- The Magazine
- Stay Curious
- The Sciences
- Environment
- Planet Earth

5 Unethical Medical Experiments Brought Out of the Shadows of History
Prisoners and other vulnerable populations often bore the brunt of unethical medical experimentation..
Most people are aware of some of the heinous medical experiments of the past that violated human rights. Participation in these studies was either forced or coerced under false pretenses. Some of the most notorious examples include the experiments by the Nazis, the Tuskegee syphilis study, the Stanford Prison Experiment, and the CIA’s LSD studies.
But there are many other lesser-known experiments on vulnerable populations that have flown under the radar. Study subjects often didn’t — or couldn’t — give consent. Sometimes they were lured into participating with a promise of improved health or a small amount of compensation. Other times, details about the experiment were disclosed but the extent of risks involved weren’t.
This perhaps isn’t surprising, as doctors who conducted these experiments were representative of prevailing attitudes at the time of their work. But unfortunately, even after informed consent was introduced in the 1950s , disregard for the rights of certain populations continued. Some of these researchers’ work did result in scientific advances — but they came at the expense of harmful and painful procedures on unknowing subjects.
Here are five medical experiments of the past that you probably haven’t heard about. They illustrate just how far the ethical and legal guidepost, which emphasizes respect for human dignity above all else, has moved.
The Prison Doctor Who Did Testicular Transplants
From 1913 to 1951, eugenicist Leo Stanley was the chief surgeon at San Quentin State Prison, California’s oldest correctional institution. After performing vasectomies on prisoners, whom he recruited through promises of improved health and vigor, Stanley turned his attention to the emerging field of endocrinology, which involves the study of certain glands and the hormones they regulate. He believed the effects of aging and decreased hormones contributed to criminality, weak morality, and poor physical attributes. Transplanting the testicles of younger men into those who were older would restore masculinity, he thought.
Stanley began by using the testicles of executed prisoners — but he ran into a supply shortage. He solved this by using the testicles of animals, including goats and deer. At first, he physically implanted the testicles directly into the inmates. But that had complications, so he switched to a new plan: He ground up the animal testicles into a paste, which he injected into prisoners’ abdomens. By the end of his time at San Quentin, Stanley did an estimated 10,000 testicular procedures .
The Oncologist Who Injected Cancer Cells Into Patients and Prisoners
During the 1950s and 1960s, Sloan-Kettering Institute oncologist Chester Southam conducted research to learn how people’s immune systems would react when exposed to cancer cells. In order to find out, he injected live HeLa cancer cells into patients, generally without their permission. When patient consent was given, details around the true nature of the experiment were often kept secret. Southam first experimented on terminally ill cancer patients, to whom he had easy access. The result of the injection was the growth of cancerous nodules , which led to metastasis in one person.
Next, Southam experimented on healthy subjects , which he felt would yield more accurate results. He recruited prisoners, and, perhaps not surprisingly, their healthier immune systems responded better than those of cancer patients. Eventually, Southam returned to infecting the sick and arranged to have patients at the Jewish Chronic Disease Hospital in Brooklyn, NY, injected with HeLa cells. But this time, there was resistance. Three doctors who were asked to participate in the experiment refused, resigned, and went public.
The scandalous newspaper headlines shocked the public, and legal proceedings were initiated against Southern. Some in the scientific and medical community condemned his experiments, while others supported him. Initially, Southam’s medical license was suspended for one year, but it was then reduced to a probation. His career continued to be illustrious, and he was subsequently elected president of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The Aptly Named ‘Monster Study’
Pioneering speech pathologist Wendell Johnson suffered from severe stuttering that began early in his childhood. His own experience motivated his focus on finding the cause, and hopefully a cure, for stuttering. He theorized that stuttering in children could be impacted by external factors, such as negative reinforcement. In 1939, under Johnson’s supervision, graduate student Mary Tudor conducted a stuttering experiment, using 22 children at an Iowa orphanage. Half received positive reinforcement. But the other half were ridiculed and criticized for their speech, whether or not they actually stuttered. This resulted in a worsening of speech issues for the children who were given negative feedback.
The study was never published due to the multitude of ethical violations. According to The Washington Post , Tudor was remorseful about the damage caused by the experiment and returned to the orphanage to help the children with their speech. Despite his ethical mistakes, the Wendell Johnson Speech and Hearing Clinic at the University of Iowa bears Johnson's name and is a nod to his contributions to the field.
The Dermatologist Who Used Prisoners As Guinea Pigs
One of the biggest breakthroughs in dermatology was the invention of Retin-A, a cream that can treat sun damage, wrinkles, and other skin conditions. Its success led to fortune and fame for co-inventor Albert Kligman, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania . But Kligman is also known for his nefarious dermatology experiments on prisoners that began in 1951 and continued for around 20 years. He conducted his research on behalf of companies including DuPont and Johnson & Johnson.
Kligman’s work often left prisoners with pain and scars as he used them as study subjects in wound healing and exposed them to deodorants, foot powders, and more for chemical and cosmetic companies. Dow once enlisted Kligman to study the effects of dioxin, a chemical in Agent Orange, on 75 inmates at Pennsylvania's Holmesburg Prison. The prisoners were paid a small amount for their participation but were not told about the potential side effects.
In the University of Pennsylvania’s journal, Almanac , Kligman’s obituary focused on his medical advancements, awards, and philanthropy. There was no acknowledgement of his prison experiments. However, it did mention that as a “giant in the field,” he “also experienced his fair share of controversy.”
The Endocrinologist Who Irradiated Prisoners
When the Atomic Energy Commission wanted to know how radiation affected male reproductive function, they looked to endocrinologist Carl Heller . In a study involving Oregon State Penitentiary prisoners between 1963 and 1973, Heller designed a contraption that would radiate their testicles at varying amounts to see what effect it had, particularly on sperm production. The prisoners also were subjected to repeated biopsies and were required to undergo vasectomies once the experiments concluded.
Although study participants were paid, it raised ethical issues about the potential coercive nature of financial compensation to prison populations. The prisoners were informed about the risks of skin burns, but likely were not told about the possibility of significant pain, inflammation, and the small risk of testicular cancer.
- personal health
- behavior & society
Already a subscriber?
Register or Log In

Keep reading for as low as $1.99!
Sign up for our weekly science updates.
Save up to 40% off the cover price when you subscribe to Discover magazine.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Controversial and Unethical Psychology Experiments
There have been a number of famous psychology experiments that are considered controversial, inhumane, unethical, and even downright cruel—here are five examples. Thanks to ethical codes and institutional review boards, most of these experiments could never be performed today.
At a Glance
Some of the most controversial and unethical experiments in psychology include Harlow's monkey experiments, Milgram's obedience experiments, Zimbardo's prison experiment, Watson's Little Albert experiment, and Seligman's learned helplessness experiment.
These and other controversial experiments led to the formation of rules and guidelines for performing ethical and humane research studies.
Harlow's Pit of Despair
Psychologist Harry Harlow performed a series of experiments in the 1960s designed to explore the powerful effects that love and attachment have on normal development. In these experiments, Harlow isolated young rhesus monkeys, depriving them of their mothers and keeping them from interacting with other monkeys.
The experiments were often shockingly cruel, and the results were just as devastating.
The Experiment
The infant monkeys in some experiments were separated from their real mothers and then raised by "wire" mothers. One of the surrogate mothers was made purely of wire.
While it provided food, it offered no softness or comfort. The other surrogate mother was made of wire and cloth, offering some degree of comfort to the infant monkeys.
Harlow found that while the monkeys would go to the wire mother for nourishment, they preferred the soft, cloth mother for comfort.
Some of Harlow's experiments involved isolating the young monkey in what he termed a "pit of despair." This was essentially an isolation chamber. Young monkeys were placed in the isolation chambers for as long as 10 weeks.
Other monkeys were isolated for as long as a year. Within just a few days, the infant monkeys would begin huddling in the corner of the chamber, remaining motionless.
The Results
Harlow's distressing research resulted in monkeys with severe emotional and social disturbances. They lacked social skills and were unable to play with other monkeys.
They were also incapable of normal sexual behavior, so Harlow devised yet another horrifying device, which he referred to as a "rape rack." The isolated monkeys were tied down in a mating position to be bred.
Not surprisingly, the isolated monkeys also ended up being incapable of taking care of their offspring, neglecting and abusing their young.
Harlow's experiments were finally halted in 1985 when the American Psychological Association passed rules regarding treating people and animals in research.
Milgram's Shocking Obedience Experiments
Isabelle Adam/Flickr/CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
If someone told you to deliver a painful, possibly fatal shock to another human being, would you do it? The vast majority of us would say that we absolutely would never do such a thing, but one controversial psychology experiment challenged this basic assumption.
Social psychologist Stanley Milgram conducted a series of experiments to explore the nature of obedience . Milgram's premise was that people would often go to great, sometimes dangerous, or even immoral, lengths to obey an authority figure.
The Experiments
In Milgram's experiment, subjects were ordered to deliver increasingly strong electrical shocks to another person. While the person in question was simply an actor who was pretending, the subjects themselves fully believed that the other person was actually being shocked.
The voltage levels started out at 30 volts and increased in 15-volt increments up to a maximum of 450 volts. The switches were also labeled with phrases including "slight shock," "medium shock," and "danger: severe shock." The maximum shock level was simply labeled with an ominous "XXX."
The results of the experiment were nothing short of astonishing. Many participants were willing to deliver the maximum level of shock, even when the person pretending to be shocked was begging to be released or complaining of a heart condition.
Milgram's experiment revealed stunning information about the lengths that people are willing to go in order to obey, but it also caused considerable distress for the participants involved.
Zimbardo's Simulated Prison Experiment
Darrin Klimek / Getty Images
Psychologist Philip Zimbardo went to high school with Stanley Milgram and had an interest in how situational variables contribute to social behavior.
In his famous and controversial experiment, he set up a mock prison in the basement of the psychology department at Stanford University. Participants were then randomly assigned to be either prisoners or guards. Zimbardo himself served as the prison warden.
The researchers attempted to make a realistic situation, even "arresting" the prisoners and bringing them into the mock prison. Prisoners were placed in uniforms, while the guards were told that they needed to maintain control of the prison without resorting to force or violence.
When the prisoners began to ignore orders, the guards began to utilize tactics that included humiliation and solitary confinement to punish and control the prisoners.
While the experiment was originally scheduled to last two full weeks it had to be halted after just six days. Why? Because the prison guards had started abusing their authority and were treating the prisoners cruelly. The prisoners, on the other hand, started to display signs of anxiety and emotional distress.
It wasn't until a graduate student (and Zimbardo's future wife) Christina Maslach visited the mock prison that it became clear that the situation was out of control and had gone too far. Maslach was appalled at what was going on and voiced her distress. Zimbardo then decided to call off the experiment.
Zimbardo later suggested that "although we ended the study a week earlier than planned, we did not end it soon enough."
Watson and Rayner's Little Albert Experiment
If you have ever taken an Introduction to Psychology class, then you are probably at least a little familiar with Little Albert.
Behaviorist John Watson and his assistant Rosalie Rayner conditioned a boy to fear a white rat, and this fear even generalized to other white objects including stuffed toys and Watson's own beard.
Obviously, this type of experiment is considered very controversial today. Frightening an infant and purposely conditioning the child to be afraid is clearly unethical.
As the story goes, the boy and his mother moved away before Watson and Rayner could decondition the child, so many people have wondered if there might be a man out there with a mysterious phobia of furry white objects.
Controversy
Some researchers have suggested that the boy at the center of the study was actually a cognitively impaired boy who ended up dying of hydrocephalus when he was just six years old. If this is true, it makes Watson's study even more disturbing and controversial.
However, more recent evidence suggests that the real Little Albert was actually a boy named William Albert Barger.
Seligman's Look Into Learned Helplessness
During the late 1960s, psychologists Martin Seligman and Steven F. Maier conducted experiments that involved conditioning dogs to expect an electrical shock after hearing a tone. Seligman and Maier observed some unexpected results.
When initially placed in a shuttle box in which one side was electrified, the dogs would quickly jump over a low barrier to escape the shocks. Next, the dogs were strapped into a harness where the shocks were unavoidable.
After being conditioned to expect a shock that they could not escape, the dogs were once again placed in the shuttlebox. Instead of jumping over the low barrier to escape, the dogs made no efforts to escape the box.
Instead, they simply lay down, whined and whimpered. Since they had previously learned that no escape was possible, they made no effort to change their circumstances. The researchers called this behavior learned helplessness .
Seligman's work is considered controversial because of the mistreating the animals involved in the study.
Impact of Unethical Experiments in Psychology
Many of the psychology experiments performed in the past simply would not be possible today, thanks to ethical guidelines that direct how studies are performed and how participants are treated. While these controversial experiments are often disturbing, we can still learn some important things about human and animal behavior from their results.
Perhaps most importantly, some of these controversial experiments led directly to the formation of rules and guidelines for performing psychology studies.
Blum, Deborah. Love at Goon Park: Harry Harlow and the science of affection . New York: Basic Books; 2011.
Sperry L. Mental Health and Mental Disorders: an Encyclopedia of Conditions, Treatments, and Well-Being . Santa Barbara, CA: Greenwood, an imprint of ABC-CLIO, LLC; 2016.
Marcus S. Obedience to Authority An Experimental View. By Stanley Milgram. illustrated . New York: Harper &. The New York Times.
Le Texier T. Debunking the Stanford Prison Experiment . Am Psychol . 2019;74(7):823‐839. doi:10.1037/amp0000401
Fridlund AJ, Beck HP, Goldie WD, Irons G. Little Albert: A neurologically impaired child . Hist Psychol. 2012;15(4):302-27. doi:10.1037/a0026720
Powell RA, Digdon N, Harris B, Smithson C. Correcting the record on Watson, Rayner, and Little Albert: Albert Barger as "psychology's lost boy" . Am Psychol . 2014;69(6):600‐611. doi:10.1037/a0036854
Seligman ME. Learned helplessness . Annu Rev Med . 1972;23:407‐412. doi:10.1146/annurev.me.23.020172.002203
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Review Highlights Unethical Moments in Medical Research History

Tuskegee syphilis study is most famous
Doctors experimented on people who did not have full rights, obama bioethics panel will set new rules for medical studies, recent posts.

A Democracy Minute: Sherrilyn Ifill on patriotism
Watch and reflect on these 60-second video clips about democracy in America

News Hour Classroom's Journalism in Action website
The site continues to grow covering the role of civic engagement in U.S. history through journalism
SUPPORTED BY VIEWERS LIKE YOU. ADDITIONAL SUPPORT PROVIDED BY:

Copyright © 2023 NewsHour Production LLC. All Rights Reserved
Illustrations by Annamaria Ward
A Brief History of Human Challenge Trials
For more than two centuries, scientists have been intentionally infecting patients with dangerous diseases in order to learn more
Theresa Machemer
Correspondent
:focal(685x708:686x709)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/97/0f/970f0f9d-8d9e-4291-9a85-b4b743aa0a43/gettyimages-1230010833_web.jpg)
Physicians promise in the Hippocratic oath to keep their patients from harm, so intentionally exposing people to a deadly disease would seem to run counter to that contract. But with human challenge studies, they do exactly that. In challenge studies, medical professionals purposefully expose patients to illnesses so that they can study the patient’s symptoms and immune system response. Such studies can also help physicians discover what vaccines will work to prevent the affliction. Historically in such experiments, the health of individual patients, usually voluntary but at times, horrifically, not, has been sacrificed for medical knowledge and future treatments.
Researchers are planning new human challenge trials as the race to develop vaccines against Covid-19 is in a full sprint, with Pfizer’s vaccine receiving authorization in several countries and Moderna’s not far behind. But the end of the pandemic won’t just come from these two pharmaceutical breakthroughs. In order to fully contain the spread of Covid-19, many treatments and vaccines may be necessary in order to vaccinate billions of people. And some experts say that the fastest way to test those second-generation vaccines is through human challenge trials.
Imperial College London intends to begin a human challenge study related to Covid-19 as soon as January. During the study, scientists would purposely infect up to 100 young, healthy volunteers with the coronavirus that causes Covid-19 in the hopes of accelerating the search for new vaccines.
Supporters of the controversial Covid-19 human challenge trial argue that if it can be done safely then it provides a uniquely controlled environment to study factors that are difficult to unravel in longer, large-scale Phase III trials of thousands of people. Critics say that challenge studies are either unnecessary because of vaccine successes so far, or should be put on pause until a later date when they can be run safely. Critics also point out that safety is a concern even for young volunteers because scientists do not know how to treat Covid-19 or what its long-term effects are, and evidence presented by the World Health Organization in September showed that at least a fifth of people between 18 and 34 who catch Covid-19 experience prolonged symptoms.
The debate over such a contentious experiment is nothing new. Human challenge trials are as old as inoculation itself. In 1796, English surgeon Edward Jenner tested the world’s first vaccine by exposing his gardener’s 8-year-old son to cowpox and then smallpox. Human challenge trials have since been used to study dozens of diseases from cholera to cancer, but early studies often put participants directly in harm’s way, not always with their knowledge.
Today, challenge studies undergo careful review by boards of experts before they can begin. A key requirement of an ethical study is that volunteers provide informed consent , proving that they understand the risks of joining a study. The first informed consent process was introduced more than a century after Jenner’s human challenge study.
In 1898, as the U.S. warred with Spain in Cuba, yellow fever —which can cause liver damage, nausea, high fever and bleeding—killed 13 times more soldiers than war wounds. So in 1900, the U.S. Army established a commission led by pathologist Walter Reed to figure out how yellow fever spread and how to stop it. Because only humans seemed to fall ill with the disease, Reed and three colleagues on the commission designed a human challenge study to test a leading theory of yellow fever transmission: mosquito bites.
Reed recognized that if he was correct, then the study itself would be incredibly risky. The need to expose volunteers to deadly disease would have to be weighed with the responsibility to keep the volunteers safe.
“The general that created the commission told Walter Reed… that he had to be absolutely sure that no harm would be caused to the volunteers,” says Enrique Chaves-Carballo , a historian of medicine at the University of Kansas. “He was pretty specific about that.”
To balance his superior’s order with the study’s inherent risk, the commission came up with a novel solution: the first informed consent contract. The commission created a document for volunteers to sign, stating that they understood the study’s risks. However, the form suggested that abstaining from the study was risky, too. The contract stated :
“The undersigned understands perfectly well that in the case of the development of yellow fever in him, that he endangers his life to a certain extent but it being entirely impossible for him to avoid the infection during his stay in the island, he prefers to take the chance of contracting it intentionally in the belief that he will receive from the said Commission the greatest care and the most skillful medical service.”
During the experiment, the scientists first allowed mosquitoes to bite yellow fever patients so the insects would pick up the disease. Then, they brought the mosquitoes to healthy volunteers, and allowed the mosquitoes to bite them. When volunteers fell ill, Reed scoured blood samples for the microbe causing their illness.
Those with yellow fever were prescribed complete bed rest and fasting except for “a few sips of champagne” and some pain medication, says Chaves-Carballo. Volunteers received a hefty payment of $100 in gold per mosquito bite, and another $100 if they fell ill.
In the first round of experiments, 11 volunteers got mosquito bites. Two fell ill, and survived. The third man to fall ill, Jesse W. Lazear, was one of the scientists running the study. He was bitten by accident and died of yellow fever 12 days later.
Though Reed considered ending the study after the death of his colleague, the commission instead named a sanitary station Camp Lazear in his honor. And by 1901 , Reed and the commission had shown through their mosquito bite experiments that the insects transmit yellow fever. Inoculation of more volunteers with yellow fever patients’ filtered blood samples showed that a virus causes the disease—making yellow fever the first human virus scientists discovered.
With the disease-causing culprit identified, Reed returned to George Washington University (then Columbian University) to teach, and other scientists picked up the search for a yellow fever vaccine. U.S. army physician William Gorgas and Cuban-born physician Juan Guiteras established an inoculation station for a new round of human challenge studies in Havana. They hoped to learn how to induce light cases of yellow fever with mosquito bites in order to give people immunity. More than 20 volunteers signed up for the first experimental inoculations in 1901, including the only woman to participate in the study, a military nurse named Clara Maass.
Maass was bitten five times without developing yellow fever, and received $100 to send home to her mother and nine siblings in New Jersey—a huge sum compared to her monthly pay of $30 .
Her sixth mosquito bite proved fatal. She and two other volunteers were infected with a particularly violent strain of the virus—the doctors didn’t know how to induce just light cases—and all three died in August of 1901.
“Some of the headlines of the newspapers are like, ‘Nurse Dies for a Hundred Dollars,’” says Chaves-Carballo. “People responded to the fact that she was a young nurse who was trying her best to help her family.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/3e/cc/3ecc2bca-8915-4c6c-bce7-b396fa7855fd/gettyimages-517447560_web.jpg)
Public outcry in the U.S. brought the Havana experiments to an end. Maass’ death brought the study’s exorbitant pay under fire, as such a large incentive may have interfered with the participants’ ability to accurately weigh the risk of joining the study. The fact that the study was run by the U.S. Army, and Reed’s participants were members of the military, also brought into question the participants’ ability to freely opt out of the study, says Monica McArthur , pediatrician and infectious disease specialist at the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health.
“In a lot of the studies early on, the Walter Reed experiment and other studies, used what we would now consider vulnerable populations,” people who couldn’t freely agree to participate or make a fully informed decision, says McArthur. “Prisoners, for example, could be enrolled in studies.”
A classic example of a challenge study that relied on a vulnerable population is the Tuskegee Syphilis Study. Beginning in 1932 , the U.S. Public Health Service recruited about 600 poor African American men from around Tuskegee, Alabama, for a study of how syphilis worsens over time. About two-thirds of the men had syphilis, but the study doctors informed them they had “bad blood.”
After receiving this phony diagnosis, the men were persuaded to join the study in exchange for free meals, hospital access and treatment for “bad blood” and other unrelated conditions. The scientists also provided participants a burial stipend that would be paid to their survivors after their deaths.
Only about half of the men with syphilis received a treatment that was usually prescribed in the 1930s: doses of toxic arsenic and mercury. The doctors subjected the participants to blood draws and spinal taps, and after they died of syphilis, autopsies, all in pursuit of more information about the natural course of the disease. The study lasted for decades, and even after the medical community established that penicillin could cure the disease in the 1940s the men did not receive the medication.
In 1972, journalist Jean Heller of the Associated Press brought the Tuskegee Syphilis Study to light and shared how the doctors involved in the study had deceived the men participating. By then, only 74 of the men with syphilis still survived. Public outrage shut the study down three months after the report.
While the Tuskegee Syphilis Study relied on participants who were already ill, other studies exposed otherwise healthy people to deadly diseases. For example, from 1955 to 1970, a pediatrician exposed more than 50 children with mental disabilities to hepatitis in order to identify different strains of the disease and eventually develop vaccines. The trial took place at Willowbrook State School, a home for children and adults with developmental disabilities in Staten Island, New York.
The school was overcrowded and had a lengthy waitlist for new patients. But the study’s principal investigator, Saul Krugman, offered several parents the opportunity to cut the line if they agreed to enroll their children in the study. Krugman told them that their children were likely to catch the disease at the facility anyway, but by joining the study, they would have access to cleaner facilities and a chance at an eventual vaccine.
“I did feel coerced,” said Diana McCourt, who enrolled her daughter in the Willowbrook study, to Forbes ’ Leah Rosenbaum. “I felt like I was denied help unless I took this [opportunity].”
The Willowbrook studies, which ended in 1970, revealed the existence of the A and B strains of hepatitis and sped up the development of a hepatitis B vaccine. But the studies progressed even as some in the medical community criticized Krugman’s methods. In 1966, anesthesiologist Henry K. Beecher published a landmark essay detailing 22 examples of ongoing unethical research on human subjects, including the Willowbrook hepatitis studies, in order to raise awareness and end unethical practices that continued despite the creation of international human experimentation guidelines—the Nuremberg Code in 1947 and the Declaration of Helsinki in 1964.
In addition to the Willowbrook study, Beecher highlighted one study in which melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer, was transferred from a woman to her mother “in the hope of gaining a little better understanding of cancer immunity.” The woman died on the same day that her mother was to receive the melanoma injection, so the doctors knew the cancer was deadly. Her mother died 451 days after receiving the injection.
Beecher concluded that an ethical approach to experimentation requires, first and foremost, the informed consent of study volunteers. “The difficulty of obtaining this is discussed in detail,” he writes, “But it is absolutely essential to strive for it for moral, sociologic and legal reasons. The statement that consent has been obtained has little meaning unless the subject or his guardian is capable of understanding what is to be undertaken and unless all hazards are made clear.”
Human challenge studies became less common after the 1970s with the conclusion of unethical studies that shocked the public. Since then, the Declaration of Helsinki has been amended seven times to clarify ethical standards for human experiments, most recently in October of 2013. The current declaration states that “While the primary purpose of medical research is to generate new knowledge, this goal can never take precedence over the rights and interests of individual research subjects.”
When run well, challenge studies are still uniquely able to provide clear data about infectious diseases. “They are now coming back in favor with very rigorous ethical principles in place,” adds McArthur.
The University of Maryland used human challenge studies in 2012 and 2013 to develop a vaccine for cholera , which was approved by the FDA in 2016. Cholera was an ideal candidate for a safe human challenge study because it is well understood by scientists, is reliably treatable with fluids and antibiotics, and has no long-term effects after the infection is gone.
Informed consent procedures have come a long way since Reed’s contract. Volunteers can ask questions and seek outside guidance, and must pass an assessment designed by the researchers to prove that they understand the risks of a study. And the volunteers have the power to quit. “Every time there’s an encounter with the volunteer, it’s reaffirming that the volunteer is still willing and able to participate,” says McArthur.
According to a statement by Imperial College London, which still needs to have its experimental plan approved by government regulators before researchers can begin recruiting participants, volunteers’ safety is the number one priority. “It would be nice to see exactly how [Imperial College London] explains the risks and benefits to those participating in this study,” says Chaves-Carballo.
Covid-19 is different from other challenge study diseases: Scientists have been studying it for less than a year, physicians have no approved treatments to intervene if a volunteer’s illness becomes severe, and early evidence suggests Covid-19 can cause long-term effects even in young, previously healthy people. The Imperial College London study aims to first identify the minimum dose of coronavirus necessary to cause disease. The study would use that dose of virus to study how vaccines work in the body to prevent Covid-19, to look at potential treatments and study the immune response. The biomedical community remains split on whether such a study should be run, given all of the unknowns around Covid-19.
When scientists develop second- and third-generation vaccines, a challenge study allows researchers to work with just 100 people instead of tens of thousands. That means fewer people are asked to go without the vaccine for the sake of research. And by waiting to conduct a challenge study on Covid-19 until a later date, researchers might get access to new information about risk factors for severe disease, which could help make the study safer.
“I am not a fan of SARS-CoV-2 challenge studies,” says McArthur. “But if I’m playing devil’s advocate against myself, some of the very reasons [not to do a challenge study] that I listed might be reasons that someone else might say that a challenge study is beneficial. Because we don’t know that much about a disease, so we could learn more about it.”
Get the latest Science stories in your inbox.
Theresa Machemer | READ MORE
Theresa Machemer is a freelance writer based in Washington DC. Her work has also appeared in National Geographic and SciShow. Website: tkmach.com
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Unethical human research in the field of neuroscience: a historical review
Affiliations.
- 1 King Abdulaziz Medical City, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, P.O. Box: 12723, Jeddah, 21483, Saudi Arabia. [email protected].
- 2 King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- 3 King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- PMID: 29460160
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-018-3245-1
Understanding the historical foundations of ethics in human research are key to illuminating future human research and clinical trials. This paper gives an overview of the most remarkable unethical human research and how past misconducts helped develop ethical guidelines on human experimentation such as The Nuremberg Code 1947 following WWII. Unethical research in the field of neuroscience also proved to be incredibly distressing. Participants were often left with life-long cognitive disabilities. This emphasizes the importance of implicating strict rules and ethical guidelines in neuroscience research that protect participants and respects their dignity. The experiments conducted by German Nazi in the concentration camps during WWII are probably the most inhumane and brutal ever conducted. The Nuremberg Code of 1947, one of the few positive outcomes of the Nazi experiments, is often considered the first document to set out ethical regulations of human research. It consists of numerous necessary criteria, to highlight a few, the subject must give informed consent, there must be a concrete scientific basis for the experiment, and the experiment should yield positive results that cannot be obtained in any other way. In the end, we must remember, the interest of the patient must always prevail over the interest of science or society.
Keywords: Ethics; History; Neuroscience; Unethical research.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- [The origin of informed consent]. Mallardi V. Mallardi V. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2005 Oct;25(5):312-27. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2005. PMID: 16602332 Italian.
- Nazi Medical Research in Neuroscience: Medical Procedures, Victims, and Perpetrators. Loewenau A, Weindling PJ. Loewenau A, et al. Can Bull Med Hist. 2016 Fall;33(2):418-446. doi: 10.3138/cbmh.33.2.152-27012015. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Can Bull Med Hist. 2016. PMID: 28155423
- Scientific misconduct and unethical human experimentation: historic parallels and moral implications. Lefor AT. Lefor AT. Nutrition. 2005 Jul-Aug;21(7-8):878-82. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2004.10.011. Nutrition. 2005. PMID: 15975498
- Retreat from Nuremberg: can we prevent unethical medical research? Horner JS. Horner JS. Public Health. 1999 Sep;113(5):205-10. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(99)00160-2. Public Health. 1999. PMID: 10557112 Review.
- The role of an independent and interdisciplinary assessment of research studies with human subjects in Europe and worldwide. Rittner C. Rittner C. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2009 Apr;11 Suppl 1:S80-1. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.01.018. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2009. PMID: 19269235 Review.
- Poor Representation of Developing Countries in Editorial Boards of Leading Obstetrics and Gynaecology Journals. Rawat S, Mathe P, Unnithan VB, Kumar P, Abhishek K, Praveen N, Guleria K. Rawat S, et al. Asian Bioeth Rev. 2023 Feb 7;15(3):241-258. doi: 10.1007/s41649-023-00241-w. eCollection 2023 Jul. Asian Bioeth Rev. 2023. PMID: 37399006 Free PMC article.
- Demographic reporting across a decade of neuroimaging: a systematic review. Sterling E, Pearl H, Liu Z, Allen JW, Fleischer CC. Sterling E, et al. Brain Imaging Behav. 2022 Dec;16(6):2785-2796. doi: 10.1007/s11682-022-00724-8. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Brain Imaging Behav. 2022. PMID: 36114313 Free PMC article. Review.
- Ethics in field experimentation: A call to establish new standards to protect the public from unwanted manipulation and real harms. McDermott R, Hatemi PK. McDermott R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 1;117(48):30014-30021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012021117. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33229586 Free PMC article.
- AAN position statement: Ethical issues in clinical research in neurology. Tolchin B, Conwit R, Epstein LG, Russell JA; Ethics, Law, and Humanities Committee, a joint committee of the American Academy of Neurology, American Neurological Association, and Child Neurology Society. Tolchin B, et al. Neurology. 2020 Apr 14;94(15):661-669. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009241. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32179700 Free PMC article. Review.
- Unethical work must be filtered out or flagged. Ruxton GD, Mulder T. Ruxton GD, et al. Nature. 2019 Aug;572(7768):171-172. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-02378-x. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31384054 No abstract available.
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources, other literature sources.
- scite Smart Citations
Miscellaneous
- NCI CPTAC Assay Portal
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

How the Classics Changed Research Ethics
Some of history’s most controversial psychology studies helped drive extensive protections for human research participants. some say those reforms went too far..
- Behavioral Research
- Institutional Review Board (IRB)
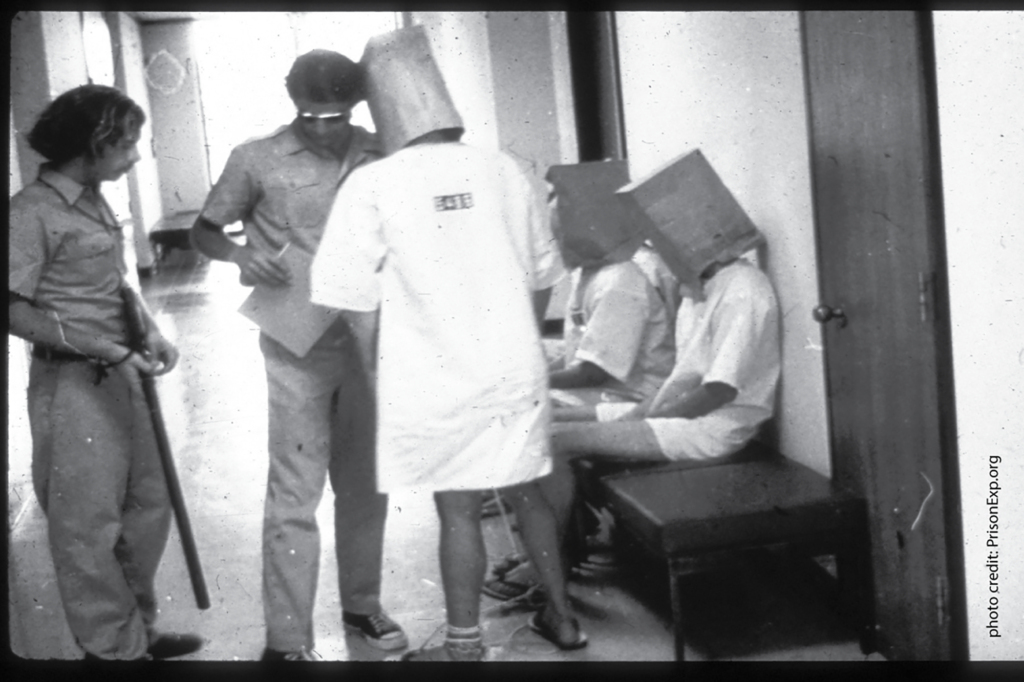
Photo above: In 1971, APS Fellow Philip Zimbardo halted his classic prison simulation at Stanford after volunteer “guards” became abusive to the “prisoners,” famously leading one prisoner into a fit of sobbing. Photo credit: PrisonExp.org
Nearly 60 years have passed since Stanley Milgram’s infamous “shock box” study sparked an international focus on ethics in psychological research. Countless historians and psychology instructors assert that Milgram’s experiments—along with studies like the Robbers Cave and Stanford prison experiments—could never occur today; ethics gatekeepers would swiftly bar such studies from proceeding, recognizing the potential harms to the participants.
But the reforms that followed some of the 20th century’s most alarming biomedical and behavioral studies have overreached, many social and behavioral scientists complain. Studies that pose no peril to participants confront the same standards as experimental drug treatments or surgeries, they contend. The institutional review boards (IRBs) charged with protecting research participants fail to understand minimal risk, they say. Researchers complain they waste time addressing IRB concerns that have nothing to do with participant safety.
Several factors contribute to this conflict, ethicists say. Researchers and IRBs operate in a climate of misunderstanding, confusing regulations, and a systemic lack of ethics training, said APS Fellow Celia Fisher, a Fordham University professor and research ethicist, in an interview with the Observer .
“In my view, IRBs are trying to do their best and investigators are trying to do their best,” Fisher said. “It’s more that we really have to enhance communication and training on both sides.”
‘Sins’ from the past
Modern human-subjects protections date back to the 1947 Nuremberg Code, the response to Nazi medical experiments on concentration-camp internees. Those ethical principles, which no nation or organization has officially accepted as law or official ethics guidelines, emphasized that a study’s benefits should outweigh the risks and that human subjects should be fully informed about the research and participate voluntarily.
See the 2014 Observer cover story by APS Fellow Carol A. Tavris, “ Teaching Contentious Classics ,” for more about these controversial studies and how to discuss them with students.
But the discovery of U.S.-government-sponsored research abuses, including the Tuskegee syphilis experiment on African American men and radiation experiments on humans, accelerated regulatory initiatives. The abuses investigators uncovered in the 1970s, 80s, and 90s—decades after the experiments had occurred—heightened policymakers’ concerns “about what else might still be going on,” George Mason University historian Zachary M. Schrag explained in an interview. These concerns generated restrictions not only on biomedical research but on social and behavioral studies that pose a minute risk of harm.
“The sins of researchers from the 1940s led to new regulations in the 1990s, even though it was not at all clear that those kinds of activities were still going on in any way,” said Schrag, who chronicled the rise of IRBs in his book Ethical Imperialism: Institutional Review Boards and the Social Sciences, 1965–2009.
Accompanying the medical research scandals were controversial psychological studies that provided fodder for textbooks, historical tomes, and movies.
- In the early 1950s, social psychologist Muzafer Sherif and his colleagues used a Boy Scout camp called Robbers Cave to study intergroup hostility. They randomly assigned preadolescent boys to one of two groups and concocted a series of competitive activities that quickly sparked conflict. They later set up a situation that compelled the boys to overcome their differences and work together. The study provided insights into prejudice and conflict resolution but generated criticism because the children weren’t told they were part of an experiment.
- In 1961, Milgram began his studies on obedience to authority by directing participants to administer increasing levels of electric shock to another person (a confederate). To Milgram’s surprise, more than 65% of the participants delivered the full voltage of shock (which unbeknownst to them was fake), even though many were distressed about doing so. Milgram was widely criticized for the manipulation and deception he employed to carry out his experiments.
- In 1971, APS Fellow Philip Zimbardo halted his classic prison simulation at Stanford after volunteer “guards” became abusive to the “prisoners,” famously leading one prisoner into a fit of sobbing.
Western policymakers created a variety of safeguards in the wake of these psychological studies and other medical research. Among them was the Declaration of Helsinki, an ethical guide for human-subjects research developed by the Europe-based World Medical Association. The U.S. Congress passed the National Research Act of 1974, which created a commission to oversee participant protections in biomedical and behavioral research. And in the 90s, federal agencies adopted the Federal Policy for the Protection of Human Subjects (better known as the Common Rule), a code of ethics applied to any government-funded research. IRBs review studies through the lens of the Common Rule. After that, social science research, including studies in social psychology, anthropology, sociology, and political science, began facing widespread institutional review (Schrag, 2010).
Sailing Through Review
Psychological scientists and other researchers who have served on institutional review boards provide these tips to help researchers get their studies reviewed swiftly.
- Determine whether your study qualifies for minimal-risk exemption from review. Online tools are even in development to help researchers self-determine exempt status (Ben-Shahar, 2019; Schneider & McClutcheon, 2018).
- If you’re not clear about your exemption, research the regulations to understand how they apply to your planned study. Show you’ve done your homework and have developed a protocol that is safe for your participants.
- Consult with stakeholders. Look for advocacy groups and representatives from the population you plan to study. Ask them what they regard as fair compensation for participation. Get their feedback about your questionnaires and consent forms to make sure they’re understandable. These steps help you better show your IRB that the population you’re studying will find the protections adequate (Fisher, 2022).
- Speak to IRB members or staff before submitting the protocol. Ask them their specific concerns about your study, and get guidance on writing up the protocol to address those concerns. Also ask them about expected turnaround times so you can plan your submission in time to meet any deadlines associated with your study (e.g., grant application deadlines).
Ben-Shahar, O. (2019, December 2). Reforming the IRB in experimental fashion. The Regulatory Review . University of Pennsylvania. https://www.theregreview.org/2019/12/02/ben-shahar-reforming-irb-experimental-fashion/
Fisher, C. B. (2022). Decoding the ethics code: A practical guide for psychologists (5 th ed.). Sage Publications.
Schneider, S. L. & McCutcheon, J. A. (2018). Proof of concept: Use of a wizard for self-determination of IRB exempt status . Federal Demonstration Partnership. http://thefdp.org/default/assets/File/Documents/wizard_pilot_final_rpt.pdf
Social scientists have long contended that the Common Rule was largely designed to protect participants in biomedical experiments—where scientists face the risk of inducing physical harm on subjects—but fits poorly with the other disciplines that fall within its reach.
“It’s not like the IRBs are trying to hinder research. It’s just that regulations continue to be written in the medical model without any specificity for social science research,” she explained.
The Common Rule was updated in 2018 to ease the level of institutional review for low-risk research techniques (e.g., surveys, educational tests, interviews) that are frequent tools in social and behavioral studies. A special committee of the National Research Council (NRC), chaired by APS Past President Susan Fiske, recommended many of those modifications. Fisher was involved in the NRC committee, along with APS Fellows Richard Nisbett (University of Michigan) and Felice J. Levine (American Educational Research Association), and clinical psychologist Melissa Abraham of Harvard University. But the Common Rule reforms have yet to fully expedite much of the research, partly because the review boards remain confused about exempt categories, Fisher said.
Interference or support?
That regulatory confusion has generated sour sentiments toward IRBs. For decades, many social and behavioral scientists have complained that IRBs effectively impede scientific progress through arbitrary questions and objections.
In a Perspectives on Psychological Science paper they co-authored, APS Fellows Stephen Ceci of Cornell University and Maggie Bruck of Johns Hopkins University discussed an IRB rejection of their plans for a study with 6- to 10-year-old participants. Ceci and Bruck planned to show the children videos depicting a fictional police officer engaging in suggestive questioning of a child.
“The IRB refused to approve the proposal because it was deemed unethical to show children public servants in a negative light,” they wrote, adding that the IRB held firm on its rejection despite government funders already having approved the study protocol (Ceci & Bruck, 2009).
Other scientists have complained the IRBs exceed their Common Rule authority by requiring review of studies that are not government funded. In 2011, psychological scientist Jin Li sued Brown University in federal court for barring her from using data she collected in a privately funded study on educational testing. Brown’s IRB objected to the fact that she paid her participants different amounts of compensation based on need. (A year later, the university settled the case with Li.)
In addition, IRBs often hover over minor aspects of a study that have no genuine relation to participant welfare, Ceci said in an email interview.
“You can have IRB approval and later decide to make a nominal change to the protocol (a frequent one is to add a new assistant to the project or to increase the sample size),” he wrote. “It can take over a month to get approval. In the meantime, nothing can move forward and the students sit around waiting.”
Not all researchers view institutional review as a roadblock. Psychological scientist Nathaniel Herr, who runs American University’s Interpersonal Emotion Lab and has served on the school’s IRB, says the board effectively collaborated with researchers to ensure the study designs were safe and that participant privacy was appropriately protected
“If the IRB that I operated on saw an issue, they shared suggestions we could make to overcome that issue,” Herr said. “It was about making the research go forward. I never saw a project get shut down. It might have required a significant change, but it was often about confidentiality and it’s something that helps everybody feel better about the fact we weren’t abusing our privilege as researchers. I really believe it [the review process] makes the projects better.”
Some universities—including Fordham University, Yale University, and The University of Chicago—even have social and behavioral research IRBs whose members include experts optimally equipped to judge the safety of a psychological study, Fisher noted.
Training gaps
Institutional review is beset by a lack of ethics training in research programs, Fisher believes. While students in professional psychology programs take accreditation-required ethics courses in their doctoral programs, psychologists in other fields have no such requirement. In these programs, ethics training is often limited to an online program that provides, at best, a perfunctory overview of federal regulations.
“It gives you the fundamental information, but it has nothing to do with our real-world deliberations about protecting participants,” she said.
Additionally, harm to a participant is difficult to predict. As sociologist Martin Tolich of University of Otago in New Zealand wrote, the Stanford prison study had been IRB-approved.
“Prediction of harm with any certainty is not necessarily possible, and should not be the aim of ethics review,” he argued. “A more measured goal is the minimization of risk, not its eradication” (Tolich, 2014).
Fisher notes that scientists aren’t trained to recognize and respond to adverse events when they occur during a study.
“To be trained in research ethics requires not just knowing you have to obtain informed consent,” she said. “It’s being able to apply ethical reasoning to each unique situation. If you don’t have the training to do that, then of course you’re just following the IRB rules, which are very impersonal and really out of sync with the true nature of what we’re doing.”
Researchers also raise concerns that, in many cases, the regulatory process harms vulnerable populations rather than safeguards them. Fisher and psychological scientist Brian Mustanski of University of Illinois at Chicago wrote in 2016, for example, that the review panels may be hindering HIV prevention strategies by requiring researchers to get parental consent before including gay and bisexual adolescents in their studies. Under that requirement, youth who are not out to their families get excluded. Boards apply those restrictions even in states permitting minors to get HIV testing and preventive medication without parental permission—and even though federal rules allow IRBs to waive parental consent in research settings (Mustanski & Fisher, 2016)
IRBs also place counterproductive safety limits on suicide and self-harm research, watching for any sign that a participant might need to be removed from a clinical study and hospitalized.
“The problem is we know that hospitalization is not the panacea,” Fisher said. “It stops suicidality for the moment, but actually the highest-risk period is 3 months after the first hospitalization for a suicide attempt. Some of the IRBs fail to consider that a non-hospitalization intervention that’s being tested is just as safe as hospitalization. It’s a difficult problem, and I don’t blame them. But if we have to take people out of a study as soon as they reach a certain level of suicidality, then we’ll never find effective treatment.”
Communication gaps
Supporters of the institutional review process say researchers tend to approach the IRB process too defensively, overlooking the board’s good intentions.
“Obtaining clarification or requesting further materials serve to verify that protections are in place,” a team of institutional reviewers wrote in an editorial for Psi Chi Journal of Psychological Research . “If researchers assume that IRBs are collaborators in the research process, then these requests can be seen as prompts rather than as admonitions” (Domenech Rodriguez et al., 2017).
Fisher agrees that researchers’ attitudes play a considerable role in the conflicts that arise over ethics review. She recommends researchers develop each protocol with review-board questions in mind (see sidebar).
“For many researchers, there’s a disdain for IRBs,” she said. “IRBs are trying their hardest. They don’t want to reject research. It’s just that they’re not informed. And sometimes if behavioral scientists or social scientists are disdainful of their IRBs, they’re not communicating with them.”
Some researchers are building evidence to help IRBs understand the level of risk associated with certain types of psychological studies.
- In a study involving more than 500 undergraduate students, for example, psychological scientists at the University of New Mexico found that the participants were less upset than expected by questionnaires about sex, trauma , and other sensitive topics. This finding, the researchers reported in Psychological Science , challenges the usual IRB assumption about the stress that surveys on sex and trauma might inflict on participants (Yeater et al., 2012).
- A study involving undergraduate women indicated that participants who had experienced child abuse , although more likely than their peers to report distress from recalling the past as part of a study, were also more likely to say that their involvement in the research helped them gain insight into themselves and hoped it would help others (Decker et al., 2011).
- A multidisciplinary team, including APS Fellow R. Michael Furr of Wake Forest University, found that adolescent psychiatric patients showed a drop in suicide ideation after being questioned regularly about their suicidal thoughts over the course of 2 years. This countered concerns that asking about suicidal ideation would trigger an increase in such thinking (Mathias et al., 2012).
- A meta-analysis of more than 70 participant samples—totaling nearly 74,000 individuals—indicated that people may experience only moderate distress when discussing past traumas in research studies. They also generally might find their participation to be a positive experience, according to the findings (Jaffe et al., 2015).
The takeaways
So, are the historians correct? Would any of these classic experiments survive IRB scrutiny today?
Reexaminations of those studies make the question arguably moot. Recent revelations about some of these studies suggest that scientific integrity concerns may taint the legacy of those findings as much as their impact on participants did (Le Texier, 2019, Resnick, 2018; Perry, 2018).
Also, not every aspect of the controversial classics is taboo in today’s regulatory environment. Scientists have won IRB approval to conceptually replicate both the Milgram and Stanford prison experiments (Burger, 2009; Reicher & Haslam, 2006). They simply modified the protocols to avert any potential harm to the participants. (Scholars, including Zimbardo himself, have questioned the robustness of those replication findings [Elms, 2009; Miller, 2009; Zimbardo, 2006].)
Many scholars believe there are clear and valuable lessons from the classic experiments. Milgram’s work, for instance, can inject clarity into pressing societal issues such as political polarization and police brutality . Ethics training and monitoring simply need to include those lessons learned, they say.
“We should absolutely be talking about what Milgram did right, what he did wrong,” Schrag said. “We can talk about what we can learn from that experience and how we might answer important questions while respecting the rights of volunteers who participate in psychological experiments.”
Feedback on this article? Email [email protected] or login to comment.
References
Burger, J. M. (2009). Replicating Milgram: Would people still obey today? American Psychologist , 64 (1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0010932
Ceci, S. J. & Bruck, M. (2009). Do IRBs pass the minimal harm test? Perspectives on Psychological Science , 4 (1), 28–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6924.2009.01084.x
Decker, S. E., Naugle, A. E., Carter-Visscher, R., Bell, K., & Seifer, A. (2011). Ethical issues in research on sensitive topics: Participants’ experiences of stress and benefit . Journal of Empirical Research on Human Research Ethics: An International Journal , 6 (3), 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1525/jer.2011.6.3.55
Domenech Rodriguez, M. M., Corralejo, S. M., Vouvalis, N., & Mirly, A. K. (2017). Institutional review board: Ally not adversary. Psi Chi Journal of Psychological Research , 22 (2), 76–84. https://doi.org/10.24839/2325-7342.JN22.2.76
Elms, A. C. (2009). Obedience lite. American Psychologist , 64 (1), 32–36. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014473
Fisher, C. B., True, G., Alexander, L., & Fried, A. L. (2009). Measures of mentoring, department climate, and graduate student preparedness in the responsible conduct of psychological research. Ethics & Behavior , 19 (3), 227–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508420902886726
Jaffe, A. E., DiLillo, D., Hoffman, L., Haikalis, M., & Dykstra, R. E. (2015). Does it hurt to ask? A meta-analysis of participant reactions to trauma research. Clinical Psychology Review , 40 , 40–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2015.05.004
Le Texier, T. (2019). Debunking the Stanford Prison experiment. American Psychologist , 74 (7), 823–839. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/amp0000401
Mathias, C. W., Furr, R. M., Sheftall, A. H., Hill-Kapturczak, N., Crum, P., & Dougherty, D. M. (2012). What’s the harm in asking about suicide ideation? Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior , 42 (3), 341–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1943-278X.2012.0095.x
Miller, A. G. (2009). Reflections on “Replicating Milgram” (Burger, 2009). American Psychologist , 64 (1), 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014407
Mustanski, B., & Fisher, C. B. (2016). HIV rates are increasing in gay/bisexual teens: IRB barriers to research must be resolved to bend the curve. American Journal of Preventive Medicine , 51 (2), 249–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2016.02.026
Perry, G. (2018). The lost boys: Inside Muzafer Sherif’s Robbers Cave experiment. Scribe Publications.
Reicher, S. & Haslam, S. A. (2006). Rethinking the psychology of tyranny: The BBC prison study. British Journal of Social Psychology , 45 , 1–40. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466605X48998
Resnick, B. (2018, June 13). The Stanford prison experiment was massively influential. We just learned it was a fraud. Vox. https://www.vox.com/2018/6/13/17449118/stanford-prison-experiment-fraud-psychology-replication
Schrag, Z. M. (2010). Ethical imperialism: Institutional review boards and the social sciences, 1965–2009 . Johns Hopkins University Press.
Tolich, M. (2014). What can Milgram and Zimbardo teach ethics committees and qualitative researchers about minimal harm? Research Ethics , 10 (2), 86–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016114523771
Yeater, E., Miller, G., Rinehart, J., & Nason, E. (2012). Trauma and sex surveys meet minimal risk standards: Implications for institutional review boards. Psychological Science , 23 (7), 780–787. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797611435131
Zimbardo, P. G. (2006). On rethinking the psychology of tyranny: The BBC prison study. British Journal of Social Psychology , 45 , 47–53. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466605X81720
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.
About the Author
Scott Sleek is a freelance writer in Silver Spring, Maryland, and the former director of news and information at APS.

Inside Grants: National Science Foundation Research Data Ecosystems (RDE)
The National Science Foundation’s Research Data Ecosystems (RDE) is a $38 million effort to improve scientific research through modernized data management collection.

Up-and-Coming Voices: Methodology and Research Practices
Talks by students and early-career researchers related to methodology and research practices.

Understanding ‘Scientific Consensus’ May Correct Misperceptions About GMOs, but Not Climate Change
Explaining the meaning of “scientific consensus” may be more effective at countering some types of misinformation than others.
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AWSELBCORS | 5 minutes | This cookie is used by Elastic Load Balancing from Amazon Web Services to effectively balance load on the servers. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| at-rand | never | AddThis sets this cookie to track page visits, sources of traffic and share counts. |
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
| uvc | 1 year 27 days | Set by addthis.com to determine the usage of addthis.com service. |
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_3507334_1 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| loc | 1 year 27 days | AddThis sets this geolocation cookie to help understand the location of users who share the information. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
Unethical human research in the field of neuroscience: a historical review
- Review Article
- Published: 19 February 2018
- Volume 39 , pages 829–834, ( 2018 )
Cite this article

- Hussein Algahtani ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9484-9838 1 ,
- Mohammed Bajunaid 2 &
- Bader Shirah 3
8525 Accesses
13 Citations
32 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Understanding the historical foundations of ethics in human research are key to illuminating future human research and clinical trials. This paper gives an overview of the most remarkable unethical human research and how past misconducts helped develop ethical guidelines on human experimentation such as The Nuremberg Code 1947 following WWII. Unethical research in the field of neuroscience also proved to be incredibly distressing. Participants were often left with life-long cognitive disabilities. This emphasizes the importance of implicating strict rules and ethical guidelines in neuroscience research that protect participants and respects their dignity. The experiments conducted by German Nazi in the concentration camps during WWII are probably the most inhumane and brutal ever conducted. The Nuremberg Code of 1947, one of the few positive outcomes of the Nazi experiments, is often considered the first document to set out ethical regulations of human research. It consists of numerous necessary criteria, to highlight a few, the subject must give informed consent, there must be a concrete scientific basis for the experiment, and the experiment should yield positive results that cannot be obtained in any other way. In the end, we must remember, the interest of the patient must always prevail over the interest of science or society.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Research Ethics and Scientific Integrity in Neuroscience

Human Brain Research and Ethics
Explore related subjects.
- Medical Ethics
Nardini C (2014) The ethics of clinical trials. Ecancermedicalscience 8:387
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Glenn Forister J, Dennis Blessing J (2015) Introduction to research and medical literature for health professionals. Jones & Bartlett Learning, Burlington
Google Scholar
NIH Clinical Center: Ethics in Clinical Research. Retrieved 24 August 2017. Available at https://clinicalcenter.nih.gov/recruit/ethics.html
Illes J, Bird SJ (2006) Neuroethics: a modern context for ethics in neuroscience. Trends Neurosci 29(9):511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2006.07.002
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Silverman F (1988) The “monster” study. J Fluen Disord 13(3):225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0094-730X(88)90049-6
Article Google Scholar
Stanford Prison Experiment. Retrieved 24 August 2017. Available at https://www.simplypsychology.org/zimbardo.html
Thomas SB, Quinn SC (1991) The Tuskegee Syphilis Study, 1932 to 1972: implications for HIV education and AIDS risk education programs in the black community. Am J Public Health 81(11):1498–1505. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.81.11.1498
Brandt AM (1978) Racism and research: the case of the Tuskegee Syphilis Study. Hast Cent Rep 8(6):21–29. https://doi.org/10.2307/3561468
Article CAS Google Scholar
Korda A The Nazi medical experiments. ADF Health [online]. Retrieved 24 August 2017. Available at: http://www.defence.gov.au/health/infocentre/journals/adfhj_apr06/adfhealth_7_1_33-37.html
The 30 most disturbing human experiments in history. Retrieved 24 August 2017. Available at http://www.bestpsychologydegrees.com/30-most-disturbing-human-experiments-in-history/
Strous RD, Edelman MC (2007) Eponyms and the Nazi era: time to remember and time for change. Isr Med Assoc J 9(3):207–214
PubMed Google Scholar
Laud Humphreys and the Tearoom Sex Study. Retrieved 24 August 2017. Available at http://www.drjkoch.org/Intro/Readings/Humphreys.htm
Harris B (1979) Whatever happened to little Albert? Am Psychol 34(2):151–160. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.34.2.151
Slater M, Antley A, Davison A, Swapp D, Guger C, Barker C, Pistrang N, Sanchez-Vives MV (2006) A virtual reprise of the Stanley Milgram obedience experiments. PLoS One 1(1):e39. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000039
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Schell BH (1994) The ominous shadow of the CIA has imprinted itself on the brain research community. J Calif Alliance Ment Ill 5(1):38–40
Wilson ST, Stanley B (2006) Ethical concerns in schizophrenia research: looking back and moving forward. Schizophr Bull 32(1):30–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbj023
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
King Abdulaziz Medical City, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, P.O. Box: 12723, Jeddah, 21483, Saudi Arabia
Hussein Algahtani
King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Mohammed Bajunaid
King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Bader Shirah
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hussein Algahtani .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Algahtani, H., Bajunaid, M. & Shirah, B. Unethical human research in the field of neuroscience: a historical review. Neurol Sci 39 , 829–834 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3245-1
Download citation
Received : 24 October 2017
Accepted : 03 January 2018
Published : 19 February 2018
Issue Date : May 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3245-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Unethical research
- Neuroscience
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- 30 Most Unethical Psychology Human Experiments
Disturbing human experiments aren’t something the average person thinks too much about. Rather, the progress achieved in the last 150 years of human history is an accomplishment we’re reminded of almost daily. Achievements made in biomedicine and the f ield of psychology mean that we no longer need to worry about things like deadly diseases or masturbation as a form of insanity. For better or worse, we have developed more effective ways to gather information, treat skin abnormalities, and even kill each other. But what we are not constantly reminded of are the human lives that have been damaged or lost in the name of this progress. The following is a list of the 30 most disturbing human experiments in history.
30. The Tearoom Sex Study

Image Source Sociologist Laud Humphreys often wondered about the men who commit impersonal sexual acts with one another in public restrooms. He wondered why “tearoom sex” — fellatio in public restrooms — led to the majority of homosexual arrests in the United States. Humphreys decided to become a “watchqueen” (the person who keeps watch and coughs when a cop or stranger get near) for his Ph.D. dissertation at Washington University. Throughout his research, Humphreys observed hundreds of acts of fellatio and interviewed many of the participants. He found that 54% of his subjects were married, and 38% were very clearly neither bisexual or homosexual. Humphreys’ research shattered a number of stereotypes held by both the public and law enforcement.
29. Prison Inmates as Test Subjects

Image Source In 1951, Dr. Albert M. Kligman, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania and future inventor of Retin-A, began experimenting on inmates at Philadelphia’s Holmesburg Prison. As Kligman later told a newspaper reporter, “All I saw before me were acres of skin. It was like a farmer seeing a field for the first time.” Over the next 20 years, inmates willingly allowed Kligman to use their bodies in experiments involving toothpaste, deodorant, shampoo, skin creams, detergents, liquid diets, eye drops, foot powders, and hair dyes. Though the tests required constant biopsies and painful procedures, none of the inmates experienced long-term harm.
28. Henrietta Lacks

Image Source In 1955, Henrietta Lacks, a poor, uneducated African-American woman from Baltimore, was the unwitting source of cells which where then cultured for the purpose of medical research. Though researchers had tried to grow cells before, Henrietta’s were the first successfully kept alive and cloned. Henrietta’s cells, known as HeLa cells, have been instrumental in the development of the polio vaccine, cancer research, AIDS research, gene mapping, and countless other scientific endeavors. Henrietta died penniless and was buried without a tombstone in a family cemetery. For decades, her husband and five children were left in the dark about their wife and mother’s amazing contribution to modern medicine.
27. Project QKHILLTOP

Image Source In 1954, the CIA developed an experiment called Project QKHILLTOP to study Chinese brainwashing techniques, which they then used to develop new methods of interrogation. Leading the research was Dr. Harold Wolff of Cornell University Medical School. After requesting that the CIA provide him with information on imprisonment, deprivation, humiliation, torture, brainwashing, hypnoses, and more, Wolff’s research team began to formulate a plan through which they would develop secret drugs and various brain damaging procedures. According to a letter he wrote, in order to fully test the effects of the harmful research, Wolff expected the CIA to “make available suitable subjects.”
26. Stateville Penitentiary Malaria Study

Image Source During World War II, malaria and other tropical diseases were impeding the efforts of American military in the Pacific. In order to get a grip, the Malaria Research Project was established at Stateville Penitentiary in Joliet, Illinois. Doctors from the University of Chicago exposed 441 volunteer inmates to bites from malaria-infected mosquitos. Though one inmate died of a heart attack, researchers insisted his death was unrelated to the study. The widely-praised experiment continued at Stateville for 29 years, and included the first human test of Primaquine, a medication still used in the treatment of malaria and Pneumocystis pneumonia.
25. Emma Eckstein and Sigmund Freud

Image Source Despite seeking the help of Sigmund Freud for vague symptoms like stomach ailments and slight depression, 27-year old Emma Eckstein was “treated” by the German doctor for hysteria and excessive masturbation, a habit then considered dangerous to mental health. Emma’s treatment included a disturbing experimental surgery in which she was anesthetized with only a local anesthetic and cocaine before the inside of her nose was cauterized. Not surprisingly, Emma’s surgery was a disaster. Whether Emma was a legitimate medical patient or a source of more amorous interest for Freud, as a recent movie suggests, Freud continued to treat Emma for three years.
24. Dr. William Beaumont and the Stomach
Image Source In 1822, a fur trader on Mackinac Island in Michigan was accidentally shot in the stomach and treated by Dr. William Beaumont. Despite dire predictions, the fur trader survived — but with a hole (fistula) in his stomach that never healed. Recognizing the unique opportunity to observe the digestive process, Beaumont began conducting experiments. Beaumont would tie food to a string, then insert it through the hole in the trader’s stomach. Every few hours, Beaumont would remove the food to observe how it had been digested. Though gruesome, Beaumont’s experiments led to the worldwide acceptance that digestion was a chemical, not a mechanical, process.
23. Electroshock Therapy on Children

Image Source In the 1960s, Dr. Lauretta Bender of New York’s Creedmoor Hospital began what she believed to be a revolutionary treatment for children with social issues — electroshock therapy. Bender’s methods included interviewing and analyzing a sensitive child in front of a large group, then applying a gentle amount of pressure to the child’s head. Supposedly, any child who moved with the pressure was showing early signs of schizophrenia. Herself the victim of a misunderstood childhood, Bender was said to be unsympathetic to the children in her care. By the time her treatments were shut down, Bender had used electroshock therapy on over 100 children, the youngest of whom was age three.
22. Project Artichoke

Image Source In the 1950s, the CIA’s Office of Scientific Intelligence ran a series of mind control projects in an attempt to answer the question “Can we get control of an individual to the point where he will do our bidding against his will and even against fundamental laws of nature?” One of these programs, Project Artichoke, studied hypnosis, forced morphine addiction, drug withdrawal, and the use of chemicals to incite amnesia in unwitting human subjects. Though the project was eventually shut down in the mid-1960s, the project opened the door to extensive research on the use of mind-control in field operations.
21. Hepatitis in Mentally Disabled Children

Image Source In the 1950s, Willowbrook State School, a New York state-run institution for mentally handicapped children, began experiencing outbreaks of hepatitis. Due to unsanitary conditions, it was virtually inevitable that these children would contract hepatitis. Dr. Saul Krugman, sent to investigate the outbreak, proposed an experiment that would assist in developing a vaccine. However, the experiment required deliberately infecting children with the disease. Though Krugman’s study was controversial from the start, critics were eventually silenced by the permission letters obtained from each child’s parents. In reality, offering one’s child to the experiment was oftentimes the only way to guarantee admittance into the overcrowded institution.
20. Operation Midnight Climax

Image Source Initially established in the 1950s as a sub-project of a CIA-sponsored, mind-control research program, Operation Midnight Climax sought to study the effects of LSD on individuals. In San Francisco and New York, unconsenting subjects were lured to safehouses by prostitutes on the CIA payroll, unknowingly given LSD and other mind-altering substances, and monitored from behind one-way glass. Though the safehouses were shut down in 1965, when it was discovered that the CIA was administering LSD to human subjects, Operation Midnight Climax was a theater for extensive research on sexual blackmail, surveillance technology, and the use of mind-altering drugs on field operations.
19. Study of Humans Accidentally Exposed to Fallout Radiation
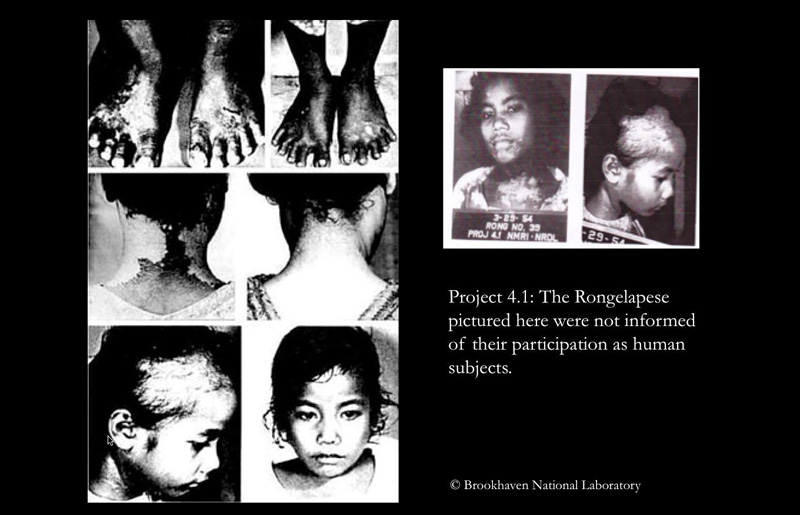
Image Source The 1954 “Study of Response of Human Beings exposed to Significant Beta and Gamma Radiation due to Fall-out from High-Yield Weapons,” known better as Project 4.1, was a medical study conducted by the U.S. of residents of the Marshall Islands. When the Castle Bravo nuclear test resulted in a yield larger than originally expected, the government instituted a top secret study to “evaluate the severity of radiation injury” to those accidentally exposed. Though most sources agree the exposure was unintentional, many Marshallese believed Project 4.1 was planned before the Castle Bravo test. In all, 239 Marshallese were exposed to significant levels of radiation.
18. The Monster Study

Image Source In 1939, University of Iowa researchers Wendell Johnson and Mary Tudor conducted a stuttering experiment on 22 orphan children in Davenport, Iowa. The children were separated into two groups, the first of which received positive speech therapy where children were praised for speech fluency. In the second group, children received negative speech therapy and were belittled for every speech imperfection. Normal-speaking children in the second group developed speech problems which they then retained for the rest of their lives. Terrified by the news of human experiments conducted by the Nazis, Johnson and Tudor never published the results of their “Monster Study.”
17. Project MKUltra

Image Source Project MKUltra is the code name of a CIA-sponsored research operation that experimented in human behavioral engineering. From 1953 to 1973, the program employed various methodologies to manipulate the mental states of American and Canadian citizens. These unwitting human test subjects were plied with LSD and other mind-altering drugs, hypnosis, sensory deprivation, isolation, verbal and sexual abuse, and various forms of torture. Research occurred at universities, hospitals, prisons, and pharmaceutical companies. Though the project sought to develop “chemical […] materials capable of employment in clandestine operations,” Project MKUltra was ended by a Congress-commissioned investigation into CIA activities within the U.S.
16. Experiments on Newborns

Image Source In the 1960s, researchers at the University of California began an experiment to study changes in blood pressure and blood flow. The researchers used 113 newborns ranging in age from one hour to three days old as test subjects. In one experiment, a catheter was inserted through the umbilical arteries and into the aorta. The newborn’s feet were then immersed in ice water for the purpose of testing aortic pressure. In another experiment, up to 50 newborns were individually strapped onto a circumcision board, then tilted so that their blood rushed to their head and their blood pressure could be monitored.
15. The Aversion Project
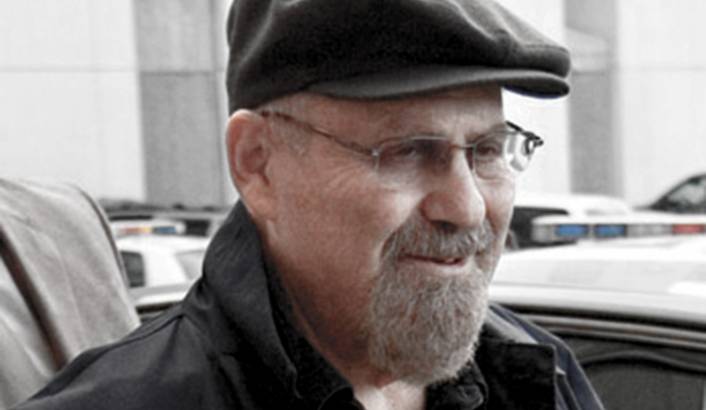

Image Source In 1969, during South Africa’s detestable Apartheid era, thousands of homosexuals were handed over to the care of Dr. Aubrey Levin, an army colonel and psychologist convinced he could “cure” homosexuals. At the Voortrekkerhoogte military hospital near Pretoria, Levin used electroconvulsive aversion therapy to “reorientate” his patients. Electrodes were strapped to a patient’s upper arm with wires running to a dial calibrated from 1 to 10. Homosexual men were shown pictures of a naked man and encouraged to fantasize, at which point the patient was subjected to severe shocks. When Levin was warned that he would be named an abuser of human rights, he emigrated to Canada where he currently works at a teaching hospital.
14. Medical Experiments on Prison Inmates

Image Source Perhaps one benefit of being an inmate at California’s San Quentin prison is the easy access to acclaimed Bay Area doctors. But if that’s the case, then a downside is that these doctors also have easy access to inmates. From 1913 to 1951, Dr. Leo Stanley, chief surgeon at San Quentin, used prisoners as test subjects in a variety of bizarre medical experiments. Stanley’s experiments included sterilization and potential treatments for the Spanish Flu. In one particularly disturbing experiment, Stanley performed testicle transplants on living prisoners using testicles from executed prisoners and, in some cases, from goats and boars.
13. Sexual Reassignment

Image Source In 1965, Canadian David Peter Reimer was born biologically male. But at seven months old, his penis was accidentally destroyed during an unconventional circumcision by cauterization. John Money, a psychologist and proponent of the idea that gender is learned, convinced the Reimers that their son would be more likely to achieve a successful, functional sexual maturation as a girl. Though Money continued to report only success over the years, David’s own account insisted that he had never identified as female. He spent his childhood teased, ostracized, and seriously depressed. At age 38, David committed suicide by shooting himself in the head.
12. Effect of Radiation on Testicles

Image Source Between 1963 and 1973, dozens of Washington and Oregon prison inmates were used as test subjects in an experiment designed to test the effects of radiation on testicles. Bribed with cash and the suggestion of parole, 130 inmates willingly agreed to participate in the experiments conducted by the University of Washington on behalf of the U.S. government. In most cases, subjects were zapped with over 400 rads of radiation (the equivalent of 2,400 chest x-rays) in 10 minute intervals. However, it was much later that the inmates learned the experiments were far more dangerous than they had been told. In 2000, the former participants settled a $2.4 million class-action settlement from the University.
11. Stanford Prison Experiment

Image Source Conducted at Stanford University from August 14-20, 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was an investigation into the causes of conflict between military guards and prisoners. Twenty-four male students were chosen and randomly assigned roles of prisoners and guards. They were then situated in a specially-designed mock prison in the basement of the Stanford psychology building. Those subjects assigned to be guards enforced authoritarian measures and subjected the prisoners to psychological torture. Surprisingly, many of the prisoners accepted the abuses. Though the experiment exceeded the expectations of all of the researchers, it was abruptly ended after only six days.
10. Syphilis Experiments in Guatemala

Image Source From 1946 to 1948, the United States government, Guatemalan president Juan José Arévalo, and some Guatemalan health ministries, cooperated in a disturbing human experiment on unwitting Guatemalan citizens. Doctors deliberately infected soldiers, prostitutes, prisoners, and mental patients with syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases in an attempt to track their untreated natural progression. Treated only with antibiotics, the experiment resulted in at least 30 documented deaths. In 2010, the United States made a formal apology to Guatemala for their involvement in these experiments.
9. Tuskegee Syphilis Study
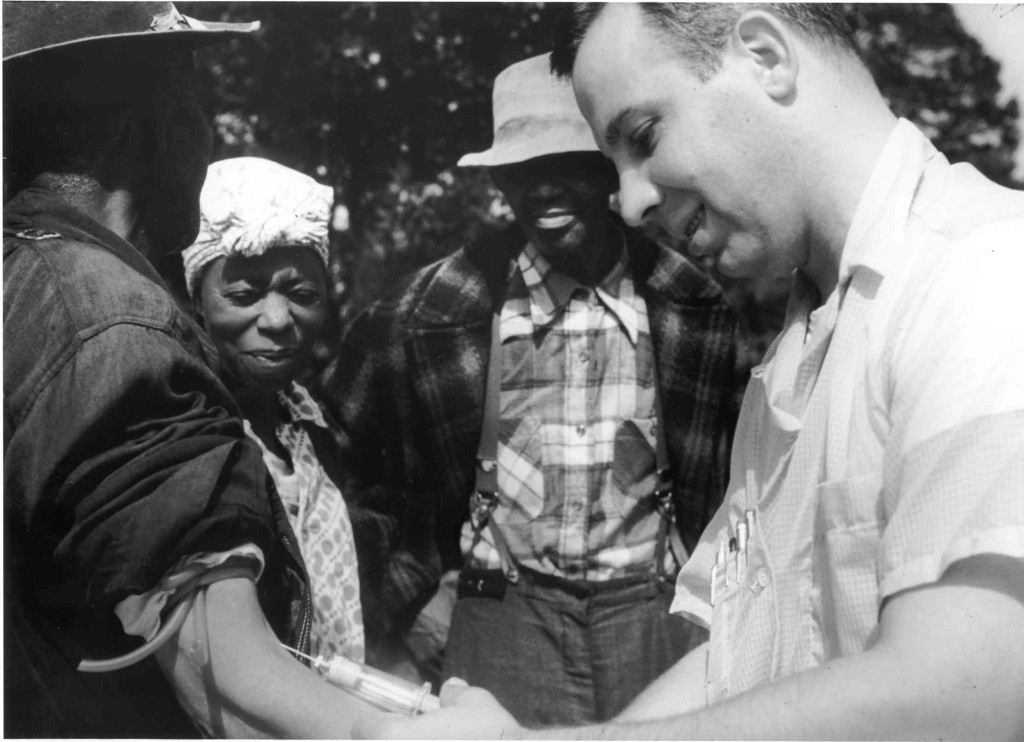

Image Source In 1932, the U.S. Public Health Service began working with the Tuskegee Institute to track the natural progression of untreated syphilis. Six hundred poor, illiterate, male sharecroppers were found and hired in Macon County, Alabama. Of the 600 men, only 399 had previously contracted syphilis, and none were told they had a life threatening disease. Instead, they were told they were receiving free healthcare, meals, and burial insurance in exchange for participating. Even after Penicillin was proven an effective cure for syphilis in 1947, the study continued until 1972. In addition to the original subjects, victims of the study included wives who contracted the disease, and children born with congenital syphilis. In 1997, President Bill Clinton formally apologized to those affected by what is often called the “most infamous biomedical experiment in U.S. history.”
8. Milgram Experiment
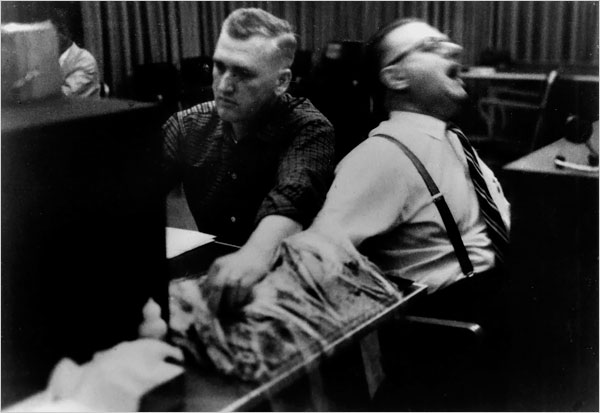

In 1961, Stanley Milgram, a psychologist at Yale University, began a series of social psychology experiments that measured the willingness of test subjects to obey an authority figure. Conducted only three months after the start of the trial of German Nazi war criminal Adolf Eichmann, Milgram’s experiment sought to answer the question, “Could it be that Eichmann and his million accomplices in the Holocaust were just following orders?” In the experiment, two participants (one secretly an actor and one an unwitting test subject) were separated into two rooms where they could hear, but not see, each other. The test subject would then read a series of questions to the actor, punishing each wrong answer with an electric shock. Though many people would indicate their desire to stop the experiment, almost all subjects continued when they were told they would not be held responsible, or that there would not be any permanent damage.
7. Infected Mosquitos in Towns

In 1956 and 1957, the United States Army conducted a number of biological warfare experiments on the cities of Savannah, Georgia and Avon Park, Florida. In one such experiment, millions of infected mosquitos were released into the two cities, in order to see if the insects could spread yellow fever and dengue fever. Not surprisingly, hundreds of researchers contracted illnesses that included fevers, respiratory problems, stillbirths, encephalitis, and typhoid. In order to photograph the results of their experiments, Army researchers pretended to be public health workers. Several people died as a result of the research.
6. Human Experimentation in the Soviet Union

Beginning in 1921 and continuing for most of the 21st century, the Soviet Union employed poison laboratories known as Laboratory 1, Laboratory 12, and Kamera as covert research facilities of the secret police agencies. Prisoners from the Gulags were exposed to a number of deadly poisons, the purpose of which was to find a tasteless, odorless chemical that could not be detected post mortem. Tested poisons included mustard gas, ricin, digitoxin, and curare, among others. Men and women of varying ages and physical conditions were brought to the laboratories and given the poisons as “medication,” or part of a meal or drink.
5. Human Experimentation in North Korea

Image Source Several North Korean defectors have described witnessing disturbing cases of human experimentation. In one alleged experiment, 50 healthy women prisoners were given poisoned cabbage leaves — all 50 women were dead within 20 minutes. Other described experiments include the practice of surgery on prisoners without anesthesia, purposeful starvation, beating prisoners over the head before using the zombie-like victims for target practice, and chambers in which whole families are murdered with suffocation gas. It is said that each month, a black van known as “the crow” collects 40-50 people from a camp and takes them to an known location for experiments.
4. Nazi Human Experimentation
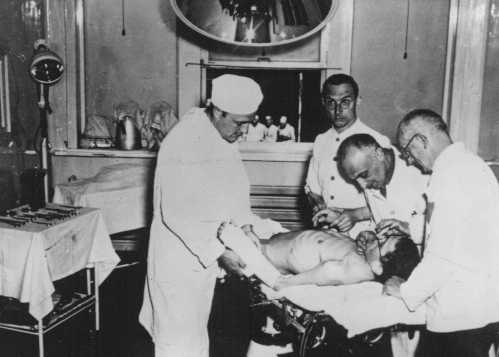
Image Source Over the course of the Third Reich and the Holocaust, Nazi Germany conducted a series of medical experiments on Jews, POWs, Romani, and other persecuted groups. The experiments were conducted in concentration camps, and in most cases resulted in death, disfigurement, or permanent disability. Especially disturbing experiments included attempts to genetically manipulate twins; bone, muscle, and nerve transplantation; exposure to diseases and chemical gasses; sterilization, and anything else the infamous Nazi doctors could think up. After the war, these crimes were tried as part of the Nuremberg Trial and ultimately led to the development of the Nuremberg Code of medical ethics.

3. Unit 731

Image Source From 1937 to 1945, the imperial Japanese Army developed a covert biological and chemical warfare research experiment called Unit 731. Based in the large city of Harbin, Unit 731 was responsible for some of the most atrocious war crimes in history. Chinese and Russian subjects — men, women, children, infants, the elderly, and pregnant women — were subjected to experiments which included the removal of organs from a live body, amputation for the study of blood loss, germ warfare attacks, and weapons testing. Some prisoners even had their stomachs surgically removed and their esophagus reattached to the intestines. Many of the scientists involved in Unit 731 rose to prominent careers in politics, academia, business, and medicine.
2. Radioactive Materials in Pregnant Women

Image Source Shortly after World War II, with the impending Cold War forefront on the minds of Americans, many medical researchers were preoccupied with the idea of radioactivity and chemical warfare. In an experiment at Vanderbilt University, 829 pregnant women were given “vitamin drinks” they were told would improve the health of their unborn babies. Instead, the drinks contained radioactive iron and the researchers were studying how quickly the radioisotope crossed into the placenta. At least seven of the babies later died from cancers and leukemia, and the women themselves experienced rashes, bruises, anemia, loss of hair and tooth, and cancer.
1. Mustard Gas Tested on American Military
Image Source In 1943, the U.S. Navy exposed its own sailors to mustard gas. Officially, the Navy was testing the effectiveness of new clothing and gas masks against the deadly gas that had proven so terrifying in the first World War. The worst of the experiments occurred at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington. Seventeen and 18-year old boys were approached after eight weeks of boot camp and asked if they wanted to participate in an experiment that would help shorten the war. Only when the boys reached the Research Laboratory were they told the experiment involved mustard gas. The participants, almost all of whom suffered severe external and internal burns, were ignored by the Navy and, in some cases, threatened with the Espionage Act. In 1991, the reports were finally declassified and taken before Congress.
28. Prison Inmates as Test Subjects Henrietta Lacks 26. Project QKHILLTOP 25. Stateville Penitentiary Malaria Study Stateville Penitentiary Malaria Study: Primaquine 24. Emma Eckstein 23. Dr. William Beaumont Dr. William Beaumont 21. Electroshock Therapy on Children 21. Project Artichoke 20. Operation Midnight Climax 19. Study of Humans Accidentally Exposed to Fallout Radiation 18. The Monster Experiment 17. Project MKUltra 16. Experiments on Newborns 15. The Aversion Project 14. Medical Experiments on Prison Inmates 13. Sexual Reassignment 12. Effect of Radiation on Testicles 11. Stanford Prison Experiment 10. Syphilis Experiment in Guatemala 9. Tuskegee Syphilis Study 8. Milgram Experiment 7. Infected Mosquitos in Towns 6. Human Experimentation in the Soviet Union 5. Human Experimentation in North Korea 4. Nazi Human Experimentation 3. Unit 731 2. Radioactive Materials in Pregnant Women 1. Mustard Gas Tested on American Military
- Psychology Education
- Bachelors in Psychology
- Masters in Psychology
- Doctorate in Psychology
- Psychology Resources
- Psychology License
- Psychology Salary
- Psychology Career
- Psychology Major
- What is Psychology
- Up & Coming Programs
- Top 10 Up and Coming Undergraduate Psychology Programs in the South
- Top 10 Up and Coming Undergraduate Psychology Programs in the Midwest
- Top 10 Up and Coming Undergraduate Psychology Programs in the West
- Top 10 Up and Coming Undergraduate Psychology Programs in the East
- Best Psychology Degrees Scholarship Opportunity
- The Pursuit of Excellence in Psychology Scholarship is Now Closed
- Meet Gemma: Our First Psychology Scholarship Winner
- 50 Most Affordable Clinical Psychology Graduate Programs
- 50 Most Affordable Selective Small Colleges for a Psychology Degree
- The 50 Best Schools for Psychology: Undergraduate Edition
- 30 Great Small Colleges for a Counseling Degree (Bachelor’s)
- Top 10 Best Online Bachelors in Psychology Degree Programs
- Top 10 Online Child Psychology Degree Programs
- 10 Best Online Forensic Psychology Degree Programs
- Top 10 Online Master’s in Psychology Degree Programs
- Top 15 Most Affordable School Psychology Programs
- Top 20 Most Innovative Graduate Psychology Degree Programs
- Top 8 Online Sports Psychology Degree Programs
- Recent Posts
- Does Psychology Require Math? – Requirements for Psychology Majors
- 10 Classes You Will Take as a Psychology Major
- Top 15 Highest-Paying Jobs with a Master’s Degree in Psychology
- The Highest Paying Jobs with an Associate’s Degree in Psychology
- The Highest-Paying Jobs with a Bachelor’s in Psychology
- Should I Major in Psychology?
- How to Become a CBT Therapist
- What is a Social Psychologist?
- How to Become a Clinical Neuropsychologist
- MA vs. MS in Psychology: What’s the Difference?
- PsyD vs. PhD in Psychology: What’s the Difference?
- What Can You Do with a Master’s in Psychology?
- What Can You Do With A PhD in Psychology?
- Master’s in Child Psychology Guide
- Master’s in Counseling Psychology – A Beginner’s Guide
- Master’s in Forensic Psychology – A Beginner’s Guide
- 8 Reasons to Become a Marriage and Family Therapist
- What Do Domestic Violence & Abuse Counselors Do?
- What Training is Needed to Be a Psychologist for People of the LGBTQ Community?
- 15 Inspiring TED Talks on Intelligence and Critical Thinking
- The 30 Most Inspiring Personal Growth and Development Blogs
- 30 Most Prominent Psychologists on Twitter
- New Theory Discredits the Myth that Individuals with Asperger’s Syndrome Lack Empathy
- 10 Crazy Things Famous People Have Believed
- Psychology Infographics
- Top Infographics About Psychology
- The Birth Order Effect [Infographic]
- The Psychology of Dogs [Infographic]
- Can Going Green Improve Your Mental Health? [Infographic]
- Surprising Alternative Treatments for Mental Disorders [Infographic]
- What Can Humans Learn From Animals? [Infographic]

ALLIANCE FOR HUMAN RESEARCH PROTECTION
Advancing Voluntary, Informed Consent to Medical Intervention

- Board of Directors
- Distinguished Advisory Board
- Honor Roll–Exemplary Professionals
- First, do no Harm
- Human Rights
- Informed Consent
- Nuremberg Code
- Discrimination
- Medicalized Racism
- Gene Modification
- Depopulation
- Technocracy
- Propaganda – Censorship
- Clinical Trials
- Concealed Data
- Public-Private Partnerships
- Pharma Corrupt Influence
- Publication Bias
- Organ Harvesting
- Bioweapon Experiments
- Transhumanism
- Current Medical Atrocities
- Japanese Atrocities
- Nazi Atrocities
- Operation Paperclip
- CIA Mind-Control
- CIA Torture
- U.S. Radiation Experiments
Unethical Experiments
- Pandemic Control
- Great Reset
- Diabolical Lockstep
- Apartheid Policies
- Coronavirus Fear
- Covid Pandemic
- Government Overreach
- Vaccine Profit Engine
- Child Sacrifice
- Vaccine Mandates
- Vaccine Risks
- Vaccine Safety
Introduction: Unethical Medical Experiments 1980–2010
“The whole discipline of biomedical ethics rises from the ashes of the Holocaust…” Arthur Caplan
The Nuremberg Code (1947) laid the foundation for biomedical ethics mandating that medical experiments conducted on human beings must conform to well-defined humane, ethical standards; foremost is immutable standard:
“The voluntary consent of the human subject is absolutely essential . The information sought is “unprocurable by other methods or means of study; the anticipated results will justify the performance of the experiment; the experiment is designed “to avoid all unnecessary physical and mental suffering or injury; risks to subjects be minimized to protect against “even remote possibilities of injury, disability or death.”
The Nuremberg Code makes clear that ethical standards protecting individual human rights supersede arguments invoking the “greater good of society.”
The Declaration of Helsinki (1964) expanded on a requirement of full disclosure:
“In medical research involving competent human subjects, each potential subject must be adequately informed of the aims, methods, sources of funding, any possible conflicts of interest, institutional affiliations of the researcher, the anticipated benefits and potential risks of the study and the discomfort it may entail, and any other relevant aspects of the study. “In any medical study, every patient – including those of a control group, if any – should be assured of the best proven diagnostic and therapeutic method.” ( World Medical Association , 1964, 1996 2000)
Thirty years after the Nuremberg Code, the United States was confronted with the infamous Tuskegee Syphilis experiment which resulted in the government forging ethical research principles. The Belmont Report (1978, 1979) provided the template for the Code of Federal Regulations (45 CFR 46) followed by The Common Rule .
The overwhelming evidence that these ethical principles were much more frequently honored in their breach than in their observance. The record is clear: dubious medical experiments that failed to meet medical ethical standards have been — and are currently — approved not only by commercial corporate entities, but by academic and government review boards and institutions whose mandate is to ensure that the safety and rights of human subjects are protected.
Conflicts of interest, rather than ideologies have derailed medicine from its ethical tradition. The entire field of medical research is now permeated by conflicts of interest. All major academic institutions government agencies, including the National Institutes of Health, the Food and Drug Administration, the Center for Disease Control, the Environmental Protection Agency, are dependent upon major corporate money. Thus business ethics has usurped medical ethics. Read Doing Harm to the Most Vulnerable ; Read NIH Under Fire ; Read Research Center Tied to Drug Company ; Read CDC Covertly Tested Experimental Vaccine on Black/Latino Babies .
The only redress and reliable source of information comes from litigation when primary secret documents are uncovered during the discovery process. Read more here and here . Finally, unless they are stopped, Medical Research Stakeholders Seek to Overturn Informed Consent .
Subscribe To Our Newsletter!
Sign up and be the first to find out the latest news and articles about what's going on in the medical field.
You may also like
July 15, 2024
Vera Sharav’s Interview at The Shannon Joy Show LIVE Exclusive
LIVE Exclusive W/ Holocaust Survivor Vera Sharav: ‘Never Again Is NOW’ – COVID Lockdown Atrocities MUST NOT
July 1, 2024
Vera Sharav’s Interview at Neil Oliver’s GB News, The Human Experience: An Illumination of Spiritual Parts of Humanity
Lessons of the 20th century have been ‘TOTALLY FORGOTTEN’ – history ‘relegated to IRRELEVANCE’ ‘We are being
- 20 Most Unethical Experiments in Psychology
Humanity often pays a high price for progress and understanding — at least, that seems to be the case in many famous psychological experiments. Human experimentation is a very interesting topic in the world of human psychology. While some famous experiments in psychology have left test subjects temporarily distressed, others have left their participants with life-long psychological issues . In either case, it’s easy to ask the question: “What’s ethical when it comes to science?” Then there are the experiments that involve children, animals, and test subjects who are unaware they’re being experimented on. How far is too far, if the result means a better understanding of the human mind and behavior ? We think we’ve found 20 answers to that question with our list of the most unethical experiments in psychology .
Emma Eckstein

Electroshock Therapy on Children

Operation Midnight Climax

The Monster Study

Project MKUltra
The Aversion Project

Unnecessary Sexual Reassignment

Stanford Prison Experiment

Milgram Experiment

The Monkey Drug Trials

Featured Programs
Facial expressions experiment.

Little Albert

Bobo Doll Experiment

The Pit of Despair

The Bystander Effect

Learned Helplessness Experiment

Racism Among Elementary School Students

UCLA Schizophrenia Experiments

The Good Samaritan Experiment

Robbers Cave Experiment

Related Resources:
- What Careers are in Experimental Psychology?
- What is Experimental Psychology?
- The 25 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History
- 5 Best Online Ph.D. Marriage and Family Counseling Programs
- Top 5 Online Doctorate in Educational Psychology
- 5 Best Online Ph.D. in Industrial and Organizational Psychology Programs
- Top 10 Online Master’s in Forensic Psychology
- 10 Most Affordable Counseling Psychology Online Programs
- 10 Most Affordable Online Industrial Organizational Psychology Programs
- 10 Most Affordable Online Developmental Psychology Online Programs
- 15 Most Affordable Online Sport Psychology Programs
- 10 Most Affordable School Psychology Online Degree Programs
- Top 50 Online Psychology Master’s Degree Programs
- Top 25 Online Master’s in Educational Psychology
- Top 25 Online Master’s in Industrial/Organizational Psychology
- Top 10 Most Affordable Online Master’s in Clinical Psychology Degree Programs
- Top 6 Most Affordable Online PhD/PsyD Programs in Clinical Psychology
- 50 Great Small Colleges for a Bachelor’s in Psychology
- 50 Most Innovative University Psychology Departments
- The 30 Most Influential Cognitive Psychologists Alive Today
- Top 30 Affordable Online Psychology Degree Programs
- 30 Most Influential Neuroscientists
- Top 40 Websites for Psychology Students and Professionals
- Top 30 Psychology Blogs
- 25 Celebrities With Animal Phobias
- Your Phobias Illustrated (Infographic)
- 15 Inspiring TED Talks on Overcoming Challenges
- 10 Fascinating Facts About the Psychology of Color
- 15 Scariest Mental Disorders of All Time
- 15 Things to Know About Mental Disorders in Animals
- 13 Most Deranged Serial Killers of All Time

Site Information
- About Online Psychology Degree Guide
FREE Shipping & FREE Returns* $49+
- Shipping + Returns
- Join Rewards
- Order Status
- Create an Account
Most Disturbing Medical Research Studies From History
One of the most frequently discussed topics of debate in healthcare is the ethics surrounding medical research and certain studies. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HSS) has been actively working to enforce new protections for research subjects, but regulations were not always stringent. Here are some of the most unethical medical studies from history:
Plutonium Trials
In 1994 President Clinton appointed a special advisory team to investigate human radiation experiments that had been conducted over the years. When the world’s first atomic bomb was about to be launched in 1945, doctors began injecting patients with plutonium to better understand the effects of radiation on the human body. Many of these patients did not consent to be a part of these studies - including children who were unknowingly fed radioactive oatmeal from Quaker Oats Company, who was a co-sponsor of the studies . Though several government officials were aware of the studies throughout the years, it took decades for details of the experiments to be brought to light. Clinton’s investigation resulted in a mandatory procedural review of all organizations conducting human research, and a new committee to oversee research efforts.
Project Bluebird
During the 1950's the CIA became interested in developing new interrogation techniques. Their goal was to learn how to prevent captured CIA agents from divulging secret information, and also how to better manipulate enemies that they imprisoned. Some methods were more or less harmless, such as hypnosis, but other commonly tested methods included administering harmful, perception-altering drugs like cocaine and heroin. In fact, over 6,000 U.S. military soldiers were given LSD without any type of consent.
Tuskegee Syphilis Study
One of the most notorious cases of unethical research, the Tuskegee Syphilis Study involved the denial of syphilis treatment to African-American males in Alabama. Subjects were lured into the study by advertisements for a special treatment, and were promised free meals, transportation, and assistance with burial costs in case of death. They were never actually given details about the disease they had been diagnosed with, nor were they aware that the spinal tap diagnostic was not actually a treatment. For most individuals there would never actually be any type of treatment, as placebos were deceptively given instead. The study started in 1932 when the treatment of syphilis was still uncertain, but by 1947 penicillin was the standard cure for the disease. The researchers did not use the drug to cure their infected subjects, and instead kept conducting research up until 1972.

A Tuskegee man receives treatment.
Between 1950 to 1973 a series of interrogative and mind-control studies were developed as a part of the MKULTRA program. Each study had different goals, but all were unethical in their own way. One study aimed to explore the effects of LSD on non-consenting individuals, and used prostitutes as test subjects. Prostitutes were hired by the CIA to take individuals back to designated “safe houses”, where they were then watched from one-way mirrors and given copious amounts of LSD.
In a separate mind-control experiment, the treatment was even worse. Dr. Ewen Cameron's mission was to mentally break the individual to the point where their mind was a clean slate. For the initial phase Cameron would use drugs to induce a longstanding state of coma, and then administer hundreds of shocks with electroshock therapy. The second phase involved being cloaked, and playing recorded voice messages for hours upon end to manipulate the subject’s thoughts. Children were also used as test subjects. In order to secure continued funding, Cameron blackmailed high-ranking officials.
Willowbrook Hepatitis Experiments
Today it is well known that there are multiple strains of Hepatitis, but that discoverycame as a result of studies conducted at the Willowbrook State School for mentally disabled children. The school was overcrowded and running rampant with the hepatitis disease. Enter Dr. Saul Krugman, who had a goal to protect children from hepatitis and saw the school as an ideal research environment. Over a span of 15 years, over 700 children were purposely infected with the disease and researchers observed varying symptoms in each child. This variation of symptoms eventually led to the realization that there were two types of Hepatitis, A and B. Parents had been given consent forms to sign, but many were led to believe that admittance to the school was contingent upon consenting to the hepatitis experiments. The study raised many important ethical questions regarding experimentation on mentally disabled children rather than consenting adults.
The AMA was founded in part to establish the first national code of medical ethics. Today the Code is widely recognized as authoritative ethics guidance for physicians through its Principles of Medical Ethics interpreted in Opinions of AMA’s Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs that address the evolving challenges of contemporary practice.
Release of Data from Unethical Experiments
Research that violates the fundamental principle of respect for persons and basic standards of human dignity, such as Nazi experiments during World War II or from the US Public Health Service Tuskegee Syphilis Study, is unethical and of questionable scientific value. Data obtained from such cruel and inhumane experiments should virtually never be published. If data from unethical experiments can be replaced by data from ethically sound research and achieve the same ends, then such must be done. In the rare instances when ethically tainted data have been validated by rigorous scientific analysis, are the only data of such nature available, and human lives would certainly be lost without the knowledge obtained from the data, it may be permissible to use or publish findings from unethical experiments.
Physicians who engage with data from unethical experiments as authors, peer reviewers, or editors of medical publications should:
- Disclose that the data derive from studies that do not meet contemporary standards for the ethical conduct of research.
- Clearly describe and acknowledge the unethical nature of the experiment(s) from which the data are derived.
- Provide ethically compelling reasons for which the data are being released or cited, such as the need to save human lives when no other relevant data are available.
- Pay respect to those who were the victims of the unethical experimentation.
Council Reports
- PDF Release of Data from Unethical Experiments
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Health Topics A-Z
About The Untreated Syphilis Study at Tuskegee
- The 40-year Untreated Syphilis Study at Tuskegee ended in 1972 and resulted in drastic changes to standard research practices.
- Read on to learn about the impact of the study on the lives of those involved.
The U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS) Untreated Syphilis Study at Tuskegee was a study conducted between 1932 and 1972. The study was supposed to observe the natural history of untreated syphilis. As part of the study, researchers did not collect informed consent from participants. They also did not offer treatment, even after it was easily available. The study ended in 1972 on the recommendation of an Ad Hoc Advisory Panel. The panel was convened by the Assistant Secretary for Health and Scientific Affairs, following publication of news articles about the study.
In 1997, President Clinton issued a formal Presidential Apology . In his apology he announced an investment to establish what became The National Center for Bioethics in Research and Health Care at Tuskegee University . Many records can be found in the National Archives .
After the study, sweeping changes to standard research practices were made. Efforts to promote the highest ethical standards in research are ongoing today.
Subjects and participation
Tuskegee community members were aware of the study but thought it was a special government health care program 1 .
According to the Assistant Secretary for Health and Scientific Affairs' Ad Hoc Advisory Panel's published report , "...the Macon County Health Department and Tuskegee Institute were cognizant of the study."
Resource
The National Archives, Southeastern Region, maintains a list of Tuskegee patient medical files .
The National Archives maintains photos related to the study .
No women were included in the study. The study was limited to Black men 25 years of age or older. However, as a result of lack of treatment, some women contracted syphilis from men who participated in the study’s syphilitic group.
Featured stories
Family members and public health officials share their memories and reflections of the United States Public Health Service Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male at Tuskegee and Macon County, Alabama, 1932 -1972.
Were men purposefully infected for the study?
No. According to a journal article about the study, published in 1936, the 399 men in the syphilitic group were initially recruited because they already had late-latent syphilis. The 201 men in the control group did not have the disease.
Why was the U.S. Public Health Service’s Untreated Syphilis Study at Tuskegee unethical?
There is no evidence that researchers obtained informed consent from participants. Also, the participants were not offered available treatments, even after penicillin became widely available.
You can learn more about changes made to standard research practices after Tuskegee in Research Implications .
How much money did the study participants receive from the 1974 out of court settlement?
The $10-million settlement was divided into four categories:
- Living syphilitic group participants received $37,500.
- Heirs of deceased syphilitic group participants received $15,000.
- Living control group participants received $16,000.
- Heirs of deceased control group participants received $5,000 2 .
50th anniversary event
This event was held Wednesday, November 30, 2022. Watch our recorded session and related videos below.
This event acknowledged the 50th anniversary of the end of the United States Public Health Service Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male at Tuskegee and Macon County, Alabama, 1932 -1972. The intention was to create a space for authentic, accurate storytelling. It was also meant to encourage discussion regarding current and future opportunities for public health leaders to move from trust to trustworthiness.
The program examined what happened, how and why it happened, lessons learned, the noticeable effects still felt today, and CDC's on-going role in addressing health equity.
Participants included experts in the fields of public health, ethics, history, and journalism. In addition to our speakers, we featured moderated panel discussions. The program was a hybrid event, available both virtually and in-person.
United States Public Health Service Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male at Tuskegee and Macon County, Alabama, 1932 -1972 Download now
Featured speakers
Xavier Becerra United States Secretary, Health and Human Services
Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH Director, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Debra Houry, MD, MPH Acting Principal Deputy Director, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Robin D. Bailey Jr., MA Chief Operating Officer, CDC
Termika Smith, Ed.D, MPA Associate Director for Policy, Communications, and Strategy, Division of Adolescent and School Health, CDC
Susan K. Laird, DNP, MSN Training and Health Education Lead, Division of Communication Science and Services, CDC
Jo Valentine, MSW Associate Director, Office of Health Equity, Division of STD Prevention, CDC
Paul Rashad Young, MD Commander, U.S. Public Health Service and Regional Associate Director, The Americas and Kenya, Division of Global HIV & TB, Center for Global Health, CDC
Discussants
James A. Curran, MD, MPH Dean Emeritus, Emory Rollins School of Public Health
Daniel E. Dawes, JD Executive Director, Satcher Health Leadership Institute at Morehouse School of Medicine
Vanessa Northington Gamble, MD, PhD University Professor of Medical Humanities, Professor of Medicine, Health Policy, and American Studies at the George Washington University.
Fred Gray, Esq. President, Tuskegee Human & Civil Rights Multicultural Center
Lillie Tyson Head, MS, EdS President, Voices for Our Fathers Legacy Foundation
Jean Heller Author, Journalist
Robert Benjamin Johnson Former Deputy Assistant to the President and Deputy Director of the Office of Public Liaison
James H. Jones, PhD Author, Bad Blood
Chris Koller President, Milbank Memorial Fund
Paul Lombardo, PhD, JD Regents' Professor and Bobby Lee Cook Professor of Law, Georgia State University College of Law
Mary Leinhos, PhD Acting Team Lead, Public Health Ethics and Strategy Unit, Office of Scientific Integrity, CDC
Ted Pestorius, MPA Deputy Director of Management and Overseas Operations, Center for Global Health, CDC
Susan Reverby, PhD Author; Marion Butler McLean Professor Emerita in the History of Ideas and Professor Emerita in Women's and Gender Studies, Wellesley College
Diane Rowley, MD, MPH Professor Emerita, Maternal and Child Health Department, Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
David Satcher, MD, PhD Founding Director and Senior Advisor, Satcher Health Leadership Institute; Former Director, CDC
Dixie E. Snider Jr., MD, MPH Former Chief Science Officer, Office of the Director, CDC
Rueben C. Warren, DDS, MPH, DrPH, MDiv Professor/Director of the National Center for Bioethics in Research and Health Care at Tuskegee University, Tuskegee, AL
- Voices for Our Fathers Legacy Foundation
- The National Archives – USPHS Untreated Syphilis Study at Tuskegee
- Facts & Information about Syphilis
- STD Health Equity
- Tuskegee University National Center for Bioethics in Research and Health Care
- Vonderlehr to Clark, October 20, 1932, Records of the USPHS Venereal Disease Division, Record Group 90, National Archives, Washington National Record Center, Suitland, Maryland.
- Gray, Fred D. The Tuskegee Syphilis Study: An Insider’s Account of the Shocking Medical Experiment Conducted by Government Doctors against African American Men. Montgomery: Fred D. Gray, 2013.
Syphilis Study
The Untreated Syphilis Study at Tuskegee was conducted between 1932 and 1972 to observe the natural history of untreated syphilis.
Creating a healthier world for all people
To create a healthier world for all people
Our Mission
To discover, develop and deliver innovative therapeutics for people with life-threatening diseases
At Gilead, we strive to create a healthier world for all people. From our pioneering virology medicines to our growing impact in oncology, we deliver innovative therapies that offer new hope to those impacted by disease. We invest in world-class science and are pursuing innovation across our therapeutic areas of virology, oncology and inflammation.
Importantly, our focus extends beyond medicine — we take action to help remedy health inequities and break down barriers to care, forming partnerships around the world to bring about change.
We believe that our people are our greatest asset. We empower our employees to bring their whole selves to work and make a direct impact in the communities we serve.
Inspired by our bold ambitions, we're committed to improving the lives of patients and the health of the world for generations to come.
Our work is powered by more than 18,000 employees, led by our Leadership Team and Board of Directors.
Going beyond medicine , removing barriers to care
Health equity.
We support and partner with organizations addressing health inequities.
Giving@Gilead
We collaborate with communities around the world to expand access, improve health equity and advance education for patient populations in need.
We prioritize corporate responsibility and are committed to addressing unmet needs, empowering communities and sustaining our shared planet.
Inclusion and Diversity
We value creating an inclusive culture that enables all people to do their best work and reflects the diversity of the communities where we live and work.
Gilead's History
Gilead was founded in 1987 to bring new hope in the face of devastating diseases. For more than 35 years, we've been at the forefront of some of the world's greatest public health challenges.
Our company is founded as Oligogen on June 22, 1987, and becomes Gilead Sciences one year later.
Gilead's research focus shifts to small molecule therapeutics.
Gilead goes public and $GILD is listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange for the first time.
Gilead’s first medicine is approved for the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis in people with AIDS. At the time, Gilead has just 250 employees.
Gilead’s first therapeutic for HIV is approved by the U.S. FDA.
The first single-tablet regimen for HIV, developed by Gilead, is approved by the U.S. FDA, helping transform care for people living with HIV.
Gilead grows to 4,000 employees in 20 countries around the world.
Gilead introduces a new therapeutic advancing a cure for chronic hepatitis C.
Gilead acquires Kite Pharma, entering the cell therapy space. Also, it launches the COMPASS Initiative® to address the HIV epidemic in the Southern U.S.
Gilead expands its reach in communities through the HIV Age Positively program, the HepConnect initiative and RADIAN, and Daniel O’Day is named Chairman and Chief Executive Officer.
Gilead’s COVID-19 antiviral receives U.S. FDA emergency use authorization and the company acquires Immunomedics to accelerate treatments for cancer.
The Gilead Foundation, which was originally established in 2005, was re-endowed.
Gilead acquires MiroBio to accelerate the development of treatment options for people with autoimmune diseases.
Gilead expands by opening a hub in Parsippany, New Jersey to serve as a center for innovation in oncology.
Gilead acquires CymaBay, advancing a transformational therapy for primary biliary cholangitis, and opens its first research lab outside of the U.S. in Oxford, England.
Ethics and Compliance
Board governance and committees, join us to solve some of the world's biggest healthcare challenges. a rewarding career awaits at gilead..
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Ann Med Surg (Lond)
- v.86(5); 2024 May
- PMC11060189

Ethics in scientific research: a lens into its importance, history, and future
Associated data.
Not applicable.
Introduction
Ethics are a guiding principle that shapes the conduct of researchers. It influences both the process of discovery and the implications and applications of scientific findings 1 . Ethical considerations in research include, but are not limited to, the management of data, the responsible use of resources, respect for human rights, the treatment of human and animal subjects, social responsibility, honesty, integrity, and the dissemination of research findings 1 . At its core, ethics in scientific research aims to ensure that the pursuit of knowledge does not come at the expense of societal or individual well-being. It fosters an environment where scientific inquiry can thrive responsibly 1 .
The need to understand and uphold ethics in scientific research is pertinent in today’s scientific community. First, the rapid advancement of technology and science raises ethical questions in fields like biotechnology, biomedical science, genetics, and artificial intelligence. These advancements raise questions about privacy, consent, and the potential long-term impacts on society and its environment 2 . Furthermore, the rise in public perception and scrutiny of scientific practices, fueled by a more informed and connected populace, demands greater transparency and ethical accountability from researchers and institutions.
This commentary seeks to bring to light the need and benefits associated with ethical adherence. The central theme of this paper highlights how upholding ethics in scientific research is a cornerstone for progress. It buttresses the fact that ethics in scientific research is vital for maintaining the trust of the public, ensuring the safety of participants, and legitimizing scientific findings.
Historical perspective
Ethics in research is significantly shaped by past experiences where a lack of ethical consideration led to negative consequences. One of the most striking examples of ethical misconduct is the Tuskegee Syphilis Study 3 conducted between 1932 and 1972 by the U.S. Public Health Service. In this study, African American men in Alabama were used as subjects to study the natural progression of untreated syphilis. They were not informed of their condition and were denied effective treatment, even after penicillin became available as a cure in the 1940s 3 .
From an ethical lens today, this is a gross violation of informed consent and an exploitation of a vulnerable population. The public outcry following the revelation of the study’s details led to the establishment of the National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioural Research 4 . This commission eventually produced the Belmont Report in 1979 4 , setting forth principles such as respect for persons, beneficence, and justice, which now underpin ethical research practices 4 .
Another example that significantly impacted ethical regulations was the thalidomide tragedy of the late 1950s and early 1960s 5 . Thalidomide was marketed as a safe sedative for pregnant women to combat morning sickness in Europe. Thalidomide resulted in the birth of approximately ten thousand children with severe deformities due to its teratogenic effects 5 , which were not sufficiently researched prior to the drug’s release. This incident underscored the critical need for comprehensive clinical testing and highlighted the ethical imperative of understanding and communicating potential risks, particularly for vulnerable groups such as pregnant women. In response, drug testing regulations became more rigorous, and the importance of informed consent, especially in clinical trials, was emphasized.
The Stanford Prison Experiment of 1971, led by psychologist Philip Zimbardo is another prime example of ethical oversight leading to harmful consequences 6 . The experiment, which aimed to study the psychological effects of perceived power, resulted in emotional trauma for participants. Underestimating potential psychological harm with no adequate systems to safeguard human participants from harm was a breach of ethics in psychological studies 6 . This case highlighted the necessity for ethical guidelines that prioritize the mental and emotional welfare of participants, especially in psychological research. It led to stricter review processes and the establishment of guidelines to prevent psychological harm in research studies. It influenced the American Psychological Association and other bodies to refine their ethical guidelines, ensuring the protection of participants’ mental and emotional well-being.
Impact on current ethical standards
These historical, ethical oversights have been instrumental in shaping the current landscape of ethical standards in scientific research. The Tuskegee Syphilis Study led to the Belmont Report in 1979, which laid out key ethical principles such as respect for persons, beneficence, and justice. It also prompted the establishment of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) to oversee research involving human subjects. The thalidomide tragedy catalyzed stricter drug testing regulations and informed consent requirements for clinical trials. The Stanford Prison Experiment influenced the American Psychological Association to refine its ethical guidelines, placing greater emphasis on the welfare and rights of participants.
These historical episodes of ethical oversights have been pivotal in forging the comprehensive ethical frameworks that govern scientific research today. They serve as stark reminders of the potential consequences of ethical neglect and the perpetual need to prioritize the welfare and rights of participants in any research endeavor.
One may ponder on the reason behind the Tuskegee Syphilis Study, where African American men with syphilis were deliberately left untreated. What led scientists to prioritize research outcomes over human well-being? At the time, racial prejudices, lack of understanding of ethical principles in human research, and regulatory oversight made such studies pass. Similarly, the administration of thalidomide to pregnant women initially intended as an antiemetic to alleviate morning sickness, resulted in unforeseen and catastrophic birth defects. This tragedy highlights a critical lapse in the pre-marketing evaluation of drugs’ safety.
Furthermore, the Stanford prison experiment, designed to study the psychological effects of perceived power, spiraled into an ethical nightmare as participants suffered emotional trauma. This begs the question on how these researchers initially justified their methods. From today’s lens of ethics, the studies conducted were a complete breach of misconduct, and I wonder if there were any standards that guided primitive research in science.
Current ethical standards and guidelines in research
Informed consent.
This mandates that participants are fully informed about the nature of the research, including its objectives, procedures, potential risks, and benefits 7 , 8 . They must be given the opportunity to ask questions and must voluntarily agree to participate without coercion 7 , 8 . This ensures respect for individual autonomy and decision-making.
Confidentiality and privacy
Confidentiality is pivotal in research involving human subjects. Participants’ personal information must be protected from unauthorized access or disclosure 7 , 8 . Researchers are obliged to take measures to preserve the anonymity and privacy of participants, which fosters trust and encourages participation in research 7 , 8 .
Non-maleficence and beneficence
These principles revolve around the obligation to avoid harm (non-maleficence) and to maximize possible benefits while minimizing potential harm (beneficence) 7 , 8 . Researchers must ensure that their studies do not pose undue risks to participants and that any potential risks are outweighed by the benefits.
Justice in research ethics refers to the fair selection and treatment of research participants 8 . It ensures that the benefits and burdens of research are distributed equitably among different groups in society, preventing the exploitation of vulnerable populations 8 .
The role of Institutional Review Boards (IRB)
Institutional Review Boards play critical roles in upholding ethical standards in research. An IRB is a committee established by an institution conducting research to review, approve, and monitor research involving human subjects 7 , 8 . Their primary role is to ensure that the rights and welfare of participants are protected.
Review and approval
Before a study commences, the IRB reviews the research proposal to ensure it adheres to ethical guidelines. This includes evaluating the risks and benefits, the process of obtaining informed consent, and measures for maintaining confidentiality 7 , 8 .
Monitoring and compliance
IRB also monitors ongoing research projects to ensure compliance with ethical standards. They may require periodic reports and can conduct audits to ensure ongoing adherence to ethical principles 7 , 8 .
Handling ethical violations
In cases where ethical standards are breached, IRB has the authority to impose sanctions, which can range from requiring modifications to the study to completely halting the research project 7 , 8 .
Other agencies and boards enforcing standards
Beyond IRB, there are other regulatory bodies and agencies at national and international levels that enforce ethical standards in research. These include:
The Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP) in the United States, which oversees compliance with the Federal Policy for the Protection of Human Subjects.
The World Health Organization (WHO) , which provides international ethical guidelines for biomedical research.
The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) , which sets ethical standards for the publication of biomedical research.
These organizations, along with IRB, form a comprehensive network that ensures the ethical conduct of scientific research. They safeguard the integrity of research using the reflections and lesson learnt from the past.
Benefits of ethical research
Credible and reliable outcomes, why is credibility so crucial in research, and how do ethical practices contribute to it.
Ethical practices such as rigorous peer review, transparent methodology, and adherence to established protocols ensure that research findings are reliable and valid 9 . When studies are conducted ethically, they are less likely to be marred by biases, fabrications, or errors that could compromise credibility. For instance, ethical standards demand accurate data reporting and full disclosure of any potential conflicts of interest 9 , which directly contribute to the integrity and trustworthiness of research findings.
How do ethical practices lead to socially beneficial outcomes?
Ethical research practices often align with broader societal values and needs, leading to outcomes that are not only scientifically significant but also socially beneficial. By respecting principles like justice and beneficence, researchers ensure that their work with human subjects contributes positively to society 7 , 8 . For example, ethical guidelines in medical research emphasize the need to balance scientific advancement with patient welfare, ensuring that new treatments are both effective and safe. This balance is crucial in addressing pressing societal health concerns while safeguarding individual rights and well-being.
Trust between the public and the scientific community
The relationship between the public and the scientific community is heavily reliant on trust, which is fostered through consistent ethical conduct in research. When the public perceives that researchers are committed to ethical standards, it reinforces their confidence in the scientific process and its outcomes. Ethical research practices demonstrate a respect for societal norms and values, reinforcing the perception that science serves the public good.
Case studies
Case study 1: the development and approval of covid-19 vaccines.
The development and approval of COVID-19 vaccines within a short time is a testament to how adherence to ethical research practices can achieve credible and beneficial outcomes. Strict adherence to ethical guidelines, even in the face of a global emergency, ensured that the vaccines were developed swiftly. However, safety standards were compromised to some extent as no animal trials were done before humans. The vaccine development was not transparent to the public, and this fuelled the anti-vaccination crowd in some regions. Ethical compliance, including rigorous testing and transparent reporting, should expedite scientific innovation while maintaining public trust.
Case study 2: The CRISPR babies
What ethical concerns were raised by the creation of the crispr babies, and what were the consequences.
The creation of the first genetically edited babies using CRISPR technology in China raised significant ethical concerns 10 . The lack of transparency, inadequate consent process, and potential risks to the children can be likened to ethical misconduct in genetic engineering research. This case resulted in widespread condemnation from the scientific community and the public, as well as international regulatory frameworks and guidelines for genetic editing research 10 .
Recommendation and conclusion
Continuous education and training.
The scientific community should prioritize ongoing education and training in ethics for researchers at all levels, ensuring awareness and understanding of ethical standards and their importance.
Enhanced dialogue and collaboration
Encourage multidisciplinary collaborations and dialogues between scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public to address emerging ethical challenges and develop adaptive guidelines.
Fostering a culture of ethical responsibility
Institutions and researchers should cultivate an environment where ethical considerations are integral to the research process, encouraging transparency, accountability, and social responsibility.
Global standards and cooperation
Work toward establishing and harmonizing international ethical standards and regulatory frameworks, particularly in areas like genetic engineering and AI, where the implications of research are global.
Ethics approval
Ethics approval was not required for this editorial.
Informed consent was not required for this editorial
Sources of funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author contribution
G.D.M. wrote this paper.
Conflicts of interest disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Research registration unique identifying number (UIN)
Goshen David Miteu.
Data availability statement
Provenance and peer review.
Not commissioned, externally peer-reviewed.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Published online 21 March 2024

COMMENTS
Learn about the shocking and harmful studies that violated human rights and dignity, such as testicular transplants, cancer cell injections, and speech therapy. These experiments were conducted on prisoners, patients, and orphans by doctors who disregarded consent and risks.
1. A DARK HISTORY OF RESEARCH. The daunting truth throughout America's dark history and present practice of American research is deeply rooted in anti‐Black racism. Research in the U.S. has been used throughout history to justify and rationalize the enslavement and experimentation of African Americans (Black people), and this racist legacy ...
With his collaborators— including Besançon—he ultimately discovered 248 studies that had used the approval number "09-022," representing a single application to the IHU ethics committee. Raoult was an author on all but 10 of these 248 studies. He told Science it is "perfectly true" that all these papers reused the ethics approval ...
At a Glance. Some of the most controversial and unethical experiments in psychology include Harlow's monkey experiments, Milgram's obedience experiments, Zimbardo's prison experiment, Watson's Little Albert experiment, and Seligman's learned helplessness experiment. These and other controversial experiments led to the formation of rules and ...
Associated Press reporters reviewed four decades of medical journals and found more than 40 studies that by modern standards would have been deemed unethical. The news comes as a federal bioethics ...
In 1966, anesthesiologist Henry K. Beecher published a landmark essay detailing 22 examples of ongoing unethical research on human subjects, including the Willowbrook hepatitis studies, in order ...
This paper gives an overview of the most remarkable unethical human research and how past misconducts helped develop ethical guidelines on human experimentation such as The Nuremberg Code 1947 following WWII. Unethical research in the field of neuroscience also proved to be incredibly distressing. Participants were often left with life-long ...
How the Classics Changed Research Ethics. Some of history's most controversial psychology studies helped drive extensive protections for human research participants. Some say those reforms went too far. Photo above: In 1971, APS Fellow Philip Zimbardo halted his classic prison simulation at Stanford after volunteer "guards" became abusive ...
Understanding the historical foundations of ethics in human research are key to illuminating future human research and clinical trials. This paper gives an overview of the most remarkable unethical human research and how past misconducts helped develop ethical guidelines on human experimentation such as The Nuremberg Code 1947 following WWII. Unethical research in the field of neuroscience ...
Background. The coerced human experiments and research under National Socialism constitute a reference point in modern bioethics. 7 Yet discussions of consent and the need for safeguards for research subjects to date lack a firm basis in historical evidence. There has been no full evaluation of the numbers of victims of Nazi research, who the victims were, and of the frequency and types of ...
A subject of the Tuskegee syphilis experiment has his blood drawn, c. 1953.. Numerous experiments which were performed on human test subjects in the United States in the past are now considered to have been unethical, because they were performed without the knowledge or informed consent of the test subjects. [1] Such tests have been performed throughout American history, but have become ...
Such experiments have been criticized as unethical but have advanced medicine and its ethical codes, such as the Nuremberg Code. When He made his claim of genetically altering humans, the response ...
The following is a list of the 30 most disturbing human experiments in history. 30. The Tearoom Sex Study. Image Source Sociologist Laud Humphreys often wondered about the men who commit impersonal sexual acts with one another in public restrooms.
"The whole discipline of biomedical ethics rises from the ashes of the Holocaust…" Arthur Caplan The Nuremberg Code (1947) laid the foundation for biomedical ethics mandating that medical experiments conducted on human beings must conform to well-defined humane, ethical standards; foremost is immutable standard: "The voluntary consent of the human subject is absolutely essential.
Stanford Prison Experiment. The Stanford Prison Experiment, perhaps one of the most famous forms of human experimentation ever conducted, took place in August of 1971. The purpose of the Stanford Prison Experiment was to study the causes of conflict between prisoners and those who guard them.
Unethical human experimentation is human experimentation that violates the principles of medical ethics.Such practices have included denying patients the right to informed consent, using pseudoscientific frameworks such as race science, and torturing people under the guise of research. Around World War II, Imperial Japan and Nazi Germany carried out brutal experiments on prisoners and ...
It is an irony of the history of medical research that this statement was part of a broad, forward-looking research policy—the Reichgesundheitsrat Circular—developed in Germany. For it was the atrocious German human experimentation of the Nazi era that led to the Nuremberg Doctors' Trial of 1946 and the resulting Nuremberg Code, the first ...
Multiple examples of unethical research studies conducted in the past throughout the world have cast a significant historical shadow on research involving human subjects. Examples include the Tuskegee Syphilis Study from 1932 to 1972, Nazi medical experimentation in the 1930s and 1940s, and research conducted at the Willowbrook State School in the 1950s and 1960s.[1] As the aftermath of these ...
Tuskegee Syphilis Study. One of the most notorious cases of unethical research, the Tuskegee Syphilis Study involved the denial of syphilis treatment to African-American males in Alabama. Subjects were lured into the study by advertisements for a special treatment, and were promised free meals, transportation, and assistance with burial costs ...
Physicians who engage with data from unethical experiments as authors, peer reviewers, or editors of medical publications should: Disclose that the data derive from studies that do not meet contemporary standards for the ethical conduct of research. Clearly describe and acknowledge the unethical nature of the experiment (s) from which the data ...
Groups ranged in size from 4-10 participants (N = 70). Mistrust of the health care system emerged as a primary barrier to participation in medical research among participants in our study. Mistrust stems from historical events including the Tuskegee syphilis study and is reinforced by health system issues and discriminatory events that ...
50th anniversary event. This event was held Wednesday, November 30, 2022. Watch our recorded session and related videos below. This event acknowledged the 50th anniversary of the end of the United States Public Health Service Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male at Tuskegee and Macon County, Alabama, 1932 -1972. The intention was to create a space for authentic, accurate storytelling.
In Dark Medicine: Rationalizing Unethical Medical Research, William LaFleur describes how rationalizations initially masquerade as reasons—but they are insufficient or invalid. 1 Even Nazi physicians experimenting in the concentration camps rationalized their actions. These acts were grossly immoral, yet behind them were moral justifications. Those involved used these justifications to ...
Learn about the biopharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences, including mission, vision, values, history, impact, leadership, therapeutic areas and other information.
Ethics are a guiding principle that shapes the conduct of researchers. It influences both the process of discovery and the implications and applications of scientific findings 1. Ethical considerations in research include, but are not limited to, the management of data, the responsible use of resources, respect for human rights, the treatment ...