- Privacy Policy

Home » Review Article vs Research Article

Review Article vs Research Article
Table of Contents

Review articles and Research Articles are two different types of scholarly publications that serve distinct purposes in the academic literature.
Research Articles
A Research Article is a primary source that presents original research findings based on a specific research question or hypothesis. These articles typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections. Research articles often include detailed descriptions of the research design, data collection and analysis procedures, and the results of statistical tests. These articles are typically peer-reviewed to ensure that they meet rigorous scientific standards before publication.
Review Articles
A Review Article is a secondary source that summarizes and analyzes existing research on a particular topic or research question. These articles provide an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic, including a critical analysis of the strengths and limitations of previous research. Review articles often include a meta-analysis of the existing literature, which involves combining and analyzing data from multiple studies to draw more general conclusions about the research question or topic. Review articles are also typically peer-reviewed to ensure that they are comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date.
Difference Between Review Article and Research Article
Here are some key differences between review articles and research articles:
| Aspect | Research Article | Review Article |
|---|---|---|
| Present original research findings based on a research question or hypothesis | Summarize and analyze existing research on a particular topic or research question | |
| Standard sections including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion | Depends on the journal and topic, but typically includes an introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion | |
| Describe the research design, data collection and analysis procedures, and results of statistical tests | Describe the methodology used to identify and analyze the literature | |
| Statistical analysis of data | Meta-analysis or systematic review of existing literature | |
| Presents original data collected through research | Does not present original data, but rather synthesizes and analyzes existing data | |
| Based on the results of the research conducted | Based on the analysis of existing literature | |
| Peer-reviewed to ensure that they meet rigorous scientific standards before publication | Peer-reviewed to ensure that they are comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date |
In summary, research articles and review articles serve different purposes in the academic literature. Research articles present original research findings based on a specific research question or hypothesis, while review articles summarize and analyze existing research on a particular topic or research question. Both types of articles are typically peer-reviewed to ensure that they meet high standards of scientific rigor and accuracy.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Hypothesis Vs Null Hypothesis

Qualitative Vs Quantitative Research

Essay Vs Research Paper

Correlational Research Vs Experimental Research

Generative Vs Evaluative Research

Clinical Research Vs Lab Research
- Study resources
- Calendar - Graduate
- Calendar - Undergraduate
- Class schedules
- Class cancellations
- Course registration
- Important academic dates
- More academic resources
- Campus services
- IT services
- Job opportunities
- Safety & prevention
- Mental health support
- Student Service Centre (Birks)
- All campus services
- Calendar of events
- Latest news
- Media Relations
- Faculties, Schools & Colleges
- Arts and Science
- Gina Cody School of Engineering and Computer Science
- John Molson School of Business
- School of Graduate Studies
- All Schools, Colleges & Departments.
- Directories
- My Library account Renew books and more
- Book a study room or scanner Reserve a space for your group online
- Interlibrary loans (Colombo) Request books from external libraries
- Zotero (formerly RefWorks) Manage your citations and create bibliographies
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver Request a PDF of an article/chapter we have in our physical collection
- Contactless Book Pickup Request books, DVDs and more from our physical collection while the Library is closed
- WebPrint Upload documents to print on campus
- Course reserves Online course readings
- Spectrum Deposit a thesis or article
- Sofia Discovery tool
- Databases by subject
- Course Reserves
- E-journals via Browzine
- E-journals via Sofia
- Article/chapter scan
- Intercampus delivery of bound periodicals/microforms
- Interlibrary loans
- Spectrum Research Repository
- Special Collections & Archives
- Additional resources & services
- Subject & course guides
- Borrowing & renewing
- Open Educational Resources Guide
- Instructional Services
- General guides for users
- Ask a librarian
- Research Skills Tutorial
- Quick Things for Digital Knowledge
- Critical Toolkit for Navigating Information
- Bibliometrics & research impact guide
- Concordia University Press
- Copyright guide
- Copyright guide for thesis preparation
- Digital scholarship
- Digital preservation
- Open Access
- ORCiD at Concordia
- Research data management guide
- Scholarship of Teaching & Learning
- Systematic Reviews
- Borrow (laptops, tablets, equipment)
- Connect (netname, Wi-Fi, guest accounts)
- Desktop computers, software & availability maps
- Group study, presentation practice & classrooms
- Printers, copiers & scanners
- Technology Sandbox
- Visualization Studio
- Webster Library
- Vanier Library
- Grey Nuns Reading Room
- Study spaces
- Floor plans
- Book a group study room/scanner
- Room booking for academic events
- Exhibitions
- Librarians & staff
- Work with us
- Memberships & collaborations
- Indigenous Student Librarian program
- Wikipedian in residence
- Researcher in residence
- Feedback & improvement
- Annual reports & fast facts
- Strategic Plan 2016/21
- Library Services Fund
- Giving to the Library
- Policies & Code of Conduct
- My Library account
- Book a study room or scanner
- Interlibrary loans (Colombo)
- Zotero (formerly RefWorks)
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver
- Contactless Book Pickup
- Course reserves
Review vs. Research Articles
How can you tell if you are looking at a research paper, review paper or a systematic review examples and article characteristics are provided below to help you figure it out., research papers.
A research article describes a study that was performed by the article’s author(s). It explains the methodology of the study, such as how data was collected and analyzed, and clarifies what the results mean. Each step of the study is reported in detail so that other researchers can repeat the experiment.
To determine if a paper is a research article, examine its wording. Research articles describe actions taken by the researcher(s) during the experimental process. Look for statements like “we tested,” “I measured,” or “we investigated.” Research articles also describe the outcomes of studies. Check for phrases like “the study found” or “the results indicate.” Next, look closely at the formatting of the article. Research papers are divided into sections that occur in a particular order: abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and references.
Let's take a closer look at this research paper by Bacon et al. published in the International Journal of Hypertension :

Review Papers
Review articles do not describe original research conducted by the author(s). Instead, they give an overview of a specific subject by examining previously published studies on the topic. The author searches for and selects studies on the subject and then tries to make sense of their findings. In particular, review articles look at whether the outcomes of the chosen studies are similar, and if they are not, attempt to explain the conflicting results. By interpreting the findings of previous studies, review articles are able to present the current knowledge and understanding of a specific topic.
Since review articles summarize the research on a particular topic, students should read them for background information before consulting detailed, technical research articles. Furthermore, review articles are a useful starting point for a research project because their reference lists can be used to find additional articles on the subject.
Let's take a closer look at this review paper by Bacon et al. published in Sports Medicine :

Systematic Review Papers
A systematic review is a type of review article that tries to limit the occurrence of bias. Traditional, non-systematic reviews can be biased because they do not include all of the available papers on the review’s topic; only certain studies are discussed by the author. No formal process is used to decide which articles to include in the review. Consequently, unpublished articles, older papers, works in foreign languages, manuscripts published in small journals, and studies that conflict with the author’s beliefs can be overlooked or excluded. Since traditional reviews do not have to explain the techniques used to select the studies, it can be difficult to determine if the author’s bias affected the review’s findings.
Systematic reviews were developed to address the problem of bias. Unlike traditional reviews, which cover a broad topic, systematic reviews focus on a single question, such as if a particular intervention successfully treats a medical condition. Systematic reviews then track down all of the available studies that address the question, choose some to include in the review, and critique them using predetermined criteria. The studies are found, selected, and evaluated using a formal, scientific methodology in order to minimize the effect of the author’s bias. The methodology is clearly explained in the systematic review so that readers can form opinions about the quality of the review.
Let's take a closer look this systematic review paper by Vigano et al. published in Lancet Oncology :
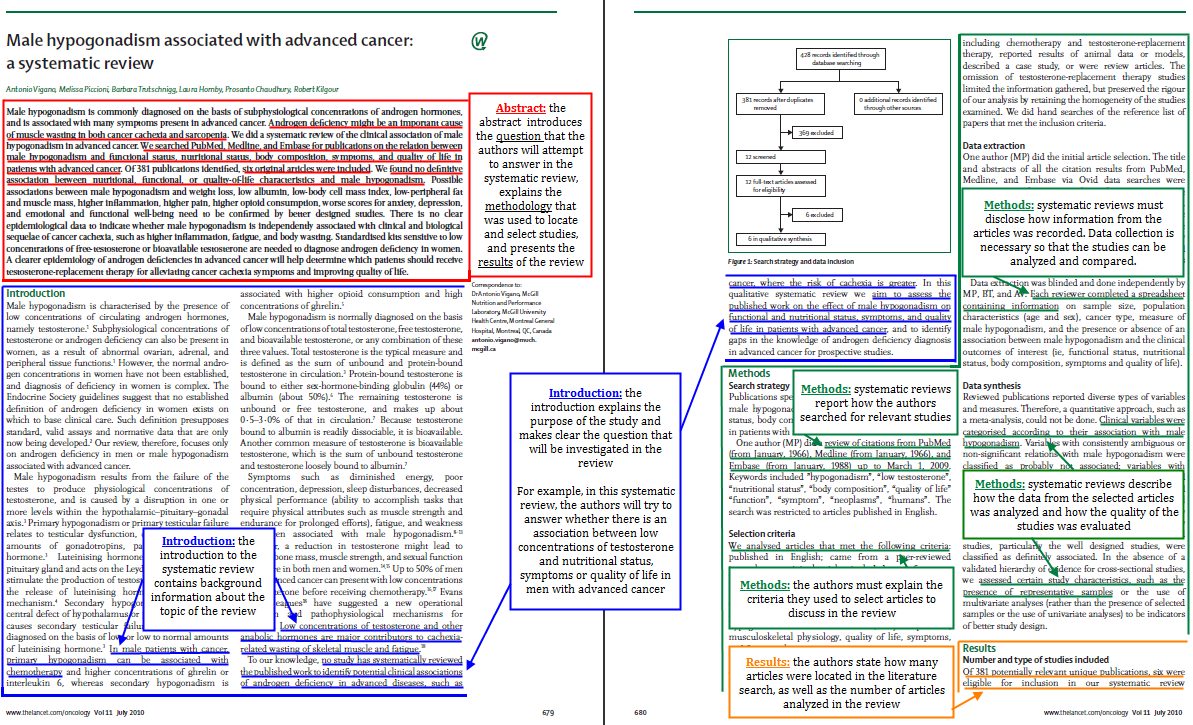
Finding Review and Research Papers in PubMed
Many databases have special features that allow the searcher to restrict results to articles that match specific criteria. In other words, only articles of a certain type will be displayed in the search results. These “limiters” can be useful when searching for research or review articles. PubMed has a limiter for article type, which is located on the left sidebar of the search results page. This limiter can filter the search results to show only review articles.
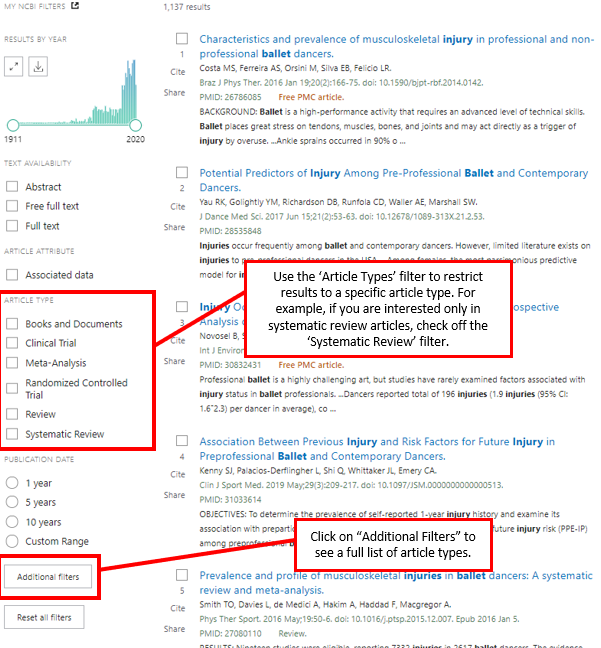
© Concordia University
NFS 4021 Contemporary Topics in Nutrition: Research Articles vs Review Articles
- Research Articles vs Review Articles
- Citation Help
Agriculture Support Librarian

Research Articles and Review Articles Defined Review
"A research article is a primary source ...that is, it reports the methods and results of an original study performed by the authors . The kind of study may vary (it could have been an experiment, survey, interview, etc.), but in all cases, raw data have been collected and analyzed by the authors, and conclusions drawn from the results of that analysis.
A review article is a secondary source ...it is written about other articles, and does not report original research of its own. Review articles are very important, as they draw upon the articles that they review to suggest new research directions, to strengthen support for existing theories and/or identify patterns among existing research studies. For student researchers, review articles provide a great overview of the existing literature on a topic. If you find a literature review that fits your topic, take a look at its references/works cited list for leads on other relevant articles and books!"
From https://apus.libanswers.com/faq/2324 , "What's the difference between a research and a review article?"
- Example of a RESEARCH Article Lin CL, Huang LC, Chang YT, Chen RY, Yang SH. Effectiveness of Health Coaching in Diabetes Control and Lifestyle Improvement: A Randomized-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021 Oct 29;13(11):3878.
- Example of a REVIEW Article Ojo O, Ojo OO, Adebowale F, Wang XH. The Effect of Dietary Glycaemic Index on Glycaemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2018 Mar 19;10(3):373.
Difference between Reviews and Research Articles

Research Article Break Down Review
Research articles follow a particular format. Look for:
- A brief introduction will often include a review of the existing literature on the topic studied, and explain the rationale of the author's study.
- A methods section, where authors describe how they collected and analyzed data. Statistical analysis are included.
- A results section describes the outcomes of the data analysis. Charts and graphs illustrating the results are typically included.
- In the discussion , authors will explain their interpretation of their results and theorize on their importance to existing and future research.
- References or works cited are always included. These are the articles and books that the authors drew upon to plan their study and to support their discussion.
- << Previous: Welcome
- Next: Databases >>
- Last Updated: Aug 19, 2024 11:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.lsu.edu/NFS4021
Provide Website Feedback Accessibility Statement
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Noro Psikiyatr Ars
- v.59(1); 2022

Basics of Writing Review Articles
Almıla erol.
Adjunct Faculty, Psychiatry & Psychology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
Evidence-based medicine forms the essence of medical practice in the modern world. No wonder review articles are the mainstay for evidence-based medicine.
Review articles provide a critical summary of the existing literature to explain the current state of scientific evidence on a particular topic. A well-written review article must summarize key research findings, reference must-read articles, describe current areas of agreement as well as controversies and debates, point out gaps in current knowledge, depict unanswered questions, and suggest directions for future research ( 1 ).
During the last decades, there has been a great expansion in the range of review methodologies resulting in many new review types ( 2 , 3 ). In an attempt to classify review types, Sutton et al. defined 48 different review types which they categorized into seven review families: traditional reviews, systematic reviews, review of reviews, rapid reviews, qualitative reviews, mixed method reviews and purpose specific reviews (for the full list of review types please see Sutton et al.) ( 2 ). To date, traditional reviews and systematic reviews have been most widely used in the field of medicine.
Traditional reviews usually cover advances in different aspects of a chosen topic and provide assessment of the subject within a broad spectrum. No formal guidance exists for traditional reviews. However, they have become increasingly more comprehensive and systematic since the emergence of systematic reviews. Narrative review, narrative summary, critical review, integrative review, and state of the art review are examples of traditional reviews ( 2 ).
Systematic reviews adopt a specific aim and a well-defined, rigorous methodology to enlighten a particular question. They usually focus on specific study types such as randomized controlled studies, observational studies, etc. They have well-defined reporting standards and guidance. Systematic reviews provide the highest level of evidence in medical sciences, playing an important role in the development of clinical guidelines ( 4 ). Meta-analysis is the most popular example of quantitative systematic review types.
- Review articles summarize the current state of evidence on a particular topic
- Review articles translate the relevance of evidence for readers
- Independent of the review type, all reviews must have a predefined methodology
- The methods utilized for the review should be explained clearly in the review paper
- Review papers should be written in a structured format
Considering the overwhelming number of diverse review types, the initial burden authors face is to choose the review type that matches their purpose best. Despite the continuous rise in the number of review types, there are sources that provide guidance about this issue ( 5 ). Authors are highly recommended to examine and learn about different review methodologies before they decide on their review approach.
International guidelines such as PRISMA ( 6 ), Cochrane ( 7 ), and JBI ( 8 ) provide detailed information about how to conduct reviews starting from the planning and protocol writing phases. The purpose of these international guidelines is to ensure transparent, unbiased, and complete reporting. Although the guidelines are focused on systematic reviews, they can also be used as bases for conducting other types of reviews. PRISMA encourages journal editors and reviewers to use the guideline for evaluation of review papers. PRISMA checklist is available online in different languages including Turkish at www.prisma-statement.org ( 9 ).
No matter what type of review is undertaken, the key points in a review article are to have a predefined methodology which is clearly explained in the text, and to have a structured format. Just like research papers, the most common and convenient practice is to write review papers in “introduction, methods, results, and discussion (IMRaD)” format accompanied by title, abstract, key words, and references.
The title makes the first introductory and is the most important sentence of the review paper. Like research paper titles, it must be brief, informative, and interesting all at the same time. It must contain the key words or their derivatives to increase the discoverability of the article via search engines. In addition, the type of the review should be accurately stated in the title.
The aim of the introduction is to explain why the review is undertaken and to persuade the readers for its necessity. In the introduction section, the authors must mention the latest developments about the subject of concern and explain why a review is needed. It is a good practice to refer to previous review papers on the subject and state what makes the current review different than the previous ones.
The methods section of the review paper should be written detailed enough to prove its adequacy and make it possible to be reconducted including more recent papers in the future. Explicit scientific methods are required for systematic reviews as defined by international guidelines ( 7 – 9 ). Although no guidelines exist for traditional narrative reviews, they too should have a rational methodology explained clearly. The methods section of every review article should state the key words used for the search, data bases screened, and the time frame chosen for the literature search. It should also explain the inclusion and exclusion criteria used for the selection of papers.
The results section should include a flow chart which shows the number of identified, included, and excluded papers along with the reasons for exclusion, as described in PRISMA flow diagram guidelines ( 9 ). Results section should cite and present characteristics and outcomes of each one of the included studies, providing the necessary information to assess their quality, validity, and contribution. The most relevant information about the included articles should be depicted in literature summary tables. They are an essential part of the review article as they provide information at one glance and make the paper more readable. Literature summary tables must contain information about methods, frameworks, strengths, limitations, and conceptual contribution of each article ( 10 ). Oversized tables must be presented as supplementary files.
Discussion section provides a general interpretation of the results and presents expert opinion. Writing a review article is not only about extracting relevant previous work and analyzing them, but also about making synthesis and drawing conclusions. Therefore, providing an objective interpretation of the results and guiding readers for better understanding of the current evidence should form the central part of the discussion. Wherever there is not enough evidence to make objective conclusions, the lack of evidence should be stated instead. Limitations, biases and gaps of the included literature should be discussed along with the limitations of the review process itself. It is critical to discuss the potential impacts of the results for future research and clinical practice.
In conclusion, reviews are objective attempts to examine the current state of evidence on a particular topic and its impacts. A review paper should explain why the review is undertaken, describe the methodology used, introduce the articles included, and provide expert opinion on the evidence achieved in a structured format. High quality reviews are essential in guiding clinical practice and future research along with policy making.
- Insights blog
What is a review article?
Learn how to write a review article.
What is a review article? A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results.
Writing a review of literature is to provide a critical evaluation of the data available from existing studies. Review articles can identify potential research areas to explore next, and sometimes they will draw new conclusions from the existing data.
Why write a review article?
To provide a comprehensive foundation on a topic.
To explain the current state of knowledge.
To identify gaps in existing studies for potential future research.
To highlight the main methodologies and research techniques.
Did you know?
There are some journals that only publish review articles, and others that do not accept them.
Make sure you check the aims and scope of the journal you’d like to publish in to find out if it’s the right place for your review article.
How to write a review article
Below are 8 key items to consider when you begin writing your review article.
Check the journal’s aims and scope
Make sure you have read the aims and scope for the journal you are submitting to and follow them closely. Different journals accept different types of articles and not all will accept review articles, so it’s important to check this before you start writing.
Define your scope
Define the scope of your review article and the research question you’ll be answering, making sure your article contributes something new to the field.
As award-winning author Angus Crake told us, you’ll also need to “define the scope of your review so that it is manageable, not too large or small; it may be necessary to focus on recent advances if the field is well established.”
Finding sources to evaluate
When finding sources to evaluate, Angus Crake says it’s critical that you “use multiple search engines/databases so you don’t miss any important ones.”
For finding studies for a systematic review in medical sciences, read advice from NCBI .

Writing your title, abstract and keywords
Spend time writing an effective title, abstract and keywords. This will help maximize the visibility of your article online, making sure the right readers find your research. Your title and abstract should be clear, concise, accurate, and informative.
For more information and guidance on getting these right, read our guide to writing a good abstract and title and our researcher’s guide to search engine optimization .
Introduce the topic
Does a literature review need an introduction? Yes, always start with an overview of the topic and give some context, explaining why a review of the topic is necessary. Gather research to inform your introduction and make it broad enough to reach out to a large audience of non-specialists. This will help maximize its wider relevance and impact.
Don’t make your introduction too long. Divide the review into sections of a suitable length to allow key points to be identified more easily.
Include critical discussion
Make sure you present a critical discussion, not just a descriptive summary of the topic. If there is contradictory research in your area of focus, make sure to include an element of debate and present both sides of the argument. You can also use your review paper to resolve conflict between contradictory studies.
What researchers say
Angus Crake, researcher
As part of your conclusion, include making suggestions for future research on the topic. Focus on the goal to communicate what you understood and what unknowns still remains.
Use a critical friend
Always perform a final spell and grammar check of your article before submission.
You may want to ask a critical friend or colleague to give their feedback before you submit. If English is not your first language, think about using a language-polishing service.
Find out more about how Taylor & Francis Editing Services can help improve your manuscript before you submit.
What is the difference between a research article and a review article?
| Differences in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| Presents the viewpoint of the author | Critiques the viewpoint of other authors on a particular topic | |
| New content | Assessing already published content | |
| Depends on the word limit provided by the journal you submit to | Tends to be shorter than a research article, but will still need to adhere to words limit |
Before you submit your review article…
Complete this checklist before you submit your review article:
Have you checked the journal’s aims and scope?
Have you defined the scope of your article?
Did you use multiple search engines to find sources to evaluate?
Have you written a descriptive title and abstract using keywords?
Did you start with an overview of the topic?
Have you presented a critical discussion?
Have you included future suggestions for research in your conclusion?
Have you asked a friend to do a final spell and grammar check?
Expert help for your manuscript

Taylor & Francis Editing Services offers a full range of pre-submission manuscript preparation services to help you improve the quality of your manuscript and submit with confidence.
Related resources
How to edit your paper
Writing a scientific literature review
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- CME Reviews
- Best of 2021 collection
- Abbreviated Breast MRI Virtual Collection
- Contrast-enhanced Mammography Collection
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Accepted Papers Resource Guide
- About Journal of Breast Imaging
- About the Society of Breast Imaging
- Guidelines for Reviewers
- Resources for Reviewers and Authors
- Editorial Board
- Advertising Disclaimer
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

- < Previous
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Scientific Review Article
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Manisha Bahl, A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Scientific Review Article, Journal of Breast Imaging , Volume 5, Issue 4, July/August 2023, Pages 480–485, https://doi.org/10.1093/jbi/wbad028
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Scientific review articles are comprehensive, focused reviews of the scientific literature written by subject matter experts. The task of writing a scientific review article can seem overwhelming; however, it can be managed by using an organized approach and devoting sufficient time to the process. The process involves selecting a topic about which the authors are knowledgeable and enthusiastic, conducting a literature search and critical analysis of the literature, and writing the article, which is composed of an abstract, introduction, body, and conclusion, with accompanying tables and figures. This article, which focuses on the narrative or traditional literature review, is intended to serve as a guide with practical steps for new writers. Tips for success are also discussed, including selecting a focused topic, maintaining objectivity and balance while writing, avoiding tedious data presentation in a laundry list format, moving from descriptions of the literature to critical analysis, avoiding simplistic conclusions, and budgeting time for the overall process.
- narrative discourse

Society of Breast Imaging members
Personal account.
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Short-term Access
To purchase short-term access, please sign in to your personal account above.
Don't already have a personal account? Register
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| May 2023 | 171 |
| June 2023 | 115 |
| July 2023 | 113 |
| August 2023 | 5,013 |
| September 2023 | 1,500 |
| October 2023 | 1,810 |
| November 2023 | 3,849 |
| December 2023 | 308 |
| January 2024 | 401 |
| February 2024 | 312 |
| March 2024 | 415 |
| April 2024 | 361 |
| May 2024 | 306 |
| June 2024 | 283 |
| July 2024 | 309 |
| August 2024 | 243 |
| September 2024 | 54 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Librarian
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 2631-6129
- Print ISSN 2631-6110
- Copyright © 2024 Society of Breast Imaging
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Biological Sciences
- Research vs. Review Articles
- Find Books & eBooks
- Reference/Web Resources
- RefWorks This link opens in a new window
Defining Article Types
Research articles.
"A research article reports the results of original research, assesses its contribution to the body of knowledge in a given area, and is published in a peer-reviewed scholarly journal." - Pen & the Pad
The study design of research articles may vary, but in all cases some form of raw data have been collected and analyzed by the author(s).
- Example of a research article Development of a nanoparticle-assisted PCR assay for detection of bovine respiratory syncytial virus
Review Articles
"A review article, also called a literature review, is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the theme and, unlike an original research article, won’t present new experimental results." - Taylor & Francis Author Services
Review articles provide a comprehensive foundation on a topic, and, as such, they are particularly useful for helping student researchers get an overview of the existing literature on a topic.
- Example of a review article Mannheimia haemolytica growth and leukotoxin production for vaccine manufacturing — A bioprocess review
Differences between Research and Review Articles
| Research Article | Review Article |
|---|---|
| Follows the scientific method. | Follows no set layout. |
| Provides background information on prior research. | Summarizes previously published research. |
| Conducts an experiment and reports what was found. | Discusses what is already known and identifies gaps. |
| Contains NEW original research data. | No original data are presented. |
| Written for advanced readers, and usually contains a lot of jargon. | Written for a general audience. |
Anatomy of a Research Article
Title & abstract.
The title of an article is a brief descriptive overview of what was the focus of the study. The abstract is a mini-summary of the study.
Introduction
This section often included an overview of the existing literature on the topic and an explanation of why the author(s) conducted the study. It frequently contains references to previous work on the topic.
In this section, the authors explain what they did. For example, they may include how they collected or analyzed data. Descriptions of statistical analysis are also included in this section.
This is where the authors describe the outcomes of their analysis. They don't include interpretation in their area, but instead just use a straightforward explanation of the data. This is the section that usually makes use of charts and graphs.
Authors use the discussion section to explain how they interpret their results and situate them in relationship to existing and future research.
References/Works Cited
This is a list of sources the authors drew upon to plan their study, understand their topic, and/or support their discussion.
- << Previous: Find Articles
- Next: Find Books & eBooks >>
- Last Updated: Jan 31, 2024 11:56 AM
- URL: https://clemson.libguides.com/biology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research articles present original research findings based on a specific research question or hypothesis, while review articles summarize and analyze existing research on a particular topic or research question.
Review articles do not describe original research conducted by the author (s). Instead, they give an overview of a specific subject by examining previously published studies on the topic. The author searches for and selects studies on the subject and then tries to make sense of their findings.
Review articles are very important, as they draw upon the articles that they review to suggest new research directions, to strengthen support for existing theories and/or identify patterns among existing research studies.
An ideal review article is supposed to motivate the research topic and describe its key concepts while delineating the boundaries of research. In this regard, experience-based information on how to methodologically develop acceptable and impactful review articles has been detailed in this paper.
The main and fundamental purpose of writing a review is to create a readable synthesis of the best resources available in the literature for an important research question or a current area of research.
A well-written review article must summarize key research findings, reference must-read articles, describe current areas of agreement as well as controversies and debates, point out gaps in current knowledge, depict unanswered questions, and suggest directions for future research (1).
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results.
A good review article provides readers with an in-depth understanding of a field and highlights key gaps and challenges to address with future research. Writing a review article also helps to expand the writer’s knowledge of their specialist area and to develop their analytical and communication skills, amongst other benefits.
Scientific review articles are comprehensive, focused reviews of the scientific literature written by subject matter experts. The task of writing a scientific review article can seem overwhelming; however, it can be managed by using an organized approach and devoting sufficient time to the process.
Differences between Research and Review Articles. Research Article. Review Article. Follows the scientific method. Follows no set layout. Provides background information on prior research. Summarizes previously published research. Conducts an experiment and reports what was found.