Paraphrasing and Summarizing Exercises with Answers

Paraphrasing and Summarizing are two skills that are highly useful for writers. With these two techniques, writers can get help creating their content and providing it to their readers in an easy-to-peruse way.
However, if you happen to be new to the field of writing, you could be a little unaware and untrained in both these skills. But don’t worry. Everyone starts out as a beginner.
In this post, we’re going to be looking at some paraphrasing and summarizing exercises along with their answers and explanations. By following along, you’ll get a good idea about how you can use these techniques in your own capacity.
Let’s begin!

What is Paraphrasing and Summarizing?
Before we get to the exercises, let’s digress a little and understand what paraphrasing and summarization actually are.
Let’s start with paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing is the process in which a particular piece of content is reworded and rephrased in such a way that it looks different from its original version but it has the same meaning and context.
A simple example of paraphrasing would be to change “John likes his cat” to “John adores his feline pet”. Paraphrasing can be as slight as merely changing some words in the text, or it can be as drastic as fully changing the tone, structure, order, and words of the content.
On the other hand, Summarizing is the process in which a piece of content is shrunk and shortened to about one-tenth of its original size. In this shortened version, the main idea and concept of the content is provided.
Summarization is usually used by authors and writers when they want to give a brief outline of a book or article to their readers.
Now that we’ve looked at the definitions of both, let’s move ahead to look at some exercises.
Paraphrasing Exercises (with Answers)
The main purpose of providing these exercises along with their answers is to help you understand what these techniques look like when they are implemented. Since we have explained their core definition above, you can try and work along the exercises to improve your skills a little as well.
Related: Difference Between Paraphrasing And Rephrasing
Paraphrasing Exercise # 1:
Here is a sample paragraph that we will be paraphrasing as an exercise. We’ll write the paragraph alone first, and then provide the answer after a brief explanation.
Sample Paragraph:
"John could not find the butter in his fridge. He went to buy some from the store. On coming back, he saw his cat sitting on the floor, smacking its lips. There was some yellow stuff smeared all around its face. Thus, John solved the mystery of the missing butter."
So, as we mentioned earlier, paraphrasing can be done simply and sparingly, or it can be done drastically.
One of the primary and basic ways of paraphrasing is to simply change some words in the provided content with their synonyms. This is, we reiterate, a very basic level of paraphrasing, and it is often very easy to see through it.
So, for this first exercise, we are going to be doing only that level of paraphrasing as a way to illustrate how it looks like.
Here is what the above paragraph looks like when paraphrased:
Paraphrased Paragraph:
"John could not locate the butter in the refrigerator. He went to purchase some from the shop. On coming back, he observed his cat sitting on the ground, licking its lips. There was some yellow material smeared all around its face. Hence, John solved the mystery of the missing butter."
While we are on this discussion, it will also be salubrious to understand that when changing words with their synonyms for the purpose of paraphrasing, you have to be careful that you pick those that don’t mess up the context and intent of the lines.
Paraphrasing Exercise # 2:
Moving on, let’s look at another paraphrasing exercise. Here is the paragraph that we will be using for this one:
"John’s cat got lost in the forest. He went looking for it in the night time. He heard some movement in one of the bushes. He put his hand in and felt the fur. He pulled the thing out, thinking it to be his cat. After coming home, he realized it was an angry raccoon."
We mentioned in the last exercise that the basic level of paraphrasing is to change some of the words in the given text with their synonyms. And we also mentioned how that sort of paraphrasing can be easily detected.
So, for writers who want to paraphrase something in such a way that it does not resemble its original form a lot, there’s a step further that they can go, and that is to change the sentence structures + phrases.
Essentially, by changing the phrases used in the content as well as the arrangement of the sentences, the overall look of the paraphrased piece looks very different. If someone wants to go even ahead of that, they can shuffle the sentence order as well.
Considering this type of ‘extensive’ paraphrasing, here is the answer to the paragraph given above:
"John’s cat went missing in the forest. He went to search for it when it was dark. He discerned some movement in the hedge. After putting his hand inside it, he felt some fur. Thinking that it was his cat, he pulled the animal out. It was only after coming home that he realized that it was a frustrated raccoon."
Read more: How And Why to Paraphrase Your Content?
Summarizing Exercises (with Answers)
Now that we have looked at the paraphrasing exercises, let’s move on to look at some for summarizing.
Just as we’ve looked at two types of paraphrasing above, we’ll also look at two different types of summarizing.
Actually, it’ll be better if we explain those two types before getting to the exercises.
Basically, there are two types of summaries . One of them is called extractive and the other is called abstractive .
In extractive summarization, the summary of a piece of content is generated merely by taking out some sentences from it and joining them together. This is usually the type of summaries that you get from automated tools.
When extractive summaries are created, there is no effort to understand the actual meaning and context of the text. Rather, the purpose is only to take some lines from it and join them together in such a way that they make sense.
On the other hand, abstractive summaries are those that are written using a completely new and different set of words, phrases and sentences than the content (that is being summarized). As opposed to extractive summarization, abstractive summarization involves understanding the meaning and context of the text, and then creating a completely new summary that features all those concepts and ideas.
Summarizing Exercise # 1 (Extractive)
In order to demonstrate and explain extractive summarization, we’re going to first write a paragraph here and then provide its summary afterwards:
Sample paragraph:
"John’s car broke down. He stopped by the road side and screamed at people to stop and help him. But no one stopped for him. He continued howling and howling for hours. People kept driving by. After getting tired, he picked up a sheet and wrapped it around himself. Then, he started spinning on his spot. He grew dizzy. He kept spinning and spinning until he fell asleep."
Now, since we have to use the “extractive” summarization technique here, we’ll create the summary using the lines and sentences used in the content itself.
"John’s car broke down. But no one stopped for him. Then, he started spinning on the spot. He kept spinning and spinning until he fell asleep."
Summarizing Exercise # 2 (Abstractive)
For this exercise, we will use the same para that we did above. However, the technique used for the summarization will be different.
Since we will be using the abstractive technique here, the summary will be created using different words and phrases as the original.
"John’s vehicle went phut. But, no one stopped their car to help him. After he was tired, he made himself dizzy by spinning and then went to sleep."
So, that’s about it.
If you were a little confused about paraphrasing and summarization techniques, hopefully you’re a little more confident about them now.
These skills can come in handy for writers in a lot of different situations. If you don’t have the hang of them already, you should try and get it as quick as you can.
Best 5 Paraphrasing Exercises
Read on to see our helpful paraphrasing exercises and tips in this article to get you started.
One of the most important skills you can hone as a student or writer is to paraphrase the words of other academics and experts effectively. Since new knowledge is built upon that which is already known, it makes sense that you’d want to reference the ideas of others in your work. However, this is often easier said than done. Paraphrasing, especially if you want to do it well, can be challenging.
Fortunately, as is the case with most other skills in life, you can improve your ability to paraphrase through practice. For instance, you can improve this skill by regularly doing paraphrasing exercises. As I was an academic for a long time in my life, I thought it might be helpful to those who have little or no experience in paraphrasing if I provided a list of paraphrasing exercises. If you’re such a person, I hope that this article will get you started on your journey toward mastering the art of paraphrasing. Your academic or writing career will undoubtedly be better off for it when you do.
The Art of Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing exercises and activities to help you master the skill, 1. broaden your vocabulary, 2. create a word map, 3. paraphrase in small chunks, 4. ways to paraphrase shorter and easier sentences, 5. imagine you’re explaining the source material to someone, helpful tips, 1. avoid plagiarism, 2. summarizing is not paraphrasing, 3. changing word order is not paraphrasing.
Although paraphrasing is an essential skill when writing papers, essays, or articles, it’s one that many find challenging to master. To paraphrase the words of others, you need first to comprehend their meaning, and then you need to express this meaning in your own words. To do this effectively requires a broad and sophisticated range of vocabulary and advanced grammar skills.
As stated in the introduction, you can improve your paraphrasing skills through paraphrasing exercises. Doing this will help you construct meaningful and original paraphrased sentences and increase the speed at which you work. Especially when you’re a student, reading, and paraphrasing the words of other scholars and experts can form a big chunk of your work. Learning how to paraphrase well and at a quick pace will enhance your academic experience and will open up your schedule for other activities, such as sports or parties.
Our paraphrasing vs. summarizing guide might be helpful.
Now that you know the importance of paraphrasing, let’s dive right in and look at some exercises and activities that can help you improve. Remember, as is the case when learning any other new skill, you need to engage with these exercises regularly.

Since you cannot paraphrase appropriately without a decent range of vocabulary, it makes sense to aim to add more words to your vocabulary bank constantly. Of course, if you’re an academic, you’ll want to focus on improving your academic vocabulary in your specific field. However, since academic language has a formal tone, you can add general terms to your vocabulary bank to help you express yourself more sophisticatedly. Examples of such words, for instance, are verbs such as “theorize,” “opine,” “constitute,” and “approximate.”
There are various ways in which you can enrich your academic vocabulary. These include:
- Keeping a word journal: A great way to learn new words is to carry a little book along with you, in which you can write down words that you don’t know. You can write down the word and then look up the meaning when you have time. It can also be helpful to construct your sentence with the word once you’ve jotted down its definition.
- Highlight words in texts: Whether you’re working with a physical copy of a text or a digital version, it’s good to highlight or underline words that you don’t know. You can then either write a definition of the words in the margin or, if you’re working with a digital copy, you can add a comment. Another good tip is to write by hand – people learn better when writing something by hand than if they typed the same information.
- Read as much as you can: Although this may be obvious, the best way to improve your vocabulary is to read as many books and articles as you can fit into your schedule. Even if you don’t have the time to look up the meaning of each word that you don’t understand, just seeing the word pop up in different contexts will help you work out the meaning for yourself over time. Apart from reading, you can also listen to podcasts or watch documentaries and news channels.
If you’re battling to paraphrase an original paragraph or sentence into your own words, it can be helpful to create a word map. You can, for instance, write a few complex words or phrases down on a piece of paper. Next, draw a box around each word or phrase, and leave enough space around each so that you can draw and link other boxes. As a next step, you can draw boxes in which you write the synonym of each word. You can also write down the definition of each word if you’re unsure of its meaning.
Next, you need to clarify the relationship between these words or terms. Draw arrows between them indicating patterns, correlation, or cause and effect. You can also add boxes between the original words or phrases in which you add other words, such as verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, or adjectives. Doing so can help you further explain the terms or link them meaningfully. Once you’ve added all the information you can think of, try to create a paraphrased sentence or paragraph from your word map.
A valuable way to learn how to paraphrase when you’re a beginner is to break sentences into smaller parts. For example, instead of paraphrasing a long and complex sentence, which can become overwhelming if you’re not used to this process, you can focus on shorter phrases. Let’s take a look at an example. Here, for instance, is a long and complex sentence:
“ Many impacts are unavoidable and will hit the world’s most vulnerable populations hardest, it warns — but collective action from governments to both curb greenhouse-gas emissions and prepare communities to live with global warming could yet avert the worst outcomes. “
You may find it challenging to paraphrase this sentence as a whole. However, breaking it into smaller chunks makes the task more doable. You can break this sentence up in the following way:
- Many impacts are unavoidable
- And will hit the world’s most vulnerable populations hardest, it warns
- But collective actions from governments
- To both curb greenhouse-gas emissions
- And prepare communities to live with global warming
- Could yet avert the worst outcomes
Remember, the sentence structure of your paraphrased version can and often will look different from the source. This means that you can form two or multiple sentences if this helps you create a meaningful paraphrased version, even if the original is one sentence.
If you want to practice your paraphrasing skills, you can do so by paraphrasing a sentence in two or three different ways. You can practice finding different synonyms, grammar, and sentence structures while retaining the meaning across all versions.
If you have time, you can do this exercise with longer sentences. However, it may be good to start by paraphrasing shorter sentences. Doing so will allow you to focus on finding multiple synonyms and different ways to write the same sentence.
Here’s an example:
“ Scientists know that bees are dying from a variety of factors. “
Paraphrased version 1:
“Experts maintain that the future of bees is in danger due to multiple causes.”
Paraphrased version 2:
“There are many different reasons why bees are going extinct, according to scientists.”
A helpful way of practicing paraphrasing while reading through articles or research papers is to recite your paraphrased version of some more complex sentences. Since the first step of paraphrasing is to ensure that you’ve correctly understood the source, repeating what you’ve just read in your own words can help you grasp the meaning of the source material.
You don’t need to use formal academic language and complex terms when doing this paraphrasing exercise. Instead, the aim is to repeat what you’ve read in plain and simple terms. Also, since you don’t need to write anything down for this paraphrasing exercise, it’s something you can regularly do while you’re reading through the source material.
It’s vital that you understand what you’re reading and that all the information is not just going over your head. Doing this exercise, primarily when you find yourself drifting off or having problems grasping a sentence, will ensure that you’ve understood the section you’ve read. At the same time, you get to practice your paraphrasing skills.
Here are some helpful tips to keep in mind while paraphrasing.
Even though you’re not using direct quotes when paraphrasing but rather stating another author’s ideas in your own words, you still need to reference their work. Failing to do so amounts to plagiarism, a serious offense, whether you’re producing academic work or an article for a web page.
The format you have to use when citing the work of others varies. For instance, in academic writing, you need to provide in-text citations and a list of references at the end of your essay, article, or thesis. The precise way you’ll write your in-text citations and list of references will be determined by the formatting style, whether this is APA , Harvard , Chicago , or MLA .
Although both tools or techniques involve using your own words to describe somebody else’s text, they are different. You need to retain the original work’s meaning with both techniques while using your own words. When you’re summarizing a work , you’re selecting only the most essential points of the text and rewriting these in your own words. This means that you provide a short overview of what a text is about.
It would be best to remain far more loyal to the source material with paraphrasing. You refer to specific ideas an author has provided to incorporate these into your work. To ensure that you’re not changing the original version too much or skewing the meaning the author intended to bring across, you have to rewrite actual sentences and paragraphs. You can’t just write a summary of large chunks of text.
Although this is a “technique” employed by lazy students, you should be aware that merely swapping around the word order of an original text does not constitute paraphrasing. It’s also not good enough to merely change a sentence from passive voice to active voice or vice versa.
Using either of these as your only paraphrasing method when rewriting somebody else’s words can amount to plagiarism since you’ve not used your own words or demonstrated your understanding of the source material. In such instances, you’d be better off simply rewriting the author’s exact words and placing these in quotation marks.
To learn more, check out our guide on paraphrasing vs. plagiarism .
Paraphrasing Exercises with Answers

If you are Looking for paraphrasing Exercises with answers, then this is the page for you!
Paraphrasing is one of the most accessible tools in the English language that allows you to create original content from scratch. Anyone can do a little bit of research of their own online and comfortably talk about their findings to make new articles or produce a research report. The scale of paraphrasing is quite an importance in the life of anyone who is into writing a lot of stuff. It is an acquired Academic skill which can be perfected with the help of some practice.
Note: If you are someone who has to write content in your day to day life regularly, then using our rewording website will help you to produce excellent articles instantly.
Let’s get back to our article, many of our readers have asked us about how one can get better at paraphrasing articles. The answer to that comes from the simple saying of practice makes perfect.
ABOUT PARAPHRASING
Paraphrasing can be put into simple words by just saying that it is the procedure of rewording information . It involves researching multiple sources online, and when one puts their understanding of the subject into their own words, It is known as paraphrasing. dig deeper and learn more about the meaning of paraphrasing .
HOW TO GET BETTER AT PARAPHRASING
To get better at paraphrasing , specific rules and regulations need to be followed while trying to create your content. Following these basic necessary steps will help you improve your technique at paraphrasing:
- Read the text thoroughly to understand it.
- When you feel that now you have enough knowledge about the subject, try to write a paraphrase about it.
- Speak your thoughts out while writing a paraphrase to write it better.
- Repeat steps 1 to 3 if you forget any essential topics from the original passage.
- After completing your paraphrase read the source material to confirm all topics have been mentioned in your paraphrase.
Paraphrasing Exercises
Here are a few paraphrasing exercises to help you practice your paraphrasing skills.
Exercise 1:
Original: Condenser microphones have been a part of society for a long time now. Because of their fantastic sound quality that has been little to no innovation in the mic industry for over 30 years now. The basics of condenser mic have remained the same which allow countless many new manufacturers to create great mic for low prices. One such example of this comes from China where the patent laws are quite loose. Now anyone can buy a decent condenser mic just under the price of a pizza.
Paraphrase: Condenser microphones have been around for a long time, maintaining the same technology for over 30 years due to their excellent sound quality. This stability has allowed many new manufacturers to produce high-quality mics at low prices. For instance, in China, where patent laws are lax, you can get a decent condenser mic for the price of a pizza.
Exercise 2:
Original: The advancements in artificial intelligence have revolutionized many industries, from healthcare to finance. Machines are now capable of learning and improving their performance without human intervention.”
Paraphrase: Artificial intelligence has transformed various fields, including healthcare and finance. Machines can now learn and enhance their performance independently.”
Exercise 3:
Original: Global warming is a pressing issue that affects every aspect of our lives. It is caused primarily by the increase in greenhouse gases due to human activities like deforestation and burning fossil fuels.
Paraphrase: Global warming impacts all areas of life and is a major concern. It’s mainly driven by higher greenhouse gas levels from activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels.
Exercise 4:
Original: Social media platforms have drastically changed the way we communicate and interact with each other. They provide instant access to information and allow people to stay connected regardless of their geographical location.
Paraphrase: Social media has significantly altered our communication and interactions. These platforms offer instant information access and keep people connected, no matter where they are.
Exercise 5:
Original: Eating a balanced diet is crucial for maintaining good health. It provides the necessary nutrients that our bodies need to function properly and helps prevent chronic diseases.
Paraphrased: A balanced diet is essential for good health. It supplies the vital nutrients our bodies need and helps prevent chronic illnesses.
Exercise 6:
Original: The rise of remote work has changed the traditional office environment. Employees now have the flexibility to work from anywhere, which has led to increased job satisfaction and productivity.
Paraphrase: “Remote work has transformed the typical office setup. Workers can now work from any location, boosting job satisfaction and productivity.”
Exercise 7:
Original: Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are becoming increasingly popular. They provide a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and help reduce our carbon footprint.
Paraphrase: Solar and wind power, as renewable energy sources, are growing in popularity. They offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and help lower our carbon footprint.
Exercise 8:
Original: Learning a new language can be challenging but rewarding. It opens up opportunities for personal and professional growth and helps you connect with people from different cultures.
Paraphrase: Learning a new language is tough but beneficial. It creates personal and professional opportunities and helps you engage with diverse cultures.
Here’s what I did to generate the paraphrased versions above:
- Read and Understand : Fully understood the original text.
- Identify Key Points : Identified the main ideas and key points.
- Rephrase : Used This tool to rewrote the sentences using different words and structures while keeping the original meaning intact.
- Simplify : Used simpler language and shorter sentences to enhance clarity.
- Maintain Context : Ensured the new version still made sense within the context.
Other Helpful Resources:
- Summarizing and Paraphrasing Examples
- When to Paraphrase ?
- The 10 types of paraphrasing
- The Best Paraphrasing tools and Apps
- How to Rewrite AI Generated Text to Human style ?
- ← Summarizing and Paraphrasing Examples
- When to Use Dashes Between Words? →
You May Also Like

Why Paraphrasing is Important?

Types of Paraphrasing
How is Paraphrasing Different From Summarizing
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
🍪 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understood our Privacy and Policy

Paraphrasing Worksheets

The Communist Manifesto

Restate The Passage

Synonymous Words

Make It Brief

Just The Main Idea


Key Details

Take Notes And Think

Listing Supporting Points
Learn The Process
Articulate The Structure

Paraphrase The Story

Conduct A Research

5 Wh And 1 H

Consulting Sources
All about these 15 worksheets.
Paraphrasing involves rephrasing the words of others to convey the same meaning in a new and original way. It’s an important skill to develop for writing essays, research papers, and for understanding complex texts. We work on a wide variety of skills including:
Passages to Paraphrase – These include short passages that students are asked to paraphrase. This helps students practice putting ideas into their own words.
Comparing Paraphrases – Students might be given an original passage and several paraphrased versions, and asked to identify the best paraphrase. This can help students understand what makes a good paraphrase.
Paraphrase and Original Side by Side – These include an original text and a paraphrase side by side, asking students to identify the similarities and differences. This can help students understand how to maintain the original meaning while changing the wording.
Originality Awareness – The focus here is on distinguishing between paraphrasing and plagiarism, teaching students the importance of changing the structure and words of the original text significantly, and of giving credit to the original source.
What Are the 3 Ways of Paraphrasing?
Here are three common techniques for paraphrasing:
1. Change the Word Order
Changing the sentence structure can be an effective way to paraphrase. Be careful to ensure that the new sentence still accurately represents the original meaning.
2. Use Synonyms
Replace words with their synonyms, but be careful about the words that have no exact synonym or whose meanings vary based on context. Always double-check to make sure that the synonyms fit the context and preserve the original meaning.
3. Change the Voice
If the sentence is in active voice, you can change it to passive voice, and vice versa. However, you should use this method judiciously as overuse of the passive voice can make your writing seem weak or awkward.
Let’s take an example sentence to illustrate these techniques:
Original sentence: “The cat chased the mouse.”
Change the Word Order: “The mouse was chased by the cat.”
Use Synonyms: “The feline pursued the rodent.”
Change the Voice: “The mouse was being chased by the cat.”
Remember, even when you paraphrase, you must provide appropriate citation. Paraphrasing is not just about changing words but about fully understanding and conveying the original idea in your own style. Even if you’ve put the idea into your own words, it’s still someone else’s idea, so it’s important to give credit where it’s due.
What Are the 5 Steps of Paraphrasing?
Step 1: Read and Understand the Original Text
First, thoroughly read the original text to ensure you fully understand the meaning. You might need to read difficult or complex texts several times before you grasp the core idea.
Step 2: Identify the Main Ideas
Once you understand the text, identify the main ideas that you want to include in your paraphrase. This step might involve taking notes or highlighting key points in the text.
Step 3: Write Without Looking at the Original
Put the original text aside and write the paraphrase in your own words. This helps to ensure that you’re not just substituting words with synonyms but truly expressing the idea in a new way.
Step 4: Compare With the Original
After writing, compare your paraphrase with the original text. Make sure you have accurately represented the main ideas and details, and that your paraphrase is significantly different from the original. Check that you haven’t inadvertently used the same phrases or sentence structures.
Step 5: Cite the Source
Even though you are paraphrasing, the ideas are still someone else’s, so it’s important to appropriately cite the source of the information. The citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) you use will depend on the academic discipline or the preference of your instructor or institution.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on April 8, 2022 by Courtney Gahan and Jack Caulfield. Revised on June 1, 2023.
Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas into your own words. Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning.
Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone’s exact words and putting them in quotation marks ). In academic writing, it’s usually better to integrate sources by paraphrasing instead of quoting. It shows that you have understood the source, reads more smoothly, and keeps your own voice front and center.
Every time you paraphrase, it’s important to cite the source . Also take care not to use wording that is too similar to the original. Otherwise, you could be at risk of committing plagiarism .
What is your plagiarism score?
Compare your paper with 99.3 billion webpages and 8 million publications.
- Best plagiarism checker of 2021
- Plagiarism report & percentage
- Largest plagiarism database
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
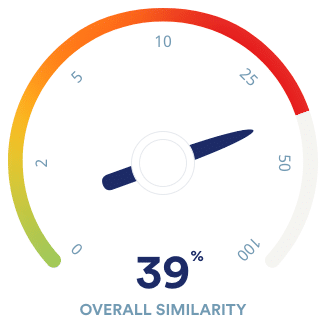
Table of contents
How to paraphrase in five easy steps, how to paraphrase correctly, examples of paraphrasing, how to cite a paraphrase, paraphrasing vs. quoting, paraphrasing vs. summarizing, avoiding plagiarism when you paraphrase, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about paraphrasing.
If you’re struggling to get to grips with the process of paraphrasing, check out our easy step-by-step guide in the video below.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Putting an idea into your own words can be easier said than done. Let’s say you want to paraphrase the text below, about population decline in a particular species of sea snails.
Incorrect paraphrasing
You might make a first attempt to paraphrase it by swapping out a few words for synonyms .
Like other sea creatures inhabiting the vicinity of highly populated coasts, horse conchs have lost substantial territory to advancement and contamination , including preferred breeding grounds along mud flats and seagrass beds. Their Gulf home is also heating up due to global warming , which scientists think further puts pressure on the creatures , predicated upon the harmful effects extra warmth has on other large mollusks (Barnett, 2022).
This attempt at paraphrasing doesn’t change the sentence structure or order of information, only some of the word choices. And the synonyms chosen are poor:
- “Advancement and contamination” doesn’t really convey the same meaning as “development and pollution.”
- Sometimes the changes make the tone less academic: “home” for “habitat” and “sea creatures” for “marine animals.”
- Adding phrases like “inhabiting the vicinity of” and “puts pressure on” makes the text needlessly long-winded.
- Global warming is related to climate change, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing.
Because of this, the text reads awkwardly, is longer than it needs to be, and remains too close to the original phrasing. This means you risk being accused of plagiarism .
Correct paraphrasing
Let’s look at a more effective way of paraphrasing the same text.
Here, we’ve:
- Only included the information that’s relevant to our argument (note that the paraphrase is shorter than the original)
- Introduced the information with the signal phrase “Scientists believe that …”
- Retained key terms like “development and pollution,” since changing them could alter the meaning
- Structured sentences in our own way instead of copying the structure of the original
- Started from a different point, presenting information in a different order
Because of this, we’re able to clearly convey the relevant information from the source without sticking too close to the original phrasing.
Explore the tabs below to see examples of paraphrasing in action.
- Journal article
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| “The current research extends the previous work by revealing that to moral dilemmas could elicit a FLE [foreign-language effect] in highly proficient bilinguals. … Here, it has been demonstrated that hearing a foreign language can even influence moral decision making, and namely promote more utilitarian-type decisions” ( , p. 874). | The research of Brouwer (2019, p. 874) suggests that the foreign-language effect can occur even among highly proficient bilinguals, influencing their moral decision making, when auditory (rather than written) prompting is given. |
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| “The Environmental Protection Agency on Tuesday proposed to ban chrysotile asbestos, the most common form of the toxic mineral still used in the United States. … Chlorine manufacturers and companies that make vehicle braking systems and sheet gaskets still import chrysotile asbestos and use it to manufacture new products. “The proposed rule would ban all manufacturing, processing, importation and commercial distribution of six categories of products containing chrysotile asbestos, which agency officials said would cover all of its current uses in the United States” ( ). | Chrysotile asbestos, which is used to manufacture chlorine, sheet gaskets, and braking systems, may soon be banned by the Environmental Protection Agency. The proposed ban would prevent it from being imported into, manufactured in, or processed in the United States (Phillips, 2022). |
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| “The concept of secrecy might evoke an image of two people in conversation, with one person actively concealing from the other. Yet, such concealment is actually uncommon. It is far more common to ruminate on our secrets. It is our tendency to mind-wander to our secrets that seems most harmful to well-being. Simply thinking about a secret can make us feel inauthentic. Having a secret return to mind, time and time again, can be tiring. When we think of a secret, it can make us feel isolated and alone” ( ). | Research suggests that, while keeping secrets from others is indeed stressful, this may have little to do with the act of hiding information itself. Rather, the act of ruminating on one’s secrets is what leads to feelings of fatigue, inauthenticity, and isolation (Slepian, 2019). |
Once you have your perfectly paraphrased text, you need to ensure you credit the original author. You’ll always paraphrase sources in the same way, but you’ll have to use a different type of in-text citation depending on what citation style you follow.
| (Brouwer, 2019, p. 874) | |
| (Brouwer 874) | |
| 1. Susanne Brouwer, “The Auditory Foreign-Language Effect of Moral Decision Making in Highly Proficient Bilinguals,” 40, no. 10 (2019): 874. https://doi.org/10.1080/01434632.2019.1585863. |
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Prevent plagiarism. run a free check..
It’s a good idea to paraphrase instead of quoting in most cases because:
- Paraphrasing shows that you fully understand the meaning of a text
- Your own voice remains dominant throughout your paper
- Quotes reduce the readability of your text
But that doesn’t mean you should never quote. Quotes are appropriate when:
- Giving a precise definition
- Saying something about the author’s language or style (e.g., in a literary analysis paper)
- Providing evidence in support of an argument
- Critiquing or analyzing a specific claim
A paraphrase puts a specific passage into your own words. It’s typically a similar length to the original text, or slightly shorter.
When you boil a longer piece of writing down to the key points, so that the result is a lot shorter than the original, this is called summarizing .
Paraphrasing and quoting are important tools for presenting specific information from sources. But if the information you want to include is more general (e.g., the overarching argument of a whole article), summarizing is more appropriate.
When paraphrasing, you have to be careful to avoid accidental plagiarism .
This can happen if the paraphrase is too similar to the original quote, with phrases or whole sentences that are identical (and should therefore be in quotation marks). It can also happen if you fail to properly cite the source.
Paraphrasing tools are widely used by students, and can be especially useful for non-native speakers who may find academic writing particularly challenging. While these can be helpful for a bit of extra inspiration, use these tools sparingly, keeping academic integrity in mind.
To make sure you’ve properly paraphrased and cited all your sources, you could elect to run a plagiarism check before submitting your paper. And of course, always be sure to read your source material yourself and take the first stab at paraphrasing on your own.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Critical thinking
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
To paraphrase effectively, don’t just take the original sentence and swap out some of the words for synonyms. Instead, try:
- Reformulating the sentence (e.g., change active to passive , or start from a different point)
- Combining information from multiple sentences into one
- Leaving out information from the original that isn’t relevant to your point
- Using synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning
The main point is to ensure you don’t just copy the structure of the original text, but instead reformulate the idea in your own words.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly cite the source . This means including an in-text citation and a full reference, formatted according to your required citation style .
As well as citing, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely in your own words and properly cite the source .
Try our services
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. & Caulfield, J. (2023, June 01). How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-paraphrase/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, how to write a summary | guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Prepositions
- Compound Words
- Infinitives
- Participles
- Interchanges
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
- Subject & Predicate
- Phrasal Verbs
- Sentence Patterns
- Idioms and Phrases
- Spot the Errors
- Punctuations
- American & British
- Questions Tags
- Reported Speech
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Rephrasing of Sentences
- Syllabification
- Types of Sentences
- Direct & Indirect
- Degrees of Comparison
- Prefix & Suffixes
- Figures of Speech
- Relative Clause
- REPHRASING SENTENCES
- Definition of Rephrasing
- Rephrashing Exercises
- My Vote For Rephrasing Sentences
- Good Average
REPHRASING ENGLISH GRAMMAR EXERCISES
Rephrase the following sentences using the ‘Starters’ given so that they express the same as the original sentences.
| 1. I would rather take Indian Medicine than Allopathic pills. ( ) : I’d prefer Indian medicine to Allopathic pills. | |
|---|---|
| 2. Andy is the cleverest boy in the class. ( ) : No other boy in the class is so clever as Andy. | |
| 3. I want to have that dictionary. ( ) : Could I have that dictionary? | |
| 4. I put the key in the lock and at once the dog sprang at me. ( ) : Hardly had I put the key in the lock when the dog sprang at me. | |
| 5. Scratch my back and I’ll scratch yours. ( ) : If you scratch my back I’ll scratch yours. | |
| 6. I reached the station on time because he helped me. ( ) : But for his help I would not have reached the station on time. | |
| 7. He is not only a thief but also a murderer. ( ) : Besides being a thief he is a murderer. | |
| 8. Your father is not so tall as you. ( ) : Your father is not so tall as you are. | |
| 9. She rarely left the house alone. ( ) : Seldom did she leave the house alone. | |
| 10. I have rarely seen anything so beautiful. ( ) : Rarely have I seen anything so beautiful. | |
| 11. In no other way can you succeed. ( ) : Only in this way can you succeed. | |
| 12. The door flew open suddenly. ( ) : Suddenly the door flew open. | |
| 13. When she will meet me next is uncertain. ( ) : It is uncertain when she will meet me next. | |
| 14. I think it’s going to rain. ( ) : It’s quite possible that it will rain. | |
| 15. Could you tell me anything about the blast in the central market? ( ) : Do you have any idea about the blast in the central market? |
The Participle
- Participle uses
- Present Participle
- Past Participle
- Adverbs of manner
- Adverbs of time
- Adverbs of place
The Pronoun
- What is a Pronoun?
- Personal Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Emphatic Pronouns
Learning Competency
Tenses The verb shows time by changing its form. These forms are called tenses.
|
| |

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A simple example of paraphrasing would be to change "John likes his cat" to "John adores his feline pet". Paraphrasing can be as slight as merely changing some words in the text, or it can be as drastic as fully changing the tone, structure, order, and words of the content. ... Paraphrasing Exercises (with Answers) The main purpose of ...
Summary. "Many thousands of Chinese are studying at schools in the United States. And writer Liel Leibovitz says the students are following an example that began in the eighteen seventies. Mr. Leibovitz and writer Matthew Miller joined forces to tell the story of the students in their book, "Fortunate Sons.".
Paraphrase Exercise. Please read the following passages carefully and paraphrase it. "In the United States, about six out of ten students in graduate schools are women. The same is true of today's young adults who already have a degree beyond college. As a result, the Census Bureau expects that more women than men will hold professions such ...
Paraphrasing refers to rewriting a given sentence using your own words. When we need to use a sentence in our writing that someone else wrote, we paraphrase it. That is, we use the same idea (s) in that sentence and write it differently. In addition to using different words, we use different grammar. The main purpose of paraphrasing has to do ...
Doing so will allow you to focus on finding multiple synonyms and different ways to write the same sentence. Here's an example: " Scientists know that bees are dying from a variety of factors. Paraphrased version 1: "Experts maintain that the future of bees is in danger due to multiple causes.". Paraphrased version 2:
Exercise 3: Original: Global warming is a pressing issue that affects every aspect of our lives. It is caused primarily by the increase in greenhouse gases due to human activities like deforestation and burning fossil fuels. Paraphrase: Global warming impacts all areas of life and is a major concern.
Example Paraphrase 7. "Over-the-top international fast-food items". Original source: "For some reason, cheese-topped donuts are quite popular in Indonesia, and in September 2013 KFC decided to get in on the action, offering a glazed donut topped with shredded Swiss and cheddar cheese.".
Paraphrasing makes a lengthy passage concise, but it can be tricky to make it original. Learn the correct way to paraphrase with these paraphrasing examples.
Before beginning this worksheet you should have completed the Principles of Paraphrasing online tutorial. The five quoted passages included in this worksheet are taken from the writings of HGSE faculty. Now that you have reviewed the rules for paraphrasing, you may want to test how well you are able to apply what you've learned to sentences ...
Step 2: Identify the Main Ideas. Once you understand the text, identify the main ideas that you want to include in your paraphrase. This step might involve taking notes or highlighting key points in the text. Step 3: Write Without Looking at the Original.
Quiz & Worksheet Goals. This paraphrasing quiz tests your ability to: Define paraphrasing. Understand what to do in order to avoid plagiarism. Recognize what happens in a paraphrase. Recall what ...
Here are sample answers for the paraphrasing exercise: According to Jacques Cousteau, the activity of people in Antarctica is jeopardizing a delicate natural mechanism that controls the earth's climate. ... One of the best examples of the anti-traditional trend was the proliferation of young "flappers," women who rebelled against custom by ...
Paraphrasing Created by: Heran Zhang 3 Paraphrasing Exercise (The answers are on the next page.) Directions: Write a paraphrase of each of the following sentences or passages. 1. The student requested that the professor excuses her absence, but the professor refused. 2. International Center is hosting English Conversation classes.
The best way to approach paraphrasing is to start by reading the work a few times. Now write an original thought based on what you have read. Make sure what you write keeps the nature and tone the author was originally trying to create. When you complete your paraphrase make sure to include a citation of where the original source is given credit.
Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning. Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone's exact words and putting them in quotation marks). In academic writing, it's usually better to integrate sources by paraphrasing instead of quoting. It shows that you have understood the ...
ans : Hardly had I put the key in the lock when the dog sprang at me. 5. Scratch my back and I'll scratch yours. (If) ans : If you scratch my back I'll scratch yours. 6. I reached the station on time because he helped me. (But for) ans : But for his help I would not have reached the station on time.
3. Of the more than 1000 bicycling deaths each year, three-fourths are caused by head injuries. Half of those killed are school-age children. One study concluded that wearing a bike helmet can reduce the risk of head injury by 85 percent. In an accident, a bike helmet absorbs the shock and cushions the head.
A collection of downloadable worksheets, exercises and activities to teach Paraphrasing, shared by English language teachers. ... My First Paraphrasing Exercises Level: intermediate Age: 13-100 Downloads: 35 : Paraphrasing Level: intermediate Age: 12-17 Downloads: 34 : Paraphrasing the sentences Level: intermediate
Paraphrase exercise. This is a letter sen. 189 uses. DarbyShaw. modal verbs paraphra. This exercise contai. 5829 uses. luchilasol. Paraphrasing for PET. This activity contai. 4064 uses. beagmeur. modals paraphrases K. Key to modals paraph. 726 uses. AimeeB. Hot Tips For Paraphr. A guide to help teac. 5980 uses.
small groups to understand and paraphrase content. Academic Skills Reading for main ideas Discussing or writing about main ideas Answering multiple-choice questions TOEFL Skills Comprehending the passage Choosing the best paraphrase of an original sentence Time 15-20 minutes Answer Key 1. b, 2. d, 3. c, 4. a. Answers will vary for items 5 and ...
Summary. 1. "Mr. Leibovitz and writer Matthew Miller joined forces to tell the story of the students in their book, "Fortunate Sons.". The book says China sent one hundred twenty boys to America to learn about developments that could help modernize their country." (American Documents the Country's First Exchange Students from China ...
6 Steps to Effective Paraphrasing. Reread the original passage until you understand its full meaning. Set the original aside, and write your paraphrase on a note card. Jot down a few words below your paraphrase to remind you later how you envision using this material. At the top of the note card, write a key word or phrase to indicate the ...