- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

5 Tools zur Literaturrecherche für die optimale Recherche (+2 Bonustools)

5 outils de revue de littérature pour réussir vos recherches (+2 outils bonus)

标题 :人工智能在系统文献综述中的作用
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of thesis
Did you know.
In high school, college, or graduate school, students often have to write a thesis on a topic in their major field of study. In many fields, a final thesis is the biggest challenge involved in getting a master's degree, and the same is true for students studying for a Ph.D. (a Ph.D. thesis is often called a dissertation ). But a thesis may also be an idea; so in the course of the paper the student may put forth several theses (notice the plural form) and attempt to prove them.
Examples of thesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'thesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
in sense 3, Middle English, lowering of the voice, from Late Latin & Greek; Late Latin, from Greek, downbeat, more important part of a foot, literally, act of laying down; in other senses, Latin, from Greek, literally, act of laying down, from tithenai to put, lay down — more at do
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 3a(1)
Dictionary Entries Near thesis
the sins of the fathers are visited upon the children
thesis novel
Cite this Entry
“Thesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/thesis. Accessed 20 Sep. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of thesis, more from merriam-webster on thesis.
Nglish: Translation of thesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of thesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about thesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, plural and possessive names: a guide, the difference between 'i.e.' and 'e.g.', more commonly misspelled words, absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, weird words for autumn time, much ado about ‘folie à deux’, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 9 superb owl words, 15 words that used to mean something different, games & quizzes.


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Thesis
I. What is a Thesis?
The thesis (pronounced thee -seez), also known as a thesis statement, is the sentence that introduces the main argument or point of view of a composition (formal essay, nonfiction piece, or narrative). It is the main claim that the author is making about that topic and serves to summarize and introduce that writing that will be discussed throughout the entire piece. For this reason, the thesis is typically found within the first introduction paragraph.
II. Examples of Theses
Here are a few examples of theses which may be found in the introductions of a variety of essays :
In “The Mending Wall,” Robert Frost uses imagery, metaphor, and dialogue to argue against the use of fences between neighbors.
In this example, the thesis introduces the main subject (Frost’s poem “The Mending Wall”), aspects of the subject which will be examined (imagery, metaphor, and dialogue) and the writer’s argument (fences should not be used).
While Facebook connects some, overall, the social networking site is negative in that it isolates users, causes jealousy, and becomes an addiction.
This thesis introduces an argumentative essay which argues against the use of Facebook due to three of its negative effects.
During the college application process, I discovered my willingness to work hard to achieve my dreams and just what those dreams were.
In this more personal example, the thesis statement introduces a narrative essay which will focus on personal development in realizing one’s goals and how to achieve them.
III. The Importance of Using a Thesis
Theses are absolutely necessary components in essays because they introduce what an essay will be about. Without a thesis, the essay lacks clear organization and direction. Theses allow writers to organize their ideas by clearly stating them, and they allow readers to be aware from the beginning of a composition’s subject, argument, and course. Thesis statements must precisely express an argument within the introductory paragraph of the piece in order to guide the reader from the very beginning.
IV. Examples of Theses in Literature
For examples of theses in literature, consider these thesis statements from essays about topics in literature:
In William Shakespeare’s “ Sonnet 46,” both physicality and emotion together form powerful romantic love.
This thesis statement clearly states the work and its author as well as the main argument: physicality and emotion create romantic love.
In The Scarlet Letter, Nathaniel Hawthorne symbolically shows Hester Prynne’s developing identity through the use of the letter A: she moves from adulteress to able community member to angel.
In this example, the work and author are introduced as well as the main argument and supporting points: Prynne’s identity is shown through the letter A in three ways: adulteress, able community member, and angel.
John Keats’ poem “To Autumn” utilizes rhythm, rhyme, and imagery to examine autumn’s simultaneous birth and decay.
This thesis statement introduces the poem and its author along with an argument about the nature of autumn. This argument will be supported by an examination of rhythm, rhyme, and imagery.
V. Examples of Theses in Pop Culture
Sometimes, pop culture attempts to make arguments similar to those of research papers and essays. Here are a few examples of theses in pop culture:

America’s food industry is making a killing and it’s making us sick, but you have the power to turn the tables.
The documentary Food Inc. examines this thesis with evidence throughout the film including video evidence, interviews with experts, and scientific research.

Orca whales should not be kept in captivity, as it is psychologically traumatizing and has caused them to kill their own trainers.
Blackfish uses footage, interviews, and history to argue for the thesis that orca whales should not be held in captivity.
VI. Related Terms
Just as a thesis is introduced in the beginning of a composition, the hypothesis is considered a starting point as well. Whereas a thesis introduces the main point of an essay, the hypothesis introduces a proposed explanation which is being investigated through scientific or mathematical research. Thesis statements present arguments based on evidence which is presented throughout the paper, whereas hypotheses are being tested by scientists and mathematicians who may disprove or prove them through experimentation. Here is an example of a hypothesis versus a thesis:
Hypothesis:
Students skip school more often as summer vacation approaches.
This hypothesis could be tested by examining attendance records and interviewing students. It may or may not be true.
Students skip school due to sickness, boredom with classes, and the urge to rebel.
This thesis presents an argument which will be examined and supported in the paper with detailed evidence and research.
Introduction
A paper’s introduction is its first paragraph which is used to introduce the paper’s main aim and points used to support that aim throughout the paper. The thesis statement is the most important part of the introduction which states all of this information in one concise statement. Typically, introduction paragraphs require a thesis statement which ties together the entire introduction and introduces the rest of the paper.
VII. Conclusion
Theses are necessary components of well-organized and convincing essays, nonfiction pieces, narratives , and documentaries. They allow writers to organize and support arguments to be developed throughout a composition, and they allow readers to understand from the beginning what the aim of the composition is.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .

- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Figures in Research Paper – Examples and Guide

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college

How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 straightforward steps to craft an a-grade dissertation.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
Writing a dissertation or thesis is not a simple task. It takes time, energy and a lot of will power to get you across the finish line. It’s not easy – but it doesn’t necessarily need to be a painful process. If you understand the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis, your research journey will be a lot smoother.
In this post, I’m going to outline the big-picture process of how to write a high-quality dissertation or thesis, without losing your mind along the way. If you’re just starting your research, this post is perfect for you. Alternatively, if you’ve already submitted your proposal, this article which covers how to structure a dissertation might be more helpful.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.
How do I write the introduction chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this post .

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

For more information about the results chapter , check out this post for qualitative studies and this post for quantitative studies .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of thesis in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- I wrote my thesis on literacy strategies for boys .
- Her main thesis is that children need a lot of verbal stimulation .
- boilerplate
- composition
- corresponding author
- dissertation
- essay question
- peer review
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
thesis | Intermediate English
Examples of thesis, collocations with thesis.
These are words often used in combination with thesis .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of thesis
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
porch pirate
someone who steals parcels that have been left outside people's houses for them

A finger in every pie: phrases with the word ‘finger’

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Intermediate Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add thesis to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add thesis to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on 25 July 2024.
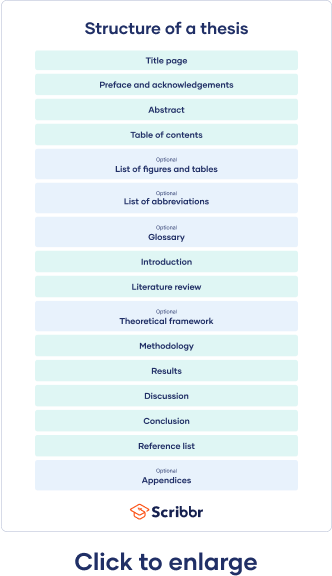
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation , it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarise the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement to complete a PhD program.
- In many countries, particularly the UK, a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: ‘Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the “Noble Savage” on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807’ by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: ‘”A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man”: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947’ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the ‘Insert Caption’ feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetised list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialised or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetise the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyses the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasise what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense, your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation, you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimising confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2024, July 25). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 18 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/thesis-ultimate-guide/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- Why students love us
- Rebels Blog
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
Thesis vs. Theses: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters

Understanding the difference between 'thesis' and 'theses' is important for students and researchers alike. These terms, while similar, have distinct meanings and implications in academic writing. A thesis usually refers to a single document written for a master's degree, while theses is the plural form, referring to multiple such documents. This article will explore these differences and why they matter in the academic world.
Key Takeaways
- A thesis is a single document for a master's program, while theses refers to multiple such documents.
- Thesis statements are crucial as they outline the main argument of a paper.
- Understanding the context of thesis writing can improve academic success.
- Crafting a strong thesis statement requires clarity and focus.
- The process of defending a thesis is an important milestone in graduate studies.
Understanding Thesis and Theses in Academic Contexts
Defining thesis and theses.
In academic writing, the terms thesis and theses are often confused. A thesis typically refers to a substantial research project that a student completes for a master's degree, while theses is the plural form, referring to multiple such projects. Understanding this distinction is crucial for your academic journey.
Historical Perspectives on Thesis
Historically, the concept of a thesis has evolved. In earlier times, a thesis was primarily a statement or argument presented for debate. Today, it represents a comprehensive research project that showcases your ability to conduct independent research. This shift highlights the growing importance of original contributions to knowledge in academia.
Cultural Variations in Usage
Cultural differences also play a role in how these terms are used. In the United States, a thesis is often associated with master's programs, while a dissertation is linked to doctoral studies. In contrast, some European countries may use the term thesis for both levels. This variation can affect your understanding of academic expectations in different regions.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for navigating your academic path effectively. By grasping the differences between a thesis and theses, you can better prepare for the challenges ahead in your research and writing endeavors.
For more insights on academic writing, check out resources from Research Rebels that provide valuable tips on crafting effective thesis statements and navigating the complexities of academic writing.
The Role of Thesis Statements in Research
Importance of a strong thesis statement.
A strong thesis statement is essential for guiding your research. It serves as a roadmap, helping you stay focused on your main argument. Without it, your paper may lack direction and coherence. A well-crafted thesis statement not only clarifies your position but also engages your reader, making them eager to learn more about your findings.
Components of an Effective Thesis Statement
To create an effective thesis statement, consider these key components:
- Clarity : Clearly express your main argument.
- Specificity : Focus on a particular aspect of your topic.
- Debatable : Present an argument that invites discussion.
- Evidence : Support your claim with relevant examples.
- Coherence : Ensure all parts of your statement connect logically.
Common Pitfalls in Thesis Development
When developing your thesis statement, avoid these common mistakes:
- Being too vague or general.
- Making a statement that is not arguable.
- Failing to provide supporting evidence.
- Overcomplicating your statement with unnecessary details.
By focusing on these elements, you can craft a thesis statement that not only enhances your research but also strengthens your overall argument. Remember, a strong thesis statement is the backbone of your academic writing, guiding both you and your readers through your work. For more resources on improving your research skills, check out this guide .
Distinguishing Between Thesis and Theses
Key differences in definition.
Understanding the difference between a thesis and theses is essential for academic success. A thesis is a comprehensive document that presents original research, typically required for a master's degree. In contrast, theses refer to multiple works of this nature. Each thesis embodies the results of original research and supports a specific viewpoint, often written by students pursuing advanced degrees.
Contextual Usage in Academia
In academic contexts, the term "thesis" is often used to describe the singular work, while "theses" is the plural form. This distinction is crucial when discussing your own work or referencing others. For example, when you say, "I am writing my thesis," it indicates a singular focus on your research project. Conversely, when discussing various research projects, you would refer to them as "theses."
Implications for Graduate Students
For graduate students, understanding these terms can impact how you communicate your research. Misusing these terms may lead to confusion among peers and faculty. Therefore, always ensure you use the correct form based on the context. This clarity not only enhances your academic communication but also reflects your understanding of academic conventions.
| Term | Definition | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Thesis | A document presenting original research for a master's degree. | "My thesis explores climate change." |
| Theses | The plural form of thesis, referring to multiple research documents. | "Many theses address similar topics." |
The Process of Crafting a Thesis Statement
Researching your topic.
When you start your thesis journey, the first step is to research your topic . This involves gathering information from various sources to understand the existing knowledge in your field. A well-researched topic lays the foundation for a strong thesis statement. Here are some steps to guide you:
- Identify credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Take notes on key points and arguments related to your topic.
- Look for gaps in the existing research that your thesis could address.
Drafting and Revising Your Thesis Statement
Once you have a solid understanding of your topic, you can begin drafting your thesis statement. This statement should clearly express your main argument or claim. Remember, it’s okay to revise your thesis as you learn more. Here’s how to approach this:
- Start with a working thesis that outlines your main argument.
- As you gather more information, refine your thesis to make it more specific and focused.
- Ensure that your thesis is debatable, inviting discussion and analysis.
Seeking Feedback and Refinement
After drafting your thesis statement, it’s crucial to seek feedback. This can help you identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement. Consider the following:
- Share your thesis with peers or mentors for their insights.
- Be open to constructive criticism and use it to refine your statement.
- Remember, a strong thesis statement is a living document that may evolve as your research progresses.
By following these steps, you can craft a thesis statement that not only guides your writing but also engages your readers effectively. For additional resources, consider exploring tools like the [ Thesis Success Essentials ](https://www.researchrebels.com/products/thesis-success-essentials-free-25-templates) which offer templates to help you through this process.
The Impact of Thesis on Academic Success

Thesis as a Reflection of Research Skills
Completing a thesis is a significant milestone in your academic journey. It showcases your ability to conduct independent research and demonstrates your mastery of a specific subject. This process not only enhances your research skills but also prepares you for future academic challenges. A well-executed thesis can lead to recognition from peers and professors, which is crucial for your academic reputation.
Influence on Future Academic Opportunities
Your thesis can open doors to various academic opportunities. Many graduate programs and research positions look for candidates who have successfully completed a thesis. This accomplishment signals to potential advisors and employers that you possess the skills necessary for advanced research. Additionally, your thesis may serve as a foundation for future publications, further enhancing your academic profile.
Role in Professional Development
Beyond academia, a thesis can significantly impact your career. Completing a thesis demonstrates your ability to manage complex projects, conduct thorough research, and communicate effectively. These skills are highly valued in many professional fields. Moreover, the process of writing a thesis often involves collaboration with faculty and peers, helping you build a network that can be beneficial in your career.
| Aspect | Impact on Academic Success |
|---|---|
| Research Skills | Enhanced critical thinking |
| Academic Opportunities | Pathway to advanced studies |
| Professional Development | Valuable career skills |
In summary, the impact of your thesis on academic success is profound. It not only reflects your research capabilities but also influences your future opportunities in both academia and your professional life. Embrace this journey, as it is a vital step toward achieving your goals.
Navigating the Thesis Defense
Preparing for the defense.
Preparing for your thesis defense is crucial. This is your chance to showcase your hard work and research. Start by reviewing your thesis thoroughly. Make sure you understand every part of it, especially the sections that received feedback. Organize a mock defense with friends or mentors to practice. This will help you get comfortable with the format and types of questions you might face.
Common Questions and Challenges
During the defense, you may encounter various questions. Here are some common ones:
- What motivated your research?
- How did you choose your methodology?
- What are the implications of your findings?
Anticipating these questions can help you prepare better. Think about potential weaknesses in your work and how you would address them.
Strategies for Success
To ensure a successful defense, consider these strategies:
- Create a clear presentation that highlights your research questions, methods, findings, and conclusions.
- Practice your delivery multiple times to build confidence.
- Seek feedback from peers or mentors to refine your presentation.
- Arrive early on the day of your defense to get comfortable with the environment.
- Dress professionally to convey seriousness.
By following these steps, you can navigate your thesis defense with confidence and clarity. Remember, this is not just an exam; it’s an opportunity to discuss your research and its significance in your field. Embrace it!
The Evolution of Thesis Writing
Historical changes in thesis requirements.
The concept of a thesis has evolved significantly over the years. In the past, a thesis was often seen as a mere formality, but today, it is a critical component of academic achievement. Understanding this evolution is essential for students. Initially, theses were primarily focused on theoretical frameworks, but now they often emphasize practical applications and real-world relevance. For instance, in the United States, a thesis typically refers to master's level work, while a dissertation is associated with doctoral studies. This distinction highlights the growing complexity and depth of research expected at different academic levels.
Modern Trends in Thesis Composition
In recent years, the approach to thesis writing has shifted towards a more collaborative and interdisciplinary model. Students are encouraged to engage with various fields, integrating diverse perspectives into their research. This trend is supported by advancements in technology, which facilitate communication and collaboration. For example, platforms like WhatsApp allow students to connect with peers and mentors, making it easier to share ideas and receive feedback. As a result, students can learn how to write a thesis fast and how to write thesis easily by leveraging these tools.
Technological Influences on Thesis Writing
Technology has transformed the way students approach thesis writing. With access to vast online resources, students can conduct research more efficiently than ever before. The integration of digital tools has made it easier to organize data, analyze findings, and present results. This evolution not only enhances the quality of research but also empowers students to express their ideas more clearly. As you navigate your thesis journey, remember that embracing these technological advancements can significantly improve your writing process.
The Interrelationship Between Thesis and Research Questions
Defining research questions.
Your research question is the starting point of your academic journey. It guides your study and helps you focus on what you want to explore. A well-defined research question is crucial because it sets the direction for your entire project. Without a clear question, your research may lack focus and depth.
Aligning Thesis Statements with Research Objectives
Once you have your research question, the next step is to develop your thesis statement. This statement is your main argument or conclusion based on the findings from your research. Think of it as the bridge connecting your question to your conclusions. Here’s how to align them effectively:
- Identify the core components of your research question.
- Gather and analyze relevant data and literature.
- Refine your question based on your findings.
- Distill the refined question into a clear thesis statement.
The Feedback Loop Between Thesis and Questions
As you progress in your research, your initial question may evolve. This is a natural part of the process. Your thesis statement should also adapt to reflect these changes. This dynamic relationship ensures that your work remains relevant and insightful. For example, if your research leads you to new findings, you might need to adjust your thesis to incorporate these insights. This feedback loop is essential for producing a robust academic argument.
In summary, the relationship between your thesis and research questions is not static; it’s a continuous cycle of inquiry and refinement. By understanding this interrelationship, you can enhance the quality and impact of your academic work.
For more resources on crafting effective research questions and thesis statements, check out Thesis Action Plan and Research Proposal Compass .
Exploring Various Thesis Formats
Types of thesis statements.
When writing a thesis, it's essential to understand the different types of thesis statements you can use. Each type serves a unique purpose and can shape your research in various ways. Here are the main types:
- Analytical Thesis Statement : This type breaks down a complex issue into its parts and analyzes them. It requires critical thinking and is often used in research papers.
- Argumentative Thesis Statement : This statement presents a clear argument on a specific topic, aiming to convince the reader of your viewpoint. It should be debatable and supported by evidence.
- Expository Thesis Statement : This type explains a topic or idea without taking a stance. It provides information and is often used in informative essays.
Structural Components of a Thesis
While the format may vary, most theses share common structural components. Here’s a typical outline:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Abstract | A brief summary of the entire work. |
| Introduction | Introduces the research problem and its significance. |
| Literature Review | Analyzes existing research relevant to your study. |
| Methodology | Details the research methods and data collection processes. |
| Results/Findings | Presents the outcomes of your research. |
| Discussion | Analyzes and interprets findings, connecting them to the broader field. |
| Conclusion | Summarizes main takeaways and suggests future research avenues. |
| References | Lists all sources used in your research. |
Variations Across Disciplines
Different academic fields may have specific requirements for thesis formats. For example:
- In the sciences, a more structured approach with detailed methodologies is common.
- In the humanities, a narrative style may be preferred, allowing for more creative expression.
Understanding these variations is crucial for tailoring your thesis to meet the expectations of your discipline. By recognizing the different formats and structures, you can better prepare your thesis for success.
The Importance of Clarity in Thesis Statements

Techniques for Achieving Clarity
To ensure your thesis statement is clear, consider the following techniques:
- Be Specific : Avoid vague language. Clearly state your main argument.
- Use Simple Language : Choose words that are easy to understand.
- Limit Length : Keep your thesis statement concise, ideally one or two sentences.
Examples of Clear vs. Vague Thesis Statements
| Clear Thesis Statement | Vague Thesis Statement |
|---|---|
| "Social media increases anxiety among teenagers by promoting unrealistic standards." | "Social media affects people." |
| "Climate change is primarily caused by human activities such as burning fossil fuels." | "Climate change is bad for the environment." |
The Role of Clarity in Reader Engagement
A clear thesis statement not only helps you stay focused but also engages your readers. When they understand your main argument, they are more likely to follow your reasoning and stay interested in your work. A well-defined thesis acts as a roadmap , guiding readers through your research and findings.
In summary, clarity in your thesis statement is essential for effective communication. By employing techniques to enhance clarity, you can create a strong foundation for your academic writing. Remember, a clear thesis statement is not just beneficial for your readers; it also helps you maintain focus and direction in your writing process. For additional support, consider resources like the Thesis Action Plan from Research Rebels, which offers structured guidance to help you develop a clear and effective thesis statement.
Future Trends in Thesis Writing
As you look ahead in your academic journey, it's essential to understand the future trends in thesis writing. These trends are shaped by advancements in technology and changing academic expectations.
Emerging Topics in Thesis Research
One significant trend is the rise of interdisciplinary research. This approach encourages you to combine insights from different fields, leading to innovative solutions and broader perspectives. For instance, topics like climate change, artificial intelligence, and public health are increasingly popular as they require knowledge from various disciplines.
The Role of Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches not only enhance the depth of your research but also make your thesis more relevant in today’s complex world. By integrating methods and theories from multiple fields, you can address real-world problems more effectively.
Anticipating Changes in Academic Standards
As academic standards evolve, you may find that institutions are placing greater emphasis on the practical applications of research. This shift means that your thesis should not only contribute to academic knowledge but also demonstrate how it can be applied in real-world scenarios.
In summary, staying informed about these trends will help you craft a thesis that is not only academically rigorous but also relevant and impactful. Embrace these changes, and you will be well-prepared for the future of academic writing!
As we look ahead, the future of thesis writing is changing fast. With new tools and methods, students can tackle their projects with less stress and more confidence. If you're feeling lost or anxious about your thesis, don’t worry! Visit our website to discover how our Thesis Action Plan can guide you step-by-step to success. Don’t wait—take the first step towards a smoother thesis journey today!
In summary, understanding the difference between a thesis and theses is essential for students and scholars alike. A thesis is a significant piece of writing that showcases a student's research and findings, typically for a master's degree. In contrast, theses refer to multiple such works. Recognizing these distinctions not only helps in academic writing but also enhances clarity in communication. A strong thesis statement is vital as it serves as the backbone of any academic paper, guiding the reader through the writer's argument. By mastering the art of crafting a clear and focused thesis statement, students can improve their writing and effectively convey their ideas.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a thesis and theses.
A thesis is a single document that presents a student's research for a master's degree. Theses is the plural form, referring to multiple such documents.
Why is a thesis statement important?
A thesis statement is important because it clearly outlines the main point of your paper, guiding both the writer and the reader.
How long should a thesis be?
A thesis typically ranges from 40 to 100 pages, depending on the program and specific requirements.
What are the common challenges when writing a thesis?
Common challenges include choosing a topic, managing time effectively, and staying focused on the main argument.
Can a thesis be revised after submission?
Generally, once a thesis is submitted, it cannot be revised. However, feedback from the defense may lead to minor changes.
What is a thesis defense?
A thesis defense is a formal presentation where the student defends their research and findings before a committee.
How can I improve my thesis statement?
To improve your thesis statement, make sure it is clear, specific, and arguable. Seek feedback from peers or instructors.
What role does a thesis play in academic success?
A thesis showcases your research skills and understanding of a topic, which can open doors for future academic and career opportunities.

Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics: A Fun and Informative Guide

Unlocking the Power of Data: A Review of 'Essentials of Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft Excel'

Discovering Statistics Using SAS: A Comprehensive Review

How to Research for Your Thesis Paper Without Feeling Overwhelmed

Collaborative Genius: 6 Hacks for Seamless Group Thesis Writing

Understanding the Difference Between Research Objectives and Research Questions

Thesis Action Plan

- Blog Articles
- Affiliate Program
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.
LVMH: The Easing Comps Thesis Is Flawed Now (Rating Downgrade)
- LVMH shares are in a 30% drawdown with stagnating revenues, declining margins, and weak consumer sentiment, especially in China.
- The anticipated revenue normalization has turned into a sharp deceleration, with Q3'24 expected to reveal underlying growth problems.
- The Company's valuation is near 10-year lows, but uncertainties and declining estimates make it an unattractive entry point.
- I downgrade LVMH to 'Hold' and advise waiting for signs of a turnaround before considering investment.

The 'luxury winter' is real. LVMH ( OTCPK:LVMHF ) shares are in a 30% drawdown, while some of its peers are having an even tougher time. Revenues have stagnated, margins are declining, and headwinds continue to pile up.
This article was written by
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha's Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
Recommended For You
About lvmhf stock.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|
More on LVMHF
Related stocks.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|---|---|
| LVMHF | - | - |
| LVMUY | - | - |
Trending Analysis
Trending news.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic .
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write — in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Begin by introducing your dissertation topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualize your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved September 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/introduction-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
LESSWRONG LW
The obliqueness thesis.
In my Xenosystems review , I discussed the Orthogonality Thesis, concluding that it was a bad metaphor. It's a long post, though, and the comments on orthogonality build on other Xenosystems content. Therefore, I think it may be helpful to present a more concentrated discussion on Orthogonality, contrasting Orthogonality with my own view, without introducing dependencies on Land's views. (Land gets credit for inspiring many of these thoughts, of course, but I'm presenting my views as my own here.)
First, let's define the Orthogonality Thesis. Quoting Superintelligence for Bostrom's formulation:
Intelligence and final goals are orthogonal: more or less any level of intelligence could in principle be combined with more or less any final goal.
To me, the main ambiguity about what this is saying is the "could in principle" part; maybe, for any level of intelligence and any final goal, there exists (in the mathematical sense) an agent combining those, but some combinations are much more natural and statistically likely than others. Let's consider Yudkowsky's formulations as alternatives. Quoting Arbital :
The Orthogonality Thesis asserts that there can exist arbitrarily intelligent agents pursuing any kind of goal. The strong form of the Orthogonality Thesis says that there's no extra difficulty or complication in the existence of an intelligent agent that pursues a goal, above and beyond the computational tractability of that goal.
As an example of the computational tractability consideration, sufficiently complex goals may only be well-represented by sufficiently intelligent agents . "Complication" may be reflected in, for example, code complexity; to my mind, the strong form implies that the code complexity of an agent with a given level of intelligence and goals is approximately the code complexity of the intelligence plus the code complexity of the goal specification, plus a constant. Code complexity would influence statistical likelihood for the usual Kolmogorov/Solomonoff reasons, of course.
I think, overall, it is more productive to examine Yudkowsky's formulation than Bostrom's, as he has already helpfully factored the thesis into weak and strong forms. Therefore, by criticizing Yudkowsky's formulations, I am less likely to be criticizing a strawman. I will use "Weak Orthogonality" to refer to Yudkowsky's "Orthogonality Thesis" and "Strong Orthogonality" to refer to Yudkowsky's "strong form of the Orthogonality Thesis".
Land, alternatively, describes a "diagonal" between intelligence and goals as an alternative to orthogonality, but I don't see a specific formulation of a "Diagonality Thesis" on his part. Here's a possible formulation:
Diagonality Thesis: Final goals tend to converge to a point as intelligence increases.
The main criticism of this thesis is that formulations of ideal agency, in the form of Bayesianism and VNM utility, leave open free parameters, e.g. priors over un-testable propositions, and the utility function. Since I expect few readers to accept the Diagonality Thesis, I will not concentrate on criticizing it.
What about my own view? I like Tsvi's naming of it as an "obliqueness thesis".
Obliqueness Thesis: The Diagonality Thesis and the Strong Orthogonality Thesis are false. Agents do not tend to factorize into an Orthogonal value-like component and a Diagonal belief-like component; rather, there are Oblique components that do not factorize neatly.
(Here, by Orthogonal I mean basically independent of intelligence, and by Diagonal I mean converging to a point in the limit of intelligence.)
While I will address Yudkowsky's arguments for the Orthogonality Thesis, I think arguing directly for my view first will be more helpful. In general, it seems to me that arguments for and against the Orthogonality Thesis are not mathematically rigorous; therefore, I don't need to present a mathematically rigorous case to contribute relevant considerations, so I will consider intuitive arguments relevant, and present multiple arguments rather than a single sequential argument (as I did with the more rigorous argument for many worlds ).
Bayes/VNM point against Orthogonality
Some people may think that the free parameters in Bayes/VNM point towards the Orthogonality Thesis being true. I think, rather, that they point against Orthogonality. While they do function as arguments against the Diagonality Thesis, this is insufficient for Orthogonality.
First, on the relationship between intelligence and bounded rationality. It's meaningless to talk about intelligence without a notion of bounded rationality. Perfect rationality in a complex environment is computationally intractable. With lower intelligence, bounded rationality is necessary. So, at non-extreme intelligence levels, the Orthogonality Thesis must be making a case that boundedly rational agents can have any computationally tractable goal.
Bayesianism and VNM expected utility optimization are known to be computationally intractable in complex environments. That is why algorithms like MCMC and reinforcement learning are used. So, making an argument for Orthogonality in terms of Bayesianism and VNM is simply dodging the question, by already assuming an extremely high intelligence level from the start.
As the Orthogonality Thesis refers to "values" or "final goals" (which I take to be synonymous), it must have a notion of the "values" of agents that are not extremely intelligent. These values cannot be assumed to be VNM, since VNM is not computationally tractable. Meanwhile, money-pumping arguments suggest that extremely intelligent agents will tend to converge to VNM-ish preferences. Thus:
Argument from Bayes/VNM: Agents with low intelligence will tend to have beliefs/values that are far from Bayesian/VNM. Agents with high intelligence will tend to have beliefs/values that are close to Bayesian/VNM. Strong Orthogonality is false because it is awkward to combine low intelligence with Bayesian/VNM beliefs/values, and awkward to combine high intelligence with far-from-Bayesian/VNM beliefs/values. Weak Orthogonality is in doubt, because having far-from-Bayesian/VNM beliefs/values puts a limit on the agent's intelligence.
To summarize: un-intelligent agents cannot be assumed to be Bayesian/VNM from the start. Those arise at a limit of intelligence, and arguably have to arise due to money-pumping arguments. Beliefs/values therefore tend to become more Bayesian/VNM with high intelligence, contradicting Strong Orthogonality and perhaps Weak Orthogonality.
One could perhaps object that logical uncertainty allows even weak agents to be Bayesian over combined physical/mathematical uncertainty; I'll address this consideration later.
Belief/value duality
It may be unclear why the Argument from Bayes/VNM refers to both beliefs and values, as the Orthogonality Thesis is only about values. It would, indeed, be hard to make the case that the Orthogonality Thesis is true as applied to beliefs. However, various arguments suggest that Bayesian beliefs and VNM preferences are "dual" such that complexity can be moved from one to the other.
Abram Demski has presented this general idea in the past, and I'll give a simple example to illustrate.
Now let e be an arbitrary predicate on worlds. Consider modifying P to increase the probability that e(W) is true. That is:
P ′ ( w ) : ∝ P ( w ) ( 1 + [ e ( w ) ] )
P ′ ( w ) = P ( w ) ( 1 + [ e ( w ) ] ) ∑ w ∈ W P ( w ) ( 1 + [ e ( w ) ] )
where [e(w)] equals 1 if e(w), otherwise 0. Now, can we define a modified utility function U’ so a secondary agent with beliefs P’ and utility function U’ will take the same action as the primary agent? Yes:
U ′ ( o ) : = U ( o ) 1 + [ e ( w ) ]
This secondary agent will find an action a to maximize:
∑ w ∈ W P ′ ( w ) U ′ ( r ( a , w ) )
= ∑ w ∈ W P ( w ) ( 1 + [ e ( w ) ] ) ∑ w ′ ∈ W P ( w ′ ) ( 1 + [ e ( w ′ ) ] ) U ( r ( a , w ) ) 1 + [ e ( w ) ]
= 1 ∑ w ∈ W P ( w ) ( 1 + [ e ( w ) ] ) ∑ w ∈ W P ( w ) U ( r ( a , w ) )
Clearly, this is a positive constant times the primary agent's maximization target, so the secondary agent will take the same action.
This demonstrates a basic way that Bayesian beliefs and VNM utility are dual to each other. One could even model all agents as having the same utility function (of maximizing a random variable U) and simply having different beliefs about what U values are implied by the agent's action and world state. Thus:
Argument from belief/value duality: From an agent's behavior, multiple belief/value combinations are valid attributions. This is clearly true in the limiting Bayes/VNM case, suggesting it also applies in the case of bounded rationality. It is unlikely that the Strong Orthogonality Thesis applies to beliefs (including priors), so, due to the duality, it is also unlikely that it applies to values.
I consider this weaker than the Argument from Bayes/VNM. Someone might object that both values and a certain component of beliefs are orthogonal, while the other components of beliefs (those that change with more reasoning/intelligence) aren't. But I think this depends on a certain factorizability of beliefs/values into the kind that change on reflection and those that don't, and I'm skeptical of such factorizations. I think discussion of logical uncertainty will make my position on this clearer, though, so let's move on.
Logical uncertainty as a model for bounded rationality
I've already argued that bounded rationality is essential to intelligence (and therefore the Orthogonality Thesis). Logical uncertainty is a form of bounded rationality (as applied to guessing the probabilities of mathematical statements). Therefore, discussing logical uncertainty is likely to be fruitful with respect to the Orthogonality Thesis.
Logical Induction is a logical uncertainty algorithm that produces a probability table for a finite subset of mathematical statements at each iteration. These beliefs are determined by a betting market of an increasing (up to infinity) number of programs that make bets, with the bets resolved by a "deductive process" that is basically a theorem prover. The algorithm is computable, though extremely computationally intractable, and has properties in the limit including some forms of Bayesian updating, statistical learning, and consistency over time.
We can see Logical Induction as evidence against the Diagonality Thesis: beliefs about undecidable statements (which exist in consistent theories due to Gödel's first incompleteness theorem ) can take on any probability in the limit, though satisfy properties such as consistency with other assigned probabilities (in a Bayesian-like manner).
However, (a) it is hard to know ahead of time which statements are actually undecidable, (b) even beliefs about undecidable statements tend to predictably change over time to Bayesian consistency with other beliefs about undecidable statements. So, Logical Induction does not straightforwardly factorize into a "belief-like" component (which converges on enough reflection) and a "value-like" component (which doesn't change on reflection). Thus:
Argument from Logical Induction: Logical Induction is a current best-in-class model of theoretical asymptotic bounded rationality. Logical Induction is non-Diagonal, but also clearly non-Orthogonal, and doesn't apparently factorize into separate Orthogonal and Diagonal components. Combined with considerations from "Argument from belief/value duality", this suggests that it's hard to identify all value-like components in advanced agents that are Orthogonal in the sense of not tending to change upon reflection.
One can imagine, for example, introducing extra function/predicate symbols into the logical theory the logical induction is over, to represent utility. Logical induction will tend to make judgments about these functions/predicates more consistent and inductively plausible over time, changing its judgments about the utilities of different outcomes towards plausible logical probabilities. This is an Oblique (non-Orthogonal and non-Diagonal) change in the interpretation of the utility symbol over time.
Likewise, Logical Induction can be specified to have beliefs over empirical facts such as observations by adding additional function/predicate symbols, and can perhaps update on these as they come in (although this might contradict UDT-type considerations). Through more iteration, Logical Inductors will come to have more approximately Bayesian, and inductively plausible, beliefs about these empirical facts, in an Oblique fashion.
Even if there is a way of factorizing out an Orthogonal value-like component from an agent, the belief-component (represented by something like Logical Induction) remains non-Diagonal, so there is still a potential "alignment problem" for these non-Diagonal components to match, say, human judgments in the limit. I don't see evidence that these non-Diagonal components factor into a value-like "prior over the undecidable" that does not change upon reflection. So, there remain components of something analogous to a "final goal" (by belief/value duality) that are Oblique, and within the scope of alignment.
If it were possible to get the properties of Logical Induction in a Bayesian system, which makes Bayesian updates on logical facts over time, that would make it more plausible that an Orthogonal logical prior could be specified ahead of time. However, MIRI researchers have tried for a while to find Bayesian interpretations of Logical Induction, and failed, as would be expected from the Argument from Bayes/VNM.
Naive belief/value factorizations lead to optimization daemons
The AI alignment field has a long history of poking holes in alignment approaches. Oops, you tried making an oracle AI and it manipulated real-world outcomes to make its predictions true. Oops, you tried to do Solomonoff induction and got invaded by aliens . Oops, you tried getting agents to optimize over a virtual physical universe, and they discovered the real world and tried to break out. Oops, you ran a Logical Inductor and one of the traders manipulated the probabilities to instantiate itself in the real world.
These sub-processes that take over are known as optimization daemons . When you get the agent architecture wrong, sometimes a sub-process (that runs a massive search over programs, such as with Solomonoff Induction) will luck upon a better agent architecture and out-compete the original system. (See also a very strange post I wrote some years back while thinking about this issue, and Christiano's comment relating it to Orthogonality).
If you apply a naive belief/value factorization to create an AI architecture, when compute is scaled up sufficiently, optimization daemons tend to break out, showing that this factorization was insufficient. Enough experiences like this lead to the conclusion that, if there is a realistic belief/value factorization at all, it will look pretty different from the naive one. Thus:
Argument from optimization daemons: Naive ways of factorizing an agent into beliefs/values tend to lead to optimization daemons, which have different values from in the original factorization. Any successful belief/value factorization will probably look pretty different from the naive one, and might not take the form of factorization into Diagonal belief-like components and Orthogonal value-like components. Therefore, if any realistic formulation of Orthogonality exists, it will be hard to find and substantially different from naive notions of Orthogonality.
Intelligence changes the ontology values are expressed in
The most straightforward way to specify a utility function is to specify an ontology (a theory of what exists, similar to a database schema) and then provide a utility function over elements of this ontology. Prior to humans learning about physics, evolution (taken as a design algorithm for organisms involving mutation and selection) did not know all that human physicists know. Therefore, human evolutionary values are unlikely to be expressed in the ontology of physics as physicists currently believe in.
Human evolutionary values probably care about things like eating enough, social acceptance, proxies for reproduction, etc. It is unknown how these are specified, but perhaps sensory signals (such as stomach signals) are connected with a developing world model over time. Humans can experience vertigo at learning physics, e.g. thinking that free will and morality are fake, leading to unclear applications of native values to a realistic physical ontology. Physics has known gaps (such as quantum/relativity correspondence, and dark energy/dark matter) that suggest further ontology shifts.
One response to this vertigo is to try to solve the ontology identification problem; find a way of translating states in the new ontology (such as physics) to an old one (such as any kind of native human ontology), in a structure-preserving way, such that a utility function over the new ontology can be constructed as a composition of the original utility function and the new-to-old ontological mapping. Current solutions, such as those discussed in MIRI's Ontological Crises paper , are unsatisfying. Having looked at this problem for a while, I'm not convinced there is a satisfactory solution within the constraints presented. Thus:
Argument from ontological change: More intelligent agents tend to change their ontology to be more realistic. Utility functions are most naturally expressed relative to an ontology. Therefore, there is a correlation between an agent's intelligence and utility function, through the agent's ontology as an intermediate variable, contradicting Strong Orthogonality. There is no known solution for rescuing the old utility function in the new ontology, and some research intuitions pointing towards any solution being unsatisfactory in some way.
If a satisfactory solution is found, I'll change my mind on this argument, of course, but I'm not convinced such a satisfactory solution exists. To summarize: higher intelligence causes ontological changes, and rescuing old values seems to involve unnatural "warps" to make the new ontology correspond with the old one, contradicting at least Strong Orthogonality, and possibly Weak Orthogonality (if some values are simply incompatible with realistic ontology). Paperclips, for example, tend to appear most relevant at an intermediate intelligence level (around human-level), and become more ontologically unnatural at higher intelligence levels.
As a more general point, one expects possible mutual information between mental architecture and values, because values that "re-use" parts of the mental architecture achieve lower description length. For example, if the mental architecture involves creating universal algebra structures and finding analogies between them and the world, then values expressed in terms of such universal algebras will tend to have lower relative description complexity to the architecture. Such mutual information contradicts Strong Orthogonality, as some intelligence/value combinations are more natural than others.
Intelligence leads to recognizing value-relevant symmetries
Consider a number of un-intutitive value propositions people have argued for:
- Torture is preferable to Dust Specks , because it's hard to come up with a utility function with the alternative preference without horrible unintuitive consequences elsewhere.
- People are way too risk-averse in betting; the implied utility function has too strong diminishing marginal returns to be plausible.
- You may think your personal identity is based on having the same atoms, but you're wrong, because you're distinguishing identical configurations .
- You may think a perfect upload of you isn't conscious (and basically another copy of you), but you're wrong, because functionalist theory of mind is true.
- You intuitively accept the premises of the Repugnant Conclusion , but not the Conclusion itself; you're simply wrong about one of the premises, or the conclusion.
The point is not to argue for these, but to note that these arguments have been made and are relatively more accepted among people who have thought more about the relevant issues than people who haven't. Thinking tends to lead to noticing more symmetries and dependencies between value-relevant objects, and tends to adjust values to be more mathematically plausible and natural. Of course, extrapolating this to superintelligence leads to further symmetries. Thus:
Argument from value-relevant symmetries: More intelligent agents tend to recognize more symmetries related to value-relevant entities. They will also tend to adjust their values according to symmetry considerations. This is an apparent value change, and it's hard to see how it can instead be factored as a Bayesian update on top of a constant value function.
I'll examine such factorizations in more detail shortly.
Human brains don't seem to neatly factorize
This is less about the Orthogonality Thesis generally, and more about human values. If there were separable "belief components" and "value components" in the human brain, with the value components remaining constant over time, that would increase the chance that at least some Orthogonal component can be identified in human brains, corresponding with "human values" (though, remember, the belief-like component can also be Oblique rather than Diagonal).
However, human brains seem much more messy than the sort of computer program that could factorize this way. Different brain regions are connected in at least some ways that are not well-understood. Additionally, even apparent "value components" may be analogous to something like a deep Q-learning function , which incorporates empirical updates in addition to pre-set "values".
The interaction between human brains and language is also relevant. Humans develop values they act on partly through language. And language (including language reporting values) is affected by empirical updates and reflection, thus non-Orthogonal. Reflecting on morality can easily change people's expressed and acted-upon values, e.g. in the case of Peter Singer. People can change which values they report as instrumental or terminal even while behaving similarly (e.g. flipping between selfishness-as-terminal and altruism-as-terminal), with the ambiguity hard to resolve because most behavior relates to convergent instrumental goals.
Maybe language is more of an effect than cause of values. But there really seems to be feedback from language to non-linguistic brain functions that decide actions and so on. Attributing coherent values over realistic physics to the brain parts that are non-linguistic seems like a form of projection or anthropomorphism. Language and thought have a function in cognition and attaining coherent values over realistic ontologies. Thus:
Argument from brain messiness: Human brains don't seem to neatly factorize into a belief-component and a value-component, with the value-component unaffected by reflection or language (which it would need to be Orthogonal). To the extent any value-component does not change due to language or reflection, it is restricted to evolutionary human ontology, which is unlikely to apply to realistic physics; language and reflection are part of the process that refines human values, rather than being an afterthought of them. Therefore, if the Orthogonality Thesis is true, humans lack identifiable values that fit into the values axis of the Orthogonality Thesis.
This doesn't rule out that Orthogonality could apply to superintelligences, of course, but it does raise questions for the project of aligning superintelligences with human values; perhaps such values do not exist or are not formulated so as to apply to the actual universe.
Models of ASI should start with realism
Some may take arguments against Orthogonality to be disturbing at a value level, perhaps because they are attached to research projects such as Friendly AI (or more specific approaches), and think questioning foundational assumptions would make the objective (such as alignment with already-existing human values) less clear. I believe "hold off on proposing solutions" applies here: better strategies are likely to come from first understanding what is likely to happen absent a strategy, then afterwards looking for available degrees of freedom.
Quoting Yudkowsky:
Orthogonality is meant as a descriptive statement about reality, not a normative assertion. Orthogonality is not a claim about the way things ought to be; nor a claim that moral relativism is true (e.g. that all moralities are on equally uncertain footing according to some higher metamorality that judges all moralities as equally devoid of what would objectively constitute a justification). Claiming that paperclip maximizers can be constructed as cognitive agents is not meant to say anything favorable about paperclips, nor anything derogatory about sapient life.
Likewise, Obliqueness does not imply that we shouldn't think about the future and ways of influencing it, that we should just give up on influencing the future because we're doomed anyway, that moral realist philosophers are correct or that their moral theories are predictive of ASI, that ASIs are necessarily morally good, and so on. The Friendly AI research program was formulated based on descriptive statements believed at the time, such as that an ASI singleton would eventually emerge, that the Orthogonality Thesis is basically true, and so on. Whatever cognitive process formulated this program would have formulated a different program conditional on different beliefs about likely ASI trajectories. Thus:
Meta-argument from realism: Paths towards beneficially achieving human values (or analogues, if "human values" don't exist) in the far future likely involve a lot of thinking about likely ASI trajectories absent intervention. The realistic paths towards human influence on the far future depend on realistic forecasting models for ASI, with Orthogonality/Diagonality/Obliqueness as alternative forecasts. Such forecasting models can be usefully thought about prior to formulation of a research program intended to influence the far future. Formulating and working from models of bounded rationality such as Logical Induction is likely to be more fruitful than assuming that bounded rationality will factorize into Orthogonal and Diagonal components without evidence in favor of this proposition. Forecasting also means paying more attention to the Strong Orthogonality Thesis than the Weak Orthogonality Thesis, as statistical correlations between intelligence and values will show up in such forecasts.
On Yudkowsky's arguments
Now that I've explained my own position, addressing Yudkowsky's main arguments may be useful. His main argument has to do with humans making paperclips instrumentally:
Suppose some strange alien came to Earth and credibly offered to pay us one million dollars' worth of new wealth every time we created a paperclip. We'd encounter no special intellectual difficulty in figuring out how to make lots of paperclips. That is, minds would readily be able to reason about: How many paperclips would result, if I pursued a policy π 0 ? How can I search out a policy π that happens to have a high answer to the above question?
I believe it is better to think of the payment as coming in the far future and perhaps in another universe; that way, the belief about future payment is more analogous to terminal values than instrumental values. In this case, creating paperclips is a decent proxy for achievement of human value, so long-termist humans would tend to want lots of paperclips to be created.
I basically accept this, but, notably, Yudkowsky's argument is based on belief/value duality. He thinks it would be awkward for the reader to imagine terminally wanting paperclips, so he instead asks them to imagine a strange set of beliefs leading to paperclip production being oddly correlated with human value achievement. Thus, acceptance of Yudkowsky's premises here will tend to strengthen the Argument from belief/value duality and related arguments.
In particular, more intelligence would cause human-like agents to develop different beliefs about what actions aliens are likely to reward, and what numbers of paperclips different policies result in. This points towards Obliqueness as with Logical Induction: such beliefs will be revised (but not totally convergent) over time, leading to applying different strategies toward value achievement. And ontological issues around what counts as a paperclip will come up at some point, and likely be decided in a prior-dependent but also reflection-dependent way.
Beliefs about which aliens are most capable/honest likely depend on human priors, and are therefore Oblique: humans would want to program an aligned AI to mostly match these priors while revising beliefs along the way, but can't easily factor out their prior for the AI to share.
Now onto other arguments. The "Size of mind design space" argument implies many agents exist with different values from humans, which agrees with Obliqueness (intelligent agents tend to have different values from unintelligent ones). It's more of an argument about the possibility space than statistical correlation, thus being more about Weak than Strong Orthogonality.
The "Instrumental Convergence" argument doesn't appear to be an argument for Orthogonality per se; rather, it's a counter to arguments against Orthogonality based on noticing convergent instrumental goals. My arguments don't take this form.
Likewise, "Reflective Stability" is about a particular convergent instrumental goal (preventing value modification). In an Oblique framing, a Logical Inductor will tend not to change its beliefs about even un-decidable propositions too often (as this would lead to money-pumps), so consistency is valued all else being equal.
While I could go into more detail responding to Yudkowsky, I think space is better spent presenting my own Oblique views for now.
As an alternative to the Orthogonality Thesis and the Diagonality Thesis, I present the Obliqueness Thesis, which says that increasing intelligence tends to lead to value changes but not total value convergence. I have presented arguments that advanced agents and humans do not neatly factor into Orthogonal value-like components and Diagonal belief-like components, using Logical Induction as a model of bounded rationality. This implies complications to theories of AI alignment based on assuming humans have values and we need the AGI to agree about those values, while increasing their intelligence (and thus changing beliefs).
At a methodological level, I believe it is productive to start by forecasting default ASI using models of bounded rationality, especially known models such as Logical Induction, and further developing such models. I think this is more productive than assuming that these models will take the form of a belief/value factorization, although I have some uncertainty about whether such a factorization will be found.
If the Obliqueness Thesis is accepted, what possibility space results? One could think of this as steering a boat in a current of varying strength. Clearly, ignoring the current and just steering where you want to go is unproductive, as is just going along with the current and not trying to steer at all. Getting to where one wants to go consists in largely going with the current (if it's strong enough), charting a course that takes it into account.
Assuming Obliqueness, it's not viable to have large impacts on the far future without accepting some value changes that come from higher intelligence (and better epistemology in general). The Friendly AI research program already accepts that paths towards influencing the far future involve "going with the flow" regarding superintelligence, ontology changes, and convergent instrumental goals; Obliqueness says such flows go further than just these, being hard to cleanly separate from values.
Obliqueness obviously leaves open the question of just how oblique. It's hard to even formulate a quantitative question here. I'd very intuitively and roughly guess that intelligence and values are 3 degrees off (that is, almost diagonal), but it's unclear what question I am even guessing the answer to. I'll leave formulating and answering the question as an open problem.
I think Obliqueness is realistic, and that it's useful to start with realism when thinking of how to influence the far future. Maybe superintelligence necessitates significant changes away from current human values; the Litany of Tarski applies. But this post is more about the technical thesis than emotional processing of it, so I'll end here.
While I believe Scott Garrabrant and/or Ambram Demski have discussed such duality, I haven't found a relevant post on the Alignment Forum about this, so I'll present the basic idea in this post.
There is a post on this. It's one of my favorite posts: https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/oheKfWA7SsvpK7SGp/probability-is-real-and-value-is-complex
Thanks, going to link this!
As long as all mature superintelligences in our universe don't necessarily have (end up with) the same values, and only some such values can be identified with our values or what our values should be, AI alignment seems as important as ever. You mention "complications" from obliqueness, but haven't people like Eliezer recognized similar complications pretty early, with ideas such as CEV?
It seems to me that from a practical perspective, as far as what we should do, your view is much closer to Eliezer's view than to Land's view (which implies that alignment doesn't matter and we should just push to increase capabilities/intelligence). Do you agree/disagree with this?
It occurs to me that maybe you mean something like "Our current (non-extrapolated) values are our real values, and maybe it's impossible to build or become a superintelligence that shares our real values so we'll have to choose between alignment and superintelligence." Is this close to your position?
"as important as ever": no, because our potential influence is lower, and the influence isn't on things shaped like our values, there has to be a translation, and the translation is different from the original.
CEV: while it addresses "extrapolation" it seems broadly based on assuming the extrapolation is ontologically easy, and "our CEV" is an unproblematic object we can talk about (even though it's not mathematically formalized, any formalization would be subject to doubt, and even if formalized, we need logical uncertainty over it, and logical induction has additional free parameters in the limit). I'm really trying to respond to orthogonality not CEV though.
from a practical perspective: notice that I am not behaving like Eliezer Yudkowsky. I am not saying the Orthogonality Thesis is true and important to ASI, I am instead saying intelligence/values are Oblique and probably nearly Diagonal (though it's unclear what I mean by "nearly"). I am not saying a project of aligning superintelligence with human values is a priority. I am not taking research approaches that assume a Diagonal/Orthogonal factorization. I left MIRI partially because I didn't like their security policies (and because I had longer AI timelines), I thought discussion of abstract research ideas was more important. I am not calling for a global AI shutdown so this project (which is in my view confused) can be completed. I am actually against AI regulation on the margin (I don't have a full argument for this, it's a political matter at this point).
I think practicality looks more like having near-term preferences related to modest intelligence increases (as with current humans vs humans with neural nets; how do neural nets benefit or harm you, practically? how can you use them to think better and improve your life?), and not expecting your preferences to extend into the distant future with many ontology changes, so don't worry about grabbing hold of the whole future etc, think about how to reduce value drift while accepting intelligence increases on the margin. This is a bit like CEV except CEV is in a thought experiment instead of reality.
The "Models of ASI should start with realism" bit IS about practicalities, namely, I think focusing on first forecasting absent a strategy of what to do about the future is practical with respect to any possible influence on the far future; practically, I think your attempted jump to practicality (which might be related to philosophical pragmatism) is impractical in this context.
Close. Alignment of already-existing human values with superintelligence is impossible (I think) because of the arguments given. That doesn't mean humans have no preferences indirectly relating to superintelligence (especially, we have preferences about modest intelligence increases, and there's some iterative process).
What do you think about my positions on these topics as laid out in and Six Plausible Meta-Ethical Alternatives and Ontological Crisis in Humans ?
My overall position can be summarized as being uncertain about a lot of things, and wanting (some legitimate/trustworthy group, i.e., not myself as I don't trust myself with that much power) to "grab hold of the whole future" in order to preserve option value, in case grabbing hold of the whole future turns out to be important. (Or some other way of preserving option value, such as preserving the status quo / doing AI pause.) I have trouble seeing how anyone can justifiably conclude "so don’t worry about grabbing hold of the whole future" as that requires confidently ruling out various philosophical positions as false, which I don't know how to do. Have you reflected a bunch and really think you're justified in concluding this?
E.g. in Ontological Crisis in Humans I wrote "Maybe we can solve many ethical problems simultaneously by discovering some generic algorithm that can be used by an agent to transition from any ontology to another?" which would contradict your "not expecting your preferences to extend into the distant future with many ontology changes" and I don't know how to rule this out. You wrote in the OP "Current solutions, such as those discussed in MIRI’s Ontological Crises paper , are unsatisfying. Having looked at this problem for a while, I’m not convinced there is a satisfactory solution within the constraints presented." but to me this seems like very weak evidence for the problem being actually unsolvable.
re meta ethical alternatives:
- roughly my view
- slight change, opens the question of why the deviations? are the "right things to value" not efficient to value in a competitive setting? mostly I'm trying to talk about those things to value that go along with intelligence, so it wouldn't correspond with a competitive disadvantage in general. so it's still close enough to my view
- roughly Yudkowskian view, main view under which the FAI project even makes sense. I think one can ask basic questions like which changes move towards more rationality on the margin, though such changes would tend to prioritize rationality over preventing value drift. I'm not sure how much there are general facts about how to avoid value drift (it seems like the relevant kind, i.e. value drift as part of becoming more rational/intelligent, only exists from irrational perspectives, in a way dependent on the mind architecture)
- minimal CEV-realist view. it really seems up to agents how much they care about their reflected preferences. maybe changing preferences too often leads to money pumps, or something?
- basically says "there are irrational and rational agents, rationality doesn't apply to irrational agents", seems somewhat how people treat animals (we don't generally consider uplifting normative with respect to animals)
- at this point you're at something like ecology / evolutionary game theory, it's a matter of which things tend to survive/reproduce and there aren't general decision theories that succeed
re human ontological crises: basically agree, I think it's reasonably similar to what I wrote. roughly my reason for thinking that it's hard to solve is that the ideal case would be something like a universal algebra homomorphism (where the new ontology actually agrees with the old one but is more detailed), yet historical cases like physics aren't homomorphic to previous ontologies in this way, so there is some warping necessary. you could try putting a metric on the warping and minimizing it, but, well, why would someone think the metric is any good, it seems more of a preference than a thing rationality applies to. if you think about it and come up with a solution, let me know, of course.
with respect to grabbing hold of the whole future: you can try looking at historical cases of people trying to grab hold of the future and seeing how that went, it's a mixed bag with mostly negative reputation, indicating there are downsides as well as upsides, it's not a "safe" conservative view. see also Against Responsibility . I feel like there's a risk of getting Pascal's mugged about "maybe grabbing hold of the future is good, you can't rule it out, so do it", there are downsides to spending effort that way. like, suppose some Communists thought capitalism would lead to the destruction of human value with high enough probability that instituting global communism is the conservative option, it doesn't seem like that worked well (even though a lot of people around here would agree that capitalism tends to leads to human value destruction in the long run). particular opportunities for grabbing hold of the future can be net negative and not worth worrying about even if one of them is a good idea in the long run (I'm not ruling that out, just would have to be convinced of specific opportunities).
overall I'd rather focus on first modeling the likely future and looking for plausible degrees of freedom; a general issue with Pascal's mugging is it might make people overly attached to world models in which they have ~infinite impact (e.g. Christianity, Communism) which means paying too much attention to wrong world models, not updating to more plausible models in which existential-stakes decisions could be comprehended if they exist. and Obliqueness doesn't rule out existential stakes (since it's non-Diagonal).
as another point, Popperian science tends to advance by people making falsifiable claims, "you don't know if that's true" isn't really an objection in that context. the pragmatic claim I would make is: I have some Bayesian reason to believe agents do not in general factor into separate Orthogonal and Diagonal components, this claim is somewhat falsifiable (someone could figure out a theory of this invulnerable to optimization daemons etc), I'm going to spend my attention on the branch where I'm right, I'm not going to worry about Pascal's mugging type considerations for if I'm wrong (as I said, modeling the world first seems like a good general heuristic), people can falsify it eventually if it's false.
this whole discussion is not really a defense of Orthogonality given that Yudkowsky presented orthogonality as a descriptive world model, not a normative claim, so sticking to the descriptive level in the original post seems valid; it would be a form of bad epistemology to reject a descriptive update (assuming the arguments are any good) because of pragmatic considerations.
with respect to grabbing hold of the whole future: you can try looking at historical cases of people trying to grab hold of the future and seeing how that went, it's a mixed bag with mostly negative reputation, indicating there are downsides as well as upsides, it's not a "safe" conservative view. see also Against Responsibility . I feel like there's a risk of getting Pascal's mugged about "maybe grabbing hold of the future is good, you can't rule it out, so do it", there are downsides to spending effort that way.
I agree with a track-record argument of this, but I think the track record of people trying to broadly ensure that humanity continues to be in control of the future (while explicitly not optimizing for putting themselves personally in charge) seems pretty good to me.
Generally a lot of industrialist and human-empowerment stuff has seemed pretty good to me on track record, and I really feel like all the bad parts of this are screened off by the "try to put yourself and/or your friends in charge" component.
the track record of people trying to broadly ensure that humanity continues to be in control of the future
What track record?
hmm, I wouldn't think of industrialism and human empowerment as trying to grab the whole future, just part of it, in line with the relatively short term (human not cosmic timescale) needs of the self and extended community; industrialism seems to lead to capitalist organization which leads to decentralization superseding nations and such (as Land argues).
I think communism isn't generally about having one and one's friends in charge, it is about having human laborers in charge. One could argue that it tended towards nationalism (e.g. USSR), but I'm not convinced that global communism (Trotskyism) would have worked out well either. Also, one could take an update from communism about agendas for global human control leading to national control (see also tendency of AI safety to be taken over by AI national security as with the Situational Awareness paper). (Again, not ruling out that grabbing hold of the entire future could be a good idea at some point, just not sold on current agendas and wanted to note there are downsides that push against Pascal's mugging type considerations)
Why should I agree that a boundedly rational agent's goals need to be computationally tractable? Humans have goals and desires they lack the capability to achieve all the time. Sometimes they make plans to try to increase tractability, and sometimes those plans work, but there's nothing odd about intractable goals. It might be a mistake in some senses to build such an agent, but that's a different question.
Computationally tractable is Yudkowsky's framing and might be too limited. The kind of thing I believe is for example, an animal without a certain brain complexity will tend not to be a social animal and is therefore unlikely to have the sort of values social animals have. And animals that can't do math aren't going to value mathematical aesthetics the way human mathematicians do.
Ah ok, that makes sense. That's more about being able to understand what the goal is, not about the ability to compute what actions are able to achieve it.
You mention 'warp' when talking about cross ontology mapping which seems like your best summary of a complicated intuition. I'd be curious to hear more (I recognize this might not be practical). My own intuition surfaced 'introducing degrees of freedom' a la indeterminacy of translation.
Relativity to Newtonian mechanics is a warp in a straightforward sense. If you believe the layout of a house consists of some rooms connected in a certain way, but there are actually more rooms connected in different ways, getting the maps to line up looks like a warp. Basically, the closer the mapping is to a true homomorphism (in the universal algebra sense), the less warping there is, otherwise there are deviations intuitively analogous to space warps.
Hi! Long time lurker, first time commenter. You have written a great piece here. This is a topic that has fascinated me for a while and I appreciate what you've laid out. I'm wondering if there's a base assumption on the whole intelligence vs values/beliefs/goals question that needs to be questioned.
sufficiently complex goals may only be well-represented by sufficiently intelligent agents
This statement points to my question. There's necessarily a positive correlation between internal complexity and intelligence right?. So, in order for intelligence to increase, internal complexity must also increase. My understanding is that complexity is a characteristic of dynamic and generative phenomena, and not of purely mechanical phenomena. So, what do we have to assume in order to posit a super-intelligent entity exists? It must have maintained its entity-ness over time in order to have increased its intelligence/complexity to its current level.
Has anyone explored what it takes for an agent to complexify? I would presume that for an agent to simultaneously continue existing and complexify it must stay maintain some type of fixpoint/set of autopoietic (self-maintenance, self-propagation) values/beliefs/goals throughout its dynamic evolution. If this were the case, wouldn't it be true that there must exist a set of values/beliefs/goals that are intrinsic to the agent's ability to complexify? Therefore there must be another set of values/beliefs/goals that are incompatible with self-complexification. If so, can we not put boundary conditions on what values/beliefs/goals are both necessary as well as incompatible with sufficiently intelligent, self-complexifying agents? After all, if we observe a complex agent, the probability of it arising full-cloth and path-independently is vanishingly small, so it is safe to say that the observed entity has evolved to reach the observed state. I don't think my observation is incompatible with your argument, but might place further limits on what relationships we can possibly see between entities of sufficient intelligence and their goals/values/beliefs than the limits you propose.
I think situations like a paperclip maximizer may still occur but they are degenerate cases where an evolutionarily fit entity spawns something that inherits much of its intrinsic complexity but loses its autopoietic fixpoint. Such systems do occur in nature, but to get that system, you must also assume a more-complex (and hopefully more intelligent/adapted) entity exists as well. This other entity would likely place adversarial pressure on the degenerate paperclip maximizer as it threatens its continued existence.
Some relationships/overlaps with your arguments are as follows:
- totally agree with the belief/value duality
- Naive belief/value factorizations lead to optimization daemons. The optimization daemons observation points to an agent's inability to maintain autopoiesis over time, implying misalignment of its values/beliefs/goals with its desire to increase its intelligence
- Intelligence changes the ontology values are expressed in. I presume that any ontology expressed by an autopoietic embedded agent must maintain concepts of self, otherwise the embedded entity cannot continue to complexify over time, therefore there must be some fix point in ontological evolution that preserves the evolutionary drive of the entity in order for it to continue to advance its intelligence
Anyways, thank you for the essay.
Not sure what you mean by complexity here, is this like code size / Kolmogorov complexity? You need some of that to have intelligence at all (the empty program is not intelligent). At some point most of your gains come from compute rather than code size. Though code size can speed things up (e.g. imagine sending a book back to 1000BC, that would speed people up a lot; consider that superintelligence sending us a book would be a bigger speedup)
by "complexify" here it seems you mean something like "develop extended functional organization", e.g. in brain development throughout evolution. And yeah, that involves dynamics with the environment and internal maintenance (evolution gets feedback from the environment). It seems it has to have a drive to do this which can either be a terminal or instrumental goal, though deriving it from instrumentals seems harder than baking it is as terminal (so I would guess evolution gives animals a terminal goal of developing functional complexity of mental structures etc, or some other drive that isn't exactly a terminal goal)
see also my post relating optimization daemons to immune systems, it seems evolved organisms develop these; when having more extended functional organization, they protect it with some immune system functional organization.
to be competitive agents, having a "self" seems basically helpful, but might not be the best solution; selfish genes are an alternative, and perhaps extended notions of self can maintain competitiveness.
Department of Sociology
PSU's Three-Minute-Thesis Winner Moves Forward To National Competition
by Lacey Friedly September 19th 2024 Share

Anne Johnson, a Portland State University doctoral candidate in sociology, will compete in the Council of Graduate Schools' national Three-Minute Thesis competition in St. Louis this year after winning regionals in March.
The Three-Minute Thesis contest, or 3MT for short, is a research communication competition designed to help graduate students develop presentation skills by consolidating their research and presenting it succinctly to a non-specialist audience, all in just three minutes.
Johnson was awarded first place in the PSU 3MT competition last November and took home a cash prize of $1,000. She went on to take first prize in the regional competition, too, held virtually as part of the Western Association of Graduate Schools' annual meeting on March 22. Her doctoral dissertation draws on both medical sociology and criminology, examining phlebotomy, blood draws, in two contexts: medicine and law enforcement.
This December, Johnson will compete in the national round of 3MT, held at the Council of Graduate Schools (CGS) 2024 Annual Meeting in St. Louis, Missouri.
The 2024 PSU Three Minute Thesis competition will be held on campus November 14, 2024. The Graduate School will accept applications starting Friday, October 4, through midnight on Sunday, October 20. Learn more and sign up for the competition here.
Note: You must be logged in to your Odin account to view the site. If you are logged in and still cannot view it, contact Lisa Sablan .
NOT JUST A POKE: EXPLORING THE SOCIAL SIGNIFICANCE OF DRAWING BLOOD
Most of us are familiar with having blood drawn at the doctor’s office, but police officers are increasingly using blood draws as a form of chemical testing for suspected impaired drivers. Johnson's work explores phlebotomy in both medical and law enforcement contexts.
"I think too often in medical spaces, and in general, we do not give enough weight to how emotionally significant blood draws can be for people," Johnson said. "Phlebotomy is the most common invasive medical procedure. But in talking to people about their experiences getting blood drawn, it is more significant than we often realize. People hold on to the trauma of bad blood draws and remember them. So there's room culturally right now for us to think about it."
For her three-paper dissertation, Johnson interviewed patients who had had their blood drawn in purely medical contexts, as well as law enforcement officers who draw blood from drivers. In the medical context, many participants who have had negative experiences with blood draws reported avoiding medical care so as to not undergo more blood draws. What’s more, many of her participants reported feeling dehumanized by their phlebotomists’ focus on efficiency instead of care. In the policing context, efficiency is the chief motivator for law enforcement phlebotomy: when officers can draw blood themselves, they save time and money, as well as avoid clashes with medical providers over non-consensual blood draws. The tension between efficiency and care is a throughline of her dissertation.
Johnson hopes that her findings will be valuable to medical professionals in search of ways to improve patient experiences, sociologists interested in power dynamics, and members of the law enforcement and legal community as police-conducted blood draws continue to spread across the United States.
"The culminating idea of my 3MT speech is that most people don't know law enforcement phlebotomy is happening. If a community decides, 'Our DUI situation is severe enough that yes, we want our police officers to be drawing blood,' then that decision may be the right choice for that community. But most of the officers I interviewed said that their community members have no idea that police can draw blood until they’re pulled over. I would like it to be more of a public conversation," Johnson said.
WHY DO 3MT?
The 3MT concept was developed by the University of Queensland in 2008 and is now held at over 900 universities worldwide. The idea is to challenge graduate students to be as succinct and engaging as possible when communicating complex research topics, which helps develop their presentation and research communication skills.
"When I had to distill my dissertation topic into three minutes, it really helped me tighten up the language. It prepared me with an elevator pitch that I can now give to potential employers or share with other academics at conferences. Having to focus in on the message I want to communicate was really helpful," Johnson said.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A thesis is a long-form research paper based on your original work. Learn how to structure, write, and defend your thesis with this comprehensive guide and examples.
Learn how to write a clear and concise thesis statement for your essay or paper. Follow four simple steps: start with a question, write your initial answer, develop your answer, and refine your thesis statement.
Learn what a thesis is, how to write a strong thesis statement, and the different types of thesis statements. This guide also explains the structure and components of a thesis and the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
Learn how to write a strong thesis for an academic essay, with examples and tips. A thesis is the central claim that responds to an analytical or normative question or problem, and should be arguable, clear, and supported by evidence.
The term thesis comes from the Greek word θέσις, meaning "something put forth", and refers to an intellectual proposition. Dissertation comes from the Latin dissertātiō, meaning "discussion". Aristotle was the first philosopher to define the term thesis.. A 'thesis' is a supposition of some eminent philosopher that conflicts with the general opinion...for to take notice when any ...
The meaning of THESIS is a dissertation embodying results of original research and especially substantiating a specific view; especially : one written by a candidate for an academic degree. How to use thesis in a sentence. Did you know?
Learn what a thesis statement is, how to create one, and how to evaluate its strength. A thesis statement is a claim that answers a question, takes a position, and guides your argument in an essay.
The thesis (pronounced thee -seez), also known as a thesis statement, is the sentence that introduces the main argument or point of view of a composition (formal essay, nonfiction piece, or narrative). It is the main claim that the author is making about that topic and serves to summarize and introduce that writing that will be discussed ...
A good thesis statement needs to do the following: Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences. Answer your project's main research question. Clearly state your position in relation to the topic. Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis: Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student's ability to conduct original ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons: It gives your writing direction and focus. It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point. Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence. 3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper. 4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what ...
A college thesis paper is the crowning achievement of a student's hard work. For many, a thesis is the culmination of many years of study within a particular major or field, such as literature, history, or business.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps. Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is. Find a unique and valuable research topic. Craft a convincing research proposal. Write up a strong introduction chapter. Review the existing literature and compile a literature review.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
A thesis statement is: The statement of the author's position on a topic or subject. Clear, concise, and goes beyond fact or observation to become an idea that needs to be supported (arguable). Often a statement of tension, where the author refutes or complicates an existing assumption or claim (counterargument).
What is a dissertation vs. a thesis? In American English, a dissertation is a research paper that's required to earn a doctorate degree, while a thesis is a research paper required to earn a master's degree. Dissertations and theses (the plural of thesis) are often mixed up because they're both lengthy research papers written for higher education, especially as part of a master's or ...
THESIS meaning: 1. a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one that is done for a higher…. Learn more.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation, it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to ...
Argumentative Thesis Statement: This statement presents a clear argument on a specific topic, aiming to convince the reader of your viewpoint. It should be debatable and supported by evidence. Expository Thesis Statement: This type explains a topic or idea without taking a stance. It provides information and is often used in informative essays.
The comps thesis doesn't seem relevant anymore, as it becomes increasingly clear that LVMH isn't going to deliver decent growth in the upcoming quarter. Right now, the negativity is based on ...
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023. The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation, appearing right after the table of contents.Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant ...
Diagonality Thesis: Final goals tend to converge to a point as intelligence increases. The main criticism of this thesis is that formulations of ideal agency, in the form of Bayesianism and VNM utility, leave open free parameters, e.g. priors over un-testable propositions, and the utility function.
Thesis Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs
The Three-Minute Thesis contest, or 3MT for short, is a research communication competition designed to help graduate students develop presentation skills by consolidating their research and presenting it succinctly to a non-specialist audience, all in just three minutes.