
- Career Consultant
- Compliance Consultant
- Financial Consultant
- Growth Consultant
- HR Consultant
- Interim Manager
- IT Consultant
- Legal Consultant
- Marketing Consultant
- Operation Consultants
- PR Consultant
- Sales Consultant
- Social Media Consultant
- Strategy Consultant
- Sustainability Consultant
- SEO Consultant

All About Consulting Case Studies [+Tips & Example]
Table of Contents
What are consulting case studies, what is the purpose of consulting case studies.
- How to Analyze Consulting Case Studies
- Tips for Crafting a Strong Consulting Case Study
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Consulting Case Study Interpretation
Why is data so important in consulting case studies .
- How to Present Your Findings from Consulting Case Studies
Example Deloitte Case Study
Consulting case studies are real-life examples of consulting projects that have been completed by consulting firms. These studies are used to showcase the expertise and problem-solving abilities of the consulting firm, as well as to provide potential clients with an understanding of the type of work that the firm can deliver. Consulting case studies typically detail the challenge that the client was facing, the approach taken by the consulting firm to address the challenge, and the outcomes and results achieved as a result of the project.
Consulting case studies are a valuable tool used by professionals in the consulting industry to showcase their expertise and problem-solving skills. These case studies typically outline a specific business challenge or issue that a client faced, and detail how the consulting firm addressed and resolved the problem. By presenting real-world examples of their work, consulting firms are able to demonstrate their capabilities to potential clients and establish credibility in the industry.
The purpose of consulting case studies is twofold. Firstly, they serve as a means for consulting firms to highlight their success stories and showcase their ability to deliver results for clients. By detailing the specific steps taken to address a particular issue, consulting firms can illustrate their problem-solving process and demonstrate the value they bring to their clients. This can be especially valuable for potential clients who are evaluating different consulting firms and looking for evidence of past success.
Secondly, consulting case studies can also serve as a learning tool for professionals in the consulting industry. By studying successful case studies, consultants can gain insights into different problem-solving approaches, strategies, and best practices. This can help them improve their own consulting skills and better understand how to approach similar challenges in the future. Overall, consulting case studies play a crucial role in showcasing the expertise of consulting firms, attracting new clients, and promoting continuous learning and improvement within the industry.
How to Analyze Consulting Case Studies
Analyzing Consulting Case Studies involves breaking down the problem statement, identifying key challenges, understanding the approach taken by the consulting firm, evaluating the effectiveness of the solutions proposed, and assessing the overall impact of the project. By closely examining the details of each case study, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the consulting process and learn valuable lessons that can be applied to their own projects.
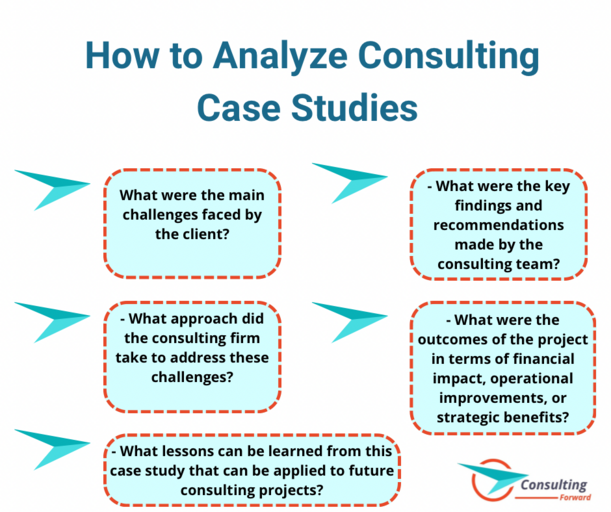
In order to effectively analyze Consulting Case Studies, it is important to ask critical questions such as:
- What were the main challenges faced by the client?
- What approach did the consulting firm take to address these challenges?
- What were the key findings and recommendations made by the consulting team?
- What were the outcomes of the project in terms of financial impact, operational improvements, or strategic benefits?
- What lessons can be learned from this case study that can be applied to future consulting projects?
By answering these questions and thoroughly examining the details presented in Consulting Case Studies, individuals can gain valuable insights into the consulting process and learn how to approach similar challenges in their own work.
Tips for Crafting a Strong Consulting Case Study
Case studies are a valuable tool for consultants to showcase their expertise and experience. By presenting a detailed analysis of a client project, consultants can demonstrate their problem-solving skills and the results they have achieved. To create a strong consulting case study, there are several tips to keep in mind.
First and foremost, it is important to choose a relevant and compelling client project to focus on. Selecting a project that highlights your expertise and showcases your ability to deliver results will help to capture the attention of potential clients. Additionally, be sure to include specific details about the client’s goals, challenges, and the solutions you implemented. Providing this context will help readers understand the complexity of the project and the impact of your work.
In addition to outlining the project details, it is important to highlight the results and outcomes of your work. Quantifying the impact of your solutions with specific metrics and data will provide concrete evidence of your success. This information can help potential clients understand the tangible benefits of working with you and can help establish your credibility as a consultant. By following these tips and creating a well-crafted case study, consultants can effectively showcase their skills and attract new clients.
Tips for Writing a Compelling Case Study Narrative
Crafting a compelling case study narrative is essential for capturing the attention of your audience and effectively communicating the value of your work. When writing your case study, it is important to create a clear and engaging narrative that highlights the problem-solving process and the impact of your solutions. Start by outlining the client’s goals and challenges, and then explain how you approached the project and developed a strategic solution.
To keep readers engaged, consider incorporating storytelling elements into your case study. By providing a narrative structure with a clear beginning, middle, and end, you can create a compelling story that draws readers in and keeps them interested. Additionally, be sure to use clear and concise language to explain complex concepts and technical details in a way that is accessible to a wide audience.
Furthermore, don’t forget to include quotes or testimonials from the client to add credibility and perspective to your case study. Hearing directly from the client about their experience working with you can help reinforce the effectiveness of your solutions and build trust with potential clients. By following these tips for writing a compelling case study narrative, consultants can effectively communicate the value of their work and attract new clients.
Tips for Designing an Engaging Case Study Layout
In addition to crafting a strong case study narrative, the design of your case study is also crucial for capturing and holding the attention of your audience. An engaging layout can help to visually communicate the key points of your case study and make it easier for readers to digest the information. When designing your case study, consider using a clean and professional layout with clear headings, bullet points, and visuals to break up the text and highlight important information.
Incorporating visual elements such as charts, graphs, and images can help to illustrate your key points and make the content more engaging and easy to understand. Including before-and-after comparisons or visual representations of the project’s impact can provide a powerful visual representation of your work. Additionally, be sure to use a consistent color scheme and typography to create a cohesive and visually appealing design.
Furthermore, consider including call-to-action buttons or contact information at the end of your case study to encourage readers to take the next step and reach out to learn more. By designing an engaging case study layout that complements your narrative, consultants can effectively showcase their work and attract new clients.
Consulting case studies are a crucial part of the interview process for landing a job in the consulting industry. In order to succeed, it’s important to avoid common mistakes in interpreting these case studies.
One common mistake is jumping to conclusions without fully understanding the problem at hand. It’s important to take the time to thoroughly analyze the case study and ask clarifying questions if needed. Another mistake is not structuring your analysis in a logical and organized way. This can make it difficult for the interviewer to follow your thought process and ultimately lead to a weaker performance.
Additionally, failing to prioritize your analysis can result in spending too much time on less important aspects of the case study. It’s crucial to identify the most critical issues and address them first in order to demonstrate your problem-solving skills effectively. Finally, overlooking the importance of communication skills can also be a mistake. Clearly articulating your analysis and insights is just as important as the analysis itself.
Overall, by avoiding these common mistakes in consulting case study interpretation, you can increase your chances of success in the interview process and ultimately secure the job of your dreams.
- Jumping to conclusions without fully understanding the problem
- Not structuring analysis in a logical and organized way
- Failing to prioritize analysis
- Overlooking the importance of communication skills
In the world of consulting, data plays a crucial role in shaping case studies and providing valuable insights for clients. When analyzing a business problem or opportunity, consultants rely on data to understand the current state of affairs, identify trends, and make informed recommendations. By collecting and analyzing data, consultants can uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and insights that can lead to more effective solutions.
Data also serves as a foundation for evidence-based decision-making in consulting. When presenting a case study to a client, consultants must back up their recommendations with solid data and analysis. This not only lends credibility to their findings but also helps clients understand the rationale behind the proposed solutions. Without data, recommendations may be perceived as subjective opinions rather than well-supported conclusions.
Data allows consultants to measure the impact of their recommendations and track progress over time. By setting clear metrics and key performance indicators, consultants can monitor the success of their interventions and make adjustments as needed. This data-driven approach helps ensure that consulting projects deliver tangible results and drive long-term value for clients. Ultimately, data is the cornerstone of consulting case studies, providing the evidence and insight needed to drive effective decision-making and create meaningful impact for clients.
How Data Improves Decision-Making in Consulting Case Studies
One of the key benefits of using data in consulting case studies is its ability to improve decision-making processes. By analyzing data, consultants can identify key opportunities and challenges, assess the potential impact of different strategies, and make informed decisions that lead to better outcomes for clients. Data provides a solid foundation for decision-making, enabling consultants to avoid relying on gut instincts or personal biases.
Moreover, data-driven decision-making in consulting case studies helps mitigate risks and uncertainties. By examining historical data, market trends, and industry benchmarks, consultants can anticipate potential obstacles and develop contingency plans to address them. This proactive approach not only minimizes the likelihood of unexpected setbacks but also increases the likelihood of success for consulting projects.
Data also empowers consultants to test hypotheses, validate assumptions, and explore alternative scenarios in their case studies. By leveraging data analytics tools and techniques, consultants can conduct robust analyses that uncover valuable insights and inform strategic decisions. This iterative process of data-driven decision-making allows consultants to refine their recommendations, optimize their strategies, and deliver greater value to their clients. Ultimately, data enhances the quality of decision-making in consulting case studies, leading to more effective solutions and positive outcomes for clients.
How to Present Your Findings from Consulting Case Studies
Consulting case studies are a valuable tool for showcasing your expertise and problem-solving skills to potential clients. When it comes to presenting your findings from these case studies, it is important to approach the task with both clarity and creativity.
One effective way to present your findings is to start by clearly outlining the problem or challenge that you were tasked with addressing. This sets the stage for the rest of your presentation and helps your audience understand the context of your work. Next, explain your approach to solving the problem, including any research or analysis you conducted. This shows your audience that your findings are backed up by solid data and evidence.
After presenting your approach, it is important to showcase the results of your work. This could include metrics such as improved efficiency or increased revenue, as well as any qualitative feedback from the client. Highlighting the positive outcomes of your consulting work helps to build credibility and demonstrate the value you provide to clients. Finally, conclude your presentation by summarizing the key takeaways from the case study and reiterating how your skills and expertise can benefit potential clients in similar situations. By following these steps, you can effectively present your findings from consulting case studies in a compelling and convincing way to get more clients .
Tips for Creating Engaging Visuals for Your Consulting Presentations
Visual aids can be a powerful tool for enhancing your consulting presentations and capturing the attention of your audience. When creating visuals for your presentations, it is important to keep a few key tips in mind to ensure that they are engaging and effective.
One important tip is to keep your visuals simple and easy to understand. Avoid cluttering your slides with too much information or complex graphics, as this can overwhelm your audience and distract from your main points. Instead, use clean and clear visuals that help to reinforce your message and make it easier for your audience to follow along.
Another tip is to use a variety of visual formats to keep your audience engaged. This could include charts, graphs, images, and even videos. By mixing up the types of visuals you use, you can create a dynamic and interesting presentation that holds the attention of your audience. Additionally, remember to use visual aids to enhance your verbal presentation, rather than replace it. Your visuals should complement your spoken content and help to reinforce your key points. By incorporating these tips into your consulting presentations, you can create engaging visual aids that help to bring your findings to life and make a lasting impression on your audience.
Deloitte published a great case study for a footwear company. In 2013, a competitor, Badger, launched a successful line of affordable work boots, prompting Duraflex, another footwear company, to rethink their strategy. With limited resources, Duraflex needed to decide whether to focus on competing in the work boot market or strengthening their position in casual boots.
Duraflex sought help from a top consulting firm in January 2014. The consultants conducted research to provide valuable insights for decision-making. They started by conducting a survey with 500 consumers in six key regions. Additionally, they analyzed Duraflex’s internal costs and pricing for both their work and casual boot lines. The analysis revealed that Duraflex was positioned at the premium end of the market for both types of boots.
This case study showcases how consulting firms like Deloitte can provide essential data and analysis to help companies make informed decisions about their business strategies. It’s worth reading as it gives a glimpse into how consulting firms work and the impact they can have on a company’s success.
Leave a Comment Reactie annuleren
Mijn naam, e-mail en site bewaren in deze browser voor de volgende keer wanneer ik een reactie plaats.
Related Posts

The 6 Phases of an Online Consulting Project?

The 8 Phases of Online Consulting | What Does an Online Consultant Do?

How to Handle Difficult Clients as a Freelance Consultant

How to Find Your Ideal Clients as a Niche Freelance Consultant?
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Become a Consultant
- Complained Consultant
- Operation Consultant
- Help & Support
- Android App
© ConsultingForward.com. 2024 . All rights reserved.

Hacking the Case Interview

Case interview frameworks or consulting frameworks are arguably the most critical component of a case interview. Outstanding case frameworks set you up for success for the case while poor frameworks make the case difficult to solve.
Struggling on how to use frameworks in your case interviews? Unsure of which frameworks to use?
Don't worry because we have you covered! We'll teach you step-by-step, how to craft tailored and unique frameworks for any case interview situation.
By the end of this article, you will learn four different strategies on how to create unique and tailored frameworks for any case interview.
Strategy #1: Creating Frameworks from Scratch
- Strategy #2: Memorizing 8 – 10 Broad Business Areas
- Strategy #3: Breaking Down Stakeholders
- Strategy #4: Breaking Down Processes
- Strategy #5: Two-Part MECE Frameworks
You will apply these strategies to learn how to create case frameworks for the six most common types of case interviews.
Profitability Framework
Market entry framework, merger and acquisition framework, pricing framework, new product framework, market sizing framework.
You will also learn six consulting frameworks that nearly every consultant knows.
Porter’s Five Forces Framework
Swot framework, 4 p’s framework, 3 c’s / business situation framework, bcg 2x2 matrix framework, mckinsey 7s framework.
If you’re looking for a step-by-step shortcut to learn case interviews quickly, enroll in our case interview course . These insider strategies from a former Bain interviewer helped 30,000+ land consulting offers while saving hundreds of hours of prep time.
What is a Case Interview Framework?
A case interview framework is simply a tool that helps you structure and break down complex problems into simpler, smaller components. Think of a framework as brainstorming different ideas and organizing them into different categories.
Let’s look at an example: Coca-Cola is a large manufacturer and retailer of non-alcoholic beverages, such as sodas, juices, sports drinks, and teas. They are looking to grow and are considering entering the beer market in the United States. Should they enter?
In order for you to decide whether Coca-Cola should enter the beer market, you likely have many different questions you’d like to ask:
- Does Coca-Cola know how to produce beer?
- Would people buy beer made by Coca-Cola?
- Where would Coca-Cola sell its beer?
- How much would it cost to enter the beer market?
- Will Coca-Cola be profitable from selling beer?
- How would Coca-Cola outcompete competitors?
- What is the size of the beer market in the United States?
This is not a very structured way of thinking through the case. The questions are listed in no particular order. Additionally, many of the questions are similar to one another and could be grouped together.
A case framework would provide a structure to organize these ideas and questions in a way that is easy to understand.
A framework for this case might look like the following.

Notice that we have simplified the list of questions we had into four main categories. These broad categories are frequently called framework “buckets.” Also notice that we have grouped similar questions together under each framework bucket.
This case framework tells us what areas we need to explore in order to make a recommendation to Coca-Cola. It also clearly shows what questions we need to answer under each area.
This is the power of a case interview framework. It simplifies a complex business problem into smaller and separate components that we can tackle one at a time.
So how do you develop a case framework? The next section will reveal four robust strategies for creating unique and tailored consulting frameworks for any case interview.
Case Interview Framework Strategies
There are four case interview framework strategies you should have in your toolkit:
When given a case interview, you will need to decide which framework strategy you want to use. Some framework strategies will be more effective than others depending on what type of case interview you get.
Therefore, choose the case framework strategy that is easiest for you given the type of case that you get.
This case framework strategy can be used for any type of case. This is the most time-consuming strategy, but yields case frameworks that are the most tailored and unique for the given case interview.
To create a framework from scratch, ask yourself what 3 – 4 statements must be true for you to be 100% confident in your recommendation. These 3 – 4 areas will become the buckets in your framework.
Once you have your framework buckets, brainstorm a few questions for each bucket that you need answers to.
Let’s return to the Coca-Cola case example in which we are asked to determine whether or not they should enter the beer market. What 3 – 4 statements must be true for us to recommend that Coca-Cola should enter the beer market?
The four major statements that must be true are:
- The beer market is an attractive market
- Competitors in the market are weak
- Coca-Cola has the capabilities to produce outstanding beer
- Coca-Cola will be highly profitable from entering the beer market
These will be the major areas or buckets in our framework.

Next, let’s add a few bullet points under each area to add more detail to our case framework.
To determine whether the beer market is attractive, we would need to know the market size, the market growth rate, and the average profit margins in the market.
To assess whether the market is competitive, we would need to know who the competitors are, how much market share they have, and if they have any differentiation or competitive advantages.
To decide whether Coca-Cola has the capabilities to produce beer, we need to know if there are any capability gaps or if there are significant synergies that Coca-Cola can leverage.
Finally, to determine the expected profitability of entering the market, we would need to know what expected revenues are, what expected costs are, and how long it would take Coca-Cola to break even.
This gives us our case framework.

You can repeat this process for any case interview that you get to create an outstanding case framework.
Strategy #2: Memorizing 8 – 10 Broad Business Areas to Make a Framework
Creating case frameworks from scratch can be quite time-consuming. Because of this, many interview candidates make the mistake of using memorized frameworks for case interviews.
Candidates will either use a single memorized framework for every case or memorize a different framework for every type of case interview.
The issue with using memorized frameworks is that they aren’t tailored to the specific case you are solving for. When given an atypical business problem, your framework areas or buckets will not be entirely relevant.
A poor framework makes the case interview significantly more difficult to solve.
Additionally, Interviewers can easily tell that you are regurgitating memorized information and not thinking critically.
Instead of creating frameworks from scratch each time, this second case framework strategy provides a method to speed up the process while still creating frameworks that are unique and tailored to the case. Additionally, you won’t need to memorize multiple different frameworks.
First, memorize a list of 8 - 10 broad business areas, such as the following:

When given a case, mentally run through this list and pick the 3 - 5 areas that are most relevant to the case.
This will be your framework.
If the list does not give you enough areas for your framework, brainstorm and add your own ideas as areas to your framework.
Finally, add a few bullet points under each area to add more detail to your case framework.
This strategy guarantees that your framework elements are relevant to the case. It also demonstrates that you can create unique, tailored frameworks for every business problem.
Let’s return to the Coca-Cola case example in which we are asked to determine whether or not they should enter the beer market.
Running through our list of memorized framework areas, the following six areas would be relevant:
- Market attractiveness : Is the beer market attractive?
- Competitive landscape : How tough is competition?
- Company capabilities : Does Coca-Cola have the capabilities to enter the market?
- Profitability : Will Coca-Cola be profitable from entering the market?
- Risks : What are the risks of entering the market?
- Strategic alternatives : Are there other more attractive markets Coca-Cola should enter?
You can pick 3 – 5 of these areas as the basis for your framework.
This strategy is a shortcut for creating unique and tailored frameworks for every business problem. Even if you and a friend used this same strategy, you both may end up with different frameworks.
That is completely fine. As long as the buckets in your framework are major areas and are relevant to the case, your case framework will be significantly better than most candidates’ frameworks.
You do not need to develop a framework entirely from scratch every time to create outstanding case frameworks. This case framework strategy can be applied to over 90% of case interviews.
For the remaining 10% of case interviews, you will need to learn and use the next two case interview framework strategies.
Strategy #3: Breaking Down Stakeholders to Make a Framework
The first two case framework strategies can be applied to over 90% of cases. However, some cases may require you to identify and focus on various stakeholders that are involved in running or operating a business.
For these cases, the primary areas of your case framework will be these major stakeholders.
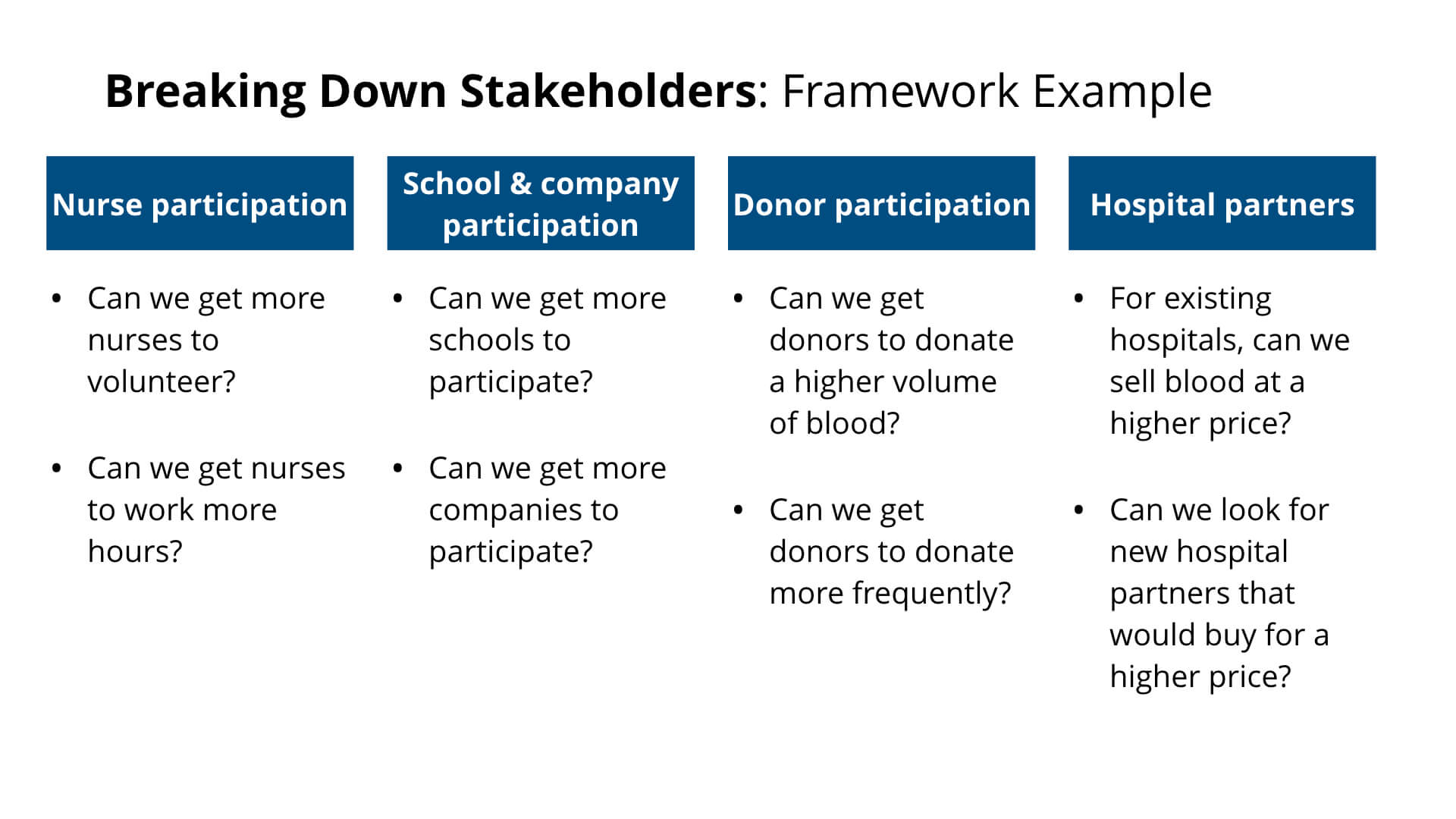
Let’s take a look at an example: Your client is a non-profit blood bank. They have volunteer nurses that go to schools and companies to collect blood from donors. They then sell this blood to hospitals, which use this blood for emergency situations when a blood transfusion is required. Currently, Hearts4Lives is not profitable because they are not able to collect enough blood to sell to their hospital partners. What can they do to fix this?
This case involves many different stakeholders:
- Volunteer nurses
- Blood donors
- Schools and companies
For cases in which many different stakeholders are involved, it will be useful to look at each stakeholder and determine what each could do to address the problem.
One potential framework could look like the following:
Strategy #4: Breaking Down Processes to make a Framework
Similar to the previous case framework strategy, some cases may require you to focus on improving or optimizing a particular process.
For these cases, the primary areas of your case framework will be each major step of the process.
Let’s take a look at an example: Your client is a waste disposal company that manages a fleet of drivers and garbage trucks that go to residential homes, collect garbage, and then dump the garbage in city landfills. They have an obligation to collect each home’s garbage once a week. Recently, they have been failing to meet this requirement and are backed up with garbage disposal requests. What is causing this issue and what should they do to fix it?
For cases involving processes and efficiencies, it can be helpful to look at the different components or steps in the process.
We can think about the process of collecting and disposing of garbage in the following steps:
- Get in a garbage truck
- Drive along a designated route
- Collect garbage at each stop
- Dispose of the garbage in the landfill
Using these steps as the primary areas of our framework, we can create the following case framework:

Once you have systematically listed all of the steps in a process, you can identify the pain points or bottlenecks that are causing the issue and determine ways to improve the process.
Strategy #5: Two-part MECE Frameworks
An easy way to make a 100% MECE framework is to use a two-part MECE framework. For the first step, start with a X and Not X framework. Some examples include:
- Internal / external
- Short-term / long-term
- Economic / non-economic
- Quantitative / qualitative
- Direct / indirect
- Supply-side / demand-side
- Upside / downside
- Benefits / cost
There are probably hundreds more frameworks that follow this pattern.
These frameworks are by definition 100% MECE. Since all of these frameworks are X or Not-X, they are mutually exclusive. There is no redundancy or overlap between X and Not-X.
Together, X and Not-X are also completely exhaustive. They cover the universe of all ideas and possibilities.
The X and Not-X framework by itself is good enough for a lot of the questions you could get asked in a case interview.
If you’re asked to brainstorm ways to decrease costs, you can create a framework consisting of decreasing variable costs and decreasing non-variable costs, also known as fixed costs.
If you’re asked to brainstorm barriers to entry, you can create a framework consisting of economic barriers to entry, such as cash and equipment, and non-economic barriers to entry, such as brand name or distribution channels.
However, to take your framework to the next level and truly impress your interviewer, we have the option of doing step two.
Step two involves adding another layer of X and Not X into your framework. What do we mean by this?
Let’s say you are trying to help a city decide whether they should host the upcoming summer Olympics. You start off with a framework consisting of benefits and costs. You can take this framework to the next level by adding another layer, such as adding in short-term and long-term.
With this additional layer, your framework now has four categories: short-term benefits, long-term benefits, short-term costs, and long-term costs. This is a 100% MECE framework that enables you to think through all possible considerations in deciding whether a city should host the Olympics.
Let’s look at another example. Suppose you are trying to figure out how to reduce a company’s costs. You start with a framework consisting of variable costs and fixed costs. You can take this framework to the next level by adding another layer, such as direct and indirect.
With this additional layer, your framework now has four categories: ways to directly reduce variable costs, ways to indirectly reduce variable costs, ways to directly reduce fixed costs, and ways to indirectly reduce fixed costs. This is another 100% MECE framework.
Case Frameworks: The 6 Most Common Frameworks
There are six common case frameworks in consulting case interviews.
Profitability frameworks are the most common types of frameworks you’ll likely use in consulting first round interviews.
A profitability case might look like this: “An electric car manufacturer has recently been experiencing a decline in profits. What should they do?”
There are two steps to solving a profitability case.
First, you need to understand quantitatively, what is the driver causing the decline in profits?
You should know the following basic profit formulas.

Is the decline in profitability due to a decline in revenue, an increase in costs, or both?
On the revenue side, what is causing the decline? Is it from a decrease in quantity of units sold? If so, is the decrease concentrated in a particular product line, geography, or customer segment?
Or is the decline due to a decrease in price? Are we selling products at a lower price? Is there a sales mix change? In other words, are we selling more low-priced products and fewer high-priced products?
On the cost side, what is causing the increase in costs? Is it from an increase in variable costs? If so, which cost elements have gone up?
Or is the increase in costs due to an increase in fixed costs? If so, which fixed costs have gone up?
Next, you need to understand qualitatively, what factors are driving the decline in profitability that you identified in the previous step.
Looking at customers, have customer needs or preferences changed? Have their purchasing habits or behaviors changed? Have their perceptions of the company changed?
Looking at competitors, have new players entered the market? Have existing competitors made any recent strategic moves? Are competitors also experiencing a decline in profitability?
Looking at the market, are there any market trends that we should be aware of? For example, are there new technology or regulatory changes? How do these trends impact profitability?
Putting all of this together, we get the following profitability framework.

Once you have gone through this profitability framework and understand both quantitatively what is causing the decline in profits and qualitatively why this is happening, you can begin brainstorming ideas to address the profitability issue.
Among the ideas that you brainstorm, you can prioritize which recommendations to focus on based on the level of impact and ease of implementation.
See the video below for an example of how to solve a profitability case using this profitability framework.
Market entry frameworks are the second most common types of frameworks you’ll likely use in consulting first round interviews.
A market entry case might look like this: “Coca-Cola is considering entering the beer market in the United States. Should they enter?”
To create a market entry framework, there are typically four statements that need to be true in order for you to recommend entering the market:
- The market is attractive
- Competition is weak
- The company has the capabilities to enter
- The company will be highly profitable from entering the market
These statements form the foundation of our market entry framework.

Note the logical order of the buckets in the framework.
We first want to determine whether the market is attractive. Then, we need to check if competition is weak and if there is an opportunity to capture meaningful market share.
If these two conditions are true, then we need to confirm that the company actually has the capabilities to enter the market.
Finally, even if the company has the capabilities to enter the market, we need to verify that they will be profitable from entering.
This is a logical progression that your market entry framework will take you through to develop a recommendation for market entry cases.
Merger and acquisition frameworks are also common frameworks you’ll use in consulting interviews.
There are two common business situations.
The first situation is a company looking to acquire another company in order to access a new market, access new customers, or to grow its revenues and profits.
Another situation is a private equity company looking to acquire a company as an investment. Their goal is to then grow the business using their operational expertise and then sell the company years later for a high return on investment. This type of case interview is called a private equity case interview .
In either of these situations, mergers and acquisition cases typically involve acquiring an attractive, successful company.
It is rare to get a case in which a company or private equity firm is looking to acquire a poorly performing company to purchase at a discount. Nevertheless, you can always clarify the goal of the merger or acquisition with the interviewer before beginning the case.
In order to recommend making an acquisition, four statements need to be true.
- The market that the acquisition target is in is attractive
- The acquisition target is an attractive company
- The acquisition generates meaningful synergies
- The acquisition target is at a great price and will generate high returns on investment
These statements become the basis of our merger and acquisition framework.

Synergies is an area that should absolutely be included in any merger or acquisition framework. A merger or acquisition can lead to revenue synergies and cost synergies.
Revenue synergies include:
- Having access to new customer segments
- Having access to new markets
- Having access to new distribution channels
- Cross-selling opportunities
- Up-selling opportunities
Cost synergies include:
- Eliminating cost redundancies
- Consolidating functions or groups
- Increasing buying power with suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, or retailers
Pricing frameworks are used in cases involving the pricing of a product or service. To develop a pricing framework, you should be familiar with the three different ways to price a product or service.
- Pricing based on costs : set a price by applying a profit margin on the total costs to produce or deliver the product or service
- Pricing based on competition : set a price based on what competitors are charging for products similar to yours
- Pricing based on value added : set a price by quantifying the benefits that the product provides customers
Your answer to pricing cases will likely involve a mix of all three of these pricing strategies.
Your pricing framework will look something like the following.

Pricing based on costs will determine the minimum price you can realistically set. Pricing based on value added will determine the maximum possible price. Pricing based on competition will determine which price in between these two price points you should set.
In order to get customers to purchase your product, the difference between your price point and the customer’s maximum willingness to pay must be greater than or equal to the difference between your competitor’s price point and the customer’s maximum willingness to pay for their product.
New product frameworks are used to help a company decide whether or not to launch a product or service.
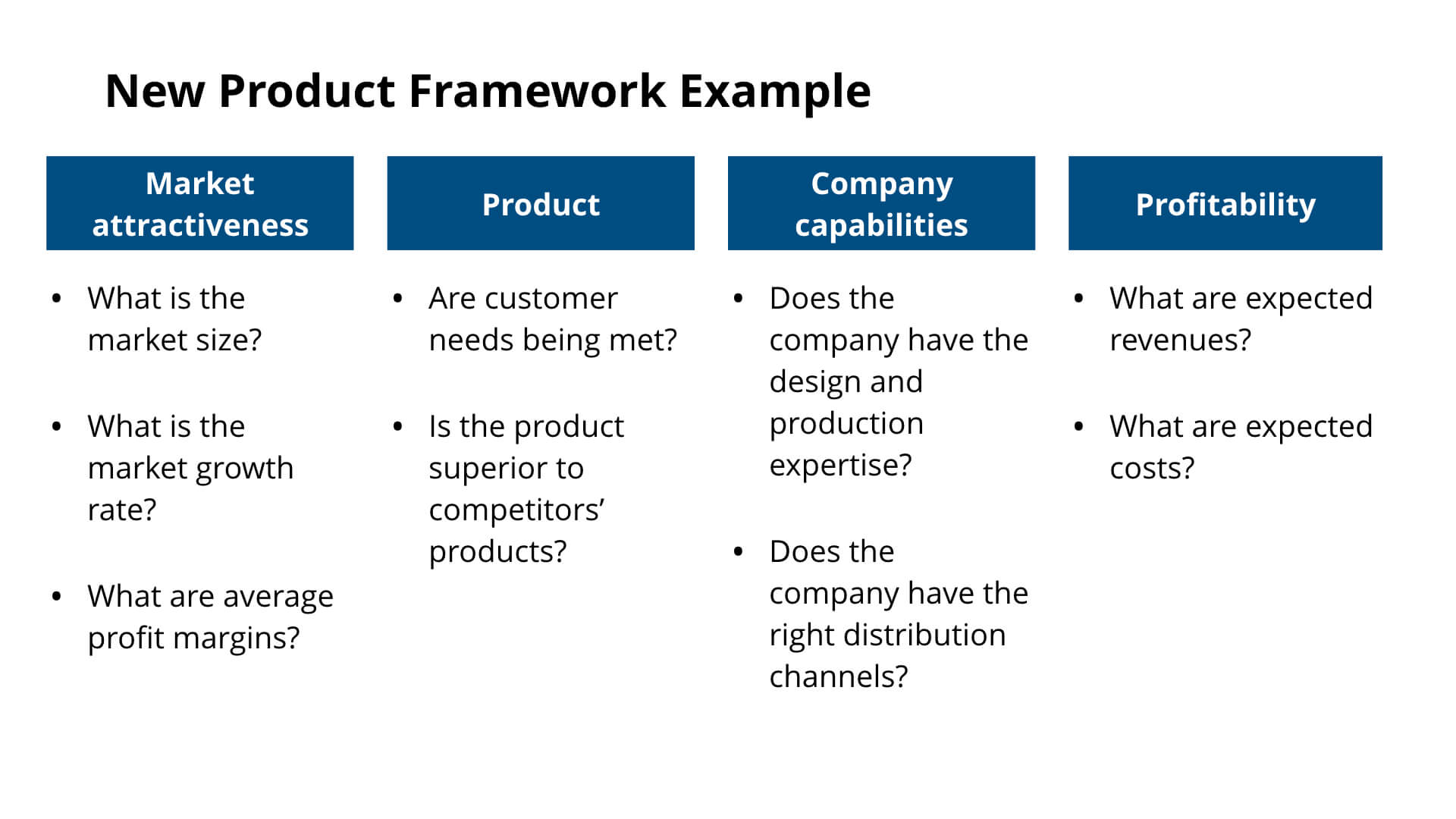
New product frameworks share many similarities with market entry frameworks. In order to recommend launching a new product, the following statements would need to be true:
- The product targets an attractive market segment
- The product meets customer needs and is superior to competitor products
- The company has the capabilities to successfully launch the product
- Launching the product will be highly profitable
Expanding on these areas, your new product framework could look like the following:
A comprehensive guide to market sizing questions and market sizing frameworks can be found in our comprehensive market sizing article. You can also watch the video below:
As a summary, market sizing or estimation questions ask you to determine the size of a particular market or to estimate a particular figure.
There are two different market sizing frameworks or approaches:
- Top-down approach : start with a large number and then refine and break down the number until you get your answer
- Bottom-up approach : start with a small number and then build up and increase the number until you get your answer
To create your market sizing framework, simply write out in bullet points, the exact steps you would take to calculate the requested market size or estimation figure.
Consulting Frameworks Every Consultant Knows
There are six consulting frameworks that nearly every consultant knows.
I would not recommend using these exact frameworks during a case interview because the interviewer may think you are just regurgitating memorized information instead of thinking critically about the case.
Instead use the four framework strategies that we covered earlier in this article to create tailored and unique frameworks for each case.
Nevertheless, it is helpful to review these common consulting frameworks in order to understand the fundamental concepts and business principles behind them.
Porter’s Five Forces framework was developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter. This framework is used to analyze the attractiveness of a particular industry.
There are five forces that determine whether an industry is attractive or unattractive.

Competitive rivalry: How competitive is the industry?
The more competitive an industry is in terms of number and strength of competitors, the less attractive the industry is. The less competitive an industry is, the more attractive the industry is.
Supplier power: How much power do suppliers have?
Suppliers are companies that provide the raw materials for your company to produce goods or services. The fewer suppliers there are, the more bargaining power suppliers have in setting prices. The more suppliers there are, the weaker bargaining power suppliers have in setting prices.
Therefore, high supplier power makes the industry less attractive while low supplier power makes the industry more attractive.
Buyer power: How much power do buyers have?
Buyers are customers or companies that purchase your company’s product. The more buyers there are, the weaker bargaining power buyers have in setting prices. The fewer buyers there are, the more bargaining power buyers have in setting prices.
Therefore, high buyer power makes the industry less attractive while low buyer power makes the industry more attractive.
Threat of substitution: How difficult is it for customers to find and use substitutes over your product?
The availability of many substitutes makes the industry less attractive while a lack of substitutes makes the industry more attractive
Threat of new entry: How difficult is it for new players to enter the market?
If barriers to entry are high, then it is difficult for new players to enter the market and it is easier for existing players to maintain their market share.
If barriers to entry are low, then it is easy for new players to enter the market and more difficult for existing players to maintain their market share.
A low threat of new entrants makes the market more attractive while a high threat of new entrants makes the market less attractive.
A SWOT framework is used to assess a company’s strategic position. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.

Strengths : What does the company do well? What qualities separate them from competitors?
Weaknesses : What does the company do poorly? What are the things that competitors do better?
Opportunities : Where are the company’s opportunities for growth or improvement?
Threats : Who are the most threatening competitors? What are the major risks to the company’s business?
The 4 P’s framework is used to develop a marketing strategy for a product. The 4 P’s in this framework are: product, place, promotion, and price.

Product : If there are multiple products or different versions of a product, you will need to decide which product to market. To do this, you will need to fully understand the benefits and points of differentiation of each product.
Select the product that best fits customer needs for the customer segment you are focusing on.
Place : You will need to decide where the product will be sold to customers. Different customer segments have different purchasing habits and behaviors. Therefore, some distribution channels will be more effective than others.
Should the product be sold directly to the customer online? Should the product be sold in the company’s stores? Should the product be sold through retail partners instead?
Promotion : You will need to decide how to spread information about the product to customers. Different customer segments have different media consumption habits and preferences. Therefore, some promotional strategies will be more effective than others.
Promotional techniques and strategies include advertising, social media marketing, email marketing, search engine marketing, video marketing, and public relations. Select the strategies and techniques that will be the most effective.
Price : You will need to decide how to price the product. Pricing is important because it determines the profits and the quantity of units sold. Pricing can also communicate information on the quality or value of the product.
If you price the product too high, you may be pricing the product above your customer segment’s willingness to pay. This would lead to lost sales.
If you price the product too low, you may be losing potential profit from customers who were willing to pay a higher price. You may also be losing profits from customers who perceive the product as low-quality due to a low price point.
In deciding on a price, you can consider the costs to produce the product, the prices of other similar products, and the value that you are providing to customers.
The 3 C’s framework is used to develop a business strategy for a company. 3 C’s stands for customers, competition, and company.
The business situation framework was developed by a former McKinsey consultant, Victor Cheng, who added a fourth component to this framework, product.
Both of these frameworks are used to develop a business strategy for a company in a variety of situations, such as market entry, new product launch, and acquisition.

There is another similar framework called the 4C framework that expands upon the 3 C's. The 4C framework stands for customer, competition, capabilities, and cost.
The BCG 2x2 Matrix Framework was developed by BCG founder Bruce Hendersen. It is used to examine all of the different businesses of a company to determine which businesses the company should invest in and focus on.
The BCG 2x2 Matrix has two different dimensions:
- Market growth : How quickly is the market growing?
- Relative market share : How much market share does the company have compared to competitors?
Each business of the company can be assessed on these two dimensions on a scale of low to high. This is what creates the 2x2 Matrix because it creates four different quadrants.
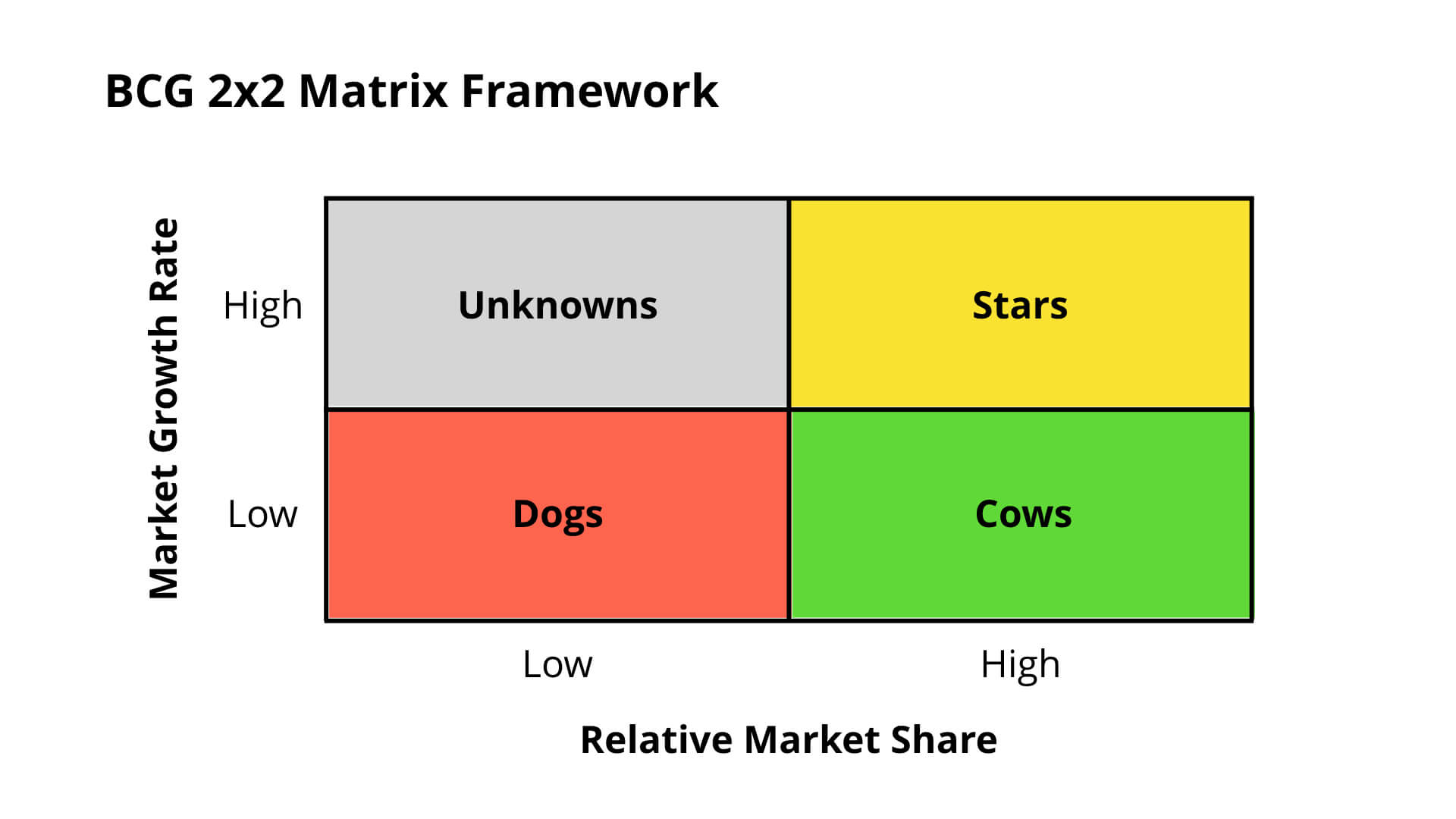
Each quadrant has a recommended strategy.
- Stars : These are businesses that have high market growth rate and high relative market share. These businesses should be heavily invested in so they can continue to grow.
- Cows : These are businesses that have low market growth rate, but high relative market share. These businesses should be maintained since they are stable, profitable businesses.
- Dogs : These are businesses that have low market growth rate and low relative market share. These businesses should not be invested in and should possibly even be divested to free up cash for other businesses.
- Unknown : These are businesses that have high market growth rate and low relative market share. The strategy for these businesses is not clear. With enough investment, these businesses could become stars. However, these businesses could also become dogs if the market growth slows or declines.
The McKinsey 7S Framework was developed by two former McKinsey consultants, Tom Peters and Robert Waterman. The 7S Framework identifies seven elements that a company needs to align on in order to be successful.

These elements are:
- Strategy : The company’s plan to grow and outcompete competitors
- Structure : The organization of the company
- Systems : The company’s daily activities and processes
- Shared values : The core beliefs, values, or mission of the company
- Style : The style of leadership or management used
- Staff : The employees that are hired
- Skills : The capabilities of the company’s employees
Land your Dream Consulting Job
Here are the resources we recommend to land your dream consulting job:
For help landing consulting interviews
- Resume Review & Editing : Transform your resume into one that will get you multiple consulting interviews
For help passing case interviews
- Comprehensive Case Interview Course (our #1 recommendation): The only resource you need. Whether you have no business background, rusty math skills, or are short on time, this step-by-step course will transform you into a top 1% caser that lands multiple consulting offers.
- Case Interview Coaching : Personalized, one-on-one coaching with a former Bain interviewer.
- Hacking the Case Interview Book (available on Amazon): Perfect for beginners that are short on time. Transform yourself from a stressed-out case interview newbie to a confident intermediate in under a week. Some readers finish this book in a day and can already tackle tough cases.
- The Ultimate Case Interview Workbook (available on Amazon): Perfect for intermediates struggling with frameworks, case math, or generating business insights. No need to find a case partner – these drills, practice problems, and full-length cases can all be done by yourself.
For help passing consulting behavioral & fit interviews
- Behavioral & Fit Interview Course : Be prepared for 98% of behavioral and fit questions in just a few hours. We'll teach you exactly how to draft answers that will impress your interviewer.
Land Multiple Consulting Offers
Complete, step-by-step case interview course. 30,000+ happy customers.
- Case Interview: A comprehensive guide
- Pyramid Principle
- Hypothesis driven structure
- Fit Interview
- Consulting math
- The key to landing your consulting job
- What is a case interview?
- Types of case interview
- How to solve cases with the Problem-Driven Structure?
- What to remember in case interviews
- Case examples or building blocks?
- How do I prepare for case interviews
- Interview day tips
- How we can help
1. The key to landing your consulting job.
Case interviews - where you are asked to solve a business case study under scrutiny - are the core of the selection process right across McKinsey, Bain and BCG (the “MBB” firms). This interview format is also used pretty much universally across other high-end consultancies; including LEK, Kearney, Oliver Wyman and the consulting wings of the “Big Four”.
If you want to land a job at any of these firms, you will have to ace multiple case interviews.
It is increasingly likely that you will also have to solve online cases given by chatbots. You might need to pass these either before making it to interview or be asked to sit them alongside first round interviews.
Importantly, case studies aren’t something you can just wing . Firms explicitly expect you to have thoroughly prepared and many of your competitors on interview day will have been prepping for months.
Don’t worry though - MCC is here to help!
This article will take you through a full overview of everything you’ll need to know to do well, linking to more detailed articles and resources at each stage to let you really drill down into the details.
As well as traditional case interviews, we’ll also attend to the new formats in which cases are being delivered and otherwise make sure you’re up to speed with recent trends in this overall part of consulting recruitment.
Before we can figure out how to prepare for a case interview, though, we will first have to properly understand in detail what exactly you are up against. What format does a standard consulting case interview take? What is expected of you? How will you be assessed?
Let's dive right in and find out!
Professional help
Before going further, if this sounds like a lot to get your head around on your own, don't worry - help is available!
Our Case Academy course gives you everything you need to know to crack cases like a pro:
Case Academy Course
To put what you learn into practice (and secure some savings in the process) you can add mock interview coaching sessions with expereinced MBB consultants:
Coaching options
And, if you just want an experienced consultant to take charge of the whole selection process for you, you can check out our comprehensive mentoring programmes:
Explore mentoring
Now, back to the article!
2. What is a case interview?
Before we can hope to tackle a case interview, we have to understand what one is.
In short, a case interview simulates real consulting work by having you solve a business case study in conversation with your interviewer.
This case study will be a business problem where you have to advise a client - that is, an imaginary business or similar organisation in need of guidance.
You must help this client solve a problem and/or make a decision. This requires you to analyse the information you are given about that client organisation and figure out a final recommendation for what they should do next.
Business problems in general obviously vary in difficulty. Some are quite straightforward and can be addressed with fairly standard solutions. However, consulting firms exist precisely to solve the tough issues that businesses have failed to deal with internally - and so consultants will typically work on complex, idiosyncratic problems requiring novel solutions.
Some examples of case study questions might be:
- How much would you pay for a banking licence in Ghana?
- Estimate the potential value of the electric vehicle market in Germany
- How much gas storage capacity should a UK domestic energy supplier build?
Consulting firms need the brightest minds they can find to put to work on these important, difficult projects. You can expect the case studies you have to solve in interview, then, to echo the unique, complicated problems consultancies deal with every day. As we’ll explain here, this means that you need to be ready to think outside the box to figure out genuinely novel solutions.
2.1. Where are case interviews in the consulting selection process?
Not everyone who applies to a consulting firm will have a case interview - far from it!
In fact, case interviews are pretty expensive and inconvenient for firms to host, requiring them to take consultants off active projects and even fly them back to the office from location for in-person interviews (although this happens less frequently now). Ideally, firms want to cut costs and save time by narrowing down the candidate pool as much as possible before any live interviews.
As such, there are some hoops to jump through before you make it to interview rounds.
Firms will typically eliminate as much as 80% of the applicant pool before interviews start . For most firms, 50%+ of applicants might be cut based on resumes, before a similar cut is made on those remaining based on aptitude tests. McKinsey currently gives their Solve assessment to most applicants, but will use their resulting test scores alongside resumes to cut 70%+ of the candidate pool before interviews.
You'll need to be on top of your game to get as far as a case interview with a top firm. Getting through the resume screen and any aptitude tests is an achievement in itself! Also we need to note that the general timeline of an application can differ depending on a series of factors, including which position you apply, your background, and the office you are applying to. For example, an undergraduate applying for a Business Analyst position (the entry level job at McKinsey) will most likely be part of a recruitment cycle and as such have pretty fixed dates when they need to sit the pre-screening test, and have the first and second round interviews (see more on those below). Conversely, an experienced hire will most likely have a much greater choice of test and interview dates as well as more time at their disposal to prepare.
For readers not yet embroiled in the selection process themselves, let’s put case interviews in context and take a quick look at each stage in turn. Importantly, note that you might also be asked to solve case studies outside interviews as well…
2.1.1. Application screen
It’s sometimes easy to forget that such a large cut is made at the application stage. At larger firms, this will mean your resume and cover letter is looked at by some combination of AI tools, recruitment staff and junior consulting staff (often someone from your own university).
Only the best applications will be passed to later stages, so make sure to check out our free resume and cover letter guides, and potentially get help with editing , to give yourself the best chance possible.
2.1.2. Aptitude tests and online cases
This part of the selection process has been changing quickly in recent years and is increasingly beginning to blur into the traditionally separate case interview rounds.
In the past, GMAT or PST style tests were the norm. Firms then used increasingly sophisticated and often gamified aptitude tests, like the Pymetrics test currently used by several firms, including BCG and Bain, and the original version of McKinsey’s Solve assessment (then branded as the Problem Solving Game).
Now, though, there is a move towards delivering relatively sophisticated case studies online. For example, McKinsey has replaced half the old Solve assessment with an online case. BCG’s Casey chatbot case now directly replaces a live first round case interview, and in the new era of AI chatbots, we expect these online cases to quickly become more realistic and increasingly start to relieve firms of some of the costs of live case interviews.
Our consultants collectively reckon that, over time, 50% of case interviews are likely to be replaced with these kinds of cases . We give some specific advice for online cases in section six. However, the important thing to note is that these are still just simulations of traditional case interviews - you still need to learn how to solve cases in precisely the same way, and your prep will largely remain the same.
2.1.3. Rounds of Interviews
Now, let’s not go overboard with talk of AI. Even in the long term, the client facing nature of consulting means that firms will have live case interviews for as long as they are hiring anyone. And in the immediate term, case interviews are still absolutely the core of consulting selection.
Before landing an offer at McKinsey, Bain, BCG or any similar firm, you won’t just have one case interview, but will have to complete four to six case interviews, usually divided into two rounds, with each interview lasting approximately 50-60 minutes .
Being invited to first round usually means two or three case interviews. As noted above, you might also be asked to complete an online case or similar alongside your first round interviews.
If you ace first round, you will be invited to second round to face the same again, but more gruelling. Only then - after up to six case interviews in total, can you hope to receive an offer.
2.2. Differences between first and second round interviews
Despite case interviews in the first and second round following the same format, second/final round interviews will be significantly more intense . The seniority of the interviewer, time pressure (with up to three interviews back-to-back), and the sheer value of the job at stake will likely make a second round consulting case interview one of the most challenging moments of your professional life.
There are three key differences between the two rounds:
- Time Pressure : Final round case interviews test your ability to perform under pressure, with as many as three interviews in a row and often only very small breaks between them.
- Focus : Since second round interviewers tend to be more senior (usually partners with 12+ years experience) and will be more interested in your personality and ability to handle challenges independently. Some partners will drill down into your experiences and achievements to the extreme. They want to understand how you react to challenges and your ability to identify and learn from past mistakes.
- Psychological Pressure: While case interviews in the first round are usually more focused on you simply cracking the case, second round interviewers often employ a "bad cop" strategy to test the way you react to challenges and uncertainty.
2.3. What skills do case interviews assess?
Reliably impressing your interviewers means knowing what they are looking for. This means understanding the skills you are being assessed against in some detail.
Overall, it’s important always to remember that, with case studies, there are no strict right or wrong answers. What really matters is how you think problems through, how confident you are with your conclusions and how quick you are with the back of the envelope arithmetic.
The objective of this kind of interview isn’t to get to one particular solution, but to assess your skillset. This is even true of modern online cases, where sophisticated AI algorithms score how you work as well as the solutions you generate.
If you visit McKinsey , Bain and BCG web pages on case interviews, you will find that the three firms look for very similar traits, and the same will be true of other top consultancies.
Broadly speaking, your interviewer will be evaluating you across five key areas:
2.1.1.One: Probing mind
Showing intellectual curiosity by asking relevant and insightful questions that demonstrate critical thinking and a proactive nature. For instance, if we are told that revenues for a leading supermarket chain have been declining over the last ten years, a successful candidate would ask:
“ We know revenues have declined. This could be due to price or volume. Do we know how they changed over the same period? ”
This is as opposed to a laundry list of questions like:
- Did customers change their preferences?
- Which segment has shown the decline in volume?
- Is there a price war in the industry?
2.1.2. Structure
Structure in this context means structuring a problem. This, in turn, means creating a framework - that is, a series of clear, sequential steps in order to get to a solution.
As with the case interview in general, the focus with case study structures isn’t on reaching a solution, but on how you get there.
This is the trickiest part of the case interview and the single most common reason candidates fail.
We discuss how to properly structure a case in more detail in section three. In terms of what your interviewer is looking for at high level, though, key pieces of your structure should be:
- Proper understanding of the objective of the case - Ask yourself: "What is the single crucial piece of advice that the client absolutely needs?"
- Identification of the drivers - Ask yourself: "What are the key forces that play a role in defining the outcome?"
Our Problem Driven Structure method, discussed in section three, bakes this approach in at a fundamental level. This is as opposed to the framework-based approach you will find in older case-solving
Focus on going through memorised sequences of steps too-often means failing to develop a full understanding of the case and the real key drivers.
At this link, we run through a case to illustrate the difference between a standard framework-based approach and our Problem Driven Structure method.
2.1.3. Problem Solving
You’ll be tested on your ability to identify problems and drivers, isolate causes and effects, demonstrate creativity and prioritise issues. In particular, the interviewer will look for the following skills:
- Prioritisation - Can you distinguish relevant and irrelevant facts?
- Connecting the dots - Can you connect new facts and evidence to the big picture?
- Establishing conclusions - Can you establish correct conclusions without rushing to inferences not supported by evidence?
2.1.4. Numerical Agility
In case interviews, you are expected to be quick and confident with both precise and approximated numbers. This translates to:
- Performing simple calculations quickly - Essential to solve cases quickly and impress clients with quick estimates and preliminary conclusions.
- Analysing data - Extract data from graphs and charts, elaborate and draw insightful conclusions.
- Solving business problems - Translate a real world case to a mathematical problem and solve it.
Our article on consulting math is a great resource here, though the extensive math content in our MCC Academy is the best and most comprehensive material available.
2.1.5. Communication
Real consulting work isn’t just about the raw analysis to come up with a recommendation - this then needs to be sold to the client as the right course of action.
Similarly, in a case interview, you must be able to turn your answer into a compelling recommendation. This is just as essential to impressing your interviewer as your structure and analysis.
Consultants already comment on how difficult it is to find candidates with the right communication skills. Add to this the current direction of travel, where AI will be able to automate more and more of the routine analytic side of consulting, and communication becomes a bigger and bigger part of what consultants are being paid for.
So, how do you make sure that your recommendations are relevant, smart, and engaging? The answer is to master what is known as CEO-level communication .
This art of speaking like a CEO can be quite challenging, as it often involves presenting information in effectively the opposite way to how you might normally.
To get it right, there are three key areas to focus on in your communications:
- Top down : A CEO wants to hear the key message first. They will only ask for more details if they think that will actually be useful. Always consider what is absolutely critical for the CEO to know, and start with that. You can read more in our article on the Pyramid Principle .
- Concise : This is not the time for "boiling the ocean" or listing an endless number possible solutions. CEOs, and thus consultants, want a structured, quick and concise recommendation for their business problem, that they can implement immediately.
- Fact-based : Consultants share CEOs' hatred of opinions based on gut feel rather than facts. They want recommendations based on facts to make sure they are actually in control. Always go on to back up your conclusions with the relevant facts.
Being concise and to the point is key in many areas, networking being one for them. For more detail on all this, check out our full article on delivering recommendations .
Prep the right way
3. types of case interview.
While most case interviews share a similar structure, firms will have some differences in the particular ways they like to do things in terms of both the case study and the fit component.
As we’ll see, these differences aren’t hugely impactful in terms of how you prepare. That said, it's always good to know as much as possible about what you will be going up against.
3.1. Different case objectives
A guiding thread throughout this article and our approach in general will be to treat each case as a self-contained problem and not try to pigeonhole it into a certain category. Having said that, there are of course similarities between cases and we can identify certain parameters and objectives.
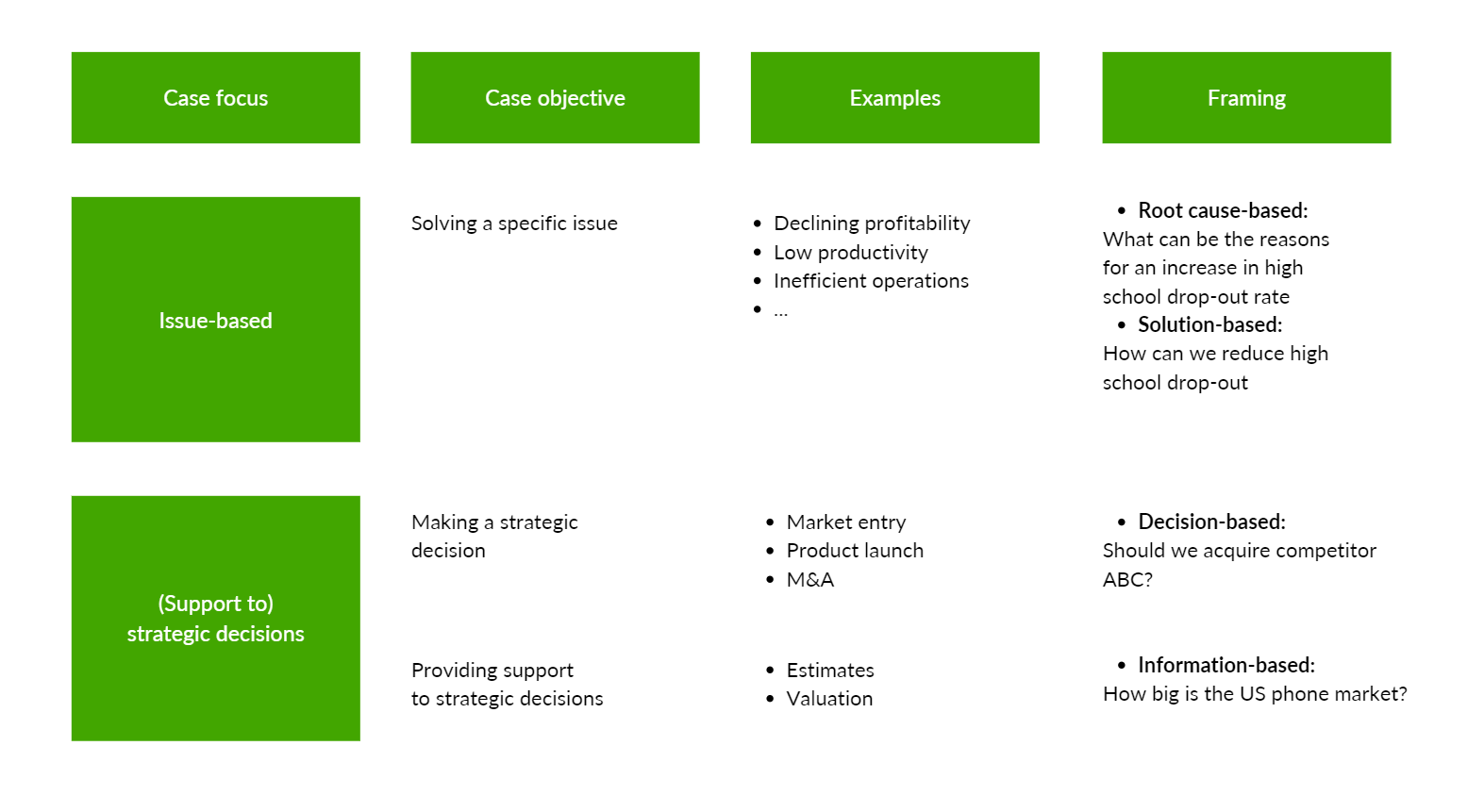
Broadly speaking, cases can be divided into issue-based cases and strategic decision cases. In the former you will be asked to solve a certain issue, such as declining profits, or low productivity whereas in the latter you will be ask whether your client should or should not do something, such as enter a specific market or acquire another company. The chart below is a good breakdown of these different objectives:
3.2. How do interviewers craft cases
While interviewers will very likely be given a case bank to choose from by their company, a good number of them will also choose to adapt the cases they would currently be working on to a case interview setting. The difference is that the latter cases will be harder to pigeonhole and apply standard frameworks to, so a tailored approach will be paramount.
If you’ve applied for a specific practice or type of consulting - such as operational consulting, for example - it’s very likely that you will receive a case geared towards that particular area alongside a ‘generalist’ consulting case (however, if that’s the case, you will generally be notified). The other main distinction when it comes to case interviews is between interviewer-led and candidate-led.
3.3. Candidate-led cases
Most consulting case interview questions test your ability to crack a broad problem, with a case prompt often going something like:
" How much would you pay to secure the rights to run a restaurant in the British Museum? "
You, as a candidate, are then expected to identify your path to solve the case (that is, provide a structure), leveraging your interviewer to collect the data and test your assumptions.
This is known as a “candidate-led” case interview and is used by Bain, BCG and other firms. From a structuring perspective, it’s easier to lose direction in a candidate-led case as there are no sign-posts along the way. As such, you need to come up with an approach that is both broad enough to cover all of the potential drivers in a case but also tailored enough to the problem you are asked to solve. It’s also up to you to figure out when you need to delve deeper into a certain branch of the case, brainstorm or ask for data. The following case from Bain is an excellent example on how to navigate a candidate-led case.
3.4. Interviewer-led cases
This type of case - employed most famously by McKinsey - is slightly different, with the interviewer controlling the pace and direction of the conversation much more than with other case interviews.
At McKinsey, your interviewer will ask you a set of pre-determined questions, regardless of your initial structure. For each question, you will have to understand the problem, come up with a mini structure, ask for additional data (if necessary) and come to the conclusion that answers the question. This more structured format of case also shows up in online cases by other firms - notably including BCG’s Casey chatbot (with the amusing result that practising McKinsey-style cases can be a great addition when prepping for BCG).
Essentially, these interviewer-led case studies are large cases made up of lots of mini-cases. You still use basically the same method as you would for standard (or candidate-led) cases - the main difference is simply that, instead of using that method to solve one big case, you are solving several mini-cases sequentially. These cases are easier to follow as the interviewer will guide you in the right direction. However, this doesn’t mean you should pay less attention to structure and deliver a generic framework! Also, usually (but not always!) the first question will ask you to map your approach and is the equivalent of the structuring question in candidate-led cases. Sometimes, if you’re missing key elements, the interviewer might prompt you in the right direction - so make sure to take those prompts seriously as they are there to help you get back on track (ask for 30 seconds to think on the prompt and structure your approach). Other times - and this is a less fortunate scenario - the interviewer might say nothing and simply move on to the next question. This is why you should put just as much thought (if not more) into the framework you build for interviewer-led cases , as you may be penalized if you produce something too generic or that doesn’t encompass all the issues of the case.
3.5. Case and fit
The standard case interview can be thought of as splitting into two standalone sub-interviews. Thus “case interviews” can be divided into the case study itself and a “fit interview” section, where culture fit questions are asked.
This can lead to a bit of confusion, as the actual case interview component might take up as little as half of your scheduled “case interview”. You need to make sure you are ready for both aspects.
To illustrate, here is the typical case interview timeline:

- First 15-30 minutes: Fit Interview - with questions assessing your motivation to be a consultant in that specific firm and your traits around leadership and teamwork. Learn more about the fit interview in our in-depth article here .
- Next 30-40 minutes: Case Interview - solving a case study
- Last 5 minutes: Fit Interview again - this time focussing on your questions for your interviewer.
Both the Case and Fit interviews play crucial roles in the finial hiring decision. There is no “average” taken between case and fit interviews: if your performance is not up to scratch in either of the two, you will not be able to move on to the next interview round or get an offer.
NB: No case without fit
Note that, even if you have only been told you are having a case interview or otherwise are just doing a case study, always be prepared to answer fit questions. At most firms, it is standard practice to include some fit questions in all case interviews, even if there are also separate explicit fit interviews, and interviewers will almost invariably include some of these questions around your case. This is perfectly natural - imagine how odd and artificial it would be to show up to an interview, simply do a case and leave again, without talking about anything else with the interviewer before or after.
3.5.1 Differences between firms
For the most part, a case interview is a case interview. However, firms will have some differences in the particular ways they like to do things in terms of both the case study and the fit component.
3.5.2. The McKinsey PEI
McKinsey brands its fit aspect of interviews as the Personal Experience Interview or PEI. Despite the different name, this is really much the same interview you will be going up against in Bain, BCG and any similar firms.
McKinsey does have a reputation for pushing candidates a little harder with fit or PEI questions , focusing on one story per interview and drilling down further into the specific details each time. We discuss this tendency more in our fit interview article . However, no top end firm is going to go easy on you and you should absolutely be ready for the same level of grilling at Bain, BCG and others. Thus any difference isn’t hugely salient in terms of prep.
3.6. What is different in 2023?
For the foreseeable future, you are going to have to go through multiple live case interviews to secure any decent consulting job. These might increasingly happen via Zoom rather than in person, but they should remain largely the same otherwise.
However, things are changing and the rise of AI in recent months seems pretty much guaranteed to accelerate existing trends.
Even before the explosive development of AI chatbots like ChatGPT we have seen in recent months, automation was already starting to change the recruitment process.
As we mentioned, case interviews are expensive and inconvenient for firms to run . Ideally, then, firms will try to reduce the number of interviews required for recruitment as far as possible. For many years, tests of various kinds served to cut down the applicant pool and thus the number of interviews. However, these tests had a limited capacity to assess candidates against the full consulting skillset in the way that case interviews do so well.
More recently, though, the development of online testing has allowed for more and more advanced assessments. Top consulting firms have been leveraging screening tests that better and better capture the same skillset as case interviews. Eventually this is converging on automated case studies. We see this very clearly with the addition of the Redrock case to McKinsey’s Solve assessment.
As these digital cases become closer to the real thing, the line between test and case interview blurs. Online cases don’t just reduce the number of candidates to case interview, but start directly replacing them.
Case in point here is BCG’s Casey chatbot . Previously, BCG had deployed less advanced online cases and similar tests to weed out some candidates before live case interviews began. Now, though, Casey actually replaces one first round case interview.
Casey, at time of writing, is still a relatively “basic” chatbot, basically running through a pre-set script. The Whatsapp-like interface does a lot of work to make it feel like one is chatting to a “real person” - the chatbot itself, though, cannot provide feedback or nudges to candidates as would a human interviewer.
We fully expect that, as soon as BCG and other firms can train a truer AI, these online cases will become more widespread and start replacing more live interviews.
We discuss the likely impacts of advanced AI on consulting recruitment and the industry more broadly in our blog.
Here, though, the real message is that you should expect to run into digital cases as well as traditional case interviews.
Luckily, despite any changes in specific case interview format, you will still need to master the same fundamental skills and prepare in much the same way.
We’ll cover a few ways to help prepare for chatbot cases in section four. Ultimately, though, firms are looking for the same problem solving ability and mindset as a real interviewer. Especially as chatbots get better at mimicking a real interviewer, candidates who are well prepared for case cracking in general should have no problem with AI administered cases.
3.6.1. Automated fit interviews
Analogous to online cases, in recent years there has been a trend towards automated, “one way” fit interviews, with these typically being administered for consultancies by specialist contractors like HireVue or SparkHire.
These are kind of like Zoom interviews, but if the interviewer didn’t show up. Instead you will be given fit questions to answer and must record your answer in your computer webcam. Your response will then go on to be assessed by an algorithm, scoring both what you say and how you say it.
Again, with advances in AI, it is easy to imagine these automated case interviews going from fully scripted interactions, where all candidates are asked the same list of questions, to a more interactive experience. Thus, we might soon arrive at a point where you are being grilled on the details of your stories - McKinsey PEI style - but by a bot rather than a human.
We include some tips on this kind of “one way” fit interview in section six here.
4. How to solve cases with the Problem-Driven Structure?
If you look around online for material on how to solve case studies, a lot of what you find will set out framework-based approaches. However, as we have mentioned, these frameworks tend to break down with more complex, unique cases - with these being exactly the kind of tough case studies you can expect to be given in your case interviews.
To address this problem, the MyConsultingCoach team has synthesized a new approach to case cracking that replicates how top management consultants approach actual engagements.
MyConsultingCoach’s Problem Driven Structure approach is a universal problem solving method that can be applied to any business problem , irrespective of its nature.
As opposed to just selecting a generic framework for each case interview, the Problem Driven Structure approach works by generating a bespoke structure for each individual question and is a simplified version of the roadmap McKinsey consultants use when working on engagements.
The canonical seven steps from McKinsey on real projects are simplified to four for case interview questions, as the analysis required for a six-month engagement is somewhat less than that needed for a 45-minute case study. However, the underlying flow is the same (see the method in action in the video below)
Let's zoom in to see how our method actually works in more detail:
4.1. Identify the problem
Identifying the problem means properly understanding the prompt/question you are given, so you get to the actual point of the case.
This might sound simple, but cases are often very tricky, and many candidates irretrievably mess things up within the first few minutes of starting. Often, they won’t notice this has happened until they are getting to the end of their analysis. Then, they suddenly realise that they have misunderstood the case prompt - and have effectively been answering the wrong question all along!
With no time to go back and start again, there is nothing to do. Even if there were time, making such a silly mistake early on will make a terrible impression on their interviewer, who might well have written them off already. The interview is scuppered and all the candidate’s preparation has been for nothing.
This error is so galling as it is so readily avoidable.
Our method prevents this problem by placing huge emphasis on a full understanding of the case prompt. This lays the foundations for success as, once we have identified the fundamental, underlying problem our client is facing, we focus our whole analysis around finding solutions to this specific issue.
Now, some case interview prompts are easy to digest. For example, “Our client, a supermarket, has seen a decline in profits. How can we bring them up?”. However, many of the prompts given in interviews for top firms are much more difficult and might refer to unfamiliar business areas or industries. For example, “How much would you pay for a banking license in Ghana?” or “What would be your key areas of concern be when setting up an NGO?”
Don’t worry if you have no idea how you might go about tackling some of these prompts!
In our article on identifying the problem and in our full lesson on the subject in our MCC Academy course, we teach a systematic, four step approach to identifying the problem , as well as running through common errors to ensure you start off on the right foot every time!
This is summarised here:

Following this method lets you excel where your competitors mess up and get off to a great start in impressing your interviewer!
4.2. Build your problem driven structure
After you have properly understood the problem, the next step is to successfully crack a case is to draw up a bespoke structure that captures all the unique features of the case.
This is what will guide your analysis through the rest of the case study and is precisely the same method used by real consultants working on real engagements.
Of course, it might be easier here to simply roll out one an old-fashioned framework, and a lot of candidates will do so. This is likely to be faster at this stage and requires a lot less thought than our problem-driven structure approach.
However, whilst our problem driven structure approach requires more work from you, our method has the advantage of actually working in the kind of complex case studies where generic frameworks fail - that is exactly the kind of cases you can expect at an MBB interview .
Since we effectively start from first principles every time, we can tackle any case with the same overarching method. Simple or complex, every case is the same to you and you don’t have to gamble a job on whether a framework will actually work
4.2.1 Issue trees
Issue trees break down the overall problem into a set of smaller problems that you can then solve individually. Representing this on a diagram also makes it easy for both you and your interviewer to keep track of your analysis.
To see how this is done, let’s look at the issue tree below breaking down the revenues of an airline:
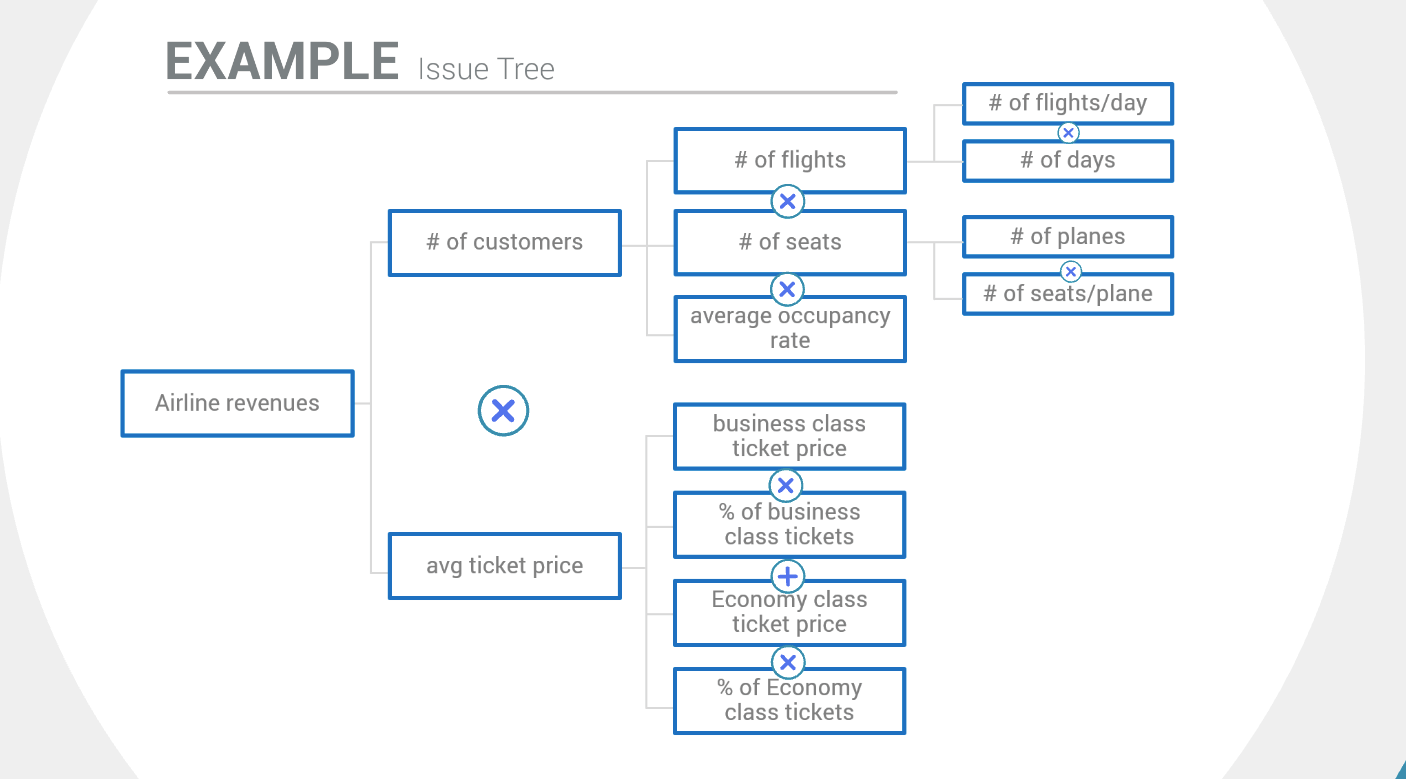
These revenues can be segmented as the number of customers multiplied by the average ticket price. The number of customers can be further broken down into a number of flights multiplied by the number of seats, times average occupancy rate. The node corresponding to the average ticket price can then be segmented further.
4.2.2 Hypothesis trees
Hypothesis trees are similar, the only difference being that rather than just trying to break up the issue into smaller issues you are assuming that the problem can be solved and you are formulating solutions.
In the example above, you would assume revenues can be increased by either increasing the average ticket price or the number of customers . You can then hypothesize that you can increase the average occupancy rate in three ways: align the schedule of short and long haul flights, run a promotion to boost occupancy in off-peak times, or offer early bird discounts.
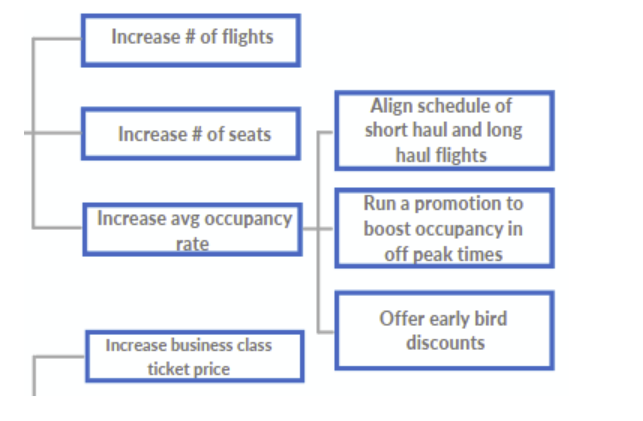
4.2.3 Other structures:structured lists
Structured lists are simply subcategories of a problem into which you can fit similar elements. This McKinsey case answer starts off by identifying several buckets such as retailer response, competitor response, current capabilities and brand image and then proceeds to consider what could fit into these categories.
Buckets can be a good way to start the structure of a complex case but when using them it can be very difficult to be MECE and consistent, so you should always aim to then re-organize them into either an issue or a hypothesis tree.
It is worth noting that the same problem can be structured in multiple valid ways by choosing different means to segment the key issues. Ultimately all these lists are methods to set out a logical hierachy among elements.
4.2.4 Structures in practice
That said, not all valid structures are equally useful in solving the underlying problem. A good structure fulfils several requirements - including MECE-ness , level consistency, materiality, simplicity, and actionability. It’s important to put in the time to master segmentation, so you can choose a scheme isn’t only valid, but actually useful in addressing the problem.
After taking the effort to identify the problem properly, an advantage of our method is that it will help ensure you stay focused on that same fundamental problem throughout. This might not sound like much, but many candidates end up getting lost in their own analysis, veering off on huge tangents and returning with an answer to a question they weren’t asked.
Another frequent issue - particularly with certain frameworks - is that candidates finish their analysis and, even if they have successfully stuck to the initial question, they have not actually reached a definite solution. Instead, they might simply have generated a laundry list of pros and cons, with no clear single recommendation for action.
Clients employ consultants for actionable answers, and this is what is expected in the case interview. The problem driven structure excels in ensuring that everything you do is clearly related back to the key question in a way that will generate a definitive answer. Thus, the problem driven structure builds in the hypothesis driven approach so characteristic of real consulting practice.
You can learn how to set out your own problem driven structures in our article here and in our full lesson in the MCC Academy course.
4.2. Lead the analysis
A problem driven structure might ensure we reach a proper solution eventually, but how do we actually get there?
We call this step " leading the analysis ", and it is the process whereby you systematically navigate through your structure, identifying the key factors driving the issue you are addressing.
Generally, this will mean continuing to grow your tree diagram, further segmenting what you identify as the most salient end nodes and thus drilling down into the most crucial factors causing the client’s central problem.
Once you have gotten right down into the detail of what is actually causing the company’s issues, solutions can then be generated quite straightforwardly.
To see this process in action, we can return to our airline revenue example:
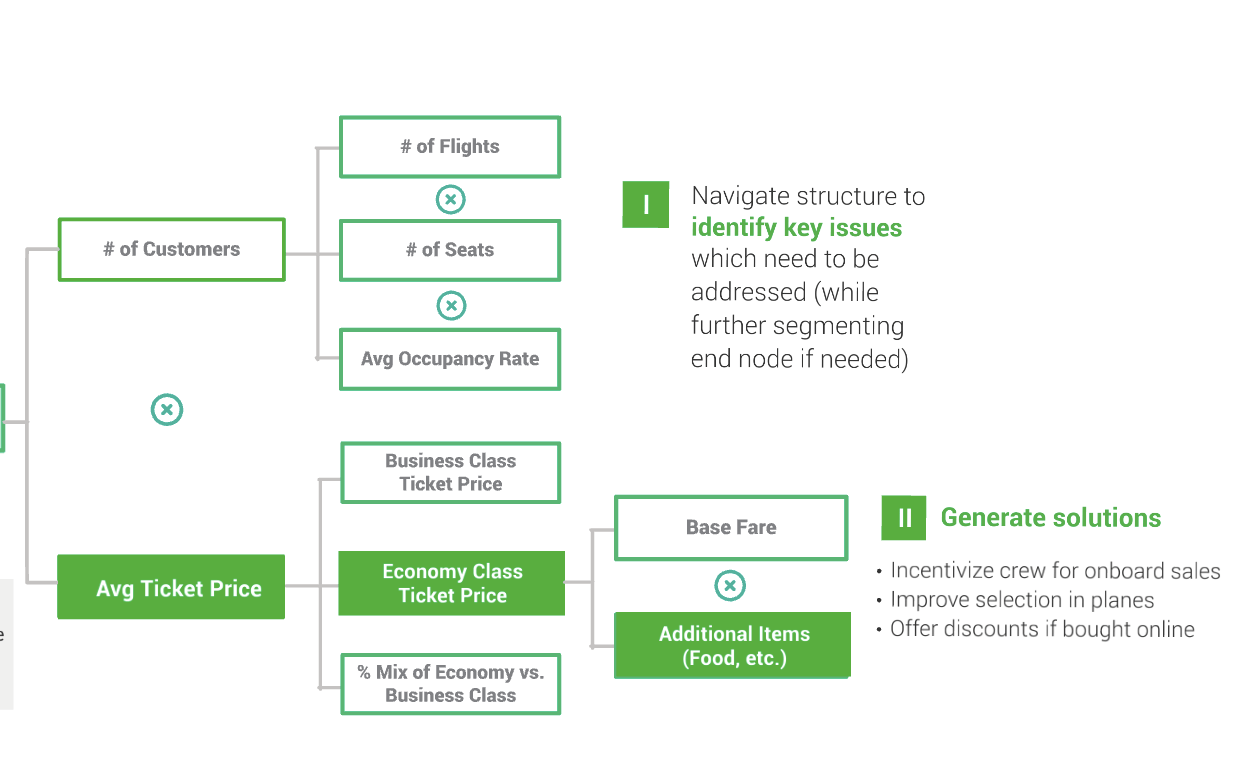
Let’s say we discover the average ticket price to be a key issue in the airline’s problems. Looking closer at the drivers of average ticket price, we find that the problem lies with economy class ticket prices. We can then further segment that price into the base fare and additional items such as food.
Having broken down the issue to such a fine-grained level and considering the 80/20 rule(see below), solutions occur quite naturally. In this case, we can suggest incentivising the crew to increase onboard sales, improving assortment in the plane, or offering discounts for online purchases.
Our article on leading the analysis is a great primer on the subject, with our video lesson in the MCC Academy providing the most comprehensive guide available.
4.4. Provide recommendations
So you have a solution - but you aren’t finished yet!
Now, you need to deliver your solution as a final recommendation.
This should be done as if you are briefing a busy CEO and thus should be a one minute, top-down, concise, structured, clear, and fact-based account of your findings.
The brevity of the final recommendation belies its importance. In real life consulting, the recommendation is what the client has potentially paid millions for - from their point of view, it is the only thing that matters.
In a case interview, your performance in this final summing up of your case is going to significantly colour your interviewer’s parting impression of you - and thus your chances of getting hired!
So, how do we do it right?
Barbara Minto's Pyramid Principle elegantly sums up almost everything required for a perfect recommendation. The answer comes first , as this is what is most important. This is then supported by a few key arguments , which are in turn buttressed by supporting facts .
Across the whole recommendation, the goal isn’t to just summarise what you have done. Instead, you are aiming to synthesize your findings to extract the key "so what?" insight that is useful to the client going forward.
All this might seem like common sense, but it is actually the opposite of how we relay results in academia and other fields. There, we typically move from data, through arguments and eventually to conclusions. As such, making good recommendations is a skill that takes practice to master.
We can see the Pyramid Principle illustrated in the diagram below:
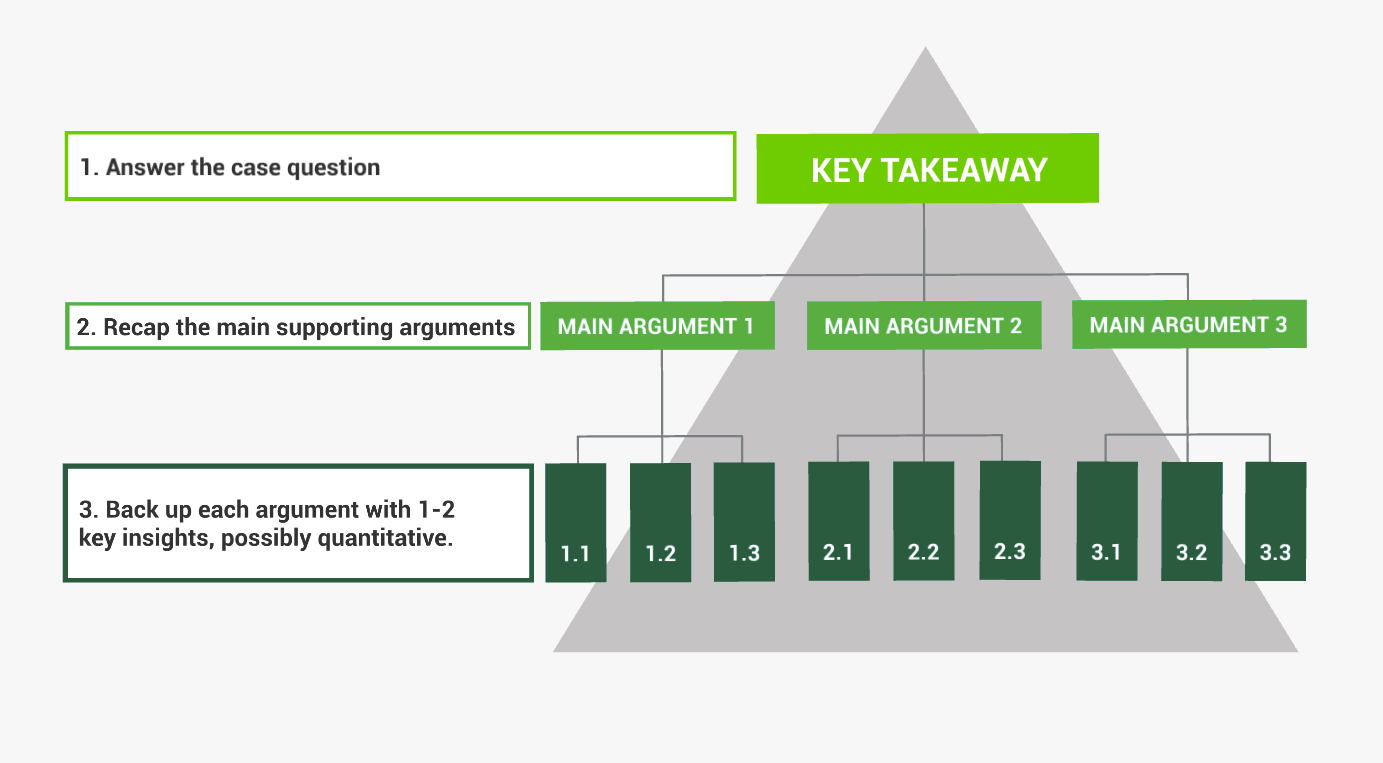
To supplement the basic Pyramid Principle scheme, we suggest candidates add a few brief remarks on potential risks and suggested next steps . This helps demonstrate the ability for critical self-reflection and lets your interviewer see you going the extra mile.
The combination of logical rigour and communication skills that is so definitive of consulting is particularly on display in the final recommendation.
Despite it only lasting 60 seconds, you will need to leverage a full set of key consulting skills to deliver a really excellent recommendation and leave your interviewer with a good final impression of your case solving abilities.
Our specific article on final recommendations and the specific video lesson on the same topic within our MCC Academy are great, comprehensive resources. Beyond those, our lesson on consulting thinking and our articles on MECE and the Pyramid Principle are also very useful.
4.5. What if I get stuck?
Naturally with case interviews being difficult problems there may be times where you’re unsure what to do or which direction to take. The most common scenario is that you will get stuck midway through the case and there are essentially two things that you should do:
- 1. Go back to your structure
- 2. Ask the interviewer for clarification
Your structure should always be your best friend - after all, this is why you put so much thought and effort into it: if it’s MECE it will point you in the right direction. This may seem abstract but let’s take the very simple example of a profitability case interview: if you’ve started your analysis by segmenting profit into revenue minus costs and you’ve seen that the cost side of the analysis is leading you nowhere, you can be certain that the declining profit is due to a decline in revenue.
Similarly, when you’re stuck on the quantitative section of the case interview, make sure that your framework for calculations is set up correctly (you can confirm this with the interviewer) and see what it is you’re trying to solve for: for example if you’re trying to find what price the client should sell their new t-shirt in order to break even on their investment, you should realize that what you’re trying to find is the break even point, so you can start by calculating either the costs or the revenues. You have all the data for the costs side and you know they’re trying to sell 10.000 pairs so you can simply set up the equation with x being the price.
As we’ve emphasised on several occasions, your case interview will be a dialogue. As such, if you don’t know what to do next or don’t understand something, make sure to ask the interviewer (and as a general rule always follow their prompts as they are trying to help, not trick you). This is especially true for the quantitative questions, where you should really understand what data you’re looking at before you jump into any calculations. Ideally you should ask your questions before you take time to formulate your approach but don’t be afraid to ask for further clarification if you really can’t make sense of what’s going on. It’s always good to walk your interviewer through your approach before you start doing the calculations and it’s no mistake to make sure that you both have the same understanding of the data. For example when confronted with the chart below, you might ask what GW (in this case gigawatt) means from the get-go and ask to confirm the different metrics (i.e. whether 1 GW = 1000 megawatts). You will never be penalised for asking a question like that.
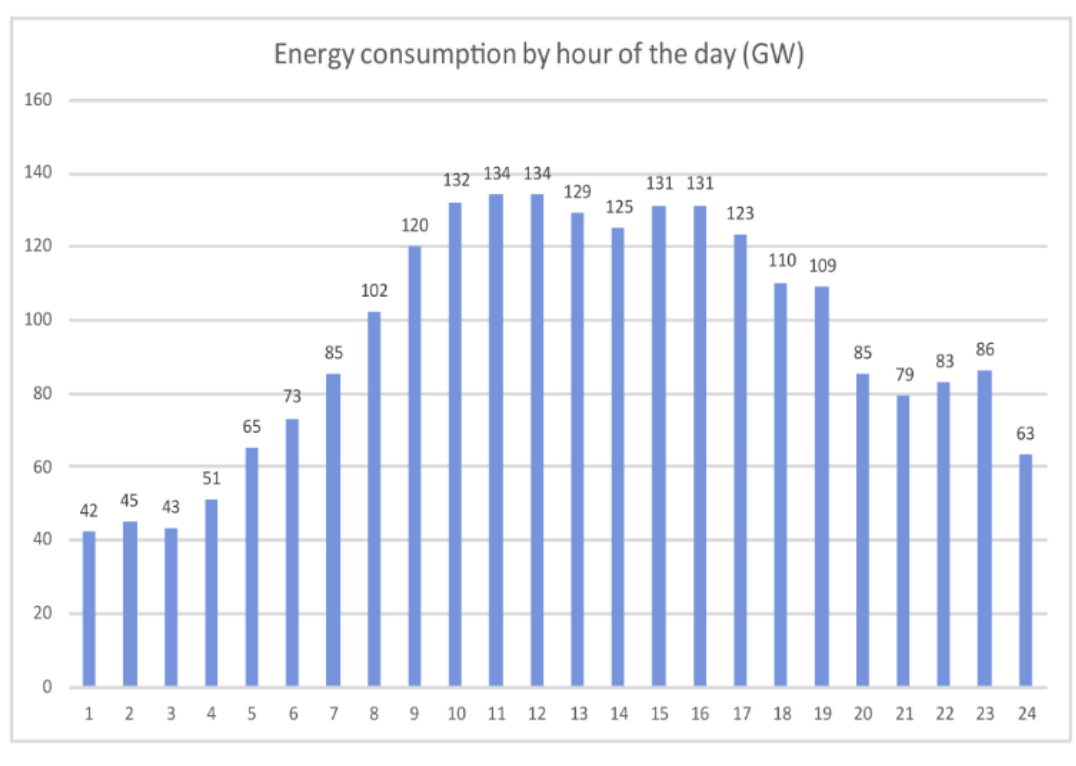
5. What to remember in case interviews
If you’re new to case cracking you might feel a bit hopeless when you see a difficult case question, not having any idea where to start.
In fact though, cracking case interviews is much like playing chess. The rules you need to know to get started are actually pretty simple. What will make you really proficient is time and practice.
In this section, we’ll run through a high level overview of everything you need to know, linking to more detailed resources at every step.
5.1. An overall clear structure
You will probably hear this more than you care for but it is the most important thing to keep in mind as you start solving cases, as not only it is a key evaluation criterion but the greatest tool you will have at your disposal. The ability to build a clear structure in all aspects of the case inteview will be the difference between breezing through a complicated case and struggling at its every step. Let’s look a bit closer at the key areas where you should be structured!
5.1.1 Structured notes
Every case interview starts with a prompt, usually verbal, and as such you will have to take some notes. And here is where your foray into structure begins, as the notes you take should be clear, concise and structured in a way that will allow you to repeat the case back to the interviewer without writing down any unnecessary information.
This may sound very basic but you should absolutely not be dismissive about it: taking clear and organized notes will allow what we found helps is to have separate sections for:
- The case brief
- Follow-up questions and answers
- Numerical data
- Case structure (the most crucial part when solving the case)
- Any scrap work during the case (usually calculations)
When solving the case - or, as we call it here, in the Lead the analysis step, it is highly recommended to keep on feeding and integrating your structure, so that you never get lost. Maintaining a clear high level view is one of the most critical aspects in case interviews as it is a key skill in consulting: by constantly keeping track of where you are following your structure, you’ll never lose your focus on the end goal.
In the case of an interviewer-led case, you can also have separate sheets for each question (e.g. Question 1. What factors can we look at that drive profitability?). If you develop a system like this you’ll know exactly where to look for each point of data rather than rummage around in untidy notes. There are a couple more sections that you may have, depending on preference - we’ll get to these in the next sections.
5.1.2 Structured communication
There will be three main types of communication in cases:
- 1. Asking and answering questions
- 2. Walking the interviewer through your structure (either the case or calculation framework - we’ll get to that in a bit!)
- 3. Delivering your recommendation
Asking and answering questions will be the most common of these and the key thing to do before you speak is ask for some time to collect your thoughts and get organised. What you want to avoid is a ‘laundry list’ of questions or anything that sounds too much like a stream of consciousness.
Different systems work for different candidates but a sure-fire way of being organised is numbering your questions and answers. So rather than saying something like ‘I would like to ask about the business model, operational capacity and customer personas’ it’s much better to break it down and say something along the lines of ‘I’ve got three key questions. Firstly I would like to inquire into the business model of our client. Secondly I would like to ask about their operational capacity. Thirdly I would like to know more about the different customer personas they are serving’.
A similar principle should be applied when walking the interviewer through your structure, and this is especially true of online case interviews (more and more frequent now) when the interviewer can’t see your notes. Even if you have your branches or buckets clearly defined, you should still use a numbering system to make it obvious to the interviewer. So, for example, when asked to identify whether a company should make an acquisition, you might say ‘I would like to examine the following key areas. Firstly the financial aspects of this issue, secondly the synergies and thirdly the client’s expertise’
The recommendation should be delivered top-down (see section 4.4 for specifics) and should employ the same numbering principle. To do so in a speedy manner, you should circle or mark the key facts that you encounter throughout the case so you can easily pull them out at the end.
5.1.3 Structured framework
It’s very important that you have a systematic approach - or framework - for every case. Let’s get one thing straight: there is a difference between having a problem-solving framework for your case and trying to force a case into a predetermined framework. Doing the former is an absolute must , whilst doing the latter will most likely have you unceremoniously dismissed.
We have seen there are several ways of building a framework, from identifying several categories of issues (or ‘buckets’) to building an issue or hypothesis tree (which is the most efficient type of framework). For the purpose of organization, we recommend having a separate sheet for the framework of the case, or, if it’s too much to manage, you can have it on the same sheet as the initial case prompt. That way you’ll have all the details as well as your proposed solution in one place.
5.1.4 Structured calculations
Whether it’s interviewer or candidate-led, at some point in the case you will get a bunch of numerical data and you will have to perform some calculations (for the specifics of the math you’ll need on consulting interviews, have a look at our Consulting Math Guide ). Here’s where we urge you to take your time and not dive straight into calculating! And here’s why: while your numerical agility is sure to impress interviewers, what they’re actually looking for is your logic and the calculations you need to perform in order to solve the problem . So it’s ok if you make a small mistake, as long as you’re solving for the right thing.
As such, make it easy for them - and yourself. Before you start, write down in steps the calculations you need to perform. Here’s an example: let’s say you need to find out by how much profits will change if variable costs are reduced by 10%. Your approach should look something like:
- 1. Calculate current profits: Profits = Revenues - (Variable costs + Fixed costs)
- 2. Calculate the reduction in variable costs: Variable costs x 0.9
- 3. Calculate new profits: New profits = Revenues - (New variable costs + Fixed costs)
Of course, there may be more efficient ways to do that calculation, but what’s important - much like in the framework section - is to show your interviewer that you have a plan, in the form of a structured approach. You can write your plan on the sheet containing the data, then perform the calculations on a scrap sheet and fill in the results afterward.
5.2. Common business knowledge and formulas
Although some consulting firms claim they don’t evaluate candidates based on their business knowledge, familiarity with basic business concepts and formulae is very useful in terms of understanding the case studies you are given in the first instance and drawing inspiration for structuring and brainstorming.
If you are coming from a business undergrad, an MBA or are an experienced hire, you might well have this covered already. For those coming from a different background, it may be useful to cover some.
Luckily, you don’t need a degree-level understanding of business to crack case interviews , and a lot of the information you will pick up by osmosis as you read through articles like this and go through cases.
However, some things you will just need to sit down and learn. We cover everything you need to know in some detail in our Case Academy Course course. However, some examples here of things you need to learn are:
- Basic accounting (particularly how to understand all the elements of a balance sheet)
- Basic economics
- Basic marketing
- Basic strategy
Below we include a few elementary concepts and formulae so you can hit the ground running in solving cases. We should note that you should not memorise these and indeed a good portion of them can be worked out logically, but you should have at least some idea of what to expect as this will make you faster and will free up much of your mental computing power. In what follows we’ll tackle concepts that you will encounter in the private business sector as well as some situations that come up in cases that feature clients from the NGO or governmental sector.
5.2.1 Business sector concepts
These concepts are the bread and butter of almost any business case so you need to make sure you have them down. Naturally, there will be specificities and differences between cases but for the most part here is a breakdown of each of them.
5.2.1.1. Revenue
The revenue is the money that the company brings in and is usually equal to the number of products they sell multiplied to the price per item and can be expressed with the following equation:
Revenue = Volume x Price
Companies may have various sources of revenue or indeed multiple types of products, all priced differently which is something you will need to account for in your case interview. Let’s consider some situations. A clothing company such as Nike will derive most of their revenue from the number of products they sell times the average price per item. Conversely, for a retail bank revenue is measured as the volume of loans multiplied by the interest rate at which the loans are given out. As we’ll see below, we might consider primary revenues and ancillary revenues: in the case of a football club, we might calculate primary revenues by multiplying the number of tickets sold by the average ticket price, and ancillary revenues those coming from sales of merchandise (similarly, let’s say average t-shirt price times the number of t-shirts sold), tv rights and sponsorships.
These are but a few examples and another reminder that you should always aim to ask questions and understand the precise revenue structure of the companies you encounter in cases.
5.2.1.2. Costs
The costs are the expenses that a company incurs during its operations. Generally, they can be broken down into fixed and variable costs :
Costs = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs
As their name implies, fixed costs do not change based on the number of units produced or sold. For example, if you produce shoes and are renting the space for your factory, you will have to pay the rent regardless of whether you produce one pair or 100. On the other hand, variable costs depend on the level of activity, so in our shoe factory example they would be equivalent to the materials used to produce each pair of shoes and would increase the more we produce.
These concepts are of course guidelines used in order to simplify the analysis in cases, and you should be aware that in reality often the situation can be more complicated. However, this should be enough for case interviews. Costs can also be quasi-fixed, in that they increase marginally with volume. Take the example of a restaurant which has a regular staff, incurring a fixed cost but during very busy hours or periods they also employ some part-time workers. This cost is not exactly variable (as it doesn’t increase with the quantity of food produced) but also not entirely fixed, as the number of extra hands will depend on how busy the restaurant is. Fixed costs can also be non-linear in nature. Let’s consider the rent in the same restaurant: we would normally pay a fixed amount every month, but if the restaurant becomes very popular we might need to rent out some extra space so the cost will increase. Again, this is not always relevant for case interviews.
5.2.1.3. Profit and profit margin
The profit is the amount of money a company is left with after it has paid all of its expenses and can be expressed as follows:
Profit = Revenue - Costs
It’s very likely that you will encounter a profitability issue in one of your case interviews, namely you will be asked to increase a company’s profit. There are two main ways of doing this: increasing revenues and reducing costs , so these will be the two main areas you will have to investigate. This may seem simple but what you will really need to understand in a case are the key drivers of a business (and this should be done through clarifying questions to the interviewer - just as a real consultant would question their client).
For example, if your client is an airline you can assume that the main source of revenue is sales of tickets, but you should inquire how many types of ticket the specific airline sells. You may naturally consider economy and business class tickets, but you may find out that there is a more premium option - such as first class - and several in-between options. Similarly to our football club example, there may be ancillary revenues from selling of food and beverage as well as advertising certain products or services on flights.
You may also come across the profit margin in case interviews. This is simply the percentage of profit compared to the revenue and can be expressed as follows:
Profit margin = Profit/Revenue x 100
5.2.1.4. Break-even point
An ancillary concept to profit, the break-even point is the moment where revenues equal costs making the profit zero and can be expressed as the following equation:
Revenues = Costs (Fixed costs + Variable costs)
This formula will be useful when you are asked questions such as ‘What is the minimum price I should sell product X?’ or ‘What quantity do I need to sell in order to recoup my investment?’. Let’s say in a case interview an owner of a sandwich store asks us to figure out how many salami and cheese salami sandwiches she needs to sell in order to break even. She’s spending $4 on salami and $2 for cheese and lettuce per sandwich, and believes she can sell the sandwiches at around $7. The cost of utilities and personnel is around $5000 per month. We could lay this all out in the break-even equation:
7 x Q ( quantity ) = (4+2) x Q + 5000 ( variable + fixed costs )
In a different scenario, we may be asked to calculate the break-even price . Let’s consider our sandwich example and say our owner knows she has enough ingredients for about 5000 sandwiches per month but is not sure how much to sell them for. In that case, if we know our break-even equation, we can simply make the following changes:
P ( price ) x 5000 = (4+2) x 5000 + 5000
By solving the equation we get to the price of $7 per sandwich.
5.2.1.5. Market share and market size
We can also consider the market closely with profit, as in fact the company’s performance in the market is what drives profits. The market size is the total number of potential customers for a certain business or product, whereas the market share is the percentage of that market that your business controls (or could control, depending on the case).
There is a good chance you will have to estimate the market size in one of your case interviews and we get into more details on how to do that below. You may be asked to estimate this in either number of potential customers or total value . The latter simply refers to the number of customers multiplied by the average value of the product or service.
To calculate the market share you will have to divide the company’s share by the total market size and multiply by 100:
Note, though, that learning the very basics of business is the beginning rather than the end of your journey. Once you are able to “speak business” at a rudimentary level, you should try to “become fluent” and immerse yourself in reading/viewing/listening to as wide a variety of business material as possible, getting a feel for all kinds of companies and industries - and especially the kinds of problems that can come up in each context and how they are solved. The material put out by the consulting firms themselves is a great place to start, but you should also follow the business news and find out about different companies and sectors as much as possible between now and interviews. Remember, if you’re going to be a consultant, this should be fun rather than a chore!
5.3 Public sector and NGO concepts
As we mentioned, there will be some cases (see section 6.6 for a more detailed example) where the key performance indicators (or KPIs in short) will not be connected to profit. The most common ones will involve the government of a country or an NGO, but they can be way more diverse and require more thought and application of first principles. We have laid out a couple of the key concepts or KPIs that come up below
5.3.1 Quantifiability
In many such scenarios you will be asked to make an important strategic decision of some kind or to optimise a process. Of course these are not restricted to non-private sector cases but this is where they really come into their own as there can be great variation in the type of decision and the types of field.
While there may be no familiar business concepts to anchor yourself onto, a concept that is essential is quantifiability . This means, however qualitative the decision might seem, consultants rely on data so you should always aim to have aspects of a decision that can be quantified, even if the data doesn’t present itself in a straightforward manner.
Let’s take a practical example. Your younger sibling asks you to help them decide which university they should choose if they want to study engineering. One way to structure your approach would be to segment the problem into factors affecting your sibling’s experience at university and experience post-university. Within the ‘at uni’ category you might think about the following:
- Financials : How much are tuition costs and accommodation costs?
- Quality of teaching and research : How are possible universities ranked in the QS guide based on teaching and research?
- Quality of resources : How well stocked is their library, are the labs well equipped etc.?
- Subject ranking : How is engineering at different unis ranked?
- Life on campus and the city : What are the living costs in the city where the university is based? What are the extracurricular opportunities and would your sibling like to live in that specific city based on them?
Within the ‘out of uni’ category you might think about:
- Exit options : What are the fields in which your sibling could be employed and how long does it take the average student of that university to find a job?
- Alumni network : What percentage of alumni are employed by major companies?
- Signal : What percentage of applicants from the university get an interview in major engineering companies and related technical fields?
You will perhaps notice that all the buckets discussed pose quantifiable questions meant to provide us with data necessary to make a decision. It’s no point to ask ‘Which university has the nicest teaching staff?’ as that can be a very subjective metric.
5.3.1 Impact
Another key concept to consider when dealing with sectors other than the private one is how impactful a decision or a line of inquiry is on the overarching issue , or whether all our branches in our issue tree have a similar impact. This can often come in the form of impact on lives, such as in McKinsey’s conservation case discussed below, namely how many species can we save with our choice of habitat.
5.4 Common consulting concepts
Consultants use basic business concepts on an every day basis, as they help them articulate their frameworks to problems. However, they also use some consulting specific tools to quality check their analysis and perform in the most efficient way possible. These principles can be applied to all aspects of a consultant’s work, but for brevity we can say they mostly impact a consultant’s systematic approach and communication - two very important things that are also tested in case interviews. Therefore, it’s imperative that you not only get to know them, but learn how and when to use them as they are at the very core of good casing. They are MECE-ness, the Pareto Principle and the Pyramid principle and are explained briefly below - you should, however, go on to study them in-depth in their respective articles.
Perhaps the central pillar of all consulting work and an invaluable tool to solve cases, MECE stands for Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive . It can refer to any and every aspect in a case but is most often used when talking about structure. We have a detailed article explaining the concept here , but the short version is that MECE-ness ensures that there is no overlap between elements of a structure (i.e. the Mutually Exclusive component) and that it covers all the drivers or areas of a problem (Collectively Exhaustive). It is a concept that can be applied to any segmentation when dividing a set into subsets that include it wholly but do not overlap.
Let’s take a simple example and then a case framework example. In simple terms, when we are asked to break down the set ‘cars’ into subsets, dividing cars into ‘red cars’ and ‘sports cars’ is neither mutually exclusive (as there are indeed red sports cars) nor exhaustive of the whole set (i.e. there are also yellow non-sports cars that are not covered by this segmentation). A MECE way to segment would be ‘cars produced before 2000’ and ‘cars produced after 2000’ as this segmentation allows for no overlap and covers all the cars in existence.
Dividing cars can be simple, but how can we ensure MECEness in a case-interview a.k.a. a business situation. While the same principles apply, a good tip to ensure that your structure is MECE is to think about all the stakeholders - i.e. those whom a specific venture involves.
Let’s consider that our client is a soda manufacturer who wants to move from a business-to-business strategy, i.e. selling to large chains of stores and supermarkets, to a business-to-consumer strategy where it sells directly to consumers. In doing so they would like to retrain part of their account managers as direct salespeople and need to know what factors to consider.
A stakeholder-driven approach would be to consider the workforce and customers and move further down the issue tree, thinking about individual issues that might affect them. In the case of the workforce, we might consider how the shift would affect their workload and whether it takes their skillset into account. As for the customers, we might wonder whether existing customers would be satisfied with this move: will the remaining B2B account managers be able to provide for the needs of all their clients and will the fact that the company is selling directly to consumers now not cannibalise their businesses? We see how by taking a stakeholder-centred approach we can ensure that every single perspective and potential issue arising from it is fully covered.
5.4.2 The Pareto Principle
Also known as the 80/20 rule, this principle is important when gauging the impact of a decision or a factor in your analysis. It simply states that in business (but not only) 80% of outcomes come from 20% of causes. What this means is you can make a few significant changes that will impact most of your business organisation, sales model, cost structure etc.
Let’s have a look at 3 quick examples to illustrate this:
- 80% of all accidents are caused by 20% of drivers
- 20% of a company’s products account for 80% of the sales
- 80% of all results in a company are driven by 20% of its employees
The 80/20 rule will be a very good guide line in real engagements as well as case interviews, as it will essentially point to the easiest and most straightforward way of doing things. Let’s say one of the questions in a case is asking you to come up with an approach to understand the appeal of a new beard trimmer. Obviously you can’t interview the whole male population so you might think about setting up a webpage and asking people to comment their thoughts. But what you would get would be a laundry list of difficult to sift through data.
Using an 80/20 approach you would segment the population based on critical factors (age groups, grooming habits etc.) and then approach a significant sample size of each (e.g. 20), analysing the data and reaching a conclusion.
5.4.3 The Pyramid Principle
This principle refers to organising your communication in a top-down , efficient manner. While this is generally applicable, the pyramid principle will most often be employed when delivering the final recommendation to your client. This means - as is implicit in the name - that you would organise your recommendation (and communication in general) as a pyramid, stating the conclusion or most important element at the top then go down the pyramid listing 3 supporting arguments and then further (ideally also 3) supporting arguments for those supporting arguments.
Let’s look at this in practice in a case interview context: your client is a German air-conditioning unit manufacturer who was looking to expand into the French market. However, after your analysis you’ve determined that the market share they were looking to capture would not be feasible. A final recommendation using the Pyramid Principle would sound something like this: ‘I recommend that we do not enter the German market for the following three reasons. Firstly, the market is too small for our ambitions of $50 million. Secondly the market is heavily concentrated, being controlled by three major players and our 5 year goal would amount to controlling 25% of the market, a share larger than that of any of the players. Thirdly, the alternative of going into the corporate market would not be feasible, as it has high barriers to entry.Then, if needed, we could delve deeper into each of our categories
6. Case examples or building blocks?
As we mentioned before, in your case interview preparation you will undoubtedly find preparation resources that claim that there are several standard types of cases and that there is a general framework that can be applied to each type of case. While there are indeed cases that are straightforward at least in appearance and seemingly invite the application of such frameworks, the reality is never that simple and cases often involve multiple or more complicated components that cannot be fitted into a simple framework.
At MCC we don’t want you to get into the habit of trying to identify which case type you’re dealing with and pull out a framework, but we do recognize that there are recurring elements in frameworks that are useful - such as the profitability of a venture (with its revenues and costs), the valuation of a business, estimating and segmenting a market and pricing a product.
We call these building blocks because they can be used to build case frameworks but are not a framework in and of themselves, and they can be shuffled around and rearranged in any way necessary to be tailored to our case. Hence, our approach is not to make you think in terms of case types but work from first principles and use these building blocks to build your own framework. Let’s take two case prompts to illustrate our point.
The first is from the Bain website, where the candidate is asked whether they think it’s a good idea for their friend to open a coffee shop in Cambridge UK (see the case here ). The answer framework provided here is a very straightforward profitability analysis framework, examining the potential revenues and potential costs of the venture:
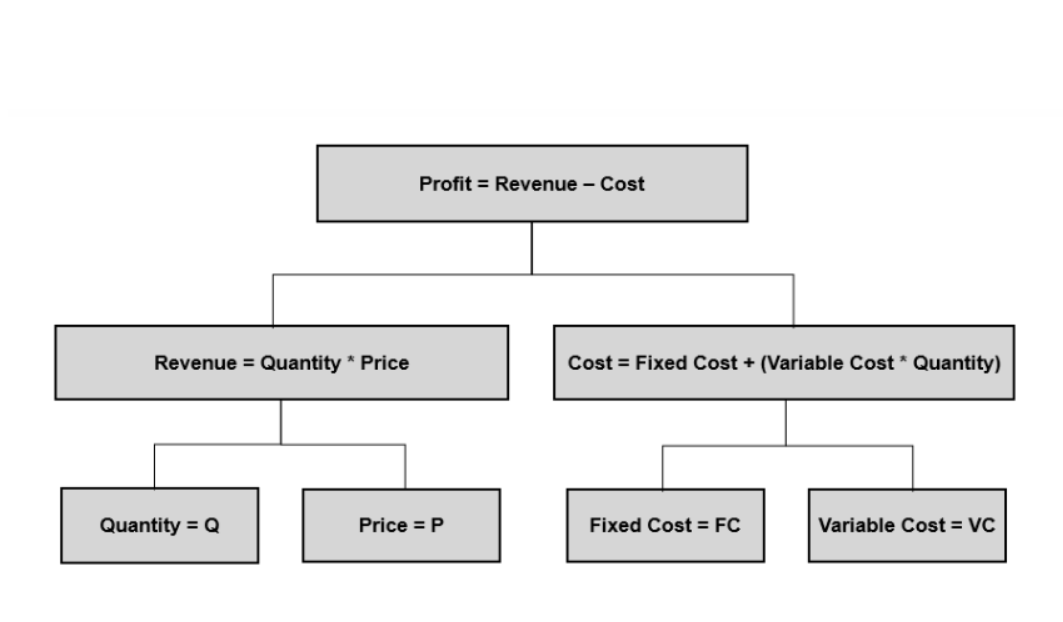
While this is a good point to start for your case interview (especially taken together with the clarifying questions), we will notice that this approach will need more tailoring to the case - for example the quantity of coffee will be determined by the market for coffee drinkers in Cambridge, which we have to determine based on preference. We are in England so a lot of people will be drinking tea but we are in a university town so perhaps more people than average are drinking coffee as it provides a better boost when studying. All these are some much needed case-tailored hypotheses that we can make based on the initial approach.
Just by looking at this case we might be tempted to say that we can just take a profitability case and apply it without any issues. However, this generic framework is just a starting point and in reality we would need to tailor it much further in the way we had started to do in order to get to a satisfactory answer. For example, the framework for this specific case interview doesn’t cover aspects such as the customer’s expertise: does the friend have any knowledge of the coffee business, such as where to source coffee and how to prepare it? Also, we could argue there may be some legal factors to consider here, such as any approvals that they might need from the city council to run a coffee shop on site, or some specific trade licences that are not really covered in the basic profitability framework.
Let’s take a different case , however, from the McKinsey website. In this scenario, the candidate is being asked to identify some factors in order to choose where to focus the client’s conservation efforts. Immediately we can realise that this case doesn’t lend itself to any pre-packaged framework and we will need to come up with something from scratch - and take a look at McKinsey’s answer of the areas to focus on:

We notice immediately that this framework is 100% tailored to the case - of course there are elements which we encounter in other cases, such as costs and risks but again these are applied in an organic way. It’s pretty clear that while no standard framework would work in this case, the aforementioned concepts - costs and risks - and the way to approach them (a.k.a building blocks ) are fundamentally similar throughout cases (with the obvious specificities of each case).
In what follows, we’ll give a brief description of each building block starting from the Bain example discussed previously, in order to give you a general idea of what they are and their adaptability, but you should make sure to follow the link to the in-depth articles to learn all their ins and outs.
6.1 Estimates and segmentation
This building block will come into play mostly when you’re thinking about the market for a certain product (but make sure to read the full article for more details). Let’s take our Bain Cambridge coffee example. As we mentioned under the quantity bucket we need to understand what the market size for coffee in Cambridge would be - so we can make an estimation based on segmentation .
The key to a good estimation is the ability to logically break down the problem into more manageable pieces. This will generally mean segmenting a wider population to find a particular target group. We can start off with the population of Cambridge - which we estimate at 100.000. In reality the population is closer to 150.000 but that doesn’t matter - the estimation has to be reasonable and not accurate , so unless the interviewer gives you a reason to reconsider you can follow your instinct. We can divide that into people who do and don’t drink coffee. Given our arguments before, we can conclude that 80% of those, so 80.000 drink coffee. Then we can further segment into those who drink regularly - let’s say every day - and those who drink occasionally - let’s say once a week. Based on the assumptions before about the student population needing coffee to function, and with Cambridge having a high student population, we can assume that 80% of those drinking coffee are regular drinkers, so that would be 64.000 regular drinkers and 16.000 occasional drinkers. We can then decide whom we want to target what our strategy needs to be:
This type of estimation and segmentation can be applied to any case specifics - hence why it is a building block.
6.2 Profitability
We had several looks at this building block so far (see an in-depth look here ) as it will show up in most case interivew scenarios, since profit is a key element in any company’s strategy. As we have seen, the starting point to this analysis is to consider both the costs and revenues of a company, and try to determine whether revenues need to be improved or whether costs need to be lowered. In the coffee example, the revenues are dictated by the average price per coffe x the number of coffees sold , whereas costs can be split into fixed and variable .
Some examples of fixed costs would be the rent for the stores and the cost of the personnel and utilities, while the most obvious variable costs would be the coffee beans used and the takeaway containers (when needed). We may further split revenues in this case into Main revenues - i.e. the sales of coffee - and Ancillary revenues , which can be divided into Sales of food products (sales of pastries, sandwiches etc., each with the same price x quantity schema) and Revenues from events - i.e renting out the coffee shop to events and catering for the events themselves. Bear in mind that revenues will be heavily influenced by the penetration rate , i.e. the share of the market which we can capture.
6.3 Pricing
Helping a company determine how much they should charge for their goods or services is another theme that comes up frequently in cases. While it may seem less complicated than the other building blocks, we assure you it’s not - you will have to understand and consider several factors, such as the costs a company is incurring, their general strategic positioning, availability, market trends as well as the customers’ willingness to pay (or WTP in short) - so make sure to check out our in-depth guide here .
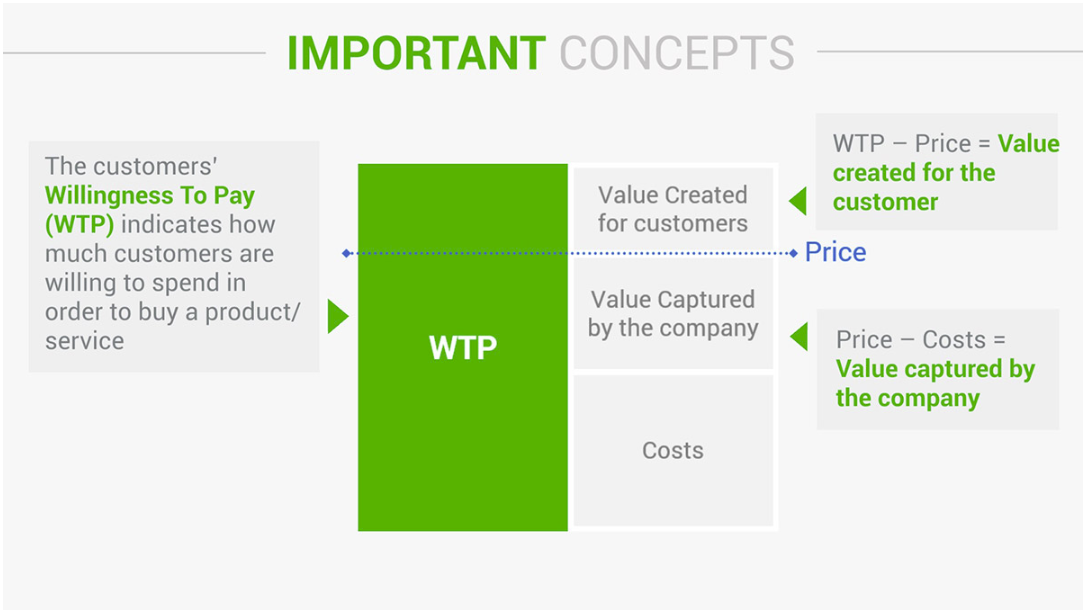
In our example, we may determine that the cost per cup (coffee beans, staff, rent) is £1. We want to be student friendly so we should consider how much students would want to pay for a coffee as well as how much are competitors are charging. Based on those factors, it would be reasonable to charge on average £2 per cup of coffee. It’s true that our competitors are charging £3 but they are targeting mostly the adult market, whose willingness to pay is higher, so their pricing model takes that into account as well as the lower volume of customers in that demographic.
6.4. Valuation
A variant of the pricing building block, a valuation problem generally asks the candidate to determine how much a client should pay for a specific company (the target of an acquisition) as well as what other factors to consider. The two most important factors (but not the only ones - for a comprehensive review see our Valuation article ) to consider are the net present value (in consulting interviews usually in perpetuity) and the synergies .
In short, the net present value of a company is how much profit it currently brings in, divided by how much that cash flow will depreciate in the future and can be represented with the equation below:
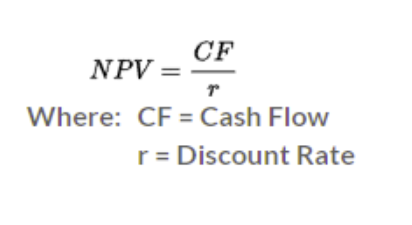
The synergies refer to what could be achieved should the companies operate as one, and can be divided into cost and revenue synergies .
Let’s expand our coffee example a bit to understand these. Imagine that our friend manages to open a chain of coffee shops in Cambridge and in the future considers acquiring a chain of take-out restaurants. The most straightforward example of revenue synergies would be cross-selling, in this case selling coffee in the restaurants as well as in the dedicated stores, and thus getting an immediate boost in market share by using the existing customers of the restaurant chain. A cost synergy would be merging the delivery services of the two businesses to deliver both food and coffee, thus avoiding redundancies and reducing costs associated with twice the number of drivers and vehicles.
6.5. Competitive interaction
This component of cases deals with situations where the market in which a company is operating changes and the company must decide what to do. These changes often have to do with a new player entering the market (again for more details make sure to dive into the Competitive Interaction article ).
Let’s assume that our Cambridge coffee shop has now become a chain and has flagged up to other competitors that Cambridge is a blooming market for coffee. As such, Starbucks has decided to open a few stores in Cambridge themselves, to test this market. The question which might be posed to a candidate is what should our coffee chain do. One way (and a MECE one) to approach the problem is to decide between doing something and doing nothing . We might consider merging with another coffee chain and pooling our resources or playing to our strengths and repositioning ourselves as ‘your student-friendly, shop around the corner’. Just as easily we may just wait the situation out and see whether indeed Starbucks is cutting into our market share - after all, the advantages of our product and services might speak for themselves and Starbucks might end up tanking. Both of these are viable options if argued right and depending on the further specifics of the case.
6.6. Special cases
Most cases deal with private sectors, where the overarching objective entails profit in some form. However, as hinted before, there are cases which deal with other sectors where there are other KPIs in place . The former will usually contain one or several of these building blocks whereas the latter will very likely have neither. This latter category is arguably the one that will stretch your analytical and organisational skills to the limit, since there will be very little familiarity that you can fall back on (McKinsey famously employs such cases in their interview process).
So how do we tackle the structure for such cases? The short answer would be starting from first principles and using the problem driven structure outlined above, but let’s look at a quick example in the form of a McKinsey case :
The first question addressed to the candidate is the following:

This is in fact asking us to build a structure for the case. So what should we have in mind here? Most importantly, we should start with a structure that is MECE and we should remember to do that by considering all the stakeholders . They are on the one hand the government and affiliated institutions and on the other the population. We might then consider which issues might arise for each shareholder and what the benefits for them would be, as well as the risks. This approach is illustrated in the answer McKinsey provides as well:
More than anything, this type of case shows us how important it is to practise and build different types of structures, and think about MECE ways of segmenting the problem.
7. How Do I prepare for case interviews
In consulting fashion, the overall preparation can be structured into theoretical preparation and practical preparation , with each category then being subdivided into individual prep and prep with a partner .
As a general rule, the level and intensity of the preparation will differ based on your background - naturally if you have a business background (and have been part of a consulting club or something similar) your preparation will be less intensive than if you’re starting from scratch. The way we suggest you go about it is to start with theoretical preparation , which means learning about case interviews, business and basic consulting concepts (you can do this using free resources - such as the ones we provide - or if you want a more through preparation you can consider joining our Case Academy as well).
You can then move on to the practical preparation which should start with doing solo cases and focusing on areas of improvement, and then move on to preparation with a partner , which should be another candidate or - ideally - an ex-consultant.
Let’s go into more details with respect to each type of preparation.
7.1. Solo practice
The two most important areas of focus in sole preparation are:
- Mental math
As we mentioned briefly, the best use of your time is to focus on solving cases. You can start with cases listed on MBB sites since they are clearly stated and have worked solutions as well (e.g. Bain is a good place to start) and then move to more complex cases (our Case Library also offers a range of cases of different complexities). To build your confidence, start out on easier case questions, work through with the solutions, and don't worry about time. As you get better, you can move on to more difficult cases and try to get through them more quickly. You should practice around eight case studies on your own to build your confidence.
Another important area of practice is your mental mathematics as this skill will considerably increase your confidence and is neglected by many applicants - much to their immediate regret in the case interview. Find our mental math tool here or in our course, and practice at least ten minutes per day, from day one until the day before the interview.
7.2. Preparation with a partner
There are aspects of a case interview - such as asking clarifying questions - which you cannot do alone and this is why, after you feel comfortable, you should move on to practice with another person. There are two options here:
- Practicing with a peer
- Practicing with an ex-consultant
In theory they can be complementary - especially if you’re peer is also preparing for consulting interviews - and each have advantages and disadvantages. A peer is likely to practice with you for free for longer, however you may end up reinforcing some bad habits or unable to get actionable feedback. A consultant will be able to provide you the latter but having their help for the same number of hours as a peer will come at a higher cost. Let’s look at each option in more detail.
7.2.1. Peer preparation
Once you have worked through eight cases solo, you should be ready to simulate the case interview more closely and start working with another person.
Here, many candidates turn to peer practice - that is, doing mock case interviews with friends, classmates or others also applying to consulting. If you’re in university, and especially in business school, there will very likely be a consulting club for you to join and do lots of case practice with. If you don’t have anyone to practice, though, or if you just want to get a bit more volume in with others, our free meeting board lets you find fellow applicants from around the world with whom to practice. We recommend practicing around 10 to 15 ‘live’ cases to really get to a point where you feel comfortable.
7.2.2. Preparation with a consultant
You can do a lot practising by yourself and with peers. However, nothing will bring up your skills so quickly and profoundly as working with a real consultant.
Perhaps think about it like boxing. You can practice drills and work on punch bags all you want, but at some point you need to get into the ring and do some actual sparring if you ever want to be ready to fight.
Practicing with an ex consultant is essentialy a simulation of a case interview. Of course, it isn’t possible to secure the time of experienced top-tier consultants for free. However, when considering whether you should invest to boost your chances of success, it is worth considering the difference in your salary over even just a few years between getting into a top-tier firm versus a second-tier one. In the light of thousands in increased annual earnings (easily accumulating into millions over multiple years), it becomes clear that getting expert interview help really is one of the best investments you can make in your own future.
Should you decide to make this step, MyConsultingCoach can help, offering bespoke mentoring programmes , where you are paired with a 5+ year experienced, ex-MBB mentor of your choosing, who will then oversee your whole case interview preparation from start to finish - giving you your best possible chance of landing a job!
7.3. Practice for online interviews
Standard preparation for interview case studies will carry directly over to online cases.
However, if you want to do some more specific prep, you can work through cases solo to a timer and using a calculator and/or Excel (online cases generally allow calculators and second computers to help you, whilst these are banned in live case interviews).
Older PST-style questions also make great prep, but a particularly good simulation is the self-assessment tests included in our Case Academy course . These multiple choice business questions conducted with a strict time limit are great preparation for the current crop of online cases.
7.4. Fit interviews
As we’ve noted, even something billed as a case interview is very likely to contain a fit interview as a subset.
We have an article on fit interviews and also include a full set of lessons on how to answer fit questions properly as a subset of our comprehensive Case Academy course .
Here though, the important thing to convey is that you take preparing for fit questions every bit as seriously as you do case prep.
Since they sound the same as you might encounter when interviewing for other industries, the temptation is to regard these as “just normal interview questions”.
However, consulting firms take your answers to these questions a good deal more seriously than elsewhere.
This isn’t just for fluffy “corporate culture” reasons. The long hours and close teamwork, as well as the client-facing nature of management consulting, mean that your personality and ability to get on with others is going to be a big part of making you a tolerable and effective co-worker.
If you know you’ll have to spend 14+ hour working days with someone you hire and that your annual bonus depends on them not alienating clients, you better believe you’ll pay attention to their character in interview.
There are also hard-nosed financial reasons for the likes of McKinsey, Bain and BCG to drill down so hard on your answers.
In particular, top consultancies have huge issues with staff retention. The average management consultant only stays with these firms for around two years before they have moved on to a new industry.
In some cases, consultants bail out because they can’t keep up with the arduous consulting lifestyle of long hours and endless travel. In many instances, though, departing consultants are lured away by exit opportunities - such as the well trodden paths towards internal strategy roles, private equity or becoming a start-up founder.
Indeed, many individuals will intentionally use a two year stint in consulting as something like an MBA they are getting paid for - giving them accelerated exposure to the business world and letting them pivot into something new.
Consulting firms want to get a decent return on investment for training new recruits. Thus, they want hires who not only intend to stick with consulting longer-term, but also have a temperament that makes this feasible and an overall career trajectory where it just makes sense for them to stay put.
This should hammer home the point that, if you want to get an offer, you need to be fully prepared to answer fit questions - and to do so excellently - any time you have a case interview.
8. Interview day - what to expect, with tips
Of course, all this theory is well and good, but a lot of readers might be concerned about what exactly to expect in real life . It’s perfectly reasonable to want to get as clear a picture as possible here - we all want to know what we are going up against when we face a new challenge!
Indeed, it is important to think about your interview in more holistic terms, rather than just focusing on small aspects of analysis. Getting everything exactly correct is less important than the overall approach you take to reasoning and how you communicate - and candidates often lose sight of this fact.
In this section, then, we’ll run through the case interview experience from start to finish, directing you to resources with more details where appropriate. As a supplement to this, the following video from Bain is excellent. It portrays an abridged version of a case interview, but is very useful as a guide to what to expect - not just from Bain, but from McKinsey, BCG and any other high-level consulting firm.
8.1. Getting started
Though you might be shown through to the office by a staff member, usually your interviewer will come and collect you from a waiting area. Either way, when you first encounter them, you should greet your interviewer with a warm smile and a handshake (unless they do not offer their hand). Be confident without verging into arrogance. You will be asked to take a seat in the interviewer’s office, where the case interview can then begin.
8.1.1. First impressions
In reality, your assessment begins before you even sit down at your interviewer’s desk. Whether at a conscious level or not, the impression you make within the first few seconds of meeting your interviewer is likely to significantly inform the final hiring decision (again, whether consciously or not).
Your presentation and how you hold yourself and behave are all important . If this seems strange, consider that, if hired, you will be personally responsible for many clients’ impressions of the firm. These things are part of the job! Much of material on the fit interview is useful here, whilst we also cover first impressions and presentation generally in our article on what to wear to interview .
As we have noted above, your interview might start with a fit segment - that is, with the interviewer asking questions about your experiences, your soft skills, and motivation to want to join consulting generally and that firm in particular. In short, the kinds of things a case study can’t tell them about you. We have a fit interview article and course to get you up to speed here.
8.1.2. Down to business
Following an initial conversation, your interviewer will introduce your case study , providing a prompt for the question you have to answer. You will have a pen and paper in front of you and should (neatly) note down the salient pieces of information (keep this up throughout the interview).
It is crucial here that you don’t delve into analysis or calculations straight away . Case prompts can be tricky and easy to misunderstand, especially when you are under pressure. Rather, ask any questions you need to fully understand the case question and then validate that understanding with the interviewer before you kick off any analysis. Better to eliminate mistakes now than experience that sinking feeling of realising you have gotten the whole thing wrong halfway through your case!
This process is covered in our article on identifying the problem and in greater detail in our Case Academy lesson on that subject.
8.1.3. Analysis
Once you understand the problem, you should take a few seconds to set your thoughts in order and draw up an initial structure for how you want to proceed. You might benefit from utilising one or more of our building blocks here to make a strong start. Present this to your interviewer and get their approval before you get into the nuts and bolts of analysis.
We cover the mechanics of how to structure your problem and lead the analysis in our articles here and here and more thoroughly in the MCC Case Academy . What it is important to convey here, though, is that your case interview is supposed to be a conversation rather than a written exam . Your interviewer takes a role closer to a co-worker than an invigilator and you should be conversing with them throughout.
Indeed, how you communicate with your interviewer and explain your rationale is a crucial element of how you will be assessed. Case questions in general, are not posed to see if you can produce the correct answer, but rather to see how you think . Your interviewer wants to see you approach the case in a structured, rational fashion. The only way they are going to know your thought processes, though, is if you tell them!
To demonstrate this point, here is another excellent video from Bain, where candidates are compared.
Note that multiple different answers to each question are considered acceptable and that Bain is primarily concerned with the thought processes of the candidate’s exhibit .
Another reason why communication is absolutely essential to case interview success is the simple reason that you will not have all the facts you need to complete your analysis at the outset. Rather, you will usually have to ask the interviewer for additional data throughout the case to allow you to proceed .
NB: Don't be let down by your math!
Your ability to quickly and accurately interpret these charts and other figures under pressure is one of the skills that is being assessed. You will also need to make any calculations with the same speed and accuracy (without a calculator!). As such, be sure that you are up to speed on your consulting math .
8.1.4. Recommendation
Finally, you will be asked to present a recommendation. This should be delivered in a brief, top-down "elevator pitch" format , as if you are speaking to a time-pressured CEO. Again here, how you communicate will be just as important as the details of what you say, and you should aim to speak clearly and with confidence.
For more detail on how to give the perfect recommendation, take a look at our articles on the Pyramid Principle and providing recommendations , as well the relevant lesson within MCC Academy .
8.1.5. Wrapping up
After your case is complete, there might be a few more fit questions - including a chance for you to ask some questions of the interviewer . This is your opportunity to make a good parting impression.
We deal with the details in our fit interview resources. However, it is always worth bearing in mind just how many candidates your interviewers are going to see giving similar answers to the same questions in the same office. A pretty obvious pre-requisite to being considered for a job is that your interviewer remembers you in the first place. Whilst you shouldn't do something stupid just to be noticed, asking interesting parting questions is a good way to be remembered.
Now, with the interview wrapped up, it’s time to shake hands, thank the interviewer for their time and leave the room .
You might have other case interviews or tests that day or you might be heading home. Either way, if know that you did all you could to prepare, you can leave content in the knowledge that you have the best possible chance of receiving an email with a job offer. This is our mission at MCC - to provide all the resources you need to realise your full potential and land your dream consulting job!
8.2. Remote and one-way interview tips
Zoom case interviews and “one-way” automated fit interviews are becoming more common as selection processes are increasingly remote, with these new formats being accompanied by their own unique challenges.
Obviously you won’t have to worry about lobbies and shaking hands for a video interview. However, a lot remains the same. You still need to do the same prep in terms of getting good at case cracking and expressing your fit answers. The specific considerations around remote case interviews are, in effect, around making sure you come across as effectively as you would in person.
8.2.1. Connection
It sounds trivial, but a successful video case interview of any kind presupposes a functioning computer with a stable and sufficient internet connection.
Absolutely don’t forget to have your laptop plugged in, as your battery will definitely let you down mid-interview. Similarly, make sure any housemates or family know not to use the microwave, vacuum cleaner or anything else that makes wifi cut out (or makes a lot of noise, obviously)
If you have to connect on a platform you don’t use much (for example, if it’s on Teams and you’re used to Zoom), make sure you have the up to date version of the app in advance, rather than having to wait for an obligatory download and end up late to join. Whilst you’re at it, make sure you’re familiar with the controls etc. At the risk of being made fun of, don’t be afraid to have a practice call with a friend.
8.2.2. Dress
You might get guidance on a slightly more relaxed dress code for a Zoom interview. However, if in doubt, dress as you would for the real thing (see our article here ).
Either way, always remember that presentation is part of what you are being assessed on - the firm needs to know you can be presentable for clients. Taking this stuff seriously also shows respect for your interviewer and their time in interviewing you.
8.2.3. Lighting
An aspect of presentation that you have to devote some thought to for a Zoom case interview is your lighting.
Hopefully, you long ago nailed a lighting set-up during the Covid lockdowns. However, make sure to check your lighting in advance with your webcam - bearing in mind what time if day your case interview actually is. If your case interview is late afternoon, don’t just check in the morning. Make sure you aren’t going to be blinded from light coming in a window behind your screen, or that you end up with the weird shadow stripes from blinds all over your face.
Natural light is always best, but if there won’t be much of that during your interview, you’ll likely want to experiment with moving some lamps around.
8.2.4. Clarity
The actual stories you tell in an automated “one-way” fit interview will be the same as for a live equivalent. If anything, things should be easier, as you can rattle off a practised monologue without an interviewer interrupting you to ask for clarifications.
You can probably also assume that the algorithm assessing your performance is sufficiently capable that it will be observing you at much the same level as a human interviewer. However, it is probably still worth speaking as clearly as possible with these kinds of interviews and paying extra attention to your lighting to ensure that your face is clearly visible.
No doubt the AIs scoring these interviews are improving all the time, but you still want to make their job as easy as possible. Just think about the same things as you would with a live Zoom case interview, but more so.
9. How we can help
There are lots of great free resources on this site to get you started with preparation, from all our articles on case solving and consulting skills to our free case library and peer practice meeting board .
To step your preparation up a notch, though, our Case Academy course will give you everything you need to know to solve the most complex of cases - whether those are in live case interviews, with chatbots, written tests or any other format.
Whatever kind of case you end up facing, nothing will bring up your skillset faster than the kind of acute, actionable feedback you can get from a mock case interview a real, MBB consultant. Whilst it's possible to get by without this kind of coaching, it does tend to be the biggest single difference maker for successful candidates.
You can find out more on our coaching page:
Explore Coaching
Of course, for those looking for a truly comprehensive programme, with a 5+ year experienced MBB consultant overseeing their entire prep personally, from networking and applications right through to your offer, we have our mentoring programmes.
You can read more here:
Comprehensive Mentoring
Account not confirmed

How To Write A Consulting Case Study: Guide, Template, & Examples
When you deliver a successful project, do you publish a consulting case study about it?
A consulting case study is a short story about a successful project that explains…
- The problem your client was dealing with before hiring you;
- your expertise and process for solving that problem;
- and the results your expertise and process created for the client and their business.
In my experience, our consulting case studies are among the most powerful pieces of content we publish. They’re a big reason why people are comfortable signing up for our Clarity Coaching Program .
Because our case studies prove our program helps our clients get results.
I can say that our coaching program is the best on the market until I’m blue in the face.
But it’s much more powerful for consultants to see the results others have experienced for themselves: through our case studies and testimonials.
If you don’t have something of value on your website like a case study — something that actually shows you can achieve results for your clients — then your website will only serve as “confirmational marketing.”
It will confirm what people hear about you. But it won’t help you generate interest and leads.
So, if you want to shift your website beyond mere confirmational marketing to an asset that helps you generate leads and conversions, consider writing consulting case studies using the method below.
In this article, you’ll learn how to write compelling case studies that help you win more consulting clients.
Ready? Let’s dive in…
Your case study is proof that not only can you talk the talk, but you can also walk the walk.
What Is A Consulting Case Study?
When a potential client is deciding on whether they will hire you or not, a big question in their mind is…
“Can this person or company really do what they say they can for my business?”
There are many forms of thought leadership you can use to prove you can deliver results.
The consulting case study is one of them.
A case study, in the context of consulting, is typically a written document that describes…
- the problem a client was facing,
- the actions you took to solve that problem,
- and the outcomes it created for your client.
You write case studies to demonstrate the results and value you created for a past or current client.
What makes them so effective as marketing material?
- They are relatively easy to put together (especially when you use our template below).
- Your potential clients enjoy reading them.
- And they are a highly effective way to demonstrate your authority and expertise in your field.
Next, I’ll walk you through how to write a consulting case study.
In our program, one of the things we teach consultants is how to better understand their clients’ problems and articulate their ability to solve those problems in a way that will attract new clients.
How To Write A Consulting Case Study
Here are the steps to writing your consulting case study. You can follow along with our consulting case study template .
1. Get Permission From The Client
You shouldn’t write a case study that names your client without their permission.
So, before you start writing it, ask them if they’d be OK with you publishing a case study about the project.
Now, I’m not a lawyer, and nothing in this article or anything I write is legal or financial advice. But here’s what we’ve found, through running consulting businesses for over two decades, often works best:
A question we often receive from consultants is “What if I can’t use the name of my client or the company I worked with?” Generally, this isn’t an issue. If your contract says you can’t use the client’s company name, or the client says “No” to your request, all is not lost.
What tends to work extremely well is still writing the case study, but without using the client’s name. Instead, describe the client.
For example, let’s say your client is the automaker Mazda. If you can’t use their name, consider “Working with a top 20 global automaker…”
This gives prospective buyers a good idea of the caliber and type of company you worked with.
When you ask your client for their permission to create a case study that features them, you’ll generally find that 9 times out of 10 they won’t have a problem with you doing so, but make sure you ask before publishing.
2. Introduce The Client’s Business
Once you’ve gotten permission from the client, you’ll begin writing your case study. Follow along using our template .
The first section is the introduction. Set the stage here by introducing your client, their business, and their industry.
This section gives context to the case study. Ideally, your ideal client is intrigued by being in a similar industry or situation as the client in your case study.
3. Describe The Problem Or Challenge
In this section, you outline the problem your client was facing.
Be as specific as you can be.
Simply saying they had marketing issues or a problem with their PR is not enough.
The more detail you include the clearer the picture will become and the more effective your case study copywriting will be.
If your ideal client reads this and has a similar problem as the client in the case study, you can guarantee that their eyes will be glued to the screen, salivating to learn how you solved it.
4. Summarize Your Action Steps
Now that you’ve described the problem your client was up against, you’ll explain what you did to help solve the problem.
In this section, break down each part of the process you used or the steps you took to solve it.
The reader should get the sense that you have a process or system capable of solving the problem and getting results.
This is where you get to demonstrate your know-how and expertise. Get as technical as you can. Show your reader “Hey, this is how I can get YOU results too.”
5. Share The Results
It’s time to demonstrate results.
Write the results that were achieved and how they impacted the business/organization/person.
In many cases, the outcome isn’t just dollars and cents — it can also be less tangible value.
Are they less stressed? Do they have more free time? Are they finding more meaning and enjoyment in their work?
Mention if you’re continuing to work with this client through a retainer . If you’re not, describe how the results will impact their business in the future.
This is also a great place to include a quote or testimonial from your client.
The “Results” section is key because it shows prospective clients that you’ve solved the problems they are facing and have delivered the actual results that they likely desire.
6. Write A Call To Action
At the end of the case study, you should always include a sentence or two inviting the ideal client to reach out.
They’ve just read about the problems you can solve, how you solve them, and the results you can create.
They are primed and ready to reach out to inquire about how you can do it for them.
But if you don’t have a direct call to action for them to do that, many of them will leave without taking action.
So, write a direct, clear call to action that takes them to a page where it’s easy to book a consultation with you or where you provide your contact information.
7. Share It
Marketing for consultants is all about providing value to your ideal clients, being known for something specific, and positioning yourself as an expert and authority that your ideal clients want to work with. So, whenever you publish a piece of valuable content like a case study, your mission is to get as many eyes on the case study as possible.
The best place to publish your case study is on your website or blog.
You can also submit case studies to industry publications. These are a great way to spread the word about you and your client’s business.
Make sure to also share your case study on all social media platforms where your ideal clients hang out online. For consultants, that means LinkedIn.
Work your “marketing muscle” by actively promoting your case study, and you’ll reap the rewards of this powerful piece of authority-building content.
Writing case studies for your consulting business not only helps you land new clients, but it’s also a great way for you to review past projects.
Doing this helps you to find what worked and what didn’t.
And you’ll continue to learn from your experiences and implement your best practices into your next consulting project.
Consulting Case Study Template
Click here to access our Consulting Case Study Template .

This template is designed using a “fill in the blank” style to make it easy for you to put together your case studies.
Save this template for yourself. Use it to follow along with the examples below.
Consulting Case Study Examples
Here are some example case studies from our Clarity Coaching Program clients.
1. Larissa Stoddart
Larissa Stoddart teaches charities and nonprofits how to raise money.
To do that, she provides her clients with a training and coaching program that walks them through twelve modules of content on raising money for their organization, creating a fundraising plan, putting an information management system into place, finding prospects, and asking those prospects for money.

Through her case studies, Larissa provides a comprehensive overview of how she helps her clients build robust fundraising plans and achieve and win more donations.
2. Dan Burgos
Danila “Dan” Burgos is the president and CEO of Alphanova Consulting, which works with US manufacturers to help them increase their profitability through operational improvements.
The goal of Alphanova is to increase their clients’ quality and on-time delivery by 99 percent and help them increase their net profits by over 25 percent.

Through his case studies, Dan lays out the problem, his solution, and the results in a clear simple way.
He makes it very easy for his prospects to envision working with his firm — and then schedule a consultation to make it happen.
3. Vanessa Bennet
Through her company Next Evolution Performance, Vanessa Bennett and her business partner Alex Davides, use neuroscience to help driven business leaders improve their productivity, energy, profitability, and staff retention, while avoiding burnout.

Through her “Clients” page, she provides a list of the specific industries she works with as well as specific case studies from clients within those industries.
She then displays in-depth testimonials that detail the results that her consulting services create for her clients.
These are powerful stories that help Vanessa’s clients see their desired future state — and how her firm is the right choice to help them get there.
As you see, our clients have taken our template and made them work for their unique style, clients, and services.
I encourage you to do the same.
And if you’d benefit from personal, 1-on-1 coaching and support from like-minded consultants, check out our Clarity Coaching Program .
Get Help & Feedback Writing Consulting Case Studies
If writing and demonstrating your authority were easy, then every consultant would be publishing case studies.
But that’s not the case.
Sometimes it helps to have a consulting coach to walk you through each step — and a community of like-minded consultants with whom you can share your work and get feedback from.
That’s why we’ve built the Clarity Coaching Program.
Inside the program, we teach you how to write case studies (among dozens of other critical subjects for consulting business founders).
And we’ve also created a network of coaches and other consultants who are in the trenches — and who are willing to share their hard-fought knowledge with you.
Inside the Clarity Coaching program , we’ve helped over 850 consultants to build a more strategic, profitable, and scalable, consulting business.
Learn More About Clarity Coaching
We’ll work hands-on with you to develop a strategic plan and then dive deep and work through your ideal client clarity, strategic messaging, consulting offers, use an effective and proven consulting pricing strategy, help you to increase your fees, business model optimization, and help you to set up your marketing engine and lead generation system to consistently attract ideal clients.
15 thoughts on “ How To Write A Consulting Case Study: Guide, Template, & Examples ”
This is a great outline and I found it quite helpful. Thanks.
Shana – glad you found this post helpful!
I have used case studies to get new clients and you're right, They work.
Jay – thanks for sharing. I've worked with many clients to implement case studies and have used them in several businesses and have always found them to be great at supporting proof and establishing authority and credibility.
Dumb question: guess you can't charge if you're doing a case study, huh?
Terri – No such thing as a dumb question where I come from. Always good to ask.
You definitely can charge for case studies. Michael Stelzner has a lot more information on writing white papers (and case studies) as projects.
This post was really aimed at using case studies to win more business and attract clients. But you can definitely offer this service to companies and they'll pay handsomely for it.
That was a great question!
Hello,I am really glad I stumbled upon your consulting site. This outline is very helpful and I love the e-mails I recieve as well Thanks!
Happy to hear that
This is a great site for consultants – great information for the team to share with consultants that reach out to us. Thank you!
Thanks Deborah
It is a good steps if we know how we start and control our working.
All I wanted to know about putting together a case study I have got. Thanks so much.
to put together your consulting case study: to put together your consulting case study:
I have used your outline today to write one case. Thank you for sharing.
Hi – This is a great piece, and covers all the core elements of a case study with impact.
Couple of extra points…
1. it’s really powerful to provide a mix of qualitative and quantitative results where possible e.g. ‘we saved the client $500 per month and feedback tells us morale improved’
2. We are seeing more and more consultancies include images and video in their case studies. This obviously depends on the context, so while it’s not necessarily appropriate within the confines of a bid, it is definitely something to think about for those case studies that you want to publish online or in a marketing brochure.
Leave a Comment, Join the Conversation! Cancel reply
Your Email will be kept private and will not be shown publicly.
Privacy Overview
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Benefits of Learning Through the Case Study Method

- 28 Nov 2023
While several factors make HBS Online unique —including a global Community and real-world outcomes —active learning through the case study method rises to the top.
In a 2023 City Square Associates survey, 74 percent of HBS Online learners who also took a course from another provider said HBS Online’s case method and real-world examples were better by comparison.
Here’s a primer on the case method, five benefits you could gain, and how to experience it for yourself.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is the Harvard Business School Case Study Method?
The case study method , or case method , is a learning technique in which you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it. After working through it yourself and with peers, you’re told how the scenario played out.
HBS pioneered the case method in 1922. Shortly before, in 1921, the first case was written.
“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it?” says HBS Professor Jan Rivkin, former senior associate dean and chair of HBS's master of business administration (MBA) program, in a video about the case method . “That skill—the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry to choose a course of action—that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
Originally developed for the in-person MBA classroom, HBS Online adapted the case method into an engaging, interactive online learning experience in 2014.
In HBS Online courses , you learn about each case from the business professional who experienced it. After reviewing their videos, you’re prompted to take their perspective and explain how you’d handle their situation.
You then get to read peers’ responses, “star” them, and comment to further the discussion. Afterward, you learn how the professional handled it and their key takeaways.
Learn more about HBS Online's approach to the case method in the video below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more.
HBS Online’s adaptation of the case method incorporates the famed HBS “cold call,” in which you’re called on at random to make a decision without time to prepare.
“Learning came to life!” said Sheneka Balogun , chief administration officer and chief of staff at LeMoyne-Owen College, of her experience taking the Credential of Readiness (CORe) program . “The videos from the professors, the interactive cold calls where you were randomly selected to participate, and the case studies that enhanced and often captured the essence of objectives and learning goals were all embedded in each module. This made learning fun, engaging, and student-friendly.”
If you’re considering taking a course that leverages the case study method, here are five benefits you could experience.
5 Benefits of Learning Through Case Studies
1. take new perspectives.
The case method prompts you to consider a scenario from another person’s perspective. To work through the situation and come up with a solution, you must consider their circumstances, limitations, risk tolerance, stakeholders, resources, and potential consequences to assess how to respond.
Taking on new perspectives not only can help you navigate your own challenges but also others’. Putting yourself in someone else’s situation to understand their motivations and needs can go a long way when collaborating with stakeholders.
2. Hone Your Decision-Making Skills
Another skill you can build is the ability to make decisions effectively . The case study method forces you to use limited information to decide how to handle a problem—just like in the real world.
Throughout your career, you’ll need to make difficult decisions with incomplete or imperfect information—and sometimes, you won’t feel qualified to do so. Learning through the case method allows you to practice this skill in a low-stakes environment. When facing a real challenge, you’ll be better prepared to think quickly, collaborate with others, and present and defend your solution.
3. Become More Open-Minded
As you collaborate with peers on responses, it becomes clear that not everyone solves problems the same way. Exposing yourself to various approaches and perspectives can help you become a more open-minded professional.
When you’re part of a diverse group of learners from around the world, your experiences, cultures, and backgrounds contribute to a range of opinions on each case.
On the HBS Online course platform, you’re prompted to view and comment on others’ responses, and discussion is encouraged. This practice of considering others’ perspectives can make you more receptive in your career.
“You’d be surprised at how much you can learn from your peers,” said Ratnaditya Jonnalagadda , a software engineer who took CORe.
In addition to interacting with peers in the course platform, Jonnalagadda was part of the HBS Online Community , where he networked with other professionals and continued discussions sparked by course content.
“You get to understand your peers better, and students share examples of businesses implementing a concept from a module you just learned,” Jonnalagadda said. “It’s a very good way to cement the concepts in one's mind.”
4. Enhance Your Curiosity
One byproduct of taking on different perspectives is that it enables you to picture yourself in various roles, industries, and business functions.
“Each case offers an opportunity for students to see what resonates with them, what excites them, what bores them, which role they could imagine inhabiting in their careers,” says former HBS Dean Nitin Nohria in the Harvard Business Review . “Cases stimulate curiosity about the range of opportunities in the world and the many ways that students can make a difference as leaders.”
Through the case method, you can “try on” roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career .
5. Build Your Self-Confidence
Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader’s perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career.
According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey , 84 percent of HBS Online learners report feeling more confident making business decisions after taking a course.
“Self-confidence is difficult to teach or coach, but the case study method seems to instill it in people,” Nohria says in the Harvard Business Review . “There may well be other ways of learning these meta-skills, such as the repeated experience gained through practice or guidance from a gifted coach. However, under the direction of a masterful teacher, the case method can engage students and help them develop powerful meta-skills like no other form of teaching.”

How to Experience the Case Study Method
If the case method seems like a good fit for your learning style, experience it for yourself by taking an HBS Online course. Offerings span eight subject areas, including:
- Business essentials
- Leadership and management
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Digital transformation
- Finance and accounting
- Business in society
No matter which course or credential program you choose, you’ll examine case studies from real business professionals, work through their challenges alongside peers, and gain valuable insights to apply to your career.
Are you interested in discovering how HBS Online can help advance your career? Explore our course catalog and download our free guide —complete with interactive workbook sections—to determine if online learning is right for you and which course to take.

About the Author
47 case interview examples (from McKinsey, BCG, Bain, etc.)

One of the best ways to prepare for case interviews at firms like McKinsey, BCG, or Bain, is by studying case interview examples.
There are a lot of free sample cases out there, but it's really hard to know where to start. So in this article, we have listed all the best free case examples available, in one place.
The below list of resources includes interactive case interview samples provided by consulting firms, video case interview demonstrations, case books, and materials developed by the team here at IGotAnOffer. Let's continue to the list.
- McKinsey examples
- BCG examples
- Bain examples
- Deloitte examples
- Other firms' examples
- Case books from consulting clubs
- Case interview preparation
Click here to practise 1-on-1 with MBB ex-interviewers
1. mckinsey case interview examples.
- Beautify case interview (McKinsey website)
- Diconsa case interview (McKinsey website)
- Electro-light case interview (McKinsey website)
- GlobaPharm case interview (McKinsey website)
- National Education case interview (McKinsey website)
- Talbot Trucks case interview (McKinsey website)
- Shops Corporation case interview (McKinsey website)
- Conservation Forever case interview (McKinsey website)
- McKinsey case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Profitability case with ex-McKinsey manager (by IGotAnOffer)
- McKinsey live case interview extract (by IGotAnOffer) - See below
2. BCG case interview examples
- Foods Inc and GenCo case samples (BCG website)
- Chateau Boomerang written case interview (BCG website)
- BCG case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Written cases guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG live case interview with notes (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG mock case interview with ex-BCG associate director - Public sector case (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG mock case interview: Revenue problem case (by IGotAnOffer) - See below
3. Bain case interview examples
- CoffeeCo practice case (Bain website)
- FashionCo practice case (Bain website)
- Associate Consultant mock interview video (Bain website)
- Consultant mock interview video (Bain website)
- Written case interview tips (Bain website)
- Bain case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Digital transformation case with ex-Bain consultant
- Bain case mock interview with ex-Bain manager (below)
4. Deloitte case interview examples
- Engagement Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Recreation Unlimited practice case (Deloitte website)
- Strategic Vision practice case (Deloitte website)
- Retail Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Finance Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Talent Management practice case (Deloitte website)
- Enterprise Resource Management practice case (Deloitte website)
- Footloose written case (by Deloitte)
- Deloitte case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
5. Accenture case interview examples
- Case interview workbook (by Accenture)
- Accenture case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
6. OC&C case interview examples
- Leisure Club case example (by OC&C)
- Imported Spirits case example (by OC&C)
7. Oliver Wyman case interview examples
- Wumbleworld case sample (Oliver Wyman website)
- Aqualine case sample (Oliver Wyman website)
- Oliver Wyman case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
8. A.T. Kearney case interview examples
- Promotion planning case question (A.T. Kearney website)
- Consulting case book and examples (by A.T. Kearney)
- AT Kearney case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
9. Strategy& / PWC case interview examples
- Presentation overview with sample questions (by Strategy& / PWC)
- Strategy& / PWC case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
10. L.E.K. Consulting case interview examples
- Case interview example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website)
- Market sizing case example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website)
11. Roland Berger case interview examples
- Transit oriented development case webinar part 1 (Roland Berger website)
- Transit oriented development case webinar part 2 (Roland Berger website)
- 3D printed hip implants case webinar part 1 (Roland Berger website)
- 3D printed hip implants case webinar part 2 (Roland Berger website)
- Roland Berger case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
12. Capital One case interview examples
- Case interview example video walkthrough (Capital One website)
- Capital One case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
12. EY Parthenon case interview examples
- Candidate-led case example with feedback (by IGotAnOffer)
14. Consulting clubs case interview examples
- Berkeley case book (2006)
- Columbia case book (2006)
- Darden case book (2012)
- Darden case book (2018)
- Duke case book (2010)
- Duke case book (2014)
- ESADE case book (2011)
- Goizueta case book (2006)
- Illinois case book (2015)
- LBS case book (2006)
- MIT case book (2001)
- Notre Dame case book (2017)
- Ross case book (2010)
- Wharton case book (2010)
Practice with experts
Using case interview examples is a key part of your interview preparation, but it isn’t enough.
At some point you’ll want to practise with friends or family who can give some useful feedback. However, if you really want the best possible preparation for your case interview, you'll also want to work with ex-consultants who have experience running interviews at McKinsey, Bain, BCG, etc.
If you know anyone who fits that description, fantastic! But for most of us, it's tough to find the right connections to make this happen. And it might also be difficult to practice multiple hours with that person unless you know them really well.
Here's the good news. We've already made the connections for you. We’ve created a coaching service where you can do mock case interviews 1-on-1 with ex-interviewers from MBB firms . Start scheduling sessions today!
Related articles:

Asking the better questions that unlock new answers to the working world's most complex issues.
Trending topics
AI insights
EY podcasts
EY webcasts
Operations leaders
Technology leaders
Marketing and growth leaders
Cybersecurity and privacy leaders
Risk leaders
EY Center for Board Matters
EY helps clients create long-term value for all stakeholders. Enabled by data and technology, our services and solutions provide trust through assurance and help clients transform, grow and operate.
- 5||See all Assurance
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Strategy, transaction and transformation consulting
Technology transformation
Tax function operations
Climate change and sustainability services
EY Ecosystems
Supply chain and operations
EY Partner Ecosystem
Explore Services
We bring together extraordinary people, like you, to build a better working world.
- 1||More about what you can do here
- 2||More about what it's like to work here
- 3||More about how to join us
- 4||More about job search
Experienced professionals
MBA and advanced-degree students
Student and entry level programs
Contract workers
EY-Parthenon careers
Discover how EY insights and services are helping to reframe the future of your industry.
Case studies
Energy and resources
How data analytics can strengthen supply chain performance
13 Jul 2023 Ben Williams
How Takeda harnessed the power of the metaverse for positive human impact
26 Jun 2023 Edwina Fitzmaurice
Banking and Capital Markets
How cutting back infused higher quality in transaction monitoring
11 Jul 2023 Ron V. Giammarco
At EY, our purpose is building a better working world. The insights and services we provide help to create long-term value for clients, people and society, and to build trust in the capital markets.
New EY research finds AI investment is surging, with senior leaders seeing more positive ROI as hype continues to become reality
15 Jul 2024 Lizzie McWilliams
New EY Consumer Products and Retail Executive Pulse reveals perception vs. reality gap for AI maturity
09 Jul 2024 EY Americas
EY Announces Winners for the Entrepreneur Of The Year® 2024 Mid-Atlantic Award
21 Jun 2024 Victoria Kasper
No results have been found
Recent Searches

CIO Survey: will you set the GenAI agenda or follow the leaders?
Get insights on how CIOs will address the challenges and capture the full benefits of GenAI in the 2024 EY CIO Sentiment Survey.

How a flexible supply chain raised the bar for the beverage industry
The client’s goal: better accommodate future growth, predict customer demands, and add agility to inventory and production lines. Learn how we did it.

How can your business go from competitive to cutting edge?
Learn how the EY-Microsoft Alliance delivers AI driven strategies and smart business solutions using cloud technology.
Select your location
Consulting case studies
Our Consulting teams work with businesses around the world to solve problems , overcome challenges, uncover opportunities and exceed expectations. Our clients’ success stories span all industry sectors — from technology companies to energy providers, financial services to consumer retailers and every strategic function in between.
EY Consulting case studies are a window into how we work alongside our clients to deliver strategic, sustainable growth and success.
- Advanced manufacturing and mobility
- Financial services
- Government and public sector
- Health sciences and wellness
- Technology, media and telecommunications
Direct to your inbox
Stay up to date with the most recent case studies

- Connect with us
- Our locations
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Legal and privacy
- Accessibility
- Open Facebook profile
- Open X profile
- Open LinkedIn profile
- Open Youtube profile
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.
28 Case Interview Examples for Consulting Interview Prep (2024)
- Last Updated January, 2024
Rebecca Smith-Allen
Former McKinsey Engagement Manager
How to Use Case Interview Examples
Video Case Interview Example: Questions & Answers
Tips for Acing Your Case
Free Case Interview Examples (Consulting Firms)
Free Case Interview Examples (Consulting Clubs)
Practice is the key to passing your consulting interviews. To practice, you’ll need some examples of case interview questions and answers to work with.
We’ve got links to loads of them below.
In addition, we have:
- Tips on how to use case interview examples to prepare for your consulting interviews,
- A video case interview example with My Consulting Offer founder Davis Nguyen, and
- Insight into the difference between average and exceptional answers to case interview questions.
Get ready to dive deep into structuring your analysis of business problems, identifying the key issues, and recommending solutions!
Keep reading to find out how to use case interview examples to ace your case.
How to Use Case Interview Examples to Ace Your Case
1. start your case interview preparation early..
You’ll need to practice dozens of case interview examples to get good enough to receive an offer from one of the top consulting firms. This is not something you can cram the night before an interview.
Start as soon as possible.
2. Don’t Read Straight through Sample Case Interview Examples or Passively Watch Videos.
Some people think that the best way to improve their chances of passing a case interview is by reading as many cases interview examples as they can.
This is like reading about how to play tennis but never picking up a racket. To get better at tennis, for example, you need to actually pick up a ball and be active. The same applies to your interview preparation.
Stop and think at each step in the case interview question. Come up with your own answer and say it out loud. Practice driving each part of the case interview example yourself.
- How would you structure your analysis of the problem?
- What questions would you ask the interviewer?
- How would you set up the case math problem?
- What recommendation would you make to the client?
After you’ve developed your answer, compare it to the suggested answer for the case.
What did you get right?
How did your answer and the case interview example answer differ?
Are there things you miss consistently across multiple case interview examples?
The answers to these case interview examples can look simple when you just read through them, but it’s not easy to come up with all the key aspects of the solution on your own.
Nail the case & fit interview with strategies from former MBB Interviewers that have helped 89.6% of our clients pass the case interview.
3. Find Partners to Practice Case Interviews with.
Teamwork is an important part of consulting work, so get ready for it now. Find a case interview practice partner, preferably someone else who’s applying to jobs in the management consulting industry because they’ll know more about what recruiters are looking for.
Practicing cases with a partner provides the opportunity to get feedback from someone else on what you’re doing well and what you need to improve. Additionally, you’ll learn a lot by watching how your partner solves sample case studies.
Look for aspects of their approach that are effective as well as what they could do better. Working with a partner will make your consulting interview practice feel more real.
Similar to how you need a tennis partner to feel what is like to play tennis, you need a case partner to experience what a case interview is like.
4. Master the 4 Parts of the Case Interview.
In our article on Case Interview Prep , we discussed the 4 parts of the case interview: the opening, structure, analysis, and conclusion. As you practice with consulting case interview examples, practice each of these 4 parts to ensure you’re strong at them all.
5. Avoid Case Burnout.
A case zombie is someone who’s grown tired of casing from doing too much of it. Their answers feel rehearsed, not conversational.
They may seem bored, not engaged in solving the problem. They’ll be less creative in their solutions. They certainly won’t pass the airport test!
Avoid becoming a case zombie by practicing smarter, not harder.
Video: Case Interview Examples – Questions & Answers
In the following case interview example, Davis Nguyen, founder of My Consulting Offer solves McKinsey’s SuperSoda case. The video is broken into 4 parts of the case interview.
Remember, don’t just watch the video. Stop the video and provide your own answer before listening to Davis’s answer to the case question.
Step 1: Case Interview Example Opening – Ensure you understand the client and the problem you’ll be solving in the case.
Step 2: case interview example structure – break the problem down into smaller parts. make sure you cover all key case issues., step 3: case interview example analysis – ask questions, gathering information from graphs and charts provided by the interviewer, do case math, and provide insight into the client’s business problem based on what you learn., step 4: case interview example recommendation – develop a rational recommendation for the client based on all you’ve learned throughout the case interview., tips for acing your consulting case interviews – the difference between average & exceptional, case interview opening.
The opening is a great point to ask “dumb” questions because, at this point, you’re not expected to know much about the client and their business.
Here your goal is to understand the client, their business, and what a successful project will look like.
Don’t shy away from asking for clarification on things that will help you better understand the business problem and solve it. For example, if you don’t know how life insurance works and the case is about life insurance, then ask.
After ensuring you understand the client and their problem, the next thing to ask about is key metrics of success.
For example, the client may want to find new avenues for growth. Are they looking for a 5% increase in revenue or to double their business?
Finding out what success looks like in the client’s eyes will ensure you work to deliver a solution that meets their expectations, not one that’s underwhelming.
After you find out what success looks like, ask further probing questions to better understand the client, their business, and any constraints on solving the case.
Examples of Relevant Questions to ask Your Interviewer
Examples of relevant questions about the client might include the geography they operate in or the sector of their industry they are strongest in.
Examples of relevant questions about their business might include what products or services are most profitable or most important to their customers.
Examples of relevant questions about the problem might include whether there are any costs that can’t be cut or what the maximum amount the client is able to invest in developing a new product.
Asking these types of questions up front will give you a better context for solving the client’s problem and make it more likely that you will solve the case interview.
Case Interview Structure
You’ll need a framework to make sure your analysis covers all key aspects of the consulting case.
You can use one of the many standard Case Interview Frameworks we’ve outlined , but top interviewees develop their own framework for analyzing the case interview question.
Their frameworks may include pieces of one or more of the standard frameworks but are tailored to the particular business problem they’re discussing.
Good frameworks are hypothesis-driven, that is to say they can be tested similar to the science experiment, so that the answer is either a “yes” or “no.” For example, examining your bank account to see, “if I have $400 for a ticket” is an example.
Second, good frameworks cover all topics relevant to the answer. For example, if the client is opening up a new hotel in a foreign country, checking out the existing competition should be part of the framework.
As you study more about interactive case interviews and practice them you’ll develop a sense for what factors are relevant or not relevant to the case at hand.
Finally, a good structure will be MECE or mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive.
This means the framework will break down the market or population being analyzed into segments that include every part of the whole (collectively exhaustive), and each segment of the market or member of the population will show up in one and only one category without overlap (mutually exclusive).
For example, if you divide the target market for a retail product into segments by age, these segments would be MECE:
- 10-19,
- 40-49, etc.
The categories 15-25, 20-30, 27-35 would not be MECE because people could be counted twice.

Case Interview Analysis
In the analysis phase of your case interview example, you’ll ask questions to get the information you need to solve the client’s business problem. Your questions will likely lead you to one of the 4 types of analysis that are common in consulting interviews: market sizing, brainstorming, quantitative reasoning (case math), or reading exhibits.
No matter which of these types of analysis comes up, there’s a 4-step method that ensures you can crack the case.
This 4-step method is:
- Ask for data,
- Interpret the data,
- Provide insight, and
- Outline next steps.
The data you ask for will depend on the case interview question you’re solving. For example, if the question is about profitability, you’ll need to know about the client’s finances: dig into revenues and costs.
For example, if you find that the client’s revenues are flat while their costs have been rising, you’ll know that the problem is in the cost structure and that you’ll need to examine costs more closely.
Next, provide insight. As you examine costs further, you’ll find out why they’ve grown faster than revenues.
This insight will naturally lead to the next steps. What does the client need to do to get costs under control and fix their profitability problem?
You may need to go through this 4-step method a couple of times, focusing on different aspects of the client’s business problem.
Once you’ve examined and developed insight into all key aspects of the problem, your next step will be to conclude the interview with a recommendation for the client.
Case Interview Conclusion
At this point, you’ve hopefully cracked the case and are ready to present your recommendations to the client (your interviewer).
The best way to do this is to use the 5R approach:
- Recap – restate the business problem you’ve analyzed. In consulting this is done because a CEO might have hired 5 McKinsey teams and can’t remember which one you are on.
- Recommendations – Provide the solution your analysis led to. We lead with the recommendation because it is the most important piece of information. Stating it first and clearly puts everyone on the same page.
- Reasons – Summarize the key facts and insights that lead you to your recommendations.
- Risks – Outline any risks the client should be aware of as they implement your recommendations. No recommendation has a 100% probability of success. Clients need to be aware of business risks in the same way patients need to understand the side effects of drugs.
- Retaining the client – Provide next steps for how you can help the client ensure success. As consultants, we are paid for helping our clients. If there is a natural extension of the work as the client implements the team’s recommendations, we should tell them how we can provide further assistance (and ultimately make money for your firm).
While most candidates will address their recommendations and possibly the reasons for their recommendations, few will hit all these points.
In particular, outlining risks and further ways you can help the client will differentiate you from other candidates and help you to advance to the second round of interviews or get the offer.
Free Online Case Interview Examples from 7 Top Consulting Firms
Now that you’re familiar with how you should use case interview examples and what differentiates an average answer from an exceptional one, you need sample questions to practice with.
Below, we provide links to dozens to help you hone your business problem-solving skills.
1. McKinsey Case Interview Examples
Disconsa – Help a not-for-profit develop better financial-service offerings for remote Mexican communities.
Electro-Light – Help a beverage manufacturer prepare for a new product launch.
GlobalPharm – Help a pharmaceutical industry client manage with its merger and acquisitions strategy.
Transforming a National Education System – Help a country’s education ministry develop a new strategy for educating the country’s children.
2. BCG Case Interview Examples
Climate Challenge – Help a global consumer goods company reduce its environmental impact.
Driving Revenue Growth at a Healthcare Company – Help a medical devices and services company to increase revenues following an acquisition. (The same one that is highlighted above in our example)
3. Bain Case Interview Examples
Coffee Shop Co. – Help a friend decide whether they should open a coffee shop.
F ashionCo. – Help a fashion company understand why its revenues have been going down.
Private Equitas – Help a private equity company maximize its investment in a portfolio company.
4. Deloitte Case Interview Examples
Footloose – Help a footwear company improve their market share in the boots category.
Recreation Unlimited – Help a global apparel and sportswear company improve its digital customer experience and its revenue.
Agency V – Help a large federal agency recover from a front-page scandal that sparked investigations and congressional hearings.
Federal Benefits Provider – Help a federal agency that provides benefits to millions of U.S. citizens prepare for a major expansion of its mandate.
5. AT Kearney Case Interview Examples
Promotion Planning – Help a national grocery and drug store chain improve its product promotion strategy.
6. PWC Case Interview Examples
Modernizing a Hotel’s Loyalty Platform – Help simplify and modernize the platform, providing customers with immediate access to their data.
Green Energy – Help an energy company transition to net zero greenhouse gas emissions.
Nonprofit Impact – Help a community organization respond to client needs during the pandemic.
Love at First Byte – Help a data management client comply with new regulations.
Prioritizing Ethics and Integrity – Help a software company leverage data analytics to comply with regulations.
7. Accenture Case Interview Examples
Sustainability – Help drive sustainability for an auto manufacturer.
IT integration strategy – Driving merger integration by linking technology systems.
We have more on how to Accenture Case Interviews in our article.
8. Capital One Case Interview Examples
Ice Cream Corporation – Help the president of Ice Cream Corporation grow profits.
9. Oliver Wyman Case Interview Examples
Wumbleworld – Help a China-based theme park operator identify the reasons for declining profits and develop options for reversing the trend.
Aqualine – Help a manufacturer of small power boats determine why its sales growth has slowed and identify opportunities to boost sales.
10. LEK Case Interview Examples
Theater chain – Help a large theater chain identify revenue growth opportunities.
Free Online Case Interview Examples from Consulting Clubs
Need more case interview examples? Here are links to MBA case books compiled by INSEAD, Harvard, Wharton, Darden, and several other business schools.
Recent Consulting Case Interview Examples
- Darden School Of Business 2021-2022 Casebook
- NYU Stern MCA 2020-2021 Casebook
- The Duke MBA Consulting Club Casebook 2021-2022
- Notre Dame Casebook 2022
- Kellogg Consulting Club 2020 Casebook
- FMS Consulting Casebook 2021-22
- INSEAD Consulting Club Casebook 2021
- IIMC Consulting Casebook 2021-22
- UCLA Case Book 2019 – 2020
- Columbia Business School 2021 Casebook
- IIM Lucknow Casebook 2022
- Cornell MBA Johnson Consulting Club Casebook 2020-2021
- Darden School Of Business 2020-2021 Casebook
Older Consulting Case Interview Examples
- 2019 Berkeley Haas School of Business Consulting Club Interview Preparation Guide and Case Interview Examples
- The Duke MBA Consulting Club Casebook 2018-2019
- 2017-2018 McCombs University of Texas at Austin Consulting Case Interview Examples
- Columbia Business School Management Consulting Association Case Interview Examples 2017
- Duke Fuqua School of Business MBA Consulting Case Interview Examples 2016-2017
- NYU Stern MBA MCA Case Interview Examples: 2017
- UCLA Anderson School of Management Consulting Association Case Interview Examples 2015-2015
- Darden Consulting Club Case Interview Examples: 2014-2015
- Yale Life Sciences Consulting Case Interview Examples 2014
- ESADE MBA Consulting Club Case Interview Examples 2014
- Darden Consulting Case Interview Examples: 2012-2013 Edition
- Kellogg Consulting Club Case Interview Examples and Interview Guide: 2012 Edition
Even More Consulting Case Interview Examples
- The Cornell Consulting Club Interview Interview Examples
- Harvard Business School Management Consulting Club Case Interview Examples
- The MIT Sloan School of Management Consulting Club Case Interview Examples and Interview Guide – October 2001
- The Berkeley MBA Haas Consulting Club 2006 Case Interview Examples
- London Business School – The 2006 Consulting Club Case Interview Examples
- Columbia Business School Management Consulting Association Case Interview Examples – 2006
- Torch the Case – The NYU Stern Consulting Case Interview Examples – 2007 edition
- Michigan – the Ross School of Business Consulting Club 2010 Case Interview Examples
- Wharton Case Interview Examples by the Wharton Consulting Club – December 2010
- The Duke MBA Consulting Club Case Interview Examples – 2010-2011
- Case Interview Examples by the ESADE MBA Consulting Club 2011
- INSEAD Consulting Club Handbook and Case Interview Examples – 2011
Still have questions?
If you still have questions on case interview examples, leave them in the comments below. We’ll ask our My Consulting Offer coaches and get back to you with answers.
We have tons of other articles to help you get an offer from one of the top consulting firms. Check out our pages on:
- Case Interview Math
- Case Interview Types
- Case Interview Formulas
- Market Sizing Questions
Help with Case Study Interview Preparation
Thanks for turning to My Consulting Offer for advice on case study interview prep. My Consulting Offer has helped almost 89.6% of the people we’ve worked with get a job with top management consulting like Bain, BCG and McKinsey . For example, here is how Conor was able to get his BCG offer after previously failing.
If you want a step-by-step solution to land more offers from consulting firms, then grab the free video training series below. It’s been created by former Bain, BCG, and McKinsey Consultants, Managers and Recruiters.
It contains the EXACT solution used by over 700 of our clients to land offers.
The best part?
It’s absolutely free. Just put your name and email address in and you’ll have instant access to the training series.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
© My CONSULTING Offer
3 Top Strategies to Master the Case Interview in Under a Week
We are sharing our powerful strategies to pass the case interview even if you have no business background, zero casing experience, or only have a week to prepare.
No thanks, I don't want free strategies to get into consulting.
We are excited to invite you to the online event., where should we send you the calendar invite and login information.
50+ Case Interview Questions and Examples From Top Firms
Discover over 50 case interview questions and examples from top consulting firms. Prepare effectively for your next interview with expert insights and tips!
Posted August 22, 2024

Featuring Garrett W.
MBB Interviews: Ask Me Anything
Starting friday, august 23.
7:00 PM UTC · 60 minutes
Table of Contents
Let’s face it, consulting interviews can be intimidating, especially with their complex case questions. These questions are designed to assess your problem-solving skills, analytical ability, and strategic thinking, crucial competencies for success in the consulting world. Recognizing the types of case interview questions and mastering them can significantly elevate your chances of landing your dream job in prestigious firms like McKinsey, BCG, or Bain.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to mastering case interview questions, providing insights into the most common consulting case interview questions and detailed case interview examples from top consulting firms. From McKinsey case interview questions to unique challenges posed by firms like Deloitte and Accenture, we've got you covered. We will also share tips on how to ace your case interview and how to prepare for different types of case interview questions effectively.
By the end of this article, you'll have a well-rounded understanding of what to expect and how to showcase your problem-solving prowess when it matters most. Let’s begin!
List of Case Interview Questions, Practice Cases, and Examples
In preparing for your consulting interviews, it's crucial to familiarize yourself with the most common types of case interview questions. On this list, we will provide sample questions from the top consulting firms.
McKinsey Case Interview Examples
To excel in McKinsey case interviews , it's crucial to practice with specific examples that mirror the real challenges you might face. Here are some detailed scenarios from McKinsey to guide your preparation:
1. Beautify Case
Sample Question #1 : Beautify is excited to support its current staff of beauty consultants on the journey to becoming virtual social media-beauty advisors. Consultants would still lead the way in terms of direct consumer engagement and would be expected to maintain and grow a group of clients. They would sell products through their own pages on beautify.com, make appearances at major retail outlets, and be active on all social media platforms.
What possible factors should Beautify consider when shifting this group of employees toward a new set of responsibilities?
Sample Question #2 : One of the key areas that Beautify wants to understand is the reaction of current and potential new customers to the virtual social media-beauty advisors.
Imagine you are a current Beautify customer and you mostly shop at your local department store because you enjoy the high-touch service offered by in-store consultants. What features would make you consider switching to a mostly virtual sales experience?
See more questions here .
2. Diconsa Case
Sample Question #1 : What should the team investigate to determine whether the Diconsa network could and should be leveraged to provide a range of basic financial services to Mexico’s rural population?
Sample Question #2: The team has estimated that it currently costs a family 50 pesos per month in transportation and food to make the journey to collect benefit payments. The team also estimates that if benefits were available for collection at local Diconsa stores, the cost would be reduced by 30 percent.
Twenty percent of Mexico’s population is rural, and of that number, half currently receive state benefits.
You can assume that Mexico has a population of 100 million.
You can also assume that families in Mexico have an average four members, and that this does not vary by region.
If every family could collect state benefits at their local Diconsa stores, how much in total per year would be saved across all Mexican rural families receiving state benefits?
3. Electro-Light Case
Sample Question #1: What key factors should SuperSoda consider when deciding whether or not to launch Electro-Light?
Sample Question #2: SuperSoda executives believe that the company's position as a top-three beverage company gives it strategic impetus toward achieving the desired market share. However, they ask the team to outline what would be needed to achieve the target 12.5 percent share of the electrolyte-drinks market. What would SuperSoda need to do to gain the required market share for Electro-Light following its launch?
4. National Education System Transformation
Sample Question #1: What issues would you want to investigate in diagnosing the current state of the Loravian school system?
Sample Question #2: One of the clients at Loravian’s educational department mentions neighbor country “C” as an example, because it’s outperforming all of Loravia's economic peers and neighbors in the international assessment. She believes that the more concentrated school structure in this country is a big reason for better outcomes in the international assessment. She suggests that having larger, less fragmented schools allows for more effective teacher selection and training, leading to improved education outcomes for students. Finally, she shares that 15 percent of Loravia's population is currently attending school.
What would be the reduction in the total number of schools in Loravia if it were to achieve the same average school size as neighbor country C?
5. Talbot Trucks Case
Sample Question #1: What information would you want to collect to understand the attractiveness for Talbot Trucks in producing and selling eTrucks in Europe?
Sample Question #2: After running focus groups with Talbot Trucks’ customers, the team concluded that the total cost of an eTruck needs to be the same as a diesel truck to be considered attractive to customers. Currently, a Talbot Trucks diesel truck costs €100,000.
Assuming that the figures above do not change, what is the maximum price Talbot Trucks can charge for its eTruck so that the total cost of ownership is equal to that of a diesel truck?
6. Shops Corporation Case
Sample Question #1: What types of factors would you want to explore to understand how Shops Corporation might improve its diversity within senior leadership?
7. Conservation Forever Case
Sample Question #1: What factors could the team consider when choosing one of the three specific geographies on which to focus the conservation efforts?
Sample Question #2: The director of CF likes these initial projections, but is not convinced that the assumptions are realistic. They tell the team, “According to your model, there are three levers we need to focus on to generate revenue from ecotourism in Peru: number of visitors, length of stay, and spending amount. What are your best ideas for how to maximize each lever? And how about some ideas outside of the constraints of this model?”
Your team is meeting in ten minutes to generate ideas in preparation for a workshop with leaders from several coastal communities, and you are jotting down some notes.
What ideas do you have to generate revenue linked to ecotourism?
McKinsey offers case interview examples that cover various industries and problem-solving scenarios, helping you prepare for any interview question. Engaging with these cases will not only boost your confidence but also enhance your ability to approach complex business problems with innovative solutions.
BCG Case Interview Examples
At BCG , the case interview process is designed to simulate the real-world problems that client teams face, allowing you to demonstrate your problem-solving abilities and specialized skills relevant to the role. Embracing the challenge with enthusiasm will not only make the experience rewarding but also provide a true taste of consulting life at BCG. Here are some of their case interview examples:
Here are a few examples of common case questions:
- Should a company enter a new market?
- Should a company pursue a new product line?
- How can a company improve its profitability?
- How can a company reduce costs?
- How can a company improve its customer satisfaction?
Read: How to Prepare for Boston Consulting Group Management Consulting Case Interviews?
Free trial!

From 128 top coaches
Access a library of videos, templates, and examples curated by Leland’s top coaches.
Example resumes.

Example Cases
Casing Drills
Mock Interviews

Bain Case Interview Examples
During your preparation for Bain case interviews, it's essential to delve into specific examples that reflect the real challenges you may encounter. Here's are five examples of practice cases and mock interview tips provided by Bain to guide your preparation:
- Coffee Shop Co. Practice Case
- FashionCo. Practice Case
- Associate Consultant Mock Interview
- Consultant Mock Interview
- Written Case Interview Tips
Read : Bain Case Interviews: A Comprehensive Preparation Guide
Deloitte Case Interview Examples
Deloitte provides a rich array of materials and interactive case studies designed to prepare you for the rigors of their case interviews. These examples reflect real client engagements, offering insights into the complex problems you may face and the analytical, creative, and strategic thinking required to solve them.
Deloitte Case Examples
Footloose Case Study sample questions:
- How big is the work boot market (expressed in euros)? Does Duraflex get more of its revenue from work boots or casual boots?
- Explain why Badger is outperforming Duraflex in the work boot market.
- What changes would you recommend to Duraflex’s work boot strategy? Why? Would you recommend they introduce a sub- branded boot line?
Engagement Strategy: Federal Agency V sample questions:
- To begin an engagement strategy, how might you establish a baseline to measure employee engagement against?
- What characteristics would you look for in external organizations to use as potential benchmarks?
- What are the various populations of the workforce and how would you engage them?
- How will you use Deloitte’s relationship with, and institutional knowledge, of Agency V to develop your deliverables?
Recreation Unlimited sample questions :
- What are potential reasons for Recreation Unlimited's poor eCommerce performance relative to competitors?
- In order to win digital customers, Recreation Unlimited wants to find ways to improve and differentiate their digital customer experience. What are some potential ways to improve the customer experience and how does improving customer experience create value for the customer and value for the business?
- As part of the digital strategy that Recreation Unlimited is considering, they are debating whether to improve the website experience or increase digital marketing. Since they are not sure they will have the budget for both, they want you to help them decide. How would you approach this question?
Strategic Vision: Federal Benefits Provider sample questions :
- What steps should the Deloitte team take to develop a 10-year strategic roadmap for the Agency?
- What are the components or metrics of a business case that should be considered to justify the development of a 10-year strategic roadmap?
- In building the 10-year strategic road map, the Deloitte team realizes there are several key challenges that pose impediments to implementing the Agency’s vision. What is the cost of each challenge to the Agency?
- Leaders in the various departments remain skeptical that the 10-year vision can positively impact their unique operations, while employees are largely unaware of the 10-year vision initiative. How might Deloitte develop an impactful change management strategy to institutionalize the goals of the 10-year vision and ensure buy-in across the Agency’s diverse workforce?
Talent Management: Federal Civil Cargo Protection Bureau sample questions:
- What data would you want to have to be able to move forward?
- What immediate steps would you take to review screening processes and training procedures?
- How would you incorporate things like job descriptions and competencies in your review in order to build a new human capital strategy?
- How will you engage and develop leadership given the Chief Administrator is new to the role and has a different background?
Click here to practice a consulting case interview.
Read : Best 30 Free Resources to Get into Management Consulting
Accenture Case Interview Examples
Accenture's case interviews serve as the final hurdle to becoming a consultant at the firm. These interviews are uniquely structured to assess a candidate's ability to solve complex business problems. The format includes both interviewer-led and candidate-led cases, providing a comprehensive evaluation of your problem-solving capabilities.
Learn more about Accenture’s Case Interview Workbook here .
OC&C Case Interview Examples
OC&C , a globally recognized but relatively smaller strategy consulting firm, is known for its rigorous case interviews that reflect real-life client challenges. These interviews are designed to assess a wide range of skills, from analytical thinking to business acumen, tailored to the firm's focus on private equity clients and seven key industries.
1. Leisure Clubs Case sample questions:
- What factors might you analyze to determine what is going to happen to demand for leisure clubs?
- What is likely to happen to demand for leisure clubs?
- What is the critical issue for our client?
2. Important Whisky in an Emerging Market Case sample questions:
- What information would you require to help explain the slowing down of growth?
- What is driving profitability down?
- What are the potential strategic options?
Oliver Wyman Case Interview Examples
Oliver Wyman's case interviews are designed to uncover how you approach unstructured challenges and evaluate data to build comprehensive solutions. The firm encourages candidates to think critically and creatively, using logical components to break down complex problems.
See how Oliver Wyman can help you with interview preparation by explaining conversational and case interviews, as well as sharing interview tips and explaining what the role of the case interview is.
A.T. Kearney Case Interview Examples
A.T. Kearney's interview process is notably rigorous, tailored to assess a wide range of abilities from analytical thinking to strategic problem-solving. Take a look at A.T. Kearney’s case example and case book to help you how to prepare effectively:
- Promotional Planning Case example
- Consulting Case Book and Tips for Interviewing
Strategy& / PWC Case Interview Examples
Strategy& / PWC focuses on executive-level strategic issues, such as capability identification, market positioning, and operational efficiency. This branch's case interviews are designed to simulate real business challenges, helping to prepare candidates for the demands of strategic consulting roles. Here's a closer look at the types of questions you might encounter:
Sample Question 1: Market sizing
- Estimate the size (by value) of the UK grocery retail market
Sample Question 2: Market sizing
- Estimate the size (by value) of the UK retail cooking sauces market
Sample Question 3: Interpreting information and drawing conclusions
- Look at the chart on the following slide
- Interpret the meaning of the chart
- How are things changing? Who's winning and who's losing?
- Given your knowledge of the UK grocery market, why might this be?
Learn more about case interview preparation by reading through Strategy& / PWC’s presentation .
L.E.K. Consulting Case Interview Examples
The case interview process at L.E.K. Consulting is rigorous – designed to evaluate a candidate's ability to solve complex business problems. The interviews are structured across multiple rounds, each focusing on different aspects of your analytical and strategic thinking abilities. Here's what you need to know to prepare effectively:
- Interview Preparation
- Market Sizing Case Example Video Walkthrough
Roland Berger Case Interview Examples
The case interviews at Roland Berger are designed to evaluate your ability to display key personality traits, with a notable preference for candidates who have international experience, as this is explicitly stated by the firm. Roland Berger has provided two case webinars on their website. Each example provides a case scenario, problem, and tips on how to answer the questions.
- 3D Printed Hip Implants Case / 3D Printed Hip Implants Case 2 sample questions:
- Based upon the explanation process: Which are the most important costs to consider?
- Is additive manufacturing of the hip implant – based upon the given information – lucrative?
- Which measures could increase the economic feasibility of the product?
- Transit Oriented Development Case / Transit Oriented Development Case 2 sample questions:
- How would you split the 416 stations between little, medium, and large revenue potential?
- How can the public transport operator of Munich increase its revenue through focusing on its existing rail stations?
Capital One Case Interview Examples
The structure of a Capital One case interview typically involves three key sections: outlining the business situation and framework, tackling quantitative questions, and formulating a recommendation based on your calculations. Expect scenarios that might not strictly adhere to the MECE principle (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive), which is often a staple in consulting case interviews. This approach reflects the real-world ambiguity you might face in business situations, requiring a flexible and adaptive problem-solving strategy. Here's a video walkthrough on everything there is need to know about Capital One case interview:
- Strategy Analyst - Case Study Guide
EY Parthenon Case Interview Examples
EY-Parthenon case interviews are designed to mimic real-life challenges, providing a glimpse into the practical work of a consultant. The interviews are candidate-led, similar to styles seen at BCG or Bain, and focus on several key areas including analytical thinking, structured problem-solving, and effective communication. The EY-Parthenon behavioral interview questions are comparable to those you would encounter in interviews for other top-tier management consulting firms. Be prepared to answer the following questions:
EY-Parthenon Case Interview Behavioral/FIT Questions
- Tell me about yourself.
- Why are you interested in consulting, and why specifically EY-Parthenon?
- Describe a time when you worked on a team project. What was your role, and how did you contribute to the team’s success?
- Can you provide an example of a challenging problem you faced at work and how you solved it?
- How do you handle tight deadlines and pressure? Can you give an example?
- Tell me about a time when you had to influence someone to achieve a goal.
- How do you prioritize tasks when you have multiple projects to manage?
- Describe a situation where you had to deal with a difficult team member. How did you handle it?
- What is your greatest professional achievement so far?
- Give an example of a time when you had to learn something new quickly.
- Why do you think you would be a good fit for EY-Parthenon’s culture?
- Tell me about a time you failed or made a mistake. How did you handle it?
- Can you provide an example of a project where you demonstrated leadership?
- How do you handle feedback and criticism?
- Are there any questions that you have for me?
- Your answer for this question must be a resounding “YES”. The more you have questions for them, the better because that shows that you’ve researched the company. You may ask about a particular previous project they did or something in particular to their operations.
Online Case Interview Examples from Consulting Clubs
Mastering the case interview is essential in consulting, and consulting clubs are key in this preparation. NYU, Duke, and Kellogg Consulting Club, for instance, provide free various interview cases, both individual and group, that mimic real consulting challenges.
- NYU Stern MCA 2020-2021 Casebook
- Columbia Business School 2021 Casebook
- The Duke MBA Consulting Club Casebook 2021-2022
- UCLA Case Book 2019 – 2020
- Darden School Of Business 2021-2022 Casebook
- Kellogg Consulting Club 2020 Casebook
- Cornell MBA Johnson Consulting Club Casebook 2020-2021
- Notre Dame Casebook 2022
- FMS Consulting Casebook 2021-22
- INSEAD Consulting Club Casebook 2021
- IIMC Consulting Casebook 2021-22
- IIM Lucknow Casebook 2022
- Harvard Business School Management Consulting Club Case Interview Examples
- Berkeley Haas School of Business Consulting Club Interview Preparation Guide and Case Interview Examples 2019
How to Ace Your Case Interview
To excel in your case interview, it's crucial to demonstrate a blend of problem-solving skills, analytical ability, strategic and logical thinking, and comfort with ambiguity. These elements are essential as they reflect real client projects that you might handle at firms like Deloitte Consulting LLP.
Read : The 15 Most Common Consulting Interview Questions — With Answers
Step-by-Step Approach to Case Interviews
- Understand the Issue : Start by clarifying the case question. Ensure you fully grasp the problem before proceeding.
- Develop a Framework : Articulate a framework and initial hypothesis to explore. This helps in structuring your response and guides your analysis.
- Analytical Execution : Engage in logical storytelling. Walk the interviewer through your thought process and explain your assumptions. Take notes and structure your analysis clearly.
- Recommendation and Next Steps : Conclude with a strong recommendation based on your findings. Outline the next steps and expected results or impacts.
Read : Mastering Consulting Cases: A Step-by-Step Approach
Tips on How to Prepare For Your Case Interview

To excel in your case interview preparation, it's essential to engage in extensive practice with a variety of case types. Successful candidates often practice with dozens of case interview scenarios, treating the preparation process with the same rigor as studying for finals or the GMAT. Here are key steps to enhance your preparation:
- Diverse Practice Cases : Ensure the practice cases you use cover a broad spectrum of problems, including profitability, market sizing, and business expansion scenarios. This variety prepares you for any curveballs and helps develop flexibility in applying different frameworks.
- Quality of Practice Materials : Select high-quality practice cases from trusted sources. The content and structure of these cases should closely mimic the types of cases presented in actual interviews at top consulting firms.
- Framework Mastery : Rather than memorizing frameworks, focus on understanding and adapting them to fit different case scenarios. This approach helps in crafting tailored solutions during your actual interview.
- Time Management : Practice managing your time effectively during mock interviews. Top consulting firms like Bain appreciate candidates who can efficiently organize and analyze information under time constraints.
- Engage with Realistic Simulations : Participate in mock interviews and case sessions that simulate the actual interview environment. This practice helps you refine your problem-solving approach and improve your communication skills under pressure.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation : Stay informed about new trends and changes in the consulting interview landscape. Engage with resources that provide updates and insights into evolving interview formats.
Personalized Coaching : Consider working with an experienced coach who can provide personalized feedback and guidance. Coaching can significantly enhance your performance by focusing on areas that need improvement.
Practice with Experts from Leland
Through an extensive exploration of the various aspects of case interviews across prestigious consulting firms like McKinsey, BCG, Bain, Deloitte, Accenture, and others, it's evident that thorough preparation and an adaptable mindset are critical for success.
Leland offers comprehensive case study interview preparation tailored to help you excel in consulting case interviews. Our experienced consultants provide personalized coaching, realistic case simulations, and strategic feedback to enhance your problem-solving skills and boost your confidence. With our expert guidance, you'll be well-prepared to tackle any case interview challenge and make a lasting impression.
What questions should you consider asking during a case study interview?
- In your case study interview, it's crucial to ask insightful questions to understand the context fully. Consider asking about how the interviewee discovered your company, the timeline of their engagement, their initial experiences with your company, the challenges they aimed to address, and whether they considered any competitors or alternative solutions.
What strategies can enhance your performance in a case interview?
- To excel in a case interview, start by taking a moment to organize your thoughts before responding. Structure your response logically, guiding the interviewer through your thought process and clarifying any assumptions you make. Maintain composure and treat the interview as a professional conversation, which can help alleviate pressure.
How can you excel in a case study interview?
- To perform well in a case study interview, make sure to take detailed notes throughout. Even if you are not familiar with the industry, focus on demonstrating your analytical skills and how you approach problem-solving. Communicate clearly and ensure you have a thorough understanding of the problem you're asked to analyze.
What types of questions are typically asked in case interviews?
- Case interviews generally include questions from nine key categories, such as framework or issue tree questions, market-sizing and guesstimate questions, valuation inquiries, brain teasers, chart interpretation, value proposition analysis, informational queries, and mathematical problems.
Preparing for consulting recruiting and/or case interviews? Here are some additional resources to help:
- Top 3 Tactics to Ace Your Case Interview
- A Comprehensive Guide to McKinsey & Co., Bain & Co., and Boston Consulting Group
- From No Offers to Multiple Offers - How to Take Your Casing to the Next Level
- Soft Skills for Consulting: Why They Matter and How to Develop Them
- Five Tips to Break Into Management Consulting
Browse hundreds of expert coaches
Leland coaches have helped thousands of people achieve their goals. A dedicated mentor can make all the difference.
Browse Related Articles

August 22, 2024
The 15 Most Common Consulting Interview Questions — With Answers
Discover the 15 most common consulting interview questions with sample answers. Prepare confidently with our friendly guide to acing your consulting interview.
August 20, 2024
Case Interview Math Guide: Everything You Need to Know
Master case interview math with our friendly guide! Learn essential tips, tricks, and strategies to ace every calculation and impress in your consulting interviews.

May 18, 2023
Victor Cheng LOMS: Is It the Ultimate Guide to Case Interviews?
Discover the ultimate guide to acing case interviews with Victor Cheng's LOMS program.

March 12, 2024
The Ultimate Guide to the Consulting Case Interview – With Examples
This guide, written by a former McKinsey consultant and Wharton MBA, breaks down the management consulting case interview into comprehensible parts with relevant, realistic examples at every turn.

How to Prepare For Your Management Consulting Interview
A former McKinsey consultant and Wharton MBA outlines her top tips for preparing for your management consulting interview. Whether you're a newbie or a seasoned professional, this article will give you the edge to impress your interviewers.

January 2, 2024
The Ultimate Guide to the EY Parthenon Case Interview Process
Are you preparing for the EY Parthenon case interview process? Look no further than our ultimate guide, packed with insider tips and strategies to help you ace the interview and land your dream job.

May 11, 2023
The Consulting Scene in Chicago: A Guide to Top Firms
Discover the top consulting firms in Chicago with our comprehensive guide. From boutique firms to global powerhouses, we've got you covered.

Market Entry Framework: The Expert Guide
Unlock success in new markets with our expert guide! Learn the market entry framework step-by-step and discover strategies to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.

August 19, 2024
The Top 10 IT Consulting Firms (2024)
Explore the top 10 IT consulting firms of 2024. Discover industry leaders shaping the future of tech with innovative solutions and expertise.
IQVIA Interview Process: A Comprehensive Guide for Success
Looking to ace your IQVIA interview? Our comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know to succeed, from the application process to common interview questions and tips for impressing your interviewer.

Navigating the Shift from Energy Sector to Management Consulting: An Insider's Guide
Are you considering a career shift from the energy sector to management consulting? Look no further than our insider's guide, filled with tips and insights to help you navigate this exciting transition.

Transportation to Management Consulting: An In-depth Look at How to Make the Transition
Are you considering a career change from transportation to management consulting? Look no further! Our in-depth article provides valuable insights and practical tips on how to successfully make the transition.
29 full cases from consulting firms
A collection of 29 sample cases from mckinsey, bcg, bain, deloitte, accenture & more..



/filters:quality(75)//case_thumb/1669783363736_case_interview_end_to_end_secrets_program.png)



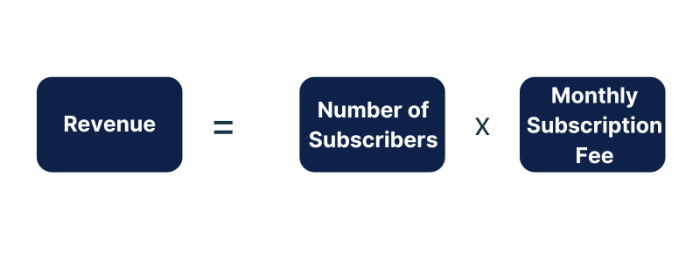
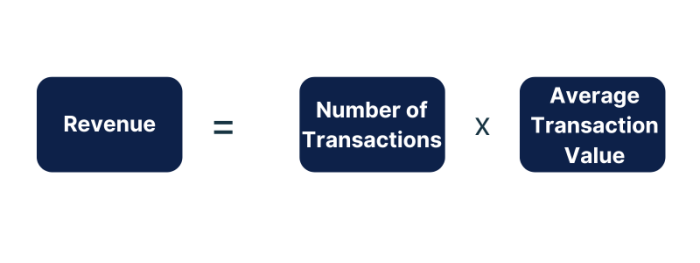

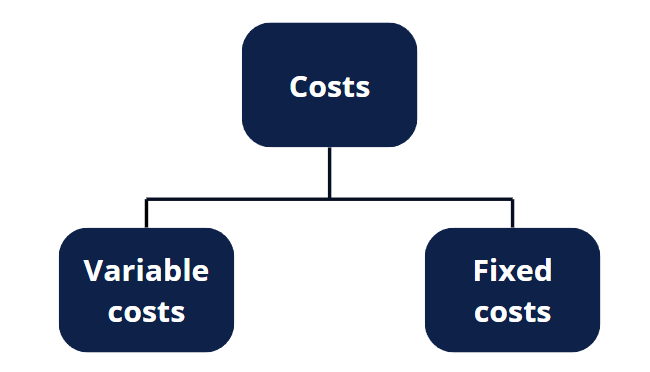
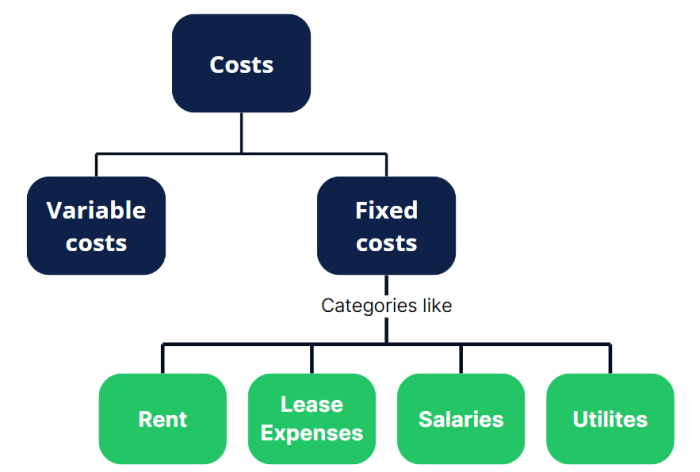
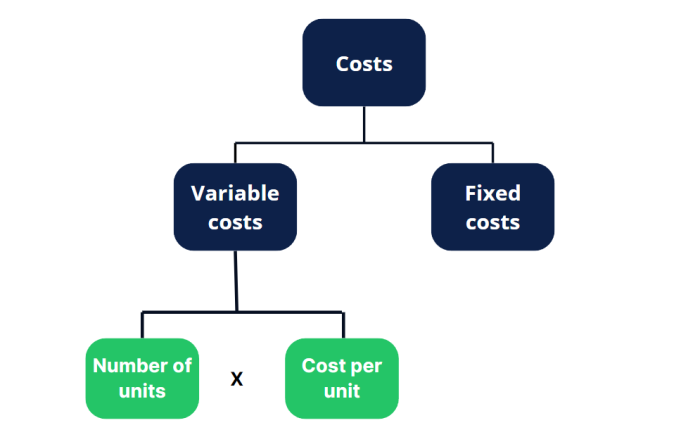

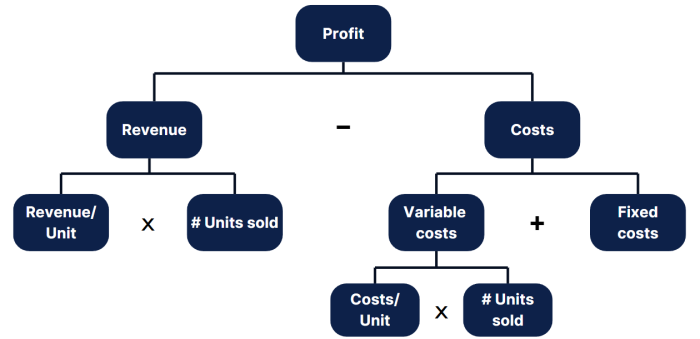


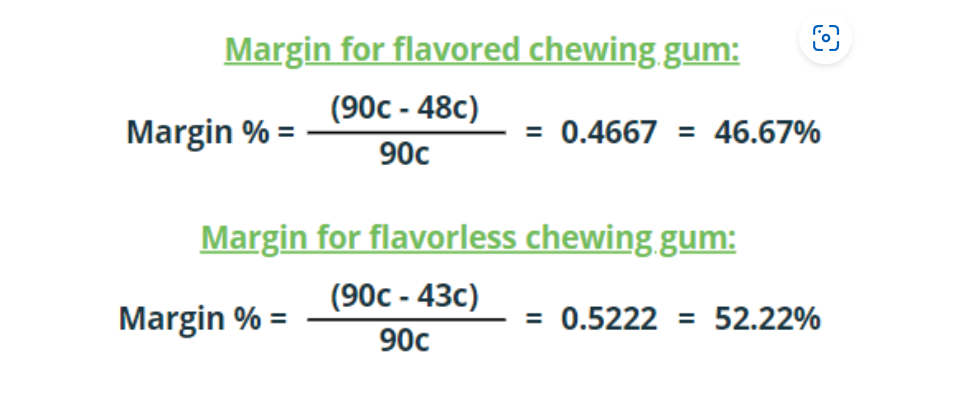
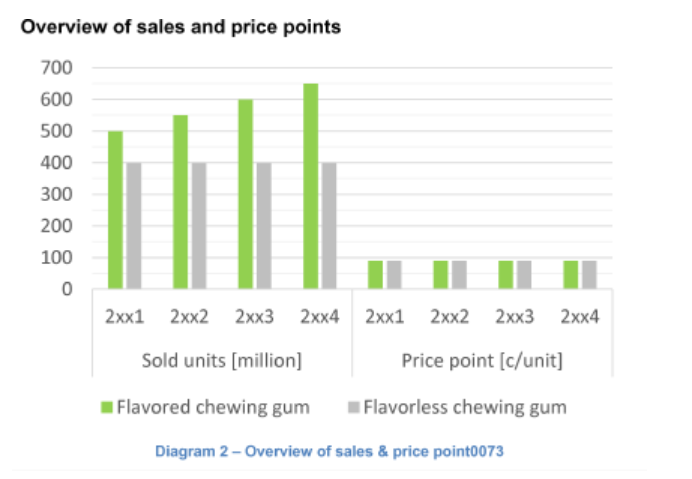











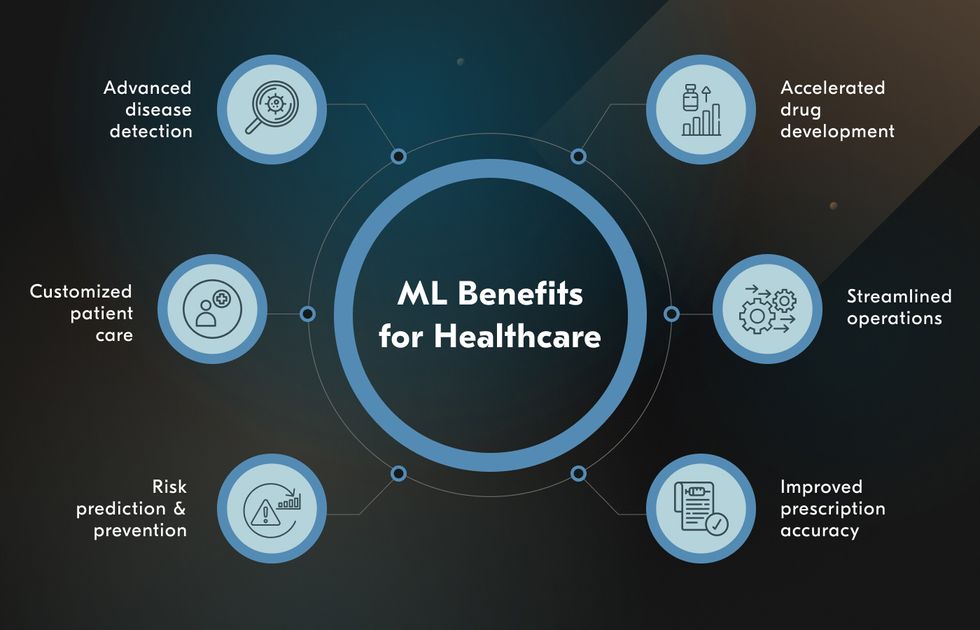
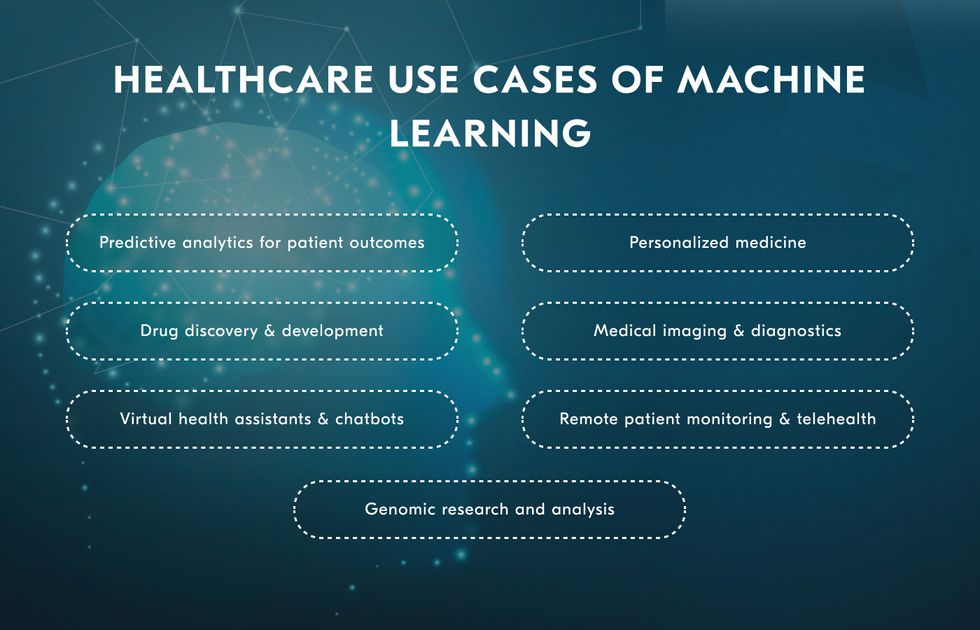

![consulting case study benefits EMR/EHR Software Development: [Benefits & Best Practices]](https://acropolium.com/img/articles/emr-ehr-software-development-implementation-tips-and-cost/img01.jpg)

![consulting case study benefits AI in Healthcare: Examples, Use Cases & Benefits [2024 Guide]](https://acropolium.com/img/articles/ai-in-healthcare-examples-use-cases-and-benefits/img01.jpg)
![consulting case study benefits Online Pharmacy App Development [2024 Guide]](https://acropolium.com/img/articles/pharmacy-app-development/img01.jpg)


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Consulting case studies typically detail the challenge that the client was facing, the approach taken by the consulting firm to address the challenge, and the outcomes and results achieved as a result of the project. ... One of the key benefits of using data in consulting case studies is its ability to improve decision-making processes. By ...
By the end of this article, you will learn four different strategies on how to create unique and tailored frameworks for any case interview. Strategy #1: Creating Frameworks from Scratch. Strategy #2: Memorizing 8 - 10 Broad Business Areas. Strategy #3: Breaking Down Stakeholders. Strategy #4: Breaking Down Processes.
1. The key to landing your consulting job. Case interviews - where you are asked to solve a business case study under scrutiny - are the core of the selection process right across McKinsey, Bain and BCG (the "MBB" firms). This interview format is also used pretty much universally across other high-end consultancies; including LEK, Kearney ...
Consulting Case Study Examples . ... And if you'd benefit from personal, 1-on-1 coaching and support from like-minded consultants, check out our Clarity Coaching Program. Get Help & Feedback Writing Consulting Case Studies . If writing and demonstrating your authority were easy, then every consultant would be publishing case studies. ...
5. Build Your Self-Confidence. Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader's perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career. According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey ...
Case Interview 2024 - Guide for Your Consulting Case Interview. A case interview is a type of job interview in which the candidate must analyze and solve a problematic business scenario (" case study "). It is used to simulate the situation on-the-job and to find out if the respective candidate meets the necessary analytical and ...
L.E.K. Consulting case interview examples. Case interview example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website) Market sizing case example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website) 11. Roland Berger case interview examples ... And also walk through a few M&A case study examples. Read more . Consulting Dec 20, 2022. The 9 most prestigious consulting firms in the ...
Non-Profitability Cases. 2.1 Lives Affected. 2.2 Retention. 2.3 Industry Landscape and Competitive Dynamics. Market Sizing Questions (also called dinner conversation cases) Case Interview Math (also known as consulting math) 4.1 Consulting Math Example. 4.2 Summary of Key Things to Remember on Consulting Math Questions.
Case Interview Frameworks: Ultimate Guide. The case interview is the ultimate challenge for most consulting candidates. Whether you're just starting your preparation or you are 30 practice cases in, it's helpful to familiarize yourself with the most popular case interview frameworks. However, the goal is not to memorize the case study ...
Generally, you must always be (1) structured, (2) fact-based, and (3) action-oriented. Additionally, common people skills and interview tips also apply - show your appreciation by thanking for their help, keep a smile on your face to maintain a positive atmosphere, etc. Tip 2: Explaining the purpose of the data.
Our 4-step approach will help you do just that. Opening - Understand and reconfirm the objective and ask clarifying questions. Structure - Develop a problem-solving structure to answer the key questions. Analysis - Dive deeper into analyzing relevant issues and use data provided by your interviewer to make conclusions.
Our clients' success stories span all industry sectors — from technology companies to energy providers, financial services to consumer retailers and every strategic function in between. EY Consulting case studies are a window into how we work alongside our clients to deliver strategic, sustainable growth and success.
Case Data (1): Production costs & pricing. Prompt: Production costs for HDTV screens have been as follows: 2015: $400/screen 2016: $250/screen 2017: $200/screen 2018: $180/screen (forecasted) The retail price (street price) each year has been $1,000/screen.
Agency V - Help a large federal agency recover from a front-page scandal that sparked investigations and congressional hearings. Federal Benefits Provider - Help a federal agency that provides benefits to millions of U.S. citizens prepare for a major expansion of its mandate. 5. AT Kearney Case Interview Examples.
Consulting firms rely heavily on case interviews to find the right candidate and therefore, you should practice strategically, early (at least 2-3 months prior to the interview), and often. ... The focus is on quantifying the benefits of new business infrastructure solutions ... Market Study Framework; Market study questions come in 3 main ...
1. Beautify Case. Sample Question #1: Beautify is excited to support its current staff of beauty consultants on the journey to becoming virtual social media-beauty advisors. Consultants would still lead the way in terms of direct consumer engagement and would be expected to maintain and grow a group of clients.
Familiarizing yourself with the case interview format is a key part of preparing for consulting interviews. This post will give you resources to learn about the format itself and 29 real case examples from leading firms like McKinsey, BCG, Bain and Deloitte. First, we recommend you get familiar with the format of a case interview.
10 example cases with 100+ real-time feedbacks on tips and techniques, 50+ exercises on business intuition and 1300+ questions for math practice! Learning 35 case interview examples, 16 casebooks, and a feedback-rich case video help you to best preparing for the management consulting recruitment process.
Five Case Studies of Transformation Excellence. , , Five Case Studies of Transformation Excellence. November 03, 2014ByLars Fæste, Jim Hemerling, Perry Keenan, and Martin Reeves. In a business environment characterized by greater volatility and more frequent disruptions, companies face a clear imperative: they must transform or fall behind.
In The Consultant's Toolkit, you will learn through a combination of lecture, case studies, and interactive group exercises. Topics covered include: An overview of the consulting industry, trends, and the role of consultants. Step by step strategic frameworks for the consulting process: Problem definition. Discovery and data collection.
Learn how to solve profitability cases in consulting case interviews. Use the profitability framwork, benefit from tips, and check out our case examples. Profitability Cases - How to Approach One of the Most Common Case Types in Consulting Interviews
Book a Case Coaching Session. Explore our Consulting Case Library. Find a Case Practice Partner. Take our Free Consulting Resume Course. Explore our consulting case library, where you can download over 100 cases with solutions that you can practice as part of your interview preparations.
See all case studies Hershey's trade promotion management transformation yields sweet reward An enhanced TPM solution and ongoing managed services help streamline operations and boost revenue
Benefits Benchmarking: Case Studies. See how Mercer assists companies in assessing and strengthening the benefits portion of their total rewards package, delivering benchmarking reports on Retirement and Savings, Health and Group, Paid Leave, Life/Disability, and Work Life Benefits.
Acropolium Case Studies. From low-code MVPs to comprehensive cloud-based medical systems, we have developed over 23 solutions that have helped our clients from the medical field grow. Here are some of the latest results our clients achieved by embracing machine learning in healthcare with us. Blockchain-based EHR Software Development