- 📝 VOCABULARY
- 🚀 GAMES/ACTIVITIES

Simple Present Tense (do-does) – With Usage, Pictures and Example Sentences

Simple present tense (present simple tense) is a verb tense that describes the events and situations that do not change over time. We use simple present tense for the actions that happen regualarly, and that is why we use some frequency adverbs to express these repititive actions. “ Do ” and “ does ” are the auxiliary verbs of present simple tense. However, “ do ” and “ does ” are not used in positive sentences. They are used only in negative and question sentences. The auxiliary verb “ does ” is used for third person singular ( He, She, It ). In other subjects ( I, You, We, They ), the auxiliary verb “ do ” is used. The following animated sentences are examples of present simple tense:

Examples with Pictures Dialogue exercise Sentence scramble game Translation exercise
⬤ Formation of simple present tense
For affirmative sentences we use the infinite form of the verb, but for negative sentences we use “ not ” after the auxiliary “do” and “does”. For questions we put “do/does” before the subject.
⬤ Which auxiliary (helping verb) to use for simple present tense?
The auxiliary verbs in simple present tense are “ do / does “. However we use “ am, is, are ” to talk about a general state or condition. Examples:
- I work in the office.
- I don’t work in the office.
- Do you work in the office?
- I am in the office.
- Are you in the office?
SIMILAR PAGES: ❯❯ Learn verb to be here ❯❯ Learn present continuous tense here ❯❯ Learn future simple tense (will) here ❯❯ Learn be going to future tense here ❯❯ Learn simple past tense here ❯❯ Learn past continuous tense here ❯❯ Learn present perfect tense here
⬤ Positive (Affirmative) sentences
For the formation of positive sentences in simple present tense we do not use “do” or “does” in front of the verb. This may sound strange. Because we know that the auxiliary verbs that precede the verbs help us understand the tense of the sentence. However, the verb is alone here. In addition, for the subjects “He, She, It”, the suffix “ -s ” is added at the end of the verb.
- I like pizza.
- We go abroad every summer.
- She speak s three languages.
- Lions eat meat.
- Oliver walk s to school.
- They play computer games.
- Maria prefer s action movies.
✎ NOTE: The verb “ have ” changes into “ has ” when it gets “-s” at the end.
- She has breakfast.
- She doesn’t have breakfast.
- Does she have breakfast?
✎ NOTE : In positive sentences, when the subject is “He, She, It”, we change “ -s ” into “ -es ” or “ -ies “. The reason is as follows:
- For the verbs ending with “ -s, -ss, -sh, -ch, -x, -o ” we add “ -es ” at the end of the verb. brush es , kiss es , catch es , fix es , go es , do es etc.
- If the verb has “ -y ” at the end and it precedes with a consonant letter, we drop the “-y” and add “ -ies ” try> tr ies , fly> fl ies , carry> carr ies etc.
⬤ Negative sentences
For the formation of negative sentences in simple present tense we use “ not ” together with “ do / does “. The short forms are “ don’t / doesn’t ”
- I don’t like cigarette.
- Sarah doesn’t need help.
- He doesn’t forget names.
- They don’t go out alone.
⬤ Interrogative sentences (questions)
For the formation of question sentences (interrogative) in simple present tense we put “ do / does ” before the subject. This also applies to the “ Wh- questions” which we call “information questions” as well.
- Do you like lemonade?
- Does she keep secret?
- Where do you live?
- Why does Molly wear pink dresses?
⬤ Sentence forms in simple present tense
| I speak | I speak | you speak? |
| You speak | You speak | you speak? |
| He speak | He speak | he speak? |
| She speak | She speak | she speak? |
| It speak | It speak | it speak? |
| We speak | We speak | we speak? |
| They speak | They speak | they speak? |
⬤ Example Sentences
- (+) They like basketball.
- (-) They don’t like basketball.
- (?) Do they like basketball?
- (?) What do they like?
- (+) He likes basketball.
- (-) He doesn’t like basketball.
- (?) Does he like basketball?
- (?) What does he like?
⬤ Explanations and usages of simple present tense
Lets go on with the explanations, usages and time adverbs of simple present tense
⬤ 1- Facts or generalizations.
It is used for events and situations that never change. Examples:
- People need food in this village.
- The wind blows a lot here.
- Trains carry many passengers.
- Smart phones cause some health problems.
- Water boils at 100C degrees.
- The earth revolves around the Sun.
- Lions don’t eat grass.
- Plants give us oxygen.
- Pandas live in China.
⬤ 2- Habits, routines or repeated actions.
We use simple present tense to talk about habits and routines. Examples:
- I get up at 8 o’clock every day.
- Do you drink coffee every day?
- She always brushes her teeth.
- Leo plays his guitar in his room.
⬤ 3- Likes and dislikes
We can also use simple present tense to talk about likes and dislikes. Some commonly used verbs are as follows: “like”,”love”, “hate”, “dislike”, “enjoy” etc. Examples:
- I love ice-cream.
- Do you like playing chess?
- She hates lies.
- Sandra doesn’t like tea with sugar.
- We like to swim.
- I dislike cold weather.
⬤ 4- Scheduled events in near future
- The train arrives at 9 AM.
- The bus arrives at 3 o’clock in the afternoon.
- When do we board the plane?
- When does the wedding ceremony start?
- The films starts at 8.30
- The bus arrives at 6PM.
- The English lesson starts at 10.30.
⬤ 5- With non-progressive verbs
Some verbs in English doesn’t have continuous forms. These verbs are called non-progressive or non-continuous verbs. We use simple present tense with these verbs. Some non-progressive verbs are: believe, know, remember, understand, need, hate, like, love, prefer, want, feel, mean etc. Examples:
- I know the answer. – CORRECT I am knowing the answer. – INCORRECT
- I want some sugar. – CORRECT I am wanting some sugar. – INCORRECT
- Brian feels cold. – CORRECT Brian isn’t feeling cold. – INCORRECT
- I don’t remember her name. – CORRECT I am not remembering her name. – INCORRECT
- Do you understand? – CORRECT Are you understanding? – INCORRECT
⬤ 6- Narrating events
Example: The man opens the door and goes out slowly. He looks around carefully. Then he sees a little cat under the tree. He grabs it and says “Oh. Are you hungry?”
⬤ Adverbs of Frequency
What are Adverbs of frequency? Simple present tense indicates repetitive actions, so it is good to say the frequency of these actions. In this case, we use some words called “Frequency adverbs”. These words are used just before the verb. This list of frequency adverbs is as follows:
⬤ List of frequency adverbs
- occasionally
- hardly ever
➔ Examples of frequency adverbs
Read the example sentences with the frequency adverbs and try to make similar sentences. Examples:
- I often eat eggs for the breakfast.
- I never smoke.
- Lisa always walks to school.
- Do you usually get up early?
- You hardly ever say “Thanks”.
- They don’t normally go out for dinner.
- My father often forgets my birthday.
- I generally have breakfast before I go out.
⬤ Memory cards to learn the adverbs of frequency
The cards below have adverbs of frequency. Click on them and try to say the meaning of them in your native language.
⬤ Time adverbs to use in simple present tense.
every ….
- I play football ever weekend.
- We go holiday ever summer.
- She gets up late every day.
once, twice, three times, ten times etc.
- I go to cinema once a month.
- She goes out with her friends twice a week.
- I call my son at least 3 times a day.
on Mondays, at the weekends, in the mornings
- I call my grandparents on Saturdays.
- In the evenings I take a taxi to go back home.
⬤ Verb to be (am, is, are)
We use am, is, are when we talk about a state rather than an action.
- ⬤ I work in London. (Action verb)
- ⬤ I am in London. (State verb)
➔ Action verbs examples (do, does)
- Frank works at the hospital.
- Frank doesn’t work at the hospital.
- Does Frank work at the hospital?
- Where does Frank work?
➔ Verb to be examples (am,is,are)
- Frank is at the hospital.
- Frank isn’t at the hospital.
- Is Frank at the hospital?
- Where is Frank?
⬤ Images and example sentences
Look at the images below and read the simple present tense sentences. Then try to understand the usage.
⬤ A dialogue example
Here is a dialogue to learn simple present tense. Read and try to make similar dialogues.
Do you go holiday every summer?
I like summer holidays very much.
Where do you go for holiday?
In fact, I don’t go to seaside.
I like camping in the mountains.
Where do you go for camping?
It is up to us.
We usually decide before we go.
If you want, you can join us.
⬤ Translate the sentences about simple present tense.
You will see some examples of simple present tense below. Translate them into your native language.
⬤ Sentence scramble game
You will see scrambled words of simple present tense sentences. Click on the words in the correct order to make meaningful sentences.
⬤ Example sentences to learn simple present tense
Here are examples of simple present tense in context below. Some are affirmative some sentences are negative and some are interrogative.
➔ 10 example sentences :
- I always get up early.
- I don’t like hot weather.
- Mr. Anderson usually forgets to lock the door.
- She keeps secrets.
- Cats don’t like swimming.
- She rarely writes emails.
- Steven looks happy.
- I like reading poems a lot.
- The children brush their teeth every day.
- When I buy something, I read the instructions.
⬤ Questions and answers
You will see 10 questions with their answers below. Try to understand the formation of the sentences.
➔ 10 questions and answers
- How do you go to school? I go to school by bus.
- Do you like ice-cream? Yes, I like ice-cream.
- Why do you always wear sunglasses? Because I have a problem with my eyes.
- Does your father help your mother at home? Yes, he does.
- What time do you go to bed? I go to bed at about 11 PM.
- Do you make noise in the classroom? No, I don’t.
- Where are you from? I am from Canada.
- How often do you watch TV? I sometimes watch TV.
- Do you agree with me? No, I don’t agree with you.
- Are you OK? Yes, I am OK.
⬤ Reading passage – Daily routine
My daily routine My name is Lydia Collins. I live in a flat. My day daily routine starts very early. Every morning I wake up at six o’clock and wear my school uniform. Then I have breakfast with my father and mother. My little brother doesn’t have breakfast with us. Because it is too early for him. After breakfast I go out and wait for the school bus. At about 7 AM I get on the bus. I come back home at 3 PM. I feel tired when I come back. I have a rest and play with Dody, our cat. Then I start doing my homework. I try to finish it before 7 PM. So that I can go out and play with my friends. We have dinner at 8 PM. We often have chicken for dinner but I hate chicken. I eat it because mum gets angry. After dinner I watch TV for an hour. I go to bed early because I’m always very tired at the end of the day.
External resources: You can also visit Wikibooks page to learn simple present tense , or watch a video for example sentences .
related pages
Fill in the blanks quiz for simple present tense, sentence scramble game for simple present tense, accessories vocabulary 👓 exercises pictures audio, body parts in english 👨 with games and listed images, classroom objects vocabulary in english 📕 with games, clothes vocabulary in english 👕 learn with images and flashcards, colour names in english 🎈 with tests and images, computer parts (hardware) vocabulary: pictures audio, verb to be (am, is, are) – with examples and online exercises, modal “can” – with explanations exercises and activities, present continuous tense – with usage examples and pictures, future simple tense (will) – with activities dialogue and exercises.
© www.english-learn-online.com All right reserved You can write us any mistakes or read our about page or see our privacy policy .
Search form
- A1-A2 grammar
Present simple
Daisy is chatting to her brother Oliver, and his best mate Alfie, about her new boyfriend. Daisy and Oliver’s mum is working in Thailand this week.
Instructions
As you watch the video, look at the examples of the present simple. They are in red in the subtitles. Then read the conversation below to learn more. Finally, do the grammar exercises to check you understand, and can use, the present simple tense.
Alfie: So, how’s it going with Jack? Daisy: Not great. I mean, I like him a lot, but it’s impossible! During the week I have swimming practice on Mondays, I do taekwondo on Tuesdays and tennis on Thursdays. Alfie: Do you see him on Wednesdays, then? Daisy: No, he watches black and white films at his cinema club on Wednesdays. Oliver: Yeah, and they’re not just really old films, Alfie, they watch foreign ones with subtitles too! Alfie: Well, there’s always the weekend. Do you go out together at the weekends? Daisy: That’s just it, it’s tricky. He works in the bookshop all day Saturday and he goes out with his mates from the book club on Saturday evenings. Alfie: Whoa! Book club? So, he loves old films and books!? Mmm ... Does he like sports? Daisy: Not really. He thinks chess is a sport! Well, he watches football on the telly sometimes, but he doesn’t play any sports. Alfie: Mmm ... I think you’re right. It’s impossible! Daisy: Right, I’m late. See you later. Alfie and Oliver: See you, Daisy.
Sophie: Hi, love. Oliver: All right, Mum? Sophie: Yeah, I’m fine. Oliver: Good trip? Sophie: Not bad, but Thailand’s really hot at this time of year. I’m off to Chiang Mai tomorrow to do a three-day trek. The train leaves at 5 in the morning. How’s Daisy? Is she with you? Oliver: No, she has tennis on Thursdays. Sophie: Ah, of course. No problem. Listen, ask Daisy to phone me later, OK? The number of the hotel is on the fridge and I’m in room 37. Oliver: All right, Mum. Speak later. Watch out for the snakes! Sophie: Thanks, Ollie! Bye, love. See you Sunday. Alfie: Is your mum in Thailand this week? Oliver: Yeah. Trekking in Chiang Mai for three days. Alfie: Wow – that beats going to college. Imagine, three days in the jungle! I can’t imagine my mum doing that. Cool. Does she like walking? Oliver: No, not really. Only if it’s to go shopping on the high street! Alfie: See you tomorrow. Oliver: Yeah, see you tomorrow.
We use the present simple to talk about repeated actions or events, permanent states or things which are always true. To find out more about the present simple, read and listen to the conversation below.
Can you give me some examples?
Yes, of course. We use the present simple to talk about things which are repeated every day, every week, every year, etc.
I usually get up at 7 o'clock. During the week I have swimming practice on Mondays, I do taekwondo on Tuesdays and tennis on Thursdays. We always go on holiday in the summer.
I see. And you use words for explaining more about the time too.
Yes, we often use adverbs of frequency sometimes , often , usually or other time expressions like on Mondays , twice a week or in the summer .
What about permanent states? What does that mean?
Permanent states are situations or feelings which are not temporary.
I like him a lot. Sophie works as a travel writer. They live in London.
We also use the present simple for general facts, for example when talking about science or geography.
Thailand is really hot at this time of year. Snakes live on the ground, in trees and in water.
So what do I need to know about forming the present simple?
The main thing is that the third person singular forms end in - s or - es . That's for he , she or it .
He watches black and white films at his cinema club on Wednesdays. He thinks chess is a sport!
OK, and the other forms don't end in - s or - es ? I watch TV a lot . We think Coldplay are boring .
What about questions and negatives?
For most verbs we use the present simple of the verb do/does + subject + infinitive without to to form questions.
Do you see him on Wednesdays then? Does Jack like sports?
For negatives we use the subject + do/does + not + infinitive without to .
Daisy and Jack don't go out together much at the weekend. I don't think Coldplay are boring.
To go back to the idea of permanent and temporary things, what about this sentence: Is your mum in Thailand this week? Isn't that temporary?
Yes, it is. That's a very good point. Normally we use the present simple for permanent states, and the present continuous for temporary states, but some verbs are thought of as State Verbs and they are not usually used in the continuous form.
And the verb to be is one of those verbs?
Exactly! So even though staying in Thailand is temporary, we use the present simple with the verb to be . Here's another example:
How' s Daisy? Is she with you?
But that isn't the question form you just told me about! Where's the do ?
Ah, no. I said 'for most verbs we use do in questions'. The verb to be is different and so are modal verbs like can . We'll look at the verb to be separately because it's different and very common.
What are the other state verbs?
We'll look at those when we look at the Present Continuous. Any more questions?
Yes, what about: The train leaves at 5 in the morning? Isn't that talking about an event in the future?
Yes, it is, but it's also a repeated event. This is sometimes called the 'timetable future'.
OK, I have a maths class in a minute, so I have to go.
Good use of the 'timetable future'! Bye!
Check your grammar: true or false - present simple
Check your grammar: multiple choice - present simple, check your grammar: gap fill - present simple, worksheets and downloads.
Tell us about your typical day. Remember to use the present simple!

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.

Present Simple Tense: How to Use It, With Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
On this page:
The present simple tense is a verb tense that is used to talk about actions or states that are habitual, repeated, or always true. It is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in English. The structure of a present simple sentence is:
Subject + base form of the verb
Let’s take a look at some examples to understand this better:
Example 1: I wake up at 6 am every day. This sentence expresses a habitual action. It means that the speaker wakes up at 6 am every day.
Example 2: She works as a teacher. This sentence expresses a present state. It means that the person is currently working as a teacher.
Example 3: He drinks coffee every morning. This sentence expresses a habitual action. It means that the person drinks coffee every morning.
Example 4: The sun rises in the east. This sentence expresses a fact that is always true. It means that the sun always rises in the east.
Example 5: I like to read books. This sentence expresses a habitual action. It means that the speaker likes to read books regularly.
How to form the simple present?
Let’s take a look how we form simple present.
Step 1: Identify the base form of the verb The base form of the verb is the infinitive form without “to” (e.g., play, eat, work). It is the form of the verb that is used to form the simple present tense.
Example: John plays tennis every day.
Step 2: Add “-s” or “-es” to the verb To form the simple present tense, we need to add “-s” or “-es” to the base form of the verb, depending on the subject of the sentence. We add “-s” to the verb when the subject is a singular third-person pronoun (he, she, it) and “-es” when the verb ends in “s,” “sh,” “ch,” “x,” or “o.”
- John plays tennis every day. (singular third-person subject “John”)
- She eats breakfast at 7 am. (singular third-person subject “she”)
- The dog barks at the mailman. (verb “bark” ends in “k,” so we add “-s”)
- He washes the dishes after dinner. (verb “wash” ends in “sh,” so we add “-es”)
- The bus passes by my house every morning. (verb “pass” ends in “s,” so we add “-es”)
Step 3: Irregular verbs Not all verbs follow the same rules when forming the simple present tense. Some verbs have irregular forms that must be memorized. For example:
I have breakfast at 8 am. (verb “have” does not follow the “-s” or “-es” rule)They go to the movies every Friday. (verb “go” has the same form for all subjects)
How to make the simple present negative?
To make the simple present negative, we need to add the word “not” after the auxiliary verb “do.”
Step 1: Identify the auxiliary verb “do” The auxiliary verb “do” is used to form questions, negatives, and emphasis in the simple present tense. It is important to identify this verb in a sentence to make the negative correctly.
Step 2: Add “do not” or “does not” To make the simple present negative, we need to add “do not” or “does not” after the auxiliary verb “do.” The word “not” negates the verb in the sentence.
Examples:
- John does not play tennis every day.
- They do not eat meat.
- She does not work on Sundays.
Step 3: Contracting “do not” or “does not” It is common to contract “do not” to “don’t” and “does not” to “doesn’t” in spoken English. This is unnecessary but it can make the sentence sound more natural.
- John doesn’t play tennis every day.
- They don’t eat meat.
- She doesn’t work on Sundays.
Step 4: Using negative adverbs Negative adverbs can also be used to make the simple present negative. Some common negative adverbs include “never,” “rarely,” “hardly ever,” and “not often.” These adverbs are placed before the main verb in the sentence.
- John never plays tennis.
- They rarely eat meat.
- She hardly ever works on Sundays.
Making the simple present negative in English is a straightforward process that requires adding the word “not” after the auxiliary verb “do.” Remember to identify the auxiliary verb and contract “do not” or “does not” if necessary. You can also use negative adverbs to add emphasis to the negative.
How to ask a question?
Step 1: Identify the auxiliary verb To form questions in the simple present tense, we need to use the auxiliary verb “do” or “does.” We use “do” for first-person and second-person subjects (I, you, we, they), and “does” for third-person singular subjects (he, she, it).
- Do you like pizza? (first-person subject “you”)
- Does she play tennis? (third-person singular subject “she”)
- Do they have a car? (third-person plural subject “they”)
Step 2: Invert the subject and auxiliary verb To form a question, we invert the subject and auxiliary verb. The subject comes after the auxiliary verb in a question.
- You like pizza. (statement)
- Do you like pizza? (question)
- She plays tennis. (statement)
- Does she play tennis? (question)
- They have a car. (statement)
- Do they have a car? (question)
Step 3: Answering questions When answering a question in the simple present tense, we use the auxiliary verb and the base form of the verb.
- Do you like pizza? – Yes, I do. / No, I don’t.
- Does she play tennis? – Yes, she does. / No, she doesn’t.
- Do they have a car? – Yes, they do. / No, they don’t.
Step 4: Tag questions A tag question is a short question added to the end of a statement to confirm or seek agreement. In the simple present tense, we use the auxiliary verb and the subject pronoun.
- You like pizza, don’t you? (tag question with the first-person subject “you” and the auxiliary verb “do”)
- She plays tennis, doesn’t she? (tag question with the third-person singular subject “she” and the auxiliary verb “does”)
- They have a car, don’t they? (tag question with the third-person plural subject “they” and the auxiliary verb “do”)
Common verbs in the simple present
1. to be: The verb “to be” is used to describe a state or condition, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe a permanent state or condition. Example: She is a doctor.
2. to have: The verb “to have” is used to indicate possession or ownership, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe something that someone has or possesses.
Example: He has a car.
3. to do: The verb “to do” is used to indicate an action or an activity, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe routine activities.
Example: I do my homework every day.
4. to go: The verb “to go” is used to indicate movement from one place to another, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe regular movements.
Example: They go to the gym every morning.
5. to come: The verb “to come” is used to indicate movement towards a person or a place, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe regular movements.
Example: She comes to work early every day.
6. to like: The verb “to like” is used to indicate preference or enjoyment, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe someone’s preferences or likes.
Example: He likes to play soccer.
7. to love: The verb “to love” is used to indicate strong affection or attachment, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe someone’s feelings towards another person or thing.
Example: She loves to read books.
8. to hate: The verb “to hate” is used to indicate strong dislike or aversion, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe someone’s feelings towards another person or thing.
Example: He hates to do housework.
9. to want: The verb “to want” is used to indicate desire or a wish, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe someone’s desires or wishes.
Example: She wants to travel the world.
10. to need: The verb “to need” is used to indicate a requirement or necessity, and it is often used in the simple present tense to describe something that someone needs.
Example: He needs to finish his work on time.
The verb to be in the simple present
The verb “to be” is one of the most important verbs in English and is used to describe a state of being or existence. In the simple present tense, “to be” is conjugated differently depending on the subject of the sentence. In this article, we will discuss how to use the verb “to be” in the simple present tense.
Positive form: The positive form of the verb “to be” in the simple present tense is as follows:
- He/She/It is
- I am a teacher.
- You are my friend.
- He is a doctor.
- She is at the park.
- It is a beautiful day.
- We are students.
- They are happy.
Negative form: The negative form of the verb “to be” in the simple present tense is formed by adding “not” after the verb “to be”. The contraction “isn’t” or “aren’t” can be used instead of “is not” or “are not”.
- You are not / You aren’t
- He/She/It is not / He/She/It isn’t
- We are not / We aren’t
- They are not / They aren’t
- I am not a doctor.
- You are not my teacher. / You aren’t my teacher.
- He is not at home. / He isn’t at home.
- She is not happy.
- It is not raining.
- We are not hungry. / We aren’t hungry.
- They are not tired. / They aren’t tired.
Interrogative form: To form a question in the simple present tense with “to be”, invert the subject and the verb “to be”. “Am” is used instead of “is” or “are” in questions with “I”.
- Is he/she/it?
- Are you coming to the party?
- Is he a good singer?
- Are we ready to go?
- Are they from Canada?
Present Simple Examples
Here’s a simple story that uses the present simple tense:
Tom wakes up early every morning. He gets out of bed, stretches, and puts on his running shoes. Then he goes for a run around his neighborhood. Tom likes to listen to music while he runs. He usually listens to upbeat pop songs that give him energy. Sometimes he sings along, but only when there’s nobody else around. After his run, Tom takes a shower and gets dressed for work. He works at a software company where he writes code all day. He enjoys his job because he loves solving problems and creating new things. In the evenings, Tom likes to relax at home. He usually watches TV or reads a book. He also enjoys cooking, and he often makes dinner for himself and his girlfriend, Sarah.
In this story, the present simple tense is used to describe things that happen regularly or habitually. For example:
Tom wakes up early every morning. He gets out of bed, stretches, and puts on his running shoes. Then he goes for a run around his neighborhood. Tom likes to listen to music while he runs. He usually listens to upbeat pop songs that give him energy. After his run, Tom takes a shower and gets dressed for work. He works at a software company where he writes code all day. In the evenings, Tom likes to relax at home. He usually watches TV or reads a book. He also enjoys cooking, and he often makes dinner for himself and his girlfriend, Sarah.
Note that the verb is in the present simple tense in each of these sentences. This is because these actions happen regularly or habitually, rather than being a one-time event in the past or future.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

How To Teach The Present Simple Tense | Step By Step
The present simple tense can be used in many different ways and so teaching the present simple tense to beginner English language learners can be quite challenging. The main goal when teaching the present simple tense should be to get your students to understand when to use the present simple tense. So, in what situations do we use the present simple tense?
To help you teach the present simple tense we have put together this step by step guide to teaching the present simple tense. In this post you’ll also find links to free resources and exercises to teach the present simple tense.
How To Teach The Present Simple Tense
Step 1: action verbs.
Alternatively, if your students are absolute beginners you can use these action verb flashcards to teach them some common verbs.
Step 2: First Person Singular Form
Next, in front of each verb you have written on the board write ‘I’ and practice saying each of these verbs together with ‘I’. For example, “I read. I write. I eat. I run.”, etc.
Do the same for other daily actions / routines and write these examples on the board. Some example present simple sentences you can elicit are:
Once students have practiced enough introduce the second person singular form.
Step 3: Second Person Singular.
To demonstrate this form to students ask one student “What time do you get up?” and that student will answer something like “I wake up at 7 o’clock.”.
After demonstrating the second person singular form of the present simple tense, go around the class and ask different students different questions. Each time they answer encourage the rest of the class to point at the student and make a present simple sentence in the second person singular form.
Step 4: Third Person Singular
Now that students have had plenty of practice making present simple tense sentences it is time to introduce the third person singular form. Explain to students that when talking about someone (singular) in the third person, the verb changes.
Students will likely notice that you added an ‘s’ to the verb ‘get’. Once students understand that when talking in the third person singular that they should ad s / es to the root form of the verb, get students to practice making these sentences themselves.
Step 5: Plural Forms
A great way to do this is by asking the whole class some simple questions. For example, ask students if they like a certain food (let’s say sushi) and ask them to raise their hand / move to one side of the room if they do. Then point at this group and say “ They like sushi.” Ask the rest of the class to do they same. Then, join those students and say “ We like sushi.”
Step 6: Negative Present Simple Sentences
A fun way to practice this is to give students a few minutes to ask their partner about food / activities that they like or don’t like. Then go around the class and ask students to tell you about what their partner likes or doesn’t like.
Step 7: Present Simple Exercises
To review everything students have learned and to check their understanding, ask students to complete some present simple exercises.
It may take your students time to master the present simple tense, and it is probably best to introduce the different forms of the present simple tense over several lessons to give them plenty of time to practice.

Present simple exercises
Negative forms
Questions - exercises
Mixed forms
Intermediate level
Worksheets - lessons
Present simple
Worksheets - pdf exercises.
- Simple present tense - pdf exercises
- Worksheet - questions pdf
- Present simple - pdf exercises
- Present simple - handout pdf
- Present simple exercises - answers
- Simple present worksheets -> answers
- Present simple - worksheets
- Present simple - negative
- Present simple - questions
- Simple present 2 -> answers
- The present simple - handout
- Affirmative, negative, questions
- Exercises : worksheets / handouts
- Present - worksheet pdf
- Worksheets pdf - print
- Grammar worksheets - handouts
Lessons - resources - videos
- Simple present tense - rules
- Present simple explanations
- Present tense - third person - rules
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer
learnEnglish-online
Learn English Online for Free
Main navigation
Simple present exercise – english grammar exercises, simple present exercise, quiz-summary.
0 of 1 questions completed
Information
Fill in the blank with the correct word.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
0 of 1 questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, ( 0 )
| Average score | |
| Your score |
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
1 . Question
Fill in the blanks with the correct word.
- Simple Present Sentences 1. She (plays) (play) baseball on Saturday. 2. We (live) (live) in an apartment. 3. The boys (eat) (eat) breakfast at 7 am. 4. He (has) (have) two brothers. 5. My mother (likes) (like) romantic movies. 6. Pedro (makes) (make) dinner every day. 7. Cynthia and Ramon (work) (work) on Monday. 8. I (go) (go) to school at 8 am. 9. The computer (is) (be) broken. 10. My brother and I (watch) (watch) TV at night. 11. Susana (tries) (try) to learn new things every day. 12. My father (runs) (run) on Saturday morning. 13. I (have) (have) three brothers. 14. Adriana (thinks) (think) pizza is delicious. 15. The girls (want) (want) more pasta. 16. She (gives) (give) money to charity. 17. The computer (works) (work) without a cable. 18. The Toronto zoo (opens) (open) on Saturday. 19. The teacher (helps) (help) the students after class. 20. Everyone (needs) (need) a pen. Negatives 21. I (do not want, don't want) (no, want) juice. 22. Sheila (is not, isn't) (no, be) happy. 23. Daniel (does not write, doesn't write) (no, write) on his tablet. 24. The girls (are not, aren't) (no, be) hungry. 25. My dog (does not sleep, doesn't sleep) (no, sleep) in the house. 26. Veronica (is not, isn't) (no, be) a nurse. 27. Paris (is not, isn't) (no, be) in Africa. 28. My teacher (does not give, doesn't give) (no, give) us homework. 29. The store (does not open, doesn't open) (no, open) on Sunday. 30. Pete (does not like, doesn't like) (no, like) sushi. Questions Fill in the blanks with the correct question words. Your options are do, does, am, is, and are. 31. (Do) you like pizza? 32. (Are) they ready? 33. (Does) your father work on the weekend? 34. (Is) my book in the class? 35. (Are) you a doctor? 36. (Do) they need more coffee? 37. (Are) your parents at home now? 38. (Is) the cat in the kitchen? 39. (Am) I in this class? 40. (Does) she need to bring a book? The Verb to Be Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb to be. Your options are am, is, and are. 41. I (am) a teacher. 42. She (is) my sister's friend. 43. My children (are) at school now. 44. The dogs (are) 3 years old. 45. The men in my office (are) older than me. 46. Everyone (is) in the kitchen. 47. The people (are) in the street. 48. My brothers (are) both engineers. 49. Chris (is) very tall. 50. Dan and Meghan (are) friends.
More Simple Present
Would you like more practice with the simple present? Here is more material:
Simple Present Test 1 Simple Present Test 2 Simple Present Questions Test
Here is a reading test you can use to practice your reading comprehension.
Simple Present Reading Test
This song by Coldplay helps you practice your listening skills and the simple present verb tense:
Simple Present Listening Exercise
Start Your Free English Course Today!
Grammar Writing Listening Reading Vocabulary
IELTS TOEFL TOEIC Business English

Chapter 3: Simple Present
Daily Habits & Routines

Learning Goals
At the end of this chapter you should be able to:
- Add -s for the third person singular verb
- Write yes/no questions and short answers
- Write information questions using wh- question words
- Add the plural marker -s ,-es, and -ies to verbs and nouns
Recognize and use
- the simple present in the affirmative and negative
- adverbs of frequency

Activity 3.1: Conversation
Directions: Ask your partner or group the following questions about your morning routines. A “routine” is a habit you usually do or a series of actions you do regularly.
- What do you do before school?
- Do you ever wake up late? Do you usually wake up early?
- Do you drink coffee or tea in the morning?
- Do you do your homework in the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening, or at night?
- How long does it take for you to get ready in the morning?
- How long does it take you to get to campus? Do you live close or far from campus?
- How do you get to campus? Drive? Bike? Bus? Walk? Carpool? Dropped-off?

Directions: Read this story out loud with a partner. One person reads a paragraph, then the other person reads the next paragraph. When you are finished, read the story again. This time, read the paragraphs, you did not read.
Yuri & Palani
Hi! My name is Yuri. I am from Ukraine. I am a student at Clackamas Community College. I have a roommate. His name is Palani. He is from Laos. We live together, but we are very different.
I wake up early at 6:00 am. Palani pushes the snooze button on his alarm clock many times, so he wakes up very late. He gets up at 7:30 am. I take a shower in the morning, but Palani takes a shower at night. I take a shower at 6:15 am. He takes a shower at 9:00 pm. I eat breakfast at home, but Palani doesn’t eat breakfast. I make coffee, and I eat cereal for breakfast. I bike to school, but Palani drives to school. I am never late. I leave at 7:30 am. Palani leaves at 7:50 am. I arrive at school early, but Palani arrives late. I arrive at school at 7:45 am. Palani arrives at 8:05 am. Palani sometimes arrives late because he can’t find parking. We are friends, so I always save him a seat next to me. We sit with Jacques and Ana. They arrive early too. Class begins at 8:00 am.
How often do you arrive late to class? Are you similar to me, or are you more similar to Palani?
Activity 3.2: Comprehension
Directions: Please write the answers to the questions in complete sentences.
1. What is the name of the man who is talking?
___________________________________________________________________
2. What is the name of his roommate?
3. What is Yuri comparing?
4. Who wakes up early? Who wakes up late?
5. What time does class begin?
6. Who arrives late? Who arrives on time?
7. How about you? Are you an early riser or a late riser?
8. What time does Yuri wake up? What time does Palani wake up?
Activity 3.3: Noticing
Part 1 Directions: Look at the story about Yuri and Palani. Choose (by underlining or otherwise markin g) the verbs you find. Don’t choose the BE verb. We are not studying that verb in this chapter.
Part 2 Directions: Complete the table with the verb forms that agree with each subject.
| Verb | Subject | Form |
|---|---|---|
| 1. wake up | I | |
| He/Palani | ||
| 2. take | I | |
| He/Palani | ||
| 3. leave | I | |
| He/Palani | ||
| 4. arrive | I | |
| He/Palani |
Activity 3.4: Try It Out!
Directions: Write the correct simple present tense form of the verb (in parentheses) on the line.
1. I (wake up)_________________________ at 6:00 am.
2. He (wake up)_________________________ at 7:30 am.
3. You (eat)_________________________ breakfast on the bus.
4. They (take)_________________________ a shower before bed.
5. He (take)_________________________ a shower in the morning.
6. We (go) _________________________ to a restaurant for lunch.
7. She (have)_________________________ cereal for breakfast.
8. His class at Oregon City (begin)_________________________ at 9:00 am.
9. My classes at Harmony (begin)_________________________ at 6:00 pm.
10. She (wash) _________________________ the dishes in the morning.

Uses of the Simple Present
The simple present is used for talking about routines, habits, and repeated activities in the present time. We use the simple present to talk about facts, which are always true. Time expressions (e.g., every day, in the summer ) and adverbs of frequency (e.g., never, sometimes, always ) signal the simple present tense.
What is a routine? Something you do every morning, every week, every year.
- I brush my teeth two times a day.
- You go to the gym three times a week.
- He makes breakfast for my children every morning.
- She starts work at 7:00 am.
- They do laundry every Saturday.
What is a habit? Something you do regularly.
- My husband reads in bed before he goes to sleep.
- My cat wakes me up on Saturdays because he is hungry.
What is a repeated action? Action that we do more than once.
- I shop at Winco (not every week, but I like to go there).
- She wears shorts in the summer.
What is a fact? Something that is always true.
- The moon revolves around the earth.
- She has two children.
- Vegetables are healthy.
- Water boils at 212 degrees Fahrenheit.
Forms of the Simple Present
Affirmative statements in the simple present.
You must add an -s to the verb with the subjects he , she , and it .
subject + verb
| Subject | Verb |
|---|---|
| I You We They | walk. |
| He She It | walks. |
Activity 3.5: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of the verbs in parentheses.
1. Yuri (wake up)______________ at 6:00 am.
2. Palani (drive)______________ to school.

4. Yuri (make)______________ coffee.
5. I (cook)______________ breakfast.
6. She (eat)______________ cereal.
7. Palani (take)______________ a shower in the evening.
8. They (carpool)______________ together.
9. She (ask)______________ for a pencil.
10. Yuri and Palani (attend) ______________ Clackamas Community College.
11. We (attend) ______________ Clackamas Community College.
12. I (take)______________ a shower in the morning.
13. He (make)______________ and (drink)______________ coffee every morning.
14. She never (arrive)______________ late.
15. Class (begin)______________ at 11:30 am.
16. He usually (find)______________ parking easily.
17. Palani (live)______________ with Yuri.
18. They (brush) ______________ their hair in the morning.
19. We (brush)______________ our teeth twice a day.
20. My cats (sleep)______________ all day.

Activity 3.6: Listening
Directions: Read the paragraph. Then, listen to your instructor read the paragraph. Listen for the verbs and write them on the line. Listen closely for the correct form of the verb.
Ana and Pedro’s Morning Routine
Ana and Pedro (1)__________ at 6:00 am. Ana (2)__________ coffee. Her brother, Pedro, (3)__________breakfast. She (4)__________a shower at 6:30 am. Her brother (5)__________ a shower at 7:00 am. They (6)__________ and (7)__________ their teeth. Ana (8)__________ the cat. Ana (9)__________ her hair and (10)__________ makeup. Pedro (11)__________ his hair. Ana’s book bag (12)__________ready. Pedro (13)__________ his books in his backpack. Ana (14)__________lunches. Class (15)__________ at 9:00 am. Ana and Pedro (16)__________ the house at 8:30 am. They (17)__________ at school at 8:45 am. Ana (18)__________ out books from the college library before class. She always (19)__________ good books to read. Ana and Pedro (20)__________ to class at 8:55 am. Their first class (21)__________ at 10:50 am.
Activity 3.7: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Interview your partner.
1. Where do you live?
2. What time do you wake up?
3. When do you eat breakfast?
4. What do you eat for breakfast?
5. How do you get to school (walk, bus, car, etc.)?
6. What time do you go to school?
7. What time do you get home?
8. When do you go to bed?
Part 2 Directions: Write 8 sentences about your own daily routine using the same questions.
1. ________________________________________________________________
2. ________________________________________________________________
3. ________________________________________________________________
4. ________________________________________________________________
5. ________________________________________________________________
6. ________________________________________________________________
7. ________________________________________________________________
8. ________________________________________________________________
Part 3 Directions: Share and compare your daily activities. Read your sentences to your partner. Your partner reads to you. See if you have the same (or different) daily activities.
Part 4 Directions: Your instructor will give you a Venn Diagram to complete. Write sentences about yourself where it says You. Write sentences about your partner where it says Partner. If you and your partner have any activities that are the same, write them where it says both.

Adverbs of Frequency with the Simple Present
Adverbs of frequency (AoF) let us talk about how often we do something.
How often do you come to class? I always come to class!
How often do you shop at Fred’s? I often shop at Fred’s.
Study the chart below to learn the meanings of the following adverbs.
| Adverb | Frequency |
|---|---|
| always | 100% |
| usually | 70-90% |
| often | 50-60% |
| sometimes | 30-40% |
| seldom/rarely | 10-20% |
| never | 0% |
Adverbs of Frequency (AoF) with the BE Verb
With the BE verb, the AoFs are added between BE and the rest of the sentence. You will see in the next section that this is different with other verbs.
subject + BE + AoF + rest of sentence
| Subject | BE | AoF | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | am | never | late. |
| He She It | is | always | on time. |
| You We They | are | sometimes | early. |
Activity 3.8: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Put the correct form of the BE verb followed by the AoF on the line.
1. I (be/always) _____________________________________ late.
2. He (be/never) _____________________________________ on time.
3. She (be/often) _____________________________________ busy on Saturday.
4. It (be/never) _____________________________________ cold in August.
5. You (be/usually) _____________________________________ cold in the morning.
6. We (be/never) _____________________________________ hungry in the morning.
7. They (be/seldom) _____________________________________ tired at 9:00 pm.
8. You (be/rarely) _____________________________________ late for school.
9. He (be/sometimes) _____________________________________ tired after work.
10. It (be/usually) _____________________________________ sunny in Los Angeles.
Activity 3.9: Fill-in-the-Blank
1. Class (usually)___________________________ interesting.
2. They (often)___________________________ busy.
3. I (always)___________________________ friendly.
4. You (never)___________________________ hungry after lunch.
5. She (always)___________________________ hungry at 3:00 pm.
6. He (rarely)___________________________ on time for class.
7. They (sometimes)___________________________ confused in class.
8. You (often)___________________________ sleepy.
Adverbs of Frequency with Other Verbs

But, what if we want to say how often we do some activity? In that case, we don’t use the BE verb. We use another verb, like eat, sleep, cook, drive, or talk.
Instead of adding the AoF after the verb, like we did with the BE verb, we add it before the verb. We do this because we are saying how often the activity of the verb happens.
subject + AoF + verb + rest of sentence
| Subject | AoF | Verb | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | always | eat | breakfast. |
| He She It | usually | does | his own laundry. |
| You We They | never | walk | to school. |
We use the AoF to talk about how often or how frequently something happens.
How often do you eat breakfast? I always eat breakfast.
In the sentence above, we are saying how often we eat breakfast (always).
How often does he cook dinner? He usually cooks dinner.
In the sentence above, we are saying how often he cooks dinner. (usually).
How often do they walk to school? They never walk to school.
In the sentence above, we are saying how often they walk to school (never).
Activity 3.10: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the Adverb of frequency (AoF) and the verb in the correct form on the line.
When we use any verb except the BE verb, the AoF goes before the verb.
1. I (never/eat) ___________________ breakfast.
2. You (often/do) ___________________ laundry on Saturdays.
3. He (usually/swim) ___________________ on weekends.
4. She (never/sing) ___________________ karaoke.
5. It (rarely/rain) ___________________ in July.
6. They (seldom/watch) ___________________ movies.
7. We (always/do) ___________________ our homework.
8. She (sometimes/make)___________________ the bed.
Activity 3.11: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Put the AoF and the verb in the correct order.
Ana and Pedro (wake up) _______________________________ at 6:00 am.
Our class (start) _________________________________________ at 6:00 pm.
The college (cancel) ________________________ classes because of snow.
The teacher (give) ____________________________________ us homework.
Vegetarians (eat) ________________________________________ vegetables.
The students (sleep) ____________________________________ during class.
7. sometimes
Ana (make) _________________________________________ lunch for Pedro.
Students (speak) ____________________________________ English in class.
Activity 3.12: Classmate Interview
| How often do you… | always | usually | often | sometimes | seldom / rarely | never |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wake up before 7:00 am? | ||||||
| eat breakfast? | ||||||
| fall asleep before 11:00 pm? | ||||||
| drive to work? | ||||||
| do laundry on the weekend? | ||||||
| eat dinner before 6:00 pm? | ||||||
| sleep in on Sundays? | ||||||
| go grocery shopping on the weekdays? | ||||||
| come to class on time? | ||||||
| do your homework before class? |
Part 2 Directions: Choose 5 of the questions (and answers) from Part 1. On your own lined paper, use the answers to write sentences about your classmate’s activities. Remember to use adverbs of frequency. Turn this in to your teacher. Write your name, the date, and Activity 3.12 on the top of your paper.
Activity 3.13: Game
Directions: The purpose of this game is to practice using adverbs of frequency. Your teacher will give you some AoF game cards (often, sometimes, never).
- Stand up and find a partner.
- Ask your partner a question. Begin the sentence “How often…”
- The partner answers the question using an AoF.
- If your partner answers your question using the AoF that you have in your hand, give your partner the card.
- If your partner answers using an AoF that you don’t have, then change to another student and try again.
- You can only ask two questions before you need to change partners.
- You can only talk to the same person after you have talked with all your other classmates.
- Talk to as many partners as you can. When you have no more cards, sit down.
The goal of the game is to give away all of your cards.
Student 1: How often do you eat french fries for breakfast?
Student 2: I never eat french fries for breakfast.
(Student 1 gives the card saying “never” to Student 2)
Student 1: How often do you do your homework?
Student 2: I usually do my homework.
(Student 1 doesn’t have a ”usually” card. Student 1 changes partners and tries again.)
Ideas for Questions: How often do you…
wash your hair?
eat at a restaurant?
call your brother?
walk to school?
Pronunciation and Spelling: Adding -s and -es
We add -s and -es for two reasons:
1. The word is a noun, and we are making it plural.
2. The word is a verb, and it agrees with the subject (he, she, or it–3rd person singular)
Pronunciation
In English the same letters can have different sounds. For example, the letter “c” can sound like /k/ in cat , but it can also sound like /s/ in ice .
For words that end in -s or -es, there are three different sounds: /s/, /z/, and /ɪz/. We can predict how the -s or -es ending will sound by the last sound of the word before we add the -s or -es ending.
| If the word ends with these sounds: | This is the sound made by adding -s or -es: | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| /f/ /k/ /p/ /θ/ or /t/ | → /s/ | laughs, drinks, sleeps, births, writes, gets |
| /b/ /d/ /g/ /l/ /m/ /n/ /ŋ/ /r/ /v/ /ð/ and all vowel sounds | → /z/ | grabs, rides, hugs, comes, runs, sings, lives, sees, goes, plays, buys, studies |
| /ʤ/ /z/ /ks/ /s/ /tʃ/ or /ʃ/ | → /ɪz/ | changes, quizzes, fixes, kisses, uses, teaches, pushes |
/θ/=th as in bath /ð/=th as in that /ʤ/=j as in judge /tʃ/=ch as in church /ʃ/=sh as in wash
Activity 3.14: Pronunciation
| Target Word | Ending Sound (Circle your choice) |
|---|---|
| 1. teaches | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 2. teachers | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 3. asks | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 4. kicks | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 5. does | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 6. reads | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 7. watches | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 8. begins | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 9. pushes | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 10. listens | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 11. She works at a hospital. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 12. He lives with his sister. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 13. He puts the book on the table. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 14. She goes to school four nights a week. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 15. He cooks for her in the evening. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 16. We need boxes to move house. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 17. The mom buys groceries after class. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 18. The mom buys groceries after class. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 19. I sweep up the leaves on the sidewalk. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 20. The boys play soccer in the park. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
Activity 3.15: Listening
Directions: Listen to the teacher say a list of words and then sentences. You will hear each word or sentence two times. Decide if the ending sound is /s/, /z/, or /ɪz/ and choose (by circling or otherwise marking) your choice.
1. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
2. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
3. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
4. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
5. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
6. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
7. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
8. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
9. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
10. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
11. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
12. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
13. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
14. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
15. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
Activity 3.16: Listening & Speaking
Part 1 Directions: Identify which of the three ending sounds (/s/, /z/, or /ɪz/) is at the end of each of the target words. Write the sound symbol on the line.
/s/ /z/ /ɪz/
1. changes _____
2. crabs _____
3. dishes _____
4. touches _____
5. helps _____
6. books _____
7. pencils _____
8. sleeps _____
9. mixes _____
10. kisses _____
11. The students eat breakfast. _____
12. My sister walks her dog. _____
13. The dogs eat peanut butter. _____
14. The student catches the bus. _____
15. I have three cats. _____
16. Most teachers have pets. _____
17. She writes a book. _____
18. Natasha buys food. _____
19. Yuri wakes up on time. _____
20. She sees her daughter. _____
Part 2 Directions: With a partner, say the word or sentence. Your partner will point to the sound they hear.
If a word ends in /s/, /z/, /ch/, /sh/ or /x/ sound → add -es
Only add -es for the he/she/it form of the verb (third person singular).
watch → watches
wash → washes
kiss → kisses
I pass out papers. → She passes out papers.
I wash the dishes. → He washes the dishes.
Activity 3.17: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of the verb in parentheses on the lines.
1. (watch) I __________ TV in the morning, but she ________ TV at night.
2. (wash) They ________ dishes together after dinner. He ________ dishes on weekends.
3. (fix) My father and I _________ cars together. My husband ________ the bicycle.
4. (teach) They ________ their daughter Ukrainian. Eva ________ her son Amharic.
5. (brush) I ________ my teeth twice a day. He _______ three times a day.
6. (kiss) She _______ her husband in the morning. I ________ my children before bed.
7. (stretch) I always ________ before exercise. Viktor ________ after exercise.
8. (guess) I never ________ the answer, but Tatiana often ________ the answer.
9. (mix) She ________ Spanish and English. They _______ English and Ukranian.
10. (splash) The kids ______ in the bathtub. My daughter always ________, too.
11. (cash) I ______ my check at the bank. He _________ his check too.
12. (latch) I ________ my screen door. She ________ her screen door.
13. (notice) I always ________ mistakes. She never ________ mistakes when she writes.
14. (touch) He ________ the door. We ________ the window.
15. (brush) They ________ their hair once a day. He _________ his hair three times a day.
16. (pass) She ________ all her classes. They ________ their ESL classes.
17. (ask) I ________ for vegetarian food. Natasha ________ for Ukrainian food.
18. (ask) He ________ a question. We ________ to play a game.
19. (watch) She ________ Jackie Chan movies. They ________ Jet Li movies.
20. (dance) I ______ twice a week. He ________ once a week.
Activity 3.18: Listening
Directions: Read the story. Then listen to your teacher read the story. Listen for the missing words and write them on the line. Remember that the subject and the verb of a sentence have to agree. If they don’t agree, you should listen again. Some verbs end in -s and some verbs end in -es.
Viktor and Tatiana
Viktor and Tatiana (1)_________ married. They (2)_________ English at Clackamas Community College. They (3)_________ from Ukraine. Tatiana sometimes (4)_________ angry with Viktor because he doesn’t help around the house. Tatiana (5)_________ dinner and Viktor (6)_________ TV. Tatiana (7)_________ the house, and Viktor (8)_________ English.
Then Tatiana remembers that Viktor (9)_________ the car while she (10)_________ books. In the grocery store, he always (11)_________ the shopping cart. He (12)_________ for her when she is sick. He also (13)_________ the socks when they (14)_________ movies at home. On school nights, Viktor (15)_________ the dishes after Tatiana cooks. He (16)_________ her every day when they leave the house, and he (17)_________ her every night before they (18)_________ asleep. Then Tatiana isn’t angry anymore.
If a word ends in a consonant plus -y, change -y to i and add -es. If the word ends in a vowel plus -y, just add -s.
Consonant + -y
Change -y to i and add -es
cry → cries
study → studies
pay → pays
buy → buys
Activity 3.19: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of the verb on the line in the sentences below.
1. (study) I ___________ in the morning, but he ___________ at night.
2. (worry) He ___________ about money. I ___________ about him.
3. (cry) The cat ___________ when I leave. The babies ___________ all the time.
4. (play) She ___________ piano. We ___________ violin.
5. (pay) I ___________ for groceries with a credit card. Tatiana ___________ with cash.
6. (stay) He ___________ after class for help. They ___________ after class to talk.
7. (stay) She ___________ at a hotel. I ___________with my mom.
8. (worry) My husband ___________ about school. I ___________ about our health.
9. (enjoy) We ___________ playing board games. He ___________ online games.
10. (say) They ___________ they are busy Friday, but she ___________ Friday is ok.
11. (fly) A bird ___________ south in winter. Birds ___________ north for the summer.
12. (buy) They ___________ paper online. She ___________ supplies at the store..
13. (fly) He ___________ to Paris today. I ___________ to Denver tomorrow.
14. (study) We ___________ before vocabulary tests. She ___________ for grammar.
15. (pay) He ___________ for 2 classes. I ___________ for 3 classes.
16. (try) I ___________ to study 3 times a week. She ___________ to study every day.
Activity 3.20: Listening
Using infinitives with like, want, & need.
Some verbs can be combined with an infinitive (to + verb) to express a different meaning or opinion about the activity.
| Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| like + to ski (Infinitive) | This shows an activity that is pleasurable or fun. Example: I like to ski. |
| want + to go (Infinitive) | This shows an activity that I have a desire to do. Example: I want to go to a movie. |
| need + to finish (Infinitive) | This shows an activity that I have to do. Example: I need to finish my homework. |
Activity 3.21: Fill-in-the-Blank
Part 1 Directions: Complete the sentences by writing like, want, or need on the line.
1. I ___________ to pay my rent.
2. She ___________ to study for the test.
3. They ___________ to buy a diamond necklace.
4. You ___________ to have an expensive new car.
5. I ___________ to read a book before bed to help me sleep.
6. You ___________ to do your homework.
7. We ___________ to eat dessert first.
8. I ___________ to sleep until 10:00 am, but I __________ to get up because work starts at 7:00 am.
Negative Statements in the Simple Present
Negatives with the be verb, activity 3.22: writing.
Directions: Make these sentences negative by adding not after the verb.
1. She is a hairdresser.
2. He is busy today.
3. They are from Colombia.
4. He is a contractor.
5. It is sunny.
6. They are students.
7. He is a teacher.
8. The dog is in the garden.
Negatives with All Other Verbs
Using auxiliary verbs.
There are three auxiliary verbs in English: BE, DO, and HAVE. We will learn about BE and DO in this class. We will learn about using HAVE as an auxiliary in the next level. You have already seen the first of our three auxiliary verbs, BE, in Chapter 2. We combine the BE verb with the -ing form of the verb to create the present progressive (an action happening now).
When we make negative sentences with other verbs, we use the auxiliary verb, DO. It has two forms: do and does . The negative not comes after do or does and is followed by the base form of the main verb.
The base form is the infinitive without the to . Instead of “to sing” (infinitive), the base form is sing . Do not add -s to the base verb. Let’s look at an example sentence.
subj do/does neg. base verb rest of sentence
He does not sing in the shower.
- He is the subject
- Does is the auxiliary verb. Do/Does agrees with the subject (3rd person singular: add -es).
- Sing is the main verb in the base form. Do not add -s to the main verb.
subject + auxiliary DO + not + base form + rest of sentence
| Subject | Auxiliary DO | Negative | Base Form of Main Verb | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I You We They | do | not | drink | coffee after 5:00 pm. |
| He She It | does |
Negative Contractions
To make negative contractions, we contract the auxiliary verb and the negative.
| Subject | Auxiliary DO + not |
|---|---|
| I You We They | do not = don’t |
| He She It | does not = doesn’t |
Activity 3.23: Choose the Correct Form
Directions: Choose the correct form, and then write the contraction on the line. Remember that the auxiliary DO (do/does) has to agree with the subject.
1. The teacher do not / does not eat meat. ___________________
2. I am a homemaker. I do not / does not work outside my home. ___________________
3. She is a driver. She do not / does not work in an office. ___________________
4. He is a vegetarian. He do not / does not eat meat. ___________________
5. They do not / does not drink coffee in the evening. ___________________
6. Palani do not / does not like to wake up early. ___________________
7. Yuri do not / does not want to come to school late. ___________________
8. Yuri do not / does not press snooze on his alarm clock. ___________________
9. They do not / does not have the same habits. ___________________
10. It do not / does not look like a good book. ___________________
11. The students do not / does not do their homework. ___________________
12. He do not / does not get good grades on tests. ___________________
Activity 3.24: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of do or does on the line.
1. (do/sing) She ___________ not ___________ in public.
2. (do/write) They ___________ not ___________ on the wall.
3. (do/drive) He ___________ not ___________ for a job.
4. (do/ask) You ___________ not ___________ for a diamond ring.
5. (do/play) We ___________ not ___________ guitar.
6. (do/like) The dog ___________ not ___________ my cat.
7. (do/type) She ___________ not ___________ fast.
8. (do/read) He ___________ not ___________ online.
Activity 3.25: Writing
Directions: Make these sentences negative. Use full forms for numbers 1-5 and contractions for numbers 6-10.
1. I go to work at 3:00 pm.
2. She wants to eat Chinese food.
3. They have two children.
4. He has a dog and two cats.
5. You need to stand in line.
6. She finishes her homework.
7. I eat breakfast.
8. You drink coffee.
9. He drinks diet soda.
10. My car has red seats.
Activity 3.26: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Use the sentences below to interview your partner. Take notes on your own lined paper.
Student A: Tell me a food you don’t like.
Student B: I don’t like eggs.

2. Tell me a movie you don’t like.
3. Tell me a place you don’t like.
4. Tell me a sport you don’t like.
5. Tell me a color you don’t like.
6. Tell me a singer or band you don’t like.
7. Tell me a type of music you don’t like.
8. Tell me a book you don’t like.
Part 2 Directions: Now, write 5 sentences about your partner. Use your notes to help you. Write your partner’s answers in FULL sentences.
Yes/No Questions & Short Answers
Yes/No questions mean that the answer to the question is either yes or no . These questions don’t use wh- question words. Remember, when we use an auxiliary verb, the main verb is in the base form. The auxiliary verb goes before the subject and the main verb goes after the subject.
auxiliary DO + subject + base verb + rest of sentence
| Auxiliary DO | Subject | Base Form of Main Verb | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do | I you we they | eat | breakfast? |
| Does | he she it |
Short Answers
Short answers are quick answers to yes/no questions. Remember that if the question uses the BE verb, use the BE verb in your answer. If the auxiliary DO is used in the question, then use DO in the answer.
Do you have cats? Yes, I do.
Are you a teacher? Yes, I am.
| Affirmative | Negative | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes, | I you we they | do. | No, | I you we they | do not. OR don’t. |
| he she it | does. | he she it | does not. OR doesn’t. | ||
Do you drink coffee in the morning? Yes, I do.
Does he drink coffee in the morning? No, he doesn’t.
Activity 3.27: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Complete the questions with the missing auxiliary verb and subject.
A: Does she wake up early?
B: No, she doesn’t.
1. A:___________________ do her homework every day?
B: Yes, she does.
2. A:___________________ wash the dishes after dinner?
B: Yes, he does.
3. A:___________________ eat dinner together?
B: Yes, they do.
4. A:___________________ work late every day?
5. A:___________________ drive to school?
6. A:___________________ study vocabulary?
B: Yes, I do.
7. A:___________________ eat lunch at home?
B: No, we don’t.
8. A:___________________ ask questions?
9. A:___________________ practice English at the grocery store?
10. A:___________________ do laundry on Saturdays?
Activity 3.28: Game
Information questions in the simple present.
We have seen several lists of wh- question words in previous chapters. Here is a bigger list. You can practice making questions with the new words and review the ones you have seen in Chapters 1 and 2.
| Wh- Question Word | Asks about... | Example Question |
|---|---|---|
| Who | a person | Who is your teacher? |
| What | information | What is your name? |
| Where | location | Where are you from? |
| When What time | Time *(specific and general) | When is your birthday? What time is your class? |
| Why | a reason | Why are you late? |
| How | directions, process, or means | How do you get home? |
| How many | a number | How many children do you have? |
| How often | frequency | How often do you drink coffee? |
| How much | an amount or money | How much is our textbook? |
| What kind | one from a group | What kind of fruit do you like? |
* What time asks about specific time. When asks about general time.
What time does class start? Class starts at 9:00 am.
When is your birthday? My birthday is in August.
We form information questions (sometimes called wh- questions) the same as yes/no questions. Add the question word (who, what, where, when, what time, etcetera) to the beginning of the question.
wh- + auxiliary DO + subject + main verb
| Wh- Question Word | Auxiliary DO | Subject | Base Form Main Verb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Who What Where When What time Why How How many How often How much | do | I you we they | see? eat? drive? write? |
| does | he she it |
Activity 3.29: Choose the Correct Form
Directions: Choose the correct question word.
1. Who/What is your teacher? My teacher is Susan.
2. Where/What is your address? My address is 19 Molalla Ave, Oregon City.
3. Where/When do you wake up? I wake up at 7:30 am.
4. Why/Who do you have an umbrella? Because it’s raining.
5. How/Where do you take ESL? I take ESL classes at CCC.
6. When/What do you work? I work at 5:00 pm.
7. Why/How do you get to school? I take the bus.
8. What/How do you cook hotdogs? I boil them, but some people grill them.
9. How much/How often milk do you want? I want 1 cup.
10. How many/Why cookies do you want? I want 2 dozen.
Activity 3.30: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct question word.
1. A:___________ do you go to work?
B: I go to work at 5:00 am.
2. A:___________ is he wearing a sweater?
B: He’s cold.
3. A:___________ do you study vocabulary?
B: I use vocabulary cards.
4. A:___________ are they from?
B: They’re from Italy.
5. A:___________ are you doing?
B: I’m doing my homework.
6. A:___________ often do you sleep in?
B: I sleep in on Saturdays.
7. A:___________ time does class start?
B: Class starts at 6:00 pm.
8. A:___________ do you study?
B: I study at the library.
9. A:___________ is your favorite actor?
B: My favorite actor is Brad Pitt.
10. A:___________ many classes do you take?
B: I take three classes each term.
Activity 3.31: Interview
Directions: Your instructor will give you a worksheet that you can use to interview a classmate.
- Match the wh- question word with the question. You can only use a word one time.
- When you finish matching you will have 10 questions and 10 answers. Choose 5 questions to ask your classmate.
- Write the answers to the 5 questions below.
1. ___________________________________________________________________
2. ___________________________________________________________________
3. ___________________________________________________________________
4. ___________________________________________________________________
5. ___________________________________________________________________
Activity 3.32: Error Correction
Directions: There are 10 mistakes in the paragraph below. Find the mistakes with the simple present, adverbs of frequency, negative sentences, or -s / -es endings and correct them.
My name is Jacques. I lives next to Yuri and Palani. I am a student at CCC also. I arrive always early to class. My brother drive me to school. I do not drives. I eat lunch with my friends. We eat often at Ana and Pedro’s house. I doesn’t cook. After class, always I study in the library. I finishes my homework in the afternoon. I study with my friend. My friend Palani finish his homework at night. I live with my family. My mother cook dinner for the family. She wash the dishes after dinner. I dry them.

Activity 3.33: Writing
Directions: Rewrite these sentences to include the adverb of frequency (AoF) in parentheses.
1. (usually) We eat dinner outside in summer.
2. (always) I wear slippers in the house.
3. (never) My family wakes up early.
4. (sometimes) My friends and I watch movies on Fridays.
5. (rarely) We eat uncooked food.
6. (often) They are late to class.
7. (never) I finish my homework on the computer.
8. (seldom) She takes her dog to the dog park.
9. (usually) You are on time.
10. (rarely) She eats fast food.
11. (never) It snows in August.
12. (always) It rains in October.
13. (often) We have homework.
14. (never) They forget books at home.
Activity 3.34: Writing
Directions: Write the question on the line below. Use the answer for extra information. Some questions are wh-questions, and some are yes/no questions.
1. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I wake up at 8:00 am.
2. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: Yes, I do (I have a dog.)
3. A:_______________________________________________________________
B: My birthday is in August.
4. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: No, I don’t. (I don’t do my homework in the morning.)
5. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I take a shower in the morning.
6. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I arrive early for class.
7. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: He drives to school.
8. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: He washes the dishes every day.
9. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: Yes, I do. (I exercise 3 times a week.)
10. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I eat fast food once a month.
Directions: Write a paragraph comparing your daily schedule with a partner’s daily schedule. Use the simple present tense, adverbs of frequency, and time expressions.
Pre-writing:
- Write 6 questions to ask your partner. Use 6 different wh-question words. There is a place to write each question in the chart that follows.
- Answer the 6 questions for yourself.
- Choose a partner, ask your questions, and then write down your partner’s answers.
| Question | My Answer | Partner’s Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
| 4. | ||
| 5. | ||
| 6. |
- Use your own 8.5″ x 11″ lined paper. Do not use other paper sizes, please.
- Heading: Put your full name, the due date, and Ch. 3 Writing Assignment at the top of your paper. Your instructor will tell you where the heading goes (left or right side).
- Indent the first sentence, skip lines (double space), and leave a 1-inch margin on the sides and bottom.
Writing and Grammar:
- First sentence: begin writing by using this topic sentence: [Partner’s name] and I are classmates, but we are very different.
- In your sentences, write your answer and your partner’s answer.
- Use 3 adverbs of frequency.
- Write 2 negative sentences.
- Use full forms; do not use contractions.
- Use capital letters and punctuation correctly.
- Use the rubric below to check your work.
Model Paragraph:
My partner and I are classmates, but we are very different. I get up very early at 5:00am. My partner doesn’t get up early. She often gets up at 9:00am. I usually drink coffee in the morning, but my partner doesn’t like coffee. She likes tea instead. I have two children, so I am busy with them. My partner is married, but she doesn’t have any children. I leave for school at 8:30am. My partners never goes straight to school. She goes to her parents house first. She always helps them because they are very old. My parents are still young at age 50 and 55.
Assignment Rubric:
| Heading: Full Name, Due Date, Ch. 3 Writing Assignment | 1 point |
|---|---|
| Format: Indent, double space, margins | 1 point |
| Your paragraph has at least 10 sentences | 1 point |
| Every sentence has a subject and verb, & they agree | 1 point |
| There are 3 adverbs of frequency | 3 points |
| There are 2 negative sentences | 4 points |
| Correct use of spelling | 1 point |
| Correct use of capital letters | 1 point |
| Correct end punctuation | 1 point |
| Total | 14 points |
Self-Assessment
These were our goals at the beginning of Chapter 3:
At the end of this chapter you will be able to:
- Add -s , -es, and -ies to verbs and nouns
Directions: Choose yes if you think you achieved the goals or no in the table below if you think you did not achieve the goals. Then, write an example of the goal in the last column.
| I can… | I achieved this goal: | My example: |
|---|---|---|
| add -s for 3rd person singular | yes no | He walks. |
| write an affirmative sentence in the simple present | yes no | |
| write a negative sentence in the simple present | yes no | |
| write yes/no questions using the simple present | yes no | |
| answer yes/no questions using short answers | yes no | |
| make information questions using wh- question words | yes no | |
| use AoF with the simple present | yes no |
Explorations 1: Grammar for the Experienced Beginner Copyright © by Susan; Jen; and Kit is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Present Simple Tense (Affirmative Sentences) - 01
| 1. She noodles every Monday. (eat) 2. Wichai computer every day. (play) 3. They English well. (speak) 4. He television every morning. (watch) 5. I up late. (get) 6. We pictures every week. (draw) 7. The boys in the pool. (swim) 8. My father a new car. (drive) | 9. You in the office. (work) 10. Mr. Manit to London. (fly) 11. I my homework. (do) 12. The teacher to school every day. (walk) 13. Jack his bicycle. (ride) 14. His mother some fruit. (buy) 15. The baby every night. (cry) . |
- English ESL Worksheets
- Grammar Topics
- Present simple tense
3,576 Present simple tense English ESL worksheets pdf & doc
ENGLISH WITH ALEX
Language you can use
- Apr 24, 2023
“Do” vs. “Does”: How and When to Use Them (AUDIO Reading Included)

Recommended level: Beginner
Quick Reference
Do and does are the present simple forms of the irregular English verb do .
Do and Does are used in present simple statements and questions.
Do and Does can be used as main verbs in affirmative sentences ("He does the dishes every day"), or as auxiliary verbs in questions ("Where do you work?").
Do is used with the subjects I , you , we , and they , and with subjects which refer to these pronouns (" Do Dan and Teresa (they) have a car?").
Does is used with the third person singular subjects he , she , and it , and with subjects which refer to these pronouns ("Marcus (He) does his homework on Saturdays").
The negative form of do is do not (contracted form: don't ).
The negative form of does is does not (contracted form: doesn't ).
Do is an irregular English verb. Do and does are the present simple forms of do . Here are some example sentences with these verbs.
"Rita does yoga every morning."
" Do your best."
"I do the dishes and my wife does the laundry."
In these sentences, do and does are used as the main verbs. They describe the main action in each sentence. You can do many things . For example, you can do exercise, do a test, do a good job, or even do nothing. Now, let's look at some more examples of do and does as the main verbs in a sentence, and let's learn when to use them.
For the best learning experience, listen to the audio and repeat the example sentences below.
When to use do
Use do with the pronouns I , you , we , and they , and with subjects which refer to these pronouns . For example:
"I do karate two times per week."
"You do it first, and then I will follow."
"Jim and I do a lot of work every day." (In this sentence, "Jim and I" can be replaced by the pronoun "we.")
"Gerald and Becky always do their grocery shopping together." (In this sentence, "Gerald and Becky" can be replaced by the pronoun "they.")
When to use does
Use does with the third person pronouns he , she , and it , and subjects which refer to these pronouns . For example:
"Mahmoud always does a good job."
"She does her homework after dinner."
"This computer does a lot of amazing things." (In this sentence, "this computer" can be replaced by the pronoun "it.")
To practice, answer this question : Who does the dishes in your house?
Okay, now you see how to use do and does as the main verbs in present simple sentences, but do and does also serve another very important function: They act as auxiliary verbs in present simple questions.
How to use do and does in present simple questions
To form a closed "yes or no" question with do or does in the present simple, we use the form do/does + subject + infinitive/base verb . The use of do or does depends on the subject. Let's look at five examples (Don't forget to listen and repeat each example):
" Do you want this?"
" Does she have any pets?"
" Do they need any help?"
" Do I look okay?"
" Does the company offer medical benefits?"
You can answer these questions with the short affirmative responses "Yes, I do," "Yes, you do," "Yes, she does," and so on. The short negative responses are "No, I don't," "No, you don't," "No, she doesn't," and so on. (Keep reading if you want to learn more about negative forms!)
For open questions that begin with the words who , what , where , when , why , and how , we use almost the same structure as above. Just add the question word in front . The structure is Wh- word + do/does + subject + infinitive/base verb . Here are six examples:
" Who do you want for this job?"
" What does he do?" (This question means "What is his job?" or "What does he do in life?")
" Where do you live?"
" When do you wake up in the morning?"
" Why do they go to sleep at midnight?"
" How does she get to the office every day?"
There are many more question structures in English, but in order to stay focused on our topic, this page will only discuss the structures above.
But wait! We have only practiced affirmative sentences. What about negative declarative sentences and negative questions? Let's look at them together.
The negative forms and uses of do and does
The negative form of do is do not , and the negative form of does is does not . In speaking and in informal writing, these words are usually contracted as don't and doesn't . Here are some examples (Remember to listen and repeat):
" I don't need your help."
" She doesn't work here anymore." ("Anymore" means she worked here before, but she doesn't work here now.)
" They don't believe that we can win."
" He doesn't like seafood."
" You don't have to do this."
" We don't own a car."
" This fruit doesn't look fresh."
And now, here are some examples of negative questions for you to practice:
" Why doesn't she buy a new one?"
" Don't you like pop music?" (In this example, I think you like pop music and I am verifying if it's true.)
" What doesn't she have ?"
" Who doesn't want one ?"
" Doesn't she live there ?" (This is the same as the pop music example before. I think she lives there, but I am not 100% sure, so I am verifying the information with someone.)
Where , when , and how can be used in negative questions with don't and doesn't , but it isn't very common. However, here are some examples to satisfy your curiosity:
" Where don't penguins live ?"
" When doesn't it rain in London?" (This could be a sarcastic question.)
" How don't you know that?"
I hope you feel more comfortable with using do and does in the present simple, and that you will recognize them more easily when you hear them in English contexts. To continue improving, practice repeating the examples on this page.
As a bonus, here is some more grammatical information about the verb do :
Present simple: do and does ("Where do you live?" / "Where does she live?")
Past simple: did ("She did her homework.")
Present participle: doing ("I'm doing my best.")
Past participle: done ("Have you done your taxes?")
Remember, there is always more to learn.
Finally, thank you for learning with me. If you enjoyed this resource and you would like to support my work, you can purchase a PDF, e-Book, or paperback copy of one of my books . I wrote all of them with English students in mind. Until next time, good luck on your learning journey, and talk to you again soon.
Recent Posts
Affect vs. Effect: What's the Difference? (Audio Lesson Included)
Third Conditional Discussion Questions (100+ Questions for English Conversation Practice)
"Because" vs. "Because of": The Difference in Usage (Includes Common Sentences and Audio Lesson)

Enter No account yet? Register Forgot your password?

Register Already have an account? Enter
Recover your password Already have an account? Enter No account yet? Register
Verb Tenses: Present - Lesson 8.1
Present simple, (el presente simple).
"I speak English", "He works at a factory". These are examples of the Present Simple, the verb form that we use for routines, repeated actions and general truths. Continue below to learn more.
When we speak of the various verb tenses, we must talk about both how to form the tense, as well as when we use it . Therefore, in this lesson, as with all the other verb tense lessons, we will look at both structure and use.
Grammatical Rules
When conjugating the verb in the present simple, we use the infinitive with the following subjects: “ I ”, “ you ”, “ we ”, and “ they ”. For the third person (“ he ”, “ she ” and “ it ”), we add an “ -s ” to the end of the verb.
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| I, you, we, they | talk, eat, learn, do, go… |
| he, she, it | talks, eats, learns, does, goes… |
Note: There are spelling exceptions in the third person , depending on the last letter(s) of the verb. The rules are the same as those for forming the plural. For more information, see the lesson on nouns .
Note: There are spelling exceptions in the third person , depending on the last letter(s) of the verb. The rules are the same as those for forming the plural. For more information, see the lesson on nouns.
1. Affirmative Sentences
| I . |
| He . |
| They . |
2. Negative Sentences
| I talk. |
| He eat. |
| They learn. |
Note: Don’t forget that in negative sentences with the auxiliary “ to do ”, it is the auxiliary verb that is conjugated in the third person, not the principal verb.
3. Interrogative Sentences
| you talk? |
| he eat? |
| they learn? |
Note: As with negative sentences, it is the auxiliary verb “ to do ” that is conjugated, depending on the subject. The principal verb remains in the infinitive. *For more information on the structure of sentences, see the lesson on constructing sentences .
Note: As with negative sentences, it is the auxiliary verb “ to do ” that is conjugated, depending on the subject. The principal verb remains in the infinitive. *For more information on the structure of sentences, see the lesson on constructing sentences.
1. We use the present simple when speaking about things that happen regularly . It is never used to speak about something that is happening at the moment in which we are speaking.
We tend to use adverbs of time with the present simple:
| I always to my mother on Sunday. |
| He never vegetables. |
| . They usually something new in class. |
Adverbs of time are generally located before the verb, except when they are used with the verb “ to be ”. When using “ to be ”, the adverb is found after the verb.
| I always happy. |
| He often sick. |
| They rarely late. |
2. The present simple is used to speak about generalities or scientific facts.
| He eat vegetables. |
| She in a hospital. |
| Elephants in Africa. |
| Bogota in Colombia. |
| children animals? |
| Adults everything. |
3. We also use the present simple for events scheduled in the near future.
| The train at 10:00. |
| The party tonight. |
| the festival tomorrow? |
| The plane arrive today. |
4. We use the present simple for giving instructions (the imperative).
| the window. |
| the vegetables. |
| . |
| your homework. |
| your mother. |
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Present simple ( I work )
Present simple: form.
We use the base form of the verb, and add -s for the third person singular.
+ |
| . . | ||||
− |
| (full form)
| . | |||
| (short form)
| |||||
? + |
|
|
| |||
? − | (full form)
|
|
|
| ||
(short form)
|
| |||||
Present simple: spelling
For most verbs we add -s to the base form to make the she, he, it (third person singular) form:
→ | → | → |
→ | → | → |
→ |
For other verbs, the spelling changes are:
verb |
| |
When the verb ends in , - or , we add . |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
When the verb ends in a consonant + - we change to and add . |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
But when the verb ends in a vowel + - we just add . |
|
|
|
| |
, , and are irregular. |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
When the verb ends in -s or -z we double the -s or -z and add -es , e.g. quiz , quizzes . These verbs are not common.
Present simple: uses
General truths and facts.
We use the present simple to talk about general facts that are always true and permanent about the world:
Ten times ten makes one hundred. (10 x 10 = 100)
There is always a holiday on the last Monday in August in the UK.
Time passes very quickly when you get older.
We use the present simple to talk about general facts that we think are true and permanent at the present time:
I really love my job.
Mrs Clare doesn’t teach me but she teaches my sister.
Do you live in Glasgow? My cousin lives there too.
Spiders don’t frighten me.
Martha does what she wants . No one tells her what to do.
Regular and habitual events
We use the present simple to talk about regular or habitual events. We often use always, often, usually, sometimes, never and other frequency adverbs for regular and habitual events:
How do you get to work? Do you get the bus?
I read every night before I go to sleep.
We always have a holiday in the summer. We never work in August.
We usually fly to France when we go. Lorea doesn’t like the ferry. It makes her feel sick.
Instructions and directions
We use the present simple when we are giving instructions or directions. We often use ordering words, such as and , first and then with this use of the present simple:
[giving directions]
You take the train into the city centre and then you take a number five bus. You don’t get off at the museum. You get off at the stop after the museum.
[giving instructions before a test]
So what you do is … you read the questions first and then you write down your answers in the box. You don’t write on the question paper.
Stories and commentaries
We often use the present simple to describe a series of actions – one action after another. We see this especially in stories, summaries of stories or reviews:
[talking about the series of events in a novel]
Alex doesn’t ring back at midnight … she waits till the morning to ring, and they get annoyed with Liz when she goes on … they know she ’s got plenty of money by their standards …
The present simple is often used by sports commentators to give commentaries or report actions as they are happening:
Mwaruwauri Benjani fouls Cahill. Habsi takes the free kick, Caicedo shoots and volleys . O’Brien blocks .
Immediate reactions
We use the present simple, often with verbs of senses and perception, to talk about feelings and reactions at the moment of speaking:
Do you think that meat is ok to eat? It doesn’t smell very good.
Where does it hurt ?
[talking about the colour of a dress]
I don’t like the colour. I think I look terrible.
It seems a bit quiet in here. Where is everyone?
Don’t you believe me? It’s true, honestly.
I promise , I swear , I agree (speech act verbs)
We use the present simple with speech act verbs (verbs which perform the act that they describe):
I will pay you back, I promise , when I get paid.
I agree with everything you say.
We also use the present simple in a similar way in formal statements and in business or legal communications:
I attach the original signed copies for your records.
On behalf of the Society, and particularly those involved in medical work, I write to thank you for your kind gift of £20,000 … (more formal than I’m writing to thank you … )
Timetables and plans
We use the present simple to talk about events that are part of a future plan or timetable:
The lesson starts at 9.30 tomorrow instead of 10.30.
Lunch is at 12.30. Don’t be late.
What time do you land ? (talking about a flight at some time in the future)
They don’t start back to school until next Monday.
We can also often use will in these sentences, with no change in meaning:
The lesson will start at 9.30 tomorrow instead of 10.30.
Future: present simple to talk about the future ( I work tomorrow )
Present simple after when , before , etc.
We use the present simple for future reference in subordinate clauses after words like when , before , as soon as , if and whether :
I’ll call you when I get there.
Not: I’ll call you when I’ll get there .
Don’t forget to ring before you go .
Not: Don’t forget to ring before you’ll go .
They hope to move in to the new house as soon as they get back from Australia next month.
Not: … as soon as they’ll get back from Australia next month .
Conditionals
Newspaper headlines
We often see the present simple in news headlines to report past events. It emphasises the drama or immediacy of an event:
Man rescues child from lake
Taiwanese envoys arrive in China

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
to do something or go somewhere very slowly, taking more time than is necessary

Like a bull in a china shop: talking about people who are clumsy

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Daily Routines in English
List of Daily Routines in English
(You can hear the pronunciation of each phrase in the video)
- I turn off my alarm
- I take a shower / I have a shower
- I get dressed
- I comb my hair
- I make breakfast
- I eat breakfast / I have breakfast
- I brush my teeth
- I go to work
- I start work at 9
- I answer emails
- I eat lunch / I have lunch
- I work on my computer
- I finish work at 5
- I arrive home
- I feed the dog
- I cook dinner
- I eat dinner / I have dinner
- I read a book
- I go to bed
- I fall asleep
Daily routines for School
- I go to school
- I have classes
- I finish school at 3
- I do my homework
Notice how in this lesson all of these phrases are in the simple present tense and have I (first person singular) as the subject. In another lesson we will look at daily routines using third person (he, she).
Practice Exercises
Try our interactive game to practice daily routines and using the correct verb: Daily Routines Vocabulary Game
Video practice: In the final section of the video there is a practice exercise where a cartoon of a daily routine appears on the screen. There are also three phrases next to the cartoon and you must choose which phrase best describes that activity. The answer appears after 5 seconds (approximately).
Daily Routines for Adults
This video has the same English vocabulary that appears as the video at the top of the page though is aimed at adults learning English. Instead of static cartoons, you will see two short videos (5 seconds each) showing adults in each daily routine mentioned above. I give the English pronunciation of each word twice (once for each short video). This lesson also includes the American English 🇺🇸 and British English 🇬🇧 versions of daily routines when there is a difference.
English Summary Chart
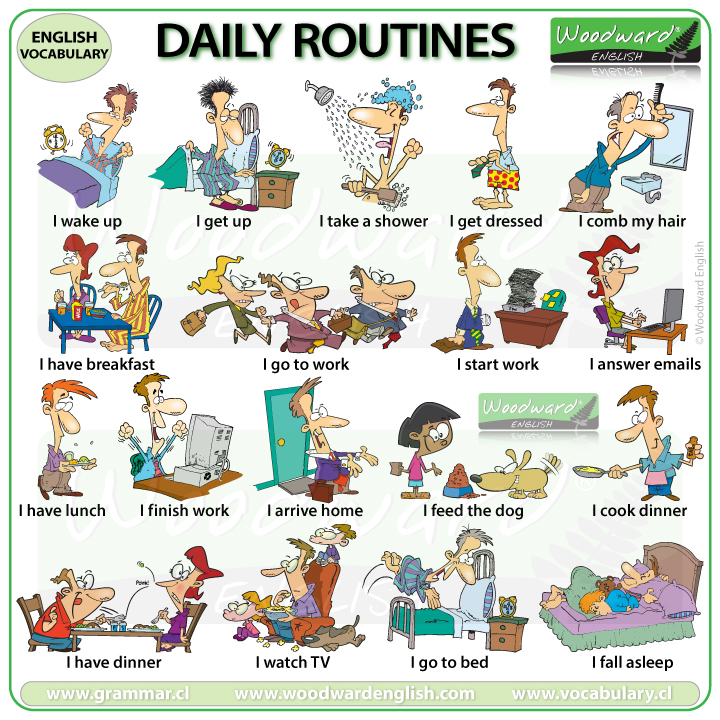
Daily Routines English Vocabulary explained in Spanish
Nuestra lección de vocabulario de las rutinas diarias en inglés explicada en español (con pronunciación):
- 980k Followers
- 217k Followers
- 126k Followers
English Course
Present simple tense.
- Present Simple Tense in English
- Day + Part of the Day
- ON + Day + Part of the Day
- Don't and Doesn't in English - Simple Present Tense - Negative Sentences
- Like - likes - don't like - doesn't like
- Like + Verb-ING - Like + Infinitive - Enjoy + Verb-ING
- How to say an email address in English
- Free Time Activities in English
- Sports in English
- I agree - I don't agree
Pin It on Pinterest
Homework -Simple present-
Simple present verbs
Loading ad...
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Simple present tense (present simple tense) is a verb tense that describes the events and situations that do not change over time. We use simple present tense for the actions that happen regualarly, and that is why we use some frequency adverbs to express these repititive actions. " Do " and " does " are the auxiliary verbs of present ...
Yes, of course. We use the present simple to talk about things which are repeated every day, every week, every year, etc. I usually get up at 7 o'clock. During the week I have swimming practice on Mondays, I do taekwondo on Tuesdays and tennis on Thursdays. We always go on holiday in the summer. I see. And you use words for explaining more ...
Step 1: Identify the auxiliary verb "do". The auxiliary verb "do" is used to form questions, negatives, and emphasis in the simple present tense. It is important to identify this verb in a sentence to make the negative correctly. Example: John plays tennis every day. Step 2: Add "do not" or "does not". To make the simple present ...
The exercises in this activity homework sheet help students practise the Present Simple in a varied and practical way. After downloading your PDF: print it immediately or save and print later. Answers are provided for teachers on the second page. Make your own worksheets with the free EnglishClub Worksheet Maker!
Present simple form. In present simple verbs, we need to use the verb do/does in questions and don't/doesn't in negatives.. Download full-size image from Pinterest Spelling of he/she/it. The form is the same for all the other persons except he/she/it.The spelling for he/she/it is different. Download full-size image from Pinterest
The first thing most, if not all your students did that day was surely 'wake up'. Write 'I wake up' on the board and then ask students what time they woke up. Then complete the sentence on the board to make the present simple sentence. For example, 'I wake up at 8.'. Do the same for other daily actions / routines and write these ...
The Present Simple Tense in English. Use the Present Simple tense ("I go", "He goes" etc) to talk about facts, things that are always true, or for routines and habits. For example: In England it often snows in winter. (a fact) I live in London (true - I don't change my house every day) John eats cereal for breakfast (routine or habit)
C. Complete the sentences using one of the verbs from the box on the left in the Present Simple form with one of the nouns from the box on the right. live not / be not / have wake not / start morning apartment work money dog
Uses of the Simple Present. The simple present is used for talking about routines, habits, and repeated activities in the present time. We use the simple present to talk about facts, which are always true. Time expressions (e.g., every day, in the summer) and adverbs of frequency (e.g., never, sometimes, always) signal the simple present tense.
Simple present tense - rules. Present simple explanations. Present tense - third person - rules. Present simple: worksheets pdf, handouts and free printable exercises online. Elementary and intermediate level.
Would you like more practice with the simple present? Here is more material: Simple Present Test 1 Simple Present Test 2 Simple Present Questions Test. Here is a reading test you can use to practice your reading comprehension. Simple Present Reading Test. This song by Coldplay helps you practice your listening skills and the simple present verb ...
Part 2 Directions: On lined paper, write one (1) sentence for each verb (like, want, need) using "I" as the subject. Then write one (1) sentence for each verb using "he" or "she" as the subject. Turn this in to your teacher. Don't forget to write your name, the date and Activity 3.21 at the top of your paper.
Lets look at its form in the simple present tense. TO DO - Present Tense. With the verb TO DO in the Present Tense… We say: I do / you do / we do / they do But we say: he does / she does / it does. Let's look at some example sentences: I do my laundry on Saturdays. (Do my laundry means I wash my clothes, well, I put in the washing machine)
Present Simple Tense (Affirmative Sentences) - 01. Fill in the blanks. Click here for more exercises about Present Tense. 1. She noodles every Monday. (eat) ... 11. I my homework. (do) 12. The teacher to school every day. (walk) 13. Jack his bicycle. (ride) 14. His mother some fruit. (buy)
Present Simple exerc. Some exercises to re. 198580 uses. redyelruc. Nelly the Nurse - Re. A short reading comp. 181893 uses. Zmarques. This is my house . Text followed by thr. 154572 uses. languageleader88. present simple. I hope you like it;) 149729 uses. giovanni. SIMPLE PRESENT READI. This worksheet will . 136138 uses. ktregh. Lionel Messi ...
5. Some students always use pens to do their homework. 6. I enjoy working in my garden in the spring time. 7. The moon shines every night in the summer. 8. A cab driver has a lot of customers. 9. We use our ears to listen to people speak. 10. My students try hard in school. 11. A doctor sees patients in hospitals. Present Continuous Tense and ...
When to use do. Use do with the pronouns I, you, we, and they, and with subjects which refer to these pronouns. For example: "I do karate two times per week." "You do it first, and then I will follow." "Jim and I do a lot of work every day." (In this sentence, "Jim and I" can be replaced by the pronoun "we.")
These are examples of the Present Simple, the verb form that we use for routines, repeated actions and general truths. Continue below to learn more. Texts in English. When we speak of the various verb tenses, we must talk about both how to form the tense, as well as when we use it. Therefore, in this lesson, as with all the other verb tense ...
Present simple ( I work ) - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Present Simple - I/you/we/they Positive I You We They get up have breakfast do my homework at 6 o'clock. everyday. at home. Negative I You We They do not don't get up have breakfast do my homework at 6 o'clock. everyday. at home. Interrogative Do I You We They get up have breakfast do my homework at 6 o'clock? everyday? at home? Short ...
I do my homework; Notice how in this lesson all of these phrases are in the simple present tense and have I (first person singular) as the subject. In another lesson we will look at daily routines using third person (he, she). Practice Exercises.
Homework -Simple present-lmnegro Member for 4 years 2 months Age: 6-9. Level: 1st. Language: English (en) ID: 404944. 06/10/2020. Country code: GT. Country: Guatemala. School subject: Grammar (1061914) Main content: Simple present (2033961) From worksheet author: Simple present verbs. Other contents: ...