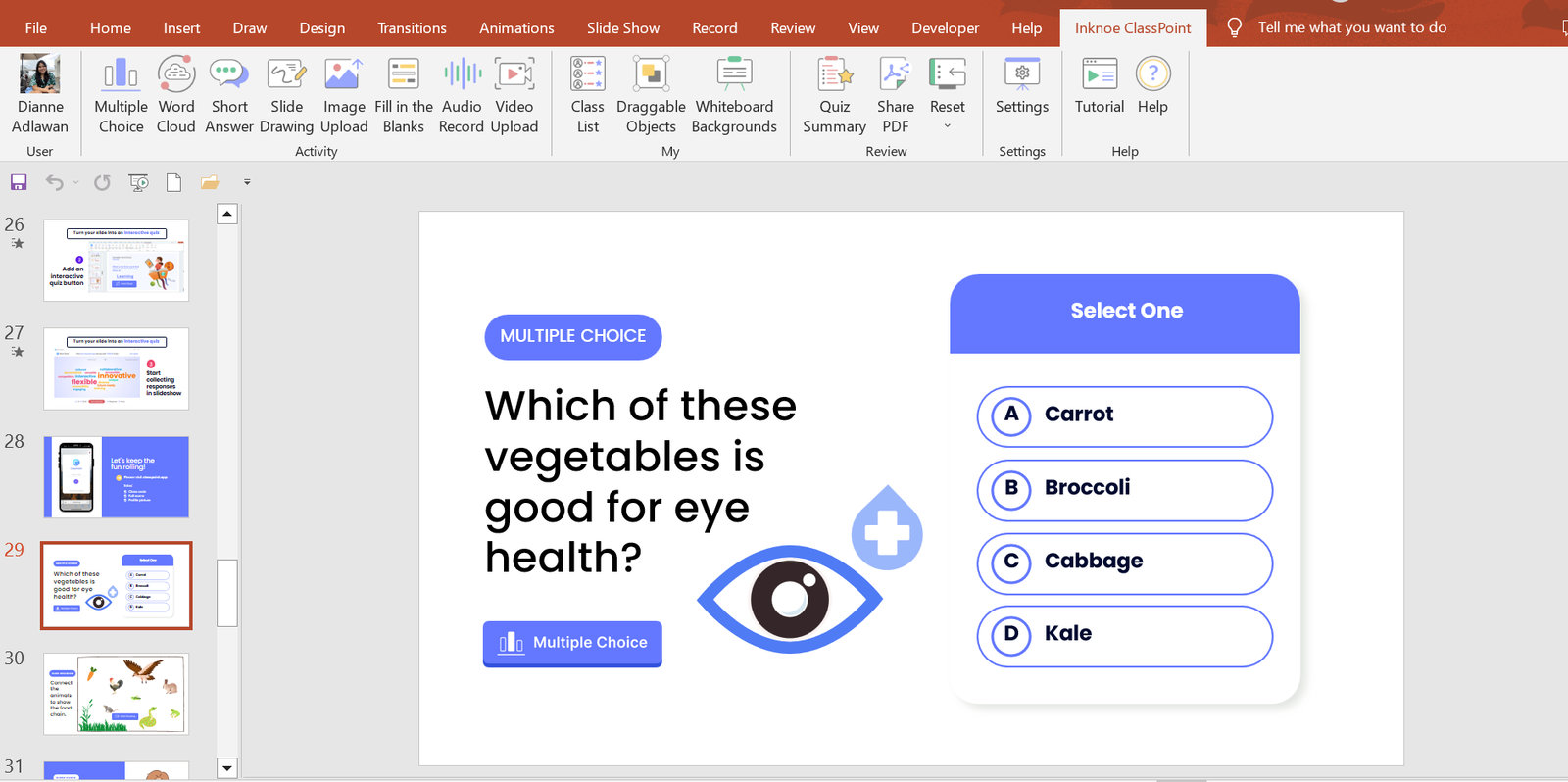
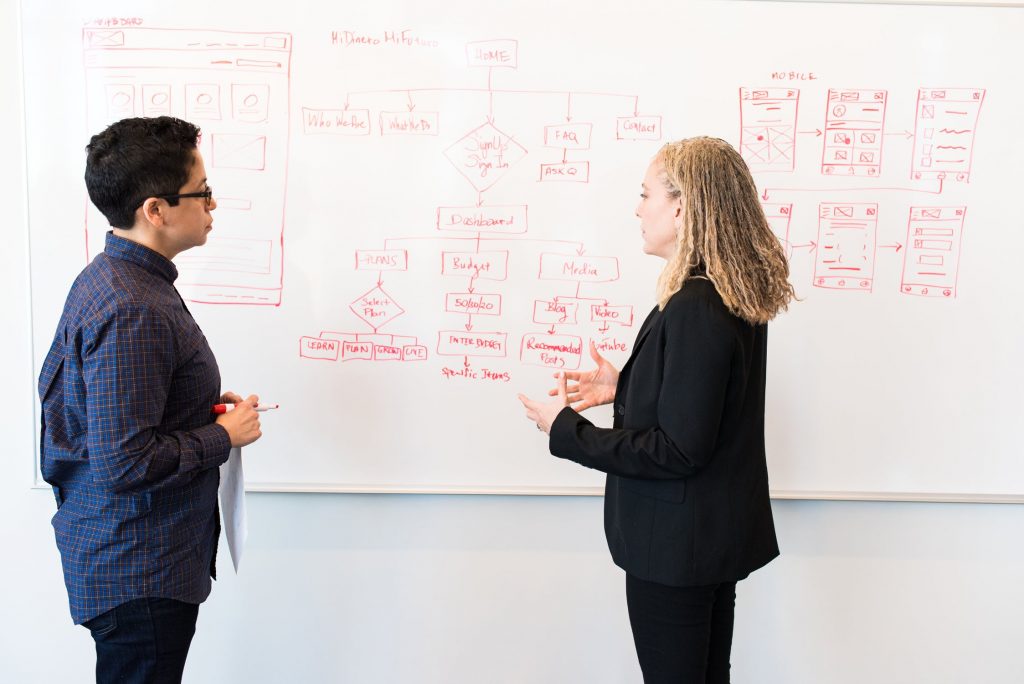
3. Use Relevant Graphics
Selecting graphics for designing your presentation depends on your audience and the goals you aim to achieve with the presentation. For example, if you are presenting in front of students and your goal is to keep them engaged, motivated, and actively participating, then you might consider incorporating charts, tables, and relevant shapes into your design.
It’s important to remember that your presentation design should align with the theme of your topic.
Free Websites to Upgrade your Presentation Graphics:
- Craiyon. com
- The Noun Project
4. Use Audience Engagement tools to Activate Learning
Want the quickest solution to an engaged audience? Well, it’s audience interactive activities! Adding interactive activities to your presentation can help keep your audience engaged and interested. One of the easiest ways to do this is to use ClassPoint, an audience engagement tool added right into PowerPoint presentations.
With ClassPoint, you no longer need to worry about strategies to keep your students engaged, as this tool transforms PowerPoint into a teacher presentation tool with a teacher toolbelt and student quizzes , polls, and games that make presentations more fun & engaging.
By combining ClassPoint with your presentation techniques, you can focus solely on setting up your lesson content in PowerPoint and allow ClassPoint to handle the rest for achieving a learning-activated presentation lesson .
🔍 Learn more about ClassPoint, the teacher add-in for better lessons & student engagement 👍
5. Use a Laser Pointer
Help focus your audience attention by using a laser pointer!
With the help of a laser pointer device, teachers are able to attract the attention of their audiences and concentrate on essential points in their presentations. Highlighting these main ideas and terms assists the speaker in organizing their speech, preventing distraction, and increasing retention of the information presented.
You can use a physical laser pointer & clicker, or with the addition of ClassPoint into PowerPoint, presenters can easily turn their cursor into a laser or a spotlight . This can make it even easier for students to follow along and is a convenient tool for creating a more captivating teacher presentation.
Secret tip: if you write on your slide with the laser, it will leave disappearing ink! 🪄
Content Tips
1. research and fact-check your presentation.
As educators, it is crucial to equip ourselves with reliable and accurate information before presenting to our students. We have a responsibility to not only educate them but to also mold them into critical thinkers who are equipped with factual knowledge. Without thorough fact-checking, we risk disseminating misinformation and hindering their intellectual growth.
To avoid such situations, we must prioritize research and fact-checking before presenting any information. Conducting research helps us not only in finding accurate information but also in ensuring that the sources we use are reliable and credible. Moreover, taking the time to fact-check demonstrates our commitment to providing students with high-quality education and the desire to create a safe and accurate learning environment.
2. Be Prepared to Anticipate Questions during the Presentation
It is important to be well-prepared for a presentation especially anticipating and addressing questions. This applies particularly to a teacher presentation, as educators face varied expectations and questions. Adequate preparation allows you to organize ideas and justifications, and it can deepen understanding, boost confidence, and improve adaptability. Addressing questions, makes your audiences feel heard and appreciated. This will result in comprehensive presentations, enhanced confidence, improved information flow, and an atmosphere of respect and understanding.
A great & visual way you can elaborate, or explain your material in new ways, is by using ClassPoint’s whiteboard tools added to PowerPoint. ClassPoint’s added toolbar presents teachers with unlimited whiteboard slides they can open whenever they need, and user-friendly yet comprehensive pen tools with available shapes, and text boxes. Plus you can also use ClassPoint’s quick poll or other question types to assess students’ understanding with hard data & insights.
Addressing questions well makes your audience or students feel heard & appreciated leading to improved learning, enhanced confidence, and a respectful, safe learning environment.
3. Provide an Outline Structure of your Content
When you are preparing your presentation, it is best to first create an effective outline structure that will guide your presentation flow and help you focus on the main learning objective. But what you may not be doing, is offering that outline structure to your students, but you should!
Providing students with a clear understanding of what this lesson is about, the structure of the lesson, and what they will be able to take away from it is important. By doing so, you can help students stay focused and follow along with the material. Additionally, you are setting expectations and ensuring that everyone is on the same page, which can help promote student autonomy. So, include an outline at the start of your presentation lesson.
Step-by-Step Strategies for a Successful Presentation
Before presentation, know your audience, your students, or observers.
Once you have completed your deck, you may want to add a guide script and any additional notes with important points you don’t want to forget or you want to highlight in your presentation to impress your students .
Practice your presentation delivery/lesson
Practice delivering your presentation give you a chance to fine-tune your content and get your facts down. This will help you become more comfortable with the material and identify areas that need improvement. You can practice in front of a mirror, record yourself and watch it back, or even rehearse with a colleague or friend. When practicing, pay attention to your posture, tone of voice, and pacing. By doing so, you’ll be able to deliver a confident and engaging presentation that will captivate your audience.
Use a friendly tone of voice and pace
Adjust your tone to match your message, and avoid speaking too quickly so that your audience will get the chance to absorb the information you’re sharing. By being mindful of these aspects, you will capture your audience’s attention and leave them feeling informed and inspired.
Use engaging body language
Body language is essential for engaging your audience during a presentation. Stand up straight, make eye contact, and use hand gestures to emphasize important points. You can also move around the classroom to keep your students’ attention. By using engaging body language, you’ll be able to convey your message more effectively and keep your students interested throughout the presentation. You’ve got this!
During Presentation
Create an icebreaker.
Having an icebreaker is a warm-up for your students’ brains, allowing you to focus and engage with the material being presented. It also helps break down any barriers or tension between the presenter and the audience, making for a more relaxed and welcoming atmosphere. Additionally, an icebreaker provides an opportunity for the presenter to showcase their creativity and personality, adding an extra level of excitement and engagement to the presentation.
Good thing that ClassPoint has numerous features to help you perform an entertaining and unforgettable icebreaker. Here are some examples that you can use during an icebreaker.
- Quick Poll : Quick Poll allows you to create interactive polls right inside your presentation. When used as an icebreaker, it can engage the audience, initiate discussions, and provide valuable insights that help tailor the content to participants’ preferences.
- Word Cloud: Presenters can ask thought-provoking questions related to the topic or general interest. Using Word Cloud, the audiences can answer through their mobile which can be instantly seen as collective responses, with the most frequently mentioned words appearing larger.
- Short Answer : In short answer, you can challenge your audiences’ thought process in a short-form writing activity with no options to get from to test their ability to understand.
- Image Upload : Using single image, audiences can interpret what they feel like, or their mood using only the photos in their gallery or surroundings. A creative yet fun way for an icebreaker!
Speak clearly
Effective communication is crucial when presenting important information to students. Speaking clearly helps ensure that students understand the concepts being taught and follow instructions effectively. As a teacher, it’s important to focus on clear speech to promote effective communication and help your students comprehend the material being presented.
Pay attention to your audience’s attention
Since distractions are aplenty, attention spans are dwindling, it’s important for presenters to captivate their audience’s attention right from the beginning. For teachers, when speaking in front of your class, you should not only focus on the content of your presentation but also on your students’ attention.
To ensure that your students won’t start drifting away or zoning out, start with a compelling opening that immediately grabs their attention. Use vivid storytelling, examples, or demonstrations to engage your students and drive home your message. Don’t forget the power of humor, and never be afraid to be yourself – authentic, passionate, and confident.
Add Personality: share short relatable stories
“A great personality makes everyone feel energized; just like a flower’s fragrance that freshens ups the complete surrounding.” 29 Personality Quotes to Achieve Greatness
As to what is stated in the quote, having a positive and vibrant personality affects the overall mood of your surrounding, it can capture the audience’s attention and maintain their interest throughout the presentation. While the ultimate goal is to deliver a presentation rich with new learnings and knowledge, adding humor can do no harm to lift up the mood in the room. You might want to start by segueing a short story that your students can relate to and make interactions by encouraging them to share a story too or ask questions.
Post-Presentation Reflection
Take the comments by heart.
Receiving feedback from your students is a great way for evaluating the efficacy of a teacher presentation. This can help you identify areas where you can improve and tailor your teaching tactics to better suit the needs of your students. Listening to your students’ feedback can also promote a feeling of cooperation and enable them to become more actively involved in the learning experience. So, don’t be afraid to ask for feedback and take it to heart in order to continually improve your presentations.
Experienced educators understand that they are perpetually crafting their skills, and feedback from their audience brings an opportunity for professional advancement. In addition, accepting audience feedback illustrates esteem and worth for the students’ views. It promotes a feeling of cooperation and enables students to become more actively involved in the learning experience.
Preparing for a presentation is essential for teachers to deliver engaging and impactful content to their students. By structuring thoughts, anticipating questions, and preparing ahead, teachers can achieve a well-organized presentation that will enhance the students’ understanding and leave them feeling confident.
By following our strategies and tips teachers can achieve successful lessons using PowerPoint presentations. And, with the help of an advanced educational technology tool like ClassPoint, teachers can create dynamic and memorable presentations that their students will enjoy and actively participate in.
Try out ClassPoint today and experience a whole teacher presentation in PowerPoint! ✨
About Dianne Adlawan
Try classpoint for free.
All-in-one teaching and student engagement in PowerPoint.
Supercharge your PowerPoint. Start today.
800,000+ people like you use ClassPoint to boost student engagement in PowerPoint presentations.
- College Prep
- Study Skills
- Career & Continuing Ed
- Online Learning
- Student Life
- Study Abroad
- Sponsorships
- Scholarships
- Student Group Shoutout
- Latest in Learning
- Success This Semester
- Educators Making an Impact
- Education News
8 Ways to Teach Your Students Presentation Skills
We are a reader-supported education publication. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission to help us keep providing content.
As an educator, it’s important to teach your students not just the subject immediately at hand, but also to build the skills and understanding that your students can carry forward into other learning environments in their future. From test taking skills and study habits to more general life skills like public speaking and self motivation, teaching is about guiding the next generation of students into their lives as functional members of society, and one of the skills you can help instill in your students is the ability to present and speak in public.
Public speaking and presentation skills can sometimes be difficult to teach on a wider scale, especially when you have a class with varying levels of comfort with presentation. Some people may be introverts, or even have anxiety around public speaking. However, managing those restless feelings is a part of learning presentation. While some teachers would rather throw their students right into things, it is completely possible to guide your students in the realm of presentation so they can broaden their skills and become truly comfortable. Here are eight ways you can teach your students about presentation and public speaking.
1. Show Examples
One of the best ways to ease your students into the world of presentation is to inspire them! There are so many great examples of public speaking, from the vast library of TED talks to guest speakers you can invite into your classroom. Show examples of public speaking and discuss them. See what your students have to say and how they react.
2. Use Small Groups
Practice often makes perfect, and sometimes that practice is best done when your students don’t even realize they’re practicing yet. Sure, presenting for a whole class can feel overwhelming, but breaking off into small groups can be a great stepping stone to practice the skills needed to present, but in a lower-stakes environment.

3. Reinforce Positive Feedback
The power of positive reinforcement can really do wonders for a student, both in terms of self esteem, and actual academic success. While some teachers evaluate based on areas in need of improvement, focusing first on what your students are doing right can give them something to focus on so they can keep up the good work and grow their confidence. This can especially help students who are nervous or struggling with self esteem.
4. Revisit Previous Projects
Sometimes, the best way to learn is by retracing your steps. And this can be true in the classroom as well as in the real world. Revisiting old projects can not only help students realize how far they have come, but also in understanding themselves a bit better overall throughout the process.
5. Encourage Questions
Teaching students is all about helping them learn what they’re missing, no matter what the subject at hand is. Even if students don’t have a lot of questions at first, encouraging them to think of ideas to ask questions and spark discussions can help engage them and guide them towards a better understanding, both of what they’re presenting about and the idea of presenting itself.
6. Run a Discussion-Based Classroom
Presenting is often all about learning to vocalize and express yourself in front of a classroom, and this can feel especially stark for students when the format is so drastically different in your traditional classroom. If your students are used to lectures all day long, finally getting the chance to speak can feel foreign. However, in a discussion-based classroom, your students can express themselves freely and practice their speaking skills regularly, so it won’t feel so odd when the time comes to do it more formally.
7. Practice One-On-One
Some students can be especially nervous and really do need that personalized instruction. When you encounter students like this, working with them individually can often help them get over the hurdles they need to overcome. Sometimes, speaking in front of just you can feel like a lot, but accomplishing that can give them a boost of confidence they need to catch up with their peers.

8. Use Self Evaluation
Just like looking back on past projects, self evaluation can not only help students recognize their own progress and strengths, but also guide them in the ways they need to grow in the future. Public speaking is a skill that’s ever-evolving, and building a self awareness and confidence in that skill can be useful in future projects, even if they don’t realize it yet.
Teaching Presentation Skills
Presentation skills are about so much more than just one project or assignment. They’re skills that will serve your students throughout life, so it’s especially important to think critically about how to best teach and assess them. When you engage with your students and push them to be better, they might just surprise you with how far they come.
Welcome to Classrooms! Whether you're a student, graduate, teacher, or professor, our team aims to educate, equip, and inspire you to keep learning.
Search Classrooms.com
Browse by category.
- Educating 98
- Experience 106
- Higher Learning Highlights 11
- Learning 238
- Student Funding 32
Latest News

Automating Administrative Tasks in Education Institutions

How to Apply for Grants for College

How to Get Local Business Sponsorship for School Events

5 Major Issues in Education Today

Does Withdrawing From a Class Look Bad?

What Companies Do Sponsorships for Student Groups?
Keep up with the latest in learning, more to learn.

What Is the Future of IoT in Education?

What Does Advocating for Students Mean as an Educator?

The Role of Big Data in Education

What You Need to Know About STEM MBA Programs

Effective Communication in the Classroom

Why is It Important?
In a student-centered classroom, the instructor should not be speaking all of the time. However, when you are speaking, students count on you to: provide clarity by highlighting key ideas; elaborate on difficult concepts; and provide clear instructions for in-class activities. These messages should be backed up by appropriate visual aids that reinforce what you are talking about: board work, slides, and/or handouts.
In-class communication can be thought of as consisting of verbal, vocal, and visual channels.
Verbal channel
The verbal channel relates to word choice: the same content or point can be delivered in different ways using different words. Those differences in delivery affect how students comprehend and engage with the material.
The verbal channel can clarify and reinforce course content by:
- Defining and using discipline-specific vocabulary.
- Verbally outlining your presentation. Verbal indicators can signal transitions between ideas, helping students make connections to their prior knowledge and experiences, follow along, and organize their notes.
The verbal channel can also be used to send growth messages and create an inclusive classroom. For example, the way you respond to students’ questions and incorrect answers can be an opportunity to create a warm classroom climate but are often not something we consider rehearsing.
When a student asks a question:
- Try to call on them by name. This will help to create a sense of belonging.
- Thank them for their question to motivate them to ask questions again in the future.
- If a question is common, say so. This will help the student see that others’ have needed clarification on this point as well.
If you pose a question and a student responds with an incorrect answer:
- Thank the student for responding.
- If the student’s response is in line with a common error, say so, so they do not feel alone in their misunderstanding.
- Ask the student about the process that they used to come up with the answer to better understand where they made a misstep. This emphasizes process over product and also teaches good troubleshooting strategies.
- If a student’s answer is partially correct, ask another student to add on or clarify the response.
Certain verbal phrases can detract from a presentation by being distracting, signaling a lack of instructor preparation, or by making students feel insecure in their ability to succeed in the course.
| Filler Phrase to Avoid | Potential Student Interpretation | Potential Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| “Um”, “you know”, “uh”, “like” | When overused, can be distracting or signal a lack of preparation. | Silence. Take time to think about what comes next. Your students can also use that silence to reflect on what they’re learning. |
| “I’ll tell you quickly…” “Details are not important, but…” | Improper planning “This isn’t important. The instructor is wasting my time.” | Consider removing this content, sharing it as an optional reading outside of class, or preparing and delivering it at an appropriate level of detail with sufficient time. |
| “This is easy.” “You should already know this.” | Students could be embarrassed or insecure if they don’t know something or think it’s easy. | Learning takes time and practice, so it’s best to avoid judgments of difficulty. When building on prior knowledge is necessary, suggest resources students can use for additional practice. |
We all use some filler phrases habitually, and we should strive to minimize them. However, over-focusing on avoiding filler phrases can distract from a clear presentation. The best strategy is to practice avoiding filler phrases when rehearsing a lecture, but when actually teaching to focus on communicating with the students.
Vocal channel
The vocal channel includes aspects of speech such as volume, pacing, and tone. The vocal channel can be used to draw students attention and convey enthusiasm.
| Effective Use | Things to Avoid | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Speak loudly enough that students throughout the room can hear you. | Sound is directional, so when turned towards a projector screen or writing on the board, speak louder or wait to speak until done gesturing or writing. Sometimes our volume decreases as we near the end of a sentence. Be mindful of this. | If you have trouble speaking loud enough to reach the back of your classroom, consider asking your students on the first day to sit near the front, or see if a microphone is available for your classroom. |
| Speak at a speed which allows students to hear and process what you’re saying. You adjust your rate and use pauses to emphasize key points or when transitioning between ideas. | Speaking too fast is overwhelming and makes it hard for students to process information. “Too fast” refers to both quantity of words and quantity of ideas. Constant speech, without pausing between ideas, doesn’t give students time to think about what they’re hearing. If you are using slides in your teaching, be particularly mindful about pacing. | It can be hard to judge appropriate pacing by yourself. Have a friend or colleague give you feedback and help you identify an appropriate speaking rate. If no one else is available, you can record yourself speaking and listen to it later to try to self-evaluate whether or not your speaking rate is appropriate. |
| Emphasize nouns and verbs, which contain the meaning in a sentence. | Not varying your tone can cause students to tune out. |
Visual channel
The visual channel includes all visual aids that support your message, including you (!), anything that you write on the board, project on the projector, or distribute as a handout.
Your physical appearance—posture, attire, expressions—are all part of your presentation and affect how students listen to you and receive your message. Here are some ways your appearance affects your presentation:
- Presence/Position/Posture : standing up straight conveys confidence and authority.
- Eye contact : helps you connect with your audience and keep your students engaged. You may tend to focus your gaze on a particular side of the classroom. Consciously make eye contact in a “W” pattern across the room.
- Movement : too much movement can be distracting, but well-timed movements emphasize key points or physically signal a transition between points – reinforce the information you’re presenting.
Plan what you will actually write on the board so you can make sure it’s organized, large, and legible. If you have limited experience writing on the board, try to practice in the room in which you will be teaching. You may be surprised at how large you have to write so that it is legible from the back of the room.
At MIT, most classrooms are outfitted with multiple, movable boards. Visit your classroom in advance to know the layout of the boards and use this information in your planning. For example, with movable boards, consider the order in which you will fill them to maximize the amount of information students can see at any given point. Students will want to write down everything that you write on the board.
Practice drawing important schematics. If a schematic is necessary but challenging to draw, consider supplementing your board work with a slide, which can also be distributed to students as a handout. Consider using color to highlight ideas, group items, or add clarity to diagrams.
Slide design
The digital nature of slides makes it easy to include more information than students can process on them. In general, try to keep the mantra of “less is more” in mind to reduce the likelihood of cognitive overload and including extraneous information.
When creating slides, words and images are better than words alone. Relevant images can help to support and clarify your message. That said, there are times when images may not be appropriate and you just need to use text. In these cases, summarize the ideas using phrases and avoid full sentences on your slide.
Simple animations of having bullets appear in a synchronized manner with your oration will help to reduce cognitive overload and help students stay focused on what you are saying. Key ideas can also be highlighted by using bolding and color.
Managing Nerves
Stage fright is natural. Almost everyone gets some degree of stage fright. Below are some things you can do at different stages of your preparation to minimize the effects of stage fright.
While preparing for class
- Acknowledge your fears by writing them down or sharing them with a friend or a trusted colleague. This will help you identify specific things you can practice to reduce your nerves.
- Practice your presentation. Try to make your practice as realistic as possible: practice in your assigned classroom with an audience of friends, colleagues, or a video camera.
Shortly before class
- Warm up your body by stretching, walking around, and standing up straight.
- Do breathing exercises to warm up your vocal cords and to regulate your breathing.
- Drink water to stay hydrated.
- Use relaxation or meditation resources to reduce nerves, like the MIT Community Wellness Relaxation Line, 617-253-2256 (CALM)
During class
- Use pauses to give yourself a chance to breathe and think. You can use longer pauses between major ideas or during active learning exercises to get a drink of water from your water bottle.
- If you find your speech rushing, try taking a longer pause after your next point. Take a couple of deep breaths and get comfortable with silence to reset your rate of speech.
- If you find yourself pacing or moving a lot, try planting your feet or putting your hands on a table or podium (if it doesn’t ruin your posture) to ground yourself. Once you’ve reset, give yourself more freedom to move around the room and interact with your students.
Additional resources
Mit school of engineering communication lab.
The Communication Lab is a discipline-specific peer-coaching program for MIT’s School of Engineering that helps graduate students with their scientific writing, speaking, and visual design.
MIT Writing and Communication Center
MIT Comparative Media Studies/Writing offers innovative programs that apply critical analysis, collaborative research, and design across a variety of media arts, forms, and practices.
- Our Mission
How a Simple Presentation Framework Helps Students Learn
Explaining concepts to their peers helps students shore up their content knowledge and improve their communication skills.

A few years ago, my colleague and I were awarded a Hawai‘i Innovation Fund Grant. The joy of being awarded the grant was met with dread and despair when we were informed that we would have to deliver a 15-minute presentation on our grant write-up to a room full of educational leaders. If that wasn’t intimidating enough, my colleague informed me that he was not going to be in Hawai‘i at the time of the presentation. I had “one shot,” just a 15-minute presentation to encapsulate all of the 17 pages of the grant I had cowritten, but how?
I worked hard to construct and deliver a presentation that was concise yet explicit. I was clear on the big picture of what the grant was composed of and provided a visual of it in practice. I made sure the audience understood the “why” behind the grant. I showed how it worked, the concrete elements of it, and how they made it successful. I finished with a scaffold that would help others know how to initiate it within their context, giving them the freedom to make it authentically their own.
I received good feedback from the presentation, and more important, what was shared positively impacted student learning in other classrooms across the state.
A Simple Framework for Presentations
That first presentation took me over a month to prepare, but afterward I noticed that my prep time for presentations shrank exponentially from a few months to a few (uninterrupted) days. Interestingly enough, as a by-product of creating the original presentation, I created an abstract framework that I have used for every professional learning presentation I have delivered since then. The “What, Why, How, and How-To” framework goes as follows:
- What? What can the audience easily connect to and know as a bridge to the unknown for the rest of the experience?
- Why? Why should they care to listen to (and learn from) the rest of the presentation? What’s in it for them to shift from passive listeners to actively engaged? The audience needs to know why you believe in this so much that you are compelled to share it.
- How? What are the key elements that make it unique? How is it effective in doing what it does? What are the intricacies of how it works?
- How-to? How could they start doing this on their own? How could this knowledge serve as a foundational springboard? Connect it to “why.”
Benefits for Students
One of the best parts of presentations is that they help the presenter to improve their communication skills. The presenter is learning how to give a presentation by doing it. To prepare a presentation, the presenter must know the intricate elements of what they are presenting and the rationale for their importance. In the presentation delivery, the presenter must be articulate and meticulous to ensure that everyone in the audience is able (and willing) to process the information provided.
It didn’t take long for me to realize that preparing and delivering presentations could provide a valuable learning opportunity for my students.
I recall teaching mathematical concepts whereby students would immediately apply knowledge learned to accomplish the task in silence and without any deeper questioning. Only after I asked them to provide presentations on these concepts did they regularly ask me, “Why is this important, again?” or “What makes this so special?” My students’ mathematical literacy grew through preparing presentations with the “What, Why, How, and How-To” framework, which supported them in their ability to demonstrate content knowledge through mathematical rigor (balancing conceptual understanding, skills and procedural fluency, and real-world application).
- The “what” served as the mathematical concept.
- The “why” demonstrated the real-world application of the concept.
- “The “how” demonstrated conceptual understanding of the concept.
- The “how-to” demonstrated skills and procedures of the concept.
In addition to content knowledge, the sequential competencies of clarity, cohesiveness, and captivation ensured that the presenter could successfully share the information with their audience. When combined, these framed a rubric that supported students in optimizing their presentation deliveries. The competencies are as follows:
1. Content knowledge. The presenter must display a deep understanding of what they are delivering in order to share the “what, why, how, and how-to” of the topic.
2. Clarity. The presenter must be clear with precise, academic language. As the content they deliver may be new to the audience, any lack of clarity will alienate the audience. Providing multiple modes of representation greatly addresses a variety of processing needs of a diverse audience.
3. Cohesiveness. When making clear connections, the presenter bridges gaps between each discrete component in how they all work together as integral elements of the topic. Any gaps too large may make the elements look disjointed or, worse, the audience feel lost.
4. Captivation. The presenter must captivate the audience through any combination of audience engagement or storytelling . They make the presentation flow with the energy of a song , and in the end, they leave the audience with a delicate balance of feeling fulfilled and inspired to learn more.
Anyone can build an effective presentation with the “What, Why, How, and How-To” framework, along with competencies of content knowledge, clarity, cohesiveness, and captivation. The better we teach and coach others on how to create and deliver presentations, the more we learn from these individuals through their work.
In my class, one multilingual learner responded to the prompt “What are the non-math (life lessons) you have found valuable from this class?” with “I learn what is learning and teaching... I truly understood how teaching is actually learning when I had presentation. I found a bit of desire to being a teacher. I hope you also learned something from this class.” I always learn from my students when they present.

5 Teacher Tips For Better Presentations In The Classroom
With slides, less is more. Here are some tips for teachers to make better presentations for engaging learning in the classroom.

What Are The Best Tips For Giving Great Presentations In The Classroom?
contributed by Catherine Willson
When you need to put together information for a presentation for students or other teachers, you can be surprisingly effective without having to do too much at all. Here are some tips for teachers making presentations for in the classroom.
See also 15 Presentation Tools for Teachers
1. Establish one clear idea.
Conventional wisdom of the past used to be about putting as much information and content into a presentation as possible. It was all about trying as hard as you could to come across as an authoritative figure who truly was a master of the subject. That barely works in higher ed, and certainly is pliable in K-12. Consider that you aren’t trying to teach someone everything you know in a short window, but rather making an impression for long-term retention. Focus on one idea with supporting information in a quick period of time.
2. Start with a compelling hook.
When you consider the average suggested presentation length is only around ten minutes, you don’t have any time to waste. Obviously the specifics of the presentation will vary depending upon the grade level, time of day, content being presented and so on. One thing that won’t vary is the need to grab students right off of the bat and have them paying attention from the first few seconds.
As Cision recommends , when the average attention spans have shrunk down to around eight seconds, you know that you need to jump right in with something captivating. Obviously your presentation needs to have a point and needs to be worthwhile as well, but if you can simply give them something that they actually want to see in the first place, you stand a much better shot of being successful in your presentation. It might not seem like a powerful point but it is true in any context.
You might even do it without noticing, but you still do it constantly. Do your ears ever perk up when someone talks about a certain subject? Or, do you hear someone start a conversation with words that bore you and immediately look for a way out? It’s the same thing when it comes to presenting. You only have a few seconds to get it right and hook your class.
3. Prioritize–only put in what’s important.
Another major item to remember is what you are putting into your presentation as far as content is concerned. If you already understand how important it is to captivate your classroom and capitalize on the short attention spans, it’s not a wise strategy to grind the presentation to a screeching halt just so that you can read boring statistics and bland figures. There does need to be some information, but you could read and reference figures without using presentation software in the first place.
By having presentation slides with tons of words, you are just wasting time and filling space that will turn off your viewers. As Mr. Media Training suggests , if you have too many words then you either don’t know your presentation well enough, or your presentation isn’t supported by any additional evidence. The good news is that the technology of companies such as LiveSlides allows you to insert video into PowerPoint so that you can truly bring any sort of evidence you want. Those sorts of slides make perfect sense because you can’t put video on a notecard. Plus, by stimulating your classr with an additional surprise and viewpoint, you aren’t risking students falling asleep because of a long, monotonous message.
4. Consider schema and background knowledge.
Familiar images, references, sounds, music, and other bits of information can act as anchors to ground student understanding, as well as disarming some of the intimidation or anxiety new content can represent for some students. Along with focusing on a single idea per presentation, this can go a long way towards making better presentations for students.
5. With slides, less is more.
Believe it or not, the most acceptable answer from professionals is that you don’t need a lot of slides in a presentation. As Six Minutes Speaking and Presentation Skills suggests , sometimes you don’t need any slides. However, if you are going to give a presentation to your class and you need to have supporting information then you can easily do that with a few slides. The short answer is you probably need fewer slides than you think.
If there’s too much information, students are instantly going to go from trying to listen to you into a mode where they simply skim the PowerPoint slide. Once they realize it is the same message, the PowerPoint slide is basically worthless. You obviously can put summarizing points, facts, and figures into your presentation. But with that being said, PowerPoint was created as a tool and you need to be comfortable with using it. By having the right type of information in it you can actually enhance the presentation and student retention.
A presentation itself isn’t that difficult of a thing to master. So many people are caught up with using PowerPoint that they forget what it is actually for. When you are going to give your next presentation to your class, you need to know your subject matter first and the essentials of PowerPoint and presentation design second. Once you’ve narrowed your content and honed your message, you can capitalize on it by adding in all of the bells, whistles, and other enhancements that will help students retain what they’ve learned.
TeachThought is an organization dedicated to innovation in education through the growth of outstanding teachers.
- Request a Consultation
- Workshops and Virtual Conversations
- Technical Support
- Course Design and Preparation
- Observation & Feedback
Teaching Resources
Improving Presentation Style
Resource overview.
Strategies for making your presentation style more effective in the classroom
Effective lecturers combine the talents of scholar, writer, producer, comedian, showman, and teacher in ways that contribute to student learning.”
Wilbert J. McKeachie, Teaching Tips
An effective teacher is an excellent communicator and therefore thinks about improving his or her presentation skills. One of the most important aspects of communicating is shaping both content and style to fit your audience. In the classroom, if you cannot communicate in a way that is both comprehensible and interesting to your students, their learning will be greatly reduced.
To strengthen your presentation skills, focus on improving your skills in these three areas:
Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication
- Find out all you can about the room in which you will be presenting. Visit the room ahead of time to familiarize yourself with its size and layout, as well as the type of chalkboards, chalk, erasers, and multimedia available. In addition, obtain any necessary training on the multimedia.
- Use the classroom as a stage. Move around to engage and interact with your audience. Do not stand in one spot the entire time. Move with purpose; do not walk aimlessly.
- Prepare. Preparation is essential. All excellent teachers are well prepared for each class. Practice in the room if you can, especially if you are new to teaching. In addition, prepare yourself emotionally and psychologically by taking the time to organize your thoughts and to look forward to teaching before every class.
- Speak loudly and clearly. Project your voice and face your audience when you are speaking. Speak slightly louder than you do in a normal conversation. Use a microphone in a medium to large classroom. The class may include students with hearing problems. Moreover, a microphone will help ensure that students can hear you even when you turn to the chalkboard momentarily.
- Modulate the tone, pitch, and speed of your speech. Do not speak in a monotone. Vary the pitch and speed of your voice for emphasis and effect. Use appropriate pauses. Rather than using filler words such as “uh,” for example, simply pause before moving on to the next idea or point.
- Use gestures and facial expressions to help you explain, emphasize, and communicate the material. However, be careful not to develop distracting habits such as pacing or repeatedly adjusting your glasses or hair. To find out if you are unconsciously doing anything that may be distracting to your audience, have a colleague observe one of your classes or have your class videotaped. To schedule a videotaping and teaching consultation, call The Teaching Center at 935-6810.
- Develop a teaching persona. Decide how you want to be perceived and what mannerisms you want to have. For example, do you want to be quiet, humorous, formal, or informal? Whatever persona is right for you, aim to convey confidence and ease. Move with certainty and assuredness, and be careful not to seem pompous or intimidating.
- Show passion and enthusiasm for the topic. If you are not interested in the subject, you cannot expect your students to be interested, either. Point out the fascinating aspects of what they are learning.
- Do not read your notes or slides. Doing so will lower your energy level and lead your audience to feel less engaged.
- Interact with and pay attention to your audience. Make eye contact with the students, not with the wall or chalkboard. Build a rapport with the class. Make sure the class is with you (following and understanding what you are discussing). If they appear to be lost, take additional time to explain points and to ask and answer questions.
- Do not take yourself too seriously. Be able to laugh at yourself and your mistakes. Feel free to bring humor into the classroom, but direct it at yourself, rather than at your students’ questions and ideas.
- Keep track of the time. Do not start early or end late. The students often do not recall or listen to information presented after the class period is technically finished.
Effective Use of the Chalkboard and Visual-Aids
Using the Chalkboard
- Write legibly and big enough that your writing can seen in the back of the room.
- Think about the organization of the material on the board.
- Fill one board at a time, starting at the top of each board and writing down.
- Do not scrunch in words at the very bottom of the board or in the margins. The students in the back will not see the words at the bottom, and no one will see the words in the margins.
- Underline or mark major assumptions, conclusions, etc.
- Use color to emphasize points.Before the course starts, determine which colors are most visible in the back of the room.
- Erase a board only when you have run out of room.
- If you find a mistake on a previous board, do not erase it. Cross it out, then write the correction in, which is what the students must do.
Using Visual Aids, such as PowerPoint Slides
- Do not use visual aids unless they serve a clear and important purpose. Visuals should aid quick comprehension and support the main points.
- Book and check out the presentation equipment in advance.
- Talk to your audience and not to the screen.
- Use the visuals to enhance your presentation, not as a substitute for a verbal presentation.
- Use a pointer, if necessary.
- Coordinate the audio and the visual.
- Design your visuals with clarity and simplicity in mind.
Effective Design and Meaningful Organization of Content
Visual Design Suggestions
- Use single words or phrases.
- Organize the content visually.
- Choose a font that is easy to see. Choose a font that is simple, plain, and easy to read such as Times New Roman, Ariel, or Helvetica. Select a font size that is large enough to be seen at the back of the room. The minimal acceptable size is typically 24-point. Use both upper- and lower-case letters; all upper-case letters are difficult to read.
- Keep the design simple. Too many words, graphics, or different colors are distracting and cause students to miss the important points.
- Use short quotes, not long extracts, from documents.
- Assign a title for each visual. Doing so will help your audience organize and retain the information on each visual.
- Use summary lists.
- Limit the number of ideas on each visual. For example, limit the number of bullets on a page to approximately 4 to 6. Each bullet should be short, approximately one line. Do not crowd the visual with text; it will be too difficult to read.
- Use color for emphasis and organization. Color is useful, but needs to be used judiciously. The color should be used for emphasis or for distinguishing among data. Think about the color wheel: adjacent colors blend together and colors directly opposite each other are contrasting and provide better readability. Reds and oranges stand out, but are hard to continually focus on; therefore, use these colors only for emphasis. Greens, blues, and browns are easier to continually focus on, but do not grab a person’s attention.
- Design diagrams and tables that are simple and clear, with readily recognized symbols. Your audience must be able to read all data in your diagrams and tables. Often, this means that you will have to simplify a more complex or detailed table or diagram that has been prepared for a printed format.
- Use horizontal (landscape) layout, not vertical (portrait). Screens, video monitors, and computer monitors are shaped for a horizontal, not a vertical, format. In addition, a horizontal format is easier to project in rooms with low ceilings.
Content Organization Suggestions
- Plan the content. Think about the type of students in the class, the goals for the course and the current session, the type of material to be presented in the current session, and the type of media, if any, that you are going to use.
- Provide a structure. Each class session or presentation should have a beginning, a middle, and an end.
- List objectives or provide an outline at the beginning of each class session. Providing an outline helps students identify the most important points and follow the lecture or discussion more effectively.
- Organize course content with a theme or storyline. How do you want to arrange the material? How does each part of the material relate to what comes next.
- Remember that a typical student’s attention span is 15-20 minutes. Every 15-20 minutes, either change your teaching method or change activities. Use different teaching methods in one session to keep the students’ attention and to reach students who have different learning preferences. (See Teaching with Lectures .)
- Allow for pauses and “wait-time.” Wait-time is the pause after the instructor either asks a question or asks for questions. Students need time to think of a response to a question, or to think of a question to ask. Do not be afraid of silence. Most instructors wait 1-3 seconds for a response. However, increasing the wait-time to 5-10 seconds dramatically increases the number and quality of responses. (See Asking Questions to Improve Learning .)

Clark, Donald. “Making Presentations that Audiences Will Love.” PowerPoint Presentation. http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/templates/presentations.ppt .
—.“Monthly Speaking Tips.” LJL Seminars. http://www.ljlseminars.com/monthtip.htm .
“Common Visual Aids.” Faculty Development Committee. Honolulu Community College. http://letsgetengaged.wikispaces.com/file/view/using_visual_aids.pdf
“Creating Visual Aids That Really Work: Designing Effective Slides Using PowerPoint.” Effective Communications Group (ECG), Inc. http://ecgcoaching.com/library/ps/powerpoint.php
Davis, Barbara Gross. “Delivering a Lecture.” Tools for Teaching. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers. 1993.
Edwards, Paul N. “How to Give an Academic Talk.” School of Information. University of Michigan. http://pne.people.si.umich.edu/PDF/howtotalk.pdf .
McKeachie, Wilbert, et al. McKeachie’s Teaching Tips: Strategies, Research, and Theory for College and University Teachers. 12th ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2005.
“Presentations.” Teaching and Learning Center. Eastern Kentucky University.
Sammons, Martha. “Students Assess Computer-Aided Classroom Presentations.” The Journal Online, May 1995. http://thejournal.com/articles/1995/05/01/students-assess-computeraided-classroom-presentations.aspx?sc_lang=en
The Center for Educational Resources (CER) is now known as the Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation (CTEI). Same great staff, same great service.
Presentation Strategies
Effective communication is essential in the classroom and in the real world. Good presentation skills, including public speaking and the design of visual materials, can be learned. Following the best practices outlined in the videos and resources below will help you become more effective at communicating your ideas in a professional way, while developing your own personal style.
Quick links:
Videos on Presenting
Videos on design principles, narrated presentations in powerpoint, best practices for effective presentations - video.
This video provides strategies for planning and delivering an oral presentation.
Creating and Presenting Your Poster - Video
This video gives tips on what to consider when planning the content, structure, and presentation of a poster.
PowerPoint Design Concept - White Space
White space is a basic design concept that will help clarify information in your PowerPoint presentations and other forms of visual content.
PowerPoint Design Concept - Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy is an important design concept that will help you communicate your main message more effectively.
Designing Effective Presentations - Fonts
Fonts can set the tone for your presentation but it is also important to understand how to make them as legible as possible while communicating your main message.
Designing Effective Presentations - Color
Making thoughtful color choices in your presentation not only helps to set the appropriate feel or style for your presentation but can also help to improve the clarity of your message.
After reviewing the materials above about presentation strategies and design principles, practice those ideas by creating a narrated presentation in PowerPoint. The newer versions of PowerPoint allow you to record yourself giving the presentation (just your voice). The result adds audio objects for each slide, which makes it possible to redo a slide or two if you make mistakes. The PowerPoint file can then be exported to a movie file, complete with slide transistions and animations, to be easily reviewed or shared. This can serve as great practice for your presentation before showtime.
Create a Narrated Presentation
The following link provides a helpful tutorial for both PC and Mac versions of PowerPoint: Recording a slide show with narrations and slide timings
Export a Video File
To export your slideshow as a MP4 file (or other video file) with your audio narrations, please review the following help page, which describes both the PC and Mac versions method: Save a presentation as a Movie file or MP4
NOTE : Not all versions of PowerPoint have the features mentioned above. Hopkins Affiliates have access to a Microsoft Office 365 license which will allow you to download the newest version of Office including PowerPoint. Please visit the following page for how to download Microsoft Office 365: Office 365 Communication Hub, Microsoft Office
- Effective Poster Presentation - Handout
- This PDF presents strategies to consider in determing poster content, structure, and graphic design. It includes tips on presentation logisitics
12 Reasons Why Presentation Skills Are Important for Students
Hrideep barot.
- Education , Presentation

Learning presentation skills as a student is like striking gold in the treasure hunt of life! It’s like having a superpower at your fingertips because, let’s be honest, your learning capacity right now is off the charts! But wait, there’s more! Presentation skills aren’t just about talking in front of the class (although that’s super cool too). They’re like the secret ingredient that helps you master the art of communication.
Think about it – you’re not just learning how to present your science project; you’re learning how to navigate the whole wide world.
So, why’s this the primo time to become a presentation ninja?
- Super Learning Mode: Your brain is in turbo mode right now, absorbing info like a champ. What you learn about presentations during this time becomes your lifelong sidekick.
- Ace Communicator: Being a student means you’re in a constant chat with teachers, friends, and books. Presentation skills give you the superpower to communicate like a pro.
- World Domination: Okay, maybe not the world, but you’re certainly setting yourself up to shine in any situation life throws at you.
Remember, these skills aren’t just for school. They’re for life! So, grab that mic (or marker or mouse) and get ready to rock those presentations. You’re gearing up to be the superhero of communication! 🎤
WHAT ARE PRESENTATION SKILLS:
Have you ever thought about what makes some presentations stick in your memory while others vanish into oblivion? Well, here’s the scoop: presentation skills are the secret sauce, and they’re not just a bag of clever tricks. Nope, they’re the mighty keys to cracking the code of effective communication, letting you hook, enlighten, and amuse your audience.
At their very core, these skills are all about forging a connection with your crowd, whether it’s your school buddies, coworkers, or even a gang of pals at a shindig. They’re like the crafters of a message that’s crystal clear, totally convincing, and as smooth as a jam session with your favorite jazz band.
But wait, there’s more! Presentation skills are your golden ticket to success in all sorts of life’s adventures, from nailing that class project to wowing your boss in a big meeting. They’re the secret tools that turn everyday tasks into unforgettable experiences, etching your message deep into the minds of your audience.
So, as you embark on the journey to master these presentation skills, remember it’s not just about what you say; it’s how you say it. Whether you’re facing a jam-packed auditorium or a cozy gathering of pals, may the enchantment of presentation skills guide you, transforming every moment into a mesmerizing performance.
The 12 Reasons Why Presentation Skills are Important:
Presentation skills are not just crucial for students but also for individuals of all ages and professions. Here’s why they matter and how they impact everyone:
1. Effective Communication :
- Effective communication is the backbone of all human interactions. Presentation skills equip individuals with the ability to convey information clearly, concisely, and persuasively. Whether it’s explaining a project at work or delivering a compelling speech, the capacity to communicate effectively is indispensable.
- Example : In a business meeting, a project manager adept in presentation skills can elucidate a complex project plan. They articulate the project’s goals, milestones, and potential challenges, ensuring that everyone understands the roadmap to success.
2. Career Advancement :
- The workplace is highly competitive, and presentation skills can be the differentiating factor that propels individuals forward in their careers. Being able to present ideas, strategies, and accomplishments with confidence and clarity garners recognition and opens up opportunities for advancement.
- Example : A marketing professional who excels in presenting marketing campaigns not only impresses the team but also demonstrates leadership qualities. This can lead to promotions and increased responsibilities.
3. Building Credibility :
- Credibility is vital in professional and personal relationships. When you can present your ideas convincingly, you gain the trust of your peers, colleagues, and superiors. Your credibility extends to the content you’re presenting, making it more likely to be accepted and acted upon.
- Example : An environmental scientist delivering a presentation on climate change with well-researched data and compelling visuals gains credibility among policymakers and the public, potentially influencing policy decisions.
4. Persuasion and Influence :
- Presentation skills encompass the art of persuasion. Individuals who can engage their audience, create a compelling narrative, and support their arguments effectively are more likely to influence others. This skill is invaluable in negotiations, sales, and leadership roles.
- Example : A charismatic motivational speaker can use their presentation skills to inspire audiences, motivating them to take action or adopt new perspectives.
5. Problem Solving :
- Strong presenters are often adept problem solvers. They can analyze complex issues, break them down into understandable components, and present solutions clearly and persuasively. This ability is crucial for addressing challenges in personal and professional life.
- Example : During a corporate crisis, a CEO who can present a well-structured crisis management plan to stakeholders demonstrates effective problem-solving skills and reassures concerned parties.
6. Personal Branding :
- Effective presentation skills contribute to personal branding. Consistently delivering engaging and informative presentations enhances one’s reputation as a knowledgeable, confident, and trustworthy professional.
- Example : A tech entrepreneur known for captivating product launch presentations builds a strong personal brand, attracting media attention, investors, and customers.
7. Adaptability :
- Presentation skills encompass the ability to adapt to various formats, audiences, and settings. This adaptability is invaluable in today’s diverse and ever-changing work environments, where individuals must navigate different communication channels and styles.
- Example : A teacher who can seamlessly transition from in-person classroom presentations to delivering engaging online lessons demonstrates adaptability in response to changing circumstances.
8. Lifelong Learning :
- Embracing presentation skills encourages individuals to engage in lifelong learning and self-improvement. As presentation techniques evolve and audiences change, individuals who continually refine their communication abilities remain relevant and effective.
- Example : A retired professional who continues to develop presentation skills for community workshops and public speaking engagements not only shares their expertise but also stays engaged in lifelong learning, adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
Presentation skills are universally essential as they enhance communication, facilitate career advancement, build credibility, enable persuasive influence, promote problem-solving, strengthen personal branding, foster adaptability, and encourage lifelong learning. These skills empower individuals to succeed in various personal and professional endeavors, making them essential for everyone.
Let’s look at a comprehensive overview of these trending presentation skills:
Allow me to introduce you to the 12 skills that encapsulate the very essence of the world’s most exceptional presenters.
1. Effective Communication:
Presentation skills are the ability to communicate ideas, information, or messages to an audience clearly and persuasively. It’s about conveying your thoughts with impact and resonance.
2. Audience Engagement:
These skills encompass techniques to engage and capture the attention of your audience. It’s not just about talking; it’s about connecting with your listeners on an intellectual and emotional level.
3. Organization and Structure:
Presentation skills involve structuring your content logically and coherently. It’s about creating a roadmap that guides your audience through your message, ensuring they follow and understand your points.
4. Visual Aids Usage:
Effective use of visual aids, such as slides, graphics, and multimedia elements, is a crucial component. It’s about enhancing your message with visuals that reinforce your content without overwhelming your audience.
5. Confidence and Presence:
Presentation skills entail projecting confidence and a strong presence while speaking. This includes body language, tone of voice, and maintaining eye contact.
6. Adaptability:
These skills are versatile. You must adapt your presentation style to suit different contexts, audiences, and purposes. Whether you’re giving an academic lecture, a business pitch, or a motivational talk, adaptability is key.
7. Preparation and Research:
A significant part of presentation skills is the preparation phase. It involves conducting thorough research on your topic, understanding your audience, and meticulously planning your content.
8. Problem Solving:
Effective presenters are skilled at handling unexpected situations, such as tough questions or technical difficulties during a presentation. Presentation skills also encompass the ability to think on your feet and respond confidently.
9. Storytelling:
Storytelling is a potent tool for presentation skills. It involves weaving narratives that resonate with your audience, making your message memorable and relatable.
10. Time Management:
Presentations often have time constraints. These skills include managing your time wisely, and ensuring you cover all key points within the allocated time frame.
11. Feedback Utilisation:
Presentation skills are a continuous learning process. It involves actively seeking and utilizing feedback to improve your future presentations. Constructive criticism is invaluable for growth.
12. Audience-Centred Approach:
A critical aspect of presentation skills is adopting an audience-centred approach. It’s about tailoring your content and delivery to meet the needs and interests of your specific audience.
What is the purpose of a presentation?
A) information sharing:.
At its core, the purpose of a presentation is to share information. Whether you’re in a classroom, boardroom, or on a stage, you’re conveying knowledge, insights, or ideas to an audience. This information can range from academic research findings, business proposals, and project updates, to even personal stories or creative concepts.
B) Education and Understanding:
Presentations are powerful tools for education and comprehension. They provide a structured format to break down complex topics into manageable, digestible pieces. By presenting information in a clear, organized manner, you help your audience grasp concepts more easily.
C) Persuasion and Influence:
In many situations, presentations aim to persuade and influence. Whether you’re convincing potential investors to fund your startup, persuading your classmates to support your project, or advocating for a cause, effective presentations can be a catalyst for change.
D) Engagement and Connection:
A well-crafted presentation can engage your audience emotionally and intellectually. It’s an opportunity to connect on a human level, share personal experiences, and evoke empathy or enthusiasm. Storytelling is a powerful technique to create this connection.
E) Problem Solving:
Presentations often tackle real-world issues and problem-solving. Whether it’s proposing solutions to business challenges, addressing societal problems, or discussing scientific breakthroughs, they serve as a platform to present ideas that can bring about positive change.
F) Decision-Making:
In professional settings, presentations play a pivotal role in decision-making processes. They provide decision-makers with the necessary information and insights to make informed choices. Presenters aim to influence these decisions in their favor through compelling arguments and evidence.
G) Inspiration and Motivation:
Some presentations are designed to inspire and motivate. They encourage the audience to take action, pursue their goals, or embrace change. This purpose often applies to keynote speeches, commencement addresses, and motivational talks.
H) Celebration and Recognition:
Presentations aren’t always about serious business; they can also serve as a platform for celebration and recognition. Think of award ceremonies, where individuals or teams are honored for their achievements.
I) Entertainment and Artistic Expression:
Presentations can be a form of entertainment and artistic expression. Think of performances, artistic displays, or creative storytelling. Here, the purpose is to captivate, entertain, and stir emotions.
J) Knowledge Transfer:
Lastly, presentations facilitate the transfer of knowledge from one person to another or from one generation to the next. This is particularly important in educational settings, where teachers present information to students in a structured manner.
In essence, presentations are versatile tools with multifaceted purposes. They are not just about delivering information but about connecting, persuading, educating, and inspiring. Understanding the specific purpose of your presentation is the first step toward creating a compelling communication experience for your audience.
Why is it important to have good presentation skills for students?
Imagine this scenario: You’re sitting in a classroom, and your professor asks you to present your research findings. Your heart races, your palms sweat, and the butterflies in your stomach have a party of their own. Sound familiar? Well, that’s where good presentation skills come into play for students, and they’re more than just a ticket to survive the classroom spotlight. They’re a gateway to personal and professional success.
First and foremost, presentation skills are the ultimate communication tool.
They help students articulate their thoughts, ideas, and findings with clarity and confidence. In an academic setting, this means you can engage your peers and professors effectively, making your voice heard and your ideas stand out.
But it doesn’t stop at the classroom door. These skills are your secret (because not everyone knows this) key in the professional world. Picture yourself in a job interview. Your potential employer asks you to discuss your qualifications and why you’re the right fit for the role. With polished presentation skills, you’re not just answering questions; you’re painting a vivid picture of your capabilities and potential.
Furthermore, good presentation skills are a confidence booster.
They transform nervous jitters into a sense of empowerment. When you can stand before an audience and convey your message convincingly, it’s a feeling like no other. This newfound confidence seeps into other aspects of your academic and professional life, making you a more resilient and adaptable individual.
In essence, good presentation skills are the key to unlocking doors of opportunity. Whether you’re excelling in class discussions, wowing your professors with a well-structured thesis defense, or nailing that crucial client pitch, these skills are your trusty companions on the journey of personal and professional growth.
So, the next time you find yourself in the spotlight, remember that presentation skills aren’t just about public speaking; they’re about showcasing your potential, building confidence, and paving the way for success. Embrace them, and watch your academic and professional horizons expand like never before.
What are the benefits of learning presentation skills for students?
I. effective communication: .
Good presentation skills are the linchpin of effective communication . In both academic and professional settings, students must articulate their thoughts, ideas, and findings clearly and persuasively. Without these skills, even the most brilliant concepts can get lost in translation.
II. Academic Success:
Strong presentation skills can significantly impact academic success. Students who can express themselves eloquently often excel in class discussions, group projects, and thesis defenses. They stand out as knowledgeable and confident learners.
III. Confidence Booster:
Public speaking and presentation practice are fantastic confidence boosters. They empower students to express themselves in front of their peers and teachers, gradually reducing anxiety and building self-assuredness.
IV. Leadership Development:
Presentation skills are often associated with leadership qualities. Students who master these skills tend to emerge as leaders in group projects, clubs, and extracurricular activities. They can effectively convey their vision and rally others behind it.
V. Professional Readiness:
In the world of work, professionals are frequently required to present their ideas, proposals, and reports. Students who develop strong presentation skills are better prepared for their future careers, making a positive impression on potential employers and clients.
VI. Critical Thinking:
Preparing a presentation necessitates critical thinking. Students must organize their thoughts, conduct research, and analyze information to craft a compelling narrative. This enhances their analytical and problem-solving skills.
VII. Time Management:
Creating a presentation involves managing time effectively. Students must set priorities, meet deadlines, and allocate resources wisely. These time management skills are valuable both in academia and the professional world.
VIII. Adaptability:
Presentation skills encompass various formats, from traditional speeches to multimedia presentations and virtual meetings. Students who can adapt to these different modes of communication are better equipped to thrive in today’s technology-driven world.
IX. Networking Opportunities:
Presentations often provide opportunities to network with peers, professors, and professionals. Building connections can open doors to collaborations, mentorships, and job opportunities down the road.
X. Problem Solving:
During presentations, unexpected challenges may arise, such as tough questions from the audience or technical glitches. Students learn to think on their feet, respond confidently, and solve problems as they arise.
XI. Enhancing Creativity:
Crafting engaging presentations encourages creativity and innovation. Students seek unique ways to capture their audience’s attention, whether through storytelling, visuals, or interactive elements.
XII. Global Communication:
In an increasingly interconnected world, students with strong presentation skills can effectively communicate with diverse audiences from different cultures and backgrounds, fostering cross-cultural understanding and collaboration.
These skills equip students for success in various aspects of life and contribute to their personal and intellectual growth.
How can students improve their presentation skills?
Improving presentation skills is a gradual process that requires dedication and practice. By following these steps and staying committed to self-improvement, students can become confident and effective presenters.
1. Practice, Practice, Practice:
The foundation of presentation mastery is practice . Start small by presenting in front of a mirror or recording yourself. Pay attention to your voice modulation, gestures, and overall delivery. This self-assessment helps you identify areas for improvement and build self-confidence.
2. Preparation is Key:
The best presenters are often those who are the most prepared. Know your topic inside-out. Create a well-structured presentation with a compelling opening to grab your audience’s attention and a memorable closing to leave a lasting impression. Visual aids can enhance your message, but use them sparingly to avoid overwhelming your audience.
3. Real-Life Experience:
Gain real-life presentation experience by participating in clubs, engaging in debates, or volunteering for class presentations. The more you expose yourself to different audiences, the more comfortable and adept you’ll become in handling diverse situations.
4. Learn from the Pros:
Study presentations by seasoned speakers and experts in various fields. Watch TED talks, analyze speeches, or follow your favorite orators. Observe their techniques, storytelling abilities, and audience engagement strategies. Incorporate these insights into your style to make your presentations more captivating.
5. Feedback Fuels Growth:
Don’t be afraid to seek feedback. Share your presentations with peers, friends, or teachers and ask for their honest opinions. Constructive criticism is like a roadmap to improvement. It highlights your strengths and pinpoints areas where you can refine your skills.
6. Embrace Growth as a Journey:
Remember that improving presentation skills is a journey, not a quick fix. It takes dedication and time to refine these skills. Be patient with yourself, and celebrate small victories along the way. With consistent effort, you’ll see significant progress and reap the benefits of enhanced communication and self-assuredness.
So, as you embark on your journey to become a presentation pro, keep these elements in mind. Each step, from practice to feedback, preparation, real-life experience, and learning from experts, contributes to your growth. Over time, you’ll not only become a confident and persuasive presenter but also open up doors to academic and professional opportunities. You’ve got the potential; now, let it shine!
Conclusion:
So, here’s the scoop—presentation skills aren’t just about fancy speeches. They’re your superpower for rocking academics, acing your career, and unleashing personal growth. Mastering these and mastering your life would be the best way to put it. We wish you all the best for your presentation and hope this article helps you.
If you wish to know more about how you can communicate effectively, you can try our coaching here .
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Brag Like a Pro as a Speaker

Less is More! Tips to Avoid Overwhelming Your Audience

What does it mean to Resonate with the Audience- Agreement, Acceptance, Approval

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
- Career Advice
Helping Students Overcome Presentation Anxiety
By Traci Levy
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

kali9/istock/getty images plus
We’ve all watched the scene in teen movies: a terrified student has to present in front of the class. The student freezes or panics. The class erupts into jeers and laughter.
Fortunately, students in my introductory politics class at Adelphi University don’t go that far. But they still don’t like presentation days, often turning into uncomfortable, flustered bundles of nerves before their classmates. Many times, they talk too fast or blunder through their hard work, losing their classmates’ attention along the way.
Sound familiar? Recasting the presentation format into a more manageable setup may ease student stress and foster more effective presentations. That’s what I found from classroom experimentation over several semesters.
As my students have said, their presentation anxiety arises largely from fear. So I imagined how I might reorganize to mitigate that worry, weighing different ways people give presentations: standing, sitting, arranging themselves behind a table, walking and talking, and so forth.
The antidote I’ve developed—the Presentation Cafe—positions student presenters around tables, one in each corner of the room. At every table, a group of three makes a presentation while three to six other students listen and ask questions. That lets students gather and engage in smaller clusters.
I chose the experience precisely because it evokes a cafe, where friends sit around tables and talk with ease. In my rendering, the research shared by presenters takes the place of croissants and coffee as the food for thought.
Upsides and Downsides
How does it work? On Presentation Cafe days, I divide the class into presentation slots, scheduling three or four groups, depending on class size, to present simultaneously. Each presenting group makes its presentation a few times. Students who are listening circulate among the tables, eventually hearing all of that day’s presentations.
The advantages I’ve discovered have a few dimensions. First, students enthusiastically and almost unanimously seem to prefer sitting around a table and presenting to smaller groups rather than 15 to 22 other students. Out of 40 students between the two sections of this class that I have taught, 38 preferred this approach, one wasn’t sure and one sheepishly admitted he liked standing in front of a class. He’s perhaps a natural politician in the making—but truly the exception to the rule.
Second, by giving their presentation three times in one day, students can practice and improve their oral presentation skills. I’ve circulated to catch at least part of every group’s presentation each time. Most students have made improvements in pacing, length and even content in subsequent presentations. They’ve also seemed more relaxed and confident with each presentation.
Third, students have scored higher on our class assessment question that was related to the presentation material. I’ve tested students on part of the information several weeks later in an essay on an exam. My department collects data on this question for assessment purposes. Correlation isn’t necessarily causation, and multiple factors could be at play with the higher scores. Still, I’ve been happy to see that a smaller percentage of students have scored “unsatisfactory,” while more have scored in the “satisfactory” and “superior” assessment ranges. That’s compared to previous semesters, when I used a traditional presentation method.
This presentation setup has worked well even with students presenting and listening wearing masks due to COVID safety rules. In fact, it’s probably worked better since presenters haven’t had to project their voice across the room.
Does this approach work in online synchronous classes? It’s easy to group students in breakout rooms on virtual platforms like Zoom. In fact, now that some Zoom settings even allow students to choose and switch between breakout rooms, this strategy is more practical than ever in online classes. From my experience, however, it’s harder to circulate as efficiently between online breakout groups. I can’t visually scan the room to see when students are starting or ending their presentations.
Admittedly, this approach has some potential downsides, even for in-person classes. Although every group can see most other presentations, they can’t see them all. I could remedy this issue by assigning more presentation days. However, time is precious, and the number of days I’ve assigned has worked well for my students.
It may also be harder for a professor to notice points that might need to be clarified or corrected. Even though I circulate throughout the room, hearing parts of all presentations, students can sometimes make mistakes. In the future, I plan to grade the papers and return feedback before students deliver their presentations to minimize the likelihood that they present any incorrect or confusing information.
All in all, however, with students less anxious, presentations improved and attendance and assessment scores up, the Presentation Cafe will be a regular feature of some of my classes. Maybe next time, I’ll even bring croissants.

Campus Engagement Tip: Offer 50 Days of Activities
Campbell University organized daily events for a month and a half to promote on-campus participation and boost feelin
Share This Article
More from career advice.


The Warning Signs of Academic Layoffs
Ryan Anderson advises on how to tell if your institution is gearing up for them and how you can prepare and protect y

Legislation Isn’t All That Negatively Impacts DEI Practitioners
Many experience incivility, bullying, belittling and a disregard for their views and feelings on their own campuses,

4 Ways to Reduce Higher Ed’s Leadership Deficit
Without good people-management skills, we’ll perpetuate the workforce instability and turnover on our campuses, warns
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
Presentations in the Classroom: Helpful Tips to Shine in School Reports
Table of Contents
Presentations in the Classroom: Standing out during school presentations can seem daunting, but it’s an essential skill that will serve you throughout your educational journey and beyond. Whether you’re delivering a solo report or part of a group project, the way you present your content can make a significant difference. Presentations in education are more than just talking in front of a class; they are a way to demonstrate your understanding, communicate ideas effectively and engage with your audience.

Crafting a compelling presentation requires thought into both the content and delivery. The content of your presentation should be clear, concise, and well-structured, ensuring that your key messages stand out. Additionally, your slides should complement your narrative, incorporating engaging designs without overwhelming your audience. Meanwhile, honing your presentation skills ensures that your delivery captures attention and maintains interest. This means practicing your timing, tone, and body language.
Maximising attendance and active participation from your audience can significantly enhance the impact of your presentation. Alongside good presentation content and delivery, leveraging technology can also contribute to a successful school report by adding interactive elements that resonate with your classmates. It’s also critical to seek feedback for continual improvement and find effective ways to manage any presentation anxiety, ensuring that you remain confident and collected.
Key Takeaways
- Effective presentations combine compelling content with engaging delivery.
- Utilising technology and interaction techniques captivates the classroom audience.
- Feedback, practice, and management of anxiety are crucial for presentation success.
The Importance of Presentations in Education
In today’s classrooms, your ability to communicate through presentations is instrumental to effective learning . When you stand up to deliver a presentation, you’re not just sharing information but also honing critical skills . It’s a chance to engage with your peers in a way that reading from a textbook simply can’t match.
Engagement is key when it comes to learning. Presentations demand your attention, not just as a speaker but as an audience member too. By listening to others, you’re exposed to diverse perspectives, encouraging a deeper understanding of the material.
Learning through presentations is interactive. It makes the abstract concrete, often requiring you to transform complex data into something visually and intellectually stimulating. You learn how to structure your thoughts logically, putting them into a format that others can follow.
The skill set you develop is comprehensive—research, organisation, design, and public speaking all come into play. Moreover, you’re tasked with mastering technology , whether it’s creating a PowerPoint presentation or integrating multimedia.
In terms of assessment , presentations offer your teachers a multifaceted view of your comprehension. They can assess not just what you know, but how you apply it, communicate it, and react to questions. This is a much richer form of assessment than standard tests.
By building your confidence and capability to express your ideas publicly, presentations prepare you for future endeavours in both education and your eventual career. So when your next presentation assignment comes around, embrace the opportunity to sharpen your skills and engage with your learning on a whole new level.
Crafting Your Presentation Content
To stand out during school reports, your presentation must be built on thorough research and organised effectively. Let’s guide you through the process of gathering substantial content and structuring your presentation for a compelling delivery.
Research and Data Collection
Begin by delving into the topic at hand with meticulous research . Collect accurate data from various sources to ensure a rich and well-rounded understanding. Embrace the spirit of an explorer, much like you would on LearningMole , seeking out statistics and evidence that support your main points. Utilise interactive tutorials or informative articles, just as LearningMole offers, ensuring that every fact you integrate into your presentation is robust and factual.
- Utilise Different Sources: Gather information from books, academic journals, and reputable websites .
- Evaluating Reliability: Cross-reference data to assess the credibility of your findings.
- Recording Information: Keep a detailed log of your sources for easy reference during your presentation.
Organising and Outlining Your Information
Once your research is complete, it’s time to organise your findings. Start by outlining your presentation’s structure with a clear introduction, a well-defined body, and a concise conclusion. Draft a framework that enables your ideas to flow logically, preventing any confusion for your audience.
- Introduction: Present your topic and main argument briefly but compellingly.
- Argument/Point: State one of your main ideas.
- Evidence: Include pertinent statistics or examples to substantiate the point.
- Explanation: Show how this evidence supports your argument.
- Conclusion: Reiterate your key points, ensuring they’re memorable.
Organising your presentation content is a craft that involves strategic planning and attention to detail. Tailor your content to your audience’s understanding level in the same way LearningMole caters to different educational needs, ensuring that everyone can grasp the message you wish to convey.
Designing Engaging Slides
Crafting slides that capture and maintain your audience’s attention is crucial in delivering an impactful presentation. Let’s discuss how to infuse your slides with the right blend of aesthetics and functionality.
Choosing the Right Font and Colours
Selecting the appropriate font is about balance; it must be readable from a distance yet stylish enough to enhance your message. Stick to sans-serif fonts like Arial or Helvetica for your body text, as their clean lines are easier on the eyes for your audience. When it comes to colour, opt for a high contrast between your background and text to ensure legibility. Utilise colour palettes that reflect the mood of your presentation, but remember — less is often more. A maximum of three to four colours should suffice to keep your slides professional and cohesive.
Creating Visuals: Images, Graphs, and Charts
Visual aids such as images, graphs, and charts can turn complex data into digestible insights. Use high-quality images that are relevant to your content and avoid stretching them out of proportion. For data-heavy presentations, employ a variety of charts and graphs to present statistics in an engaging way. For instance, pie charts work well for displaying proportions, whereas bar graphs can effectively compare different groups. The key is to ensure these visuals complement your spoken words, not overshadow them.
Incorporating Audio and Video Elements
Multimedia elements like audio and video can be powerful tools to complement your PowerPoint or Google Slides presentation. Embed short, relevant clips to illustrate your points or introduce new sections. For audio, subtle background music during breaks or sound effects can enhance engagement, but make sure they are not disruptive. As with all elements of your slides, moderation is key — use audio and video judiciously to support your narrative and maintain a professional tone.
Remember, the objective of your slides is to support your story, not to tell it. Keep text to a minimum, use visuals to punctuate your points, and leverage multimedia elements to add depth to your presentation. Your slides are the visual foundation that can help you stand out during school reports.
Presentation Skills and Delivery

Developing strong presentation skills and mastering the art of delivery can dramatically enhance your performance when you are tasked with speaking in front of a class. Acquiring these skills will allow you not only to convey your message effectively but also to engage your audience and leave a lasting impression.
Mastering Oral Presentation Techniques
To excel in oral presentations , it is vital to organize your material coherently and practise speaking clearly and confidently. Start by outlining the main points you want to address, ensuring that there is a logical progression of ideas. Practise your speech multiple times, paying attention to areas where you can insert examples or ask rhetorical questions to hold the audience’s interest. Always be prepared to receive and implement feedback , as it is an indispensable part of honing your presentation skills.
Using Non-verbal Communication Skills
Your body language speaks volumes during presentations; thus, using non-verbal communication skills effectively is key. Maintain eye contact with your audience to create a rapport and use hand gestures to emphasize points. However, be mindful of overdoing it, as excessive movements can be distracting. A poised stance and appropriate facial expressions can significantly enhance your message and audience engagement. Remember, your aim is to support your spoken words with your actions, creating a cohesive and compelling delivery.
Practising Your Timing and Pacing
Effective time management is crucial in delivering a well-paced presentation. Aim to distribute your content evenly across the available time, avoiding the common pitfall of rushing through the final slides due to a lack of practise. Utilize pause effectively; it serves as a powerful tool to highlight important points and allows your audience to absorb the information. Consider practising with a timer to ensure that you stay within the allotted time frame, and always account for a brief Q&A session at the end, if applicable.
Engaging the Classroom Audience
When striving to hold the attention of your class during presentations, it’s essential to tailor your approach, engage actively with diverse learning preferences, and create a supportive environment that encourages participation.
Understanding Your Audience
To captivate your audience during school reports, it’s crucial that you understand who you’re presenting to. Your classmates may have varying degrees of familiarity with your topic, so determine the appropriate depth of content. Factor in the diversity of your audience, considering different learning styles and interests. This understanding can significantly boost their engagement and your presentation’s motivation .
Interactive Elements and Audience Engagement
Integrating interactive elements such as polls or question-and-answer sessions can transform passive listeners into active participants. This not only increases audience engagement but also allows you to gauge their understanding in real-time. For example, asking thought-provoking questions throughout the presentation encourages your audience to think critically and maintains their interest.
Managing Classroom Environment
The classroom environment plays a pivotal role in the success of your presentation. It should be arranged in a way that every student feels included. Consider seating arrangements and the visibility of your visual aids. A comfortable and inviting atmosphere can help lower barriers to engagement , making your presentation more effective and enjoyable for everyone.
Group Presentations and Collaboration
When engaging in group presentations, the success largely hinges on effective teamwork and collaboration. These are active learning opportunities where each member’s contribution is vital.
Coordinating with Team Members
Organising your team is crucial. Start by agreeing on common goals and a schedule that suits everyone. Regular meetings, whether face-to-face or virtual, will ensure ongoing communication and the ability to rapidly address any concerns or adjustments. Using digital platforms can enhance this process by enabling real-time collaboration even if you can’t meet in person.
Distributing Roles and Responsibilities
Assigning clear roles and responsibilities maximises the efficiency of your team. Here’s how you might distribute these:
- Researcher: Gathers necessary content.
- Writer: Synthesises research into a script.
- Designer: Creates visual aids like slides.
- Speaker: Delivers the presentation.
To support active learning, swap roles occasionally to ensure every member develops a well-rounded skill set. Keep track of who’s doing what to maintain accountability within your group.
Leveraging Technology in Presentations
Integrating modern technology in your classroom presentations can significantly enhance engagement and learning. From advanced tools that add a layer of sophistication to accessibility options that ensure all students benefit, here’s how you can stand out during your next school report.
Advanced Presentation Tools
When you’re ready to take your presentations beyond the basics, consider using advanced presentation tools like Google Slides . These platforms offer dynamic features such as animation and slide transitions that will make your presentation visually appealing. Moreover, embedding videos can provide a multimedia experience that may help clarify complex subjects and keep the audience’s attention.
Online Resources and Accessibility
Access to online resources enhances both the quality of presentations and their reach. Platforms like LearningMole offer a variety of engaging, educational content that can bring new dimensions to your presentations. Utilising such online resources can be a game-changer, especially when considering accessibility . Features like screen readers and captioned videos make sure that learning is inclusive for all students, regardless of their needs.
Assessment and Feedback for Improvement
When you’re tasked with delivering presentations in the classroom, both assessment and feedback are crucial for honing your skills and ensuring learning success. Here’s how they can help you stand out when delivering school reports.
Assessment takes many forms, from teacher observations to self-evaluations. It serves as a yardstick for measuring how effectively you’re communicating your knowledge. It’s not just about content; it assesses delivery, clarity, and your ability to engage with the audience.
Formative Assessment : This ongoing process helps you receive constructive feedback to modify your learning behaviours and presentation strategies. For instance, teachers may provide a feedback rubric that breaks down different aspects of your presentation skills.
Summative Assessment : This typically comes after a presentation has been delivered, possibly in the form of grades or scores, summarising your performance’s effectiveness.
Feedback is the information you receive based on the assessment.
It should be specific , timely , and relevant , guiding you on where to improve. When you receive feedback, it’s important to reflect and act upon it to make your next presentation even better.
Teachers can greatly influence learning success through the way they give feedback. When it’s done right, it acts as a powerful tool that encourages you to take control of your learning process. Articles like this one provide insights into the principles of effective feedback.
Remember, the goal of any assessment and feedback is to improve. Embrace both with an open mind, and use them as stepping stones to deliver more compelling, impactful presentations that stand out.
Coping with Presentation Anxiety
Feeling anxious before a class presentation is a common experience, but there are several strategies that can help you manage this anxiety . Here are a few to consider:
Preparation : Being well-prepared is essential. Spend time researching your topic and practising your speech multiple times. This boosts your confidence and reduces the likelihood of going blank during the presentation.
Relaxation Techniques : Use relaxation methods such as deep breathing exercises or mindfulness meditation to calm your nerves before and during your presentation. These techniques can help to lower anxiety levels and improve focus.
Positive Visualisation : Envision yourself giving a successful presentation. Imagine the audience responding positively to your speech. Positive visualisation can be a powerful tool for building motivation and confidence.
Feedback : Ask for constructive feedback from friends or family before the actual presentation. This can provide valuable insights and help improve your performance.
Support : Lean on your peers or educators for support . Discussing your worries with them can offer reassurance and practical advice. Knowing you have this support can be a tremendous comfort.
Mental Health : If your anxiety is significantly impacting your well-being, don’t hesitate to speak to a mental health professional. Ensuring that your mental health is taken care of is crucial.
By implementing these strategies, you can start to overcome your fears and stand out during school reports. Remember, presentation skills improve with practice, so each time you present, it will get a little easier.
Maximising Attendance and Participation
When you are involved in student presentations, fostering attendance and engagement is crucial for successful knowledge assimilation. Here’s how you can encourage student presence and active participation:
Interactive Elements : Add quizzes or polls to your presentations to keep students involved. For instance, using a question that requires a show of hands can engage students and maintain attentiveness.
Group Activities : Break down topics into smaller parts assigned to groups. This collaborative approach encourages students to participate and ensures they are actively learning.
| Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Enables collaborative learning and peer support. | |
| Makes learning fun and interactive. | |
| Applies theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, increasing relevance. |
Feedback Loops : Establish a system where students can give and receive feedback. By implementing peer reviews, you enhance their critical thinking and engagement.
Clear Objectives : Set and communicate clear goals for each session. When students know what’s expected, they are more likely to participate.
Remember, active learning isn’t just about being physically present; it’s about being mentally invested in the classroom activities. Use a variety of teaching methods to cater to different learning styles, and integrate technology to make lessons more dynamic and relatable.
Lastly, don’t underestimate the power of personal interaction. Greet students as they enter and show interest in their progress. Your enthusiasm as a presenter can be quite contagious and is often the key to encouraging students to be interested and involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
As you prepare for your next classroom presentation, you might be looking for ways to stand out and effectively communicate your ideas. The following frequently asked questions cover the essentials to help you make a lasting impression.
What are the best strategies for making your classroom presentation stand out?
To make your presentation memorable, utilise engaging visuals, incorporate interactive elements, and ensure your content is well-structured. Telling a story related to your topic can also captivate your audience and make your presentation more relatable.
In what ways can you present a report in class effectively?
An effective report presentation is clear, concise, and well-rehearsed. Use supportive evidence and data to back up your points and practise your delivery to maintain steady pacing and clear articulation.
What are the key purposes of giving presentations in the classroom?
Presentations aim to develop your communication skills, encourage you to engage with your topic deeply, and allow you to practise public speaking. They also provide a platform to share knowledge and learn from peer feedback.
Could you suggest some creative ideas for student presentations?
Consider using multimedia elements such as videos or music to add a creative edge. Interactive quizzes or polls can engage your classmates and make the learning experience more dynamic.
What are some examples of expectations teachers may have for student presentations?
Teachers often expect presentations to be well-researched, logically organised, and delivered with clarity. They may also look for original thinking and the ability to answer questions competently.
What methods can students use to enhance their presentation skills in the classroom?
Regular practise is crucial for enhancing presentation skills. Recording yourself to identify areas for improvement and seeking constructive feedback from teachers or peers can also be very helpful.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts

Memory Boosters: Engaging Strategies for Improved Learning Outcomes

Organisational Skills for Students: Enhancing Study Habits with Strategic Tools and Tips

The Power of Mind Maps: Unlocking Visual Learning for Every Generation
What are Presentation Skills? A Comprehensive Guide
Explore essential presentation skills for professional success, including planning, delivery, and audience engagement techniques.
What are Presentation Skills?
Key components of presentation skills.
- Planning and Preparation : This involves researching the topic, understanding the audience, and organizing the content in a logical flow.
- Delivery : This includes the use of voice modulation, pacing, and body language to convey the message effectively.
- Use of Visual Aids : Skillfully incorporating tools like PowerPoint slides, charts, and videos to support the presentation.
- Audience Engagement : Techniques to keep the audience interested and interactive, such as asking questions, using humor, and showing enthusiasm.
- Feedback Handling : Responding to questions and feedback in a constructive manner.
Why are Presentation Skills Important?
Advantages in the workplace.
- Career Advancement : Effective presentation skills can lead to new opportunities and visibility in the workplace.
- Enhanced Communication : They help in communicating project updates, pitching new ideas, and leading meetings more effectively.
- Leadership Development : Strong presentation skills are a key attribute of good leadership.
Impact in Academia and Everyday Life
- Educational Success : Students with good presentation skills often perform better academically by clearly expressing their ideas.
- Personal Relationships : These skills can improve personal interactions by enabling clearer communication of thoughts and feelings.
How to Develop Effective Presentation Skills
Understand your audience.
- Tailor your content to meet the audience's needs and knowledge level. This ensures engagement and receptiveness.
Structure Your Content
- Organize your presentation into a clear beginning, middle, and end. Use signposts to guide your audience through the material.
Practice Your Delivery
- Rehearse your presentation multiple times. This helps in smoothing out any rough edges and refining your delivery style.
Use Visual Aids Wisely
- Design visual aids that complement and enhance your message. Avoid clutter and ensure that every slide or visual is meaningful.
Engage With Your Audience
- Use questions, polls, and discussions to make your presentation interactive. Pay attention to the audience's cues and adapt accordingly.
Seek Feedback and Reflect
- After your presentation, seek feedback from peers or mentors. Reflect on what went well and what could be improved for future presentations.
Create PPT using AI
Just Enter Topic, Youtube URL, PDF, or Text to get a beautiful PPT in seconds. Use the bulb for AI suggestions.
character count: 0 / 6000 (we can fetch data from google)
upload pdf, docx, .png
less than 2 min
Ayan Ahmad Fareedi
writer at MagicSlides
Real Estate Listing Presentation: Essential Points to Address for Success
23 August 2024
When Giving a Presentation, What Is a Good Tactic for Engaging the Audience?
What to Include in an "All About Me" Presentation
22 August 2024
In Which Three Ways Can a Video Do More Harm Than Good in a Speech?
Who Am I Presentation: How To Make Presentation About Yourself
How to Apply a Template to an Existing PowerPoint Presentation
Which of the Following is NOT a Financing Option Suggested in the Presentation?
19 August 2024
In a Presentation, What is Layout?
What Activity Can Help You Improve Your Presentation?
Stunning presentations in seconds with AI
Install MagicSlides app now and start creating beautiful presentations. It's free!

Get AI-Generated Presentations Ready in Seconds
Free AI PPT Tools
- Skip to right header navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Teaching Effective Presentation Skills in English Language Arts Classrooms

March 27, 2023 // by Lindsay Ann // Leave a Comment
Sharing is caring!
Presentation skills are a worry for most people . And, let’s face it… public speaking is a part of life (even if it’s just life in middle school or high school).
In fact, according to a Gallup poll, 40% of Americans indicated public speaking as their biggest fear . Snakes came in first place at 51%.
Now, I speak in front of a classroom full of teenagers five days a week, and my audience is arguably one of the toughest audiences out there.
While I wouldn’t want to be trapped in a room full of snakes (pythons in particular), I don’t mind the thought of presenting or delivering information in front of others.
But based on how often I’ve seen students get up in front of the class in order to present a project, idea, or understanding, only to turn red, mumble through their slide decks, or freeze altogether, I’m betting many of my students would consider their chances with boa constrictors as a presentation looms.
Public speaking and presenting can be tough for anyone .
There are some days when I don’t even I don’t want to have to do it, but regardless of how we feel about it, it’s an integral part of postsecondary life and it’s important for our students to be able to do well and feel confident when speaking in small or large groups , whether they are participating in a discussion or sharing their ideas more formally.

Today we’re going to explore presentation skills , why they’re important , classroom activities that can make everyone feel less miserable, and how to support students who are struggling to overcome their public speaking anxiety. Let’s jump in!
What are Presentation Skills?
First things first, let’s define what I mean by presentation skills.
To define it simply, presentation skills are the ability to effectively communicate a message to an audience. Speaking can be done in a variety of ways, such as through oral presentations, multimedia presentations (which are very popular with students, but more on that later!), and even written reports.
Presentation skills are not just defined by the clarity of the message, but also by the delivery .
Body language, vocal inflection and tone, audience engagement, and creativity are also important nonverbal characteristics and presentation skills.

Why are Presentation Skills Important?
In today’s world, communication skills are more valuable than ever. No matter your students’ path in life, they will need to be able to effectively communicate with others.

I don’t know about you, but when I think of presentation skills, I think about boardroom presentations and closing big deals. Ya know the kind with big posters of arrows going up?
This vision may be a by-product of my age and TV shows in the 80s and 90s, but our world is more connected than ever before, and we’re communicating more than ever in ways that weren’t even possible for my beloved 80s and 90s TV characters.
Our students may never grow up to present in a boardroom, but they’ll likely need to communicate with their own child’s teacher, present at a city council meeting, share their findings with members of their HOA, or even go live on Instagram. We need to make sure our students are prepared for this reality.
What are Some Examples of Presentation Skills?
Before I share some ideas on how to help your students improve their presentation skills, I want to take a moment to look at what good presentation skills look like.
Here are some examples:
- Clear and concise messaging: A good presenter can take complex ideas and explain them in easy to understand, plain language.
- Engaging visuals: Strategic use of visuals is important when public speaking. A good presenter will keep their presentation clean and free from clutter (sorry to Mrs. Smith who had to endure my 7th grade PowerPoint presentations that used all of the transitions…I didn’t know what I was doing).
- Confident body language: Confident body language, including making eye contact, standing up straight, and using gestures to emphasize important points are tell tale signs of a good presenter.
- Effective use of tone and pace: Knowing how to vary one’s tone and pace when presenting is an essential presentation skill. A good presenter knows when to speed up to build excitement and how to use tone and pacing to emphasize important points.
How to Improve Presentation Skills
Now that we’ve looked at some examples of good presentation skills, let’s explore some tips and tricks to help your students improve their own presentation skills.
- Practice, practice, practice: The more your students practice presenting, the more comfortable and confident they will become. Build in public speaking to your lessons as often as possible. Even if it’s not a full-length presentation, students can practice this presentation skills by engaging in think, pair, shares , chalk talks, gallery walks, etc.
- Focus on the audience: Remind your students that their presentation is not about them, it’s about the audience. Encourage them to think about what the audience wants to hear and tailor their message accordingly. Passion projects and other activities that allow students choice and authentic engagement can help them focus on the audience rather than the task at hand.
- Use storytelling: People love stories, so storytelling is an essential presentation skill. Encourage your students to use storytelling in their presentations, and demonstrate this skill for them by infusing your own lessons with stories. This can be as simple as starting with a personal anecdote or using case studies to illustrate their points. Ted Talks make great mentor texts to show students how professional presenters use storytelling to connect to their audience.
- Manage anxiety: It’s natural to feel anxious when presenting, but there are things your students can do to manage their anxiety . Encourage them to take deep breaths, practice relaxation techniques, and visualize themselves giving a successful presentation. As students have more experience (and more success!) with public speaking and presenting, their anxiety will decrease. Focus on helping students practice coping skills and manage their anxiety while providing multiple (and fun) opportunities for them to work through their jitters.
- Use visuals: Multimedia presentations are a favorite for our Digital Natives. Students love to create and embed memes and gifs, videos, songs, and things you and I probably don’t even know exist into their presentations. Creating these things feels natural for most of our students, and visual aids are an important presentation skill, so encourage them to use their existing skills and get creative!
- Get feedback: Feedback is essential to improving presentation skills. Encourage your students to ask for feedback from their peers or even record themselves and watch it back to see where they can improve. As students are practicing their public speaking skills, have them use Flip to record themselves. Students can post their Flip on the classroom grid (that you have total control over) to provide feedback and encouraging words to their classmates.
Public Speaking Exercises and Games
Okay, so we’re all in agreement that public speaking is tough but necessary and that presentation skills are important. So…how do we make it more fun and less…like a room full of snakes?
There are some really fun (like, legit fun, I know this because high schoolers told me they’re fun and after all, they’re the kings and queens of cool) exercises and games to help practice public speaking skills and shake off the jitters.
Here are some to try:
- Impromptu speeches: Have your students pick a random topic and give a two-minute impromptu speech or debate . This will help them practice thinking on their feet and organizing their thoughts quickly.
- Campfire story: You start a story. Something like, “Two friends are hiking in the woods when they lose track of the trail…” and each student takes turns adding to it. The last student must provide a satisfying ending to the story. To lessen student anxiety, this works in pairs and groups of three, too!
- Photo story: Show students a photo online (the New York Times Learning Network has a great section for this type of exercise) without any context. Students will share what they think the backstory is, who the people are, their dreams, their motivations, conflicts, and anything else that’ll tell a compelling story about them.
- What grinds my gears: Have students take the spotlight to share about their biggest pet peeves. What really grinds their gears?
- Gush about a basic object: On the opposite end of the spectrum from sharing about what annoys them, have students pick a basic, everyday object they’re indifferent about. Something like a blender, pencil, a chair in the classroom. The challenge is they have to develop a speech to deliver in which they absolutely gush about that object. What makes it so great? This particular exercise really challenges students to use body language and voice to accomplish the task.
- Minute to Win It: Want to create a little friendly competition in your public speaking practice? Minute to Win It improv debates will up the ante for your students. The gist is this: Students are given one minute to plead their case in front of the class on a topic given to them only when the timer starts. The audience votes for the best case, so their arguments better be good .
- Commercial: Students can make a commercial for an object of their choosing. This allows them to be serious or playful, to bring in props and other visual aids, and to practice with body language and vocal inflection. This exercise works well for groups, which can really help ease student anxiety when speaking in front of the class.
- Balderdash: Students write made up words on slips of paper. Place the slips with the made up words in a bin for students to blindly grab from. Taking turns pulling a slip from the bin, students must on the fly create a definition for that word and share it with the class.

Wrapping Up
I hope you’ve been inspired to bring some fun ways to practice important presentation and public speaking skills into your curriculum. The speaking and listening standards in the ELA curriculum present a unique challenge for us to prepare students for life after high school while still honoring that public speaking is difficult (and downright terrifying for some). We know our students can do difficult things, and we can help them do so with confidence!
About Lindsay Ann
Lindsay has been teaching high school English in the burbs of Chicago for 19 years. She is passionate about helping English teachers find balance in their lives and teaching practice through practical feedback strategies and student-led learning strategies. She also geeks out about literary analysis, inquiry-based learning, and classroom technology integration. When Lindsay is not teaching, she enjoys playing with her two kids, running, and getting lost in a good book.
Related Posts
You may be interested in these posts from the same category.

Common Lit Curriculum: An Honest Review

Incorporating Media Analysis in English Language Arts Instruction

How to Write a Descriptive Essay: Creating a Vivid Picture with Words

The Power of Book Tasting in the Classroom

20 Short Stories Students Will Read Gladly

6 Fun Book Project Ideas

Tailoring Your English Curriculum to Diverse Learning Styles

Teacher Toolbox: Creative & Effective Measures of Academic Progress for the Classroom

10 Most Effective Teaching Strategies for English Teachers

Beyond Persuasion: Unlocking the Nuances of the AP Lang Argument Essay

Book List: Nonfiction Texts to Engage High School Students

12 Tips for Generating Writing Prompts for Writing Using AI

Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
The importance of presentation skills in the classroom: Students and instructors perspectives
- January 2004
- Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges 19(4):6-15

- Qatar University

- Lusail University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
No full-text available
To read the full-text of this research, you can request a copy directly from the authors.
- N L A Halim

- Educ Res Rev

- Margana Margana
- Priyanto Priyanto
- Slađana Živković
- Santi Agustin
- Ribut Wahyudi

- Khương Lưu Quý
- Thi Luu Ngoc Bao
- Jan Rich Guira

- Jamie Whelan

- Tamara Ćurlin

- Ivan Miloloža

- Colin Depradine

- Syafryadin Syafryadin

- Xiaofang Gao

- Jane D. Parent

- E. Joseph Derrick
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

7 Essential Presentation Skills Examples, Techniques & Tips for Freelance Trainers
Last updated January 29, 2024
With some very simple and basic but essential tips, you can quite quickly learn effective presentation skills and become a more effective trainer or teacher. So in this post, here are 7 tips for you that you can use, whether you are a freelance or corporate trainer, teacher, someone doing a presentation at work, or a student learning to do presentations. These tips should help you all!
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here .
Taken from our >> ‘ Online Train the Trainer Course ‘.
Page Contents
Tip 1: Body Language (Face and Hands)
One of the first things to consider when presenting is to think about how you use your face and hands.
Always make eye contact and look at all of your participants . Do not stare at them but do make an effort to appear to speak to each and every person present.

If the venue is big and the number of attendees numerous (let’s say more than 20) then at least look or glance at each section of people from time to time.
A word of warning though! In some cultures, it is considered rude or aggressive to look someone in the eye . So do factor in the culture and audience to whom you are speaking or teaching, and adapt accordingly.
KEY TIP : Make a point to sometimes speak and do gestures (positive ones of course) to those sitting the furthest from you to make them feel included.
Do also remember to use facial expressions that are congruent with your words. In other words, what you say should match your facial expression so as to avoid confusion. If you are saying something exciting try and look excited by it, for example.
Avoid : No playing with markers, touching your head, or crossing your arms; no hands in pockets unless it is to show informality and relaxation! A great way to avoid these things is to record yourself at home with any camera (a cellphone will do) and practice presenting. You will soon see the habits you have!
Tip 2: Posture and Body Language When Presenting
If you want to make the right impression with your students or whoever you are presenting to, it is important to maintain good posture .
Good posture also helps to project the voice better , in addition to making you look more confident.
If you wish to, you can also highlight a new section in the presentation by changing your posture or position. Opening up your shoulders and arms, for example, could be used to express the idea of something starting.
KEY TIP: The key from our experience is that it often simply comes down to practice! The more times you run through your speech or lesson, the smoother and more fluent you will become. The TRUTH is that most great speakers are only the best because they practice and practice. It is that simple. With this in mind, avoid continuously reading off a piece of paper or script.
Tip 3: Positioning Your Body When Presenting

Body language is also important and given that most eyes will be on you, as the trainer at the front of the room, any unusual actions you do will of course easily be noticed and can distract your audience from focusing on the content that you are delivering.
So, when standing at the front of the room, plant your feet and do not shift your weight, and avoid pacing back and forth on the same spot.
Also, be aware that sitting changes the tone and makes the atmosphere informal. If teaching or presenting to a small group of people (i.e. everyone can easily see you if you are sitting down), you might want to use sitting down as a strategy for mixing the formal with informal.
Never have your back to the group (or as little as possible if you are writing on a board).
Tip 4: Voice – Volume, Pitch, and Pauses

I was at a conference recently and a well-renowned academic was presenting in front of 100+ people and, despite being in the front row, it was impossible to make out what he was saying.
Make sure when presenting to project your voice ! Also, change the volume and pitch of your voice to add emphasis! If you need to, just ask the people at the back of the venue if they can hear you okay?
KEY TIP : Also learn to use pauses to emphasize something important. Furthermore, pauses are also useful to give time to reflect and for you to observe participants. Do not be afraid of silence!
Tip 5: Fillers and Elocution

One of the things that most of us do when first learning how to give effective presentations, is to use fillers!
Fillers are the words we unconsciously use to try and fill in between the things we are meant to say. Common fillers include ‘ah’, ‘err’, ‘ok’, ‘like’, ‘er’, ‘um’, and ‘right then’.
We all use fillers and trying to avoid using them is not easy at first.
To learn to stop using fillers the best way is the tip I gave earlier and which is to record yourself speaking and play it back. Just grab your iPhone and use the camera on the phone, for example, and record a 3-minute speech (it doesn’t matter what you speak about or how you look). Then play the video back and see what fillers you used when speaking. Keep practicing and you will begin to avoid fillers very quickly.
Finally, do not rush the end of sentences, and do not be afraid to use an informal voice. You want to sound professional of course, but you also want to speak in a way that is friendly and warm.
Tip 6: Making Use of Space in the Training Room or Classroom

Think carefully also about the space that you have available to you in the training room or classroom.
It can be a great idea to move around among participants . Move around the room looking first at a group, then another group. Do not neglect any section of the room.
Also, never sit behind a desk (unless used temporarily and as part of an intentional informal act). You might, for example, want to sit down whilst your participants are doing an activity or task that you have set them.
Or you might sit to emphasize something. Generally speaking though, for the most part, you should be standing when presenting. Also, stand close to the class unless you are using the board a lot.
Tip 7: Extra Presentation Skills Ideas

Let’s finish with four final tips.
It can be difficult when teaching or providing training to find the balance between providing enough explanation and information and giving too much.
Do not though, go on and on about something and be too repetitive. You can lose the attention of your audience if you do this too much.
Be Careful with Jargon
You will also want to be careful with the jargon you use (or what is known as ‘discourse’ in academia). In different social and cultural circles, we have different ways of speaking in terms of terminology. Even between the UK and the United States, for example, our ways of speaking are different. Differences can include:
- soccer (USA) = football (UK)
- pants (USA) = trousers (UK)
- gasoline (USA = petrol (UK)
The key is to make sure you are speaking with your audience in mind . Know who your audience is and tailor your speech, if necessary, for them.
The best presenters are the best really because of one key reason. They practice and they learn to be great presenters.
That really is the secret! Having interviewed hundreds of presenters, the idea of practicing to improve and become a good presenter was always mentioned as the key tip to presenting well.
Certainly, a few people (the lucky ones) are born with a natural ability just to be brilliant presenters.
The majority though become proficient through practice.
Watching Great Presenters
It can also be worth watching some TED talks to get a feel for what great presenting looks like.
When watching these presentations, observe the pauses at key moments, the way they move or do not move around the stage, the change of intonation for emphasis, the way they use their hands or not, and their facial expressions. And what do they do wrong that you don’t like? Try these two videos:
- Tyler DeWitt : Hey science teachers. Make it fun!
- Nadia Lopez : Open a school to close a prison!
Show Enthusiasm!
If you are not actually that interested in the topic you are teaching or presenting, TRY TO FIND something about it interesting and show enthusiasm.
If you really can find nothing to be enthusiastic about in terms of what you are teaching, then looking for a new job might be the best option here. Otherwise, be cheerful and you will find that this alone can help you win over those sitting in front of you as you speak. Smiling and being happy can be infectious!

- Recent Posts
- 21 Types of Market Research and Examples - August 20, 2024
- 5 Free Qualitative Teaching Activities for Market Research Training - August 19, 2024
- 21 Effective and Essential Coaching Skills for Managers - August 15, 2024

Explanation is simple and clear. Very useful tips.
This analysis is outstanding ,thank you
Thank you, great post. I have learned a lot about presentation skills. Thank you.
The post is great… I have learnt alot as a teacher student in Kenya
Helped me a lot! Thank you.

>> View All Training Course Materials
Training Materials Catalogue & Prices

Payment Options

Bulk Discounts

What Is Included in Our Training Packages?

Like what you're reading?
Creating engaging teacher presentations: tips, ideas, and tools
Get your team on prezi – watch this on demand video.
Anete Ezera August 21, 2024
Teacher presentations should effectively convey information, engage students, and enrich the learning process. While business presentations often focus on sales or data analysis, educational presentations aim to foster comprehension and spark curiosity. This article delves into the differences between teacher presentations and other presentation types, provides practical tips for educators, and shares design strategies for creating engaging teacher presentations. Additionally, we’ll highlight Prezi , a tool known for its format that offers a refreshing take on educational presentations.

Understanding teacher presentations
Purpose and audience.
The main objective of a teacher presentation is to educate. Whether the presentations are used to introduce new ideas, revisit old topics, or help students understand complex concepts, the main aim is to make the content easy to understand and interesting. In contrast, business presentations usually seek to convince or update stakeholders. A teacher presentation is tailored for the student audience. Ultimately, it should accommodate learning preferences, keep students engaged, and promote participation.
Design and structure
When preparing a teacher presentation, it’s crucial to maintain simplicity. Steer clear of overcrowding slides with information or incorporating flashy visuals that could divert attention from the main message. Opt for a balanced layout that leverages visuals to complement the delivery rather than overshadowing it. Using Prezi , with its non-linear format, empowers teachers to create compelling presentations that flow seamlessly and engage students effectively.
Tips for creating effective teacher presentations
1. know your audience.
Knowing the age, background knowledge, and learning preferences of your students is essential when creating a teacher presentation. Customize your material to suit their requirements, making sure it strikes a balance between being overly complicated and overly simplistic. When presenting to students, make sure to include plenty of visuals and interactive features, and focus on providing in-depth explanations and fostering discussions.
2. Focus on clarity and simplicity
Avoid cluttering your presentation with too much text or too many graphics. Use bullet points to break down information and keep the slides clean. Remember, presentation is a tool to support your teaching, not to replace your voice. The content on your slides should be clear, concise, and directly related to your lesson objectives.
3. Use engaging visuals and media
Using aids like pictures, videos, and diagrams can help improve comprehension and memory of information. Prezi enables you to design captivating presentations with zoom features that assist students in engagingly exploring the material. In contrast to slide decks, Prezi’s canvas offers a natural progression of content, simplifying the task of emphasizing relationships between ideas.
4. Encourage interaction
Incorporate interactive elements into your presentation to keep students engaged. Ask questions, use polls, or include discussion points that require student participation. Prezi’s format supports this by allowing teachers to zoom in on specific points for discussion, making the presentation feel more like a conversation than a lecture.
5. Rehearse and time your presentation
Practicing your presentation ensures that you can deliver it smoothly and confidently. Time your presentation to fit within the class period, leaving room for questions and discussions. A well-timed teacher presentation keeps students engaged and allows for a natural flow of information.
Things to keep in mind when creating a teacher presentation
When preparing a teacher presentation, it’s important to concentrate on developing a useful resource that improves student’s understanding. Here are some dos and don’ts to consider, especially when incorporating images and text, and designing the layout:
Teacher presentation dos:
Use high-quality visuals: Include clear, high-resolution images and graphics that support your lesson content. Visual aids can significantly improve understanding, especially for visual learners. Infographics, charts, and diagrams can be powerful tools to illustrate complex concepts.
Keep text minimal: When creating slides, opt for bullet points and concise phrases. Ensure that your slide content supports your spoken presentation rather than duplicating it. Also, highlight the points that students should keep in mind.
Incorporate multimedia: Use videos, audio clips, and animations where appropriate. These elements can help bring your lesson to life and maintain student interest. However, ensure that any multimedia used directly relates to and enhances the lesson.
Ensure consistent design: Maintain a consistent design throughout your presentation. Use the same font, color scheme, and layout style across all slides. Consistency helps create a professional look and makes the presentation easier to follow.
Use contrasting colors: Choose colors that contrast well, especially between text and background. This ensures that your content is easily readable, even from the back of the classroom. For example, dark text on a light background works well, as does light text on a dark background.

Teacher presentation don’ts:
Avoid overloading slides with information: Avoid overcrowding a slide with information. Too much content on one slide can be daunting for students, and it may distract from the key messages you intend to communicate. Strive for a clear design instead.
Don’t use distracting fonts or colors: Avoid using fonts or colors that clash. Opt for fonts and colors that improve visibility without taking attention from the content. Limit yourself to two or three fonts, and avoid using more than four colors in your presentation.
Don’t overuse animations or transitions: Avoid using too many animations or transitions when switching between slides. Although these elements can make the presentation engaging, excessive movement might become a distraction and take away from the educational material. It’s best to use them with intent.
Avoid irrelevant visuals: Avoid adding any pictures or illustrations that aren’t closely tied to the lesson. Even though visuals can improve a presentation, unrelated ones might perplex students and lessen the significance of your points.
Don’t neglect accessibility: Remember to take into account the learning requirements of students. Make sure your presentation is easy for all students to access by using clear fonts, including text for images, and providing transcripts for any video or audio materials.
By following these guidelines, you can create a teacher presentation that not only looks good but also effectively conveys your lesson material. Keep in mind that the aim is to leverage visuals and design features to enrich learning rather than detract from the information.
Exploring teacher presentation tools: spotlight on Prezi
When it comes to creating captivating teacher presentations, selecting the right tool is key. Although PowerPoint and Google Slides are commonly used, Prezi presents an option that can revolutionize the way educators deliver information.
What makes Prezi stand out?
Prezi’s unique presentation style allows educators to deliver information in a more captivating manner. Rather than following a slide progression, Prezi empowers teachers to explore various aspects of their presentations by zooming in and out, creating a storytelling experience rather than a traditional lecture. This method can engage students effectively and simplify subjects by visually emphasizing the relationships among concepts.

According to research from Prezi, this format is more engaging and memorable compared to traditional slide-based presentations. The study found that Prezi presentations are 25% more effective in keeping audience attention and 20% more effective in making content memorable.
Examples of engaging teacher presentations using Prezi
To illustrate how Prezi can be used effectively in the classroom, here are a few teacher presentation ideas that stand out:
Literacy Genres Prezi Video : This presentation gives a look at types of literary genres using Prezi’s zoom function to delve into each genre extensively. It serves as a method to familiarize students with ideas in an interactive and visually captivating way.
Board Game Lesson Plan Template : This template uses the concept of a board game to structure the lesson, making learning feel like an adventure. It’s perfect for gamifying lessons and keeping students excited about the material.
The Civil Rights Movement VOR : This presentation explores the background of the Civil Rights Movement, showcasing Prezi features to zoom in on events and individuals. It illustrates how Prezi can animate narratives effectively.
Back to School Template VOR : Ideal for the first day of school, this presentation helps teachers introduce themselves and outline class expectations in a fun and engaging way. It’s a great alternative to a traditional teacher introduction PowerPoint.
Light Book Report Template VOR : This is a creative template that inspires students to showcase their book reports, encouraging them to analyze and share their opinions thoughtfully.
For more inspiration, teachers can explore the Prezi Gallery’s Teacher Picks , which offers a variety of templates and examples designed specifically for educational purposes.
Additional teacher presentation ideas
Teacher introduction presentation.
At the start of the year, teachers have a chance to introduce themselves to their students. Using platforms like Prezi, educators can create a narrative that showcases their personality, teaching style, and what learners can expect in the course. Incorporating anecdotes and engaging elements helps in building a rapport with students from the beginning.
Interactive lesson recaps
To enrich learning, think about using Prezi for making summaries of lessons. When wrapping up a unit or lesson, a recap presentation can go over aspects, pose queries, and even incorporate a quiz to improve comprehension. This method strengthens the content and maintains student interest and active participation in their educational journey.
Virtual field trips
The increasing use of tools in education has made virtual field trips more popular as a means to explore the world without leaving the classroom. Teachers can now create tours using platforms such as Prezi, giving students a look at different locations and providing them with an engaging learning experience that improves their knowledge of geography, history, and science subjects.

Try Prezi for your next teacher presentation
In summary, preparing a teacher presentation entails capturing the needs of your audience, emphasizing clarity, promoting interaction, and sharpening your delivery skills. Through platforms such as Prezi, educators can enhance their presentations to captivate students with engaging content. Whether you’re introducing yourself at the beginning of the year, revisiting topics, or guiding students through a virtual excursion, a thoughtfully prepared presentation can enrich the learning experience and leave a lasting impact on your teaching.

Give your team the tools they need to engage
Like what you’re reading join the mailing list..
- Prezi for Teams
- Top Presentations

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend







IMAGES
COMMENTS
Page numbers in slides really don't provide any useful information -- they just remind your students how long they've been watching. 5. Go BIG. Pursuant to tips #1 and #2, you're not going to win awards by cramming the most content on the fewest slides. Make text and visuals as large as you can.
Presenting in a classroom doesn't have to be daunting. With proper planning, practice, and engagement strategies, you can deliver informative and memorable presentations. Remember, every presentation is an opportunity to improve your public speaking skills and make an impact on your audience.
The Ultimate Guide to Effective Teacher Presentations: Strategies & Tips. Dianne Adlawan. January 08, 2024. Teachers, by nature, are considered professional presenters. Their main responsibility is to talk in front of their students to relay educational knowledge, sharpen their minds and skills, and even serve as a second guide alongside their ...
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
1. Show Examples. One of the best ways to ease your students into the world of presentation is to inspire them! There are so many great examples of public speaking, from the vast library of TED talks to guest speakers you can invite into your classroom. Show examples of public speaking and discuss them. See what your students have to say and ...
Presence/Position/Posture: standing up straight conveys confidence and authority. Eye contact: helps you connect with your audience and keep your students engaged. You may tend to focus your gaze on a particular side of the classroom. Consciously make eye contact in a "W" pattern across the room.
When combined, these framed a rubric that supported students in optimizing their presentation deliveries. The competencies are as follows: 1. Content knowledge. The presenter must display a deep understanding of what they are delivering in order to share the "what, why, how, and how-to" of the topic. 2.
Here are some tips for teachers making presentations for in the classroom. See also 15 Presentation Tools for Teachers. 5 Teacher Tips For Better Presentations In The Classroom. 1. Establish one clear idea. ... As Six Minutes Speaking and Presentation Skills suggests, sometimes you don't need any slides. However, if you are going to give a ...
In the classroom, if you cannot communicate in a way that is both comprehensible and interesting to your students, their learning will be greatly reduced. To strengthen your presentation skills, focus on improving your skills in these three areas: Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication. Find out all you can about the room in which you will be ...
Last updated: May 18, 2022 • 2 min read. Body language, eye contact, and time management are all key to leading an effective presentation. Learn how to improve your presentation skills and confidence speaking in front of an audience.
Presentation Strategies. Effective communication is essential in the classroom and in the real world. Good presentation skills, including public speaking and the design of visual materials, can be learned. Following the best practices outlined in the videos and resources below will help you become more effective at communicating your ideas in a ...
Graphic Organizer Prompt 1: Create a poster, chart, or some other type of graphic organizer that lists the importance of good presentation skills for both the audience and the presenter. Example ...
1. Effective Communication: Effective communication is the backbone of all human interactions. Presentation skills equip individuals with the ability to convey information clearly, concisely, and persuasively. Whether it's explaining a project at work or delivering a compelling speech, the capacity to communicate effectively is indispensable.
Second, by giving their presentation three times in one day, students can practice and improve their oral presentation skills. I've circulated to catch at least part of every group's presentation each time. Most students have made improvements in pacing, length and even content in subsequent presentations. They've also seemed more relaxed ...
Presentations in the Classroom: A student confidently presents in front of a class. Crafting a compelling presentation requires thought into both the content and delivery. The content of your presentation should be clear, concise, and well-structured, ensuring that your key messages stand out.
Key Components of Presentation Skills. Planning and Preparation: This involves researching the topic, understanding the audience, and organizing the content in a logical flow.; Delivery: This includes the use of voice modulation, pacing, and body language to convey the message effectively.; Use of Visual Aids: Skillfully incorporating tools like PowerPoint slides, charts, and videos to support ...
Presentation skills are a worry for most people.And, let's face it…public speaking is a part of life (even if it's just life in middle school or high school). In fact, according to a Gallup poll, 40% of Americans indicated public speaking as their biggest fear.Snakes came in first place at 51%.
Presentation skills are extremely useful both in and outside the classroom. After completing a project, a presentation is a channel for students to share with others what they have learned. ... Classroom Management I find that presentation lessons pass very quickly, due the large amount of preparation involved. With a class of 20 students, it ...
The first one is that a professor keep in mind that the classroom communication behavior influences students' communication behavior. The professor serves as a viable role model. ... instructors customizing the strategies to fit the oral presentation skills specifically needed by his or her students. Some that may be considered are the course ...
Employers are demanding graduates with excellent communication (written, oral, and listening) skills. Thus, a student's presentation in the classroom becomes an important element in delivering ...
Toggle. Tip 1: Body Language (Face and Hands) Tip 2: Posture and Body Language When Presenting. Tip 3: Positioning Your Body When Presenting. Tip 4: Voice - Volume, Pitch, and Pauses. Tip 5: Fillers and Elocution. Tip 6: Making Use of Space in the Training Room or Classroom. Tip 7: Extra Presentation Skills Ideas. Be Concise.
Whether the presentations are used to introduce new ideas, revisit old topics, or help students understand complex concepts, the main aim is to make the content easy to understand and interesting. In contrast, business presentations usually seek to convince or update stakeholders. A teacher presentation is tailored for the student audience.
ESL has come a long way since the days of rote-learning and translation, and we now have the opportunity to develop skills which provide for a much more interactive model of presentation. Well, the teacher can do a great deal. ESL has come a long way since the days of rote-learning and translation, and we now have the opportunity to develop ...
This activity is also free for up to 10 people and is easy to personalize. . 6. The Get to Know You Game. This activity is one of the best presentation games if you have a small group that doesn't really know each other. The Get to Know You Game is a creative way to do introductions, and it's really simple.
This is not surprising. Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget ...