
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic – 9 Steps

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
Choosing a dissertation topic is really difficult.
When I had to choose dissertation topic I agonized for weeks.
And I’ve supervised over 50 students’ dissertations across undergraduate, masters and PhD levels. All of my students agonized over their topics, too.
So you’re not alone in your struggle.
The below tips for choosing a dissertation topic are the ones I wish I was given when I was in the process of looking for a suitable topic.
If only I’d known these points, I would have saved a lot of time and stress for myself. So if these tips only help one person out, I’ll be happy.
These tips really work for just about anybody. They’re particularly useful for undergraduate and Masters level students who are writing dissertations. But, I’m sure most doctoral students will also find these points relevant, too. Especially tips 1 – 3.
Here are my tips on how to choose a dissertation topic – I hope they come in handy, and good luck on your research journey!
Read Also: 25 Sociology Dissertation Ideas
1. It Doesn’t have to be Unique (Yet).
This is the one piece of advice I wish I had gotten when I was choosing my dissertation topic.
Many students feel like they need to find a unique topic that will blow their markers away.
I was this student.
I thought that I had to choose a topic and idea that was going to make a unique contribution to knowledge. I thought I had to discover something, or, at the very least, choose a topic that no one has ever done before.
So here’s what I wish someone had told me:
It doesn’t matter if other people have done the same topic as you.
Don’t even let it phase you for a moment if someone else has chosen your topic. Just choose whatever topic you want.
Well, because your unique contribution doesn’t come at the start. It comes at the end!
You’ll find a way to make a unique contribution after you have completed your literature review . There is always time and space to find a new angle or different way of doing the topic than other people.
So, don’t choose your topic because it’s unique or different.
Then … how should you choose your topic? Points 2 and 3 give you some tips…
2. Make it Relevant to your Career Goals.
The first thing I recommend to all my students is to consider how their topic can help progress their careers.
When giving guidance to my students, I ask them these three questions:
- a) What sort of specialization do you want in your career? If you’re studying teaching, your questions might be: do you want to be a specialized literacy teacher? do you want to be an expert on behavior management? Do you want to be specialized in play-based learning ?
- b) How do you want to differentiate yourself from your competition? Your dissertation topic is going to be the topic you ‘sell’ as your area of expertise in future job interviews. If you want to get a great job, choose a topic that really stands out in the marketplace. Have a think right now for yourself: what areas of your industry are booming? For example, would it be better to specialize in coal or solar panels? Which one would be best to talk about in a job interview in the 21 st Century?
- c) Do you want to be a research pro? Most of my students don’t want to be researchers as a career. They do their dissertations to prove mastery of their topic – that’s all. The research is a means to an end. But, if you think you want to go on to do the next level degree (a PhD one day?) then you’ll want to focus on having a high quality methodology, not just an interesting topic.
So, have a think now: is there a topic that will help you get to where you plan on going? What expert knowledge do you want to be able to ‘sell’ in a future interview?
3. Ensure it’s Interesting to You.
You’re going to be wedded to your chosen for a long time. And by the end of this journey you’re going to hate it.
To make your life easier, choose a topic you’re interested in.
Here’s two ways of approaching this:
Choose a Topic you Think About a Lot.
Choose a dissertation topic that you find yourself talking about, complaining about or raving about to your parents. Choose something that makes you angry, inspired or intrigued.
For the next week or so, I recommend taking notes whenever you find yourself thinking idly about something. Is that something you’ve thought about a lot?
Or, Choose a Topic by Looking over Past Assessment Tasks.
Another way of approaching the search for an interesting topic is to look over past assignments.
What assessment task have you done in the past few years that gripped you? Which one did you enjoy the most when you were studying it?
Zoom in on that topic and see if you can turn it into a dissertation.
Bonus tip: If you found a topic that was based on a previous assessment task, see if you can convince the person who taught that subject to be your dissertation supervisor.
4. Keep it Simple.
Too often, students want to choose a topic that is complex and complicated. They come up with a long, detailed research question (usually with the help of their professor) that, really, is hard to understand!
The best strategy is to come up with a topic that is really, really straightforward. At least, the topic should start as simple and straightforward.
Your topic is going to grow and expand into a monster. It’ll be hard to tame and control. You’ll be following random tangents down rabbit holes that end up being dead-ends. You’ll research aspects of the topic and realize it was a completely pointless exercise.
The way to minimize the crazy growth of your research project is to simplify it right from the start. Make it a really simple idea.
For example, I had a student who wanted to research:
“How big is the gap in mathematics outcomes between children from middle-class and working-class backgrounds by age 16?”
I would think that this topic may be achievable by a top academic with a sizeable research grant, but my student was completing a 10,000 word dissertation for graduating her Bachelor of Arts with Honours.
After several agonizing research meetings, we peeled it back over and again until we ended up with something much simpler and more specific:
“What are teachers’ opinions of the impact of poverty on learning?”
Why is this simpler and more specific?
Well, with the second study, my student has a clear focus group (teachers) and an achievable methodology (interviews). This will be far simpler than somehow conducting tests on 16-year old children, getting a significant amount of children to participate in the study, and then dissecting their mathematics test results by income level.
Instead, we aimed small and simple to ensure the task itself was achievable.
We’re not here to win a Nobel prize. You can do that with your multi-million-dollar post-doctoral research grant. Get your degree first.
5. Ensure it’s Achievable.
This piece of advice builds on the previous advice, to “keep it simple”.
Keeping it simple means making sure you have a clear, small-scale focus.
Esuring the project is achievable means choosing a methodology that won’t break you.
Small Scale Qualitative Studies are Achievable for Anyone
I always suggest to my Undergraduate and Masters level students to aim for a small scale study with no more than 20 research participants.
Now, I know there will be many of you out there who want to do quantitative research studies. And in reality, you can do a quantitative study with a small group of students. These usually involve quantitative action research case studies.
If you’re set on a quantitative study, that’s fine. But find a supervisor with the right experience.
Personally, I usually recommend a qualitative focus group analysis for anyone doing their first dissertation.
The biggest mistake you can make is biting off more than you can chew.
Small scale qualitative studies are the easiest option . They can be achieved within your time frame. And you can certainly still get a very high grade.
So, let’s take the example of the previous research question, which we changed from:
For the first study, you will have to develop skills in quantitative data analysis , find a sizeable cohort of students, get permission from their parents, get special permission to study children you’re your university ethics committee, develop a quality testing mechanism, pilot the test, conduct the test, analyze the data, then interpret it.
For the second study, you will not have to develop complex mathematical skills, bother with getting permission to research children, or deal with the rigor of quantitative analysis.
In other words, you will be able to bypass many hurdles you may face.
That’s the benefit of a small-scale qualitative study. It’s a nice easy first dissertation methodology. You can do it and do it well.
I know my position is controversial, but hey … I’m here to tell you how to avoid problems, not to stand on a soapbox.
Consider Textual Analysis, Semiotic Analysis or Secondary Research
Finding people to interview, survey or participate in your study in any way at all can be intimidating.
I find it interesting and really fulfilling. But I understand if you think it’s too much for you at this point in time.
If you don’t want to have to go out and find research participants for your study, I recommend one of these types of study:
- Textual Analysis : you can look at policy documents or newspaper articles and analyze their ideological positioning , for example;
- Semiotic Analysis : The quintessential semiotic analysis is the analysis of advertising images or movies and the examination of the ways they depict people of different races, social classes or genders;
- Secondary Research: Look over other people’s research and try to identify themes across a range of research studies.
Now, these three different methodologies are far outside of the scope of this discussion, but consult with your dissertation supervisor if you’re overwhelmed by the idea of conducting research with real human beings. One of these three methodologies may help you bypass that process, and make the dissertation feel more achievable for you.
6. Search Online for Inspiration
If you’re still struggling to choose a dissertation topic, go online to get inspiration!
There’s a few ways you can do this. Here’s a few good ones:
a) Google Previous Dissertation Topics
Many universities upload their students’ dissertations onto an online repository. This means there are a ton of open, free to access databases of previous students’ dissertations all over the internet.
Simply google “Dissertation” + “pdf” + a topic you’re interested in. If you’re a masters student, you can do “masters dissertation” + “pdf” + the topic; and if you’re an undegrad, then simply do “undergraduate dissertation” + “pdf” + the topic;. Simple!
Up will pop a ton of dissertations that you can instantly download to check out previous students’ successful dissertation topics.
Another benefit of doing this is that you’ll be able to view and model the structure that previous students have used as well. This can be super beneficial for you early on!
b) Look at Recent Articles Published in Journals focused on your Topic
If you scroll through the recent issues of journals in your topic, you’ll find a range of research topic ideas.
To get access to top journals in your topic, simply google “Scholarly Journal” + your topic. For example, I am a professor in education. So I’d google “Scholarly journal” + “Education”.
The homepages for a ton of journals will pop up in the Google search. Quickly scan through the recent issues of those journals to see if any ideas will pop up that interest you!
c) If you’re Studying Education or Teaching, Check Here
Lastly, a quick plug for another post I’ve written for dissertation students:
- 51+ Dissertation Ideas for Education students .
Go check that out if you want to write a dissertation on the ‘education’ topic.
7. Trust your Dissertation Supervisor
Your dissertation supervisor will have walked many students just like you through the research process before.
Look, I know many dissertation supervisors can be disappointingly aloof and disconnected from your research. And relationships can get very frosty with your supervisors indeed.
Trust your supervisor. They make recommendations for a reason. They know how to navigate the dissertation writing process. If your supervisor makes a recommendation, strong – very strongly – consider it.
Your supervisor also has expertise in one area of research or another. Take advantage of their expertise. Be flexible and let them sway you down certain paths. You need a knowledgeable partner in the research process.
So, trust your supervisor. You need their expertise more than you know.
8. Come up with 3-5 Ideas and Bring them to your Supervisor for Feedback
Your initial dissertation topic ideas will probably need a lot of refinement.
The person who will help you to refine your topic will be your dissertation supervisor. Their main job, unfortunately, is to curb your enthusiasm. It’s to show you what problems you’ll face if you follow certain paths and recommend alterations to ensure your topic is achievable.
So, approach your supervisor with your 3-5 top ideas and watch them do their magic. They should advise you on how to turn your ideas into reality.
Your ideas can be specific or broad – really, it doesn’t matter because you’ll walk out of your supervision meeting with a lot of changed ideas. It doesn’t need to be set in stone.
You could, for example, go up to your supervisor and say something like:
- “I’m interested in Erikson’s theory of development. Do you have any suggestions of how I can use Erikson’s ideas for a dissertation?”
- “I’m really into conservative politics. What ideas do you have for an achievable topic?”
- Any other ideas…
They’ll help you shape and mold your topic into something achievable.
9. Lastly, Stick to your Choice

When I did my dissertation, I questioned my topic daily: I’d always be thinking up new, better ideas for my dissertation!
But once you’re locked in, it’s hard to change your mind. You’re going to get ethics permission to conduct your study, not anyone else’s!
So, my advice is simple:
Once you’ve chosen your topic, commit.
If you’re desperate to do another topic, fine, do another degree. If you’re doing your Master’s right now, bank those other ideas for a potential PhD down the track.
But once you’ve made your choice, really … you’ve got to commit, block out all your regrets and dig in.
Don’t worry about your friends who chose a dissertation topic that is better than yours. Stay in your lane, be content with your topic, and create a great product.
Writing a dissertation is an exercise in being practical more than anything. That start from the very first choice: choosing a dissertation topic that’s achievable and good for your career, and will also put you on the path for top marks.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Green Flags in a Relationship
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Signs you're Burnt Out, Not Lazy
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to come up with a topic for your thesis

Finding a thesis topic
The easiest method to choose a thesis topic, how to choose a thesis topic that will get you a job, ask your supervisor for help, found my thesis topic, now what, further tips on finding a thesis topic, frequently asked questions about coming up with a topic for your thesis, related articles.
Depending on the level of your studies, you will be required to come up with a topic for your thesis by yourself or to choose from a list of broad topics. In either case, you will need to:
- Choose a specific scope
- Narrow it down as much as you can.
- Find a topic by considering specific debates or discussions that interest you.
- Choose a topic based on phenomenon, point of view, and context.
- Consider the relevance of your topic in relation to job market realities.
- Ask your supervisor for help and guidance, as needed.
Tip: Balance your own interests with what can help you grow in your field..
In any case, you can start by asking yourself if you’ve attended any lecture where you were particularly interested in a certain subject and go from there. The following questions might help you shine a light on personal topics of interest:
- What aspect of your studies holds a particular interest for you?
- Was something mentioned in a discussion that you found intriguing?
- Did you read about a theory or idea that spoke to you?
Ideas for a thesis can stem from many sources, so let your mind wander and see if anything tickles your curiosity. A thesis is a chance for you to spend some quality time with a certain aspect of your studies, so you better think of a topic that not only appeals to you but will also help you grow in your field.
Tip: Use phenomenon, point of view, and context to help you choose a balanced thesis topic.
We can all agree that choosing a topic for a thesis or any paper is one, if not the most, difficult steps in writing. However, according to Sahlman's How to Write a Master Thesis Fast , choosing a topic for your thesis is rather easy if you focus on the three following areas:
- Point of view
Focus on a specific phenomenon as the center of your thesis. For example, "queer rights" or "climate change". Next, you choose a point of view. From what perspective do you see the phenomenon? For instance, “American culture” or “legally/ financially”. Finally, you narrow it down to a particular context, such as “from 2000 to 2010” or “small German enterprises in 2017”.
By combining the examples of these three areas, we come up with two potential thesis topics:
The development of queer rights in American culture from 2000 to 2010
Emerging climate change regulations of small German enterprises in 2017
The topic doesn't need to be perfect at first. The idea is to brainstorm with the topics that most interest you in the beginning and slowly come up with with a compelling topic you can brag about at friends’ dinner parties. Here is a list of the top 100 research paper topics for some inspiration.
Tip: Think about how your potential topic can make an intervention into your field of study.
If you will be writing extensively about a specific topic it does not only have to meet the requirements of the academia but it should also expand your professional horizons. According to the article how to pick a masters thesis topic , you should be thinking beyond the completion of your degree.
The author states "use your time as a student to make yourself as attractive to employers as possible." In order to achieve this, make sure that at least one of the three components (phenomenon, point of view and context) is of interest in your desired professional field.
For example, the thesis topics mentioned above would be of great help to people interested in working in the field of human rights and climate change. By choosing a thesis topic related to your professional future, your chances of landing your desired job will be higher, as you could bring fresh and valuable knowledge to your field.
Tip: Ask your supervisor for advice early in the process.
If your topic is still not fully shaped, then take advantage of the greater wisdom of your supervisor and ask for guidance. Arm yourself with enough possible topics and pay your supervisor a visit. Explain what’s your specific point of view and/or context of interest and, luckily, they will steer you in the right direction.
It is certainly not enough to find a topic for your thesis. You also need to make sure that it is a relevant topic and that you will be able to develop it.
- 5 Tips for selecting a thesis topic
- How to come up with a thesis topic
- How to pick a Masters thesis topic
Choosing a topic for your thesis is easy if you focus on the three following areas:
Focus on a specific phenomenon as the center of your thesis. From what perspective do you see the phenomenon? Finally, narrow it down to a particular context . By combining these three areas, you can come up with several possible thesis topics.
Here is a list of the top 100 research paper topics for some inspiration.
The amount of time you need to choose a thesis topic depends on you. If you use the method we explained above, it can take very short time. If you doubt yourself too much, you might end up spending many days choosing a topic.
Here's a YouTube tutorial on How To Choose A Research Topic For A Dissertation Or Thesis (7 Step Method + Examples) by the Grad Coach.
The first person to ask for help if you have trouble finding a thesis topic is your supervisor. Take advantage of their greater wisdom and ask for guidance. Explain them your interests, and, luckily, they will steer you in the right direction.

Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- 100+ Writing Prompts for College Students (10+ Categories!)
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Know Everything About How to Make an Audiobook
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
- 10 Best AI Essay Outline Generators of 2024
- The Best Essay Graders of 2024 That You Can Use for Free!
- Top 10 Free Essay Writing Tools for Students in 2024
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!

Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.

- Tags: Dissertation
Choosing the right dissertation topic is pivotal in our academic and career paths. Your dissertation topic should capture your interest, meet academic requirements, and contribute to your field of study. Whether you’re just starting to think about your dissertation or trying to refine your ideas, this guide is designed to help you in choosing a perfect dissertation topic.
Let our professional editors refine your dissertation! Learn more
Without further ado, let’s see how to find a dissertation topic:
How to choose a dissertation topic
The following steps will help you select a dissertation topic that resonates with you and will be interesting to work on!
1. Understand your interests and strengths
Take some time to think about what you’re passionate about academically and where you excel. What topics have caught your eye during your studies or previous research? A dissertation is a long-term engagement, and genuine interest in your topic can be a great motivator when challenges arise.
- Reflect on past courses and projects: Review your coursework and past research. Identify patterns in your interests and consider how these can evolve into a dissertation topic.
- Write down ideas: Keep a journal or digital note of ideas as they come to you over days or weeks. This can help you see which topics consistently engage your interest.
2. Research existing literature
Before you settle on a topic, it’s important to see what research has already been done in your field. Do a deep dive into the existing literature to see what gaps your dissertation could fill. Use academic resources , databases, journals , and books to get a good background on your potential topic.
- Utilize academic databases: Make extensive use of databases like JSTOR, PubMed, and Google Scholar to access existing research.
- Create an annotated bibliography : As you review the literature , summarize key points and how they might relate to your potential topic. This will be invaluable as you narrow down your topic.
3. Define the specifics of your problem statement
Once you have a broad understanding of your area of interest and have reviewed the existing literature, it’s time to articulate the specifics of your problem statement. This step is critical as it forms the backbone of your dissertation.
- Narrow your focus: Use the issues identified to narrow down your topic to a specific problem that is manageable and significant. The specificity will help in focusing your research and discussions.
- Draft a preliminary problem statement: Write a clear and concise statement that describes the problem your research intends to address. This should indicate the scope, aim, and rationale of your study.
4. Consider the scope and resources available
One common mistake is picking a topic that’s either too broad or too narrow. Consider how much ground your topic covers and if you have the time and sources to do it justice. This includes access to data, research materials, or people for surveys and interviews.
- Assess resource availability: List the resources you need (e.g., data sets, lab equipment, specific populations for surveys) and confirm access to them.
- Set realistic goals: Ensure the scope of your topic matches the time and word count limits for your dissertation. Too broad or too narrow can lead to significant problems later.
5. Get feedback
Once you’ve got a few ideas, talk them over with your advisor and peers. They can give you valuable advice on whether your topics are relevant and doable. This step can also help you tweak your ideas based on practical considerations.
- Consult with advisors: Regular meetings with your advisor can provide guidance and insight into the feasibility and academic value of your topic.
- Engage with peers: Discussing your ideas in study groups or seminars can provide new perspectives and constructive criticism that refine your topic further.
6. Evaluate the impact
Consider what impact your research could have. Ask yourself: “What makes a great dissertation topic?” Ideally, it should contribute something new to your field, whether that’s solving a problem, filling a knowledge gap, or challenging existing ideas. Your topic should also fit with current trends and debates in your field.
- Identify the contribution to the field: Clearly define how your research will contribute to existing knowledge. Could it change how people think about the subject?
- Align with current trends: Research current trends in your field. Attending conferences and reading recent journal articles and publications can help you understand what is relevant and in demand.
7. Finalize and get approval
With insights from your research and feedback from your peers, refine your topic until it’s just right. Make sure it meets all the requirements of your department and get the green light from your dissertation committee. This step is key to making sure you’re on the right track and have the support you need to move forward.
- Prepare a formal proposal: Write a detailed proposal including your research question, methodology , and expected outcomes. This will be crucial for approval from your committee.
- Seek pre-approval feedback: Before submitting your proposal for final approval, get feedback from trusted mentors or colleagues. This can help catch any potential issues early.
Choosing the right dissertation topic is a thoughtful process that can set the foundation for a rewarding research experience. By understanding your interests, conducting thorough research, and seeking guidance from advisors, you are well on your way to selecting a topic that not only meets academic standards but also holds personal significance.
Remember, once you’ve chosen your dissertation topic and are ready to present your findings, professional editing and proofreading services are critical to ensuring clarity, coherence, and a polished presentation of your research. PaperTrue can enhance your dissertation, ensuring it communicates your ideas effectively and meets the highest academic standards!
Here are some more dissertation-related resources for you:
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- The Title Page of a Dissertation
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i know if my dissertation topic is original enough, can i change my dissertation topic after i have started my research, what should i do if i'm struggling to narrow down my dissertation topic.
Found this article helpful?

One comment on “ A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic ”

This was very detailed. Thanks! 🙂
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your Organization Needs a Technical Editor: Here’s Why

Your Guide to the Best eBook Readers in 2024

Writing for the Web: 7 Expert Tips for Web Content Writing
Subscribe to our Newsletter
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

Library Guides
Dissertations 1: getting started: choosing a topic and researching.
- Starting Your Dissertation
- Choosing A Topic and Researching
- Devising An Approach/Method
- Thinking Of A Title
- Writing A Proposal
Choosing a Topic
The first step to take when writing a dissertation is to choose a topic. The following is a list of ideas that may help you to do this:
Consider something that interests you
Talk to academic staff
Create a mind map to generate ideas.
Draw on reading and knowledge from modules you have studied
Consider topical issues in news/media
Look through dissertations written by previous students
Search for academic articles and read around a topic
Consider limitations and future research discussed in journals
How about a topic that...
You can investigate in your own country or area?
Would help you find a job?
Mind Maps to Generate Ideas
Mind-mapping is a simple, practical tool for improving creative thinking, planning and problem-solving abilities. It can help you to generate more ideas and make new connections.
How to draw a mind map
Place a blank sheet in landscape position and write the topic you have in mind in the middle. Draw branches from the centre, The branches are possible ideas and topics to include in the dissertation. Add sub-topics (“leaves”) and connect ideas and evidence from your reading. You can use colours and images to stimulate your thinking.

Tips for choosing a good topic:
Choose a topic you will enjoy. Your dissertation is an opportunity to explore, in depth, a topic of interest. It will be challenging, so pick a topic that will sustain your interest. Doing the initial research in your areas of interest will help you choose a topic that will be both viable and enjoyable.
Consider the time and resources you will need to successfully complete your dissertation - be realistic! Research, particularly gathering primary data (such as interviews, experiments or archival research), takes time and may involve other challenges such as travel, language skills, ethical considerations etc. Make sure you speak to your supervisor/tutor early on to ensure that your project is achievable. Additionally, check out the Time Management Guide for tips on sticking to deadlines.
If your topic is too broad, try to narrow it down , perhaps focusing on a specific sector, country or case study.
If your topic is too narrow, you can broaden it by contextualising it within the literature.

Researching for your Dissertation
This presentation explores effective strategies for locating, evaluating, and organising sources to enable you to produce a comprehensive and well researched dissertation. It also covers where you can find further help, as and when you need it.

Link to video on Researching for Your Dissertation
- PPT slides on Researching for your Dissertation
Conducting a Literature Search
To find a suitable topic you will need to conduct a literature search to identify what has been done before, what information is available and what gaps there are in the research. To carry out a successful literature search, you can try the following steps:
Define your terms. Ask yourself what the key concepts of your research idea are. Then, compile a list of keywords with their synonyms to help you develop a research strategy. Google and Google Scholar are good places to start.
Identify relevant information sources . These may include libraries, indexes, archives, the internet (especially, Google Scholar ) and electronic databases.
Make use of the University library. If you require help with locating texts, you can book an appointment with an Academic Engagement Librarian. Also, the British Library has a copy of every book published in the UK, which is helpful to know if you cannot get hold of a particular text.
Use journals. Journals are the best place to find the most up to date research in any field. These are now mostly published online.
Ensure that you keep records of what you have read. You will need them to write a literature review. For more detailed information about this dissertation chapter, visit the Literature Review Guide.
- << Previous: Starting Your Dissertation
- Next: Devising An Approach/Method >>
- Last Updated: Aug 1, 2023 2:36 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/starting-your-dissertation
CONNECT WITH US
- Home »
find your perfect postgrad program Search our Database of 30,000 Courses
How to write a masters dissertation or thesis: top tips.
It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at undergraduate level. Though, don’t feel put off by the idea. You’ll have plenty of time to complete it, and plenty of support from your supervisor and peers.
One of the main challenges that students face is putting their ideas and findings into words. Writing is a skill in itself, but with the right advice, you’ll find it much easier to get into the flow of writing your masters thesis or dissertation.
We’ve put together a step-by-step guide on how to write a dissertation or thesis for your masters degree, with top tips to consider at each stage in the process.
1. Understand your dissertation or thesis topic
There are slight differences between theses and dissertations , although both require a high standard of writing skill and knowledge in your topic. They are also formatted very similarly.
At first, writing a masters thesis can feel like running a 100m race – the course feels very quick and like there is not as much time for thinking! However, you’ll usually have a summer semester dedicated to completing your dissertation – giving plenty of time and space to write a strong academic piece.
By comparison, writing a PhD thesis can feel like running a marathon, working on the same topic for 3-4 years can be laborious. But in many ways, the approach to both of these tasks is quite similar.
Before writing your masters dissertation, get to know your research topic inside out. Not only will understanding your topic help you conduct better research, it will also help you write better dissertation content.
Also consider the main purpose of your dissertation. You are writing to put forward a theory or unique research angle – so make your purpose clear in your writing.
Top writing tip: when researching your topic, look out for specific terms and writing patterns used by other academics. It is likely that there will be a lot of jargon and important themes across research papers in your chosen dissertation topic.
2. Structure your dissertation or thesis
Writing a thesis is a unique experience and there is no general consensus on what the best way to structure it is.
As a postgraduate student , you’ll probably decide what kind of structure suits your research project best after consultation with your supervisor. You’ll also have a chance to look at previous masters students’ theses in your university library.
To some extent, all postgraduate dissertations are unique. Though they almost always consist of chapters. The number of chapters you cover will vary depending on the research.
A masters dissertation or thesis organised into chapters would typically look like this:
| Section | Description |
| Title page | The opening page includes all relevant information about the project. |
| Abstract | A brief project summary including background, methodology and findings. |
| Contents | A list of chapters and figures from your project. |
| Chapter 1 – Background | A description of the rationale behind your project. |
| Chapter 2 – Literature Review | A summary and evaluation of the literature supporting your project. |
| Chapter 3 – Methodology | A description of the specific methodology used in your project. |
| Chapter 4-6 – Data analysis and Findings | An overview of the key findings and data from your research. |
| Chapter 7 - Discussion and Evaluation | A description of what the data means and what you can draw from the findings. |
| Chapter 8 - Conclusion | Main summary of your overall project and key findings. |
| Bibliography | A list of the references cited in your dissertation or thesis. |
| Appendices | Additional materials used in your research. |
Write down your structure and use these as headings that you’ll write for later on.
Top writing tip : ease each chapter together with a paragraph that links the end of a chapter to the start of a new chapter. For example, you could say something along the lines of “in the next section, these findings are evaluated in more detail”. This makes it easier for the reader to understand each chapter and helps your writing flow better.
3. Write up your literature review
One of the best places to start when writing your masters dissertation is with the literature review. This involves researching and evaluating existing academic literature in order to identify any gaps for your own research.
Many students prefer to write the literature review chapter first, as this is where several of the underpinning theories and concepts exist. This section helps set the stage for the rest of your dissertation, and will help inform the writing of your other dissertation chapters.
What to include in your literature review
The literature review chapter is more than just a summary of existing research, it is an evaluation of how this research has informed your own unique research.
Demonstrate how the different pieces of research fit together. Are there overlapping theories? Are there disagreements between researchers?
Highlight the gap in the research. This is key, as a dissertation is mostly about developing your own unique research. Is there an unexplored avenue of research? Has existing research failed to disprove a particular theory?
Back up your methodology. Demonstrate why your methodology is appropriate by discussing where it has been used successfully in other research.
4. Write up your research
For instance, a more theoretical-based research topic might encompass more writing from a philosophical perspective. Qualitative data might require a lot more evaluation and discussion than quantitative research.
Methodology chapter
The methodology chapter is all about how you carried out your research and which specific techniques you used to gather data. You should write about broader methodological approaches (e.g. qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods), and then go into more detail about your chosen data collection strategy.
Data collection strategies include things like interviews, questionnaires, surveys, content analyses, discourse analyses and many more.
Data analysis and findings chapters
The data analysis or findings chapter should cover what you actually discovered during your research project. It should be detailed, specific and objective (don’t worry, you’ll have time for evaluation later on in your dissertation)
Write up your findings in a way that is easy to understand. For example, if you have a lot of numerical data, this could be easier to digest in tables.
This will make it easier for you to dive into some deeper analysis in later chapters. Remember, the reader will refer back to your data analysis section to cross-reference your later evaluations against your actual findings – so presenting your data in a simple manner is beneficial.
Think about how you can segment your data into categories. For instance, it can be useful to segment interview transcripts by interviewee.
Top writing tip : write up notes on how you might phrase a certain part of the research. This will help bring the best out of your writing. There is nothing worse than when you think of the perfect way to phrase something and then you completely forget it.
5. Discuss and evaluate
Once you’ve presented your findings, it’s time to evaluate and discuss them.
It might feel difficult to differentiate between your findings and discussion sections, because you are essentially talking about the same data. The easiest way to remember the difference is that your findings simply present the data, whereas your discussion tells the story of this data.
Your evaluation breaks the story down, explaining the key findings, what went well and what didn’t go so well.
In your discussion chapter, you’ll have chance to expand on the results from your findings section. For example, explain what certain numbers mean and draw relationships between different pieces of data.
Top writing tip: don’t be afraid to point out the shortcomings of your research. You will receive higher marks for writing objectively. For example, if you didn’t receive as many interview responses as expected, evaluate how this has impacted your research and findings. Don’t let your ego get in the way!
6. Write your introduction
Your introduction sets the scene for the rest of your masters dissertation. You might be wondering why writing an introduction isn't at the start of our step-by-step list, and that’s because many students write this chapter last.
Here’s what your introduction chapter should cover:
Problem statement
Research question
Significance of your research
This tells the reader what you’ll be researching as well as its importance. You’ll have a good idea of what to include here from your original dissertation proposal , though it’s fairly common for research to change once it gets started.
Writing or at least revisiting this section last can be really helpful, since you’ll have a more well-rounded view of what your research actually covers once it has been completed and written up.
Masters dissertation writing tips
When to start writing your thesis or dissertation.
When you should start writing your masters thesis or dissertation depends on the scope of the research project and the duration of your course. In some cases, your research project may be relatively short and you may not be able to write much of your thesis before completing the project.
But regardless of the nature of your research project and of the scope of your course, you should start writing your thesis or at least some of its sections as early as possible, and there are a number of good reasons for this:
Academic writing is about practice, not talent. The first steps of writing your dissertation will help you get into the swing of your project. Write early to help you prepare in good time.
Write things as you do them. This is a good way to keep your dissertation full of fresh ideas and ensure that you don’t forget valuable information.
The first draft is never perfect. Give yourself time to edit and improve your dissertation. It’s likely that you’ll need to make at least one or two more drafts before your final submission.
Writing early on will help you stay motivated when writing all subsequent drafts.
Thinking and writing are very connected. As you write, new ideas and concepts will come to mind. So writing early on is a great way to generate new ideas.
How to improve your writing skills
The best way of improving your dissertation or thesis writing skills is to:
Finish the first draft of your masters thesis as early as possible and send it to your supervisor for revision. Your supervisor will correct your draft and point out any writing errors. This process will be repeated a few times which will help you recognise and correct writing mistakes yourself as time progresses.
If you are not a native English speaker, it may be useful to ask your English friends to read a part of your thesis and warn you about any recurring writing mistakes. Read our section on English language support for more advice.
Most universities have writing centres that offer writing courses and other kinds of support for postgraduate students. Attending these courses may help you improve your writing and meet other postgraduate students with whom you will be able to discuss what constitutes a well-written thesis.
Read academic articles and search for writing resources on the internet. This will help you adopt an academic writing style, which will eventually become effortless with practice.
Keep track of your bibliography
The easiest way to keep the track of all the articles you have read for your research is to create a database where you can summarise each article/chapter into a few most important bullet points to help you remember their content.
Another useful tool for doing this effectively is to learn how to use specific reference management software (RMS) such as EndNote. RMS is relatively simple to use and saves a lot of time when it comes to organising your bibliography. This may come in very handy, especially if your reference section is suspiciously missing two hours before you need to submit your dissertation!
Avoid accidental plagiarism
Plagiarism may cost you your postgraduate degree and it is important that you consciously avoid it when writing your thesis or dissertation.
Occasionally, postgraduate students commit plagiarism unintentionally. This can happen when sections are copy and pasted from journal articles they are citing instead of simply rephrasing them. Whenever you are presenting information from another academic source, make sure you reference the source and avoid writing the statement exactly as it is written in the original paper.
What kind of format should your thesis have?
Read your university’s guidelines before you actually start writing your thesis so you don’t have to waste time changing the format further down the line. However in general, most universities will require you to use 1.5-2 line spacing, font size 12 for text, and to print your thesis on A4 paper. These formatting guidelines may not necessarily result in the most aesthetically appealing thesis, however beauty is not always practical, and a nice looking thesis can be a more tiring reading experience for your postgrad examiner .
When should I submit my thesis?
The length of time it takes to complete your MSc or MA thesis will vary from student to student. This is because people work at different speeds, projects vary in difficulty, and some projects encounter more problems than others.
Obviously, you should submit your MSc thesis or MA thesis when it is finished! Every university will say in its regulations that it is the student who must decide when it is ready to submit.
However, your supervisor will advise you whether your work is ready and you should take their advice on this. If your supervisor says that your work is not ready, then it is probably unwise to submit it. Usually your supervisor will read your final thesis or dissertation draft and will let you know what’s required before submitting your final draft.
Set yourself a target for completion. This will help you stay on track and avoid falling behind. You may also only have funding for the year, so it is important to ensure you submit your dissertation before the deadline – and also ensure you don’t miss out on your graduation ceremony !
To set your target date, work backwards from the final completion and submission date, and aim to have your final draft completed at least three months before that final date.
Don’t leave your submission until the last minute – submit your work in good time before the final deadline. Consider what else you’ll have going on around that time. Are you moving back home? Do you have a holiday? Do you have other plans?
If you need to have finished by the end of June to be able to go to a graduation ceremony in July, then you should leave a suitable amount of time for this. You can build this into your dissertation project planning at the start of your research.
It is important to remember that handing in your thesis or dissertation is not the end of your masters program . There will be a period of time of one to three months between the time you submit and your final day. Some courses may even require a viva to discuss your research project, though this is more common at PhD level .
If you have passed, you will need to make arrangements for the thesis to be properly bound and resubmitted, which will take a week or two. You may also have minor corrections to make to the work, which could take up to a month or so. This means that you need to allow a period of at least three months between submitting your thesis and the time when your program will be completely finished. Of course, it is also possible you may be asked after the viva to do more work on your thesis and resubmit it before the examiners will agree to award the degree – so there may be an even longer time period before you have finished.
How do I submit the MA or MSc dissertation?
Most universities will have a clear procedure for submitting a masters dissertation. Some universities require your ‘intention to submit’. This notifies them that you are ready to submit and allows the university to appoint an external examiner.
This normally has to be completed at least three months before the date on which you think you will be ready to submit.
When your MA or MSc dissertation is ready, you will have to print several copies and have them bound. The number of copies varies between universities, but the university usually requires three – one for each of the examiners and one for your supervisor.
However, you will need one more copy – for yourself! These copies must be softbound, not hardbound. The theses you see on the library shelves will be bound in an impressive hardback cover, but you can only get your work bound like this once you have passed.
You should submit your dissertation or thesis for examination in soft paper or card covers, and your university will give you detailed guidance on how it should be bound. They will also recommend places where you can get the work done.
The next stage is to hand in your work, in the way and to the place that is indicated in your university’s regulations. All you can do then is sit and wait for the examination – but submitting your thesis is often a time of great relief and celebration!
Some universities only require a digital submission, where you upload your dissertation as a file through their online submission system.
Related articles
What Is The Difference Between A Dissertation & A Thesis
How To Get The Most Out Of Your Writing At Postgraduate Level
Dos & Don'ts Of Academic Writing
Dispelling Dissertation Drama
Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Complete Our Destination Survey

Take 2 minutes to complete our Destination Survey for the chance to win a Postgrad Study Bursary worth £2,000.
All we need to know is:
- Your university
- Your PG course
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Published on September 21, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic .
The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development of your research. It helps you choose a type of research to pursue, as well as whether to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
You can download our templates in the format of your choice below.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What should your proposal contain, dissertation question examples, what should your proposal look like, dissertation prospectus examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about proposals.
Prior to jumping into the research for your thesis or dissertation, you first need to develop your research proposal and have it approved by your supervisor. It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives .
Depending on your department’s requirements, there may be a defense component involved, where you present your research plan in prospectus format to your committee for their approval.
Your proposal should answer the following questions:
- Why is your research necessary?
- What is already known about your topic?
- Where and when will your research be conducted?
- Who should be studied?
- How can the research best be done?
Ultimately, your proposal should persuade your supervisor or committee that your proposed project is worth pursuing.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Strong research kicks off with a solid research question , and dissertations are no exception to this.
Dissertation research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
- What are the main factors enticing people under 30 in suburban areas to engage in the gig economy?
- Which techniques prove most effective for 1st-grade teachers at local elementary schools in engaging students with special needs?
- Which communication streams are the most effective for getting those aged 18-30 to the polls on Election Day?
An easy rule of thumb is that your proposal will usually resemble a (much) shorter version of your thesis or dissertation. While of course it won’t include the results section , discussion section , or conclusion , it serves as a “mini” version or roadmap for what you eventually seek to write.
Be sure to include:
- A succinct introduction to your topic and problem statement
- A brief literature review situating your topic within existing research
- A basic outline of the research methods you think will best answer your research question
- The perceived implications for future research
- A reference list in the citation style of your choice
The length of your proposal varies quite a bit depending on your discipline and type of work you’re conducting. While a thesis proposal is often only 3-7 pages long, a prospectus for your dissertation is usually much longer, with more detailed analysis. Dissertation proposals can be up to 25-30 pages in length.
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we’ve compiled some examples for you to get your started.
- Example #1: “Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907” by Maria Lane
- Example #2: “Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society” by Dimitri Nakassis
- Example #3: “Manhood Up in the Air: A Study of Male Flight Attendants, Queerness, and Corporate Capitalism during the Cold War Era” by Phil Tiemeyer
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis-dissertation-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, a step-by-step guide to the writing process, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, what is your plagiarism score.

10 Essential Steps To Writing A Research Paper
Research papers are a cornerstone of academic growth, serving as a critical tool for students to delve deep into subject matters, enhance their analytical skills, and contribute to academic discourse. See also What Is The Writing Process? Let’s try to demystify the process of writing a research paper by providing a clear, step-by-step approach that…
Research papers are a cornerstone of academic growth, serving as a critical tool for students to delve deep into subject matters, enhance their analytical skills, and contribute to academic discourse.
See also What Is The Writing Process?
Let’s try to demystify the process of writing a research paper by providing a clear, step-by-step approach that can be adapted to any academic level or subject. Planning and organization can make writing a research paper less daunting. Students are encouraged to confidently approach this intellectual journey, using this guide as a roadmap to navigate the complexities of research writing.
The first step in any academic writing project, particularly a research paper, is to understand the assignment thoroughly. Misunderstanding the prompt can lead to significant missteps down the line. It’s important to read the assignment prompt carefully and use it to plan your paper. Students should consider consulting a paper writing service to guide interpreting complex instructions or academic expectations. Essential questions to ask include: What is the purpose of the paper? Who is the audience? What is the required scope and format?
- Understanding the Assignment
Selecting a topic is more than just picking an area of interest; it involves balancing personal curiosity with academic value and resource availability. A good topic should allow you to explore questions or issues you care about while meeting the assignment’s requirements. Strategies for topic selection include brainstorming, preliminary reading, and discussing ideas with peers or instructors.
- Conducting Preliminary Research
Begin with general sources to gain an overview of your topic’s broader context. This can include textbooks, encyclopedias, or reliable online resources. Identify key themes, concepts, and terminology relevant to your subject during this phase.
As you gather more information, start focusing your research on a specific aspect of the topic. This will help you develop a focused research question or a strong thesis statement that will guide the rest of your research and writing process.
See also Writing
- Developing a Research Plan
Determine what types of sources are most appropriate for your topic. This might include books, peer-reviewed journal articles, interviews, or primary documents. Plan a realistic timeline for your research and writing, setting key milestones to ensure steady progress.
Use digital tools such as citation management software, note-taking apps, and organizational platforms to organize your research. These tools can help manage sources, keep track of important quotes, and structure your paper’s outline.
- Conducting In-Depth Research
Distinguish between scholarly and non-scholarly sources. Utilize academic databases and libraries to access credible and relevant material. Internet sources should be cautiously approached and evaluated for credibility and relevance.
Learn to assess the reliability, bias, and usefulness of each source. Critical reading and analytical note-taking are essential at this stage to ensure that you gather strong evidence to support your thesis.
- Crafting a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a concise summary of your paper’s main point or claim. It is typically one sentence long and states your position clearly. The thesis is crucial as it guides the structure and argumentation of your research paper.
As your research progresses, revisit and possibly refine your thesis statement to reflect deeper insights and stronger evidence. This may involve tightening its focus, adjusting its angle, or strengthening its argumentative power. Examples of effective thesis statements will illustrate how specificity and clarity contribute to a compelling argument.
- Creating an Outline
An outline is a blueprint for your paper; it organizes your thoughts and lays out the structure of your argument coherently. This helps prevent structural issues later in the writing process and ensures that each part of your argument flows logically into the next.
Start by outlining the main points of your introduction, body, and conclusion. Under each main point, list subpoints and supporting evidence, which can be detailed from your research that backs up your thesis. Consulting an online paper writing service can provide additional structure and guidance for students feeling overwhelmed by this stage.
- Writing the First Draft
Begin writing with the body of your paper, as it contains the bulk of information and analysis. Don’t worry about getting everything perfect on the first try. The goal is to put your research and ideas into a coherent structure.
Keep your writing clear and focused. Employ a mix of summarization, direct analysis, and critical thinking. Ensure that each paragraph opens with a clear topic sentence and closes with a transition to the next idea, ensuring smooth, logical flow.
- Revising and Editing
Once your first draft is complete, take time to revise it thoroughly. Look for ways to strengthen your argument, clarify your points, and improve the overall flow of the paper. Ensure that each section contributes directly to supporting your thesis. Don’t hesitate to rewrite sections for better clarity and impact if necessary.
After revising the content, focus on grammar, punctuation, and style. Look for mistakes like misplaced commas, incorrect verb tenses, or inconsistent formatting. Using tools from the best paper writing service can help ensure your paper meets academic standards.
- Formatting and Citations
Please familiarize yourself with the required citation style for your paper, whether it’s APA, MLA, Chicago, or another format. Proper citation is crucial to avoid plagiarism and to give proper credit to the sources of your research.
Ensure your paper is formatted correctly according to your assignment requirements. This includes setting the correct margins, using the appropriate font size, and including all necessary sections like a title page, headings, and a bibliography. Many students find this step meticulous; however, a paper writer skilled in formatting can assist in polishing the final document.
- Final Proofreading and Submission
Carefully proofread your paper to catch any lingering errors and ensure it reads smoothly. Techniques such as reading aloud or having a peer review of your work can be invaluable. Check for consistency in your arguments, accuracy in your information, and completeness in your research.
Create a checklist for all elements needed for submission, including additional materials like appendices or abstracts. Ensure everything is in order before you submit your paper, whether online or in person. Double-check that all guidelines are followed to avoid last-minute surprises.
Writing a research paper is a demanding but rewarding process. By following these steps, students can produce well-organized, insightful, and high-quality research papers that meet academic standards and enhance their understanding and expertise in the chosen subject area.
Remember, using resources such as a paper writing service should complement your efforts and provide support as you develop your skills as a researcher and writer. Dedication and attention to detail make the journey from a blank page to a completed research paper a significant academic achievement.
TeachThought is an organization dedicated to innovation in education through the growth of outstanding teachers.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
Published on 11 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
Choosing your dissertation topic is the first step in making sure your research goes as smoothly as possible. When choosing a topic, it’s important to consider:
- Your institution and department’s requirements
- Your areas of knowledge and interest
- The scientific, social, or practical relevance
- The availability of data and resources
- The timeframe of your dissertation
You can follow these steps to begin narrowing down your ideas.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Step 1: check the requirements, step 2: choose a broad field of research, step 3: look for books and articles, step 4: find a niche, step 5: consider the type of research, step 6: determine the relevance, step 7: make sure it’s plausible, step 8: get your topic approved, frequently asked questions.
The very first step is to check your program’s requirements. This determines the scope of what it is possible for you to research.
- Is there a minimum and maximum word count?
- When is the deadline?
- Should the research have an academic or a professional orientation?
- Are there any methodological conditions? Do you have to conduct fieldwork, or use specific types of sources?
Some programs have stricter requirements than others. You might be given nothing more than a word count and a deadline, or you might have a restricted list of topics and approaches to choose from. If in doubt about what is expected of you, always ask your supervisor or department coordinator.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Start by thinking about your areas of interest within the subject you’re studying. Examples of broad ideas include:
- Twentieth-century literature
- Economic history
- Health policy
To get a more specific sense of the current state of research on your potential topic, skim through a few recent issues of the top journals in your field. Be sure to check out their most-cited articles in particular. For inspiration, you can also search Google Scholar , subject-specific databases , and your university library’s resources.
As you read, note down any specific ideas that interest you and make a shortlist of possible topics. If you’ve written other papers, such as a 3rd-year paper or a conference paper, consider how those topics can be broadened into a dissertation.
After doing some initial reading, it’s time to start narrowing down options for your potential topic. This can be a gradual process, and should get more and more specific as you go. For example, from the ideas above, you might narrow it down like this:
- Twentieth-century literature Twentieth-century Irish literature Post-war Irish poetry
- Economic history European economic history German labor union history
- Health policy Reproductive health policy Reproductive rights in South America
All of these topics are still broad enough that you’ll find a huge amount of books and articles about them. Try to find a specific niche where you can make your mark, such as: something not many people have researched yet, a question that’s still being debated, or a very current practical issue.
At this stage, make sure you have a few backup ideas – there’s still time to change your focus. If your topic doesn’t make it through the next few steps, you can try a different one. Later, you will narrow your focus down even more in your problem statement and research questions .
There are many different types of research , so at this stage, it’s a good idea to start thinking about what kind of approach you’ll take to your topic. Will you mainly focus on:
- Collecting original data (e.g., experimental or field research)?
- Analysing existing data (e.g., national statistics, public records, or archives)?
- Interpreting cultural objects (e.g., novels, films, or paintings)?
- Comparing scholarly approaches (e.g., theories, methods, or interpretations)?
Many dissertations will combine more than one of these. Sometimes the type of research is obvious: if your topic is post-war Irish poetry, you will probably mainly be interpreting poems. But in other cases, there are several possible approaches. If your topic is reproductive rights in South America, you could analyse public policy documents and media coverage, or you could gather original data through interviews and surveys .
You don’t have to finalise your research design and methods yet, but the type of research will influence which aspects of the topic it’s possible to address, so it’s wise to consider this as you narrow down your ideas.
It’s important that your topic is interesting to you, but you’ll also have to make sure it’s academically, sociallym or practically relevant to your field.
- Academic relevance means that the research can fill a gap in knowledge or contribute to a scholarly debate in your field.
- Social relevance means that the research can advance our understanding of society and inform social change.
- Practical relevance means that the research can be applied to solve concrete problems or improve real-life processes.
The easiest way to make sure your research is relevant is to choose a topic that is clearly connected to current issues or debates, either in society at large or in your academic discipline. The relevance must be clearly stated when you define your research problem .
Before you make a final decision on your topic, consider again the length of your dissertation, the timeframe in which you have to complete it, and the practicalities of conducting the research.
Will you have enough time to read all the most important academic literature on this topic? If there’s too much information to tackle, consider narrowing your focus even more.
Will you be able to find enough sources or gather enough data to fulfil the requirements of the dissertation? If you think you might struggle to find information, consider broadening or shifting your focus.
Do you have to go to a specific location to gather data on the topic? Make sure that you have enough funding and practical access.
Last but not least, will the topic hold your interest for the length of the research process? To stay motivated, it’s important to choose something you’re enthusiastic about!
Most programmes will require you to submit a brief description of your topic, called a research prospectus or proposal .
Remember, if you discover that your topic is not as strong as you thought it was, it’s usually acceptable to change your mind and switch focus early in the dissertation process. Just make sure you have enough time to start on a new topic, and always check with your supervisor or department.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
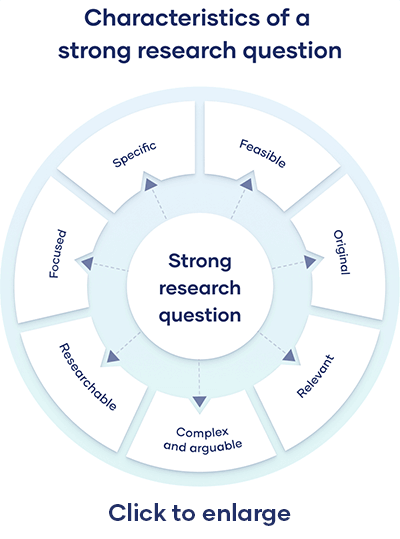
You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 11). How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/choosing-a-topic/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.

Writing Lab
Writing your paper.
- Topic of Paper
- Brainstorming
What is an outline?
Types of outlines, outline template.
- Revising and Editing
- Proofreading
An outline is a tool to organize written ideas about a topic or thesis logically. Outlines arrange major topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Writers use outlines when writing their papers to know which topic to cover in what order. Outlines for papers can be very general or very detailed. Check with your instructor to understand what is expected of you.
Alphanumeric Outline
I. Roman Numerals
A. I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, etc.
B. Represent main ideas to be covered in the paper in the order they will be presented
II. Uppercase Letters
A. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, etc.
B. Represent subtopics within each main idea
III. Arabic Numbers
A. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, etc.
B. Represent details or subdivisions within subtopics
IV. Lowercase Letters
A. a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, l, m, etc.
B. Represent details within subdivisions
Full-sentence outline
- Each roman numeral (I, II, III, IV…) indicates the start of a new paragraph. So I. is the first sentence of the introduction, II. is the first sentence of the first paragraph of the body, III. is the first sentence of the second paragraph of the body, and so on.
- Each capital letter (A, B, C, D…) indicates a main point within the structure of the paragraph. So in our introduction, A. is the attention getter, B. is another attention getter, C. describes a point that makes the topic personal, and D. is the thesis statement.
- Each Arabic numeral (1, 2, 3, 4…) indicates a sentence or piece of supporting evidence for each main point. So in the first body paragraph (II.), point A. is a general statement that needs some additional support, so 1. provides a supporting statement of fact and the citation of where that information came from. 2. provides another sentence with supporting evidence, as does 3.
There are no formal APA guidelines for creating an outline. We recommend you follow standard APA formatting rules for accepted fonts, double spacing, one-inch margins, page numbers, and header . A cover or title page should also be included if you are handing in the outline as an assignment. Include a References page if outside resources are used while drafting your outline.
- Outline Template
- << Previous: Organizing
- Next: Drafting >>
- Last Updated: Aug 26, 2024 12:20 PM
- URL: https://guides.rasmussen.edu/writingpaper

- University Reviews
- Career Guide
Important Facts
Ask any Question - CV Forum

PhD Thesis: Topics, Example, Process, Tips, How to Write?
Muhammad Hasim Sheikh Aug 28, 2024 1K Reads
PhD Thesis or PhD Dissertation is an important component in the process of getting a doctorate. If you are pursuing PhD or deciding to pursue it, it will be mandatory for you to prepare and submit your PhD Thesis.
All the details and information collected during the PhD research are presented in the form of a PhD Thesis. It is a detailed description of the research process of research outcomes that can contribute to the original field of knowledge in the particular field.
The PhD candidates prepare the PhD Thesis to showcase their research findings. A PhD Thesis is the backbone of the doctoral degree and plays an important role in showcasing the research ability and competency in conducting independent and original research.
A PhD Thesis not only demonstrates the research competency of the candidates but also exhibits their expertise, critical thinking, and research skills. The preparation of a PhD Thesis is a very difficult and challenging task and you need to take the utmost precautions while preparing it.
Here in this blog, we will discuss all the procedures adopted while preparing a detailed PhD and high-quality PhD Thesis:
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the need for PhD Thesis Preparation?
The preparation of a PhD Thesis is crucial as it represents the cumulative research work and outcomes. The PhD Thesis provides a detailed description of the comprehensive research in the particular field. If you are a PhD Scholar, it will be mandatory for you to prepare a PhD Thesis to complete your degree.
It acts as proof of document of your research and findings while pursuing the PhD program. A PhD Thesis also guides the new PhD scholars for reference. Newly enrolled PhD scholars who have just begun their research work can refer to the previous research works conducted by a different researcher in the field to begin his journey.
PhD Thesis is a document that also provides a pathway to new research scholars in the field. The PhD thesis preparation involves organizing and assembling the research findings in a coherent structure. This allows you to refine ideas, identify gaps in the research, and ensure that the arguments are logically presented.
Additionally, you will be able to develop essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication that are highly valuable in both academic and professional settings.
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Beginning of the PhD Thesis Writing
PhD Thesis writing begins after completion of the PhD coursework. Every PhD Scholar has to go through a PhD coursework. PhD coursework is offered in the initial years to provide a strong foundation in the research aptitude in the given field.
Once the coursework is completed, a comprehensive exam is conducted to examine and evaluate the ability of the scholars to conduct original research. Generally, the examination is conducted in the 3rd year of the PhD program. Once the examinations are concluded for the coursework, PhD scholars can start working on their PhD Thesis/Dissertation.
Process and Structure of PhD Thesis Writing
Writing a PhD Thesis is a daunting task and one has to go through a prolonged process. It involves several stages and PhD scholars need to through all the stages to prepare a highly inclusive Thesis.
Here is the detailed process and structure of the PhD Thesis:
- Cover Page: The PhD Thesis writing begins with the preparation of the cover page. The cover page includes the title of the research topic, the name of the university, the name of the scholar, and the supervisor. Generally, the cover page of the thesis is designed to catch the attention of the viewers.
- Preface: The cover page is followed by the Preface of the PhD Thesis. The Preface is written by the PhD scholars. In the preface of the thesis, they explain the reasons for taking up a particular research topic and their experiences while conducting the research and writing the PhD Thesis. Generally, the preface is written after writing the thesis but arranged after the cover page.
- Acknowledgment: After writing the Preface of the thesis, PhD scholars begin with the acknowledgment page. Generally, the acknowledgment page of the thesis recognizes all those people who have contributed and given their support in conducting the research. PhD scholars acknowledge the contribution of all the people who have professionally and personally helped in the research.
- Introduction: In the Introduction, PhD scholars introduce their research topic and explain how this study contributes to the original knowledge of the field. The introduction in the PhD Thesis is a summary of all the key objectives of the research and an explanation of why the particular research is needed.
- Literature Review: The literature Review in the PhD Thesis is a summary of all the works done by previous researchers and academicians in the same field or field relevant to the topic. In the literature review, all the scholarly works whether books, research journals, research papers, or previous research thesis related to the subject are cited in the PhD Thesis. A literature review is done to support the current research by analyzing the previous works done on the same subject.
- Research Chapters: Research Chapters are the crux of the PhD Thesis. In this stage, the PhD Thesis is divided into various chapters. The research conducted by the PhD scholars is recorded in detail in this section. Research Chapters broadly explain the methodology, hypothesis, and original research. The research chapter includes the process of conducting the research on a particular area and the explanation of the research questions.
- Conclusion: After writing all the research chapters in the PhD Thesis, the conclusion of the research is added. The conclusion is the final chapter of the PhD Thesis Writing that concludes all the research edvideces and findings to reach to a final result. The conclusion also includes the possibilities of further research in the same field and its application to enhance the knowledge of the particular subject.
- Bibliography and Appendices: The bibliography is written at the end of the PhD Thesis. The Bibliography lists all sources such as books, journals, research papers, thesis, etc used in the PhD Thesis writing. It is written in alphabetical order and includes the author's name, title, publication year, etc. The PhD Scholar may be required to provide supplementary materials that aren't essential to the PhD Thesis in the form of appendices.
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
What is the Length of the PhDThesis/Dissertation?
The length of the PhD Thesis (or dissertation) greatly depends on the field of the study. Generally, the length of the PhD Thesis ranges between 60,000 to 1,20,000 words which can curated in 150 pages to 300 pages. The average length of the PhD Thesis is around 80,000 words.In general, the length of the PhD Thesis in Engineering and Sciences is shorter than that of Humanities and Social Sciences.
The average length of a PhD Thesis in different disciplines is explained in the table below:
How to Write Up PhD Thesis
Once all the research related to the relevant topics and subjects has been conducted and all the data and results are collected, you can start with your PhD Thesis Writing.
This period is also known as the Writing Up period. The writing-up stage in a PhD Thesis starts when the original research has already been completed.
In this stage, you only focus on the PhD Thesis Writing and do not conduct any additional research.
In research related to Humanities and Social sciences, you may already have a large amount of chapter drafts and papers which makes writing up easy. You only need to redraft and assemble these chapter drafts and research papers to formulate a PhD Thesis.
However, writing a PhD Thesis for a Science and Engineering subject may be different. If you are conducting research in these fields, a major part of your research depends on collecting and analyzing data.
Writing Up a PhD Thesis in Science and Engineering fields may require findings and conclusions from the data collected.
Regardless of the subject and process of PhD Thesis Writing, it should be able to reflect your findings which can be applied in the particular discipline to enhance knowledge.
Role of PhD Thesis Feedback
Feedback from the supervisor while writing the PhD Thesis plays a crucial role. It helps in formulating a well-organized and highly structured PhD Thesis. You must seek constant feedback from your supervisor on your chapter drafts while writing the PhD Thesis.
When the thesis writing is in progress, comments and feedback from the supervisor who has significant research experience will ensure that the research is going in the right direction. You must regularly attend the supervisory meeting and present your chapter drafts for review.
Your PhD supervisor will be more than happy to help and guide you through your PhD Thesis Writing. However, PhD supervisor is not responsible for grammatical mistakes. You must ensure that your thesis is free from grammatical errors.
Levels of Plagiarism in PhD Thesis
While writing the PhD Thesis, you must ensure that your thesis is free from plagiarism. The PhD Thesis must contain your original research and not be copied from anywhere. Plagiarism in a PhD Thesis is considered a serious academic offense and can lead to severe consequences.
If you are giving references to works from other authors, you must give proper citations. Paraphrasing and rephrasing of other’s work must be duly acknowledged. In PhD Thesis Writing, plagiarism is defined on various levels.
Here are the different levels of plagiarism in PhD Thesis Writing:
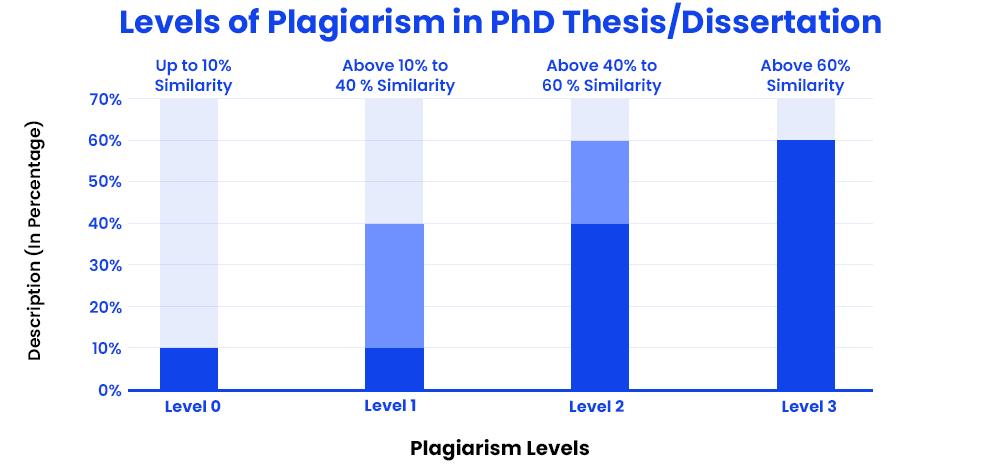
Penalty for Plagiarism in PhD Thesis/Dissertation
The University Grants Commission (UGC) takes plagiarism very seriously and sets the penalty standards for different levels of plagiarism.
Here is the punishment for Plagiarism in the PhD Thesis:
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Finishing PhD Thesis and Final Submission
Once you are done with the final draft of the PhD Thesis, you will need to send it to your supervisor. The supervisor will go through the thesis and after reviewing it, approve it for final submission.
Once your supervisor has approved you thesis, submit it for the examination. The Departmental Research Committee (DRC) will examine the PhD Thesis and you will have to appear for the Grand PhD Viva. In this Viva, you will need to defend your research findings and conclusions in the PhD Thesis.
PhD Thesis submission is done in physical form and you will have to take a printout of the thesis. You should always take multiple printouts of the thesis to avoid any printing mistakes and glitches. At the time of final submission, generally, multiple copies of the thesis are required which makes it more important.
PhD Viva is conducted within 3 months of thesis submission. Once the viva has been completed, the examiners will let you know whether or not you need to make any changes to your PhD Thesis.
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
These could be 3 outcomes after thesis submission and viva. All are mentioned below:
|
|
|
|
| You will receive your Doctorate. |
|
| Usually, these are just minor adjustments, modifications, and enhancements to your thesis, and you will have three months to put them into practice. |
|
| You might need to rewrite a portion of your dissertation or conduct additional research to make these significant modifications, and you have a six-month deadline. |
If you asked for a correction, you will have to fix the errors and re-submit the PhD thesis again. The re-submission of PhD is usually done digitally.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
⭐ what is a phd thesis.
A PhD Thesis is a well-structured and well-organized piece of original research that every PhD scholar has to prepare and submit to get their doctorate.
⭐ Is PhD Viva mandatory after the final submission of the PhD Thesis?
Yes, PhD Viva is mandatory for every PhD Candidate once they have made the final submission of their thesis. In PhD Viva, candidates defend their research and findings before the departmental research committee.
⭐ What is the ideal length of a PhD Thesis?
There is no ideal length for a PhD Thesis. However, the length of the PhD thesis is greatly influenced by the disciplines of the research. The length of PhD in Engineering and Sciences is comparatively less than that of PhD in Humanities and Social Sciences. The PhD thesis ranges between 60,000 words to 1,20,000 words.
⭐ What percentage of Plagiarism is allowed for a PhD Thesis?
The University Grants Commission (UGC) allows a maximum of 10 percent plagiarism in the PhD Thesis. The candidates whose thesis plagiarism falls within 10% are not penalized.
⭐ What is the penalty for Level 2 Plagiarism?
Level 2 plagiarism means that the PhD Thesis has a similarity above 40% to 60%. For this level of plagiarism, the PhD candidate will be asked to withdraw the manuscript and debarred from the annual increment for one year. The supervisor of such PhD scholar will also be penalized with a ban on any PhD supervision for 2 years.
⭐ What is the Penalty for Level 3 Plagiarism?
Level 3 plagiarism exhibits a similarity above 60% in the PhD Thesis. The PhD Scholars will be asked to withdraw their manuscript and they will be prohibited to annual increments for 2 consecutive years. The supervisor will not be allowed to supervise any new Master’s and PhD Thesis/dissertation for 3 consecutive years.
By Muhammad Hasim Sheikh
10 Years of Experience / Storyteller / Research-driven Writer
As an Academic Content Writer and Content strategist, I have great experience in crafting high-quality, research-based content across diverse subjects. My academic background with a doctorate in business Management allows me to create informative and engaging academic materials for students, educators, and institutions. I have expertise in developing well-researched course materials, academic blog
Every query is essential.
Our team of experts, or experienced individuals, will answer it within 24 hours.
Recommended for you
Tired of dealing with call centers!
Get a professional advisor for Career!
LIFETIME FREE
Rs.1499 (Exclusive offer for today)

MBA 7 yrs exp

M.Com 4 yrs exp

Kapil Gupta
MCA 5 yrs exp

How to Write a Research Proposal: A Complete Guide
.webp)
A research proposal is a piece of writing that basically serves as your plan for a research project. It spells out what you’ll study, how you’ll go about it, and why it matters. Think of it as your pitch to show professors or funding bodies that your project is worth their attention and support.
This task is standard for grad students, especially those in research-intensive fields. It’s your chance to showcase your ability to think critically, design a solid study, and articulate why your research could make a difference.
In this article, we'll talk about how to craft a good research proposal, covering everything from the standard format of a research proposal to the specific details you'll need to include.
Feeling overwhelmed by the idea of putting one together? That’s where DoMyEssay comes in handy. Whether you need a little push or more extensive guidance, we’ll help you nail your proposal and move your project forward.
Research Proposal Format
When you're putting together a research proposal, think of it as setting up a roadmap for your project. You want it to be clear and easy to follow so everyone knows what you’re planning to do, how you’re going to do it, and why it matters.
Whether you’re following APA or Chicago style, the key is to keep your formatting clean so that it’s easy for committees or funding bodies to read through and understand.
Here’s a breakdown of each section, with a special focus on formatting a research proposal:
- Title Page : This is your first impression. Make sure it includes the title of your research proposal, your name, and your affiliations. Your title should grab attention and make it clear what your research is about.
- Abstract : This is your elevator pitch. In about 250 words, you need to sum up what you plan to research, how you plan to do it, and what impact you think it will have.
- Introduction : Here’s where you draw them in. Lay out your research question or problem, highlight its importance, and clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your study.
- Literature Review : Show that you’ve done your homework. In this section, demonstrate that you know the field and how your research fits into it. It’s your chance to connect your ideas to what’s already out there and show off a bit about what makes your approach unique or necessary.
- Methodology : Dive into the details of how you’ll get your research done. Explain your methods for gathering data and how you’ll analyze it. This is where you reassure them that your project is doable and you’ve thought through all the steps.
- Timeline : Keep it realistic. Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into manageable stages and assigning a timeline for each phase.
- Budget : If you need funding, lay out a budget that spells out what you need money for. Be clear and precise so there’s no guesswork involved about what you’re asking for.
- References/Bibliography : List out all the works you cited in your proposal. Stick to one citation style to keep things consistent.
Get Your Research Proposal Right
Let our experts guide you through crafting a research proposal that stands out. From idea to submission, we've got you covered.

Research Proposal Structure
When you're writing a research proposal, you're laying out your questions and explaining the path you're planning to take to tackle them. Here’s how to structure your proposal so that it speaks to why your research matters and should get some attention.
Introduction
An introduction is where you grab attention and make everyone see why what you're doing matters. Here, you’ll pose the big question of your research proposal topic and show off the potential of your research right from the get-go:
- Grab attention : Start with something that makes the reader sit up — maybe a surprising fact, a challenging question, or a brief anecdote that highlights the urgency of your topic.
- Set the scene : What’s the broader context of your work? Give a snapshot of the landscape and zoom in on where your research fits. This helps readers see the big picture and the niche you’re filling.
- Lay out your plan : Briefly mention the main goals or questions of your research. If you have a hypothesis, state it clearly here.
- Make it matter : Show why your research needs to happen now. What gaps are you filling? What changes could your findings inspire? Make sure the reader understands the impact and significance of your work.
Literature Review
In your research proposal, the literature review does more than just recap what’s already out there. It's where you get to show off how your research connects with the big ideas and ongoing debates in your field. Here’s how to make this section work hard for you:
- Connect the dots : First up, highlight how your study fits into the current landscape by listing what others have done and positioning your research within it. You want to make it clear that you’re not just following the crowd but actually engaging with and contributing to real conversations.
- Critique what’s out there : Explore what others have done well and where they’ve fallen short. Pointing out the gaps or where others might have missed the mark helps set up why your research is needed and how it offers something different.
- Build on what’s known : Explain how your research will use, challenge, or advance the existing knowledge. Are you closing a key gap? Applying old ideas in new ways? Make it clear how your work is going to add something new or push existing boundaries.
Aims and Objectives
Let's talk about the aims and objectives of your research. This is where you set out what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there:
- Main Goal : Start by stating your primary aim. What big question are you trying to answer, or what hypothesis are you testing? This is your research's main driving force.
- Detailed Objectives : Now, break down your main goal into smaller, actionable objectives. These should be clear and specific steps that will help you reach your overall aim. Think of these as the building blocks of your research, each one designed to contribute to the larger goal.
Research Design and Method
This part of your proposal outlines the practical steps you’ll take to answer your research questions:
- Type of Research : First off, what kind of research are you conducting? Will it be qualitative or quantitative research , or perhaps a mix of both? Clearly define whether you'll be gathering numerical data for statistical analysis or exploring patterns and theories in depth.
- Research Approach : Specify whether your approach is experimental, correlational, or descriptive. Each of these frameworks has its own way of uncovering insights, so choose the one that best fits the questions you’re trying to answer.
- Data Collection : Discuss the specifics of your data. If you’re in the social sciences, for instance, describe who or what you’ll be studying. How will you select your subjects or sources? What criteria will you use, and how will you gather your data? Be clear about the methods you’ll use, whether that’s surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments.
- Tools and Techniques : Detail the tools and techniques you'll use to collect your data. Explain why these tools are the best fit for your research goals.
- Timeline and Budget : Sketch out a timeline for your research activities. How long will each phase take? This helps everyone see that your project is organized and feasible.
- Potential Challenges : What might go wrong? Think about potential obstacles and how you plan to handle them. This shows you’re thinking ahead and preparing for all possibilities.
Ethical Considerations
When you're conducting research, especially involving people, you've got to think about ethics. This is all about ensuring everyone's rights are respected throughout your study. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Participant Rights : You need to protect your participants' rights to privacy, autonomy, and confidentiality. This means they should know what the study involves and agree to participate willingly—this is what we call informed consent.
- Informed Consent : You've got to be clear with participants about what they’re signing up for, what you’ll do with the data, and how you'll keep it confidential. Plus, they need the freedom to drop out any time they want.
- Ethical Approval : Before you even start collecting data, your research plan needs a green light from an ethics committee. This group checks that you’re set up to keep your participants safe and treated fairly.
You need to carefully calculate the costs for every aspect of your project. Make sure to include a bit extra for those just-in-case scenarios like unexpected delays or price hikes. Every dollar should have a clear purpose, so justify each part of your budget to ensure it’s all above board. This approach keeps your project on track financially and avoids any surprises down the line.
The appendices in your research proposal are where you stash all the extra documents that back up your main points. Depending on your project, this could include things like consent forms, questionnaires, measurement tools, or even a simple explanation of your study for participants.
Just like any academic paper, your research proposal needs to include citations for all the sources you’ve referenced. Whether you call it a references list or a bibliography, the idea is the same — crediting the work that has informed your research. Make sure every source you’ve cited is listed properly, keeping everything consistent and easy to follow.
Research Proposal Got You Stuck?
Get expert help with your literature review, ensuring your research is grounded in solid scholarship.

How to Write a Research Proposal?
Whether you're new to this process or looking to refine your skills, here are some practical tips to help you create a strong and compelling proposal.
| Tip | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Stay on Target 🎯 | Stick to the main points and avoid getting sidetracked. A focused proposal is easier to follow and more compelling. |
| Use Visuals 🖼️ | Consider adding charts, graphs, or tables if they help explain your ideas better. Visuals can make complex info clearer. |
| Embrace Feedback 🔄 | Be open to revising your proposal based on feedback. The best proposals often go through several drafts. |
| Prepare Your Pitch 🎤 | If you’re going to present your proposal, practice explaining it clearly and confidently. Being able to pitch it well can make a big difference. |
| Anticipate Questions ❓ | Think about the questions or challenges reviewers might have and prepare clear responses. |
| Think Bigger 🌍 | Consider how your research could impact your field or even broader society. This can make your proposal more persuasive. |
| Use Strong Sources 📚 | Always use credible and up-to-date sources. This strengthens your arguments and builds trust with your readers. |
| Keep It Professional ✏️ | While clarity is key, make sure your tone stays professional throughout your proposal. |
| Highlight What’s New 💡 | Emphasize what’s innovative or unique about your research. This can be a big selling point for your proposal. |
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a simple and handy research proposal example in PDF format to help you get started and keep your work organized:
Writing a research proposal can be straightforward if you break it down into manageable steps:
- Pick a strong research proposal topic that interests you and has enough material to explore.
- Craft an engaging introduction that clearly states your research question and objectives.
- Do a thorough literature review to see how your work fits into the existing research landscape.
- Plan out your research design and method , deciding whether you’ll use qualitative or quantitative research.
- Consider the ethical aspects to ensure your research is conducted responsibly.
- Set up a budget and gather any necessary appendices to support your proposal.
- Make sure all your sources are cited properly to add credibility to your work.
If you need some extra support, DoMyEssay is ready to help with any type of paper, including crafting a strong research proposal.
What Is a Research Proposal?
How long should a research proposal be, how do you start writing a research proposal.
Examples of Research proposals | York St John University. (n.d.). York St John University. https://www.yorksj.ac.uk/study/postgraduate/research-degrees/apply/examples-of-research-proposals/
.webp)

How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
We Trust in Human Precision
20,000+ Professional Language Experts Ready to Help. Expertise in a variety of Niches.
API Solutions
- API Pricing
- Cost estimate
- Customer loyalty program
- Educational Discount
- Non-Profit Discount
- Green Initiative Discount1
Value-Driven Pricing
Unmatched expertise at affordable rates tailored for your needs. Our services empower you to boost your productivity.
- Special Discounts
- Enterprise transcription solutions
- Enterprise translation solutions
- Transcription/Caption API
- AI Transcription Proofreading API
Trusted by Global Leaders
GoTranscript is the chosen service for top media organizations, universities, and Fortune 50 companies.
GoTranscript
One of the Largest Online Transcription and Translation Agencies in the World. Founded in 2005.
Speaker 1: Thanks for watching. Hello, my name is Dr Derek Watson from the University of Sunderland and I've come along here today to talk to you about dissertations or how to successfully complete a dissertation for your undergraduate or postgraduate degree. So what I'm going to be doing is, I'm going to be sharing with you some techniques on how to successfully complete your thesis. First of all, we'll start off with the title. The title of a thesis or your research area is instrumental in two ways. One, you've got to pass your degree, a postgraduate degree and secondly, you've got to create a gateway to employability. So what I'm about to say today is possibly going to shock you or surprise you. Most students will pick a topic of interest to themselves and they pass. But then when they start applying for a career, a credible career, they find that they struggle in the interview. So what I'm suggesting is, pick a topic that will appeal to organisations, almost any type of organisation. So a key area that you might want to think about is potentially quality. It affects all organisations. Or how do we motivate staff without paying them extra? How do you motivate staff through non-monetary mechanisms? But try to pick a topic whereby once you've completed your qualification, you can actually use it. And what I mean by using it is taking your thesis along to an interview and presenting that to the panel so they can see your theme, your topic, your contribution and also the professional structure of what you're capable of doing. So bear that in mind. So after the title, abstract. Abstracts, I would suggest that you leave it till the end. It's the last section that you feed in. Although it's at the beginning of the structure. And it's a bit like going to the movies. You will see clips of future movies to whet your appetite to come along to watch them at a later date. Your abstract has to be concise. It's got to summarise your research contribution. But it's got to be motivating. It's got to inspire the reader, particularly your first marker, your second marker and also your external examiner. And it should be a paragraph, approximately 150 words, rather like the abstracts for journal papers. Next section. Introduction. Introduction has to be very concise. Why are you writing the thesis? What is the purpose of your research? And more importantly, what is the aim and your objectives for researching that particular area? And bear in mind, a future employer may want to read your thesis. Hence the importance of your title. After your introduction, what you have is your literature. Your literature review. Now once again, from experience, and I've read many theses, many dissertations, students tend to, because they've got such easy access to the internet and electronic journals and also through university internal intranets, there's potentially too much information out there. So what I see in many submissions that I haven't supervised is whereby students simply shotgun the information into the literature review. And the literature review has to be concise. You have to justify what are the key things in the literature. So what I recommend students do is create diagrams throughout your thesis. And once again, this will help signpost your assessors and the external examiner on what your thought process is. So the literature review, you'll create a diagram. You will have your question in the middle. And this will be figure one. And what you will do is, from reading the journal papers, your first journal paper, what you'll do, you'll add key themes on that. Then when you come to read your second journal paper, use a different pen. And then, if you come across additional subject areas, you can add to them. However, hopefully, you will be duplicating current themes. And as you build up this diagram, make sure you put your reference, your reference source, so the reader, the examiners, can identify, this is your diagram, this is your question, these are the key themes relevant. And you've duplicated it because you've been reading various journals. And you've identified that these are the key themes. And they're referenced. So what you will then do in your literature review, you will talk about these themes and how they are connected. They're not in isolation. How they are connected in a logical structure within that. Next section is your methodology. Your methodology. And if you can imagine your methodology, which sometimes students struggle with, many students submit theses or dissertations with a weak methodology section and lose marks. So it's critical that your methodology justifies the tools in which you're using. So think about a plumber. A plumber receives a call to go around to a property to fix a leaky pipe or a leaky radiator. The plumber will attend with a box of tools. They are your research tools. The plumber then looks at the problem and decides which tools they are going to use. And it's very similar to your research methodology. You will have to justify your approach. You will have to justify why you are selecting specific tools to answer your research question. In addition to your methodology, you need to think about how we're going to test. This is what we've read about in the literature. This is what the literature says. But what does the commercial environment say? So what we need is gateways to try and collect data. So, for example, questionnaires, interviews, focus groups. And this is one technique that you need to adopt, which will enhance your overall grade. Having looked at your literature review, which have identified key themes, you will then develop a set of questions. And this is what students don't do. Most students don't do. And they're missing out on marks. What they need to do, they need to develop a table. And on the left-hand side, you will write your questions. Questions 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, up to 15, 20 questions. Now, these can be open-ended or closed questions. However, these questions have to be linked to your literature review. And many students simply pluck questions out of the air, construct a questionnaire, ship it off to an organisation. But when they come to submit the paper, the thesis, comments come back. Lack of linkage to the literature review. How have you justified these questions? So what I'm proposing is, you list the questions on the left-hand column. On the right-hand column, you justify why you've selected that question. But you also reference it to a reference source which is identifiable in your literature review. There you have the linkage. That's what many students don't do. So let me just repeat that. You justify the tools that you're going to use. You then, having reflected on your literature review, you extract questions. Those questions go into a table. On the right-hand side, you justify a sentence or two sentences. Why have you selected those questions? And you make a reference that you've specifically referenced from your literature review. You have the linkage. Next section. Findings. Or data analysis. Or discussion. Or a combination of all three. But your title is relevant to employability. You've got your introduction, concise, which has identified your introduction, your aims, your objectives. Your literature review has been justified as in figure one. You've got the structure. And you know you're talking about the key areas because you've superimposed different journal papers. And you've identified the relevant areas. From that, you develop questions, which has been identified in your methodology, via the table. Now your findings section. Your findings section is very important. Because it will identify themes. And what many students do is they distribute a questionnaire. They get the responses back from the organisation. And then their findings section is nothing better than a regurgitation of that data. For example, question one responses were, and students do a nice pie chart. 70% of the responses said this. 30% of the responses said X, or the opposite. And they systematically go through each question. A cure for insomnia. And also a mechanism not to demonstrate your analysis. So this is what I suggest. You look at the feedback from the question. And what you've got is you've got various responses. What I suggest that you do. You identify themes. So, for example, theme one could consist of answers one, three, five and six. Theme two, you've clustered the responses into two, four, eleven and fifteen and so on. And what this shows the assessors is that you have the ability to look at raw data and cluster it into key themes. So what you'll do is you'll create a diagram. Or better still, you'll have a diagram where you've got your table. You've got the raw responses. And then you have clustered them into key themes. And when you come to write it up, you've got specific sections or specific paragraphs. Addressing each of these themes going through your finding section. However, what students also fail to do. They will talk about the findings, but they will not link it to the literature review. So what you've got to do as you're working through each of these sections systematically through your finding section. You need to make reference to your literature review. You're not repeating your literature review. But what you're doing is, for example, theme one. The data supports the commentary of. And you link it back to a researcher which you've referenced in your literature review. Theme two, maybe. The data is very interesting. This further supports or casts doubt or raises a question mark about what's being said in the literature. You are demonstrating that you have the ability of analysis and application within that. The next section. Your conclusion section. A bit like a court case where the judge summarises. What are the general findings of the research? What did you find? And what are those implications for an organisation or particular market or service sector? A key area which is also neglected is the recommendation section. Quite often, I will look at theses as an external and I will say, at best, a paragraph. Now, really, to a certain extent, as academics, we know the literature. We know the different types of methodology. We don't know how you can structure the theming. So if you can do that, you're going to get extra marks. Yes, you can demonstrate your ability to summarise in a conclusion, which should be approximately half a page. But then comes the recommendations. And this is the key part of your contribution. It's your thumbprint. It's what you can contribute to the bedrock of knowledge or your community of practice within that. So, recommendations. Recommendations. And what I'm going to do is I'm going to show you a technique to make sure you can't just submit a paragraph. So going back to the diagram of themes. So this could be, if we've got figure one there, this would be figure two. What you would create in here, in your recommendations, is a diagram. And what you would do, you would have theme one, two, three, theme four. They're your issues that you've identified in your findings that are linked to your recommendations. Your recommendations are, well, so what? You've identified the problems. What are you going to recommend? What are your commercial, viable recommendations that you can present to the organisation or to the market sector? So this is what I suggest students do. You create another diagram. You've got your themes there. You create an organisational structure. With STO. S stands for Strategic. T stands for Tactical. O stands for Operational. So what I'm doing is I'm creating a diagram where you've identified the themes. We've got the organisational structure. Strategic, Senior Management. Tactical, Middle Management. Operational, Frontline Staff. On the front line of the organisation. So what we have to do. Theme one. What are our recommendations? What are we going to recommend at a strategic level to resolve this problem? What are we going to resolve or recommend at a tactical and at an operational? Now the reason I'm structuring it like that is any recommendation has to be brought in by the organisation. You've got to get the support from senior management, strategic. You've got to get support from middle management, the tactical. And you've got to get support from the frontline troops interacting on the frontline. What are you going to recommend there? Theme two. What are you going to recommend at a strategic, tactical, operational? Theme three. What are you going to recommend at a strategic, tactical, operational? And last theme. Strategic, tactical, operational. Now your recommendations need to start off by stating. You will be structuring your recommendations under three distinct headings. Strategic, tactical, operational. And justify why you're doing that. You need to do that to get the full commitment of the organisation to buy into your solutions. If you just go for senior management. What about middle management? And the operatives, frontline staff. Everyone needs to be on the same page with the solutions. So what you'll then do is, systematically, you'll have a paragraph or two paragraphs on strategic challenges. Recommendations. Tactical recommendations. And operational recommendations within that. Now, what I do recommend that you do is, in addition, which isn't always asked for, is what we call an action sheet. Meaning, you've done your literature review. You've justified your methodology with your questions linked to your literature review. You've gone through your findings section. You've clustered the key themes together. You've summarised it. You've come up with commercially viable, saleable recommendations. And this is what a future employee will look at. This is what they'll home in on. Has this student or potential candidates got the ability, not just to identify problems, but to structure solutions? But you're going to go the extra nine yards. What you're going to do is, you're going to produce an action sheet. One page, electronic. And what it has is, it's got the issue. And these are the issues that need to be addressed. You've also got person responsible. You've got to give someone the responsibility. You've got the resources required. You've got the cost. And you've also got the time frame. So many theses, dissertations, include recommendations. Although I've said very short recommendations. This avoids it. You've got three distinct sections within your recommendations. So your recommendations should be running approximately two, possibly three pages in length. And then, what you will do, you will have your themes. One, two, three, four. There might be more than four themes. There might be five, six. I wouldn't go above more than six because it would be too bulky. Person responsible. So who do we choose? You're not going to lose marks by identifying somebody in the organisation. Whereby, the ultimate organisation might say, well, that's not specifically for that person. What the examiners and the assessors want to know is, have you identified, say, someone in the, for example, the HR manager? And with regards to, if we run and keep the theme on the HR manager, the resource might be training. One of your recommendations must probably be training or repeat training. It will be, well, if everyone needs to be trained, what, how much is that going to cost? Once again, you're not going to lose marks if you don't get the exact cost right. What the examiners want to see is, have you thought about the cost? So, for example, a member of staff might work out £100 to be trained if you've got a cohort of 15. So what you would do is, you would guesstimate the likely cost. This section here, timeframe, would be short-term, medium-term, long-term. And what I mean by long-term, 12 months. This action sheet involves a 12-month scenario. So short-term could be 1 to 3 months. Medium-term could be 3 to 6 months. Long-term could be 6 months to 12 months. But make sure that you include that. And when that's completed, you can go back and say, right, that's my action sheet, that's the sheet of paper, I could go in on Monday morning and give the organisation. Those themes are linked to these recommendations, which are linked to these themes, which were extracted or clustered in your filing section from your methodology, which you have justified in the table. Your literature review is being justified because it's systematic and you've duplicated, you know these are the common themes from the journal papers which you've read and you've documented. There you can put in your abstract now. You can summarise what was your area of research, what was important about it, what did you contribute within that, in your abstract. So don't forget, your literature review links to your methodology. Your findings section links back to your literature review. Because when you're talking about the themes, you're making reference, you're not rewriting your literature review, you're making reference to your literature review there, just in reference only. Your conclusion links to your findings. Your recommendations link to your findings. And your recommendations are developed into an action sheet within that. And there you have a structured dissertation that links, that demonstrates your analysis, your synthesis, your application of viable commercial recommendations, and the extra bit is your action sheet. One page, 12 months advice, what you would recommend to the organisation to help eradicate these problems. And if you do that, you should pass your dissertation and it should give you a good crack at getting your first job interview. Thank you very much.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Check the requirements. Step 2: Choose a broad field of research. Step 3: Look for books and articles. Step 4: Find a niche. Step 5: Consider the type of research. Step 6: Determine the relevance. Step 7: Make sure it's plausible. Step 8: Get your topic approved. Other interesting articles.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps. Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is. Find a unique and valuable research topic. Craft a convincing research proposal. Write up a strong introduction chapter. Review the existing literature and compile a literature review.
Go check that out if you want to write a dissertation on the 'education' topic. 7. Trust your Dissertation Supervisor. Your dissertation supervisor will have walked many students just like you through the research process before. Look, I know many dissertation supervisors can be disappointingly aloof and disconnected from your research.
Step 5: Narrow down, then evaluate. By this stage, you should have a healthy list of research topics. Step away from the ideation and thinking for a few days, clear your mind. The key is to get some distance from your ideas, so that you can sit down with your list and review it with a more objective view.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
To recap, the "Big 5" assessment criteria include: Topic originality and novelty. Value and significance. Access to data and equipment. Time requirements. Ethical compliance. Be sure to grab a copy of our free research topic evaluator sheet here to fast-track your topic selection process.
Content: Depending on the level of your studies, you will be required to come up with a topic for your thesis by yourself or to choose from a list of broad topics. In either case, you will need to: Choose a specific scope. Narrow it down as much as you can. Organize your papers in one place.
An important key to choosing a dissertation topic that is both feasible and engaging is to understand that a topic isn't so much an idea as a question. The goal of your dissertation isn't to create a scholarly work about existing knowledge, it is to answer a question that is timely and relevant. Keep this in mind as you work through the ...
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
Set realistic goals: Ensure the scope of your topic matches the time and word count limits for your dissertation. Too broad or too narrow can lead to significant problems later. 5. Get feedback. Once you've got a few ideas, talk them over with your advisor and peers.
A dissertation is a lengthy research paper written as a requirement to earn an academic degree. Typically, students must write a dissertation toward the end of their program to both prove their knowledge and contribute new research to their field. The term dissertation is sometimes used interchangeably with thesis paper.
How to Write a Dissertation. Here are some general steps to help guide you through the process of writing a dissertation: Choose a topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about and that is relevant to your field of study. It should be specific enough to allow for in-depth research but broad enough to be interesting and engaging.
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter). The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes: An introduction to your topic. A literature review that surveys relevant sources.
Find a niche: Look for a specific area where you can add value or a new perspective. The ideal topic will build on existing work while offering something original. Evaluate the Feasibility of Your Topic: Resources: Determine what resources, including equipment, funding, and time, you will need to complete the research.
Place a blank sheet in landscape position and write the topic you have in mind in the middle. Draw branches from the centre, The branches are possible ideas and topics to include in the dissertation. Add sub-topics ("leaves") and connect ideas and evidence from your reading. You can use colours and images to stimulate your thinking.
A dissertation proposal should include: An introduction to your dissertation topic. Aims and objectives of your dissertation. A literature review of the current research undertaken in your field. Proposed methodology to be used. Implications of your research. Limitations of your research.
Writing a masters dissertation or thesis is a sizable task. It takes a considerable amount of research, studying and writing. Usually, students need to write around 10,000 to 15,000 words. It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at ...
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough. Note.
A research topic is the subject of a research project or study - for example, a dissertation or thesis. A research topic typically takes the form of a problem to be solved, or a question to be answered. A good research topic should be specific enough to allow for focused research and analysis. For example, if you are interested in studying ...
A doctoral degree is a common path if you want to pursue your academic interests in a rigorous and research-oriented program. Many doctoral programs consist of several years of classes and one or more years of research, culminating in the defense of your dissertation. If you're wondering what a dissertation is or how to choose a direction for such a lofty endeavor, you've come to the right ...
that the dissertation or thesis approval forms may be properly prepared to match your title page. • The table of contents and the lists of tables of figures do not match what is actually in text. You must make a systematic check of each of these pages against the text to be certain that titles and page numbers are inexact match. •
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic. The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development ...
This will help you develop a focused research question or a strong thesis statement that will guide the rest of your research and writing process. See also Writing . Developing a Research Plan; Determine what types of sources are most appropriate for your topic. This might include books, peer-reviewed journal articles, interviews, or primary ...
Step 2: Choose a broad field of research. Step 3: Look for books and articles. Step 4: Find a niche. Step 5: Consider the type of research. Step 6: Determine the relevance. Step 7: Make sure it's plausible. Step 8: Get your topic approved. Frequently asked questions.
An outline is a tool to organize written ideas about a topic or thesis logically. Outlines arrange major topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Writers use outlines when writing their papers to know which topic to cover in what order. Outlines for papers can be very general or very detailed.
How to Write Up PhD Thesis . Once all the research related to the relevant topics and subjects has been conducted and all the data and results are collected, you can start with your PhD Thesis Writing. This period is also known as the Writing Up period. The writing-up stage in a PhD Thesis starts when the original research has already been ...
To Sum Up. Writing a research proposal can be straightforward if you break it down into manageable steps: Pick a strong research proposal topic that interests you and has enough material to explore.; Craft an engaging introduction that clearly states your research question and objectives.; Do a thorough literature review to see how your work fits into the existing research landscape.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
Learn how to craft a dissertation that not only helps you pass your degree but also boosts your employability. Dr. Derek Watson from the University of Sunderland shares key strategies on selecting the right topic, writing an impactful abstract, conducting a thorough literature review, and more. Perfect for undergraduate and postgraduate students.
This AI tool helps you read faster and write better. You can quickly find information in documents, simplify complex topics, take notes, and write with the power of AI. Thousands of researchers and students trust Unriddle. It generates an AI assistant on top of any document so you can quickly find and summarize information.