Albert Einstein
One of the most influential scientists of the 20 th century, Albert Einstein was a physicist who developed the theory of relativity.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.

Who Was Albert Einstein?
Quick facts, early life, family, and education, einstein’s iq, patent clerk, inventions and discoveries, nobel prize in physics, wives and children, travel diaries, becoming a u.s. citizen, einstein and the atomic bomb, time travel and quantum theory, personal life, death and final words, einstein’s brain, einstein in books and movies: "oppenheimer" and more.
Albert Einstein was a German mathematician and physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. In the following decade, he immigrated to the United States after being targeted by the German Nazi Party. His work also had a major impact on the development of atomic energy. In his later years, Einstein focused on unified field theory. He died in April 1955 at age 76. With his passion for inquiry, Einstein is generally considered the most influential physicist of the 20 th century.
FULL NAME: Albert Einstein BORN: March 14, 1879 DIED: April 18, 1955 BIRTHPLACE: Ulm, Württemberg, Germany SPOUSES: Mileva Einstein-Maric (1903-1919) and Elsa Einstein (1919-1936) CHILDREN: Lieserl, Hans, and Eduard ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Pisces
Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany. He grew up in a secular Jewish family. His father, Hermann Einstein, was a salesman and engineer who, with his brother, founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a Munich-based company that mass-produced electrical equipment. Einstein’s mother, the former Pauline Koch, ran the family household. Einstein had one sister, Maja, born two years after him.
Einstein attended elementary school at the Luitpold Gymnasium in Munich. However, he felt alienated there and struggled with the institution’s rigid pedagogical style. He also had what were considered speech challenges. However, he developed a passion for classical music and playing the violin, which would stay with him into his later years. Most significantly, Einstein’s youth was marked by deep inquisitiveness and inquiry.
Toward the end of the 1880s, Max Talmud, a Polish medical student who sometimes dined with the Einstein family, became an informal tutor to young Einstein. Talmud had introduced his pupil to a children’s science text that inspired Einstein to dream about the nature of light. Thus, during his teens, Einstein penned what would be seen as his first major paper, “The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields.”
Hermann relocated the family to Milan, Italy, in the mid-1890s after his business lost out on a major contract. Einstein was left at a relative’s boarding house in Munich to complete his schooling at the Luitpold.
Faced with military duty when he turned of age, Einstein allegedly withdrew from classes, using a doctor’s note to excuse himself and claim nervous exhaustion. With their son rejoining them in Italy, his parents understood Einstein’s perspective but were concerned about his future prospects as a school dropout and draft dodger.
Einstein was eventually able to gain admission into the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, specifically due to his superb mathematics and physics scores on the entrance exam. He was still required to complete his pre-university education first and thus attended a high school in Aarau, Switzerland, helmed by Jost Winteler. Einstein lived with the schoolmaster’s family and fell in love with Winteler’s daughter Marie. Einstein later renounced his German citizenship and became a Swiss citizen at the dawn of the new century.
Einstein’s intelligence quotient was estimated to be around 160, but there are no indications he was ever actually tested.
Psychologist David Wechsler didn’t release the first edition of the WAIS cognitive test, which evolved into the WAIS-IV test commonly used today, until 1955—shortly before Einstein’s death. The maximum score of the current version is 160, with an IQ of 135 or higher ranking in the 99 th percentile.
Magazine columnist Marilyn vos Savant has the highest-ever recorded IQ at 228 and was featured in the Guinness Book of World Records in the late 1980s. However, Guinness discontinued the category because of debates about testing accuracy. According to Parade , individuals believed to have higher IQs than Einstein include Leonardo Da Vinci , Marie Curie , Nikola Tesla , and Nicolaus Copernicus .
After graduating from university, Einstein faced major challenges in terms of finding academic positions, having alienated some professors over not attending class more regularly in lieu of studying independently.
Einstein eventually found steady work in 1902 after receiving a referral for a clerk position in a Swiss patent office. While working at the patent office, Einstein had the time to further explore ideas that had taken hold during his university studies and thus cemented his theorems on what would be known as the principle of relativity.
In 1905—seen by many as a “miracle year” for the theorist—Einstein had four papers published in the Annalen der Physik , one of the best-known physics journals of the era. Two focused on the photoelectric effect and Brownian motion. The two others, which outlined E=MC 2 and the special theory of relativity, were defining for Einstein’s career and the course of the study of physics.
As a physicist, Einstein had many discoveries, but he is perhaps best known for his theory of relativity and the equation E=MC 2 , which foreshadowed the development of atomic power and the atomic bomb.
Theory of Relativity
Einstein first proposed a special theory of relativity in 1905 in his paper “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies,” which took physics in an electrifying new direction. The theory explains that space and time are actually connected, and Einstein called this joint structure space-time.
By November 1915, Einstein completed the general theory of relativity, which accounted for gravity’s relationship to space-time. Einstein considered this theory the culmination of his life research. He was convinced of the merits of general relativity because it allowed for a more accurate prediction of planetary orbits around the sun, which fell short in Isaac Newton ’s theory. It also offered a more expansive, nuanced explanation of how gravitational forces worked.
Einstein’s assertions were affirmed via observations and measurements by British astronomers Sir Frank Dyson and Sir Arthur Eddington during the 1919 solar eclipse, and thus a global science icon was born. Today, the theories of relativity underpin the accuracy of GPS technology, among other phenomena.
Even so, Einstein did make one mistake when developing his general theory, which naturally predicted the universe is either expanding or contracting. Einstein didn’t believe this prediction initially, instead holding onto the belief that the universe was a fixed, static entity. To account for, this he factored in a “cosmological constant” to his equation. His later theories directly contracted this idea and asserted that the universe could be in a state of flux. Then, astronomer Edwin Hubble deduced that we indeed inhabit an expanding universe. Hubble and Einstein met at the Mount Wilson Observatory near Los Angeles in 1931.
Decades after Einstein’s death, in 2018, a team of scientists confirmed one aspect of Einstein’s general theory of relativity: that the light from a star passing close to a black hole would be stretched to longer wavelengths by the overwhelming gravitational field. Tracking star S2, their measurements indicated that the star’s orbital velocity increased to over 25 million kph as it neared the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy, its appearance shifting from blue to red as its wavelengths stretched to escape the pull of gravity.
Einstein’s E=MC²
Einstein’s 1905 paper on the matter-energy relationship proposed the equation E=MC²: the energy of a body (E) is equal to the mass (M) of that body times the speed of light squared (C²). This equation suggested that tiny particles of matter could be converted into huge amounts of energy, a discovery that heralded atomic power.
Famed quantum theorist Max Planck backed up the assertions of Einstein, who thus became a star of the lecture circuit and academia, taking on various positions before becoming director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics (today is known as the Max Planck Institute for Physics) from 1917 to 1933.
In 1921, Einstein won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect, since his ideas on relativity were still considered questionable. He wasn’t actually given the award until the following year due to a bureaucratic ruling, and during his acceptance speech, he still opted to speak about relativity.
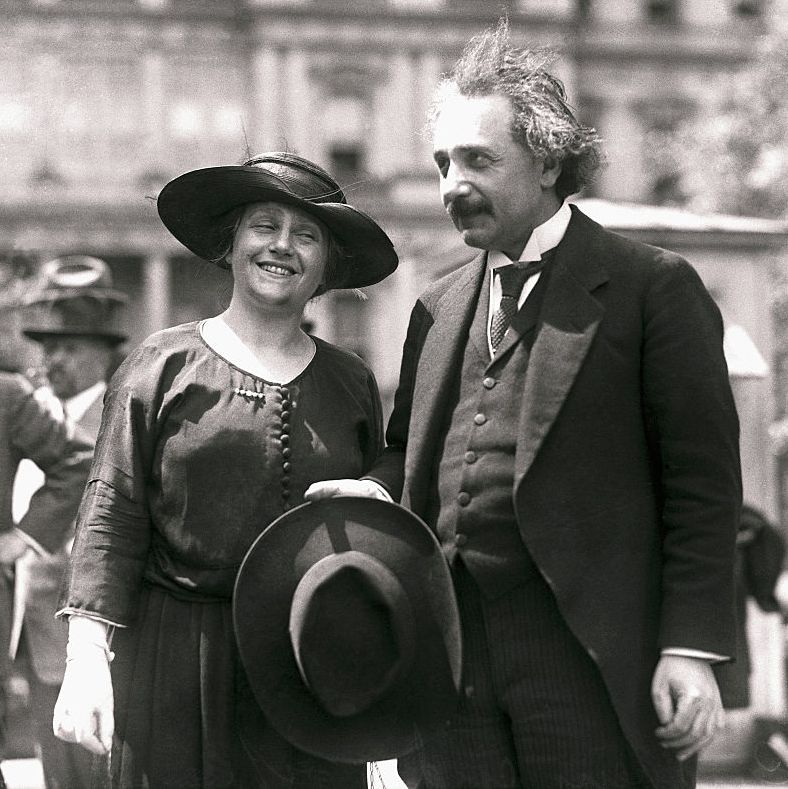

Einstein married Mileva Maric on January 6, 1903. While attending school in Zurich, Einstein met Maric, a Serbian physics student. Einstein continued to grow closer to Maric, but his parents were strongly against the relationship due to her ethnic background.
Nonetheless, Einstein continued to see her, with the two developing a correspondence via letters in which he expressed many of his scientific ideas. Einstein’s father passed away in 1902, and the couple married shortly thereafter.
Einstein and Mavic had three children. Their daughter, Lieserl, was born in 1902 before their wedding and might have been later raised by Maric’s relatives or given up for adoption. Her ultimate fate and whereabouts remain a mystery. The couple also had two sons: Hans Albert Einstein, who became a well-known hydraulic engineer, and Eduard “Tete” Einstein, who was diagnosed with schizophrenia as a young man.
The Einsteins’ marriage would not be a happy one, with the two divorcing in 1919 and Maric having an emotional breakdown in connection to the split. Einstein, as part of a settlement, agreed to give Maric any funds he might receive from possibly winning the Nobel Prize in the future.
During his marriage to Maric, Einstein had also begun an affair some time earlier with a cousin, Elsa Löwenthal . The couple wed in 1919, the same year of Einstein’s divorce. He would continue to see other women throughout his second marriage, which ended with Löwenthal’s death in 1936.
In his 40s, Einstein traveled extensively and journaled about his experiences. Some of his unfiltered private thoughts are shared two volumes of The Travel Diaries of Albert Einstein .
The first volume , published in 2018, focuses on his five-and-a-half month trip to the Far East, Palestine, and Spain. The scientist started a sea journey to Japan in Marseille, France, in autumn of 1922, accompanied by his second wife, Elsa. They journeyed through the Suez Canal, then to Sri Lanka, Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Japan. The couple returned to Germany via Palestine and Spain in March 1923.
The second volume , released in 2023, covers three months that he spent lecturing and traveling in Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil in 1925.
The Travel Diaries contain unflattering analyses of the people he came across, including the Chinese, Sri Lankans, and Argentinians, a surprise coming from a man known for vehemently denouncing racism in his later years. In an entry for November 1922, Einstein refers to residents of Hong Kong as “industrious, filthy, lethargic people.”
In 1933, Einstein took on a position at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, where he would spend the rest of his life.
At the time the Nazis, led by Adolf Hitler , were gaining prominence with violent propaganda and vitriol in an impoverished post-World War I Germany. The Nazi Party influenced other scientists to label Einstein’s work “Jewish physics.” Jewish citizens were barred from university work and other official jobs, and Einstein himself was targeted to be killed. Meanwhile, other European scientists also left regions threatened by Germany and immigrated to the United States, with concern over Nazi strategies to create an atomic weapon.
Not long after moving and beginning his career at IAS, Einstein expressed an appreciation for American meritocracy and the opportunities people had for free thought, a stark contrast to his own experiences coming of age. In 1935, Einstein was granted permanent residency in his adopted country and became an American citizen five years later.
In America, Einstein mostly devoted himself to working on a unified field theory, an all-embracing paradigm meant to unify the varied laws of physics. However, during World War II, he worked on Navy-based weapons systems and made big monetary donations to the military by auctioning off manuscripts worth millions.
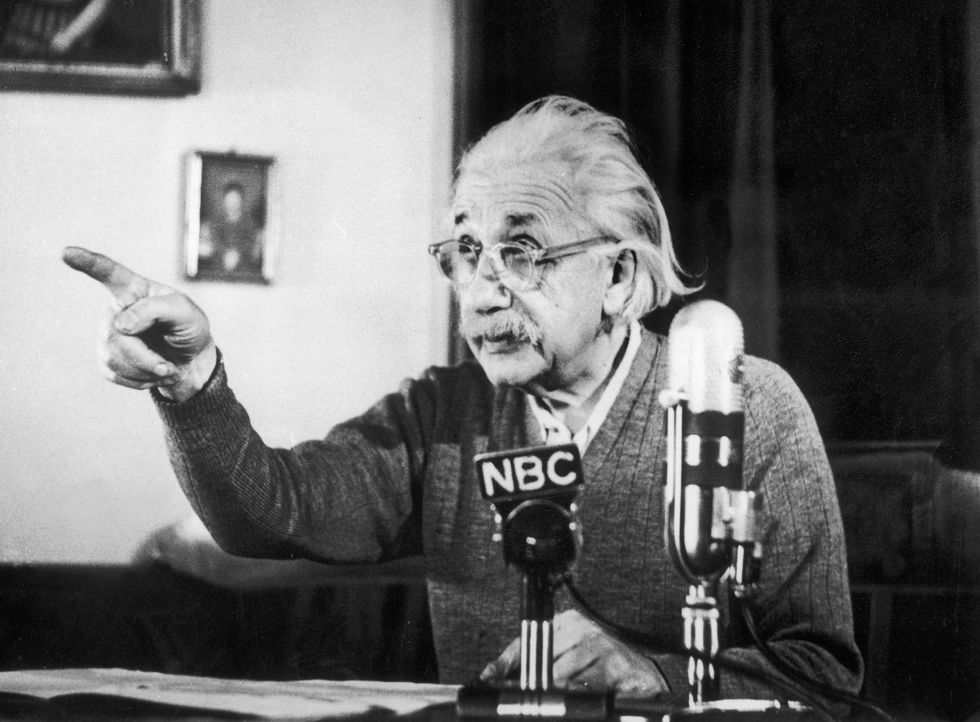

In 1939, Einstein and fellow physicist Leo Szilard wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt to alert him of the possibility of a Nazi bomb and to galvanize the United States to create its own nuclear weapons.
The United States would eventually initiate the Manhattan Project , though Einstein wouldn’t take a direct part in its implementation due to his pacifist and socialist affiliations. Einstein was also the recipient of much scrutiny and major distrust from FBI director J. Edgar Hoover . In July 1940, the U.S. Army Intelligence office denied Einstein a security clearance to participate in the project, meaning J. Robert Oppenheimer and the scientists working in Los Alamos were forbidden from consulting with him.
Einstein had no knowledge of the U.S. plan to use atomic bombs in Japan in 1945. When he heard of the first bombing at Hiroshima, he reportedly said, “Ach! The world is not ready for it.”
Einstein became a major player in efforts to curtail usage of the A-bomb. The following year, he and Szilard founded the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists, and in 1947, via an essay for The Atlantic Monthly , Einstein espoused working with the United Nations to maintain nuclear weapons as a deterrent to conflict.
After World War II, Einstein continued to work on his unified field theory and key aspects of his general theory of relativity, including time travel, wormholes, black holes, and the origins of the universe.
However, he felt isolated in his endeavors since the majority of his colleagues had begun focusing their attention on quantum theory. In the last decade of his life, Einstein, who had always seen himself as a loner, withdrew even further from any sort of spotlight, preferring to stay close to Princeton and immerse himself in processing ideas with colleagues.
In the late 1940s, Einstein became a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), seeing the parallels between the treatment of Jews in Germany and Black people in the United States. He corresponded with scholar and activist W.E.B. Du Bois as well as performer Paul Robeson and campaigned for civil rights, calling racism a “disease” in a 1946 Lincoln University speech.
Einstein was very particular about his sleep schedule, claiming he needed 10 hours of sleep per day to function well. His theory of relativity allegedly came to him in a dream about cows being electrocuted. He was also known to take regular naps. He is said to have held objects like a spoon or pencil in his hand while falling asleep. That way, he could wake up before hitting the second stage of sleep—a hypnagogic process believed to boost creativity and capture sleep-inspired ideas.
Although sleep was important to Einstein, socks were not. He was famous for refusing to wear them. According to a letter he wrote to future wife Elsa, he stopped wearing them because he was annoyed by his big toe pushing through the material and creating a hole.
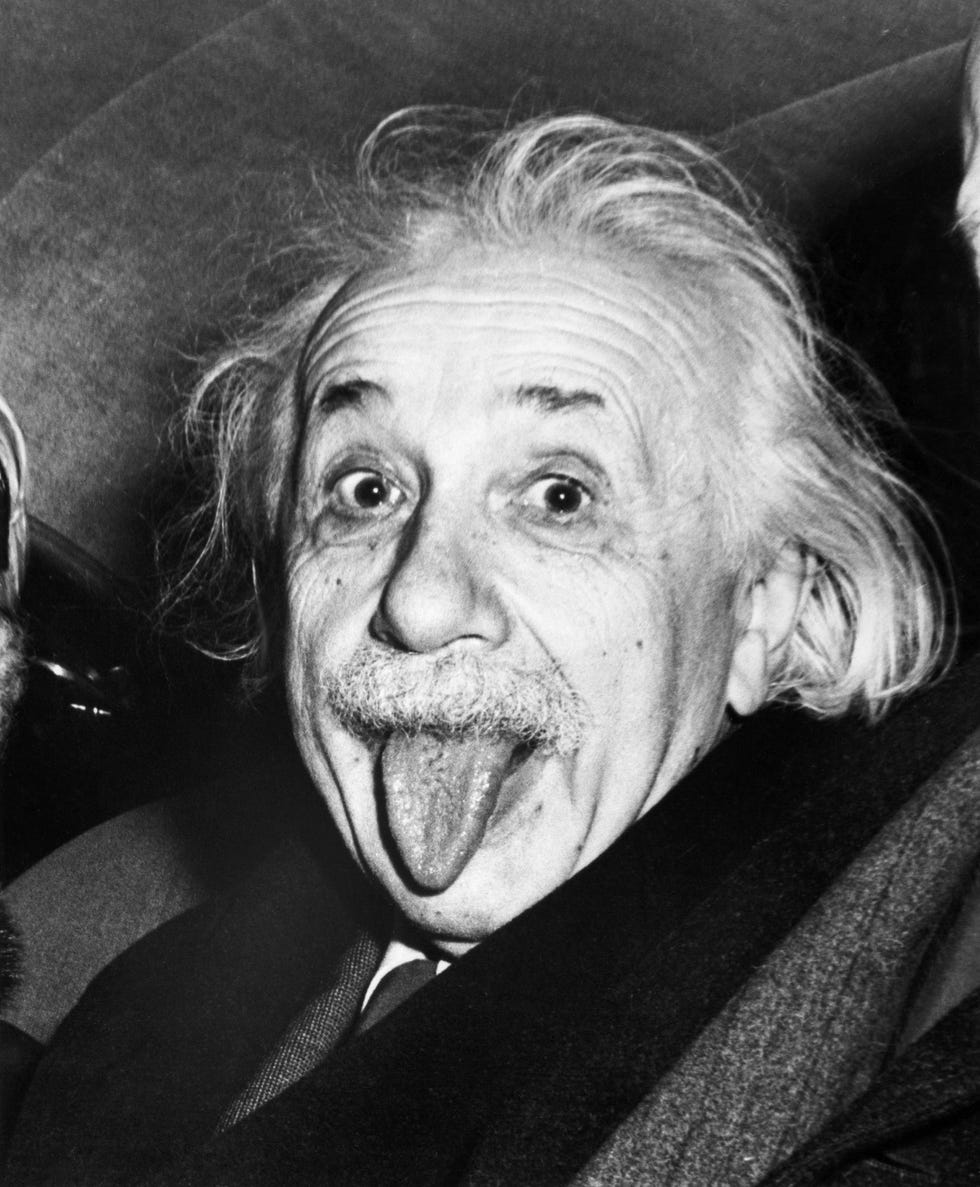

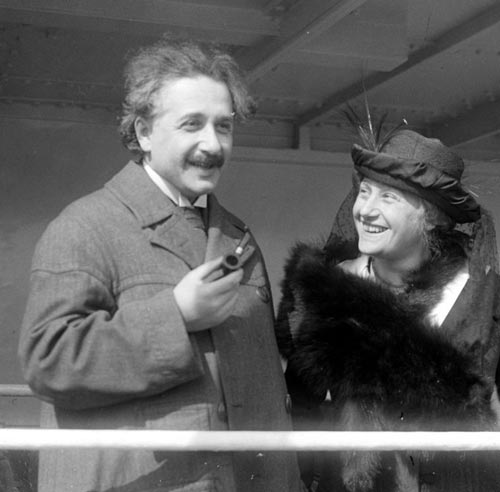
One of the most recognizable photos of the 20 th century shows Einstein sticking out his tongue while leaving his 72 nd birthday party on March 14, 1951.
According to Discovery.com , Einstein was leaving his party at Princeton when a swarm of reporters and photographers approached and asked him to smile. Tired from doing so all night, he refused and rebelliously stuck his tongue out at the crowd for a moment before turning away. UPI photographer Arthur Sasse captured the shot.
Einstein was amused by the picture and ordered several prints to give to his friends. He also signed a copy of the photo that sold for $125,000 at a 2017 auction.
Einstein died on April 18, 1955, at age 76 at the University Medical Center at Princeton. The previous day, while working on a speech to honor Israel’s seventh anniversary, Einstein suffered an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
He was taken to the hospital for treatment but refused surgery, believing that he had lived his life and was content to accept his fate. “I want to go when I want,” he stated at the time. “It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.”
According to the BBC, Einstein muttered a few words in German at the moment of his death. However, the nurse on duty didn’t speak German so their translation was lost forever.
In a 2014 interview , Life magazine photographer Ralph Morse said the hospital was swarmed by journalists, photographers, and onlookers once word of Einstein’s death spread. Morse decided to travel to Einstein’s office at the Institute for Advanced Studies, offering the superintendent alcohol to gain access. He was able to photograph the office just as Einstein left it.
After an autopsy, Einstein’s corpse was moved to a Princeton funeral home later that afternoon and then taken to Trenton, New Jersey, for a cremation ceremony. Morse said he was the only photographer present for the cremation, but Life managing editor Ed Thompson decided not to publish an exclusive story at the request of Einstein’s son Hans.
During Einstein’s autopsy, pathologist Thomas Stoltz Harvey had removed his brain, reportedly without his family’s consent, for preservation and future study by doctors of neuroscience.
However, during his life, Einstein participated in brain studies, and at least one biography claimed he hoped researchers would study his brain after he died. Einstein’s brain is now located at the Princeton University Medical Center. In keeping with his wishes, the rest of his body was cremated and the ashes scattered in a secret location.
In 1999, Canadian scientists who were studying Einstein’s brain found that his inferior parietal lobe, the area that processes spatial relationships, 3D-visualization, and mathematical thought, was 15 percent wider than in people who possess normal intelligence. According to The New York Times , the researchers believe it might help explain why Einstein was so intelligent.
In 2011, the Mütter Museum in Philadelphia received thin slices of Einstein’s brain from Dr. Lucy Rorke-Adams, a neuropathologist at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and put them on display. Rorke-Adams said she received the brain slides from Harvey.
Since Einstein’s death, a veritable mountain of books have been written on the iconic thinker’s life, including Einstein: His Life and Universe by Walter Isaacson and Einstein: A Biography by Jürgen Neffe, both from 2007. Einstein’s own words are presented in the collection The World As I See It .
Einstein has also been portrayed on screen. Michael Emil played a character called “The Professor,” clearly based on Einstein, in the 1985 film Insignificance —in which alternate versions of Einstein, Marilyn Monroe , Joe DiMaggio , and Joseph McCarthy cross paths in a New York City hotel.
Walter Matthau portrayed Einstein in the fictional 1994 comedy I.Q. , in which he plays matchmaker for his niece played by Meg Ryan . Einstein was also a character in the obscure comedy films I Killed Einstein, Gentlemen (1970) and Young Einstein (1988).
A much more historically accurate depiction of Einstein came in 2017, when he was the subject of the first season of Genius , a 10-part scripted miniseries by National Geographic. Johnny Flynn played a younger version of the scientist, while Geoffrey Rush portrayed Einstein in his later years after he had fled Germany. Ron Howard was the director.
Tom Conti plays Einstein in the 2023 biopic Oppenheimer , directed by Christopher Nolan and starring Cillian Murphy as scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer during his involvement with the Manhattan Project.
- The world is a dangerous place to live; not because of the people who are evil, but because of the people who don’t do anything about it.
- A question that sometimes drives me hazy: Am I or are the others crazy?
- A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new.
- Logic will get you from A to B. Imagination will take you everywhere.
- I want to go when I want. It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.
- If you can’t explain it simply, you don’t understand it well enough.
- Nature shows us only the tail of the lion. But there is no doubt in my mind that the lion belongs with it even if he cannot reveal himself to the eye all at once because of his huge dimension. We see him only the way a louse sitting upon him would.
- [T]he distinction between past, present, and future is only an illusion, however persistent.
- Living in this “great age,” it is hard to understand that we belong to this mad, degenerate species, which imputes free will to itself. If only there were somewhere an island for the benevolent and the prudent! Then also I would want to be an ardent patriot.
- I, at any rate, am convinced that He [God] is not playing at dice.
- How strange is the lot of us mortals! Each of us is here for a brief sojourn; for what purpose he knows not, though he sometimes thinks he senses it.
- I regard class differences as contrary to justice and, in the last resort, based on force.
- I have never looked upon ease and happiness as ends in themselves—this critical basis I call the ideal of a pigsty. The ideals that have lighted my way, and time after time have given me new courage to face life cheerfully, have been Kindness, Beauty, and Truth.
- My political ideal is democracy. Let every man be respected as an individual and no man idolized. It is an irony of fate that I myself have been the recipient of excessive admiration and reverence from my fellow-beings, through no fault and no merit of my own.
- The most beautiful experience we can have is the mysterious. It is the fundamental emotion that stands at the cradle of true art and true science. Whoever does not know it and can no longer wonder, no longer marvel, is as good as dead, and his eyes are dimmed.
- An autocratic system of coercion, in my opinion, soon degenerates. For force always attracts men of low morality, and I believe it to be an invariable rule that tyrants of genius are succeeded by scoundrels.
- My passionate interest in social justice and social responsibility has always stood in curious contrast to a marked lack of desire for direct association with men and women. I am a horse for single harness, not cut out for tandem or team work. I have never belonged wholeheartedly to country or state, to my circle of friends, or even to my own family.
- Everybody is a genius.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Tyler Piccotti first joined the Biography.com staff as an Associate News Editor in February 2023, and before that worked almost eight years as a newspaper reporter and copy editor. He is a graduate of Syracuse University. When he's not writing and researching his next story, you can find him at the nearest amusement park, catching the latest movie, or cheering on his favorite sports teams.
Nobel Prize Winners

Alice Munro
Chien-Shiung Wu

The Solar Eclipse That Made Albert Einstein a Star

14 Hispanic Women Who Have Made History

Marie Curie

Martin Luther King Jr.

Henry Kissinger

Malala Yousafzai

Jimmy Carter

10 Famous Poets Whose Enduring Works We Still Read

22 Famous Scientists You Should Know

Wole Soyinka
Biography Online

Albert Einstein Biography

Einstein is also well known as an original free-thinker, speaking on a range of humanitarian and global issues. After contributing to the theoretical development of nuclear physics and encouraging F.D. Roosevelt to start the Manhattan Project, he later spoke out against the use of nuclear weapons.
Born in Germany to Jewish parents, Einstein settled in Switzerland and then, after Hitler’s rise to power, the United States. Einstein was a truly global man and one of the undisputed genius’ of the Twentieth Century.
Early life Albert Einstein
Einstein was born 14 March 1879, in Ulm the German Empire. His parents were working-class (salesman/engineer) and non-observant Jews. Aged 15, the family moved to Milan, Italy, where his father hoped Albert would become a mechanical engineer. However, despite Einstein’s intellect and thirst for knowledge, his early academic reports suggested anything but a glittering career in academia. His teachers found him dim and slow to learn. Part of the problem was that Albert expressed no interest in learning languages and the learning by rote that was popular at the time.
“School failed me, and I failed the school. It bored me. The teachers behaved like Feldwebel (sergeants). I wanted to learn what I wanted to know, but they wanted me to learn for the exam.” Einstein and the Poet (1983)
At the age of 12, Einstein picked up a book on geometry and read it cover to cover. – He would later refer to it as his ‘holy booklet’. He became fascinated by maths and taught himself – becoming acquainted with the great scientific discoveries of the age.

Albert Einstein with wife Elsa
Despite Albert’s independent learning, he languished at school. Eventually, he was asked to leave by the authorities because his indifference was setting a bad example to other students.
He applied for admission to the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich. His first attempt was a failure because he failed exams in botany, zoology and languages. However, he passed the next year and in 1900 became a Swiss citizen.
At college, he met a fellow student Mileva Maric, and after a long friendship, they married in 1903; they had two sons before divorcing several years later.
In 1896 Einstein renounced his German citizenship to avoid military conscription. For five years he was stateless, before successfully applying for Swiss citizenship in 1901. After graduating from Zurich college, he attempted to gain a teaching post but none was forthcoming; instead, he gained a job in the Swiss Patent Office.
While working at the Patent Office, Einstein continued his own scientific discoveries and began radical experiments to consider the nature of light and space.

Einstein in 1921
He published his first scientific paper in 1900, and by 1905 had completed his PhD entitled “ A New Determination of Molecular Dimensions . In addition to working on his PhD, Einstein also worked feverishly on other papers. In 1905, he published four pivotal scientific works, which would revolutionise modern physics. 1905 would later be referred to as his ‘ annus mirabilis .’
Einstein’s work started to gain recognition, and he was given a post at the University of Zurich (1909) and, in 1911, was offered the post of full-professor at the Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague (which was then part of Austria-Hungary Empire). He took Austrian-Hungary citizenship to accept the job. In 1914, he returned to Germany and was appointed a director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics. (1914–1932)
Albert Einstein’s Scientific Contributions
Quantum Theory
Einstein suggested that light doesn’t just travel as waves but as electric currents. This photoelectric effect could force metals to release a tiny stream of particles known as ‘quanta’. From this Quantum Theory, other inventors were able to develop devices such as television and movies. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
Special Theory of Relativity
This theory was written in a simple style with no footnotes or academic references. The core of his theory of relativity is that:
“Movement can only be detected and measured as relative movement; the change of position of one body in respect to another.”
Thus there is no fixed absolute standard of comparison for judging the motion of the earth or plants. It was revolutionary because previously people had thought time and distance are absolutes. But, Einstein proved this not to be true.
He also said that if electrons travelled at close to the speed of light, their weight would increase.
This lead to Einstein’s famous equation:
Where E = energy m = mass and c = speed of light.
General Theory of Relativity 1916
Working from a basis of special relativity. Einstein sought to express all physical laws using equations based on mathematical equations.
He devoted the last period of his life trying to formulate a final unified field theory which included a rational explanation for electromagnetism. However, he was to be frustrated in searching for this final breakthrough theory.
Solar eclipse of 1919
In 1911, Einstein predicted the sun’s gravity would bend the light of another star. He based this on his new general theory of relativity. On 29 May 1919, during a solar eclipse, British astronomer and physicist Sir Arthur Eddington was able to confirm Einstein’s prediction. The news was published in newspapers around the world, and it made Einstein internationally known as a leading physicist. It was also symbolic of international co-operation between British and German scientists after the horrors of the First World War.
In the 1920s, Einstein travelled around the world – including the UK, US, Japan, Palestine and other countries. Einstein gave lectures to packed audiences and became an internationally recognised figure for his work on physics, but also his wider observations on world affairs.
Bohr-Einstein debates
During the 1920s, other scientists started developing the work of Einstein and coming to different conclusions on Quantum Physics. In 1925 and 1926, Einstein took part in debates with Max Born about the nature of relativity and quantum physics. Although the two disagreed on physics, they shared a mutual admiration.
As a German Jew, Einstein was threatened by the rise of the Nazi party. In 1933, when the Nazi’s seized power, they confiscated Einstein’s property, and later started burning his books. Einstein, then in England, took an offer to go to Princeton University in the US. He later wrote that he never had strong opinions about race and nationality but saw himself as a citizen of the world.
“I do not believe in race as such. Race is a fraud. All modern people are the conglomeration of so many ethnic mixtures that no pure race remains.”
Once in the US, Einstein dedicated himself to a strict discipline of academic study. He would spend no time on maintaining his dress and image. He considered these things ‘inessential’ and meant less time for his research. Einstein was notoriously absent-minded. In his youth, he once left his suitcase at a friends house. His friend’s parents told Einstein’s parents: “ That young man will never amount to anything, because he can’t remember anything.”
Although a bit of a loner, and happy in his own company, he had a good sense of humour. On January 3, 1943, Einstein received a letter from a girl who was having difficulties with mathematics in her studies. Einstein consoled her when he wrote in reply to her letter
“Do not worry about your difficulties in mathematics. I can assure you that mine are still greater.”
Einstein professed belief in a God “Who reveals himself in the harmony of all being”. But, he followed no established religion. His view of God sought to establish a harmony between science and religion.
“Science without religion is lame, religion without science is blind.”
– Einstein, Science and Religion (1941)
Politics of Einstein
Einstein described himself as a Zionist Socialist. He did support the state of Israel but became concerned about the narrow nationalism of the new state. In 1952, he was offered the position as President of Israel, but he declined saying he had:
“neither the natural ability nor the experience to deal with human beings.” … “I am deeply moved by the offer from our State of Israel, and at once saddened and ashamed that I cannot accept it.”

Einstein receiving US citizenship.
Albert Einstein was involved in many civil rights movements such as the American campaign to end lynching. He joined the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) and considered racism, America’s worst disease. But he also spoke highly of the meritocracy in American society and the value of being able to speak freely.
On the outbreak of war in 1939, Einstein wrote to President Roosevelt about the prospect of Germany developing an atomic bomb. He warned Roosevelt that the Germans were working on a bomb with a devastating potential. Roosevelt headed his advice and started the Manhattan project to develop the US atom bomb. But, after the war ended, Einstein reverted to his pacifist views. Einstein said after the war.
“Had I known that the Germans would not succeed in producing an atomic bomb, I would not have lifted a finger.” (Newsweek, 10 March 1947)
In the post-war McCarthyite era, Einstein was scrutinised closely for potential Communist links. He wrote an article in favour of socialism, “Why Socialism” (1949) He criticised Capitalism and suggested a democratic socialist alternative. He was also a strong critic of the arms race. Einstein remarked:
“I do not know how the third World War will be fought, but I can tell you what they will use in the Fourth—rocks!”

Rabindranath Tagore and Einstein
Einstein was feted as a scientist, but he was a polymath with interests in many fields. In particular, he loved music. He wrote that if he had not been a scientist, he would have been a musician. Einstein played the violin to a high standard.
“I often think in music. I live my daydreams in music. I see my life in terms of music… I get most joy in life out of music.”
Einstein died in 1955, at his request his brain and vital organs were removed for scientific study.
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “ Biography of Albert Einstein ”, Oxford, www.biographyonline.net 23 Feb. 2008. Updated 2nd March 2017.
Albert Einstein – His Life and Universe

Albert Einstein – His Life at Amazon
Related pages

53 Interesting and unusual facts about Albert Einstein.

19 Comments
Albert E is awesome! Thanks for this website!!
- January 11, 2019 3:00 PM
Albert Einstein is the best scientist ever! He shall live forever!
- January 10, 2019 4:11 PM
very inspiring
- December 23, 2018 8:06 PM
Wow it is good
- December 08, 2018 10:14 AM
Thank u Albert for discovering all this and all the wonderful things u did!!!!
- November 15, 2018 7:03 PM
- By Madalyn Silva
Thank you so much, This biography really motivates me a lot. and I Have started to copy of Sir Albert Einstein’s habit.
- November 02, 2018 3:37 PM
- By Ankit Gupta
Sooo inspiring thanks Albert E. You helped me in my report in school I love you Albert E. 🙂 <3
- October 17, 2018 4:39 PM
- By brooklynn
By this inspired has been I !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
- October 12, 2018 4:25 PM
- By Richard Clarlk
- Understanding Tsunami in Japan
- Marie Curie: A Pioneer in Science and History
- Understanding Indian Culture: A Journey Through Time
- Exploring the World Through Educational Games
- Knights and Chivalry
- Code of Conduct
- Armor and Weapons
- Medieval Life
- Health and Medicine
- Holidays and Celebrations
- Serfs and Peasants
- Kings and Lords
- City-States
- Gods and Goddesses
- Julius Caesar
- Industrial Revolution
- Impact on Society
- World War II
- Allied Powers
- Atomic Bomb
- World War I
- Treaty of Versailles
- Major Battles
- Leaders and Rulers
- Alexander the Great
- Queen Elizabeth I
- Napoleon Bonaparte
- Activists and Reformers
- Nelson Mandela
- Susan B. Anthony
- Mahatma Gandhi
- Scientists and Inventors
- Thomas Edison
- Marie Curie
- Albert Einstein
- Fall of the Berlin Wall
- Cuban Missile Crisis
- Civil Rights Movement
- Martin Luther King Jr.
- Segregation
- Climate Change
- Renewable Energy
- Greenhouse Effect
- Impact on Environment
- African Cultures
- Egyptian Culture
- Nigerian Culture
- Asian Cultures
- Japanese Culture
- Indian Culture
- Chinese Culture
- Latin American Cultures
- Aztec Civilization
- Mayan Civilization
- Inca Civilization
- Natural Disasters
- Tsunami in Japan
- Hurricane Katrina
- Pompeii Eruption
- Important Events
- Signing of the Declaration of Independence
- Discovery of Penicillin
- Moon Landing
- Cultural Achievements
- Renaissance Art
- Ancient Chinese Inventions
- Assessment Tools
- Projects and Presentations
- Writing Assignments
- Quizzes and Tests
- Teaching Methods
- Interactive Learning
- Primary Sources
- Role-playing
- Educational Resources
- Online Databases
- Educational Games
- Museums and Exhibits
- Photographs and Artifacts
- Government Documents
- Diaries and Letters
- Online Sources
- Websites and Blogs
- Digital Archives
- Books and Literature
- Historical Fiction
- Biographies
- A Brief Overview of Albert Einstein's Life and Contributions
- Historical Figures
Albert Einstein is a name that needs no introduction. Known as one of the greatest scientists and thinkers of all time, Einstein's contributions have shaped the way we understand the world today. From his groundbreaking theories to his humanitarian efforts, Einstein's legacy continues to inspire and influence generations. In this article, we will take a closer look at the life and achievements of this remarkable historical figure, and gain a deeper understanding of his impact on science and society. Albert Einstein is a name that is known worldwide.
He was not only a brilliant scientist, but also a cultural icon whose contributions have shaped our understanding of the universe. In this article, we will take a closer look at his life, his achievements, and his lasting impact on the world. First, let's delve into Einstein's early life and education. Born in Ulm, Germany in 1879, he showed an early interest in mathematics and physics. His parents, who were both Jewish, encouraged his curiosity and provided him with a supportive environment to explore his interests. Einstein's education was unconventional, as he struggled with the strict discipline of traditional schools.
However, he excelled in subjects like mathematics and physics, and eventually went on to study at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology. It was during this time that he developed his groundbreaking theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. Einstein's theories revolutionized the field of physics and challenged traditional beliefs about space and time. His theory of general relativity, published in 1915, explained the force of gravity in terms of the curvature of space-time. This theory has been confirmed through various experiments and has had a significant impact on our understanding of the universe. In addition to his work in physics, Einstein also made contributions in other areas such as political activism and philosophy.
He was a vocal advocate for peace and social justice, using his platform as a respected scientist to speak out against war and discrimination. However, Einstein's influence extended beyond just his scientific and political endeavors. His role in the development of nuclear weapons during World War II has sparked ethical debates that continue to this day. He also had a significant impact on popular culture, with his iconic image and famous equation E=mc² becoming synonymous with genius. Today, Einstein's legacy lives on through his contributions to science and society. For those interested in learning more about this remarkable historical figure, there are many educational resources available.
Early Life and Education
However, his parents' marriage began to deteriorate and they eventually separated. As a result, Einstein's mother moved to Switzerland with him and his younger sister, Maja. It was in Switzerland where Einstein received most of his formal education. Einstein attended the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich, where he studied physics and mathematics. He graduated in 1900 with a teaching diploma in physics and mathematics.
After graduation, he struggled to find a job as a teacher and eventually took on various odd jobs while continuing his scientific research. In conclusion, Albert Einstein's impact on world history cannot be overstated. His work in science and philosophy has shaped our understanding of the universe and has influenced countless individuals across generations. Through this article, we hope to have provided a glimpse into the life and legacy of this extraordinary scientist.

Grace Thompson
Grace Thompson is a dedicated historian and writer, contributing extensively to the field of world history. Her work covers a wide range of topics, including ancient civilizations, cultural histories, and significant global events like the World Wars. Known for her meticulous research and clear, engaging writing style, Grace makes complex historical subjects accessible to readers. Her articles are a valuable resource for both students and educators, providing deep insights into how historical events shape the modern world.
New Articles

- Podcasts for Exploring World History
A Comprehensive Look at How Podcasts Can Help You Learn About World History

Discover the Life and Achievements of Marie Curie, a Groundbreaking Scientist

- The Cuban Missile Crisis: A Defining Moment in World History
Explore the events and significance of the Cuban Missile Crisis in the context of global history and the Cold War.

Unleashing the Power of Education with Games
Top Articles

- The Fall of the Berlin Wall: A Defining Moment in World History

- Writing Assignments: A Comprehensive Guide to World History Education

- Uncovering the Mysteries of Mummies

- Discovering Daily Life in Medieval Times
- Impact on Society During the Industrial Revolution
- The Signing of the Declaration of Independence: A Pivotal Moment in World History
The Devastating Pompeii Eruption: A Comprehensive Look into One of the World's Most Notorious Natural Disasters
- The Power of Online Databases: Unlocking the Secrets of World History
- Discover the Impact of Susan B. Anthony on World History
- Understanding Segregation: A Comprehensive Look at Global Events and the Civil Rights Movement
- Exploring Ancient Chinese Inventions
- Exploring the World of Manors
- Exploring the Fascinating World of Armor and Weapons
- The Fascinating World of Renaissance Art
- Understanding Historical Fiction: A Comprehensive Overview
- A Brief History of Major Battles in World War I
- A Brief History of Factories in the Modern Era
- The Impact on the Environment: Understanding the Effects of Climate Change
- Inventions Throughout History: A Journey Through the Modern Era and Industrial Revolution
- Julius Caesar: The Life and Legacy of a Roman Emperor
- A Fascinating Look into the World of Pharaohs
- Exploring the World of Renewable Energy
- Diaries and Letters: Exploring Primary Sources of World History
- The Rise and Fall of Gladiators in Ancient Rome
- A Journey Through the City-States of Ancient Greece
- Exploring Projects and Presentations in World History
- The Marvelous Pyramids of Ancient Egypt: An Introduction to One of the World's Greatest Wonders
- Exploring the Life and Reign of Queen Elizabeth I
Rosa Parks: The Mother of the Civil Rights Movement
- The Discovery of Penicillin: Uncovering the Life-Saving Antibiotic
- The Life and Legacy of Mahatma Gandhi
- A Journey to the Moon: Exploring the History of the Moon Landing
- Exploring Nigerian Culture
- Discovering Egyptian Culture
- Textbooks: A Comprehensive Resource for Understanding World History
- Exploring the Rich History of the Aztec Civilization
- Websites and Blogs: A Comprehensive Overview of World History Resources
- The Impact and Significance of the Treaty of Versailles in World History
- Exploring World History Through Interactive Learning
- Discover the Richness of Chinese Culture
- Alexander the Great: The Legendary Leader Who Conquered the World
- A Brief History of Kings and Lords: Exploring Medieval Times and Feudalism
- Exploring Primary Sources in World History
- The Fascinating World of the Inca Civilization: A Journey Through Latin American Cultures
- Understanding the Causes of World War I
- The Cold War's Impact on the Space Race: A Comprehensive Overview
- Napoleon Bonaparte: The Rise and Fall of a Revolutionary Leader
- Exploring the World of Gods and Goddesses
- Understanding the Impact of the Atomic Bomb
- A Brief Overview of the Fascinating Inca Civilization
- Exploring the Fascinating Mayan Civilization: A Journey Through Time
- Understanding the Greenhouse Effect: An Overview of Global Climate Change
- Holidays and Celebrations: Exploring World History Through Medieval Times
- Understanding Serfs and Peasants in Medieval Times
- Martin Luther King Jr.: A Champion for Civil Rights
- Understanding the Crusades: A Journey Through Medieval Times
- A Journey Through History: Exploring Digital Archives
- Discovering the Genius of Thomas Edison
- Understanding Quizzes and Tests in World History
- Museums and Exhibits: Unlocking the Secrets of World History
- Exploring World History Through Government Documents
The Fascinating World of Biographies: A Comprehensive Look into Historical Figures and Events
- The Devastation of Hurricane Katrina: A Look Back at One of the Deadliest Natural Disasters in World History
- An Overview of Mythology in Ancient Greece
- Health and Medicine in Medieval Times: Exploring the Connection between Body and Mind
- Photographs and Artifacts: Exploring the Past Through Primary Sources
- The Power of Role-Playing: Exploring World History Through Immersive Education
- Understanding the Allied Powers in World War II
- Nelson Mandela: A Leader in the Fight for Equality
- Discovering the Richness of Japanese Culture
- Exploring the Rise and Fall of the Empire: A Journey Through Ancient Rome
- Understanding the Code of Conduct in Medieval Times

Which cookies do you want to accept?

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
- Childhood and education
- From graduation to the “miracle year” of scientific theories
- General relativity and teaching career
- World renown and Nobel Prize
- Nazi backlash and coming to America
- Personal sorrow, World War II, and the atomic bomb
- Increasing professional isolation and death

- What did Albert Einstein do?
- What is Albert Einstein known for?
- What influence did Albert Einstein have on science?
- What was Albert Einstein’s family like?
- What did Albert Einstein mean when he wrote that God “does not play dice”?

From graduation to the “miracle year” of scientific theories of Albert Einstein
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Wolfram Research - Eric Weisstein's World of Scientific Biography - Biography of Albert Einstein
- Nobel Prize - Biography of Albert Einstein
- PBS - A Science Odyssey: People and Discoveries: Albert Einstein
- DigitalCommons@CalPoly - Einstein’s 1935 Derivation of E=mc2
- Space.com - Albert Einstein: His life, theories and impact on science
- American Museum of Natural History - Albert Einstein
- Institute for Advanced Study - Albert Einstein: In Brief
- Famous Scientists - Albert Einstein
- The MY HERO Project - Albert Einstein
- Jewish Virtual Library - Biography of Albert Einstein
- Albert Einstein - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- Albert Einstein - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

After graduation in 1900, Einstein faced one of the greatest crises in his life. Because he studied advanced subjects on his own, he often cut classes; this earned him the animosity of some professors, especially Heinrich Weber. Unfortunately, Einstein asked Weber for a letter of recommendation. Einstein was subsequently turned down for every academic position that he applied to. He later wrote,
I would have found [a job] long ago if Weber had not played a dishonest game with me.
Meanwhile, Einstein’s relationship with Maric deepened, but his parents vehemently opposed the relationship. His mother especially objected to her Serbian background (Maric’s family was Eastern Orthodox Christian ). Einstein defied his parents, however, and in January 1902 he and Maric even had a child, Lieserl, whose fate is unknown. (It is commonly thought that she died of scarlet fever or was given up for adoption .)
In 1902 Einstein reached perhaps the lowest point in his life. He could not marry Maric and support a family without a job, and his father’s business went bankrupt. Desperate and unemployed, Einstein took lowly jobs tutoring children, but he was fired from even these jobs.
The turning point came later that year, when the father of his lifelong friend Marcel Grossmann was able to recommend him for a position as a clerk in the Swiss patent office in Bern . About then, Einstein’s father became seriously ill and, just before he died, gave his blessing for his son to marry Maric. For years, Einstein would experience enormous sadness remembering that his father had died thinking him a failure.
With a small but steady income for the first time, Einstein felt confident enough to marry Maric, which he did on January 6, 1903. Their children, Hans Albert and Eduard, were born in Bern in 1904 and 1910, respectively. In hindsight , Einstein’s job at the patent office was a blessing. He would quickly finish analyzing patent applications, leaving him time to daydream about the vision that had obsessed him since he was 16: What would happen if you raced alongside a light beam? While at the polytechnic school he had studied Maxwell’s equations , which describe the nature of light, and discovered a fact unknown to James Clerk Maxwell himself—namely, that the speed of light remains the same no matter how fast one moves. This violates Newton’s laws of motion , however, because there is no absolute velocity in Isaac Newton ’s theory. This insight led Einstein to formulate the principle of relativity : “the speed of light is a constant in any inertial frame (constantly moving frame).”

During 1905, often called Einstein’s “miracle year,” he published four papers in the Annalen der Physik , each of which would alter the course of modern physics:
- 1. “Über einen die Erzeugung und Verwandlung des Lichtes betreffenden heuristischen Gesichtspunkt” (“On a Heuristic Viewpoint Concerning the Production and Transformation of Light”), in which Einstein applied the quantum theory to light in order to explain the photoelectric effect . If light occurs in tiny packets (later called photons ), then it should knock out electrons in a metal in a precise way.
- 2. “Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen” (“On the Movement of Small Particles Suspended in Stationary Liquids Required by the Molecular-Kinetic Theory of Heat”), in which Einstein offered the first experimental proof of the existence of atoms . By analyzing the motion of tiny particles suspended in still water, called Brownian motion , he could calculate the size of the jostling atoms and Avogadro’s number ( see Avogadro’s law ).
- 3. “Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper” (“On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies”), in which Einstein laid out the mathematical theory of special relativity .
- 4. “Ist die Trägheit eines Körpers von seinem Energieinhalt abhängig?” (“Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?”), submitted almost as an afterthought, which showed that relativity theory led to the equation E = m c 2 . This provided the first mechanism to explain the energy source of the Sun and other stars .
Einstein also submitted a paper in 1905 for his doctorate.
Other scientists, especially Henri Poincaré and Hendrik Lorentz , had pieces of the theory of special relativity, but Einstein was the first to assemble the whole theory together and to realize that it was a universal law of nature , not a curious figment of motion in the ether , as Poincaré and Lorentz had thought. (In one private letter to Mileva, Einstein referred to “our theory,” which has led some to speculate that she was a cofounder of relativity theory. However, Mileva had abandoned physics after twice failing her graduate exams, and there is no record of her involvement in developing relativity. In fact, in his 1905 paper, Einstein only credits his conversations with Besso in developing relativity.)
In the 19th century there were two pillars of physics: Newton’s laws of motion and Maxwell’s theory of light. Einstein was alone in realizing that they were in contradiction and that one of them must fall.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.
Enhanced Page Navigation
- Albert Einstein - Facts
Albert Einstein

Photo from the Nobel Foundation archive.
Albert Einstein The Nobel Prize in Physics 1921
Born: 14 March 1879, Ulm, Germany
Died: 18 April 1955, Princeton, NJ, USA
Affiliation at the time of the award: Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut (now Max-Planck-Institut) für Physik, Berlin, Germany
Prize motivation: “for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect”
Albert Einstein received his Nobel Prize one year later, in 1922.
Prize share: 1/1
Albert Einstein grew up in Munich, where his father founded an electrical engineering company. After studying at the ETH university in Zurich, Einstein worked at the patent office in Bern, during which time he produced several pioneering works in the field of physics. He was later employed at universities in Bern, Zurich, and Prague, and from 1914, in Berlin. After the Nazis seized power in Germany, Einstein immigrated to the US, where he worked at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. Einstein married twice and had three children by his first marriage.
If metal electrodes are exposed to light, electrical sparks between them occur more readily. For this photoelectric effect to occur, the light waves must be above a certain frequency, however. According to physics theory, the light's intensity should be critical. In one of several epoch-making studies beginning in 1905, Albert Einstein explained that light consists of quanta—packets with fixed energies corresponding to certain frequencies. One such light quantum, a photon, must have a certain minimum frequency before it can liberate an electron.
2024 Nobel Prize announcements
Six days, six prizes.

Explore prizes and laureates
Albert Einstein: Biography, facts and impact on science
A brief biography of Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879 - April 18, 1955), the scientist whose theories changed the way we think about the universe.

- Einstein's birthday and education
Einstein's wives and children
How einstein changed physics.
- Later years and death
Gravitational waves and relativity
Additional resources.
Albert Einstein was a German-American physicist and probably the most well-known scientist of the 20th century. He is famous for his theory of relativity , a pillar of modern physics that describes the dynamics of light and extremely massive entities, as well as his work in quantum mechanics , which focuses on the subatomic realm.
Albert Einstein's birthday and education
Einstein was born in Ulm, in the German state of Württemberg, on March 14, 1879, according to a biography from the Nobel Prize organization . His family moved to Munich six weeks later, and in 1885, when he was 6 years old, he began attending Petersschule, a Catholic elementary school.
Contrary to popular belief, Einstein was a good student. "Yesterday Albert received his grades, he was again number one, and his report card was brilliant," his mother once wrote to her sister, according to a German website dedicated to Einstein's legacy. But when he later switched to the Luitpold grammar school, young Einstein chafed under the school's authoritarian attitude, and his teacher once said of him, "never will he get anywhere."
In 1896, at age 17, Einstein entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. A few years later, he gained his diploma and acquired Swiss citizenship but was unable to find a teaching post. So he accepted a position as a technical assistant in the Swiss patent office.
Related: 10 discoveries that prove Einstein was right about the universe — and 1 that proves him wrong
Einstein married Mileva Maric, his longtime love and former student, in 1903. A year prior, they had a child out of wedlock, who was discovered by scholars only in the 1980s, when private letters revealed her existence. The daughter, called Lieserl in the letters, may have been mentally challenged and either died young or was adopted when she was a year old. Einstein had two other children with Maric, Hans Albert and Eduard, born in 1904 and 1910, respectively.
Einstein divorced Maric in 1919 and soon married his cousin Elsa Löwenthal, with whom he had been in a relationship since 1912.
Einstein obtained his doctorate in physics in 1905 — a year that's often known as his annus mirabilis ("year of miracles" in Latin), according to the Library of Congress . That year, he published four groundbreaking papers of significant importance in physics.
The first incorporated the idea that light could come in discrete particles called photons. This theory describes the photoelectric effect , the concept that underpins modern solar power. The second explained Brownian motion, or the random motion of particles or molecules. Einstein looked at the case of a dust mote moving randomly on the surface of water and suggested that water is made up of tiny, vibrating molecules that kick the dust back and forth.
The final two papers outlined his theory of special relativity, which showed how observers moving at different speeds would agree about the speed of light, which was a constant. These papers also introduced the equation E = mc^2, showing the equivalence between mass and energy. That finding is perhaps the most widely known aspect of Einstein's work. (In this infamous equation, E stands for energy, m represents mass and c is the constant speed of light).
In 1915, Einstein published four papers outlining his theory of general relativity, which updated Isaac Newton's laws of gravity by explaining that the force of gravity arose because massive objects warp the fabric of space-time. The theory was validated in 1919, when British astronomer Arthur Eddington observed stars at the edge of the sun during a solar eclipse and was able to show that their light was bent by the sun's gravitational well, causing shifts in their perceived positions.
Related: 8 Ways you can see Einstein's theory of relativity in real life
In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the photoelectric effect, though the committee members also mentioned his "services to Theoretical Physics" when presenting their award. The decision to give Einstein the award was controversial because the brilliant physicist was a Jew and a pacifist. Anti-Semitism was on the rise and relativity was not yet seen as a proven theory, according to an article from The Guardian .
Einstein was a professor at the University of Berlin for a time but fled Germany with Löwenthal in 1933, during the rise of Adolf Hitler. He renounced his German citizenship and moved to the United States to become a professor of theoretical physics at Princeton, becoming a U.S. citizen in 1940.
During this era, other researchers were creating a revolution by reformulating the rules of the smallest known entities in existence. The laws of quantum mechanics had been worked out by a group led by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr , and Einstein was intimately involved with their efforts.
Bohr and Einstein famously clashed over quantum mechanics. Bohr and his cohorts proposed that quantum particles behaved according to probabilistic laws, which Einstein found unacceptable, quipping that " God does not play dice with the universe ." Bohr's views eventually came to dominate much of contemporary thinking about quantum mechanics.

Einstein's later years and death
After he retired in 1945, Einstein spent most of his later years trying to unify gravity with electromagnetism in what's known as a unified field theory . Einstein died of a burst blood vessel near his heart on April 18, 1955, never unifying these forces.
Einstein's body was cremated and his ashes were spread in an undisclosed location, according to the American Museum of Natural History . But a doctor performed an unauthorized craniotomy before this and removed and saved Einstein's brain.
The brain has been the subject of many tests over the decades, which suggested that it had extra folding in the gray matter, the site of conscious thinking. In particular, there were more folds in the frontal lobes, which have been tied to abstract thought and planning. However, drawing any conclusions about intelligence based on a single specimen is problematic.
Related: Where is Einstein's brain?
In addition to his incredible legacy regarding relativity and quantum mechanics, Einstein conducted lesser-known research into a refrigeration method that required no motors, moving parts or coolant. He was also a tireless anti-war advocate, helping found the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists , an organization dedicated to warning the public about the dangers of nuclear weapons .
Einstein's theories concerning relativity have so far held up spectacularly as a predictive models. Astronomers have found that, as the legendary physicist anticipated, the light of distant objects is lensed by massive, closer entities, a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, which has helped our understanding of the universe's evolution. The James Webb Space Telescope , launched in Dec. 2021, has utilized gravitational lensing on numerous occasions to detect light emitted near the dawn of time , dating to just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang.
In 2016, the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory also announced the first-ever direct detection of gravitational waves , created when massive neutron stars and black holes merge and generate ripples in the fabric of space-time. Further research published in 2023 found that the entire universe may be rippling with a faint "gravitational wave background," emitted by ancient, colliding black holes.
Find answers to frequently asked questions about Albert Einstein on the Nobel Prize website. Flip through digitized versions of Einstein's published and unpublished manuscripts at Einstein Archives Online. Learn about The Einstein Memorial at the National Academy of Sciences building in Washington, D.C.
This article was last updated on March 11, 2024 by Live Science editor Brandon Specktor to include new information about how Einstein's theories have been validated by modern experiments.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Adam Mann is a freelance journalist with over a decade of experience, specializing in astronomy and physics stories. He has a bachelor's degree in astrophysics from UC Berkeley. His work has appeared in the New Yorker, New York Times, National Geographic, Wall Street Journal, Wired, Nature, Science, and many other places. He lives in Oakland, California, where he enjoys riding his bike.
Stephen Hawking's black hole radiation paradox could finally be solved — if black holes aren't what they seem
Physicists unveil 1D gas made of pure light
Humans have long been a 'geophysical force on a planetary scale,' says philosopher Timothy Morton. That's neither good nor bad.
Most Popular
- 2 Drinking wastewater, building an island from scratch and creating an urban forest: 3 bold ways cities are already adapting to climate change
- 3 Ancient civilizations knew how to keep cool in deadly heat. We need to resurrect that lost knowledge now.
- 4 Men have a daily hormone cycle — and it's synced to their brains shrinking from morning to night
- 5 'All it takes is a predator to learn that children are easier prey': Why India's 'wolf' attacks may not be what they seem
Biography: Albert Einstein
- Famous Inventions
- Famous Inventors
- Patents & Trademarks
- Invention Timelines
- Computers & The Internet
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
Legendary scientist Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) first gained worldwide prominence in 1919 after British astronomers verified predictions of Einstein's general theory of relativity through measurements taken during a total eclipse. Einstein's theories expanded upon universal laws formulated by physicist Isaac Newton in the late seventeenth century.
Before E=MC2
Einstein was born in Germany in 1879. Growing up, he enjoyed classical music and played the violin. One story Einstein liked to tell about his childhood was when he came across a magnetic compass. The needle's invariable northward swing, guided by an invisible force, profoundly impressed him as a child. The compass convinced him that there had to be "something behind things, something deeply hidden."
Even as a small boy Einstein was self-sufficient and thoughtful. According to one account, he was a slow talker, often pausing to consider what he would say next. His sister would recount the concentration and perseverance with which he would build houses of cards.
Einstein's first job was that of patent clerk. In 1933, he joined the staff of the newly created Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. He accepted this position for life, and lived there until his death. Einstein is probably familiar to most people for his mathematical equation about the nature of energy, E = MC2.
E = MC2, Light and Heat
The formula E=MC2 is probably the most famous calculation from Einstein's special theory of relativity . The formula basically states that energy (E) equals mass (m) times the speed of light (c) squared (2). In essence, it means mass is just one form of energy. Since the speed of light squared is an enormous number, a small amount of mass can be converted to a phenomenal amount of energy. Or if there's a lot of energy available, some energy can be converted to mass and a new particle can be created. Nuclear reactors, for instance, work because nuclear reactions convert small amounts of mass into large amounts of energy.
Einstein wrote a paper based on the new understanding of the structure of light. He argued that light can act as though it consists of discrete, independent particles of energy similar to particles of a gas. A few years before, Max Planck's work had contained the first suggestion of discrete particles in energy. Einstein went far beyond this though and his revolutionary proposal seemed to contradict the universally accepted theory that light consists of smoothly oscillating electromagnetic waves. Einstein showed that light quanta, as he called the particles of energy, could help to explain phenomena being studied by experimental physicists. For example, he explained how light ejects electrons from metals.
While there was a well-known kinetic energy theory that explained heat as an effect of the ceaseless motion of atoms, it was Einstein who proposed a way to put the theory to a new and crucial experimental test. If tiny but visible particles were suspended in a liquid, he argued, the irregular bombardment by the liquid's invisible atoms should cause the suspended particles to move in a random jittering pattern. This should be observable through a microscope. If the predicted motion is not seen, the whole kinetic theory would be in grave danger. But such a random dance of microscopic particles had long since been observed. With the motion demonstrated in detail, Einstein had reinforced the kinetic theory and created a powerful new tool for studying the movement of atoms.
- The Manhattan Project and the Invention of the Atomic Bomb
- A Brief History of Lasers
- The Invention of the Coat Hanger
- Inventors of the Spark Plug
- Britain's Great Exhibition of 1851
- The History of Marshmallows
- Alfred Nobel and the History of Dynamite
- The History of Vacuum Tubes and Their Uses
- Greener Pastures: The Story of the First Lawn Mower
- The History of Penicillin and Antibiotics
- Joseph Nicephor Niepce
- History of Papermaking
- The Long History of the Parachute
- Who Invented the Computer Mouse?
- The History of Spacewar: The First Computer Game
- Thomas Jefferson's Life as an Inventor

The embodiment of genius and the pre-eminent scientist of the modern age, his theories and discoveries have profoundly affected the way people view and understand the world and their place in it. Einstein was also known as a philosopher and humanist who was keenly interested in and concerned about the affairs of the world.
His sagacious, wise, and humorous quotations, letters, and articles are widely used throughout popular culture as well as in historical and academic works. Einstein’s name and image are instantly recognizable everywhere in the world.
Albert Einstein was a theoretical physicist and the most famous scientist in human history. He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics, alongside quantum mechanics. He is perhaps best known in popular culture for his mass/energy equivalence formula E=mc2. In 1921 he received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his “services to theoretical physics”, and in particular his discovery of the photoelectric effect, a pivotal step in the evolution of quantum theory.
Einstein was born in Ulm, Germany on March 14, 1879. As a child, he exhibited an extraordinary curiosity for and understanding of the mysteries of science. The young Einstein also took music lessons, playing both violin and piano; stoking a passion for music that he maintained throughout his life. Moving first to Italy and then Switzerland, the young prodigy graduated from high school in 1896.
In 1905, while working as a patent clerk in Bern, Switzerland, Einstein had what came to be known as his “Annus Mirabilis” (miracle year). It was during this time that the young physicist obtained his Doctorate degree and published four of his most influential research papers, including the Special Theory of Relativity, the Photoelectric Effect, Brownian Motion, and Mass/Energy Equivalence, and his worldwide fame was assured. In 1915, Einstein completed his General Theory of Relativity, and brought to the world a fuller understanding of the interaction of space, time and gravity.
The practical applications of Einstein’s theories include the development of everyday and indispensable items such as Televisions, Remote Controls, Digital Cameras, and GPS tracking systems.
In 1999 Albert Einstein was recognized by TIME Magazine as the “Person of the Century”. Einstein’s intellect, along with his wise and passionate dedication to the causes of social justice and pacifism, left humanity with a fuller understanding of its place in the universe and with pioneering moral guidance for future generations.
Einstein's Influence
Below you will find a selection of the industries and fields of research still reverberating from Einstein’s genius.
Theoretical Physics
Special Relativity, General Relativity, Brownian Motion, Photoelectric Effect
Patent Industry
Founded Swiss Patent Office
GPS Technologies
Theories of Relativity Applied to Satellite Navigation Systems
Mathematics
Differential Geometry, Tensor Calculus
Aerospace and Aeronautics
Early Theories on Relativity Impacting Space Travel
Computing and Information Theory
Early Work on Quantum Computing and Information Theory
Theoretical Cosmology, Cosmological Constant, Expanding Universe Theory
Early Work on Nuclear Energy, Advocacy for Peaceful use of Nuclear Power
Philosophy of Science
Discussions on the Nature of Reality and Scientific Theories
Quantum Theory
Wave-Particle Duality, Quantum Entanglement
Nuclear Technology
Theoretical Foundations for Nuclear Fission and Fusion
Social Sciences
Advocacy for Civil Rights and Social Justice Change
Academia and Education
University Teaching. Scientific Research Institutions
Photonics and Quantum Optics
Quantum Theory of Light, Photoelectric Cells
Military Technology
Indirect Influence through the Development of the Atomic Bomb
Albert Einstein: His life, theories and impact on science
Where would science be without Albert Einstein?
- Early years
Career highlights
Einstein's remarkable brain, einstein's scientific legacy.
- Astronomical legacy
Additional resources
Albert Einstein is often cited as one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century. His work continues to help astronomers study everything from gravitational waves to Mercury 's orbit.
The scientist's equation that helped explain special relativity – E = mc^2 – is famous even among those who don't understand its underlying physics. Einstein is also known for his theory of general relativity (an explanation of gravity ), and the photoelectric effect (which explains the behavior of electrons under certain circumstances); his work on the latter earned him a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
Einstein also tried in vain to unify all the forces of the universe in a single theory, or a theory of everything, which he was still working on at the time of his death.
Related: What is the Theory of Everything?
Einstein's early years
Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Germany, a town that today has a population of just more than 120,000. There is a small commemorative plaque where his house used to stand (it was destroyed during World War II). The family moved to Munich shortly after his birth, according to the Nobel Prize website , and later to Italy when his father faced problems with running his own business. Einstein's father, Hermann, ran an electrochemical factory and his mother Pauline took care of Albert and his younger sister, Maria.
— What is wormhole theory?
— Was Einstein wrong? Why some astrophysicists are questioning the theory of space-time
— Albert Einstein: Before and after relativity
Einstein would write in his memoirs that two "wonders" deeply affected his early years, according to Hans-Josef Küpper, an Albert Einstein scholar. Young Einstein encountered his first wonder — a compass — at age 5: He was mystified that invisible forces could deflect the needle. This would lead to a lifelong fascination with unseen forces. The second wonder came at age 12 when he discovered a book of geometry, which he worshipped, calling it his "holy geometry book."
Contrary to popular belief, young Albert was a good student, according to an online archive . He excelled in physics and mathematics , but was a more "moderate" pupil in other subjects, Küpper wrote on his website. However, Einstein rebelled against the authoritarian attitude of some of his teachers and dropped out of school at 16. He later took an entrance exam for the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich, and while his performances in physics and math were excellent, his marks in other areas were subpar, and he did not pass the exam. The aspiring physicist took additional courses to close the gap in his knowledge and was admitted to the Swiss Polytechnic in 1896. In 1901 he received his diploma to teach physics and mathematics.

However, Einstein could not find a teaching position, and began work in a Bern patent office in 1901, according to his Nobel Prize biography . It was while there that, in between analyzing patent applications, he developed his work in special relativity and other areas of physics that later made him famous.
Einstein married Mileva Maric, a longtime love of his from Zurich, in 1903. Their children, Hans Albert and Eduard, were born in 1904 and 1910. (The fate of a child born to them in 1902 before their marriage, Lieserl, is unknown.) Einstein divorced Maric in 1919 and soon after married Elsa Löwenthal. Löwenthal died in 1933.
Einstein's career sent him to multiple countries. He earned his doctorate from the University of Zurich in 1905 and subsequently took on professor positions in Zurich (1909), Prague (1911) and Zurich again (1912). Next, he moved to Berlin to become director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Physical Institute and a professor at the University of Berlin (1914). He also became a German citizen.
A major validation of Einstein's work came in 1919, when Sir Arthur Eddington, secretary of the Royal Astronomical Society, led an expedition to Africa that measured the position of stars during a total solar eclipse . The group found that the position of stars was shifted due to the bending of light around the sun . (In 2008, a BBC/HBO production dramatized the story in " Einstein and Eddington .")
Einstein remained in Germany until 1933 when dictator Adolf Hitler rose to power. The physicist then renounced his German citizenship and moved to the United States to become a professor of theoretical physics at Princeton. He became a U.S. citizen in 1940 and retired in 1945.
Einstein remained active in the physics community throughout his later years. In 1939, he famously penned a letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt warning that uranium could be used for an atomic bomb.
Late in Einstein's life, he engaged in a series of private debates with physicist Niels Bohr about the validity of quantum theory . Bohr's theories held the day, and Einstein later incorporated quantum theory into his own calculations.

Einstein's death
Einstein died of an aortic aneurysm on April 18, 1955. A blood vessel burst near his heart, according to the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) . When asked if he wanted to have surgery, Einstein refused. "I want to go when I want to go," he said. "It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share; it is time to go. I will do it elegantly."
Einstein's body — most of it, anyway — was cremated; his ashes were spread in an undisclosed location, according to the AMNH. However, a doctor at Princeton Hospital, Thomas Harvey, had controversially performed an autopsy, and removed Einstein's brain and eyeballs, according to the BBC .
Harvey sliced hundreds of thin sections of brain tissue to place on microscope slides and snapped 14 photos of the brain from several angles. He took the brain tissue, slides and images with him when he moved to Wichita, Kansas, where he was a medical supervisor in a biological testing lab.
Over the next 30 years, Harvey sent a few slides to other researchers who requested them, but kept the rest of the brain in two glass jars, sometimes in a cider box under a beer cooler. The story of Einstein's brain was largely forgotten until 1985, when Harvey and his colleagues published their study results in the journal Experimental Neurology .
Harvey failed a competency exam in 1988, and his medical license was revoked, Blitz wrote. Harvey eventually donated the brain to Princeton Hospital, where the brain's journey had begun. Harvey died in 2007. Pieces of Einstein's brain are now at the Mütter Museum in Philadelphia, Live Science reported .
Harvey's 1985 study authors reported that Einstein's brain had a higher number of glial cells (those that support and insulate the nervous system) per neurons (nerve cells) than other brains they examined. They concluded that it might indicate the neurons had a higher metabolic need — in other words, Einstein's brain cells needed and used more energy, which could have been why he had such advanced thinking abilities and conceptual skills.
However, other researchers have pointed out a few problems with that study, according to Eric H. Chudler , a neuroscientist at the University of Washington. First, for example, the other brains used in the study were all younger than Einstein's brain. Second, the "experimental group" had only one subject — Einstein. Additional studies are needed to see if these anatomical differences are found in other people. And third, only a small part of Einstein's brain was studied.
Another study, published in 1996 in the journal Neuroscience Letters , found that Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 g). Also, the scientist's cerebral cortex was thinner than that of five control brains, but the density of neurons was higher.
A study published in 2012 in the journal Brain revealed that Einstein's brain had extra folding in the gray matter , the site of conscious thinking. In particular, the frontal lobes, regions tied to abstract thought and planning, had unusually elaborate folding.

Einstein's legacy in physics is significant. Here are some of the key scientific principles that he pioneered:
Theory of special relativity : Einstein showed that physical laws are identical for all observers, as long as they are not under acceleration. However, the speed of light in a vacuum is always the same, no matter at what speed the observer is traveling. This work led to his realization that space and time are linked to what we now call space-time . So, an event seen by one observer may also be seen at a different time by another observer.
Theory of general relativity : This was a reformulation of the law of gravity. In the 1600s, Newton formulated three laws of motion, among them, outlining how gravity works between two bodies. The force between them depends on how massive each object is, and how far apart the objects are. Einstein determined that when thinking about space-time, a massive object causes a distortion in space-time (like putting a heavy ball on a trampoline). Gravity is exerted when other objects fall into the "well" created by the distortion in space-time, like a marble rolling towards a large ball. General relativity passed a major test in 2019 in an experiment involving a supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way .
Photoelectric effect : Einstein's work in 1905 proposed that light should be thought of as a stream of particles (photons) instead of just a single wave, as was commonly thought at the time. His work helped decipher curious results scientists were previously unable to explain.
Unified field theory : Einstein spent much of his later years trying to merge the fields of electromagnetism and gravity. He was unsuccessful but may have been ahead of his time. Other physicists are still working on this problem.
Einstein's astronomical legacy
There are many applications of Einstein's work, but here are some of the most notable ones in astronomy :
Gravitational waves : In 2016, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detected space-time ripples — otherwise known as gravitational waves— that occurred after black holes collided about 1.4 billion light-years from Earth . LIGO also made an initial detection of gravitational waves in 2015, a century after Einstein predicted these ripples existed. The waves are a facet of Einstein's theory of general relativity.
Mercury's orbit : Mercury is a small planet orbiting close to a very massive object relative to its size — the sun. Its orbit could not be understood until general relativity showed that the curvature of space-time is affecting Mercury's motions and changing its orbit. There is a small chance that over billions of years, Mercury could be ejected from our solar system due to these changes (with an even smaller chance that it could collide with Earth).
Gravitational lensing : This is a phenomenon by which a massive object (like a galaxy cluster or a black hole) bends light around it. Astronomers looking at that region through a telescope can then see objects directly behind the massive object, due to the light being bent. A famous example of this is Einstein's Cross, a quasar in the constellation Pegasus : A galaxy roughly 400 million light-years away bends the light of the quasar so that it appears four times around the galaxy.
Black holes : In April 2019, the Event Horizon telescope showed the first-ever images of a black hole . The photos again confirmed several facets of general relativity, including not only that black holes exist, but also that they have a circular event horizon — a point at which nothing can escape, not even light.
To find the answers to frequently asked questions about Albert Einstein , visit The Nobel Prize website. Additionally, you can learn about The Einstein Memorial at the National Academy of Sciences building in Washington, D.C.
Bibliography
"Einstein: The Life and Times". American Journal of Physics (1973). https://aapt.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1119/1
"On the brain of a scientist: Albert Einstein". Experimental Neurology (1985). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3979509/
"The fascinating life and theory of Albert Einstein". Mih, W. C. Nova Publishers (2000). https://books.google.co.uk/books
"Alterations in cortical thickness and neuronal density in the frontal cortex of Albert Einstein". Neuroscience Letters (1996). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8805120/
"The cerebral cortex of Albert Einstein: a description and preliminary analysis of unpublished photographs". Brain, Volume 136, Issue 4 (2012). https://academic.oup.com/brain/article/136/4/1304/356614?login=true
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
The bubbling surface of a distant star was captured on video for the 1st time ever
Just how dark is the universe? NASA's New Horizons probe gives us best estimate yet
Boeing Space & Defense chief Ted Colbert is leaving: reports
Most Popular
- 2 Cards Against Humanity sues SpaceX for $15 million over land dispute
- 3 India aims for 2028 launch of Venus orbiter as part of ambitious space roadmap
- 4 SpaceX practices for epic Starship booster catch attempt (photos)
- 5 Astronaut captures stunning timelapse of Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS from ISS (video)

Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955)
Albert Einstein was born at Ulm in Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879, into a non-observant Jewish family. At age five, his father showed him a pocket compass, and Einstein realized that something in "empty" space acted upon the needle; he would later describe the experience as one of the most revelatory of his life.
Although considered a slow learner, possibly due to dyslexia, simply shyness or the significantly rare and unusual structure his brain (examined after his death), Einstein built models and mechanical devices for fun. Another, more recent, theory about his mental development is that he had Asperger's syndrome, a condition related to autism.
Einstein began to learn mathematics around age 12. In 1894, his family moved from Munich to Pavia, Italy (near Milan), and this same year Einstein wrote his first scientific work, The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields. He continued his education at Aarau, Switzerland, and in 1896, he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. In 1901, he gained his diploma and acquired Swiss citizenship. Unable to find a teaching post, he accepted a position as technical assistant in the Swiss Patent Office, obtaining his doctor's degree in 1905.
In 1908, Einstein was appointed Privadozent in Berne. The next year, he became Professor Extraordinary in Zurich, and in 1911 Professor of Theoretical Physics at Prague, returning to Zurich in 1912 to fill a similar post. In 1914, he was appointed Director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Physical Institute and Professor in the University of Berlin. He became a German citizen in 1914 and remained in Berlin until 1933, when he renounced his citizenship for political reasons and emigrated to America to take the position of Professor of Theoretical Physics at Princeton. He became a U.S. citizen in 1940 and retired from his post in 1945.
In his early days in Berlin, Einstein postulated that they correct interpretation of the special theory of relativity must also furnish a theory of gravitation, and in 1916 he published his paper on the general theory of relativity. During this time, he also contributed to the problems of the theory of radiation and statistical mechanics. In the 1920s, he embarked on the construction of unified field theories, continuing to work on the probabilistic interpretation of quantum theory, and he persevered with this work in America. He won a Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921 "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect." He contributed to statistical mechanics by his development of the quantum theory of a monatomic gas, and he has also accomplished valuable work in connection with atomic transition probabilities and relativistic cosmology.
Einstein initially favored construction of the atomic bomb, in order to ensure that Hitler did not do so first, and even sent a letter, dated August 2, 1939, to President Roosevelt encouraging him to initiate a program to create a nuclear weapon. Roosevelt responded to this by setting up a committee for the investigation of using uranium as a weapon, which in a few years was superseded by the Manhattan Project.
After the war, however, Einstein lobbied for nuclear disarmament and a world government. Along with Albert Schweitzer and Bertrand Russell, he fought against nuclear tests and bombs. As his last public act, and just days before his death, he signed the Russell-Einstein Manifesto, which led to the Pugwash Conferences on Science and World Affairs.
Einstein's latter years were also spent searching for a unified field theory, for a universal force that would link gravitation with electromagnetic and subatomic forces, a problem on which no one to date has been entirely successful.
Einstein received honorary doctorate degrees in science, medicine and philosophy from many European and American universities. During the 1920s, he lectured in Europe, America and the Far East and was awarded Fellowships or Memberships to all of the leading scientific academies throughout the world. He gained numerous awards in recognition of his work, including the Copley Medal of the Royal Society of London in 1925, and the Franklin Medal of the Franklin Institute in 1935.
Einstein married Mileva Maric in 1903, and they had a daughter and two sons; the marriage was dissolved in 1919, and that same year he married his cousin Elsa Lowenthal, who died in 1936. Einstein died on April 18, 1955, in Princeton, New Jersey. Element 99 was named einsteinium (Es) in his honor.
Albert Einstein
- Occupation: Scientist and Inventor
- Born: March 14,1879 Ulm, in Germany
- Died: 18 April 1955 in Princeton, New Jersey
- Best known for: Theory of Relativity and E=mc2

- Albert experienced speech problems as a child. His parents were worried that he wasn't very smart!
- He failed his first try on his entrance exam for college (this gives us all hope!).
- He was offered the presidency of Israel .
- He auctioned off a hand written version of his Theory of Relativity in 1940 for 6 million dollars in order to help with the war effort.
- Albert had a sister named Maja.
- Listen to a recorded reading of this page:
| |
Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius Essay (Biography)
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Albert Einstein is arguably one of the most influential individuals in the modern world. He played a role in the development and physics, and also dabbled with the politics of his day-even though at a small scale level. During the period around the First World War, Einstein was among the individuals that were against the usage of violence in resolution of conflicts. This was one of the ethical standpoints that have made him receive credence, years after his death.
Albert Einstein was born in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879 (Meltzer 2). Less than two months after his birth his family relocated to Munich where he started his education. As years passed by, Einstein and his family again relocated, this time to Switzerland, where the young Albert gained a diploma in physics and mathematics (Lakin 20). After his graduation, Einstein tried to find a job as a teacher but instead landed a position in Switzerland’s patent office (Frisch 12).
In 1905, at just 26, Einstein received a doctoral degree. It was during this period that he published most his remarkable theories. By 1911 he had been declared Professor Extraordinary and Professor of Theoretical Physics in different cities across Switzerland (Frisch 23). Einstein was fundamentally a pacifist when it came to conflict resolution and this was well manifested in the First World War.
During this time, 93 German professors supported a manifesto for the conduct of the nation in war, while Einstein and three other intellectuals gave their support to an anti-war counter manifesto (Calaprice and Lipscombe 121).
Einstein played a critical role in the establishment of a non-partisan coalition that fronted the idea of just piece and international cooperation in the prevention of wars in the future. During his stay in Switzerland, Einstein spent his days as a theoretical physicist but also dedicated some time to uniting the warring factions. He even once declared his stand thus:
“My pacifism is an instinctive feeling, a feeling that possesses me because the murder of men is disgusting. My attitude is not derived from any intellectual theory but is based on my deepest antipathy to every kind of cruelty and hatred ” (Calaprice and Lipscombe 55.)
In 1914, he moved back to Germany where he stayed as a citizen for the next nineteen years, only to renounce his citizenship on political grounds. He moved the United States where he stayed for seven years before acquiring American Citizenship. In the meantime, he continued teaching Theoretical Physics at Princeton University.
After the Second World War, Albert Einstein was a key official in the World Government Movement. He was even accorded the presidency of Israel but he turned down the offer instead choosing to spearhead the establishment of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
When it came to science, Einstein had a proper knowledge of the challenges in the field and also had a well developed way of dealing with them. His was a methodological approach with clear-cut steps towards the attainment of the goal. According to Einstein, any of his achievements was merely seen as a stepping stone to even more achievements.
In his early professional years, Albert Einstein hypothesized that the right explanation of the special theory of relativity should also inform the theory of gravitation (McPherson 21). In 1916 he published his paper on the general theory of relativity (McPherson 26). It was around this period that he took time to find solutions to the challenges of the theory of radiation. In the 1920’s, Einstein started working on the unified field theories but still continued his work on the quantum theory (Calaprice and Lipscombe 92). By the time he was retiring, Einstein had made substantial achievements in relativistic cosmology and unification of basic concepts of Physics.
Owing to his accomplishments, Einstein was awarded several honorary doctorate degrees in various scientific fields by many European and American universities (Lakin 33-35). A number of prestigious societies also accorded him awards, most notably the Copley Medal of the Royal Society of London in 1925 (Lakin 43). Because of his involvement in research, Einstein spent a lot of time in solitude and his only form of recreation was listening to music. In 1903, he got married and had two children before filing for a divorce sixteen years later only to marry his cousin, Elsa Löwenthal, who passed away in 1936 (Meachen 13). Einstein died in New Jersey, 19 years after Elsa’s death
Einstein’s theories survived the test of time primarily because of two reasons. One, because most of his work was based on the findings of scholars that became before him, and two because the field in which he was involved had no room for more advancement without scholars taking his findings into consideration.
His ethical views regarding the war have long been overshadowed by the entry of other more popular individuals, most of them being politicians. As a pacifist, his political views did not initially find popularity with the rulers of his time because most of them believed in national supremacy. As a matter of fact, most individuals dismissed his and his associate’s viewpoints as the ranting of mad scientists.
Various life lessons can be picked from how Einstein conducted himself. First is the commitment to one’s job. Most individuals always complain of how bad their current job is without even making an effort to attain their best in what they do. For instance, with the global boundaries becoming more and more irrelevant owing to increasing international migration, the United States is gradually becoming multicultural. Individuals from all over the world have over time appreciated the United States as the land of opportunity.
Hence, most persons ranging from professionals to unskilled individuals are looking for ways to gain an entry into America where they earnings are thought to be better than in other regions around the world.
The search for jobs and better livelihoods has resulted in an increased diversification of the American workforce which in turn calls for institutions to adopt and develop strategies for strengthening the relationship between individuals of varied socio-cultural backgrounds. What most individuals fail to notice, is that if they commit themselves to what they are good at, they can end up making notable achievements in their lives.
Another ethical lesson that can be picked from Einstein’s life is his belief in peaceful resolution of national and international conflicts. This is something that Einstein directly linked to leadership whereby leadership is the definite role assigned to each and every president/country.
The most common and wrong presumption by most presidents is that since their job title puts them in a position of leadership, the individuals who work under them will automatically be subject to their every word. In actual sense, however, the title presidency is not necessarily directly linked to leadership.
Einstein believed in proper communication among communities as a way of reaching amicable solutions to disagreements. Community communication is the practice of sharing information amongst individual of a given society. Communication has always been hailed as one of the key unifiers of members of particular communities. The easier it is for individuals to share what is in their minds, the easier it is for them to relate with one another.
Communication as a social aspect is multi faceted in the sense that it comprises various different aspects working both independently and in conjunction with other components to maintain a harmonious understanding between parties. In most societies around the world business is regarded as the mainstay. All activities within a given community generally tend to be under the influence of economic activities both directly and indirectly.
In order for effectiveness to be achieved in leadership, the person in charge must constantly ensure that his/her influence to the people subordinate to him/her is always positive and intended to achieve the unique goals of the country. Furthermore, and in line with Einstein’s beliefs, it has been proven that the leadership style adopted can make people in governmental control either excellent or terrible leaders. In this regard, if the leaders of two nations are pacifiers, then there is a reduced likelihood of international wars.
Another trait that made Einstein a great person was his belief in giving everyone a chance to be heard. Good listenership has been given immense appreciation amongst the most successful communities in the world. The doctrines of these societies propose that for anyone to have a meaningful conversation and particularly in business, he or she must be in a position to take time and listen to what the other person is saying. It is quite unlikely that communication can occur if both of the parties involved talk at the same time.
Communication is a two way event that calls for one of the parties to stay quite and receive the message and then respond as the other party stays quiet. At national levels, if all the leaders sit down and agree to communicate sanely, then there is little likelihood of disagreements occurring on account of misunderstanding.
Einstein’s persona and ethical beliefs redefined the meaning of the word school as a place where people spend time with an aim of becoming more knowledgeable. According to him, it is in schools that students are exposed to basic political values particularly of their country as well as going through extensive studies of how political systems operate.
As a result, the students are able to come up with independent opinions regarding politics and the political elites. This is fundamentally the root of conservatism which has a number of assumptions. One of these sensible assumptions is the imperfection of the human nature. This is because human beings are inherently selfish and will generally be driven to act in ways that are only beneficial to them.
Human imperfection also reveals in the corruptible nature of persons. Another sensible assumption of conservatism, and which was also reflected in Einstein’s persona, is the belief that people basically get their individual identity from their nation and family.
This is practically true because the learning process demands that persons learn from the people closest to them as well as from their country of habitation. The traditionalism ideology based on the fact that institutions which have existed for long periods of time have most credibility also makes a lot of sense. This is a self-explanatory concept especially since it is well known that experience makes the best teacher.
Einstein also put strong emphasis on respect of the rule of law by citizens. This is a very sensible conservative assumption as it is by individuals observing established regulations and trusting the various arms of government to implement such regulations that stability can be obtained now and in the future.
Annotated Bibliography
Calaprice, Alice and Trevor Lipscombe. Albert Einstein: A biography. Connecticut: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005. Print.
Selecting this book for research was practically easy owing to the usage of online library catalogues. The search word used was Einstein which was a straight forward choice and it listed this book as one of the favorite choices. The authors of this book recognize Einstein as one of the most recognizable scientists of all time. They however go on to point out that most people do not know much about Einstein’s life outside his profession.
This book provides a clear evaluation of his life beginning with his birth going all the way to his marriage and children. The authors, in this book, confirm that aside from being a genius, Einstein was just an average person with weaknesses. This is clearly presented in the way Einstein comfortably went through school only to fail to get a job, ending up as a government clerk.
His difficult marriages and family life as well as his use of his international acclaim to fight from world peace has also been given a critical review in the book. This book also carries a bibliography of publications that can be used to properly analyze Einstein’s life and this is one of the fundamental reasons as to why it was selected to inform the research.
Frisch, Aaron. Albert Einstein. Minnesota: The Creative Company, 2005. Print.
In this book, the author also looks at the entire life of Albert Einstein. As far as his younger life was concerned, Aaron tries to dispel the myth that Einstein had learning difficulties.
The failures of his marriages and his inappopriate relation with his children have also been well described. Aaron also goes a step further to analyze the scientists life in peace activism while emphasizing the importance of the theoretical findings that Einstein made as far as the development of physics is concerned. The search word was Einstein and this book was listed among the most appropriate publications to guide any research into the life of the scientist
Lakin, Patricia. Albert Einstein: Genius of the Twentieth Century. North Carolina: Baker & Taylor, 2009. Print
This book was easy to find in the library especially by using the online catalogues. The search words were Albert Einstein, and this book was listed among the most appropriate volumes that fitted the description. In this publication, the author looks at younger life of the world renowned scientist and the challenges that he went through on his way to gaining international acclaim in science.
The author analyzes both the public and private lives of Einstein giving particular emphasis to his overshadowed family life. This book covers almost every aspect of the scientist’s life and this is the primary reason as to why it has been selected for the bibliography of this essay.
McPherson, Stephanie S. Albert Einstein. Minnesota:Lerner Publications, 2004. Print.
In identifying this book, a library was visited and the online catalogue utilized to list the most recent and relevant publication as far as the topic of research was concerned. The search words used were Albert Einstein and this publication showed up among the ideal choices. This book analyzes the life and times of Albert Einstein with particular focus on his lifetime achievements. The authors provide a timeline listing the particular periods around which the great scientist made certain discoveries.
The author also looks at the younger years of Einstein while dispelling the myth that he had learning difficulties. His short-lived marriages and his poor relation with his children has also been well highlighted. The strength of Albert Einstein’s scientific theories and his entry into world politics through advocating for peaceful resolution of conflicts have also been well addressed in the publication.
Towards the end of the book is a bibliography listing all the books and journals that have been consulted by this particular author hence making it an ideal starting point for any research into Einstein’s life.
Meachen, Dana R. Albert Einstein. Minneapolis: Compass Point Books, 2003. Print
Dana Meachen Rau writes about Albert Einstein’s life. The book is in light of the scientist’s private and public eventful life. The author elicits that Einstein, after graduation, missed an opportunity to be a teacher, as he had wished, and had to settle for a job as a government clerk.
In later pages, Rau looks at how Einstein continued studying and became a professor at various universities in Germany, Switzerland and in the United States of America, as well as how he came up with the quantum theory in physics and contributed greatly in the science field. One fact that have been presented in the book and which is very little known is that Einstein married and had three children with his first wife. He divorced after seventeen years and married his cousin.
They never had children. He had a stint in politics which did not last long. Einstein thought governments should use peaceful means to solve conflicts rather than always going to war. This publication is very relevant in the investigation of Einstein’s life as it clearly analyzes his life as a person and as a celebrity physicist.
Meltzer, Milton. Albert Einstein: A Biography. New York: Holiday House, 2007. Print
In this publication, the author defines Albert Einstein as a man who always questioned and provided answers. He notes the fact that aside from being a well-known physicist, Einstein also doubled up as a peace activist. The author studies the entire life of Einstein, from the time of his birth, all the way to his death while giving appropriate details pertaining to his private life.
This book contains numerous pictures of the scientist and this makes it an even more interesting piece of literature for the research. In looking for the book, a library was visited and the online catalogue utilized. The search word was Einstein and this publication showed up among the most recent and ideal publications.
- Zora Hurston, a World-Renowned Writer and Anthropologist
- Cleopatra - The Queen of Egypt
- Important Questions on America Since World War II
- The Common Sense Science
- The Life Accomplishments of John von Neumann
- Albert Einstein, His Life and Outstanding Discoveries
- Nikola Tesla Biography and Contribution
- Nelson Mandela: Biography and Influences
- Life and Carrier of Dmitry Medvedev
- Fatima bint Muhammad, the Daughter of a Prophet
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, April 24). Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/
"Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." IvyPanda , 24 Apr. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius'. 24 April.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." April 24, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/.
1. IvyPanda . "Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." April 24, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." April 24, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
MacTutor
Albert einstein.
If I were to have the good fortune to pass my examinations, I would go to Zürich. I would stay there for four years in order to study mathematics and physics. I imagine myself becoming a teacher in those branches of the natural sciences, choosing the theoretical part of them. Here are the reasons which lead me to this plan. Above all, it is my disposition for abstract and mathematical thought, and my lack of imagination and practical ability.
I have given up the ambition to get to a university ...
To my great joy, I completely succeeded in convincing Hilbert and Klein .
Revolution in science - New theory of the Universe - Newtonian ideas overthrown.
... a German national with or without swastika instead of a Jew with liberal international convictions...
I never realised that so many Americans were interested in tensor analysis.
... said hardly anything beyond presenting a very simple objection to the probability interpretation .... Then he fell back into silence ...
I have locked myself into quite hopeless scientific problems - the more so since, as an elderly man, I have remained estranged from the society here...
References ( show )
- N L Balazs, M J Klein, Biography in Dictionary of Scientific Biography ( New York 1970 - 1990) . See THIS LINK .
- Biography in Encyclopaedia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/biography/Albert-Einstein
- P C Aichelburg and Roman U Sexl ( ed. ) , Albert Einstein: his influence on physics, philosophy and politics ( Braunschweig, 1979) .
- L Barnett, The Universe and Dr Einstein (1974) .
- M Beller, J Renn and R S Cohen ( eds. ) , Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) .
- J Bernstein, Einstein (1973) .
- D Brian, Einstein - a life ( New York, 1996) .
- E Broda, The intellectual quadrangle : Mach - Boltzmann - Planck - Einstein ( Geneva, 1981) .
- W Buchheim, Albert Einstein als Wegbereiter nachklassischer Physik ( Berlin, 1981) .
- U Charpa, Albert Einstein ( Frankfurt, 1993) .
- E M Chudinov ( ed. ) , Einstein and philosophical problems of physics of the twentieth century ( Russian ) 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1979) .
- R W Clark, Einstein: The Life and Times (1979) .
- H Dukas and B Hoffmann ( eds. ) , Albert Einstein : the human side. New glimpses from his archives ( Princeton, N.J., 1979) .
- J Earman, M Janssen and J D Norton ( eds. ) , The attraction of gravitation : new studies in the history of general relativity ( Boston, 1993) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 1 : The early years, 1879 - 1902 ( Princeton, NJ, 1987) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 2 : The Swiss years: writings, 1900 - 1909 ( Princeton, NJ, 1989) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 3 : The Swiss years: writings, 1909 - 1911 ( German ) ( Princeton, NJ, 1993) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 3 : The Swiss years: writings, 1909 - 1911 ( Princeton, NJ, 1993) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 4 . The Swiss years: writings, 1912 - 1914 ( German ) ( Princeton, NJ, 1995) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 4 : The Swiss years: writings, 1912 - 1914 ( Princeton, NJ, 1996) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 5 : The Swiss years : correspondence, 1902 - 1914 ( German ) ( Princeton, NJ, 1993) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 5 : The Swiss years: correspondence, 1902 - 1914 ( Princeton, NJ, 1995) .
- A Einstein, The collected papers of Albert Einstein. Vol. 6 : The Berlin years: writings, 1914 - 1917 ( German ) ( Princeton, NJ, 1996) .
- A Forsee, Albert Einstein : theoretical physicist ( New York, 1963) .
- P Frank, Einstein : His Life and Times (1972) .
- P Frank, Einstein : Sein Leben und seine Zeit ( Braunschweig, 1979) .
- A P French ( ed. ) , Einstein. A centenary volume ( Cambridge, Mass., 1979) .
- V Ya Frenkel and B E Yavelov, Einstein the inventor ( Russian ) 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1981) .
- V Ya Frenkel and B E Yavelov, Einstein : inventions and experiment ( Russian ) 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1990) .
- H Freudenthal, Inleiding tot het denken van Einstein ( Assen, 1952) .
- D P Gribanov, Albert Einstein's philosophical views and the theory of relativity 'Progress' ( Moscow, 1987) .
- D P Gribanov, The philosophical views of A Einstein and the development of the theory of relativity ( Russian ) 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1987) .
- W Heisenberg, Encounters with Einstein. And other essays on people, places, and particles ( Princeton, NJ, 1989) .
- F Herneck, Albert Einstein. Zweite, durchgesehene Auflage ( Leipzig, 1975) .
- T Hey and P Walters, Einstein's mirror ( Cambridge, 1997) .
- G Holton and Y Elkana ( eds. ) , Albert Einstein : Historical and cultural perspectives ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) .
- G Holton, Einstein, history, and other passions ( Woodbury, NY, 1995) .
- D Howard and J Stachel ( eds. ) , Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) .
- C Jungnickel and R McCormmach, Intellectual Mastery of Nature 2 Vols ( Chicago, 1986) .
- B Khofman, Albert Einstein : creator and rebel ( Russian ) 'Progress' ( Moscow, 1983) .
- C Kirsten and H-J Treder ( eds. ) , Albert Einstein in Berlin 1913 - 1933 . Teil I. Darstellung und Dokumente ( Berlin, 1979) .
- C Kirsten and H-J Treder ( eds. ) , Albert Einstein in Berlin 1913 - 1933 . Teil II. Spezialinventar ( Berlin, 1979) .
- B G Kuznetsov, Einstein ( French ) ( Moscow, 1989) .
- B G Kuznetsov, Einstein. Life, death, immortality ( Rusian ) 'Nauka', ( Moscow, 1979) .
- B G Kuznetsov, Einstein: Leben -Tod - Unsterblichkeit ( German ) ( Berlin, 1979) .
- B G Kuznetsov, Einstein ( Moscow, 1965) .
- B G Kuznetsov, Einstein : Vida. Muerte. Inmortalidad ( Moscow, 1990) .
- C Lánczos, The Einstein decade (1905 - 1915) ( New York-London, 1974) .
- H Melcher, Albert Einstein wider Vorurteile und Denkgewohnheiten ( Berlin, 1979) .
- A I Miller, Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity : Emergence (1905) and early interpretation (1905 - 1911) ( Reading, Mass., 1981) .
- L Navarro Veguillas, Einstein, profeta y hereje ( Barcelona, 1990) .
- A Pais , 'Subtle is the Lord...' The Science and the life of Albert Einstein ( Oxford, 1982) .
- A Pais, The science and life of Albert Einstein ( Russian ) 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1989) .
- A Pais, Raffiniert ist der Herrgott ... : Albert Einstein-eine wissenschaftliche Biographie ( Braunschweig, 1986) .
- M Pantaleo and F de Finis ( ed. ) , Relativity, quanta, and cosmology in the development of the scientific thought of Albert Einstein. Vol. I, II. ( New York, 1979) .
- W Pauli, Wissenschaftlicher Briefwechsel mit Bohr, Einstein, Heisenberg u.a. Band I: 1919 - 1929 ( New York-Berlin, 1979) .
- W Pauli, Wissenschaftlicher Briefwechsel mit Bohr, Einstein, Heisenberg u.a. Band II ( Berlin-New York, 1985) .
- I Rosenthal-Schneider, Begegnungen mit Einstein, von Laue und Planck ( Braunschweig, 1988) .
- P A Schilipp ( ed. ) , Albert Einstein : Philosopher- Scientist (2 Vols ) (1969) .
- P A Schilpp ( ed. ) , Albert Einstein als Philosoph und Naturforscher ( Braunschweig, 1979) .
- P A Schilpp ( ed. ) , Albert Einstein : Philosopher-Scientist ( Evanston, Ill., 1949) .
- C Seelig, Albert Einstein : A Documentary Biography ( London, 1956) .
- H-J Treder ( ed. ) , Einstein-Centenarium 1979 ( German ) ( Berlin, 1979) .
- A Whitaker, Einstein, Bohr and the quantum dilemma ( Cambridge, 1996) .
- M White, Albert Einstein : a life in science ( London, 1993) .
- J Wickert, Albert Einstein ( German ) ( Reinbek, 1983) .
- J Wickert, Albert Einstein in Selbstzeugnissen und Bilddokumenten ( Reinbek bei Hamburg, 1972) .
- G Wolters, Mach I, Mach II, Einstein und die Relativitätstheorie ( Berlin-New York, 1987) .
- A I Akhiezer, Einstein and modern physics ( Russian ) , in The scientific picture of the world 'Naukova Dumka' ( Kiev, 1983) , 175 - 194 .
- R A Aronov, B M Bolotovskii and N V Mickevic, Elements of materialism and dialectics in shaping A Einstein's philosophical views ( Russian ) , Voprosy Filos. (11) (1979) , 56 - 66 ; 187 .
- R A Aronov and B Ya Pakhomov, Philosophy and physics in the discussions of N Bohr and A Einstein ( Russian ) , Voprosy Filos. (10) (1985) , 59 - 73 ; 172 - 173 .
- A Avramesco, The Einstein-Bohr debate. I. The background, in Microphysical reality and quantum formalism ( Dordrecht, 1988) , 299 - 308 .
- A Bach, Eine Fehlinterpretation mit Folgen : Albert Einstein und der Welle-Teilchen Dualismus, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 40 (2) (1989) , 173 - 206 .
- N L Balazs, The acceptability of physical theories : Poincaré versus Einstein, in General relativity : papers in honour of J. L Synge ( Oxford, 1972) , 21 - 34 .
- A Baracca and R Rechtman, Einstein's statistical mechanics, Rev. Mexicana Fis. 31 (4) (1985) , 695 - 722 .
- J B Barbour, Einstein and Mach's principle, in Studies in the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1992) , 125 - 153 , 460 .
- M Beller, Einstein and Bohr's rhetoric of complementarity, in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 241 - 255 .
- D W Belousek, Einstein's 1927 unpublished hidden-variable theory : its background, context and significance, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. B Stud. Hist. Philos. Modern Phys. 27 (4) (1996) , 437 - 461 .
- Y Ben-Menahem, Struggling with causality : Einstein's case, in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 291 - 310 .
- G Berg, On the origin of the concept of an Einstein space, in Studies in the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1992) , 336 - 343 ; 460 .
- S Bergia and L Navarro, Recurrences and continuity in Einstein's research on radiation between 1905 and 1916 , Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 38 (1) (1988) , 79 - 99 .
- S Bergia, Who discovered the Bose-Einstein statistics?, in Symmetries in physics (1600 - 1980) ( Barcelona, 1987) , 221 - 250 .
- P Bernardini, Einstein's statistics and second quantization : what continuity? ( Italian ) , Physis-Riv. Internaz. Storia Sci. 23 (3) (1981) , 337 - 374 .
- J Bicák, Einstein's Prague articles on gravitation, in Proceedings of the Fifth Marcel Grossmann Meeting on General Relativity ( Teaneck, NJ, 1989) , 1325 - 1333 .
- M Biezunski, Inside the coconut : the Einstein-Cartan discussion on distant parallelism, in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 315 - 324 .
- J Blackmore, Mach competes with Planck for Einstein's favor, Historia Sci. No. 35 (1988) , 45 - 89 .
- M Born, Erinnerungen an Albert Einstein, Math. Naturwiss. Unterricht 9 (1956 / 57) , 97 - 105 .
- M Born, Recollections of Einstein ( Bulgarian ) , Fiz.-Mat. Spis. Bulgar. Akad. Nauk. 22(55) (3) (1979) , 204 - 216 .
- M Born, Albert Einstein und das Lichtquantum, Naturwissenschaften 42 (1955) , 425 - 431 .
- J Bosquet, Théophile De Donder et la gravifique einsteinienne, Acad. Roy. Belg. Bull. Cl. Sci. (5) 73 (5) (1987) , 209 - 253 .
- E Broda, The intellectual quadrangle Mach-Boltzmann-Planck-Einstein ( Bulgarian ) , Fiz.-Mat. Spis. Bulgar. Akad. Nauk. 25(58) (3) (1983) , 195 - 211 .
- P H Byrne, Statistical and causal concepts in Einstein's early thought, Ann. of Sci. 37 (2) (1980) , 215 - 228 .
- P H Byrne, The origins of Einstein's use of formal asymmetries, Ann. of Sci. 38 (2) (1981) , 191 - 206 .
- P H Byrne, The significance of Einstein's use of the history of science, Dialectica 34 (4) (1980) , 263 - 276 .
- B Carazza, Historical considerations on the conceptual experiment by Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen, in The nature of quantum paradoxes ( Dordrecht, 1988) , 355 - 369 .
- D C Cassidy, Biographies of Einstein ( Polish ) , Kwart. Hist. Nauk. Tech. 24 (4) (1979) , 813 - 822 .
- D C Cassidy, Biographies of Einstein, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 490 - 500 .
- C Cattani and M De Maria, Einstein's path toward the generally covariant formulation of gravitational field equations : the contribution of Tullio Levi-Civita, in Proceedings of the fourth Marcel Grossmann meeting on general relativity ( Amsterdam-New York, 1986) , 1805 - 1826 .
- C Cattani and M De Maria, Gravitational waves and conservation laws in general relativity : A Einstein and T Levi-Civita, 1917 correspondence, in Proceedings of the Fifth Marcel Grossmann Meeting on General Relativity ( Teaneck, NJ, 1989) , 1335 - 1342 .
- C Cattani and M De Maria, Max Abraham and the reception of relativity in Italy : his 1912 and 1914 controversies with Einstein, in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 160 - 174 .
- C Cattani and M De Maria, The 1915 epistolary controversy between Einstein and Tullio Levi-Civita, in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 175 - 200 .
- S Chandrasekhar, Einstein and general relativity : historical perspectives, Amer. J. Phys. 47 (3) (1979) , 212 - 217 .
- S D Chatterji, Two documents on Albert Einstein, in Yearbook : surveys of mathematics 1980 ( Mannheim, 1980) , 143 - 154 .
- B Cimbleris, Einstein's works on thermodynamics (1902 - 1904) and the statistical mechanics of Gibbs ( Portuguese ) , in The XIXth century : the birth of modern science ( Campinas, 1992) , 405 - 412 .
- D M Clark, Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox : a mathematically complete exposition, Bol. Soc. Parana. Mat. (2) 15 (1 - 2) (1995) , 67 - 81 .
- L F Cook, Einstein and DtDE, Amer. J. Phys. 48 (2) (1980) , 142 - 145 .
- Correspondence of A Einstein and M Besso, 1903 - 1955 ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1977 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1980) , 5 - 72 ; 327 .
- O Costa de Beauregard, The 1927 Einstein and 1935 EPR paradox, Physis-Riv. Internaz. Storia Sci. 22 (2) (1980) , 211 - 242 .
- C Curry, The naturalness of the cosmological constant in the general theory of relativity, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 23 (4) (1992) , 657 - 664 .
- S D'Agostino and L Orlando, The correspondence principle and the origin of Einstein's theory of gravity ( Italian ) , Riv. Stor. Sci. (2) 2 (1) (1994) , 51 - 74 .
- S D'Agostino, The problem of the empirical bases of Einstein's general theory of relativity : some recent historico-critical research ( Italian ) , Riv. Stor. Sci. (2) 3 (2) (1995) , 191 - 207 .
- B d'Espagnat, Einstein et la causalité, in Einstein : 1879 - 1955 ( Paris, 1980) , 31 - 44 .
- B K Datta, Development of Einstein's general theory of relativity (1907 - 1916) , Bull. Satyendranath Bose Inst. Phys. Sci. 5 (2) (1980) , 3 - 20 .
- M De Maria, The first reactions to general relativity in Italy : the polemics between Max Abraham and Albert Einstein ( Italian ) , in Italian mathematics between the two world wars ( Bologna, 1987) , 143 - 159 .
- L de Broglie, Notice nécrologique sur Albert Einstein, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 240 (1955) , 1741 - 1745 .
- B de Finetti, Einstein : originality and intuition, Scientia ( Milano ) 113 (1 - 4) (1978) , 115 - 128 .
- R Debever, Publication de la correspondance Cartan-Einstein, Acad. Roy. Belg. Bull. Cl. Sci. (5) (3) 64 (1978) , 61 - 63 .
- L Debnath, Albert Einstein-scientific epistemology, in Selected studies : physics-astrophysics, mathematics, history of science ( Amsterdam-New York, 1982) , 315 - 327 .
- L Debnath, and N C Debnath, Albert Einstein-the man-scientist duality, Internat. J. Math. Ed. Sci. Tech. 10 (4) (1979) , 475 - 491 .
- R Deltete and R Guy, Einstein and EPR, Philos. Sci. 58 (3) (1991) , 377 - 397 .
- P A M Dirac, The perfection of Einstein's theory of gravitation ( Bulgarian ) , Fiz.-Mat. Spis. Bulgar. Akad. Nauk. 22(55) (3) (1979) , 216 - 218 .
- R Disalle, Gereon Wolters' 'Mach I, Mach II, Einstein, und die Relativitätstheorie', Philos. Sci. 57 (4) (1990) , 712 - 723 .
- R Dugas, Einstein et Gibbs devant la thermodynamique statistique, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 241 (1955) , 1685 - 1687 .
- J Earman and C Glymour, Einstein and Hilbert : two months in the history of general relativity, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 19 (3) (1978 / 79) , 291 - 308 .
- Einstein and quantum theory : Excerpts from the correspondence of A Einstein with M Besso ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tehn. (3)(52) (1975) , 30 - 37 ; 101 .
- A Einstein, Le memorie fondamentali di Albert Einstein ( Italian ) , in Cinquant'anni di Relatività, 1905 - 1955 ( Firenze, 1955) , 477 - 611 .
- J Eisenstaedt, Toward a history of Einstein's theory of gravitation, in Fifth Brazilian School of Cosmology and Gravitation ( Teaneck, NJ, 1987) , 552 - 565 .
- M A Elyashevich, Einstein's part in the development of quantum concepts, Soviet Phys. Uspekhi 22 (7) (1979) , 555 - 575 .
- M A Elyashevich, Einstein's part in the development of quantum concepts ( Russian ) , Uspekhi Fiz. Nauk 128 (3) (1979) , 503 - 536 .
- H Ezawa, Einstein's contribution to statistical mechanics, classical and quantum, Japan. Stud. Hist. Sci. No. 18 (1979) , 27 - 72 .
- Y Ezrahi, Einstein and the light of reason, in Albert Einstein, Jerusalem, 1979 ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) , 253 - 278 .
- W L Fadner, Did Einstein really discover E=mc€?, Amer. J. Phys. 56 (2) (1988) , 114 - 122 .
- E L Feinberg, The relation between science and art in Einstein's world view ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1977 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1980) , 187 - 213 ; 327 .
- M Ferraris, M Francaviglia and C Reina, Variational formulation of general relativity from 1915 to 1925 : 'Palatini's method' discovered by Einstein in 1925 , Gen. Relativity Gravitation 14 (3) (1982) , 243 - 254 .
- P K Feyerabend, Mach's theory of research and its relation to Einstein, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 15 (1) (1984) , 1 - 22 .
- P K Feyerabend, Machs Theorie der Forschung und ihre Beziehung zu Einstein, in Ernst Mach-Werk und Wirkung ( Vienna, 1988) , 435 - 462 .
- A Fine, Einstein's interpretations of the quantum theory, in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 257 - 273 .
- A Fine, What is Einstein's statistical interpretation, or, is it Einstein for whom Bell's theorem tolls?, Topoi 3 (1) (1984) , 23 - 36 .
- B Finzi, Commemorazione di Alberto Einstein, Ist. Lombardo Sci. Lett. Rend. Parte Gen. Atti Ufficiali (3) 19 (88) (1955) , 106 - 120 .
- A D Fokker, Albert Einstein, inventor of chronogeometry, Synthese 9 (1954) , 442 - 444 .
- A D Fokker, Albert Einstein : 14 March 1878 - 18 April 1955 ( Dutch ) , Nederl. Tijdschr. Natuurk. 21 (1955) , 125 - 129 .
- M Francaviglia, History of a work of Albert Einstein ( Italian ) , Atti Accad. Sci. Torino Cl. Sci. Fis. Mat. Natur. 112 (1 - 2) (1978) , 43 - 48 .
- I M Frank, Einstein und die Probleme der Optik, Astronom. Nachr. 301 (6) (1980) , 261 - 275 .
- P G Frank, Einstein, Synthese 9 (1954) , 435 - 437 .
- A Franke and F Franke, Paul Langevin und Albert Einstein-eine Freundschaft zwischen Relativitätstheorie und politischer Realität, Ber. Wiss.-Gesch. 20 (2 - 3) (1997) , 199 - 215 .
- V Ya Frenkel, Einstein and the Soviet physicists ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tehn. (3)(52) (1975) , 25 - 30 ; 101 .
- V Ya Frenkel, A Einstein's doctoral dissertation ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tekhn. (2) (1983) , 136 - 141 .
- H Freudenthal, Einstein und das wissenschaftliche Weltbild des 20 . Jahrhunderts, Janus 46 (1957) , 63 - 76 .
- D Galletto, The ideas of Einstein in the works of Guido Fubini and Francesco Severi ( Italian ) , Atti Accad. Sci. Torino Cl. Sci. Fis. Mat. Natur. 115 ( Suppl. ) (1981) , 205 - 216 .
- M Garcia Doncel, The genesis of special relativity and Einstein's epistemology ( Spanish ) , Three lectures about Albert Einstein, Mem. Real Acad. Cienc. Artes Barcelona 45 (4) (1981) , 7 - 35 .
- C Gearhart, A Einstein before 1905 : the early papers on statistical mechanics, Amer. J. Phys. 58 (5) (1990) , 468 - 480 .
- Gh Gheorghiev, Albert Einstein and the development of differential geometry ( Romanian ) , An. Stiint. Univ. 'Al. I. Cuza' Iasi Sect. I a Mat. ( N.S. ) 25 (2) (1979) , 435 - 438 .
- O Godart, and M Heller, Einstein-Lemaitre: rencontre d'idées, Rev. Questions Sci. 150 (1) (1979) , 23 - 43 .
- H Goenner, The reaction to relativity theory. I. The anti-Einstein campaign in Germany in 1920 , in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 107 - 133 .
- H Goenner and G Castagnetti, Albert Einstein as pacifist and Democrat during World War I, Sci. Context 9 (4) (1996) , 325 - 386 .
- I Gottlieb, Albert Einstein-a pathfinder in physics, An. Stiint. Univ. 'Al. I. Cuza' Iasi Sect. I b Fiz. ( N.S. ) 25 (1979) , i-v.
- L R Graham, The reception of Einstein's ideas : two examples from contrasting political cultures, in Albert Einstein, Jerusalem, 1979 ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) , 107 - 136 .
- J J Gray, Poincaré, Einstein, and the theory of special relativity, Math. Intelligencer 17 (1) (1995) , 65 - 67 ; 75 .
- D P Gribanov, The relationship between the empirical and the rational in Einstein's scientific creation ( Russian ) , Voprosy Filos. (9) (1980) , 40 - 50 ; 185 - 186 .
- D Gribanov, The philosophy of Albert Einstein, in Science and technology: humanism and progress I ( Moscow, 1981) , 158 - 180 .
- A T Grigorian, On the centenary of Einstein's birth ( Polish ) , Kwart. Hist. Nauk. Tech. 24 (4) (1979) , 805 - 811 .
- A T Grigorjan, Albert Einstein as a historian of natural science ( Russian ) , Vestnik Akad. Nauk SSSR (4) (1979) , 99 - 104 .
- A T Grigoryan, Albert Einstein as a historian of natural science ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tekhn. (1) (1990) , 85 - 89 .
- F Gürsey, Obituary : Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) , Rev. Fac. Sci. Univ. Istanbul. Sér. A. 20 (1955) , 101 - 104 .
- A Harder, The Copernican character of Einstein's cosmology, Ann. of Sci. 29 (1972) , 339 - 347 .
- K Hentschel, Die Korrespondenz Einstein - Schlick : zum Verhältnis der Physik zur Philosophie, Ann. of Sci. 43 (5) (1986) , 475 - 488 .
- K Hentschel, Einstein's attitude towards experiments : testing relativity theory 1907 - 1927 , Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 23 (4) (1992) , 593 - 624 .
- K Hentschel, Erwin Finlay Freundlich and testing Einstein's theory of relativity, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 47 (2) (1994) , 143 - 201 .
- A Hermann, Einstein und Deutschland, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 537 - 550 .
- F Herneck, Die Einstein-Dokumente im Archiv der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, NTM Schr. Geschichte Naturwiss. Tech. Medizin 10 (2) (1973) , 32 - 38 .
- F R Hickman, Electrodynamical origins of Einstein's theory of general relativity, Internat. J. Theoret. Phys. 23 (6) (1984) , 535 - 566 .
- C Hoefer, Einstein's struggle for a Machian gravitation theory, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 25 (3) (1994) , 287 - 335 .
- C Hoenselaers, Correspondence: Einstein - Kaluza, in Unified field theories of more than 4 dimensions ( Singapore, 1983) , 447 - 457 .
- B Hoffmann, Einstein and Zionism, in General relativity and gravitation , in Proc. Seventh Internat. Conf. ( GR 7) Ramat-Aviv, 1974 ( New York, 1975) , 233 - 242 .
- B Hoffmann, Some Einstein anomalies, in Albert Einstein, Jerusalem, 1979 ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) , 91 - 105 .
- S H Hollingdale, Albert Einstein, born March 14 th, 1879 , Bull. Inst. Math. Appl. 15 (2 - 3) (1979) , 34 - 50 .
- G Holton, Introduction : Einstein and the shaping of our imagination, in Albert Einstein, Jerusalem, 1979 ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) , vii-xxxii.
- G Holton, Spengler, Einstein and the controversy over the end of science, Physis Riv. Internaz. Storia Sci. ( N.S. ) 28 (2) (1991) , 543 - 556 .
- G Hon, Disturbing, but not surprising : did Gödel surprise Einstein with a rotating universe and time travel?, Found. Phys. 26 (4) (1996) , 501 - 521 .
- C A Hooker, Projection, physical intelligibility, objectivity and completeness : the divergent ideals of Bohr and Einstein, British J. Philos. Sci. 42 (4) (1991) , 491 - 511 .
- H Hora, Einstein's photon distribution for blackbodies and the discovery of the laser, in General relativity and gravitation 1 ( New York-London, 1980) , 17 - 21 .
- D Howard, Einstein and Eindeutigkeit : a neglected theme in the philosophical background to general relativity, in Studies in the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1992) , 154 - 243 ; 462 .
- D Howard, Einstein on locality and separability, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 16 (3) (1985) , 171 - 201 .
- D Howard, Realism and conventionalism in Einstein's philosophy of science : the Einstein - Schlick correspondence, Philos. Natur. 21 (2 - 4) (1984) , 616 - 629 .
- D Howard, Was Einstein really a realist?, Perspect. Sci. 1 (2) (1993) , 204 - 251 .
- T P Hughes, Einstein, inventors, and invention, in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 25 - 42 .
- J Illy, Albert Einstein and Prague ( Czech ) , DVT-Dejiny Ved Tech. 12 (2) (1979) , 65 - 79 .
- J Illy, Albert Einstein in Prague, Isis 70 (251) (1979) , 76 - 84 .
- J Illy, Einstein teaches Lorentz, Lorentz teaches Einstein : Their collaboration in general relativity, 1913 - 1920 , Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 39 (3) (1989) , 247 - 289 .
- J Illy, Einstein und der Eotvos-Versuch : Ein Brief Albert Einsteins an Willy Wien, Ann. of Sci. 46 (4) (1989) , 17 - 422 .
- J Illy, The correspondence of Albert Einstein and Gustav Mie, 1917 - 1918 , in Studies in the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1992) , 244 - 259 ; 462 .
- In commemoration of the centenary of the birth of Einstein ( Chinese ) , J. Huazhong Inst. Tech. 7 (1) (1979) , 1 - 6 .
- J Ishiwara, Jun Ishiwaras Text über Albert Einsteins Gastvortrag an der Universität zu Kyoto am 14 . Dezember 1922 , Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 36 (3) (1986) , 271 - 279 .
- T Isnardi, Albert Einstein ( Spanish ) , An. Soc. Ci. Argentina 159 (1955) , 3 - 8 .
- D D Ivanenko, The timeliness of Einstein's works ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tehn. (3)(52) (1975) , 13 - 16 ; 101 .
- M Jammer, Albert Einstein und das Quantenproblem, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 146 - 167 .
- M Jammer, Einstein and quantum physics, in Albert Einstein, Jerusalem, 1979 ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) , 59 - 76 .
- D Jedinák, Statements of Albert Einstein ( Slovak ) , Pokroky Mat. Fyz. Astronom. 20 (6) (1975) , 315 - 319 .
- J L Jiménez and G del Valle, The Einstein and Hopf work revisited, Rev. Mexicana Fis. 29 (2) (1983) , 259 - 266 .
- R Jost, Boltzmann und Planck : die Krise des Atomismus um die Jahrhundertwende und ihre überwindung durch Einstein, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 128 - 145 .
- N Kalicin, Albert Einstein ( on the occasion of the ninetieth anniversary of his birth ) ( Bulgarian ) , Fiz.-Mat. Spis. Bulgar. Akad. Nauk. 12 (45) (1969) , 169 - 171 .
- N V Karlov and A M Prokhorov, Quantum electronics and Einstein's theory of radiation, Soviet Phys. Uspekhi 22 (7) (1979) , 576 - 579 .
- N V Karlov and A M Prokhorov, Quantum electronics and Einstein's theory of radiation ( Russian ) , Uspekhi Fiz. Nauk 128 (3) (1979) , 537 - 543 .
- A S Karmin, Scientific thought and intuition: Einstein's formulation of the problem ( Russian ) , in The scientific picture of the world 'Naukova Dumka' ( Kiev, 1983) , 240 - 259 .
- A Kastler, Albert Einstein, à propos du centenaire de sa naissance, Acad. Roy. Belg. Cl. Sci. Mém. Collect. (2) 44 (1) (1981) , 13 - 27 .
- M Katsumori, Einstein's philosophical turn and the theory of relativity, in Grenzfragen zwischen Philosophie und Naturwissenschaft ( Vienna, 1989) , 98 - 101 .
- M Katsumori, The theories of relativity and Einstein's philosophical turn, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 23 (4) (1992) , 557 - 592 .
- P Kerszberg, The Einstein-de Sitter controversy of 1916 - 1917 and the rise of relativistic cosmology, in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 325 - 366 .
- B Khofman, V Bargman, P Bergman and E Shtraus, Working with Einstein ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1982 - 1983 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1986) , 170 - 195 .
- B Khofman, V Bargman, P Bergman and E Shtraus, Working with Einstein, in Some strangeness in the proportion ( Reading, Mass., 1980) , 475 - 489 .
- D Khofman, Albert Einstein as a patent referee ( a new Einstein document ) ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1984 - 1985 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1988) , 143 - 147 .
- M J Klein, Fluctuations and statistical physics in Einstein's early work, in Albert Einstein, Jerusalem, 1979 ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) , 39 - 58 .
- M J Klein and A Needell, Some unnoticed publications by Einstein, Isis 68 (244) (1977) , 601 - 604 .
- A Kleinert, Nationalistische und antisemitische Ressentiments von Wissenschaftlern gegen Einstein, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 501 - 516 .
- L Kostro, An outline of the history of Einstein's relativistic ether concept, in Studies in the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1992) , 260 - 280 ; 463 .
- L Kostro, Einstein's relativistic ether, its history, physical meaning and updated applications, Organon No. 24 (1988) , 219 - 235 .
- A J Kox, Einstein and Lorentz: more than just good colleagues, in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 43 - 56 .
- A J Kox, Einstein, Lorentz, Leiden and general relativity, Classical Quantum Gravity 10 ( Suppl. ) (1993) S 187 -S 191 .
- A J Kox, Einstein, specific heats, and residual rays : the history of a retracted paper, in No truth except in the details ( Dordrecht, 1995) , 245 - 257 .
- A B Kozhevnikov, Einstein's formula for fluctuations and particle-wave dualism ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1986 - 1990 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1990) , 102 - 124 .
- F Krull, Albert Einstein in seinen erkenntnistheoretischen Auss erungen, Sudhoffs Arch. 78 (2) (1994) , 154 - 170 .
- B G Kuznetsov, Einstein and classical science ( Russian ) , Vestnik Akad. Nauk SSSR (4) (1979) , 91 - 98 .
- B G Kuznetsov, Einstein and de Broglie : Historico-scientific and historico-philosophical notes ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tekhn. (1) (1981) , 47 - 57 .
- B G Kuznetsov, From Einstein's correspondence with de Broglie ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tekhn. (1) (1981) , 58 - 59 .
- B G Kuznetsov, The Einstein - Bohr dispute, the Einstein - Bergson dispute and the science of the second half of the twentieth century ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1980 - 1981 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1985) , 49 - 85 , 334 .
- C Lanczos, Albert Einstein and the theory of relativity, Nuovo Cimento (10) 2 ( Suppl. ) (1955) 1193 - 1220 .
- C Lanczos, Einstein's path from special to general relativity, in General relativity : papers in honour of J L Synge ( Oxford, 1972) , 5 - 19 .
- P T Landsberg, Einstein and statistical thermodynamics. I. Relativistic thermodynamics, European J. Phys. 2 (4) (1981) , 203 - 207 .
- P T Landsberg, Einstein and statistical thermodynamics. II. Oscillator quantisation, European J. Phys. 2 (4) (1981) , 208 - 212 .
- P T Landsberg, Einstein and statistical thermodynamics. III. The diffusion-mobility relation in semiconductors, European J. Phys. 2 (4) (1981) , 213 - 219 .
- P T Landsberg, Einstein and statistical thermodynamics, in Proceedings of the Einstein Centennial Symposium on Fundamental Physics ( Bogotá, 1981) , 73 - 117 .
- F Laudisa, Physical reality and the principle of separability in the Einstein-Bohr debate ( Italian ) , Riv. Stor. Sci. (2) 3 (2) (1995) , 47 - 76 .
- K V Laurikainen, Albert Einstein, 14 . 3 . 1879 ( Finnish ) , Arkhimedes 31 (2) (1979) , 61 - 67 .
- N B Lavrova, The works by Einstein and the Russian-language papers about him published in the USSR ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tehn. (3)(52) (1975) , 38 - 42 ; 101 .
- F Le Lionnais, Descartes et Einstein, Rev. Hist. Sci. Appl. 5 (1952) , 139 - 154 .
- G Lemaitre, L'oeuvre scientifique d'Albert Einstein, Rev. Questions Sci. (5) 16 (1955) , 475 - 487 .
- T Levi-Chivita, Analytic expression for the gravitation tensor in Einstein's theory ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1980 - 1981 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1985) , 191 - 203 , 335 .
- N A Licis and V A Markov, Lobacevskii and Einstein. Sources of the general theory of relativity ( Russian ) , Latvijas PSR Zinatn. Akad. Vestis (12)(389) (1979) , 18 - 32 .
- C Liu, Einstein and relativistic thermodynamics in 1952 : a historical and critical study of a strange episode in the history of modern physics, British J. Hist. Sci. 25 (85)(2) (1992) , 185 - 206 .
- G A Lorentz, On Einstein's theory of gravitation ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1980 - 1981 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1985) , 169 - 190 ; 335 .
- A S Luchins and E H Luchins, The Einstein-Wertheimer correspondence on geometric proofs and mathematical puzzles, Math. Intelligencer 12 (2) (1990) , 35 - 43 .
- V S Lukyanets, The problem of the justification of physics in the works of Einstein ( Russian ) , in The scientific picture of the world 'Naukova Dumka' ( Kiev, 1983) , 195 - 211 .
- G Maltese, The rejection of the Ricci tensor in Einstein's first tensorial theory of gravitation, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 41 (4) (1991) , 363 - 381 .
- G Mannoury, The cultural phenomenon Albert Einstein, Synthese 9 (1954) , 438 - 441 .
- N Maxwell, Induction and scientific realism : Einstein versus van Fraassen. I. How to solve the problem of induction, British J. Philos. Sci. 44 (1) (1993) , 61 - 79 .
- N Maxwell, Induction and scientific realism : Einstein versus van Fraassen. II. Aim-oriented empiricism and scientific essentialism, British J. Philos. Sci. 44 (1) (1993) , 81 - 101 .
- N Maxwell, Induction and scientific realism : Einstein versus van Fraassen. III. Einstein, aim-oriented empiricism and the discovery of special and general relativity, British J. Philos. Sci. 44 (2) (1993) , 275 - 305 .
- W H McCrea and R W Lawson, Obituary : Albert Einstein, Nature 175 (1955) , 925 - 927 .
- H A Medicus, A comment on the relations between Einstein and Hilbert, Amer. J. Phys. 52 (3) (1984) , 206 - 208 .
- J Mehra, Niels Bohr's discussions with Albert Einstein, Werner Heisenberg, and Erwin Schrödinger : the origins of the principles of uncertainty and complementarity, Found. Phys. 17 (5) (1987) , 461 - 506 .
- J Mehra, Niels Bohr's discussions with Albert Einstein, Werner Heisenberg, and Erwin Schrödinger: the origins of the principles of uncertainty and complementarity, in Symposium on the Foundations of Modern Physics 1987 ( Teaneck, NJ, 1987) , 19 - 64 .
- H Melcher, Some supplements to Einstein-documents, in Proceedings of the ninth international conference on general relativity and gravitation ( Cambridge, 1983) , 271 - 284 .
- H Melcher, Atherdrift und Relativität : Michelson, Einstein, Fizeau und Hoek, NTM Schr. Geschichte Natur. Tech. Medizin 19 (1) (1982) , 46 - 67 .
- D Michelson Livingston, Einstein and Michelson-artists in science, Astronom. Nachr. 303 (1) (1982) , 15 - 16 .
- A I Miller, Albert Einstein's 1907 Jahrbuch paper : the first step from SRT to GRT, in Studies in the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1992) , 319 - 335 ; 464 .
- A I Miller, Symmetry and imagery in the physics of Bohr, Einstein and Heisenberg, in Symmetries in physics (1600 - 1980) ( Barcelona, 1987) , 299 - 327 .
- A I Miller, The special relativity theory : Einstein's response to the physics of 1905 , in Albert Einstein, Jerusalem, 1979 ( Princeton, NJ, 1982) , 3 - 26 .
- V V Narlikar, Einstein and the unity of nature, in Gravitation, quanta and the universe ( New York, 1980) , 1 - 12 .
- L Navarro, On Einstein's statistical-mechanical approach to the early quantum theory (1904 - 1916) , Historia Sci. (2) 1 (1) (1991) , 39 - 58 .
- Z Nikol, Einstein and Langevin ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tehn. (3)(52) (1975) , 37 - 38 ; 101 .
- D J F Nonnenmacher, T F Nonnenmacher and P F Zweifel, Kepler, Einstein, and Ulm, Math. Intelligencer 15 (2) (1993) , 50 - 51 .
- D Norton, Einstein's battle for general covariance ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1982 - 1983 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1986) , 57 - 84 .
- J Norton, Erratum: 'What was Einstein's principle of equivalence?', Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 17 (1) (1986) , 131 .
- J Norton, Coordinates and covariance : Einstein's view of space-time and the modern view, Found. Phys. 19 (10) (1989) , 1215 - 1263 .
- J D Norton, Did Einstein stumble? The debate over general covariance. Reflections on spacetime : foundations, philosophy, history, Erkenntnis 42 (2) (1995) , 223 - 245 .
- J D Norton, Einstein, Nordstrom and the early demise of scalar, Lorentz-covariant theories of gravitation, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 45 (1) (1992) , 17 - 94 .
- J Norton, John Einstein's discovery of the field equations of general relativity : some milestones, in Proceedings of the fourth Marcel Grossmann meeting on general relativity ( Amsterdam-New York, 1986) , 1837 - 1848 .
- J Norton, How Einstein found his field equations, 1912 - 1915 , in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 101 - 159 .
- J Norton, What was Einstein's principle of equivalence?, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 16 (3) (1985) , 203 - 246 .
- J Norton, What was Einstein's principle of equivalence?, in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 5 - 47 .
- R M Nugayev, The history of quantum mechanics as a decisive argument favoring Einstein over Lorentz, Philos. Sci. 52 (1) (1985) , 44 - 63 .
- Obituary : Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) ( Russian ) , Z. Eksper. Teoret. Fiz. 28 (1955) , 637 - 638 .
- T Ogawa, Japanese evidence for Einstein's knowledge of the Michelson-Morley experiment, Japan. Stud. Hist. Sci. No. 18 (1979) , 73 - 81 .
- M E Omeljanovskii, Einstein, the foundations of modern physics and dialectics ( Russian ) , Vestnik Akad. Nauk SSSR (4) (1979) , 74 - 90 .
- Y A Ono, Einstein's speech at Kyoto University, December 14 , 1922 , NTM Schr. Geschichte Natur. Tech. Medizin 20 (1) (1983) , 25 - 28 .
- N F Ovcinnikov, On the problem of the formation of Einstein's creative personality ( Russian ) , Voprosy Filos. (9) (1979) , 70 - 84 ; 186 .
- A Pais, Einstein and the quantum theory, Rev. Modern Phys. 51 (4) (1979) , 863 - 914 .
- A Pais, How Einstein got the Nobel prize ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1982 - 1983 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1986) , 85 - 105 .
- A Pais, How Einstein got the Nobel Prize, Amer. Sci. 70 (4) (1982) , 358 - 365 .
- P Pascual, Einstein and the development of cosmology ( Spanish ) , Three lectures about Albert Einstein, Mem. Real Acad. Cienc. Artes Barcelona 45 (4) (1981) , 53 - 72 .
- M Paty, Einstein et la complémentarité au sens de Bohr: du retrait dans le tumulte aux arguments d'incomplétude, Bohr et la complémentarité, Rev. Histoire Sci. 38 (3 - 4) (1985) , 325 - 351 .
- M Paty, Physical geometry and special relativity. Einstein et Poincaré, 1830 - 1930 : a century of geometry ( Berlin, 1992) , 127 - 149 .
- M Paty, The nature of Einstein's objections to the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics, Found. Phys. 25 (1) (1995) , 183 - 204 .
- G Petiau, Albert Einstein, 1879 - 1955 , Rev. Gén. Sci. Pures Appl. 62 (1955) , 227 - 236 .
- A Polikarov, Über den Charakter von Einsteins philosophischem Realismus, Philos. Natur. 26 (1) (1989) , 135 - 158 .
- A Popovici, Albert Einstein ( Romanian ) , Gaz. Mat. Fiz. Ser. A 9 (62) (1957) , 207 - 213 .
- W Purkert, Die Bedeutung von A Einsteins Arbeit über Brownsche Bewegung für die Entwicklung der modernen Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie, Mitt. Math. Ges. DDR No. 3 (1983) , 41 - 49 .
- L Pyenson, Einstein's education : mathematics and the laws of nature, Isis 71 (258) (1980) , 399 - 425 .
- C Ray, The cosmological constant : Einstein's greatest mistake?, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 21 (4) (1990) , 589 - 604 .
- T Regge, Albert Einstein in the centenary of his birth ( Italian ) , Rend. Accad. Naz. Sci. XL Mem. Sci. Fis. Natur. 4 (1979 / 80) , 41 - 47 .
- J Renn, Einstein as a disciple of Galileo : a comparative study of concept development in physics, in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 311 - 341 .
- J Renn, Von der klassischen Trägheit zur dynamischen Raumzeit : Albert Einstein und Ernst Mach, Ber. Wiss.-Gesch. 20 (2 - 3) (1997) , 189 - 198 .
- J Renn, T Sauer, and J Stachel, The origin of gravitational lensing. A postscript to Einstein's 1936 Science paper: 'Lens-like action of a star by the deviation of light in the gravitational field', Science 275 (5297) (1997) , 184 - 186 .
- A Rossi, Mach and Einstein : Influence of Mach's 'Mechanics' on Einstein's thought ( Italian ) , Physis-Riv. Internaz. Storia Sci. 22 (2) (1980) , 279 - 292 .
- M Sachs, Einstein and the evolution of twentieth-century physics, Phys. Essays 3 (1) (1990) , 80 - 85 .
- M Sachs, On Einstein's later view of the twin paradox, Found. Phys. 15 (9) (1985) , 977 - 980 .
- A Salam, Einstein's last project : the unification of the basic interactions and properties of space-time ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1980 - 1981 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1985) , 102 - 110 ; 334 .
- H E Salzer, Two letters from Einstein concerning his distant parallelism field theory, Arch. History Exact Sci. 12 (1974) , 89 - 96 .
- R A Sardaryan, The first translations of A Einstein's work into Armenian ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1986 - 1990 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1990) , 98 - 101 .
- W Schlicker, Albert Einstein and the political reaction in imperialist Germany after the First World War ( Czech ) , Pokroky Mat. Fyz. Astronom. 24 (3) (1979) , 153 - 160 .
- W Schlicker, Genesis and duration of quarrels about Albert Einstein in Germany from 1920 to 1922 / 23 ( Polish ) , Kwart. Hist. Nauk. Tech. 24 (4) (1979) , 789 - 804 .
- H-G Schöpf, Albert Einstein und die ersten Anfänge der Quantentheorie, Wiss. Z. Tech. Univ. Dresden 28 (1) (1979) , 79 - 83 .
- H-G Schöpf, Zum 100 . Geburtstag von A Einstein : Albert Einsteins annus mirabilis 1905 , NTM Schr. Geschichte Natur. Tech. Medizin 15 (2) (1978) , 1 - 17 .
- W Schroder, Albert Einstein in seinen Beziehungen zu Mitgliedern der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften in Göttingen, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 39 (2) (1988) , 157 - 171 .
- W Schröder and H-J Treder, Zu Einsteins letzter Vorlesung-Beobachtbarkeit, Realität und Vollständigkeit in Quanten- und Relativitätstheorie, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 48 (2) (1994) , 149 - 154 .
- R Schulmann, Einstein at the Patent Office : exile, salvation, or tactical retreat?, in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 17 - 24 .
- R Schulmann, From periphery to center : Einstein's path from Bern to Berlin (1902 - 1914) , in No truth except in the details ( Dordrecht, 1995) , 259 - 271 .
- K K Sen, Life of Einstein, Math. Medley 7 (1) (1979) , 8 - 12 .
- F Severi, An effort to clarify Einstein's doctrine, recalling the man ( Italian ) , Archimede 31 (4) (1979) , 238 - 244 .
- J Shelton, The role of observation and simplicity in Einstein's epistemology, Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 19 (1) (1988) , 103 - 118 .
- J Soucek and V Soucek, 'Einstein's model A' deduced by de Sitter is not that of Einstein, Astrophys. Space Sci. 159 (2) (1989) , 317 - 331 .
- J Stachel, Einstein and Michelson : the context of discovery and the context of justification, Astronom. Nachr. 303 (1) (1982) , 47 - 53 .
- J Stachel, How Einstein discovered general relativity : a historical tale with some contemporary morals, in General relativity and gravitation ( Cambridge-New York, 1987) , 200 - 208 .
- J Stachel, 'A man of my type'-editing the Einstein papers, British J. Hist. Sci. 20 (64)(1) (1987) , 57 - 66 .
- J Stachel, Einstein and quantum mechanics, in Conceptual problems of quantum gravity ( Boston, MA, 1991) , 13 - 42 .
- J Stachel, Einstein and the quantum : fifty years of struggle, in From quarks to quasars ( Pittsburgh, PA, 1986) , 349 - 385 .
- J Stachel, Einstein's search for general covariance, 1912 - 1915 , in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 63 - 100 .
- J Stachel, Lanczos's early contributions to relativity and his relationship with Einstein, in Proceedings of the Cornelius Lanczos International Centenary Conference, Raleigh 1993 ( Philadelphia, PA, 1994) , 201 - 221 .
- J Stachel, The other Einstein : Einstein contra field theory., in Einstein in context ( Cambridge, 1993) , 275 - 290 .
- J Stachel and R Torretti, Einstein's first derivation of mass-energy equivalence, Amer. J. Phys. 50 (8) (1982) , 760 - 763 .
- E Stipanich, Boskovic and Einstein ( Russian ) , in Investigations in the history of mechanics 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1983) , 219 - 245 .
- P Straneo, Genesi ed evoluzione della concezione relativistica di Albert Einstein, in Cinquant'anni di Relatività, 1905 - 1955 ( Firenze, 1955) , 29 - 134 .
- J Strnad, Einstein and Planck's law ( Slovenian ) , Obzornik Mat. Fiz. 26 (3) (1979) , 74 - 85 .
- J Strnad, Einstein and quanta ( Slovenian ) , Obzornik Mat. Fiz. 42 (3) (1995) , 80 - 87 .
- S G Suvorov, Einstein : the creation of the theory of relativity and some gnosiological lessons, Soviet Phys. Uspekhi 22 (7) (1979) , 528 - 554 .
- S G Suvorov, Einstein : the creation of the theory of relativity and some gnosiological lessons ( Russian ) , Uspekhi Fiz. Nauk 128 (3) (1979) , 459 - 501 .
- Y Tanaka, Einstein and Whitehead : The principle of relativity reconsidered, Historia Sci. No. 32 (1987) , 43 - 61 .
- G Temple, Obituary : Albert Einstein, J. London Math. Soc. 31 (1956) , 501 - 507 .
- J Thiele, Briefe Albert Einsteins an Joseph Petzoldt, NTM Schr. Geschichte Naturwiss. Tech. Medizin 8 (1) (1971) , 70 - 74 .
- V Tonini, Continuity and discontinuity : the Einstein-Bohr conflict of ideas and the Bohr-Fock discussion, in The nature of quantum paradoxes ( Dordrecht, 1988) , 371 - 384 .
- M-A Tonnelat, Einstein : les influences philosophiques, in Einstein : 1879 - 1955 ( Paris, 1980) , 11 - 30 .
- M-A Tonnelat, Science et philosophie : Einstein et Spinoza, Bull. Soc. Math. Belg. Sér. A 33 (2) (1981) , 183 - 205 .
- M-A Tonnelat, Einstein, mythe et réalité, Scientia ( Milano ) 114 (5 - 8) (1979) , 297 - 369 .
- I Toth, Spekulationen über die Möglichkeit eines nicht euklidischen Raumes vor Einstein, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 46 - 83 .
- H-J Treder, Antimatter and the particle problem in Einstein's cosmology and field theory of elementary particles : an historical essay on Einstein's work at the Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin, Astronom. Nachr. 296 (4) (1975) , 149 - 161 .
- Tres conferencias sobre Albert Einstein, Mem. Real Acad. Cienc. Artes Barcelona 45 (4) (1981) , 1 - 72 .
- I Z Tsekhmistro, The Einstein - Podolsky - Rosen paradox and the concept of integrity ( Russian ) , Voprosy Filos. (4) (1985) , 84 - 94 .
- J M Vidal Llenas, Einstein and his nonrelativistic contributions to physics ( Spanish ) , Three lectures about Albert Einstein, Mem. Real Acad. Cienc. Artes Barcelona 45 (4) (1981) , 37 - 51 .
- E Vigner, Thirty years of knowing Einstein ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1982 - 1983 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1986) , 149 - 169 .
- E Vigner, Thirty years of knowing Einstein, Some strangeness in the proportion ( Reading, Mass., 1980)) , 461 - 472
- V P Vizgin, Einstein, Hilbert, Weyl : Genesis des Programms der einheitlichen geometrischen Feldtheorien, NTM Schr. Geschichte Natur. Tech. Medizin 21 (2) (1984) , 23 - 33 .
- V P Vizgin, Einstein, Hilbert, Weyl: the genesis of the program of unified geometrized field theories ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1980 - 1981 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1985) , 86 - 101 ; 334 .
- V P Vizgin, Correspondence between Einstein and de Broglie in the early fifties ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tekhn. (3) (1982) 169 - 170 .
- V P Vizgin, Eötvös and Einstein ( Russian ) , in History of science 'Metsniereba' ( Tbilisi, 1984) , 86 - 89 .
- V P Vizgin, On the history of the discovery of equations of gravitation ( Einstein and Hilbert ) ( Russian ) , Istor.-Mat. Issled. No. 25 (1980) , 261 - 265 ; 379 .
- V P Vizgin, One of the aspects of Einstein's methodology ( Russian ) , Voprosy Istor. Estestvoznan. i Tehn. (3)(52) (1975) , 16 - 24 ; 101 .
- V P Vizgin, Einstein, Hilbert, and Weyl : the genesis of the geometrical unified field theory program, in Einstein and the history of general relativity ( Boston, MA, 1989) , 300 - 314 .
- M von Laue, Einstein und die Relativitätstheorie, Naturwissenschaften 43 (1956) , 1 - 8 .
- K von Meyenn, Einsteins Dialog mit den Kollegen, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 464 - 489 .
- E T Whittaker, Aristotle, Newton, Einstein, Philos. Mag. (7) 34 (1943) , 266 - 280 .
- E T Whittaker, Aristotle, Newton, Einstein, Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh A 61 (1942) , 231 - 246 .
- J Wickert, Zum produktiven Denken bei Einstein. Ein Beitrag zur Erkenntnispsychologie, in Einstein Symposion, Berlin 1979 ( Berlin-New York, 1979) , 443 - 463 .
- C M Will, General relativity at 75 : how right was Einstein?, in The Sixth Marcel Grossmann Meeting, Kyoto 1991 ( River Edge, NJ, 1992) , 769 - 786 .
- A M Yaglom, Einstein's 1914 paper on the theory of randomly fluctuating series of observations ( Russian ) , Problemy Peredachi Informatsii 21 (4) (1985) , 101 - 107 .
- C N Yang, Einstein and the physics of the second half of the twentieth century, in Selected studies : physics-astrophysics, mathematics, history of science ( Amsterdam-New York, 1982) , 139 - 146 .
- C N Yang, Einstein's impact on theoretical physics, Phys. Today 33 (6) (1980) , 42 - 44 ; 48 - 49 .
- L V Yatsenko, The problem of scientific work and A Einstein ( Russian ) , in The scientific picture of the world 'Naukova Dumka' ( Kiev, 1983) , 211 - 240 .
- B E Yavelov, Einstein and the problem of superconductivity ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1977 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1980) , 158 - 186 ; 327 .
- B E Yavelov, Einstein's Zurich colloquium ( Russian ) , in Einstein collection, 1982 - 1983 'Nauka' ( Moscow, 1986) , 106 - 148 .
- E Zahar, Einstein, Meyerson and the role of mathematics in physical discovery, British J. Philos. Sci. 31 (1) (1980) , 1 - 43 .
- R Zajac, Albert Einstein and twentieth century physics ( Czech ) , Pokroky Mat. Fyz. Astronom. 24 (2) (1979) , 61 - 77 .
- A Zeilinger, Physik und Wirklichkeit-neuere Entwicklungen zum Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen Paradoxon, in Naturwissenschaft und Weltbild ( Vienna, 1992) , 99 - 121 .
- Ja B Zeldovic, A Einstein and modern science ( Russian ) , Vestnik Akad. Nauk SSSR (7) (1980) , 40 - 46 .
- R E Zimmermann, Albert Einstein-Versuch einer totalisierenden Würdigung, Philos. Natur. 21 (1) (1984) , 126 - 138 .
- P F Zweifel, The scientific work of Albert Einstein, Ann. Nuclear Energy 7 (4 - 5) (1980) , 279 - 287 .
Additional Resources ( show )
Other pages about Albert Einstein:
- A meeting with Einstein
- Ether and Relativity
- Geometry and Experience
- Einstein; the Nazis and the German Academies
- Max Herzberger on Albert Einstein
- Times obituary
- Multiple entries in The Mathematical Gazetteer of the British Isles ,
- Astronomy: The Infinite Universe
- Astronomy: The Reaches of the Milky Way
- Einstein's 1929 New York Times article
- Carlos Graef argues with Albert Einstein
- D D Kosambi on Einstein
- Miller's postage stamps
Other websites about Albert Einstein:
- Dictionary of Scientific Biography
- Encyclopaedia Britannica
- History of Computing Project
- Princeton University Press
- American Institute of Physics
- Albert Einstein Online
- Plus Magazine ( Einstein and relativity )
- Kevin Brown ( Reflections on Relativity )
- Mathematics Today
- Nobel prizes site ( A biography of Einstein and his Nobel prize presentation speech )
- Mathematical Genealogy Project
- MathSciNet Author profile
- zbMATH entry
Honours ( show )
Honours awarded to Albert Einstein
- Nobel Prize 1921
- Fellow of the Royal Society 1921
- LMS Honorary Member 1924
- Royal Society Copley Medal 1925
- Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh 1927
- AMS Gibbs Lecturer 1934
- Lunar features Crater Einstein
- Popular biographies list Number 13
Cross-references ( show )
- History Topics: A brief history of cosmology
- History Topics: A history of Quantum Mechanics
- History Topics: A history of time: 20 th century time
- History Topics: A visit to James Clerk Maxwell's house
- History Topics: General relativity
- History Topics: Greek astronomy
- History Topics: Light through the ages: Relativity and quantum era
- History Topics: Newton's bucket
- History Topics: Orbits and gravitation
- History Topics: Special relativity
- History Topics: The development of the 'black hole' concept
- History Topics: Wave versus matrix mechanics
- Societies: Brazilian Academy of Sciences
- Societies: Canadian Mathematical Society
- Societies: Irish Royal Academy
- Societies: Israel Academy of Sciences
- Societies: Kaiser Wilhelm Society
- Societies: Max Planck Society for Advancement of Science
- Societies: Pontifical Academy of Sciences
- Societies: Zurich Scientific Research Society
- Student Projects: James Clerk Maxwell - The Great Unknown: Chapter 1
- Student Projects: James Clerk Maxwell - The Great Unknown: Chapter 7
- Student Projects: James Clerk Maxwell - The Great Unknown: Chapter 8
- Other: 14th September
- Other: 1932 ICM - Zurich
- Other: 2009 Most popular biographies
- Other: 25th November
- Other: 29th May
- Other: 4th June
- Other: 4th May
- Other: 5th April
- Other: 5th December
- Other: 9th June
- Other: Cambridge Individuals
- Other: Earliest Known Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics (B)
- Other: Earliest Known Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics (E)
- Other: Earliest Known Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics (G)
- Other: Earliest Known Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics (T)
- Other: Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh
- Other: Jeff Miller's postage stamps
- Other: London Learned Societies
- Other: London Museums
- Other: London individuals H-M
- Other: Most popular biographies – 2024
- Other: Oxford Institutions and Colleges
- Other: Oxford individuals
- Other: Popular biographies 2018
- Other: The Infinite Universe
- Other: The Reaches of the Milky Way

- DIGITAL MAGAZINE
MOST POPULAR
10 facts about Albert Einstein
Find out about this extraordinary physicist….
Discover the scientist whose ideas and theories about time and space changed the world and what we think about the universe in our 10 facts about Albert Einstein…
Albert Einstein Facts

Full name: Albert Einstein
Born: 14 March 1879
Occupation: Scientist specialising in physics, also known as a theoretical physicist*
Died: 18 April 1955
Best known for: His theory of relativity*
1. Albert Einstein was born in Germany, but lived in Italy, Switzerland and Czechia (which was then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire), until he eventually moved to the United States in 1933.
Albert never went back to Germany after moving to the USA . He didn’t feel safe in Germany because of the events that led to World War 2 , and instead settled down to life in the American town of Princeton , New Jersey .
2. When Albert was a boy, he fell in love with physics when his father gifted him a compass.
He was fascinated by the way the magnets moved inside of the compass, and thought about this when he was older and coming up with his theories around relativity.
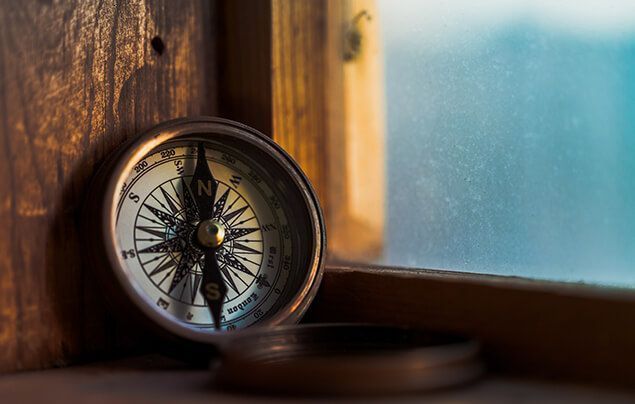

3. Albert hated the strict discipline of the grammar school he attended as a teenager, and left aged 15…
While at school, he excelled at maths , physics , and philosophy , but struggled with other subjects like languages .
4. …but he still managed to write his first scholarly paper at just 16 years old!
The paper was inspired by his compass, and discussed the force of magnetism .
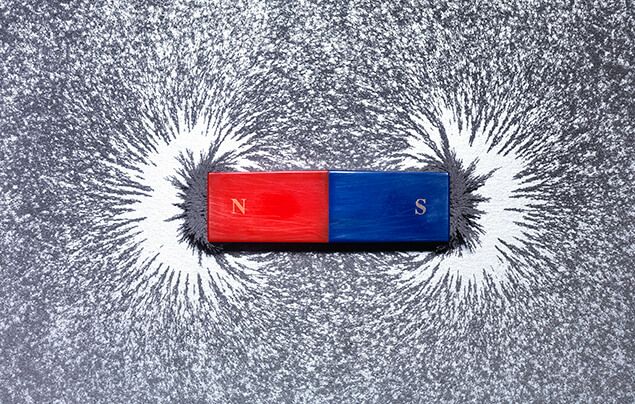
5. Rather than becoming a physicist straight away, Albert first trained as a teacher.
In 1896 , he was accepted into the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zürich, Switzerland. He originally failed the entrance exam, but was let anyway due to his exceptional maths results ! However, this was on the condition that Albert also went to high school and finished his formal schooling.
6. After failing to find work as a maths and physics teacher, Albert decided to obtain a Ph.D. in physics.
He obtained this degree in 1905 – a year that came to be known as Albert’s “ year of miracles “, because he published four groundbreaking papers in just 12 months!

7. One of the discoveries Albert announced in 1905 was his famous formula: E=mc 2
Albert figured out that matter – the tiny particles that make up everything in the world – can be turned into energy . The equation, E=mc 2 , describes how this conversion can be achieved. This amazing breakthrough made the 26-year-old Albert Einstein a star!
8. The formula formed part of Albert’s ‘general theory of relativity’, which he worked on over the next ten years.
Other scientists, for example Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz , had already been forming pieces of the theory. However, Albert was the first one to put the whole thing together. He published the complete theory in 1915 , where it wowed the world!

9. Albert’s theory of relativity helped scientists understand how the universe works.
Albert’s theory showed that the effects of gravity result from the ways that objects affect space and time . These interactions can only been seen on enormous objects like the planets. As a result, Albert’s general theory of relativity describes the way that amazing phenomena like the movement of planets, the birth and death of stars, black holes, and evolution of the universe, are possible.
Check out our space facts article to learn more about these out-of-this-world places!
10. He went on to win The Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
The Nobel Prize is an award for major scientific accomplishments – and by the time Albert won it, he and his discoveries were famous around the world. He continued working on theories until his death in 1955 , aged 76.
*A theoretical physicist is a scientist who try to figure out how the world and universe works.
Did you learn something new from our Albert Einstein facts? Let us know in the comments!
Leave a comment.
Your comment will be checked and approved shortly.
WELL DONE, YOUR COMMENT HAS BEEN ADDED!
Great for me and for anybody who wants to find out about Albert Einstein : )
Nice. he also sold that prize money away
He is a very smart person.
How old was he when he died?
HE INSPIRE ME LOT....
it helped with homework
great facts
love your facts they helped me with my homework.
my class is doing a project and this helped
it was nice and gooooooooood
damm my i q went up reading this
This information will really help me for my history and geography project. Thanks for the facts!
Wow this helped me so much!! Thank u i never knew this stuff and believe it or not i couldn't find a lot of websites that had this much amazing information!!!!! Thanks a lot! Very well done website!!
wow so helpful i learned so much things ty!
this helped me with a biogerfy packet
Thanks for the facts.
Helps me a lot for my inventor report
This information helps with my biography!
This is an amazing website
he is my hero
love it you helped me in my project thanks
That was good fafcts
awsome i like albert einstine
Very interesting
Interesting..
It’s so cool
Cool! I want to learn more!
this is amazing and interesting
Nice its got good info!
Wow! That’s amazing!
I loved it it had tons of fackes for my report for school.
wow!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
HE IS SO COOL
Love this story!
wow some cool facts!!!:)
This is a good app
Wow excellent....
This really helped me in my homework thanks
Wow that's really interesting
Woah never knew these things
WOW WOW WOWWOW WOWOWOWWOWOW
AMAZING world of SCINCE
this website is amazing.
really good
LOVE IT!!!!!!
I Love Albert Einsteins work and lifestyle!
Thank you for your information it helped me a lot!
Thank you for giving me information
I love Albert E!
I love it!!!
This is amazing
This was good for my PowerPoint thx
I Love His Work
I like him (and siance i think that's how it's spelled
Great job doing this! I loved it
GOOD FACTS DEFINTLY THE BEST I HEARD
It was really helpful and I can't wait to read facts about other things
Interesting, I love the fact that this was made for kids like me. And how intelligent Albert Einstein was. This shows everything the we need to know
CUSTOMIZE YOUR AVATAR
More like general science.
What is coronavirus?

10 facts about Stephen Hawking
Your Amazing Brain!

Enter The Eurekas now!

Sign up to our newsletter
Get uplifting news, exclusive offers, inspiring stories and activities to help you and your family explore and learn delivered straight to your inbox.
You will receive our UK newsletter. Change region
WHERE DO YOU LIVE?
COUNTRY * Australia Ireland New Zealand United Kingdom Other
By entering your email address you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy and will receive emails from us about news, offers, activities and partner offers.
You're all signed up! Back to subscription site
Type whatever you want to search
More Results

You’re leaving natgeokids.com to visit another website!
Ask a parent or guardian to check it out first and remember to stay safe online.

You're leaving our kids' pages to visit a page for grown-ups!
Be sure to check if your parent or guardian is okay with this first.
- Fundamentals NEW
- Biographies
- Compare Countries
- World Atlas
Albert Einstein
Introduction.

Scientific Breakthroughs
In 1905 Einstein caused a stir by publishing five major research papers. These papers forever changed the way people thought about the universe. One of these papers contained completely new ideas about the properties of light. Einstein received the Nobel prize for physics in 1921, mainly for the work in this paper.
In another paper, Einstein presented what is now called the special theory of relativity. This theory states that measurements of space and time are relative. That is, they change when taken by people moving at different speeds. This idea was entirely new. The special theory of relativity also changed how scientists thought about energy and matter . (Matter is everything that takes up space.)
Later Years
When the Nazi Party took over Germany in 1933, Einstein left the country. He eventually settled in the United States.
During World War II Einstein urged the United States to build nuclear weapons . He felt that these weapons might be needed to defeat the Nazis. The United States did create the first atomic bomb in 1945. Einstein, however, did not work to develop the bomb. After World War II he tried to prevent any future use of atomic weapons. Einstein died in Princeton, New Jersey, on April 18, 1955.
It’s here: the NEW Britannica Kids website!
We’ve been busy, working hard to bring you new features and an updated design. We hope you and your family enjoy the NEW Britannica Kids. Take a minute to check out all the enhancements!
- The same safe and trusted content for explorers of all ages.
- Accessible across all of today's devices: phones, tablets, and desktops.
- Improved homework resources designed to support a variety of curriculum subjects and standards.
- A new, third level of content, designed specially to meet the advanced needs of the sophisticated scholar.
- And so much more!
Want to see it in action?
Start a free trial
To share with more than one person, separate addresses with a comma
Choose a language from the menu above to view a computer-translated version of this page. Please note: Text within images is not translated, some features may not work properly after translation, and the translation may not accurately convey the intended meaning. Britannica does not review the converted text.
After translating an article, all tools except font up/font down will be disabled. To re-enable the tools or to convert back to English, click "view original" on the Google Translate toolbar.
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- general knowledge
Albert Einstein Biography: Birth, Early Life, Education, Scientific Career, Inventions, Awards, and Honours, Legacy, and More
Albert einstein biography: he was born on 14 march 1879 in ulm, wurttemberg, germany. he was a physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity. in 1921, he won the nobel prize for physics. read more about his early life, education, his inventions, scientific career, awards, honours, and more..

Albert Einstein Biography
| Born | 14 March 1879 |
| Place of Birth | Ulm, Wurttemberg, Germany |
| Died | 18 April 1955 |
| Place of Death | Princeton, New Jersey, U.S. |
| Education | Federal polytechnic school in Zurich, University of Zurich (PhD) |
| Spouse(s) | |
| Children | Lieserl Einstein Hans Albert Einstein Eduard Einstein |
| Awards And Honours | Copley Medal (1925), Nobel Prize (1921) |
| Subjects of Study | Brownian motion, gravitational wave, light, photon unified field theory |
| Known for |
Albert Einstein: Early Life, Education, Marriage, Children, Teaching Career
He was born on 14 March 1879 in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany, to a secular, middle-class Jews . His father was Hermann Einstein, and his mother was Pauline Koch. His father was a featherbed salesman, and later he ran an electrochemical factory with moderate success. Albert Einstein had one sister, named Maria. His family moved to Munich, where he started his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Later, his parents moved to Italy, where he continued his education at Arau, Switzerland. He went to the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich in 1896. There, he was trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. In 1901, Albert gained his diploma and acquired Swiss citizenship. At that time, he didn't get the teaching post, but he took a position as a technical assistant in the Swiss Patent Office. He gained his doctor's degree in 1905.
Albert Einstein would write that in his early years, two wonders deeply affected him. The first was his encounter with the compass. At that time, he was five years old. He was puzzled that invisible forces could deflect the needle. And the second one was when he discovered a book of geometry at the age of 12 and called it his "sacred little geometry book".
In the Swiss Patent Office, when he got spare time, he produced much of his remarkable work. He was appointed Privatdozent in Berne in 1908. He became Professor Extraordinary at Zurich in 1909 and Professor of Theoretical Physics at Prague in 1911. In the following year, he returned to Zurich to fill a similar post.
He was also appointed Director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Physical Institute in 1914 and Professor at the University of Berlin. In 1914, he became a citizen of Germany and remained in Berlin until 1933. In 1940, he became a United States citizen and retired from his post in 1945.
Albert Einstein married Mileva Maric in 1903. The couple had a daughter and two sons. In 1919, they divorced. In the same year, Albert married his cousin, Elsa Lowenthal, who died in 1936.
Albert Einstein: Scientific Career and Inventions
Albert Einstein was a leading figure in the World Government Movement after World War II. He was also offered the Presidency of the State of Israel, but he declined it, and he collaborated with Dr. Chaim Weizmann in developing the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
He was always interested in solving the problems of physics and also had a clear view and determination to solve them. He made his strategy his own and was able to visualise the main stages on the way to his goal. In fact, he saw his critical achievements as merely one more step toward the next level of advancement.
When his scientific work started, Albert Einstein realised the inadequacies of Newtonian mechanics and his special theory of relativity emanated from an attempt to reconcile the laws of mechanics with the laws of the electromagnetic field.
He worked on classical problems of statistical mechanics and problems in which they were merged with quantum theory. This paved the way for an explanation of the Brownian movement of molecules. He explored the properties of light with a low radiation density, and his observations and survey laid the foundation of the photon theory of light.
He postulated the correct interpretation of the special theory of relativity in the early days of Berlin and also furnished a theory of gravitation. He published his paper on the general theory of relativity in 1916. At this point in time, he also contributed to the problems of the theory of radiation and statistical mechanics.
He embarked on the construction of unified field theories in the 1920s, and he was also working on the probabilistic interpretation of quantum theory. He preserved this work in America.
By developing a quantum theory of monoatomic gas, he contributed to statistical mechanics. He also did valuable work in connection with atomic transition probabilities and relativistic cosmology.
After taking retirement, he continued to work towards the unification of the basic concepts of physics. He took the opposite approach to geometrisation as the majority of physicists.
Albert Einstein: Important Works
His important works include:
Special Theory of Relativity (1905),
Relativity (English translations, 1920 and 1950),
General Theory of Relativity (1916),
Investigations on Theory of Brownian Movement (1926), and
The Evolution of Physics (1938).
Non-scientific works are:
About Zionism (1930),
Why War? (1933),
My Philosophy (1934), and
Out of My Later Years (1950)
Albert Einstein: Awards and Honours
Barnard Medal (1920) Nobel Prize in Physics (1921) Matteucci Medal (1921) ForMemRS (1921) Copley Medal (1925) Gold Medal (1926) Max Planck Medal (1929)
Albert Einstein: Legacy
The work of Einstein continues to win Nobel Prizes for successful physicists.
A Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of Bose-Einstein condensates in 1995.
Black holes are now known to number in the thousands.
Also, new generations of space satellites have continued to verify the cosmology of Einstein.
Without Nobel Laureate Albert Einstein’s many contributions to theory of quantum mechanics, enhanced oil recovery in Oil & Gas Industry would be but a dream. On his birthday & International Day of #Mathematics , #ONGCCelebrates India’s pivotal role in its development. @g20org pic.twitter.com/z1tCPSnX1Y — Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC) (@ONGC_) March 14, 2023
Warm tributes to Nobel laureate Albert Einstein, 20th century’s most celebrated scientist.After contributing to theoretical development of nuclear physics,he later spoke out against the use of nuclear weapons & started believing in the Gandhian philosophy preaching non-violence. pic.twitter.com/TovBlAavDj — Dr Harsh Vardhan (@drharshvardhan) March 14, 2023
Albert Einstein, born on this day, met fellow Nobel Prize laureate Rabindranath Tagore at his home in Germany on 14 July 1930. The two minds explored the concepts of science, religion and philosophy. Read an excerpt from their conversation: https://t.co/h638caaAYZ #Einstein144 pic.twitter.com/GeCjDSX8A0 — The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) March 14, 2023
On April 17, 1955, Einstein experienced internal bleeding caused by a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm that Rudolph Nissen had previously surgically confirmed in 1948. He brought with him to the hospital a speech that he had prepared for a television show to celebrate the seventh anniversary of the State of Israel, but he did not finish it in time. Einstein refused the operation, saying: "I want to go when I want. It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I've done my part; it's time to go. I'll do it elegantly."
Get here current GK and GK quiz questions in English and Hindi for India , World, Sports and Competitive exam preparation. Download the Jagran Josh Current Affairs App .
- September Important Days 2024
- Daughters Day Quotes, Wishes
- Top Cities to Study Abroad
- NPS Vatsalya Scheme
- Daughters Day 2024
- Virat Kohli Net Worth
- New Delhi CM List
- India PM List 2024
- President of India List
- Daughters Day Quotes
Latest Education News
Brain Teaser: Only Geniuses with an IQ Over 135 Can Beat This 9-Second Brain Teaser Challenge!
UPSC Mains Question Paper 2024: Download Essay and GS Papers
Today’s School Assembly News Headlines (23rd September): PM Modi, Biden Firm up Drone Deal, Setting up of Semiconductor Plant in India, India Probing Netflix for Racial Discrimination and More
Top 5 Words Of the Day For Morning School Assembly: 23rd September 2024
Prove Your Genius! Only 3 in 39 People with High IQ Can Spot the Hidden Bell
Brain Teaser IQ Test: Test Your Brainpower! Only High IQ Individuals Can Solve This Matchstick Math Puzzle Fast!
Brain Teaser: Feeling Smart? Only People With a High IQ Above 150 Can Find the Robot in 7 Seconds!
Optical Illusion: Only People with Flawless Vision Ace This 15-Second IQ Test – Can You Find the Hidden Ring?
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Can You Find the Hidden Candle? Prove Your IQ Is Above 125
What is the Difference between Asteroid, Comet, and Meteor?
RRB NTPC Recruitment Notification 2024: Registration Link for 12th (UG) 3445 Vacancies Available at rrbapply.gov.in From 21 September
CBDT Launches Direct Tax Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme: Settle Tax Disputes Easily; Check Forms and Benefits
IPL 2025 मेगा ऑक्शन कब और कहां, ये दो शहर रेस में सबसे आगे, देखें पूरी डिटेल्स
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz (17-22 Sept 2024): Boost Your Exam Score With Top Insights!
Current Affairs Quiz 17 September 2024: Atishi Succeeds Arvind Kejriwal as New Delhi CM
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz Hindi: 17 सितंबर 22 सितंबर 2024
Unified Pension Scheme: लाभ, पात्रता, न्यूनतम पेंशन राशि, पेंशन कैलकुलेटर सहित सभी डिटेल्स यहां देखें
टेस्ट क्रिकेट में सर्वाधिक विकेट लेने वाले टॉप 10 गेंदबाज कौन है? देखें यहां
उत्तर प्रदेश के इन जिलों को मिली नई ई-बसों की सौगात, देखें किराया और बसों का रूट
उत्तर प्रदेश के 8 रेलवे स्टेशनों को मिले नए नाम, यहां देखें सभी नाम
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
9 Things You May Not Know About Albert Einstein
By: Evan Andrews
Updated: August 29, 2018 | Original: October 26, 2015

1. Einstein didn’t fail math as a child.

Underachieving school kids have long taken solace in the claim that Einstein flunked math as a youth, but the records show that he was actually an exceptional, if not reluctant, student. He scored high grades during his school days in Munich, and was only frustrated by what he described as the “mechanical discipline” demanded by his teachers. The future Nobel Laureate dropped out of school at age 15 and left Germany to avoid state-mandated military service, but before then he was consistently at the top of his class and was even considered something of a prodigy for his grasp of complex mathematical and scientific concepts. When later presented with a news article claiming he’d failed grade-school math, Einstein dismissed the story as a myth and said, “Before I was 15 I had mastered differential and integral calculus.”
2. No one knows what happened to his first daughter.
In 1896, Einstein renounced his German citizenship and enrolled at the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich. There, he began a passionate love affair with Mileva Maric, a fellow physicist-in-training originally from Serbia. The couple later married and had two sons after graduating, but a year before they tied the knot, Maric gave birth to an illegitimate daughter named Lieserl. Einstein never spoke about the child to his family, and biographers weren’t even aware of her existence until examining his private papers in the late-1980s. Her fate remains a mystery to this day. Some scholars think Lieserl died from scarlet fever in 1903, while others believe she survived the sickness and was given up for adoption in Maric’s native Serbia.
3. It took Einstein nine years to get a job in academia.

Einstein showed flashes of brilliance during his years at the Zurich Polytechnic, but his rebellious personality and penchant for skipping classes saw his professors give him less than glowing recommendations upon his graduation in 1900. The young physicist later spent two years searching for an academic position before settling for a gig at the Swiss patent office in Bern. Though menial, the job turned out to be a perfect fit for Einstein, who found he could breeze through his office duties in a few hours and spend the rest of the day writing and conducting research. In 1905—often called his “miracle year”—the lowly clerk published four revolutionary articles that introduced his famous equation E=mc2 and the theory of special relativity. While the discoveries marked Einstein’s entrance onto the physics world stage, he didn’t win a full professorship until 1909—nearly a decade after he had left school.
4. He offered his wife his Nobel Prize as part of their divorce settlement.

After his marriage to Mileva Maric hit the rocks in the early 1910s, Einstein left his family, moved to Berlin and started a new relationship with his cousin, Elsa. He and Maric finally divorced several years later in 1919. As part of their separation agreement, Einstein promised her an annual stipend plus whatever money he might receive from the Nobel Prize—which he was supremely confident he would eventually win. Maric agreed, and Einstein later handed over a small fortune upon receiving the award in 1922 for his work on the photoelectric effect. By then, he had already remarried to Elsa, who remained his wife until her death in 1936.
5. A solar eclipse helped make Einstein world famous.

In 1915, Einstein published his theory of general relativity, which stated that gravitational fields cause distortions in the fabric of space and time. Because it was such a bold rewriting of the laws of physics, the theory remained controversial until May 1919, when a total solar eclipse provided the proper conditions to test its claim that a supermassive object—in this case the sun—would cause a measurable curve in the starlight passing by it. Hoping to prove Einstein’s theory once and for all, English astronomer Arthur Eddington journeyed to the coast of West Africa and photographed the eclipse. Upon analyzing the pictures, he confirmed that the sun’s gravity had deflected the light by roughly 1.7 arc-seconds—exactly as predicted by general relativity. The news made Einstein an overnight celebrity. Newspapers hailed him as the heir to Sir Isaac Newton, and he went on to travel the world lecturing on his theories about the cosmos. According to Einstein biographer Walter Isaacson, in the six years after the 1919 eclipse, more than 600 books and articles were written about the theory of relativity.
6. The FBI spied on him for decades.
Shortly before Hitler rose to power in 1933, Einstein left Berlin for the United States and took a position at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. His support for pacifist, civil rights and left-wing causes had already drawn suspicion from J. Edgar Hoover’s FBI, and after his arrival on American shores, the Bureau launched what would eventually become a 22-year surveillance campaign. Agents listened to the physicist’s phone calls, opened his mail and rooted through his trash in the hope of unmasking him as a subversive or a Soviet spy. They even investigated tips that he was building a death ray. The project came up empty handed, but by the time Einstein died in 1955, his FBI file totaled a whopping 1,800 pages.
7. Einstein urged the building of the atomic bomb—and later became a proponent of nuclear disarmament.
In the late-1930s, Einstein learned that new research had put German scientists on a path toward creating the atom bomb. The prospect of a doomsday weapon in the hands of the Nazis convinced him to set aside his pacifist principles and team up with Hungarian physicist Leo Szilard, who helped him write a letter urging President Franklin D. Roosevelt to conduct atomic research. Though Einstein never participated directly in the Manhattan Project, he later expressed deep regrets about his minor role in bringing about the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings. “Had I known that the Germans would not succeed in producing an atomic bomb, I never would have lifted a finger,” he told Newsweek. He went on to become an impassioned advocate of nuclear disarmament, controls on weapons testing and unified world government. Shortly before his death in 1955, he joined with philosopher Bertrand Russell in signing the “Russell-Einstein Manifesto,” a public letter that stressed the risks of nuclear war and implored governments to “find peaceful means for the settlement of all disputes between them.”
8. He was asked to be president of Israel.

Though not traditionally religious, Einstein felt a deep connection to his Jewish heritage and often spoke out against anti-Semitism. He was never a staunch Zionist, but when head of state Chaim Weizmann died in 1952, the Israeli government offered to appoint him as the nation’s second president. The 73-year-old wasted little time in declining the honor. “All my life I have dealt with objective matters,” Einstein wrote in a letter to the Israeli ambassador, “hence I lack both the natural aptitude and the experience to deal properly with people and to exercise official function.”
9. Einstein’s brain was stolen after his death.

Einstein died in April 1955 from an abdominal aortic aneurysm. He had requested that his body be cremated, but in a bizarre incident, Princeton pathologist Thomas Harvey removed his famous brain during his autopsy and kept it in the hope of unlocking the secrets of his genius. After winning a reluctant approval from Einstein’s son, Harvey later had the brain cut into pieces and sent to various scientists for research. A handful of studies have been conduced on it since the 1980s, but most have either been dismissed or discredited. Perhaps the most famous came in 1999, when a team from a Canadian university published a controversial paper claiming Einstein possessed unusual folds on his parietal lobe, a part of the brain associated with mathematical and spatial ability.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Albert Einstein (born March 14, 1879, Ulm, Württemberg, Germany—died April 18, 1955, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.) was a German-born physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity and won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921 for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. Einstein is generally considered the most ...
Physicist Albert Einstein developed the theory of relativity and won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics. Read about his inventions, IQ, wives, death, and more.
Albert Einstein was born in Ulm, [21] in the Kingdom of Württemberg in the German Empire, on 14 March 1879. ... He was asked to lend his support by writing a letter, with Szilárd, to President Roosevelt, recommending the US pay attention and engage in its own nuclear weapons research.
Born in Germany in 1879, Albert Einstein is one of the most celebrated scientists of the Twentieth Century. His theories on relativity laid the framework for a new branch of physics, and Einstein's E = mc 2 on mass-energy equivalence is one of the most famous formulas in the world. In 1921, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his contributions to theoretical physics and the ...
Albert Einstein was born at Ulm, in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879. Six weeks later the family moved to Munich, where he later on began his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Later, they moved to Italy and Albert continued his education at Aarau, Switzerland and in 1896 he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be ...
Einstein's Early Life (1879-1904) Born on March 14, 1879, in the southern German city of Ulm, Albert Einstein grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Munich.
Jennifer Rosenberg. Updated on August 26, 2019. Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879-April 18, 1955), a German-born theoretical physicist who lived during the 20th century, revolutionized scientific thought. Having developed the Theory of Relativity, Einstein opened the door for the development of atomic power and the creation of the atomic bomb.
Einstein's early years were marked by curiosity and a strong interest in science. He was known to be a quiet and introverted child, spending much of his time reading and conducting experiments. When Einstein was five years old, his family moved to Munich, Germany. However, his parents' marriage began to deteriorate and they eventually separated.
Albert Einstein, (born March 14, 1879, Ulm, Württemberg, Ger.—died April 18, 1955, Princeton, N.J., U.S.), German-born Swiss-U.S. scientist.Born to a Jewish family in Germany, he grew up in Munich, and in 1894 he moved to Aarau, Switz. He attended a technical school in Zürich (graduating in 1900) and during this period renounced his German citizenship; stateless for some years, he became a ...
Albert Einstein - Physics, Relativity, Nobel Prize: After graduation in 1900, Einstein faced one of the greatest crises in his life. Because he studied advanced subjects on his own, he often cut classes; this earned him the animosity of some professors, especially Heinrich Weber. Unfortunately, Einstein asked Weber for a letter of recommendation. Einstein was subsequently turned down for every ...
Albert Einstein. The Nobel Prize in Physics 1921. Born: 14 March 1879, Ulm, Germany. Died: 18 April 1955, Princeton, NJ, USA. Affiliation at the time of the award: Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut (now Max-Planck-Institut) für Physik, Berlin, Germany. Prize motivation: "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the ...
A brief biography of Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879 - April 18, 1955), the scientist whose theories changed the way we think about the universe.
Before E=MC2. Einstein was born in Germany in 1879. Growing up, he enjoyed classical music and played the violin. One story Einstein liked to tell about his childhood was when he came across a magnetic compass. The needle's invariable northward swing, guided by an invisible force, profoundly impressed him as a child.
Albert Einstein was a theoretical physicist and the most famous scientist in human history. He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics, alongside quantum mechanics. He is perhaps best known in popular culture for his mass/energy equivalence formula E=mc2. In 1921 he received the Nobel Prize in ...
Albert Einstein aged 14 (Image credit: Getty Images) However, Einstein could not find a teaching position, and began work in a Bern patent office in 1901, according to his Nobel Prize biography ...
Einstein died on April 18, 1955, in Princeton, New Jersey. Element 99 was named einsteinium (Es) in his honor. One of the world's most famous scientists. In 1922, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics. In 1939 Einstein wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt warning him that this scientific knowledge could lead to Germany's developing an atomic bomb.
Go here to watch a video about Albert Einstein. Occupation: Scientist and Inventor. Born: March 14,1879 Ulm, in Germany. Died: 18 April 1955 in Princeton, New Jersey. Best known for: Theory of Relativity and E=mc2. Biography: Albert Einstein was a scientist in the early 1900s. He came up with some of the most important discoveries and theories ...
Albert Einstein is arguably one of the most influential individuals in the modern world. He played a role in the development and physics, and also dabbled with the politics of his day-even though at a small scale level. During the period around the First World War, Einstein was among the individuals that were against the usage of violence in ...
In 1944 he made a contribution to the war effort by hand writing his 1905 paper on special relativity and putting it up for auction. It raised six million dollars, the manuscript today being in the Library of Congress. ... C Seelig, Albert Einstein : A Documentary Biography (London, 1956). H-J Treder (ed.), Einstein-Centenarium 1979 (German ...
9. Albert's theory of relativity helped scientists understand how the universe works. Albert's theory showed that the effects of gravity result from the ways that objects affect space and time.These interactions can only been seen on enormous objects like the planets.As a result, Albert's general theory of relativity describes the way that amazing phenomena like the movement of planets ...
Albert Einstein was born to Jewish parents in Ulm, Germany, on March 14, 1879. He did not do well in school, but he did take an interest in mathematics and science. While at college, he studied physics and math. After graduating in 1900, he worked in a government office. Meanwhile, he continued studying physics on his own.
Albert Einstein Biography: He was born on 14 March 1879 in Ulm,Wurttemberg, Germany. He was a physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity and won the Nobel Prize for ...
Her fate remains a mystery to this day. Some scholars think Lieserl died from scarlet fever in 1903, while others believe she survived the sickness and was given up for adoption in Maric's ...