Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base

Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples
Published on November 8, 2019 by Rebecca Bevans . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics . It is most often used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses, that arise from theories.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o ) and (H a or H 1 ).
- Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test .
- Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
- Present the findings in your results and discussion section.
Though the specific details might vary, the procedure you will use when testing a hypothesis will always follow some version of these steps.
Table of contents
Step 1: state your null and alternate hypothesis, step 2: collect data, step 3: perform a statistical test, step 4: decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis, step 5: present your findings, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about hypothesis testing.
After developing your initial research hypothesis (the prediction that you want to investigate), it is important to restate it as a null (H o ) and alternate (H a ) hypothesis so that you can test it mathematically.
The alternate hypothesis is usually your initial hypothesis that predicts a relationship between variables. The null hypothesis is a prediction of no relationship between the variables you are interested in.
- H 0 : Men are, on average, not taller than women. H a : Men are, on average, taller than women.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

For a statistical test to be valid , it is important to perform sampling and collect data in a way that is designed to test your hypothesis. If your data are not representative, then you cannot make statistical inferences about the population you are interested in.
There are a variety of statistical tests available, but they are all based on the comparison of within-group variance (how spread out the data is within a category) versus between-group variance (how different the categories are from one another).
If the between-group variance is large enough that there is little or no overlap between groups, then your statistical test will reflect that by showing a low p -value . This means it is unlikely that the differences between these groups came about by chance.
Alternatively, if there is high within-group variance and low between-group variance, then your statistical test will reflect that with a high p -value. This means it is likely that any difference you measure between groups is due to chance.
Your choice of statistical test will be based on the type of variables and the level of measurement of your collected data .
- an estimate of the difference in average height between the two groups.
- a p -value showing how likely you are to see this difference if the null hypothesis of no difference is true.
Based on the outcome of your statistical test, you will have to decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
In most cases you will use the p -value generated by your statistical test to guide your decision. And in most cases, your predetermined level of significance for rejecting the null hypothesis will be 0.05 – that is, when there is a less than 5% chance that you would see these results if the null hypothesis were true.
In some cases, researchers choose a more conservative level of significance, such as 0.01 (1%). This minimizes the risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis ( Type I error ).
The results of hypothesis testing will be presented in the results and discussion sections of your research paper , dissertation or thesis .
In the results section you should give a brief summary of the data and a summary of the results of your statistical test (for example, the estimated difference between group means and associated p -value). In the discussion , you can discuss whether your initial hypothesis was supported by your results or not.
In the formal language of hypothesis testing, we talk about rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis. You will probably be asked to do this in your statistics assignments.
However, when presenting research results in academic papers we rarely talk this way. Instead, we go back to our alternate hypothesis (in this case, the hypothesis that men are on average taller than women) and state whether the result of our test did or did not support the alternate hypothesis.
If your null hypothesis was rejected, this result is interpreted as “supported the alternate hypothesis.”
These are superficial differences; you can see that they mean the same thing.
You might notice that we don’t say that we reject or fail to reject the alternate hypothesis . This is because hypothesis testing is not designed to prove or disprove anything. It is only designed to test whether a pattern we measure could have arisen spuriously, or by chance.
If we reject the null hypothesis based on our research (i.e., we find that it is unlikely that the pattern arose by chance), then we can say our test lends support to our hypothesis . But if the pattern does not pass our decision rule, meaning that it could have arisen by chance, then we say the test is inconsistent with our hypothesis .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bevans, R. (2023, June 22). Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/hypothesis-testing/
Is this article helpful?
Rebecca Bevans
Other students also liked, choosing the right statistical test | types & examples, understanding p values | definition and examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive
Hypothesis Testing: Uses, Steps & Example
By Jim Frost 4 Comments
What is Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing in statistics uses sample data to infer the properties of a whole population . These tests determine whether a random sample provides sufficient evidence to conclude an effect or relationship exists in the population. Researchers use them to help separate genuine population-level effects from false effects that random chance can create in samples. These methods are also known as significance testing.

For example, researchers are testing a new medication to see if it lowers blood pressure. They compare a group taking the drug to a control group taking a placebo. If their hypothesis test results are statistically significant, the medication’s effect of lowering blood pressure likely exists in the broader population, not just the sample studied.
Using Hypothesis Tests
A hypothesis test evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement the sample data best supports. These two statements are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . The following are typical examples:
- Null Hypothesis : The effect does not exist in the population.
- Alternative Hypothesis : The effect does exist in the population.
Hypothesis testing accounts for the inherent uncertainty of using a sample to draw conclusions about a population, which reduces the chances of false discoveries. These procedures determine whether the sample data are sufficiently inconsistent with the null hypothesis that you can reject it. If you can reject the null, your data favor the alternative statement that an effect exists in the population.
Statistical significance in hypothesis testing indicates that an effect you see in sample data also likely exists in the population after accounting for random sampling error , variability, and sample size. Your results are statistically significant when the p-value is less than your significance level or, equivalently, when your confidence interval excludes the null hypothesis value.
Conversely, non-significant results indicate that despite an apparent sample effect, you can’t be sure it exists in the population. It could be chance variation in the sample and not a genuine effect.
Learn more about Failing to Reject the Null .
5 Steps of Significance Testing
Hypothesis testing involves five key steps, each critical to validating a research hypothesis using statistical methods:
- Formulate the Hypotheses : Write your research hypotheses as a null hypothesis (H 0 ) and an alternative hypothesis (H A ).
- Data Collection : Gather data specifically aimed at testing the hypothesis.
- Conduct A Test : Use a suitable statistical test to analyze your data.
- Make a Decision : Based on the statistical test results, decide whether to reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject it.
- Report the Results : Summarize and present the outcomes in your report’s results and discussion sections.
While the specifics of these steps can vary depending on the research context and the data type, the fundamental process of hypothesis testing remains consistent across different studies.
Let’s work through these steps in an example!
Hypothesis Testing Example
Researchers want to determine if a new educational program improves student performance on standardized tests. They randomly assign 30 students to a control group , which follows the standard curriculum, and another 30 students to a treatment group, which participates in the new educational program. After a semester, they compare the test scores of both groups.
Download the CSV data file to perform the hypothesis testing yourself: Hypothesis_Testing .
The researchers write their hypotheses. These statements apply to the population, so they use the mu (μ) symbol for the population mean parameter .
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ) : The population means of the test scores for the two groups are equal (μ 1 = μ 2 ).
- Alternative Hypothesis (H A ) : The population means of the test scores for the two groups are unequal (μ 1 ≠ μ 2 ).
Choosing the correct hypothesis test depends on attributes such as data type and number of groups. Because they’re using continuous data and comparing two means, the researchers use a 2-sample t-test .
Here are the results.

The treatment group’s mean is 58.70, compared to the control group’s mean of 48.12. The mean difference is 10.67 points. Use the test’s p-value and significance level to determine whether this difference is likely a product of random fluctuation in the sample or a genuine population effect.
Because the p-value (0.000) is less than the standard significance level of 0.05, the results are statistically significant, and we can reject the null hypothesis. The sample data provides sufficient evidence to conclude that the new program’s effect exists in the population.
Limitations
Hypothesis testing improves your effectiveness in making data-driven decisions. However, it is not 100% accurate because random samples occasionally produce fluky results. Hypothesis tests have two types of errors, both relating to drawing incorrect conclusions.
- Type I error: The test rejects a true null hypothesis—a false positive.
- Type II error: The test fails to reject a false null hypothesis—a false negative.
Learn more about Type I and Type II Errors .
Our exploration of hypothesis testing using a practical example of an educational program reveals its powerful ability to guide decisions based on statistical evidence. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, understanding and applying these procedures can open new doors to discovering insights and making informed decisions. Let this tool empower your analytical endeavors as you navigate through the vast seas of data.
Learn more about the Hypothesis Tests for Various Data Types .
Share this:

Reader Interactions
June 10, 2024 at 10:51 am
Thank you, Jim, for another helpful article; timely too since I have started reading your new book on hypothesis testing and, now that we are at the end of the school year, my district is asking me to perform a number of evaluations on instructional programs. This is where my question/concern comes in. You mention that hypothesis testing is all about testing samples. However, I use all the students in my district when I make these comparisons. Since I am using the entire “population” in my evaluations (I don’t select a sample of third grade students, for example, but I use all 700 third graders), am I somehow misusing the tests? Or can I rest assured that my district’s student population is only a sample of the universal population of students?
June 10, 2024 at 1:50 pm
I hope you are finding the book helpful!
Yes, the purpose of hypothesis testing is to infer the properties of a population while accounting for random sampling error.
In your case, it comes down to how you want to use the results. Who do you want the results to apply to?
If you’re summarizing the sample, looking for trends and patterns, or evaluating those students and don’t plan to apply those results to other students, you don’t need hypothesis testing because there is no sampling error. They are the population and you can just use descriptive statistics. In this case, you’d only need to focus on the practical significance of the effect sizes.
On the other hand, if you want to apply the results from this group to other students, you’ll need hypothesis testing. However, there is the complicating issue of what population your sample of students represent. I’m sure your district has its own unique characteristics, demographics, etc. Your district’s students probably don’t adequately represent a universal population. At the very least, you’d need to recognize any special attributes of your district and how they could bias the results when trying to apply them outside the district. Or they might apply to similar districts in your region.
However, I’d imagine your 3rd graders probably adequately represent future classes of 3rd graders in your district. You need to be alert to changing demographics. At least in the short run I’d imagine they’d be representative of future classes.
Think about how these results will be used. Do they just apply to the students you measured? Then you don’t need hypothesis tests. However, if the results are being used to infer things about other students outside of the sample, you’ll need hypothesis testing along with considering how well your students represent the other students and how they differ.
I hope that helps!
June 10, 2024 at 3:21 pm
Thank you so much, Jim, for the suggestions in terms of what I need to think about and consider! You are always so clear in your explanations!!!!
June 10, 2024 at 3:22 pm
You’re very welcome! Best of luck with your evaluations!
Comments and Questions Cancel reply

User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
S.3 hypothesis testing.
In reviewing hypothesis tests, we start first with the general idea. Then, we keep returning to the basic procedures of hypothesis testing, each time adding a little more detail.
The general idea of hypothesis testing involves:
- Making an initial assumption.
- Collecting evidence (data).
- Based on the available evidence (data), deciding whether to reject or not reject the initial assumption.
Every hypothesis test — regardless of the population parameter involved — requires the above three steps.
Example S.3.1
Is normal body temperature really 98.6 degrees f section .
Consider the population of many, many adults. A researcher hypothesized that the average adult body temperature is lower than the often-advertised 98.6 degrees F. That is, the researcher wants an answer to the question: "Is the average adult body temperature 98.6 degrees? Or is it lower?" To answer his research question, the researcher starts by assuming that the average adult body temperature was 98.6 degrees F.
Then, the researcher went out and tried to find evidence that refutes his initial assumption. In doing so, he selects a random sample of 130 adults. The average body temperature of the 130 sampled adults is 98.25 degrees.
Then, the researcher uses the data he collected to make a decision about his initial assumption. It is either likely or unlikely that the researcher would collect the evidence he did given his initial assumption that the average adult body temperature is 98.6 degrees:
- If it is likely , then the researcher does not reject his initial assumption that the average adult body temperature is 98.6 degrees. There is not enough evidence to do otherwise.
- either the researcher's initial assumption is correct and he experienced a very unusual event;
- or the researcher's initial assumption is incorrect.
In statistics, we generally don't make claims that require us to believe that a very unusual event happened. That is, in the practice of statistics, if the evidence (data) we collected is unlikely in light of the initial assumption, then we reject our initial assumption.
Example S.3.2
Criminal trial analogy section .
One place where you can consistently see the general idea of hypothesis testing in action is in criminal trials held in the United States. Our criminal justice system assumes "the defendant is innocent until proven guilty." That is, our initial assumption is that the defendant is innocent.
In the practice of statistics, we make our initial assumption when we state our two competing hypotheses -- the null hypothesis ( H 0 ) and the alternative hypothesis ( H A ). Here, our hypotheses are:
- H 0 : Defendant is not guilty (innocent)
- H A : Defendant is guilty
In statistics, we always assume the null hypothesis is true . That is, the null hypothesis is always our initial assumption.
The prosecution team then collects evidence — such as finger prints, blood spots, hair samples, carpet fibers, shoe prints, ransom notes, and handwriting samples — with the hopes of finding "sufficient evidence" to make the assumption of innocence refutable.
In statistics, the data are the evidence.
The jury then makes a decision based on the available evidence:
- If the jury finds sufficient evidence — beyond a reasonable doubt — to make the assumption of innocence refutable, the jury rejects the null hypothesis and deems the defendant guilty. We behave as if the defendant is guilty.
- If there is insufficient evidence, then the jury does not reject the null hypothesis . We behave as if the defendant is innocent.
In statistics, we always make one of two decisions. We either "reject the null hypothesis" or we "fail to reject the null hypothesis."
Errors in Hypothesis Testing Section
Did you notice the use of the phrase "behave as if" in the previous discussion? We "behave as if" the defendant is guilty; we do not "prove" that the defendant is guilty. And, we "behave as if" the defendant is innocent; we do not "prove" that the defendant is innocent.
This is a very important distinction! We make our decision based on evidence not on 100% guaranteed proof. Again:
- If we reject the null hypothesis, we do not prove that the alternative hypothesis is true.
- If we do not reject the null hypothesis, we do not prove that the null hypothesis is true.
We merely state that there is enough evidence to behave one way or the other. This is always true in statistics! Because of this, whatever the decision, there is always a chance that we made an error .
Let's review the two types of errors that can be made in criminal trials:
| Jury Decision | Truth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Not Guilty | Guilty | ||
| Not Guilty | OK | ERROR | |
| Guilty | ERROR | OK | |
Table S.3.2 shows how this corresponds to the two types of errors in hypothesis testing.
| Decision | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Null Hypothesis | Alternative Hypothesis | ||
| Do not Reject Null | OK | Type II Error | |
| Reject Null | Type I Error | OK | |
Note that, in statistics, we call the two types of errors by two different names -- one is called a "Type I error," and the other is called a "Type II error." Here are the formal definitions of the two types of errors:
There is always a chance of making one of these errors. But, a good scientific study will minimize the chance of doing so!
Making the Decision Section
Recall that it is either likely or unlikely that we would observe the evidence we did given our initial assumption. If it is likely , we do not reject the null hypothesis. If it is unlikely , then we reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. Effectively, then, making the decision reduces to determining "likely" or "unlikely."
In statistics, there are two ways to determine whether the evidence is likely or unlikely given the initial assumption:
- We could take the " critical value approach " (favored in many of the older textbooks).
- Or, we could take the " P -value approach " (what is used most often in research, journal articles, and statistical software).
In the next two sections, we review the procedures behind each of these two approaches. To make our review concrete, let's imagine that μ is the average grade point average of all American students who major in mathematics. We first review the critical value approach for conducting each of the following three hypothesis tests about the population mean $\mu$:
| : = 3 | : > 3 | |
| : = 3 | : < 3 | |
| : = 3 | : ≠ 3 |
In Practice
- We would want to conduct the first hypothesis test if we were interested in concluding that the average grade point average of the group is more than 3.
- We would want to conduct the second hypothesis test if we were interested in concluding that the average grade point average of the group is less than 3.
- And, we would want to conduct the third hypothesis test if we were only interested in concluding that the average grade point average of the group differs from 3 (without caring whether it is more or less than 3).
Upon completing the review of the critical value approach, we review the P -value approach for conducting each of the above three hypothesis tests about the population mean \(\mu\). The procedures that we review here for both approaches easily extend to hypothesis tests about any other population parameter.

Hypothesis Testing – A Deep Dive into Hypothesis Testing, The Backbone of Statistical Inference
- September 21, 2023
Explore the intricacies of hypothesis testing, a cornerstone of statistical analysis. Dive into methods, interpretations, and applications for making data-driven decisions.

In this Blog post we will learn:
- What is Hypothesis Testing?
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing 2.1. Set up Hypotheses: Null and Alternative 2.2. Choose a Significance Level (α) 2.3. Calculate a test statistic and P-Value 2.4. Make a Decision
- Example : Testing a new drug.
- Example in python
1. What is Hypothesis Testing?
In simple terms, hypothesis testing is a method used to make decisions or inferences about population parameters based on sample data. Imagine being handed a dice and asked if it’s biased. By rolling it a few times and analyzing the outcomes, you’d be engaging in the essence of hypothesis testing.
Think of hypothesis testing as the scientific method of the statistics world. Suppose you hear claims like “This new drug works wonders!” or “Our new website design boosts sales.” How do you know if these statements hold water? Enter hypothesis testing.
2. Steps in Hypothesis Testing
- Set up Hypotheses : Begin with a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha).
- Choose a Significance Level (α) : Typically 0.05, this is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true. Think of it as the chance of accusing an innocent person.
- Calculate Test statistic and P-Value : Gather evidence (data) and calculate a test statistic.
- p-value : This is the probability of observing the data, given that the null hypothesis is true. A small p-value (typically ≤ 0.05) suggests the data is inconsistent with the null hypothesis.
- Decision Rule : If the p-value is less than or equal to α, you reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative.
2.1. Set up Hypotheses: Null and Alternative
Before diving into testing, we must formulate hypotheses. The null hypothesis (H0) represents the default assumption, while the alternative hypothesis (H1) challenges it.
For instance, in drug testing, H0 : “The new drug is no better than the existing one,” H1 : “The new drug is superior .”
2.2. Choose a Significance Level (α)
When You collect and analyze data to test H0 and H1 hypotheses. Based on your analysis, you decide whether to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative, or fail to reject / Accept the null hypothesis.
The significance level, often denoted by $α$, represents the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true.
In other words, it’s the risk you’re willing to take of making a Type I error (false positive).
Type I Error (False Positive) :
- Symbolized by the Greek letter alpha (α).
- Occurs when you incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis . In other words, you conclude that there is an effect or difference when, in reality, there isn’t.
- The probability of making a Type I error is denoted by the significance level of a test. Commonly, tests are conducted at the 0.05 significance level , which means there’s a 5% chance of making a Type I error .
- Commonly used significance levels are 0.01, 0.05, and 0.10, but the choice depends on the context of the study and the level of risk one is willing to accept.
Example : If a drug is not effective (truth), but a clinical trial incorrectly concludes that it is effective (based on the sample data), then a Type I error has occurred.
Type II Error (False Negative) :
- Symbolized by the Greek letter beta (β).
- Occurs when you accept a false null hypothesis . This means you conclude there is no effect or difference when, in reality, there is.
- The probability of making a Type II error is denoted by β. The power of a test (1 – β) represents the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis.
Example : If a drug is effective (truth), but a clinical trial incorrectly concludes that it is not effective (based on the sample data), then a Type II error has occurred.
Balancing the Errors :

In practice, there’s a trade-off between Type I and Type II errors. Reducing the risk of one typically increases the risk of the other. For example, if you want to decrease the probability of a Type I error (by setting a lower significance level), you might increase the probability of a Type II error unless you compensate by collecting more data or making other adjustments.
It’s essential to understand the consequences of both types of errors in any given context. In some situations, a Type I error might be more severe, while in others, a Type II error might be of greater concern. This understanding guides researchers in designing their experiments and choosing appropriate significance levels.
2.3. Calculate a test statistic and P-Value
Test statistic : A test statistic is a single number that helps us understand how far our sample data is from what we’d expect under a null hypothesis (a basic assumption we’re trying to test against). Generally, the larger the test statistic, the more evidence we have against our null hypothesis. It helps us decide whether the differences we observe in our data are due to random chance or if there’s an actual effect.
P-value : The P-value tells us how likely we would get our observed results (or something more extreme) if the null hypothesis were true. It’s a value between 0 and 1. – A smaller P-value (typically below 0.05) means that the observation is rare under the null hypothesis, so we might reject the null hypothesis. – A larger P-value suggests that what we observed could easily happen by random chance, so we might not reject the null hypothesis.
2.4. Make a Decision
Relationship between $α$ and P-Value
When conducting a hypothesis test:
- We first choose a significance level ($α$), which sets a threshold for making decisions.
We then calculate the p-value from our sample data and the test statistic.
Finally, we compare the p-value to our chosen $α$:
- If $p−value≤α$: We reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. The result is said to be statistically significant.
- If $p−value>α$: We fail to reject the null hypothesis. There isn’t enough statistical evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
3. Example : Testing a new drug.
Imagine we are investigating whether a new drug is effective at treating headaches faster than drug B.
Setting Up the Experiment : You gather 100 people who suffer from headaches. Half of them (50 people) are given the new drug (let’s call this the ‘Drug Group’), and the other half are given a sugar pill, which doesn’t contain any medication.
- Set up Hypotheses : Before starting, you make a prediction:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): The new drug has no effect. Any difference in healing time between the two groups is just due to random chance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): The new drug does have an effect. The difference in healing time between the two groups is significant and not just by chance.
- Choose a Significance Level (α) : Typically 0.05, this is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true
Calculate Test statistic and P-Value : After the experiment, you analyze the data. The “test statistic” is a number that helps you understand the difference between the two groups in terms of standard units.
For instance, let’s say:
- The average healing time in the Drug Group is 2 hours.
- The average healing time in the Placebo Group is 3 hours.
The test statistic helps you understand how significant this 1-hour difference is. If the groups are large and the spread of healing times in each group is small, then this difference might be significant. But if there’s a huge variation in healing times, the 1-hour difference might not be so special.
Imagine the P-value as answering this question: “If the new drug had NO real effect, what’s the probability that I’d see a difference as extreme (or more extreme) as the one I found, just by random chance?”
For instance:
- P-value of 0.01 means there’s a 1% chance that the observed difference (or a more extreme difference) would occur if the drug had no effect. That’s pretty rare, so we might consider the drug effective.
- P-value of 0.5 means there’s a 50% chance you’d see this difference just by chance. That’s pretty high, so we might not be convinced the drug is doing much.
- If the P-value is less than ($α$) 0.05: the results are “statistically significant,” and they might reject the null hypothesis , believing the new drug has an effect.
- If the P-value is greater than ($α$) 0.05: the results are not statistically significant, and they don’t reject the null hypothesis , remaining unsure if the drug has a genuine effect.
4. Example in python
For simplicity, let’s say we’re using a t-test (common for comparing means). Let’s dive into Python:
Making a Decision : “The results are statistically significant! p-value < 0.05 , The drug seems to have an effect!” If not, we’d say, “Looks like the drug isn’t as miraculous as we thought.”
5. Conclusion
Hypothesis testing is an indispensable tool in data science, allowing us to make data-driven decisions with confidence. By understanding its principles, conducting tests properly, and considering real-world applications, you can harness the power of hypothesis testing to unlock valuable insights from your data.
More Articles
F statistic formula – explained, correlation – connecting the dots, the role of correlation in data analysis, sampling and sampling distributions – a comprehensive guide on sampling and sampling distributions, law of large numbers – a deep dive into the world of statistics, central limit theorem – a deep dive into central limit theorem and its significance in statistics, similar articles, complete introduction to linear regression in r, how to implement common statistical significance tests and find the p value, logistic regression – a complete tutorial with examples in r.
Subscribe to Machine Learning Plus for high value data science content
© Machinelearningplus. All rights reserved.

Machine Learning A-Z™: Hands-On Python & R In Data Science
Free sample videos:.

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Hypothesis Testing?
- How It Works
4 Step Process
The bottom line.
- Fundamental Analysis
Hypothesis Testing: 4 Steps and Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ChristinaMajaski-5c9433ea46e0fb0001d880b1.jpeg)
Hypothesis testing, sometimes called significance testing, is an act in statistics whereby an analyst tests an assumption regarding a population parameter. The methodology employed by the analyst depends on the nature of the data used and the reason for the analysis.
Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data. Such data may come from a larger population or a data-generating process. The word "population" will be used for both of these cases in the following descriptions.
Key Takeaways
- Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data.
- The test provides evidence concerning the plausibility of the hypothesis, given the data.
- Statistical analysts test a hypothesis by measuring and examining a random sample of the population being analyzed.
- The four steps of hypothesis testing include stating the hypotheses, formulating an analysis plan, analyzing the sample data, and analyzing the result.
How Hypothesis Testing Works
In hypothesis testing, an analyst tests a statistical sample, intending to provide evidence on the plausibility of the null hypothesis. Statistical analysts measure and examine a random sample of the population being analyzed. All analysts use a random population sample to test two different hypotheses: the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
The null hypothesis is usually a hypothesis of equality between population parameters; e.g., a null hypothesis may state that the population mean return is equal to zero. The alternative hypothesis is effectively the opposite of a null hypothesis. Thus, they are mutually exclusive , and only one can be true. However, one of the two hypotheses will always be true.
The null hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter, such as the population mean, that is assumed to be true.
- State the hypotheses.
- Formulate an analysis plan, which outlines how the data will be evaluated.
- Carry out the plan and analyze the sample data.
- Analyze the results and either reject the null hypothesis, or state that the null hypothesis is plausible, given the data.
Example of Hypothesis Testing
If an individual wants to test that a penny has exactly a 50% chance of landing on heads, the null hypothesis would be that 50% is correct, and the alternative hypothesis would be that 50% is not correct. Mathematically, the null hypothesis is represented as Ho: P = 0.5. The alternative hypothesis is shown as "Ha" and is identical to the null hypothesis, except with the equal sign struck-through, meaning that it does not equal 50%.
A random sample of 100 coin flips is taken, and the null hypothesis is tested. If it is found that the 100 coin flips were distributed as 40 heads and 60 tails, the analyst would assume that a penny does not have a 50% chance of landing on heads and would reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis.
If there were 48 heads and 52 tails, then it is plausible that the coin could be fair and still produce such a result. In cases such as this where the null hypothesis is "accepted," the analyst states that the difference between the expected results (50 heads and 50 tails) and the observed results (48 heads and 52 tails) is "explainable by chance alone."
When Did Hypothesis Testing Begin?
Some statisticians attribute the first hypothesis tests to satirical writer John Arbuthnot in 1710, who studied male and female births in England after observing that in nearly every year, male births exceeded female births by a slight proportion. Arbuthnot calculated that the probability of this happening by chance was small, and therefore it was due to “divine providence.”
What are the Benefits of Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing helps assess the accuracy of new ideas or theories by testing them against data. This allows researchers to determine whether the evidence supports their hypothesis, helping to avoid false claims and conclusions. Hypothesis testing also provides a framework for decision-making based on data rather than personal opinions or biases. By relying on statistical analysis, hypothesis testing helps to reduce the effects of chance and confounding variables, providing a robust framework for making informed conclusions.
What are the Limitations of Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing relies exclusively on data and doesn’t provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject being studied. Additionally, the accuracy of the results depends on the quality of the available data and the statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or inappropriate hypothesis formulation may lead to incorrect conclusions or failed tests. Hypothesis testing can also lead to errors, such as analysts either accepting or rejecting a null hypothesis when they shouldn’t have. These errors may result in false conclusions or missed opportunities to identify significant patterns or relationships in the data.
Hypothesis testing refers to a statistical process that helps researchers determine the reliability of a study. By using a well-formulated hypothesis and set of statistical tests, individuals or businesses can make inferences about the population that they are studying and draw conclusions based on the data presented. All hypothesis testing methods have the same four-step process, which includes stating the hypotheses, formulating an analysis plan, analyzing the sample data, and analyzing the result.
Sage. " Introduction to Hypothesis Testing ," Page 4.
Elder Research. " Who Invented the Null Hypothesis? "
Formplus. " Hypothesis Testing: Definition, Uses, Limitations and Examples ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Autocorrelation-FINAL-3b2d9f40e52d4d85aa399528e7133083.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Reset password New user? Sign up
Existing user? Log in
Hypothesis Testing
Already have an account? Log in here.
A hypothesis test is a statistical inference method used to test the significance of a proposed (hypothesized) relation between population statistics (parameters) and their corresponding sample estimators . In other words, hypothesis tests are used to determine if there is enough evidence in a sample to prove a hypothesis true for the entire population.
The test considers two hypotheses: the null hypothesis , which is a statement meant to be tested, usually something like "there is no effect" with the intention of proving this false, and the alternate hypothesis , which is the statement meant to stand after the test is performed. The two hypotheses must be mutually exclusive ; moreover, in most applications, the two are complementary (one being the negation of the other). The test works by comparing the \(p\)-value to the level of significance (a chosen target). If the \(p\)-value is less than or equal to the level of significance, then the null hypothesis is rejected.
When analyzing data, only samples of a certain size might be manageable as efficient computations. In some situations the error terms follow a continuous or infinite distribution, hence the use of samples to suggest accuracy of the chosen test statistics. The method of hypothesis testing gives an advantage over guessing what distribution or which parameters the data follows.
Definitions and Methodology
Hypothesis test and confidence intervals.
In statistical inference, properties (parameters) of a population are analyzed by sampling data sets. Given assumptions on the distribution, i.e. a statistical model of the data, certain hypotheses can be deduced from the known behavior of the model. These hypotheses must be tested against sampled data from the population.
The null hypothesis \((\)denoted \(H_0)\) is a statement that is assumed to be true. If the null hypothesis is rejected, then there is enough evidence (statistical significance) to accept the alternate hypothesis \((\)denoted \(H_1).\) Before doing any test for significance, both hypotheses must be clearly stated and non-conflictive, i.e. mutually exclusive, statements. Rejecting the null hypothesis, given that it is true, is called a type I error and it is denoted \(\alpha\), which is also its probability of occurrence. Failing to reject the null hypothesis, given that it is false, is called a type II error and it is denoted \(\beta\), which is also its probability of occurrence. Also, \(\alpha\) is known as the significance level , and \(1-\beta\) is known as the power of the test. \(H_0\) \(\textbf{is true}\)\(\hspace{15mm}\) \(H_0\) \(\textbf{is false}\) \(\textbf{Reject}\) \(H_0\)\(\hspace{10mm}\) Type I error Correct Decision \(\textbf{Reject}\) \(H_1\) Correct Decision Type II error The test statistic is the standardized value following the sampled data under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true, and a chosen particular test. These tests depend on the statistic to be studied and the assumed distribution it follows, e.g. the population mean following a normal distribution. The \(p\)-value is the probability of observing an extreme test statistic in the direction of the alternate hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true. The critical value is the value of the assumed distribution of the test statistic such that the probability of making a type I error is small.
Methodologies: Given an estimator \(\hat \theta\) of a population statistic \(\theta\), following a probability distribution \(P(T)\), computed from a sample \(\mathcal{S},\) and given a significance level \(\alpha\) and test statistic \(t^*,\) define \(H_0\) and \(H_1;\) compute the test statistic \(t^*.\) \(p\)-value Approach (most prevalent): Find the \(p\)-value using \(t^*\) (right-tailed). If the \(p\)-value is at most \(\alpha,\) reject \(H_0\). Otherwise, reject \(H_1\). Critical Value Approach: Find the critical value solving the equation \(P(T\geq t_\alpha)=\alpha\) (right-tailed). If \(t^*>t_\alpha\), reject \(H_0\). Otherwise, reject \(H_1\). Note: Failing to reject \(H_0\) only means inability to accept \(H_1\), and it does not mean to accept \(H_0\).
Assume a normally distributed population has recorded cholesterol levels with various statistics computed. From a sample of 100 subjects in the population, the sample mean was 214.12 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter), with a sample standard deviation of 45.71 mg/dL. Perform a hypothesis test, with significance level 0.05, to test if there is enough evidence to conclude that the population mean is larger than 200 mg/dL. Hypothesis Test We will perform a hypothesis test using the \(p\)-value approach with significance level \(\alpha=0.05:\) Define \(H_0\): \(\mu=200\). Define \(H_1\): \(\mu>200\). Since our values are normally distributed, the test statistic is \(z^*=\frac{\bar X - \mu_0}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}=\frac{214.12 - 200}{\frac{45.71}{\sqrt{100}}}\approx 3.09\). Using a standard normal distribution, we find that our \(p\)-value is approximately \(0.001\). Since the \(p\)-value is at most \(\alpha=0.05,\) we reject \(H_0\). Therefore, we can conclude that the test shows sufficient evidence to support the claim that \(\mu\) is larger than \(200\) mg/dL.
If the sample size was smaller, the normal and \(t\)-distributions behave differently. Also, the question itself must be managed by a double-tail test instead.
Assume a population's cholesterol levels are recorded and various statistics are computed. From a sample of 25 subjects, the sample mean was 214.12 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter), with a sample standard deviation of 45.71 mg/dL. Perform a hypothesis test, with significance level 0.05, to test if there is enough evidence to conclude that the population mean is not equal to 200 mg/dL. Hypothesis Test We will perform a hypothesis test using the \(p\)-value approach with significance level \(\alpha=0.05\) and the \(t\)-distribution with 24 degrees of freedom: Define \(H_0\): \(\mu=200\). Define \(H_1\): \(\mu\neq 200\). Using the \(t\)-distribution, the test statistic is \(t^*=\frac{\bar X - \mu_0}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}=\frac{214.12 - 200}{\frac{45.71}{\sqrt{25}}}\approx 1.54\). Using a \(t\)-distribution with 24 degrees of freedom, we find that our \(p\)-value is approximately \(2(0.068)=0.136\). We have multiplied by two since this is a two-tailed argument, i.e. the mean can be smaller than or larger than. Since the \(p\)-value is larger than \(\alpha=0.05,\) we fail to reject \(H_0\). Therefore, the test does not show sufficient evidence to support the claim that \(\mu\) is not equal to \(200\) mg/dL.
The complement of the rejection on a two-tailed hypothesis test (with significance level \(\alpha\)) for a population parameter \(\theta\) is equivalent to finding a confidence interval \((\)with confidence level \(1-\alpha)\) for the population parameter \(\theta\). If the assumption on the parameter \(\theta\) falls inside the confidence interval, then the test has failed to reject the null hypothesis \((\)with \(p\)-value greater than \(\alpha).\) Otherwise, if \(\theta\) does not fall in the confidence interval, then the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternate \((\)with \(p\)-value at most \(\alpha).\)
- Statistics (Estimation)
- Normal Distribution
- Correlation
- Confidence Intervals
Problem Loading...
Note Loading...
Set Loading...

Hypothesis Testing: Understanding the Basics, Types, and Importance
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine whether a hypothesis about a population parameter is true or not. This technique helps researchers and decision-makers make informed decisions based on evidence rather than guesses. Hypothesis testing is an essential tool in scientific research, social sciences, and business analysis. In this article, we will delve deeper into the basics of hypothesis testing, types of hypotheses, significance level, p-values, and the importance of hypothesis testing.
- Introduction
What is a hypothesis?
What is hypothesis testing, types of hypotheses, null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, one-tailed and two-tailed tests, significance level and p-values, avoiding type i and type ii errors, making informed decisions, testing business strategies, a/b testing, formulating the null and alternative hypotheses, selecting the appropriate test, setting the level of significance, calculating the p-value, making a decision, common misconceptions about hypothesis testing, understanding hypothesis testing.
A hypothesis is an assumption or a proposition made about a population parameter. It is a statement that can be tested and either supported or refuted. For example, a hypothesis could be that a new medication reduces the severity of symptoms in patients with a particular disease.
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that helps to determine whether a hypothesis is true or not. It is a procedure that involves collecting and analyzing data to evaluate the probability of the null hypothesis being true. The null hypothesis is the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between a sample and the population.
In hypothesis testing, there are two types of hypotheses: null and alternative.
The null hypothesis, denoted by H0, is a statement of no effect, no relationship, or no difference between the sample and the population. It is assumed to be true until there is sufficient evidence to reject it. For example, the null hypothesis could be that there is no significant difference in the blood pressure of patients who received the medication and those who received a placebo.
The alternative hypothesis, denoted by H1, is a statement of an effect, relationship, or difference between the sample and the population. It is the opposite of the null hypothesis. For example, the alternative hypothesis could be that the medication reduces the blood pressure of patients compared to those who received a placebo.
There are two types of alternative hypotheses: one-tailed and two-tailed. A one-tailed test is used when there is a directional hypothesis. For example, the hypothesis could be that the medication reduces blood pressure. A two-tailed test is used when there is a non-directional hypothesis. For example, the hypothesis could be that there is a significant difference in blood pressure between patients who received the medication and those who received a placebo.
The significance level, denoted by α, is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. It is set at the beginning of the test, usually at 5% or 1%. The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as
or more extreme than the observed one, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. If the p-value is less than the significance level, we reject the null hypothesis.
Importance of Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing helps to avoid Type I and Type II errors. Type I error occurs when we reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true. Type II error occurs when we fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false. By setting a significance level and calculating the p-value, we can control the probability of making these errors.
Hypothesis testing helps researchers and decision-makers make informed decisions based on evidence. For example, a medical researcher can use hypothesis testing to determine the effectiveness of a new drug. A business analyst can use hypothesis testing to evaluate the performance of a marketing campaign. By testing hypotheses, decision-makers can avoid making decisions based on guesses or assumptions.
Hypothesis testing is widely used in business analysis to test strategies and make data-driven decisions. For example, a business owner can use hypothesis testing to determine whether a new product will be profitable. By conducting A/B testing, businesses can compare the performance of two versions of a product and make data-driven decisions.
Examples of Hypothesis Testing
- A/B testing is a popular technique used in online marketing and web design. It involves comparing two versions of a webpage or an advertisement to determine which one performs better. By conducting A/B testing, businesses can optimize their websites and advertisements to increase conversions and sales.
A t-test is used to compare the means of two samples. It is commonly used in medical research, social sciences, and business analysis. For example, a researcher can use a t-test to determine whether there is a significant difference in the cholesterol levels of patients who received a new drug and those who received a placebo.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a statistical technique used to compare the means of more than two samples. It is commonly used in medical research, social sciences, and business analysis. For example, a business owner can use ANOVA to determine whether there is a significant difference in the sales performance of three different stores.
Steps in Hypothesis Testing
The first step in hypothesis testing is to formulate the null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis is the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between the sample and the population, while the alternative hypothesis is the opposite.
The second step is to select the appropriate test based on the type of data and the research question. There are different types of tests for different types of data, such as t-test for continuous data and chi-square test for categorical data.
The third step is to set the level of significance, which is usually 5% or 1%. The significance level represents the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true.
The fourth step is to calculate the p-value, which represents the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as or more extreme than the observed one, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
The final step is to make a decision based on the p-value and the significance level. If the p-value is less than the significance level, we reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
There are several common misconceptions about hypothesis testing. One of the most common misconceptions is that rejecting the null hypothesis means that the alternative hypothesis is true. However
this is not necessarily the case. Rejecting the null hypothesis only means that there is evidence against it, but it does not prove that the alternative hypothesis is true. Another common misconception is that hypothesis testing can prove causality. However, hypothesis testing can only provide evidence for or against a hypothesis, and causality can only be inferred from a well-designed experiment.
Hypothesis testing is an important statistical technique used to test hypotheses and make informed decisions based on evidence. It helps to avoid Type I and Type II errors, and it is widely used in medical research, social sciences, and business analysis. By following the steps in hypothesis testing and avoiding common misconceptions, researchers and decision-makers can make data-driven decisions and avoid making decisions based on guesses or assumptions.
- What is the difference between Type I and Type II errors in hypothesis testing?
- Type I error occurs when we reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true, while Type II error occurs when we fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false.
- How do you select the appropriate test in hypothesis testing?
- The appropriate test is selected based on the type of data and the research question. There are different types of tests for different types of data, such as t-test for continuous data and chi-square test for categorical data.
- Can hypothesis testing prove causality?
- No, hypothesis testing can only provide evidence for or against a hypothesis, and causality can only be inferred from a well-designed experiment.
- Why is hypothesis testing important in business analysis?
- Hypothesis testing is important in business analysis because it helps businesses make data-driven decisions and avoid making decisions based on guesses or assumptions. By testing hypotheses, businesses can evaluate the effectiveness of their strategies and optimize their performance.
- What is A/B testing?
If you want to learn more about statistical analysis, including central tendency measures, check out our comprehensive statistical course . Our course provides a hands-on learning experience that covers all the essential statistical concepts and tools, empowering you to analyze complex data with confidence. With practical examples and interactive exercises, you’ll gain the skills you need to succeed in your statistical analysis endeavors. Enroll now and take your statistical knowledge to the next level!
If you’re looking to jumpstart your career as a data analyst, consider enrolling in our comprehensive Data Analyst Bootcamp with Internship program . Our program provides you with the skills and experience necessary to succeed in today’s data-driven world. You’ll learn the fundamentals of statistical analysis, as well as how to use tools such as SQL, Python, Excel, and PowerBI to analyze and visualize data. But that’s not all – our program also includes a 3-month internship with us where you can showcase your Capstone Project.
2 Responses
This is a great and comprehensive article on hypothesis testing, covering everything from the basics to practical examples. I particularly appreciate the section on common misconceptions, as it’s important to understand what hypothesis testing can and cannot do. Overall, a valuable resource for anyone looking to understand this statistical technique.
Thanks, Ana Carol for your Kind words, Yes these topics are very important to know in Artificial intelligence.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Tutorial Playlist
Statistics tutorial, everything you need to know about the probability density function in statistics, the best guide to understand central limit theorem, an in-depth guide to measures of central tendency : mean, median and mode, the ultimate guide to understand conditional probability.
A Comprehensive Look at Percentile in Statistics
The Best Guide to Understand Bayes Theorem
Everything you need to know about the normal distribution, an in-depth explanation of cumulative distribution function, chi-square test, what is hypothesis testing in statistics types and examples, understanding the fundamentals of arithmetic and geometric progression, the definitive guide to understand spearman’s rank correlation, mean squared error: overview, examples, concepts and more, all you need to know about the empirical rule in statistics, the complete guide to skewness and kurtosis, a holistic look at bernoulli distribution.
All You Need to Know About Bias in Statistics
A Complete Guide to Get a Grasp of Time Series Analysis
The Key Differences Between Z-Test Vs. T-Test
The Complete Guide to Understand Pearson's Correlation
A complete guide on the types of statistical studies, everything you need to know about poisson distribution, your best guide to understand correlation vs. regression, the most comprehensive guide for beginners on what is correlation, hypothesis testing in statistics - types | examples.
Lesson 10 of 24 By Avijeet Biswal

Table of Contents
In today’s data-driven world, decisions are based on data all the time. Hypothesis plays a crucial role in that process, whether it may be making business decisions, in the health sector, academia, or in quality improvement. Without hypothesis and hypothesis tests, you risk drawing the wrong conclusions and making bad decisions. In this tutorial, you will look at Hypothesis Testing in Statistics.
What Is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis Testing is a type of statistical analysis in which you put your assumptions about a population parameter to the test. It is used to estimate the relationship between 2 statistical variables.
Let's discuss few examples of statistical hypothesis from real-life -
- A teacher assumes that 60% of his college's students come from lower-middle-class families.
- A doctor believes that 3D (Diet, Dose, and Discipline) is 90% effective for diabetic patients.
Now that you know about hypothesis testing, look at the two types of hypothesis testing in statistics.
The Ultimate Ticket to Top Data Science Job Roles
Importance of Hypothesis Testing in Data Analysis
Here is what makes hypothesis testing so important in data analysis and why it is key to making better decisions:
Avoiding Misleading Conclusions (Type I and Type II Errors)
One of the biggest benefits of hypothesis testing is that it helps you avoid jumping to the wrong conclusions. For instance, a Type I error could occur if a company launches a new product thinking it will be a hit, only to find out later that the data misled them. A Type II error might happen when a company overlooks a potentially successful product because their testing wasn’t thorough enough. By setting up the right significance level and carefully calculating the p-value, hypothesis testing minimizes the chances of these errors, leading to more accurate results.
Making Smarter Choices
Hypothesis testing is key to making smarter, evidence-based decisions. Let’s say a city planner wants to determine if building a new park will increase community engagement. By testing the hypothesis using data from similar projects, they can make an informed choice. Similarly, a teacher might use hypothesis testing to see if a new teaching method actually improves student performance. It’s about taking the guesswork out of decisions and relying on solid evidence instead.
Optimizing Business Tactics
In business, hypothesis testing is invaluable for testing new ideas and strategies before fully committing to them. For example, an e-commerce company might want to test whether offering free shipping increases sales. By using hypothesis testing, they can compare sales data from customers who received free shipping offers and those who didn’t. This allows them to base their business decisions on data, not hunches, reducing the risk of costly mistakes.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Z = ( x̅ – μ0 ) / (σ /√n)
- Here, x̅ is the sample mean,
- μ0 is the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation,
- n is the sample size.
How Hypothesis Testing Works?
An analyst performs hypothesis testing on a statistical sample to present evidence of the plausibility of the null hypothesis. Measurements and analyses are conducted on a random sample of the population to test a theory. Analysts use a random population sample to test two hypotheses: the null and alternative hypotheses.
The null hypothesis is typically an equality hypothesis between population parameters; for example, a null hypothesis may claim that the population means return equals zero. The alternate hypothesis is essentially the inverse of the null hypothesis (e.g., the population means the return is not equal to zero). As a result, they are mutually exclusive, and only one can be correct. One of the two possibilities, however, will always be correct.
Your Dream Career is Just Around The Corner!
Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
The Null Hypothesis is the assumption that the event will not occur. A null hypothesis has no bearing on the study's outcome unless it is rejected.
H0 is the symbol for it, and it is pronounced H-naught.
The Alternate Hypothesis is the logical opposite of the null hypothesis. The acceptance of the alternative hypothesis follows the rejection of the null hypothesis. H1 is the symbol for it.
Let's understand this with an example.
A sanitizer manufacturer claims that its product kills 95 percent of germs on average.
To put this company's claim to the test, create a null and alternate hypothesis.
H0 (Null Hypothesis): Average = 95%.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): The average is less than 95%.
Another straightforward example to understand this concept is determining whether or not a coin is fair and balanced. The null hypothesis states that the probability of a show of heads is equal to the likelihood of a show of tails. In contrast, the alternate theory states that the probability of a show of heads and tails would be very different.
Become a Data Scientist with Hands-on Training!
Hypothesis Testing Calculation With Examples
Let's consider a hypothesis test for the average height of women in the United States. Suppose our null hypothesis is that the average height is 5'4". We gather a sample of 100 women and determine their average height is 5'5". The standard deviation of population is 2.
To calculate the z-score, we would use the following formula:
z = ( x̅ – μ0 ) / (σ /√n)
z = (5'5" - 5'4") / (2" / √100)
z = 0.5 / (0.045)
We will reject the null hypothesis as the z-score of 11.11 is very large and conclude that there is evidence to suggest that the average height of women in the US is greater than 5'4".
Steps in Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method to determine if there is enough evidence in a sample of data to infer that a certain condition is true for the entire population. Here’s a breakdown of the typical steps involved in hypothesis testing:
Formulate Hypotheses
- Null Hypothesis (H0): This hypothesis states that there is no effect or difference, and it is the hypothesis you attempt to reject with your test.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1 or Ha): This hypothesis is what you might believe to be true or hope to prove true. It is usually considered the opposite of the null hypothesis.
Choose the Significance Level (α)
The significance level, often denoted by alpha (α), is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. Common choices for α are 0.05 (5%), 0.01 (1%), and 0.10 (10%).
Select the Appropriate Test
Choose a statistical test based on the type of data and the hypothesis. Common tests include t-tests, chi-square tests, ANOVA, and regression analysis. The selection depends on data type, distribution, sample size, and whether the hypothesis is one-tailed or two-tailed.
Collect Data
Gather the data that will be analyzed in the test. To infer conclusions accurately, this data should be representative of the population.
Calculate the Test Statistic
Based on the collected data and the chosen test, calculate a test statistic that reflects how much the observed data deviates from the null hypothesis.
Determine the p-value
The p-value is the probability of observing test results at least as extreme as the results observed, assuming the null hypothesis is correct. It helps determine the strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis.
Make a Decision
Compare the p-value to the chosen significance level:
- If the p-value ≤ α: Reject the null hypothesis, suggesting sufficient evidence in the data supports the alternative hypothesis.
- If the p-value > α: Do not reject the null hypothesis, suggesting insufficient evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
Report the Results
Present the findings from the hypothesis test, including the test statistic, p-value, and the conclusion about the hypotheses.
Perform Post-hoc Analysis (if necessary)
Depending on the results and the study design, further analysis may be needed to explore the data more deeply or to address multiple comparisons if several hypotheses were tested simultaneously.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
To determine whether a discovery or relationship is statistically significant, hypothesis testing uses a z-test. It usually checks to see if two means are the same (the null hypothesis). Only when the population standard deviation is known and the sample size is 30 data points or more, can a z-test be applied.
A statistical test called a t-test is employed to compare the means of two groups. To determine whether two groups differ or if a procedure or treatment affects the population of interest, it is frequently used in hypothesis testing.
3. Chi-Square
You utilize a Chi-square test for hypothesis testing concerning whether your data is as predicted. To determine if the expected and observed results are well-fitted, the Chi-square test analyzes the differences between categorical variables from a random sample. The test's fundamental premise is that the observed values in your data should be compared to the predicted values that would be present if the null hypothesis were true.
ANOVA , or Analysis of Variance, is a statistical method used to compare the means of three or more groups. It’s particularly useful when you want to see if there are significant differences between multiple groups. For instance, in business, a company might use ANOVA to analyze whether three different stores are performing differently in terms of sales. It’s also widely used in fields like medical research and social sciences, where comparing group differences can provide valuable insights.
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Both confidence intervals and hypothesis tests are inferential techniques that depend on approximating the sample distribution. Data from a sample is used to estimate a population parameter using confidence intervals. Data from a sample is used in hypothesis testing to examine a given hypothesis. We must have a postulated parameter to conduct hypothesis testing.
Bootstrap distributions and randomization distributions are created using comparable simulation techniques. The observed sample statistic is the focal point of a bootstrap distribution, whereas the null hypothesis value is the focal point of a randomization distribution.
A variety of feasible population parameter estimates are included in confidence ranges. In this lesson, we created just two-tailed confidence intervals. There is a direct connection between these two-tail confidence intervals and these two-tail hypothesis tests. The results of a two-tailed hypothesis test and two-tailed confidence intervals typically provide the same results. In other words, a hypothesis test at the 0.05 level will virtually always fail to reject the null hypothesis if the 95% confidence interval contains the predicted value. A hypothesis test at the 0.05 level will nearly certainly reject the null hypothesis if the 95% confidence interval does not include the hypothesized parameter.
Become a Data Scientist through hands-on learning with hackathons, masterclasses, webinars, and Ask-Me-Anything sessions! Start learning!
Simple and Composite Hypothesis Testing
Depending on the population distribution, you can classify the statistical hypothesis into two types.
Simple Hypothesis: A simple hypothesis specifies an exact value for the parameter.
Composite Hypothesis: A composite hypothesis specifies a range of values.
A company is claiming that their average sales for this quarter are 1000 units. This is an example of a simple hypothesis.
Suppose the company claims that the sales are in the range of 900 to 1000 units. Then this is a case of a composite hypothesis.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The One-Tailed test, also called a directional test, considers a critical region of data that would result in the null hypothesis being rejected if the test sample falls into it, inevitably meaning the acceptance of the alternate hypothesis.
In a one-tailed test, the critical distribution area is one-sided, meaning the test sample is either greater or lesser than a specific value.
In two tails, the test sample is checked to be greater or less than a range of values in a Two-Tailed test, implying that the critical distribution area is two-sided.
If the sample falls within this range, the alternate hypothesis will be accepted, and the null hypothesis will be rejected.
Become a Data Scientist With Real-World Experience
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
If the larger than (>) sign appears in your hypothesis statement, you are using a right-tailed test, also known as an upper test. Or, to put it another way, the disparity is to the right. For instance, you can contrast the battery life before and after a change in production. Your hypothesis statements can be the following if you want to know if the battery life is longer than the original (let's say 90 hours):
- The null hypothesis is (H0 <= 90) or less change.
- A possibility is that battery life has risen (H1) > 90.
The crucial point in this situation is that the alternate hypothesis (H1), not the null hypothesis, decides whether you get a right-tailed test.
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
Alternative hypotheses that assert the true value of a parameter is lower than the null hypothesis are tested with a left-tailed test; they are indicated by the asterisk "<".
Suppose H0: mean = 50 and H1: mean not equal to 50
According to the H1, the mean can be greater than or less than 50. This is an example of a Two-tailed test.
In a similar manner, if H0: mean >=50, then H1: mean <50
Here the mean is less than 50. It is called a One-tailed test.
Type 1 and Type 2 Error
A hypothesis test can result in two types of errors.
Type 1 Error: A Type-I error occurs when sample results reject the null hypothesis despite being true.
Type 2 Error: A Type-II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false, unlike a Type-I error.
Suppose a teacher evaluates the examination paper to decide whether a student passes or fails.
H0: Student has passed
H1: Student has failed
Type I error will be the teacher failing the student [rejects H0] although the student scored the passing marks [H0 was true].
Type II error will be the case where the teacher passes the student [do not reject H0] although the student did not score the passing marks [H1 is true].
Serious About Success? Don't Settle for Less
Practice Problems on Hypothesis Testing
Here are the practice problems on hypothesis testing that will help you understand how to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios:
A telecom service provider claims that customers spend an average of ₹400 per month, with a standard deviation of ₹25. However, a random sample of 50 customer bills shows a mean of ₹250 and a standard deviation of ₹15. Does this sample data support the service provider’s claim?
Solution: Let’s break this down:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): The average amount spent per month is ₹400.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H1): The average amount spent per month is not ₹400.
- Population Standard Deviation (σ): ₹25
- Sample Size (n): 50
- Sample Mean (x̄): ₹250
1. Calculate the z-value:
z=250-40025/50 −42.42
2. Compare with critical z-values: For a 5% significance level, critical z-values are -1.96 and +1.96. Since -42.42 is far outside this range, we reject the null hypothesis. The sample data suggests that the average amount spent is significantly different from ₹400.
Out of 850 customers, 400 made online grocery purchases. Can we conclude that more than 50% of customers are moving towards online grocery shopping?
Solution: Here’s how to approach it:
- Proportion of customers who shopped online (p): 400 / 850 = 0.47
- Null Hypothesis (H0): The proportion of online shoppers is 50% or more.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H1): The proportion of online shoppers is less than 50%.
- Sample Size (n): 850
- Significance Level (α): 5%
z=p-PP(1-P)/n
z=0.47-0.500.50.5/850 −1.74
2. Compare with the critical z-value: For a 5% significance level (one-tailed test), the critical z-value is -1.645. Since -1.74 is less than -1.645, we reject the null hypothesis. This means the data does not support the idea that most customers are moving towards online grocery shopping.
In a study of code quality, Team A has 250 errors in 1000 lines of code, and Team B has 300 errors in 800 lines of code. Can we say Team B performs worse than Team A?
Solution: Let’s analyze it:
- Proportion of errors for Team A (pA): 250 / 1000 = 0.25
- Proportion of errors for Team B (pB): 300 / 800 = 0.375
- Null Hypothesis (H0): Team B’s error rate is less than or equal to Team A’s.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H1): Team B’s error rate is greater than Team A’s.
- Sample Size for Team A (nA): 1000
- Sample Size for Team B (nB): 800
p=nApA+nBpBnA+nB
p=10000.25+8000.3751000+800 ≈ 0.305
z=pA−pBp(1-p)(1nA+1nB)
z=0.25−0.3750.305(1-0.305) (11000+1800) ≈ −5.72
2. Compare with the critical z-value: For a 5% significance level (one-tailed test), the critical z-value is +1.645. Since -5.72 is far less than +1.645, we reject the null hypothesis. The data indicates that Team B’s performance is significantly worse than Team A’s.
Our Data Scientist Master's Program will help you master core topics such as R, Python, Machine Learning, Tableau, Hadoop, and Spark. Get started on your journey today!

Applications of Hypothesis Testing
Apart from the practical problems, let's look at the real-world applications of hypothesis testing across various fields:
Medicine and Healthcare
In medicine, hypothesis testing plays a pivotal role in assessing the success of new treatments. For example, researchers may want to find out if a new exercise regimen improves heart health. By comparing data from patients who followed the program to those who didn’t, they can determine if the exercise significantly improves health outcomes. Such rigorous testing allows medical professionals to rely on proven methods rather than assumptions.
Quality Control and Manufacturing
In manufacturing, ensuring product quality is vital, and hypothesis testing helps maintain those standards. Suppose a beverage company introduces a new bottling process and wants to verify if it reduces contamination. By analyzing samples from the new and old processes, hypothesis testing can reveal whether the new method reduces the risk of contamination. This allows manufacturers to implement improvements that enhance product safety and quality confidently.
Education and Learning
In education and learning, hypothesis testing is a tool to evaluate the impact of innovative teaching techniques. Imagine a situation where teachers introduce project-based learning to boost critical thinking skills. By comparing the performance of students who engaged in project-based learning with those in traditional settings, educators can test their hypothesis. The results can help educators make informed choices about adopting new teaching strategies.
Environmental Science
Hypothesis testing is essential in environmental science for evaluating the effectiveness of conservation measures. For example, scientists might explore whether a new water management strategy improves river health. By collecting and comparing data on water quality before and after the implementation of the strategy, they can determine whether the intervention leads to positive changes. Such findings are crucial for guiding environmental decisions that have long-term impacts.
Marketing and Advertising
In marketing, businesses use hypothesis testing to refine their approaches. For instance, a clothing brand might test if offering limited-time discounts increases customer loyalty. By running campaigns with and without the discount and analyzing the outcomes, they can assess if the strategy boosts customer retention. Data-driven insights from hypothesis testing enable companies to design marketing strategies that resonate with their audience and drive growth.
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing has some limitations that researchers should be aware of:
- It cannot prove or establish the truth: Hypothesis testing provides evidence to support or reject a hypothesis, but it cannot confirm the absolute truth of the research question.
- Results are sample-specific: Hypothesis testing is based on analyzing a sample from a population, and the conclusions drawn are specific to that particular sample.
- Possible errors: During hypothesis testing, there is a chance of committing type I error (rejecting a true null hypothesis) or type II error (failing to reject a false null hypothesis).
- Assumptions and requirements: Different tests have specific assumptions and requirements that must be met to accurately interpret results.
Learn All The Tricks Of The BI Trade
After reading this tutorial, you would have a much better understanding of hypothesis testing, one of the most important concepts in the field of Data Science . The majority of hypotheses are based on speculation about observed behavior, natural phenomena, or established theories.
If you are interested in statistics of data science and skills needed for such a career, you ought to explore the Post Graduate Program in Data Science.
1. What is hypothesis testing in statistics with example?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine if there is enough evidence in a sample data to draw conclusions about a population. It involves formulating two competing hypotheses, the null hypothesis (H0) and the alternative hypothesis (Ha), and then collecting data to assess the evidence. An example: testing if a new drug improves patient recovery (Ha) compared to the standard treatment (H0) based on collected patient data.
2. What is H0 and H1 in statistics?
In statistics, H0 and H1 represent the null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis, H0, is the default assumption that no effect or difference exists between groups or conditions. The alternative hypothesis, H1, is the competing claim suggesting an effect or a difference. Statistical tests determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis based on the data.
3. What is a simple hypothesis with an example?
A simple hypothesis is a specific statement predicting a single relationship between two variables. It posits a direct and uncomplicated outcome. For example, a simple hypothesis might state, "Increased sunlight exposure increases the growth rate of sunflowers." Here, the hypothesis suggests a direct relationship between the amount of sunlight (independent variable) and the growth rate of sunflowers (dependent variable), with no additional variables considered.
4. What are the 3 major types of hypothesis?
The three major types of hypotheses are:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): Represents the default assumption, stating that there is no significant effect or relationship in the data.
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): Contradicts the null hypothesis and proposes a specific effect or relationship that researchers want to investigate.
- Nondirectional Hypothesis: An alternative hypothesis that doesn't specify the direction of the effect, leaving it open for both positive and negative possibilities.
5. What software tools can assist with hypothesis testing?
Several software tools offering distinct features can help with hypothesis testing. R and RStudio are popular for their advanced statistical capabilities. The Python ecosystem, including libraries like SciPy and Statsmodels, also supports hypothesis testing. SAS and SPSS are well-established tools for comprehensive statistical analysis. For basic testing, Excel offers simple built-in functions.
6. How do I interpret the results of a hypothesis test?
Interpreting hypothesis test results involves comparing the p-value to the significance level (alpha). If the p-value is less than or equal to alpha, you can reject the null hypothesis, indicating statistical significance. This suggests that the observed effect is unlikely to have occurred by chance, validating your analysis findings.
7. Why is sample size important in hypothesis testing?
Sample size is crucial in hypothesis testing as it affects the test’s power. A larger sample size increases the likelihood of detecting a true effect, reducing the risk of Type II errors. Conversely, a small sample may lack the statistical power needed to identify differences, potentially leading to inaccurate conclusions.
8. Can hypothesis testing be used for non-numerical data?
Yes, hypothesis testing can be applied to non-numerical data through non-parametric tests. These tests are ideal when data doesn't meet parametric assumptions or when dealing with categorical data. Non-parametric tests, like the Chi-square or Mann-Whitney U test, provide robust methods for analyzing non-numerical data and drawing meaningful conclusions.
9. How do I choose the proper hypothesis test?
Selecting the right hypothesis test depends on several factors: the objective of your analysis, the type of data (numerical or categorical), and the sample size. Consider whether you're comparing means, proportions, or associations, and whether your data follows a normal distribution. The correct choice ensures accurate results tailored to your research question.
Find our PL-300 Microsoft Power BI Certification Training Online Classroom training classes in top cities:
| Name | Date | Place | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 Oct -27 Oct 2024, Weekend batch | Your City | ||
| 26 Oct -10 Nov 2024, Weekend batch | Your City | ||
| 9 Nov -24 Nov 2024, Weekend batch | Your City |
About the Author
Avijeet is a Senior Research Analyst at Simplilearn. Passionate about Data Analytics, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning, Avijeet is also interested in politics, cricket, and football.
Recommended Resources
Free eBook: Top Programming Languages For A Data Scientist
Normality Test in Minitab: Minitab with Statistics
Machine Learning Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Machine Learning Engineer
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Data Science
- Data Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Computer Vision
- Artificial Intelligence
- AI ML DS Interview Series
- AI ML DS Projects series
- Data Engineering
- Web Scrapping
Understanding Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing involves formulating assumptions about population parameters based on sample statistics and rigorously evaluating these assumptions against empirical evidence. This article sheds light on the significance of hypothesis testing and the critical steps involved in the process.
What is Hypothesis Testing?
A hypothesis is an assumption or idea, specifically a statistical claim about an unknown population parameter. For example, a judge assumes a person is innocent and verifies this by reviewing evidence and hearing testimony before reaching a verdict.
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
To test the validity of the claim or assumption about the population parameter:
- A sample is drawn from the population and analyzed.
- The results of the analysis are used to decide whether the claim is true or not.
Example: You say an average height in the class is 30 or a boy is taller than a girl. All of these is an assumption that we are assuming, and we need some statistical way to prove these. We need some mathematical conclusion whatever we are assuming is true.
Defining Hypotheses
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): In statistics, the null hypothesis is a general statement or default position that there is no relationship between two measured cases or no relationship among groups. In other words, it is a basic assumption or made based on the problem knowledge. Example : A company’s mean production is 50 units/per da H 0 : [Tex]\mu [/Tex] = 50.
- Alternative hypothesis (H 1 ): The alternative hypothesis is the hypothesis used in hypothesis testing that is contrary to the null hypothesis. Example: A company’s production is not equal to 50 units/per day i.e. H 1 : [Tex]\mu [/Tex] [Tex]\ne [/Tex] 50.
Key Terms of Hypothesis Testing
- Level of significance : It refers to the degree of significance in which we accept or reject the null hypothesis. 100% accuracy is not possible for accepting a hypothesis, so we, therefore, select a level of significance that is usually 5%. This is normally denoted with [Tex]\alpha[/Tex] and generally, it is 0.05 or 5%, which means your output should be 95% confident to give a similar kind of result in each sample.
- P-value: The P value , or calculated probability, is the probability of finding the observed/extreme results when the null hypothesis(H0) of a study-given problem is true. If your P-value is less than the chosen significance level then you reject the null hypothesis i.e. accept that your sample claims to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Test Statistic: The test statistic is a numerical value calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It is compared to a critical value or p-value to make decisions about the statistical significance of the observed results.
- Critical value : The critical value in statistics is a threshold or cutoff point used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in a hypothesis test.
- Degrees of freedom: Degrees of freedom are associated with the variability or freedom one has in estimating a parameter. The degrees of freedom are related to the sample size and determine the shape.
Why do we use Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is an important procedure in statistics. Hypothesis testing evaluates two mutually exclusive population statements to determine which statement is most supported by sample data. When we say that the findings are statistically significant, thanks to hypothesis testing.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Test
One tailed test focuses on one direction, either greater than or less than a specified value. We use a one-tailed test when there is a clear directional expectation based on prior knowledge or theory. The critical region is located on only one side of the distribution curve. If the sample falls into this critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
One-Tailed Test
There are two types of one-tailed test:
- Left-Tailed (Left-Sided) Test: The alternative hypothesis asserts that the true parameter value is less than the null hypothesis. Example: H 0 : [Tex]\mu \geq 50 [/Tex] and H 1 : [Tex]\mu < 50 [/Tex]
- Right-Tailed (Right-Sided) Test : The alternative hypothesis asserts that the true parameter value is greater than the null hypothesis. Example: H 0 : [Tex]\mu \leq50 [/Tex] and H 1 : [Tex]\mu > 50 [/Tex]
Two-Tailed Test
A two-tailed test considers both directions, greater than and less than a specified value.We use a two-tailed test when there is no specific directional expectation, and want to detect any significant difference.
Example: H 0 : [Tex]\mu = [/Tex] 50 and H 1 : [Tex]\mu \neq 50 [/Tex]
To delve deeper into differences into both types of test: Refer to link
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors in Hypothesis Testing?
In hypothesis testing, Type I and Type II errors are two possible errors that researchers can make when drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. These errors are associated with the decisions made regarding the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
- Type I error: When we reject the null hypothesis, although that hypothesis was true. Type I error is denoted by alpha( [Tex]\alpha [/Tex] ).
- Type II errors : When we accept the null hypothesis, but it is false. Type II errors are denoted by beta( [Tex]\beta [/Tex] ).
Null Hypothesis is True | Null Hypothesis is False | |
|---|---|---|
Null Hypothesis is True (Accept) | Correct Decision | Type II Error (False Negative) |
Alternative Hypothesis is True (Reject) | Type I Error (False Positive) | Correct Decision |
How does Hypothesis Testing work?
Step 1: define null and alternative hypothesis.
State the null hypothesis ( [Tex]H_0 [/Tex] ), representing no effect, and the alternative hypothesis ( [Tex]H_1 [/Tex] ), suggesting an effect or difference.
We first identify the problem about which we want to make an assumption keeping in mind that our assumption should be contradictory to one another, assuming Normally distributed data.
Step 2 – Choose significance level
Select a significance level ( [Tex]\alpha [/Tex] ), typically 0.05, to determine the threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis. It provides validity to our hypothesis test, ensuring that we have sufficient data to back up our claims. Usually, we determine our significance level beforehand of the test. The p-value is the criterion used to calculate our significance value.
Step 3 – Collect and Analyze data.
Gather relevant data through observation or experimentation. Analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods to obtain a test statistic.
Step 4-Calculate Test Statistic
The data for the tests are evaluated in this step we look for various scores based on the characteristics of data. The choice of the test statistic depends on the type of hypothesis test being conducted.
There are various hypothesis tests, each appropriate for various goal to calculate our test. This could be a Z-test , Chi-square , T-test , and so on.
- Z-test : If population means and standard deviations are known. Z-statistic is commonly used.
- t-test : If population standard deviations are unknown. and sample size is small than t-test statistic is more appropriate.
- Chi-square test : Chi-square test is used for categorical data or for testing independence in contingency tables
- F-test : F-test is often used in analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare variances or test the equality of means across multiple groups.
We have a smaller dataset, So, T-test is more appropriate to test our hypothesis.
T-statistic is a measure of the difference between the means of two groups relative to the variability within each group. It is calculated as the difference between the sample means divided by the standard error of the difference. It is also known as the t-value or t-score.
Step 5 – Comparing Test Statistic:
In this stage, we decide where we should accept the null hypothesis or reject the null hypothesis. There are two ways to decide where we should accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Method A: Using Crtical values
Comparing the test statistic and tabulated critical value we have,
- If Test Statistic>Critical Value: Reject the null hypothesis.
- If Test Statistic≤Critical Value: Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Note: Critical values are predetermined threshold values that are used to make a decision in hypothesis testing. To determine critical values for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Method B: Using P-values
We can also come to an conclusion using the p-value,
- If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level i.e. ( [Tex]p\leq\alpha [/Tex] ), you reject the null hypothesis. This indicates that the observed results are unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, providing evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than the significance level i.e. ( [Tex]p\geq \alpha[/Tex] ), you fail to reject the null hypothesis. This suggests that the observed results are consistent with what would be expected under the null hypothesis.
Note : The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one observed in the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true. To determine p-value for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Step 7- Interpret the Results
At last, we can conclude our experiment using method A or B.
Calculating test statistic
To validate our hypothesis about a population parameter we use statistical functions . We use the z-score, p-value, and level of significance(alpha) to make evidence for our hypothesis for normally distributed data .
1. Z-statistics:
When population means and standard deviations are known.
[Tex]z = \frac{\bar{x} – \mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}[/Tex]
- [Tex]\bar{x} [/Tex] is the sample mean,
- μ represents the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation
- and n is the size of the sample.
2. T-Statistics
T test is used when n<30,
t-statistic calculation is given by:
[Tex]t=\frac{x̄-μ}{s/\sqrt{n}} [/Tex]
- t = t-score,
- x̄ = sample mean
- μ = population mean,
- s = standard deviation of the sample,
- n = sample size
3. Chi-Square Test
Chi-Square Test for Independence categorical Data (Non-normally distributed) using:
[Tex]\chi^2 = \sum \frac{(O_{ij} – E_{ij})^2}{E_{ij}}[/Tex]
- [Tex]O_{ij}[/Tex] is the observed frequency in cell [Tex]{ij} [/Tex]
- i,j are the rows and columns index respectively.
- [Tex]E_{ij}[/Tex] is the expected frequency in cell [Tex]{ij}[/Tex] , calculated as : [Tex]\frac{{\text{{Row total}} \times \text{{Column total}}}}{{\text{{Total observations}}}}[/Tex]
Real life Examples of Hypothesis Testing
Let’s examine hypothesis testing using two real life situations,
Case A: D oes a New Drug Affect Blood Pressure?
Imagine a pharmaceutical company has developed a new drug that they believe can effectively lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Before bringing the drug to market, they need to conduct a study to assess its impact on blood pressure.
- Before Treatment: 120, 122, 118, 130, 125, 128, 115, 121, 123, 119
- After Treatment: 115, 120, 112, 128, 122, 125, 110, 117, 119, 114
Step 1 : Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis : (H 0 )The new drug has no effect on blood pressure.
- Alternate Hypothesis : (H 1 )The new drug has an effect on blood pressure.
Step 2: Define the Significance level
Let’s consider the Significance level at 0.05, indicating rejection of the null hypothesis.
If the evidence suggests less than a 5% chance of observing the results due to random variation.
Step 3 : Compute the test statistic
Using paired T-test analyze the data to obtain a test statistic and a p-value.
The test statistic (e.g., T-statistic) is calculated based on the differences between blood pressure measurements before and after treatment.
t = m/(s/√n)
- m = mean of the difference i.e X after, X before
- s = standard deviation of the difference (d) i.e d i = X after, i − X before,
- n = sample size,
then, m= -3.9, s= 1.8 and n= 10
we, calculate the , T-statistic = -9 based on the formula for paired t test
Step 4: Find the p-value
The calculated t-statistic is -9 and degrees of freedom df = 9, you can find the p-value using statistical software or a t-distribution table.
thus, p-value = 8.538051223166285e-06
Step 5: Result
- If the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, the researchers reject the null hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than 0.05, they fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion: Since the p-value (8.538051223166285e-06) is less than the significance level (0.05), the researchers reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
Python Implementation of Case A
Let’s create hypothesis testing with python, where we are testing whether a new drug affects blood pressure. For this example, we will use a paired T-test. We’ll use the scipy.stats library for the T-test.
Scipy is a mathematical library in Python that is mostly used for mathematical equations and computations.
We will implement our first real life problem via python,
import numpy as np from scipy import stats # Data before_treatment = np . array ([ 120 , 122 , 118 , 130 , 125 , 128 , 115 , 121 , 123 , 119 ]) after_treatment = np . array ([ 115 , 120 , 112 , 128 , 122 , 125 , 110 , 117 , 119 , 114 ]) # Step 1: Null and Alternate Hypotheses # Null Hypothesis: The new drug has no effect on blood pressure. # Alternate Hypothesis: The new drug has an effect on blood pressure. null_hypothesis = "The new drug has no effect on blood pressure." alternate_hypothesis = "The new drug has an effect on blood pressure." # Step 2: Significance Level alpha = 0.05 # Step 3: Paired T-test t_statistic , p_value = stats . ttest_rel ( after_treatment , before_treatment ) # Step 4: Calculate T-statistic manually m = np . mean ( after_treatment - before_treatment ) s = np . std ( after_treatment - before_treatment , ddof = 1 ) # using ddof=1 for sample standard deviation n = len ( before_treatment ) t_statistic_manual = m / ( s / np . sqrt ( n )) # Step 5: Decision if p_value <= alpha : decision = "Reject" else : decision = "Fail to reject" # Conclusion if decision == "Reject" : conclusion = "There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different." else : conclusion = "There is insufficient evidence to claim a significant difference in average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug." # Display results print ( "T-statistic (from scipy):" , t_statistic ) print ( "P-value (from scipy):" , p_value ) print ( "T-statistic (calculated manually):" , t_statistic_manual ) print ( f "Decision: { decision } the null hypothesis at alpha= { alpha } ." ) print ( "Conclusion:" , conclusion )
T-statistic (from scipy): -9.0 P-value (from scipy): 8.538051223166285e-06 T-statistic (calculated manually): -9.0 Decision: Reject the null hypothesis at alpha=0.05. Conclusion: There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
In the above example, given the T-statistic of approximately -9 and an extremely small p-value, the results indicate a strong case to reject the null hypothesis at a significance level of 0.05.
- The results suggest that the new drug, treatment, or intervention has a significant effect on lowering blood pressure.
- The negative T-statistic indicates that the mean blood pressure after treatment is significantly lower than the assumed population mean before treatment.
Case B : Cholesterol level in a population
Data: A sample of 25 individuals is taken, and their cholesterol levels are measured.
Cholesterol Levels (mg/dL): 205, 198, 210, 190, 215, 205, 200, 192, 198, 205, 198, 202, 208, 200, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205.
Populations Mean = 200
Population Standard Deviation (σ): 5 mg/dL(given for this problem)
Step 1: Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H 1 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL.
As the direction of deviation is not given , we assume a two-tailed test, and based on a normal distribution table, the critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) can be calculated through the z-table and are approximately -1.96 and 1.96.
The test statistic is calculated by using the z formula Z = [Tex](203.8 – 200) / (5 \div \sqrt{25}) [/Tex] and we get accordingly , Z =2.039999999999992.
Step 4: Result
Since the absolute value of the test statistic (2.04) is greater than the critical value (1.96), we reject the null hypothesis. And conclude that, there is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL
Python Implementation of Case B
import scipy.stats as stats import math import numpy as np # Given data sample_data = np . array ( [ 205 , 198 , 210 , 190 , 215 , 205 , 200 , 192 , 198 , 205 , 198 , 202 , 208 , 200 , 205 , 198 , 205 , 210 , 192 , 205 , 198 , 205 , 210 , 192 , 205 ]) population_std_dev = 5 population_mean = 200 sample_size = len ( sample_data ) # Step 1: Define the Hypotheses # Null Hypothesis (H0): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL. # Alternate Hypothesis (H1): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL. # Step 2: Define the Significance Level alpha = 0.05 # Two-tailed test # Critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) critical_value_left = stats . norm . ppf ( alpha / 2 ) critical_value_right = - critical_value_left # Step 3: Compute the test statistic sample_mean = sample_data . mean () z_score = ( sample_mean - population_mean ) / \ ( population_std_dev / math . sqrt ( sample_size )) # Step 4: Result # Check if the absolute value of the test statistic is greater than the critical values if abs ( z_score ) > max ( abs ( critical_value_left ), abs ( critical_value_right )): print ( "Reject the null hypothesis." ) print ( "There is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL." ) else : print ( "Fail to reject the null hypothesis." ) print ( "There is not enough evidence to conclude that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL." )
Reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL.
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
- Although a useful technique, hypothesis testing does not offer a comprehensive grasp of the topic being studied. Without fully reflecting the intricacy or whole context of the phenomena, it concentrates on certain hypotheses and statistical significance.
- The accuracy of hypothesis testing results is contingent on the quality of available data and the appropriateness of statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or poorly formulated hypotheses can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Relying solely on hypothesis testing may cause analysts to overlook significant patterns or relationships in the data that are not captured by the specific hypotheses being tested. This limitation underscores the importance of complimenting hypothesis testing with other analytical approaches.
Hypothesis testing stands as a cornerstone in statistical analysis, enabling data scientists to navigate uncertainties and draw credible inferences from sample data. By systematically defining null and alternative hypotheses, choosing significance levels, and leveraging statistical tests, researchers can assess the validity of their assumptions. The article also elucidates the critical distinction between Type I and Type II errors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the nuanced decision-making process inherent in hypothesis testing. The real-life example of testing a new drug’s effect on blood pressure using a paired T-test showcases the practical application of these principles, underscoring the importance of statistical rigor in data-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what are the 3 types of hypothesis test.
There are three types of hypothesis tests: right-tailed, left-tailed, and two-tailed. Right-tailed tests assess if a parameter is greater, left-tailed if lesser. Two-tailed tests check for non-directional differences, greater or lesser.
2.What are the 4 components of hypothesis testing?
Null Hypothesis ( [Tex]H_o [/Tex] ): No effect or difference exists. Alternative Hypothesis ( [Tex]H_1 [/Tex] ): An effect or difference exists. Significance Level ( [Tex]\alpha [/Tex] ): Risk of rejecting null hypothesis when it’s true (Type I error). Test Statistic: Numerical value representing observed evidence against null hypothesis.
3.What is hypothesis testing in ML?
Statistical method to evaluate the performance and validity of machine learning models. Tests specific hypotheses about model behavior, like whether features influence predictions or if a model generalizes well to unseen data.
4.What is the difference between Pytest and hypothesis in Python?
Pytest purposes general testing framework for Python code while Hypothesis is a Property-based testing framework for Python, focusing on generating test cases based on specified properties of the code.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- data-science
- OpenAI o1 AI Model Launched: Explore o1-Preview, o1-Mini, Pricing & Comparison
- How to Merge Cells in Google Sheets: Step by Step Guide
- How to Lock Cells in Google Sheets : Step by Step Guide
- PS5 Pro Launched: Controller, Price, Specs & Features, How to Pre-Order, and More
- #geekstreak2024 – 21 Days POTD Challenge Powered By Deutsche Bank
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid.
A null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis are set up before performing the hypothesis testing. This helps to arrive at a conclusion regarding the sample obtained from the population. In this article, we will learn more about hypothesis testing, its types, steps to perform the testing, and associated examples.
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. | |
| 6. | |
| 7. | |
| 8. |
What is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis testing uses sample data from the population to draw useful conclusions regarding the population probability distribution . It tests an assumption made about the data using different types of hypothesis testing methodologies. The hypothesis testing results in either rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing Definition
Hypothesis testing can be defined as a statistical tool that is used to identify if the results of an experiment are meaningful or not. It involves setting up a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. These two hypotheses will always be mutually exclusive. This means that if the null hypothesis is true then the alternative hypothesis is false and vice versa. An example of hypothesis testing is setting up a test to check if a new medicine works on a disease in a more efficient manner.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a concise mathematical statement that is used to indicate that there is no difference between two possibilities. In other words, there is no difference between certain characteristics of data. This hypothesis assumes that the outcomes of an experiment are based on chance alone. It is denoted as \(H_{0}\). Hypothesis testing is used to conclude if the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. Suppose an experiment is conducted to check if girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5. The null hypothesis will say that they are the same height.
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is an alternative to the null hypothesis. It is used to show that the observations of an experiment are due to some real effect. It indicates that there is a statistical significance between two possible outcomes and can be denoted as \(H_{1}\) or \(H_{a}\). For the above-mentioned example, the alternative hypothesis would be that girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5.
Hypothesis Testing P Value
In hypothesis testing, the p value is used to indicate whether the results obtained after conducting a test are statistically significant or not. It also indicates the probability of making an error in rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.This value is always a number between 0 and 1. The p value is compared to an alpha level, \(\alpha\) or significance level. The alpha level can be defined as the acceptable risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis. The alpha level is usually chosen between 1% to 5%.
Hypothesis Testing Critical region
All sets of values that lead to rejecting the null hypothesis lie in the critical region. Furthermore, the value that separates the critical region from the non-critical region is known as the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Depending upon the type of data available and the size, different types of hypothesis testing are used to determine whether the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. The hypothesis testing formula for some important test statistics are given below:
- z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\). \(\overline{x}\) is the sample mean, \(\mu\) is the population mean, \(\sigma\) is the population standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
- t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\). s is the sample standard deviation.
- \(\chi ^{2} = \sum \frac{(O_{i}-E_{i})^{2}}{E_{i}}\). \(O_{i}\) is the observed value and \(E_{i}\) is the expected value.
We will learn more about these test statistics in the upcoming section.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
Selecting the correct test for performing hypothesis testing can be confusing. These tests are used to determine a test statistic on the basis of which the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected. Some of the important tests used for hypothesis testing are given below.
Hypothesis Testing Z Test
A z test is a way of hypothesis testing that is used for a large sample size (n ≥ 30). It is used to determine whether there is a difference between the population mean and the sample mean when the population standard deviation is known. It can also be used to compare the mean of two samples. It is used to compute the z test statistic. The formulas are given as follows:
- One sample: z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing t Test
The t test is another method of hypothesis testing that is used for a small sample size (n < 30). It is also used to compare the sample mean and population mean. However, the population standard deviation is not known. Instead, the sample standard deviation is known. The mean of two samples can also be compared using the t test.
- One sample: t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: t = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{s_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{s_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing Chi Square
The Chi square test is a hypothesis testing method that is used to check whether the variables in a population are independent or not. It is used when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed.
One Tailed Hypothesis Testing
One tailed hypothesis testing is done when the rejection region is only in one direction. It can also be known as directional hypothesis testing because the effects can be tested in one direction only. This type of testing is further classified into the right tailed test and left tailed test.
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The right tail test is also known as the upper tail test. This test is used to check whether the population parameter is greater than some value. The null and alternative hypotheses for this test are given as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≤ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is > some value.
If the test statistic has a greater value than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected
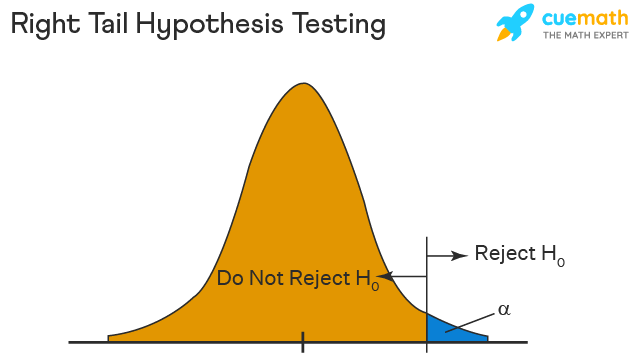
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The left tail test is also known as the lower tail test. It is used to check whether the population parameter is less than some value. The hypotheses for this hypothesis testing can be written as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≥ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is < some value.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value lesser than the critical value.
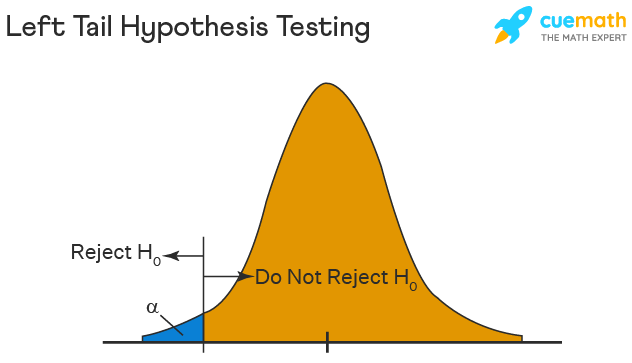
Two Tailed Hypothesis Testing
In this hypothesis testing method, the critical region lies on both sides of the sampling distribution. It is also known as a non - directional hypothesis testing method. The two-tailed test is used when it needs to be determined if the population parameter is assumed to be different than some value. The hypotheses can be set up as follows:
\(H_{0}\): the population parameter = some value
\(H_{1}\): the population parameter ≠ some value
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value that is not equal to the critical value.
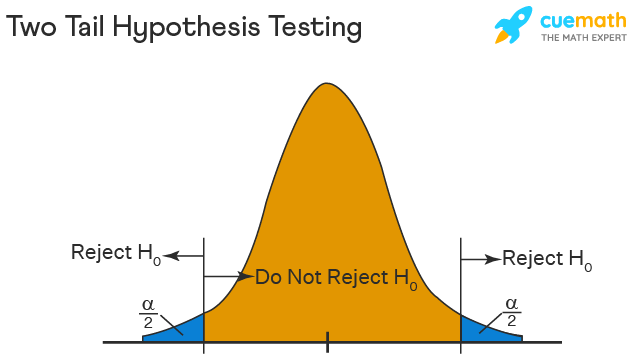
Hypothesis Testing Steps
Hypothesis testing can be easily performed in five simple steps. The most important step is to correctly set up the hypotheses and identify the right method for hypothesis testing. The basic steps to perform hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Step 1: Set up the null hypothesis by correctly identifying whether it is the left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed hypothesis testing.
- Step 2: Set up the alternative hypothesis.
- Step 3: Choose the correct significance level, \(\alpha\), and find the critical value.
- Step 4: Calculate the correct test statistic (z, t or \(\chi\)) and p-value.
- Step 5: Compare the test statistic with the critical value or compare the p-value with \(\alpha\) to arrive at a conclusion. In other words, decide if the null hypothesis is to be rejected or not.
Hypothesis Testing Example
The best way to solve a problem on hypothesis testing is by applying the 5 steps mentioned in the previous section. Suppose a researcher claims that the mean average weight of men is greater than 100kgs with a standard deviation of 15kgs. 30 men are chosen with an average weight of 112.5 Kgs. Using hypothesis testing, check if there is enough evidence to support the researcher's claim. The confidence interval is given as 95%.
Step 1: This is an example of a right-tailed test. Set up the null hypothesis as \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 100.
Step 2: The alternative hypothesis is given by \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 100.
Step 3: As this is a one-tailed test, \(\alpha\) = 100% - 95% = 5%. This can be used to determine the critical value.
1 - \(\alpha\) = 1 - 0.05 = 0.95
0.95 gives the required area under the curve. Now using a normal distribution table, the area 0.95 is at z = 1.645. A similar process can be followed for a t-test. The only additional requirement is to calculate the degrees of freedom given by n - 1.
Step 4: Calculate the z test statistic. This is because the sample size is 30. Furthermore, the sample and population means are known along with the standard deviation.
z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
\(\mu\) = 100, \(\overline{x}\) = 112.5, n = 30, \(\sigma\) = 15
z = \(\frac{112.5-100}{\frac{15}{\sqrt{30}}}\) = 4.56
Step 5: Conclusion. As 4.56 > 1.645 thus, the null hypothesis can be rejected.
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals form an important part of hypothesis testing. This is because the alpha level can be determined from a given confidence interval. Suppose a confidence interval is given as 95%. Subtract the confidence interval from 100%. This gives 100 - 95 = 5% or 0.05. This is the alpha value of a one-tailed hypothesis testing. To obtain the alpha value for a two-tailed hypothesis testing, divide this value by 2. This gives 0.05 / 2 = 0.025.
Related Articles:
- Probability and Statistics
- Data Handling
Important Notes on Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis testing is a technique that is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are statistically significant.
- It involves the setting up of a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis.
- There are three types of tests that can be conducted under hypothesis testing - z test, t test, and chi square test.
- Hypothesis testing can be classified as right tail, left tail, and two tail tests.
Examples on Hypothesis Testing
- Example 1: The average weight of a dumbbell in a gym is 90lbs. However, a physical trainer believes that the average weight might be higher. A random sample of 5 dumbbells with an average weight of 110lbs and a standard deviation of 18lbs. Using hypothesis testing check if the physical trainer's claim can be supported for a 95% confidence level. Solution: As the sample size is lesser than 30, the t-test is used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 5, s = 18. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 Using the t-distribution table, the critical value is 2.132 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = 2.484 As 2.484 > 2.132, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: The average weight of the dumbbells may be greater than 90lbs
- Example 2: The average score on a test is 80 with a standard deviation of 10. With a new teaching curriculum introduced it is believed that this score will change. On random testing, the score of 38 students, the mean was found to be 88. With a 0.05 significance level, is there any evidence to support this claim? Solution: This is an example of two-tail hypothesis testing. The z test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 80, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) ≠ 80 \(\overline{x}\) = 88, \(\mu\) = 80, n = 36, \(\sigma\) = 10. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 / 2 = 0.025 The critical value using the normal distribution table is 1.96 z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) z = \(\frac{88-80}{\frac{10}{\sqrt{36}}}\) = 4.8 As 4.8 > 1.96, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: There is a difference in the scores after the new curriculum was introduced.
- Example 3: The average score of a class is 90. However, a teacher believes that the average score might be lower. The scores of 6 students were randomly measured. The mean was 82 with a standard deviation of 18. With a 0.05 significance level use hypothesis testing to check if this claim is true. Solution: The t test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) < 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 6, s = 18 The critical value from the t table is -2.015 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = \(\frac{82-90}{\frac{18}{\sqrt{6}}}\) t = -1.088 As -1.088 > -2.015, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Answer: There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
FAQs on Hypothesis Testing
What is hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing in statistics is a tool that is used to make inferences about the population data. It is also used to check if the results of an experiment are valid.
What is the z Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The z test in hypothesis testing is used to find the z test statistic for normally distributed data . The z test is used when the standard deviation of the population is known and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30.
What is the t Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The t test in hypothesis testing is used when the data follows a student t distribution . It is used when the sample size is less than 30 and standard deviation of the population is not known.
What is the formula for z test in Hypothesis Testing?
The formula for a one sample z test in hypothesis testing is z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) and for two samples is z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
What is the p Value in Hypothesis Testing?
The p value helps to determine if the test results are statistically significant or not. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected based on the comparison between the p value and the alpha level.
What is One Tail Hypothesis Testing?
When the rejection region is only on one side of the distribution curve then it is known as one tail hypothesis testing. The right tail test and the left tail test are two types of directional hypothesis testing.
What is the Alpha Level in Two Tail Hypothesis Testing?
To get the alpha level in a two tail hypothesis testing divide \(\alpha\) by 2. This is done as there are two rejection regions in the curve.
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Hypothesis testing, p values, confidence intervals, and significance.
Jacob Shreffler ; Martin R. Huecker .
Affiliations
Last Update: March 13, 2023 .
- Definition/Introduction
Medical providers often rely on evidence-based medicine to guide decision-making in practice. Often a research hypothesis is tested with results provided, typically with p values, confidence intervals, or both. Additionally, statistical or research significance is estimated or determined by the investigators. Unfortunately, healthcare providers may have different comfort levels in interpreting these findings, which may affect the adequate application of the data.
- Issues of Concern
Without a foundational understanding of hypothesis testing, p values, confidence intervals, and the difference between statistical and clinical significance, it may affect healthcare providers' ability to make clinical decisions without relying purely on the research investigators deemed level of significance. Therefore, an overview of these concepts is provided to allow medical professionals to use their expertise to determine if results are reported sufficiently and if the study outcomes are clinically appropriate to be applied in healthcare practice.
Hypothesis Testing
Investigators conducting studies need research questions and hypotheses to guide analyses. Starting with broad research questions (RQs), investigators then identify a gap in current clinical practice or research. Any research problem or statement is grounded in a better understanding of relationships between two or more variables. For this article, we will use the following research question example:
Research Question: Is Drug 23 an effective treatment for Disease A?
Research questions do not directly imply specific guesses or predictions; we must formulate research hypotheses. A hypothesis is a predetermined declaration regarding the research question in which the investigator(s) makes a precise, educated guess about a study outcome. This is sometimes called the alternative hypothesis and ultimately allows the researcher to take a stance based on experience or insight from medical literature. An example of a hypothesis is below.
Research Hypothesis: Drug 23 will significantly reduce symptoms associated with Disease A compared to Drug 22.
The null hypothesis states that there is no statistical difference between groups based on the stated research hypothesis.
Researchers should be aware of journal recommendations when considering how to report p values, and manuscripts should remain internally consistent.
Regarding p values, as the number of individuals enrolled in a study (the sample size) increases, the likelihood of finding a statistically significant effect increases. With very large sample sizes, the p-value can be very low significant differences in the reduction of symptoms for Disease A between Drug 23 and Drug 22. The null hypothesis is deemed true until a study presents significant data to support rejecting the null hypothesis. Based on the results, the investigators will either reject the null hypothesis (if they found significant differences or associations) or fail to reject the null hypothesis (they could not provide proof that there were significant differences or associations).
To test a hypothesis, researchers obtain data on a representative sample to determine whether to reject or fail to reject a null hypothesis. In most research studies, it is not feasible to obtain data for an entire population. Using a sampling procedure allows for statistical inference, though this involves a certain possibility of error. [1] When determining whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, mistakes can be made: Type I and Type II errors. Though it is impossible to ensure that these errors have not occurred, researchers should limit the possibilities of these faults. [2]
Significance
Significance is a term to describe the substantive importance of medical research. Statistical significance is the likelihood of results due to chance. [3] Healthcare providers should always delineate statistical significance from clinical significance, a common error when reviewing biomedical research. [4] When conceptualizing findings reported as either significant or not significant, healthcare providers should not simply accept researchers' results or conclusions without considering the clinical significance. Healthcare professionals should consider the clinical importance of findings and understand both p values and confidence intervals so they do not have to rely on the researchers to determine the level of significance. [5] One criterion often used to determine statistical significance is the utilization of p values.
P values are used in research to determine whether the sample estimate is significantly different from a hypothesized value. The p-value is the probability that the observed effect within the study would have occurred by chance if, in reality, there was no true effect. Conventionally, data yielding a p<0.05 or p<0.01 is considered statistically significant. While some have debated that the 0.05 level should be lowered, it is still universally practiced. [6] Hypothesis testing allows us to determine the size of the effect.
An example of findings reported with p values are below:
Statement: Drug 23 reduced patients' symptoms compared to Drug 22. Patients who received Drug 23 (n=100) were 2.1 times less likely than patients who received Drug 22 (n = 100) to experience symptoms of Disease A, p<0.05.
Statement:Individuals who were prescribed Drug 23 experienced fewer symptoms (M = 1.3, SD = 0.7) compared to individuals who were prescribed Drug 22 (M = 5.3, SD = 1.9). This finding was statistically significant, p= 0.02.
For either statement, if the threshold had been set at 0.05, the null hypothesis (that there was no relationship) should be rejected, and we should conclude significant differences. Noticeably, as can be seen in the two statements above, some researchers will report findings with < or > and others will provide an exact p-value (0.000001) but never zero [6] . When examining research, readers should understand how p values are reported. The best practice is to report all p values for all variables within a study design, rather than only providing p values for variables with significant findings. [7] The inclusion of all p values provides evidence for study validity and limits suspicion for selective reporting/data mining.
While researchers have historically used p values, experts who find p values problematic encourage the use of confidence intervals. [8] . P-values alone do not allow us to understand the size or the extent of the differences or associations. [3] In March 2016, the American Statistical Association (ASA) released a statement on p values, noting that scientific decision-making and conclusions should not be based on a fixed p-value threshold (e.g., 0.05). They recommend focusing on the significance of results in the context of study design, quality of measurements, and validity of data. Ultimately, the ASA statement noted that in isolation, a p-value does not provide strong evidence. [9]
When conceptualizing clinical work, healthcare professionals should consider p values with a concurrent appraisal study design validity. For example, a p-value from a double-blinded randomized clinical trial (designed to minimize bias) should be weighted higher than one from a retrospective observational study [7] . The p-value debate has smoldered since the 1950s [10] , and replacement with confidence intervals has been suggested since the 1980s. [11]
Confidence Intervals
A confidence interval provides a range of values within given confidence (e.g., 95%), including the accurate value of the statistical constraint within a targeted population. [12] Most research uses a 95% CI, but investigators can set any level (e.g., 90% CI, 99% CI). [13] A CI provides a range with the lower bound and upper bound limits of a difference or association that would be plausible for a population. [14] Therefore, a CI of 95% indicates that if a study were to be carried out 100 times, the range would contain the true value in 95, [15] confidence intervals provide more evidence regarding the precision of an estimate compared to p-values. [6]
In consideration of the similar research example provided above, one could make the following statement with 95% CI:
Statement: Individuals who were prescribed Drug 23 had no symptoms after three days, which was significantly faster than those prescribed Drug 22; there was a mean difference between the two groups of days to the recovery of 4.2 days (95% CI: 1.9 – 7.8).
It is important to note that the width of the CI is affected by the standard error and the sample size; reducing a study sample number will result in less precision of the CI (increase the width). [14] A larger width indicates a smaller sample size or a larger variability. [16] A researcher would want to increase the precision of the CI. For example, a 95% CI of 1.43 – 1.47 is much more precise than the one provided in the example above. In research and clinical practice, CIs provide valuable information on whether the interval includes or excludes any clinically significant values. [14]
Null values are sometimes used for differences with CI (zero for differential comparisons and 1 for ratios). However, CIs provide more information than that. [15] Consider this example: A hospital implements a new protocol that reduced wait time for patients in the emergency department by an average of 25 minutes (95% CI: -2.5 – 41 minutes). Because the range crosses zero, implementing this protocol in different populations could result in longer wait times; however, the range is much higher on the positive side. Thus, while the p-value used to detect statistical significance for this may result in "not significant" findings, individuals should examine this range, consider the study design, and weigh whether or not it is still worth piloting in their workplace.
Similarly to p-values, 95% CIs cannot control for researchers' errors (e.g., study bias or improper data analysis). [14] In consideration of whether to report p-values or CIs, researchers should examine journal preferences. When in doubt, reporting both may be beneficial. [13] An example is below:
Reporting both: Individuals who were prescribed Drug 23 had no symptoms after three days, which was significantly faster than those prescribed Drug 22, p = 0.009. There was a mean difference between the two groups of days to the recovery of 4.2 days (95% CI: 1.9 – 7.8).
- Clinical Significance
Recall that clinical significance and statistical significance are two different concepts. Healthcare providers should remember that a study with statistically significant differences and large sample size may be of no interest to clinicians, whereas a study with smaller sample size and statistically non-significant results could impact clinical practice. [14] Additionally, as previously mentioned, a non-significant finding may reflect the study design itself rather than relationships between variables.
Healthcare providers using evidence-based medicine to inform practice should use clinical judgment to determine the practical importance of studies through careful evaluation of the design, sample size, power, likelihood of type I and type II errors, data analysis, and reporting of statistical findings (p values, 95% CI or both). [4] Interestingly, some experts have called for "statistically significant" or "not significant" to be excluded from work as statistical significance never has and will never be equivalent to clinical significance. [17]
The decision on what is clinically significant can be challenging, depending on the providers' experience and especially the severity of the disease. Providers should use their knowledge and experiences to determine the meaningfulness of study results and make inferences based not only on significant or insignificant results by researchers but through their understanding of study limitations and practical implications.
- Nursing, Allied Health, and Interprofessional Team Interventions
All physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals should strive to understand the concepts in this chapter. These individuals should maintain the ability to review and incorporate new literature for evidence-based and safe care.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Jacob Shreffler declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Martin Huecker declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Shreffler J, Huecker MR. Hypothesis Testing, P Values, Confidence Intervals, and Significance. [Updated 2023 Mar 13]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- The reporting of p values, confidence intervals and statistical significance in Preventive Veterinary Medicine (1997-2017). [PeerJ. 2021] The reporting of p values, confidence intervals and statistical significance in Preventive Veterinary Medicine (1997-2017). Messam LLM, Weng HY, Rosenberger NWY, Tan ZH, Payet SDM, Santbakshsing M. PeerJ. 2021; 9:e12453. Epub 2021 Nov 24.
- Review Clinical versus statistical significance: interpreting P values and confidence intervals related to measures of association to guide decision making. [J Pharm Pract. 2010] Review Clinical versus statistical significance: interpreting P values and confidence intervals related to measures of association to guide decision making. Ferrill MJ, Brown DA, Kyle JA. J Pharm Pract. 2010 Aug; 23(4):344-51. Epub 2010 Apr 13.
- Interpreting "statistical hypothesis testing" results in clinical research. [J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2012] Interpreting "statistical hypothesis testing" results in clinical research. Sarmukaddam SB. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2012 Apr; 3(2):65-9.
- Confidence intervals in procedural dermatology: an intuitive approach to interpreting data. [Dermatol Surg. 2005] Confidence intervals in procedural dermatology: an intuitive approach to interpreting data. Alam M, Barzilai DA, Wrone DA. Dermatol Surg. 2005 Apr; 31(4):462-6.
- Review Is statistical significance testing useful in interpreting data? [Reprod Toxicol. 1993] Review Is statistical significance testing useful in interpreting data? Savitz DA. Reprod Toxicol. 1993; 7(2):95-100.
Recent Activity
- Hypothesis Testing, P Values, Confidence Intervals, and Significance - StatPearl... Hypothesis Testing, P Values, Confidence Intervals, and Significance - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Present the findings in your results and discussion section. Though the specific details might vary, the procedure you will use when testing a hypothesis will always follow some version of these steps. Table of contents. Step 1: State your null and alternate hypothesis. Step 2: Collect data. Step 3: Perform a statistical test.
In hypothesis testing, the goal is to see if there is sufficient statistical evidence to reject a presumed null hypothesis in favor of a conjectured alternative hypothesis.The null hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_0\) while the alternative hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_1\). An hypothesis test is a statistical decision; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor ...
The researchers write their hypotheses. These statements apply to the population, so they use the mu (μ) symbol for the population mean parameter.. Null Hypothesis (H 0): The population means of the test scores for the two groups are equal (μ 1 = μ 2).; Alternative Hypothesis (H A): The population means of the test scores for the two groups are unequal (μ 1 ≠ μ 2).
A statistical hypothesis is an assumption about a population parameter.. For example, we may assume that the mean height of a male in the U.S. is 70 inches. The assumption about the height is the statistical hypothesis and the true mean height of a male in the U.S. is the population parameter.. A hypothesis test is a formal statistical test we use to reject or fail to reject a statistical ...
S.3 Hypothesis Testing. In reviewing hypothesis tests, we start first with the general idea. Then, we keep returning to the basic procedures of hypothesis testing, each time adding a little more detail. The general idea of hypothesis testing involves: Making an initial assumption. Collecting evidence (data).
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method to determine whether a hypothesis that you have holds true or not. The hypothesis can be with respect to two variables within a dataset, an association between two groups or a situation. ... P-value is the probability that the test statistic you have obtained is by random chance which would mean the ...
Explore the intricacies of hypothesis testing, a cornerstone of statistical analysis. Dive into methods, interpretations, and applications for making data-driven decisions. In this Blog post we will learn: What is Hypothesis Testing? Steps in Hypothesis Testing 2.1. Set up Hypotheses: Null and Alternative 2.2. Choose a Significance Level (α) 2.3.
Hypothesis testing is the process that an analyst uses to test a statistical hypothesis. The methodology depends on the nature of the data used and the reason for the analysis.
Hypothesis Testing. A hypothesis test is a statistical inference method used to test the significance of a proposed (hypothesized) relation between population statistics (parameters) and their corresponding sample estimators. In other words, hypothesis tests are used to determine if there is enough evidence in a sample to prove a hypothesis ...
Hypothesis testing is a method of statistical inference that considers the null hypothesis H ₀ vs. the alternative hypothesis H a, where we are typically looking to assess evidence against H ₀. Such a test is used to compare data sets against one another, or compare a data set against some external standard. The former being a two sample ...
Testing Hypotheses using Confidence Intervals. We can start the evaluation of the hypothesis setup by comparing 2006 and 2012 run times using a point estimate from the 2012 sample: x¯12 = 95.61 x ¯ 12 = 95.61 minutes. This estimate suggests the average time is actually longer than the 2006 time, 93.29 minutes.
The above image shows a table with some of the most common test statistics and their corresponding tests or models.. A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data sufficiently supports a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a test statistic.Then a decision is made, either by comparing the ...
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that helps to determine whether a hypothesis is true or not. It is a procedure that involves collecting and analyzing data to evaluate the probability of the null hypothesis being true. The null hypothesis is the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between a sample and the population.
a. x = salary of teacher. μ = mean salary of teacher. The guess is that μ> $30, 000 and that is the alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis has the same parameter and number with an equal sign. H0: μ = $30, 000 HA: μ> $30, 000. b. x = number od students who like math. p = proportion of students who like math.
To put this company's claim to the test, create a null and alternate hypothesis. H0 (Null Hypothesis): Average = 95%. Alternative Hypothesis (H1): The average is less than 95%. Another straightforward example to understand this concept is determining whether or not a coin is fair and balanced.
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
Hypothesis testing; T-test definition and formula explanation; Choosing the level of significance; T-distribution and p-value; Conclusion; Hypothesis testing. Meet David! He is a high school student and he has started to study statistics recently. ... There is a 5-point grading system at school, where 5 is the best score. ...
A hypothesis test is a procedure used in statistics to assess whether a particular viewpoint is likely to be true. They follow a strict protocol, and they generate a 'p-value', on the basis of which a decision is made about the truth of the hypothesis under investigation.All of the routine statistical 'tests' used in research—t-tests, χ 2 tests, Mann-Whitney tests, etc.—are all ...
To understand hypothesis testing, there's some terminology that you have to understand: Null Hypothesis: the hypothesis that sample observations result purely from chance. The null hypothesis tends to state that there's no change. Alternative Hypothesis: the hypothesis that sample observations are influenced by some non-random cause.
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid. A null hypothesis and an alternative ...
Definition/Introduction. Medical providers often rely on evidence-based medicine to guide decision-making in practice. Often a research hypothesis is tested with results provided, typically with p values, confidence intervals, or both. Additionally, statistical or research significance is estimated or determined by the investigators.
148. 4. Photo by Anna Nekrashevich from Pexels. Hypothesis testing is a common statistical tool used in research and data science to support the certainty of findings. The aim of testing is to answer how probable an apparent effect is detected by chance given a random data sample. This article provides a detailed explanation of the key concepts ...