Please beware of fraud schemes by third parties falsely using our company and imprint names to solicit money and personal information. Learn More .


Book details
50 Successful Harvard Medical School Essays
Author: Staff of the Harvard Crimson

INTRODUCTION Competition for admittance into the nation’s top medical schools has never been more intense and it has become increasingly important to write a personal statement that sets you apart from thousands of other medical school applicants. However, that is a daunting task—in less than fifty-three hundred characters, you must weave together your experiences, interests, and passions into a memorable and evocative narrative that resonates with a panel of admissions officers. While there is no magic formula for writing the perfect essay, by picking up this helpful book you are already on the right track. Whether you are just beginning to write your essay or have written several drafts already, this book will provide you with the insights and guidance you need to succeed. On these next pages, you will find fifty standout essays that helped students successfully secure a spot at Harvard Medical School, one of the best medical schools in the country. No two essays are the same: A young woman describes creating mental health awareness in her community. A hockey player opens up about their unexpected entrance into sports medicine. A pianist explores the intersection between music and care. Each student presents a different set of experiences, ideas, and perspectives that informs their path to medicine. Each essay is coupled with analysis by a Crimson editor or editors on specific essay qualities and techniques that worked, so you can learn from their example and apply it to your own writing. You will find that for many of these essays, their strengths lie not in the writer’s topic of choice, but instead, in the writer’s ability to forward an argument about their character, drive, and passion for medicine with elegant prose, precise organization, and sometimes even a sprinkle of unexpectedly charming humor. We have divided the book into five thematic categories: Passion, Influential Figure, Impactful Experience, Identity, and Intellectual Desire. While these broad themes by no means fully encapsulate the complexity and depth of each of these essays, we hope they will serve as helpful guiding points as you pinpoint the types of stories you want to tell. At the end of this book, you will find a chapter filled with words of wisdom from some of the students behind these essays. We hope their words will encourage and guide you as you embark on this journey. We wish you the best of luck with writing your essay and finding the medical school that is right for you. —Sabrina W. ChokPublishing Manager,146th Guard of The Harvard Crimson J UN L IU Hometown: Nanjing, China Undergraduate School: Private, Williams College Major: Biology GPA: 3.86 MCAT: 36. PS: 10, V: 14, BS: 12. ESSAY Detention. The word filled me with youthful indignation. I knew I was being punished for tasting the alkali earth metal salts we were categorizing in the science lab, but from my 12-year-old’s perspective, I was in legendary company. My hero, Dr. Shizhen Li, the 16th century Chinese herbalist from my history books, had famously risked his own health to locate and sample the thousands of medicines he exhaustively researched for his Compendium of Materia Medica. Though the punishment tempered my reckless tasting of lab materials, it failed to restrain my adventurous spirit. Like the relentless Dr. Li, my aspirations to become a physician-scientist have spanned the globe and led to unexpected journeys. In my early years, two very important women inspired me to carefully question conventional wisdom. My grandmother was obsessed with the medicinal properties of food. Diagnosed with severe diabetes in her 70s, she ignored her physician’s advice to begin insulin shots and successfully controlled her condition with diet and exercise. As a child, I eagerly followed her maverick example. I must have seemed an earnest little quack, “prescribing” all kinds of foods to “cure” my friends’ ailments. But it wasn’t simply play. I still find myself resorting to some of my grandmother’s herbal solutions. I even converted my undergraduate thesis advisor into the habit of drinking Chinese Tieguanyin tea to fight his Coca-Cola “addiction.” My close relationship with my grandmother prompted an early interest in nutrition and natural remedies. But it was my admiration for my mother’s work as a leading HIV/STD epidemiologist for China’s CDC that introduced me to the essential roles of public outreach and research in battling diseases. As a teen, I took on the tasks of performing simple data analysis in my mother’s lab and distributing handouts from the CDC detailing STD support resources in clinics. I particularly enjoyed face-to-face interaction with patients, and was intrigued by the close collaboration between doctors and epidemiologists. Moreover, I began to understand the stake we have in overcoming cultural taboos in order to prevent, detect and treat infectious diseases. Talking with young AIDS patients fighting uphill battles, I realized I didn’t have the patience to wait until I received a physician’s license to spread the “gospel” of preventive care. I felt compelled to act. Recognizing that a Chinese medical education would focus almost exclusively on the hard sciences, I decided to instead pursue a US liberal arts education despite considerable obstacles. I yearned for the freedom to engage with the public to promote disease prevention and explore the diversity of factors affecting health. Williams College offered me the opportunity to connect my passion for medical science with my concern for the community through the student organization Public Health Alliance. First as a participant, and then as Chair, I worked with campus and community leaders to raise awareness of preventable and sometimes controversial health issues since my sophomore year—ranging from sports injuries to HPV awareness—facing the Williams community. My undergraduate years also sparked my love for the interdisciplinary nature of neuroscience and deepened my interest in research. Rewarding laboratory experience, clinical shadowing, and mentorship from physician-scientists reinforced my aspiration to work at the exciting interface between brain research and medicine. After graduation, winning the Herchel Smith Fellowship allowed me to embark on another journey to the University of Cambridge, UK. I enjoyed in-depth research training in the lab of Prof. Andrea Brand, who pioneers in genetic strategies to study neural stem cell (NSC) regulation. I believe that understanding fundamental mechanisms in this field will be key to preventing and curing many fatal CNS diseases, such as certain types of neurodegenerative disorders and brain tumors. My PhD research investigates mechanisms of amino acid regulation of NSCs, which enabled me to unite my earlier interests in nutrition and the brain. Outside the lab, I sought to understand neuronal diseases from both the doctor’s and patient’s perspective by shadowing neuroradiologists and volunteering at a dementia care center. The exposure to laboratory and clinical neuroscience in the past 2.5 years has motivated me to continue investigating NSC biology as a physician-scientist. With the aid of a comprehensive medical training, I am eager to extend my current interest in nutritional control of NSCs to improving brain care. Understanding the regulation of NSCs on a molecular level will help me to develop targeted approaches for interventional therapies. When screening for potential therapeutics, I am particularly interested in expanding the current range of available synthetic compounds to naturally occurring ones derived from plant extracts. Ultimately, I hope to contribute to the prevention and treatment of neuronal diseases by developing novel therapies that will benefit patients. ANALYSIS From the start of the essay, it is clear that Jun is a natural storyteller and this aids him when sharing a compelling narrative of his aspirations towards becoming a physician-scientist. Whether it’s phrases like “legendary company” from his introductory anecdote in which he perfectly conveys the sense of triumph his twelve-year-old self felt after landing himself in detention or the way he describes himself as an “earnest little quack,” Jun skillfully adds snippets of his personality and witty humor into his essay. He uses specificity and imagery to his advantage, employing telling examples that show readers the experiences that not only connect him to medicine but also convey his curious and defiant nature. In doing so, he successfully keeps his readers engaged as he transitions into the second half of his essay, where he details his medicine-motivated journey around the world. Though he pivots to a less playful style of writing in the latter half of his essay, he is able to elegantly weave together his collective experiences into a coherent narrative. With each experience, more than simply exploring the nuances behind the impact it had on him, he describes how it compelled him to take action and to further his relationship with medicine. By the conclusion of his essay, he demonstrates his ability to be a passionate and proactive learner through highly specific examples and successfully leaves readers with a clear idea of his character and aspirations. —Sabrina Chok Copyright © 2020 by The Harvard Crimson

Buy This Book From:
Reviews from goodreads, about this book.
Fifty all-new essays that got their authors into Harvard Medical School, including MCAT scores, showing what worked, what didn’t, and how you can do it too. Competition...
Book Details
Fifty all-new essays that got their authors into Harvard Medical School, including MCAT scores, showing what worked, what didn’t, and how you can do it too. Competition to get into the nation’s top medical schools has never been more intense. Harvard Medical School in particular draws thousands of elite applicants from around the world. As admissions departments become increasingly selective, even the best and brightest need an edge. Writing a personal statement is a daunting part of the application process. In less than 5,300 characters, applicants must weave together experiences and passions into a memorable narrative to set them apart from thousands of other applicants. While there is no magic formula for writing the perfect essay, picking up this book will put them on the right track. 50 Successful Harvard Medical School Essays is the first in a new line of books published by the Staff of the Harvard Crimson. It includes fifty standout essays from students who successfully secured a spot at Harvard Medical School. Each student has a unique set of experiences that led them to medicine. Each essay includes analysis by Crimson editors on essay qualities and techniques that worked, so readers can apply them to their own writing. This book will aid applicants in composing essays that reveal their passion for medicine and the discipline they will bring to this demanding program and profession. It will give them the extra help they need to get into the best medical school programs in the world.
Imprint Publisher
St. Martin's Griffin
9781250244475
About the Creators
Medical School Examples

Craft a Winning Medical School Essay with Examples and Proven Tips
Published on: May 8, 2023
Last updated on: Jul 19, 2024

Share this article
Are you dreaming of becoming a doctor or a health care professional?
The first step towards achieving that goal is to get accepted into a top-tier medical school.
But with so many other qualified medical students competing for the same spot, how do you stand out from the crowd?
It all starts with your medical school essay.
Your essay is your opportunity to your unique qualities, experiences, and aspirations.
In this blog, we'll provide you with examples that will help you catch the attention of admissions committees.
From purpose to common mistakes to avoid, we'll cover everything you need to get accepted into the medical school of your dreams.
So, let's dive in!
On This Page On This Page -->
Types of Medical School Examples
Medical school essays come in many different forms, each with its own unique requirements and purpose.
In this section, we'll discuss some of the most common types of medical school essays and what you need to know to write them successfully.
Personal Statements
Personal statements are the most common type of medical school essay. They are usually a one-page essay that introduces you to the admissions officers.
It explains why you want to pursue medicine as a career. Personal statements should be engaging, and memorable, and show off your unique qualities.
An outline offers a framework to help you craft a compelling narrative that showcases your strengths and experiences.
A. Opening statement
A. Brief summary of educational background
A. Specific experiences that influenced your decision to pursue medicine
A. Unique qualities and characteristics that make you a strong candidate for medical school
A. Long-term career goals in medicine
A. Recap of main points
|
Check out this personal statement example that can help future physicians getting into the schools of their dreams.
Medical School Personal Statement Examples pdf
Secondary Essays
Secondary essays are additional essays that some medical schools require in addition to the personal statement.
They often ask specific questions about your background, experiences, or interests. They give you an opportunity to show off your future patient care and problem-solving skills.
Here is a brief example of a secondary application medical school essay:
As a pre-medical student, I found myself struggling to balance the demands of coursework, research, and clinical experience. However, the most challenging situation I faced occurred during my sophomore year when my mother was diagnosed with cancer. As an only child, I felt a tremendous sense of responsibility to support my mother during this difficult time while continuing to pursue my academic and extracurricular commitments. At first, I felt overwhelmed and unsure of how to manage my time effectively. But I quickly realized that I needed to prioritize my responsibilities and seek out support from others. I reached out to my professors and academic advisors to explain my situation and ask for accommodations. They were incredibly understanding and provided me with the flexibility I needed to balance my academic and personal responsibilities. I also became involved with a cancer support group on campus, where I found a community of individuals who understood what I was going through. Through this group, I was able to connect with other students who had experienced similar challenges and gain valuable insights and coping strategies. Ultimately, my mother's cancer diagnosis taught me the importance of resilience, adaptability, and community. It reminded me that while the path to becoming a physician may be challenging, it is also deeply rewarding. I am grateful for the experiences that have shaped me and look forward to using them to serve others in the future. |

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Diversity Essays
Diversity essays ask you to write about your experiences with diversity and how they have influenced you to pursue a career and your interest in medicine.
These essays are becoming increasingly common in medical school applications as schools strive to build a more diverse and inclusive student body.
| As an Asian-American, I have always been interested in exploring the unique perspectives and experiences of different cultures. Growing up, my family instilled in me a strong sense of cultural pride, which drove me to learn more about my heritage and seek out opportunities to connect with others from diverse backgrounds. This passion for diversity has also shaped my academic and career goals, leading me to pursue a degree in anthropology and, ultimately a career in medicine. During my undergraduate studies, I had the opportunity to participate in a medical mission trip to a rural community in Thailand. While there, I was struck by the stark contrast between the healthcare systems in the United States and Thailand, as well as the cultural differences that influence healthcare practices. Despite language and cultural barriers, I was able to connect with patients on a personal level and gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of cultural competence in healthcare. Through my experiences in the science of medicine, I have come to appreciate the value of diversity in healthcare and the critical role that healthcare providers play in ensuring that all patients receive equitable and culturally competent care. I am committed to continuing to develop my cultural competency skills and to advocating for the needs of diverse patient populations. As a future physician, I hope to promote cultural sensitivity and understanding among my colleagues and to help bridge the gap in healthcare disparities for underserved and marginalized communities. |
Good Medical School Essay Examples
Are you struggling to write a standout medical school essay? They say that the best way to learn is by example. That's especially true when it comes to public health school essays.
We'll provide you with some of the best examples to help you craft an essay that will help your career in medicine.
Medical College Essay Examples
Personal Statement Medical School Examples Pdf
Medical School Covid Essay Examples
Challenging Medical School Essay Examples
Writing a medical school essay is more than just telling a story about yourself. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your critical thinking and analytical skills.
In this section, we'll highlight some of the challenging medical school essay examples. This will give you a sense of what admissions committees are looking for. You can learn how to exceed those expectations by writing a successful medical school essay.
Greatest Challenge Medical School Essay Examples
Successful Medicine Personal Statement Examples
Medical School Scholarship Essay Examples
Medical School Essay Examples for Different Schools
Each medical school has its own unique mission, values, and admissions criteria, and your essay should reflect that.
In this section, we'll explore how to tailor your medical school essay for different schools and showcase some examples of successful essays.
Letâs explore these Stanford and Harvard medical school essay examples:
Medical School Personal Statement Examples Harvard
Medical School Personal Statement Examples Stanford
Tips on Crafting an Excellent Medical School Personal Statement
The medical school personal statement is your opportunity to showcase your unique qualities and experiences.
Here are some tips to help you craft an excellent personal statement:
Start Early
Don't wait until the last minute to start writing your personal statement. Give yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, write, and revise your essay. Starting early also allows you to get feedback from mentors, professors, or peers.
Focus on Your Story
Your personal statement should tell a story that showcases your journey to medicine. Highlight the experiences and qualities that have led you to pursue a career in medicine. Tell them how you plan to use your skills to make a difference.
Be Specific
Use specific examples to illustrate your experiences and achievements. Don't just list your accomplishments, but show how they have prepared you for a career in medicine. Use concrete details to make your essay more engaging and memorable.
Show, Don't Tell
Instead of simply stating your qualities, show them through your experiences and actions. For example, donât say you're a team player. Describe a time when you worked effectively in a team to achieve a goal.
Tailor Your Essay to the School
As mentioned earlier, each medical school has its own unique mission and values. Tailor your personal statement to each school to demonstrate your fit with their program and values.
Mistakes to Avoid in a Medical School Personal Statement
When it comes to your medical school personal statement, there are some common mistakes you should avoid:
Avoid using cliched phrases and ideas that are overused in personal statements. Admissions committees want to see your unique perspective and experiences. They do not want generic statements that could apply to anyone.
Negativity
Don't focus on negative experiences or aspects of your life in your personal statement. Instead, focus on your strengths and how you have grown from challenges.
Lack of Focus
Make sure your personal statement has a clear focus and theme. Don't try to cover too many topics or experiences in one essay. Instead, focus on one or two experiences that are meaningful to you and illustrate your journey to medicine.
Too Formal or Informal Tone
Make sure your personal statement strikes the right tone. Avoid being too formal or using overly complex language. Also, avoid being too informal or using slang.
Plagiarism
Never copy someone else's personal statement or use a template to write your own. Admissions committees can easily spot plagiarism, and it will result in an immediate rejection.
Grammatical and Spelling Errors
Proofread your personal statement thoroughly for grammatical and spelling errors. Even a few small errors can detract from the overall quality of your essay.
Lack of Authenticity
Be true to yourself in your personal statement. Don't try to present an image of yourself that is not authentic or that you think the admissions committee wants to see. Be honest and genuine in your writing.
In conclusion, crafting a winning medical school essay is a crucial step toward securing admission to the medical school of your dreams.
This blog has provided examples of essays along with tips to craft an excellent medical school personal statement. By avoiding mistakes, you can increase your chances of standing out from the crowd and impressing the admissions committee.
Struggling with your medical school essays or college papers? Look no further!
Our college paper writing service specializes in crafting exceptional papers tailored to your academic needs, including medical school essays. And for an extra boost in your writing tasks, don't forget to explore our AI essay generator .
Elevate your academic performance with our medical school essay writing service and unlock the potential of our AI essay tools.
Get started today!
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
What is the ideal med school personal statement word limit.
There is no set length for a medical school personal statement, but most schools typically require a personal statement of 500-800 words.
How do I choose a topic for my medical school essay?
Choose a topic that showcases your unique perspective and experiences, and illustrates your journey to medicine. Consider what makes you stand out and what you are passionate about.
Should I mention my grades and test scores in my medical school essay?
It is not necessary to mention your grades and test scores in your medical school essay as they are already included in your application. Instead, focus on showcasing your unique qualities, experiences, and perspective.
Can I get help with writing my medical school essay?
Yes, there are various resources available to help you with writing your medical school essay. Consider seeking help from a writing tutor, career services office, or professional writing service like ours.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
6 Tips for Writing Your AMCAS® Personal Comments Essay
New section.
The Personal Comments Essay section of the American Medical College Application Service® (AMCAS®) application is your opportunity to tell medical school admissions officers who you are and what makes you unique. Here are some tips to help you as you write your essay.

The AMCAS® application to medical school asks for a lot of information about yourself. It includes biographical information, courses taken, and work experiences just to name a few. The application also requires you to include a Personal Comments Essay, which is entered in Section 8 of the application. This essay provides an opportunity to distinguish yourself from other applicants and provide admissions officers with more insight into why you have chosen to pursue a career in medicine.
Many admissions committees place significant weight on this section, so we have compiled a list of tips to help you craft a well-organized and compelling essay.
- Take time to think about the content of your essay before writing a first draft. As you’re thinking about the structure of your essay, remember to keep the content general because it will go to all medical schools you apply to. Try not to duplicate information provided elsewhere in the application. Some questions you may want to consider before you begin writing include: What are some of your personal values and how have they influenced your desire to enter the medical profession? What motivates you to learn more about medicine? What should medical schools know about you that isn’t described in other sections of the application?
- Show, don't tell. If challenges in your childhood or a defining experience led you to consider medicine, use details to describe those experiences and bring your essay to life. Try to include content that aligns with the premed competencies for entering medical students . Write in your authentic voice; your essay can help you contextualize and elaborate on topics during your interview.
- Stay on topic. There is a 5,300 character limit (including spaces) in this section. This equals about 1 1/2 pages of writing, single-spaced. Make sure your essay is interesting, follows a logical and orderly flow, relates to your reasons for choosing medicine, and describes why you believe you will be successful as a physician.
- Don’t be afraid of the editing process. Be sure to write more than one draft and make edits to your essay. Find a reviewer who does not have a personal relationship with you, as an external reviewer will help you gain new perspectives on your writing and refine the story you want to tell admissions committees.
- Remember to proofread and be mindful of formatting. The AMCAS application does not include spell -check, so be sure to proofread your essay for any typos or grammatical errors. You will not be able to go back into this section to make any edits after submitting your application. To avoid formatting issues, we recommend that you draft your essay in text-only word processing software, such as Microsoft Notepad or Mac TextEdit, then copy and paste your essay into the application. You can also type your essay directly into the AMCAS application.
- If you are applying to MD-PhD programs, there are two additional essays you will need to complete. The first essay asks your reasons for pursuing the combined degree and is relatively short. The second essay asks you to describe your research activities and is about three pages long. You can read more about these additional essays in the 2024 AMCAS® Applicant Guide (PDF) or get further guidance from your prehealth advisor or career counselor.
For more AMCAS program-related tips, please check out the AMCAS Tools and Tutorials page . There, you’ll find video tutorials, presentations, guides, and recordings of past webinars. For further advice from current prehealth advisors, access our “Advisor Corner: Crafting Your Personal Statement” article .
Don't have an Account?
Register Now!

- International Student
- Essay Writing Center
- Sample Essays
Sample Medical School Essays
Applying to medical school is an exciting decision, but the application process is very competitive. This means when it comes to your application you need to ensure you’ve put your best foot forward and done everything you can to stand out from other applicants. One great way to provide additional information on why you have decided to pursue a career in medicine and why you’re qualified, is your medical school essay. Read these samples to get a good idea on how you can write your own top-notch essay.
This section contains five sample medical school essays
- Medical School Sample Essay One
- Medical School Sample Essay Two
- Medical School Sample Essay Three
- Medical School Sample Essay Four
- Medical School Sample Essay Five
Medical School Essay One
When I was twelve years old, a drunk driver hit the car my mother was driving while I was in the backseat. I have very few memories of the accident, but I do faintly recall a serious but calming face as I was gently lifted out of the car. The paramedic held my hand as we traveled to the hospital. I was in the hospital for several weeks and that same paramedic came to visit me almost every day. During my stay, I also got to know the various doctors and nurses in the hospital on a personal level. I remember feeling anxiety about my condition, but not sadness or even fear. It seemed to me that those around me, particularly my family, were more fearful of what might happen to me than I was. I don’t believe it was innocence or ignorance, but rather a trust in the abilities of my doctors. It was as if my doctors and I had a silent bond. Now that I’m older I fear death and sickness in a more intense way than I remember experiencing it as a child. My experience as a child sparked a keen interest in how we approach pediatric care, especially as it relates to our psychological and emotional support of children facing serious medical conditions. It was here that I experienced first-hand the power and compassion of medicine, not only in healing but also in bringing unlikely individuals together, such as adults and children, in uncommon yet profound ways. And it was here that I began to take seriously the possibility of becoming a pediatric surgeon.
My interest was sparked even more when, as an undergraduate, I was asked to assist in a study one of my professors was conducting on how children experience and process fear and the prospect of death. This professor was not in the medical field; rather, her background is in cultural anthropology. I was very honored to be part of this project at such an early stage of my career. During the study, we discovered that children face death in extremely different ways than adults do. We found that children facing fatal illnesses are very aware of their condition, even when it hasn’t been fully explained to them, and on the whole were willing to fight their illnesses, but were also more accepting of their potential fate than many adults facing similar diagnoses. We concluded our study by asking whether and to what extent this discovery should impact the type of care given to children in contrast to adults. I am eager to continue this sort of research as I pursue my medical career. The intersection of medicine, psychology, and socialization or culture (in this case, the social variables differentiating adults from children) is quite fascinating and is a field that is in need of better research.
Although much headway has been made in this area in the past twenty or so years, I feel there is a still a tendency in medicine to treat diseases the same way no matter who the patient is. We are slowly learning that procedures and drugs are not always universally effective. Not only must we alter our care of patients depending upon these cultural and social factors, we may also need to alter our entire emotional and psychological approach to them as well.
It is for this reason that I’m applying to the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, as it has one of the top programs for pediatric surgery in the country, as well as several renowned researchers delving into the social, generational, and cultural questions in which I’m interested. My approach to medicine will be multidisciplinary, which is evidenced by the fact that I’m already double-majoring in early childhood psychology and pre-med, with a minor in cultural anthropology. This is the type of extraordinary care that I received as a child—care that seemed to approach my injuries with a much larger and deeper picture than that which pure medicine cannot offer—and it is this sort of care I want to provide my future patients. I turned what might have been a debilitating event in my life—a devastating car accident—into the inspiration that has shaped my life since. I am driven and passionate. And while I know that the pediatric surgery program at Johns Hopkins will likely be the second biggest challenge I will face in my life, I know that I am up for it. I am ready to be challenged and prove to myself what I’ve been telling myself since that fateful car accident: I will be a doctor.
Tips for a Successful Medical School Essay
- If you’re applying through AMCAS, remember to keep your essay more general rather than tailored to a specific medical school, because your essay will be seen by multiple schools.
- AMCAS essays are limited to 5300 characters—not words! This includes spaces.
- Make sure the information you include in your essay doesn't conflict with the information in your other application materials.
- In general, provide additional information that isn’t found in your other application materials. Look at the essay as an opportunity to tell your story rather than a burden.
- Keep the interview in mind as you write. You will most likely be asked questions regarding your essay during the interview, so think about the experiences you want to talk about.
- When you are copying and pasting from a word processor to the AMCAS application online, formatting and font will be lost. Don’t waste your time making it look nice. Be sure to look through the essay once you’ve copied it into AMCAS and edit appropriately for any odd characters that result from pasting.
- Avoid overly controversial topics. While it is fine to take a position and back up your position with evidence, you don’t want to sound narrow-minded.
- Revise, revise, revise. Have multiple readers look at your essay and make suggestions. Go over your essay yourself many times and rewrite it several times until you feel that it communicates your message effectively and creatively.
- Make the opening sentence memorable. Admissions officers will read dozens of personal statements in a day. You must say something at the very beginning to catch their attention, encourage them to read the essay in detail, and make yourself stand out from the crowd.
- Character traits to portray in your essay include: maturity, intellect, critical thinking skills, leadership, tolerance, perseverance, and sincerity.
Medical School Essay Two
If you had told me ten years ago that I would be writing this essay and planning for yet another ten years into the future, part of me would have been surprised. I am a planner and a maker of to-do lists, and it has always been my plan to follow in the steps of my father and become a physician. This plan was derailed when I was called to active duty to serve in Iraq as part of the War on Terror.
I joined the National Guard before graduating high school and continued my service when I began college. My goal was to receive training that would be valuable for my future medical career, as I was working in the field of emergency health care. It was also a way to help me pay for college. When I was called to active duty in Iraq for my first deployment, I was forced to withdraw from school, and my deployment was subsequently extended. I spent a total of 24 months deployed overseas, where I provided in-the-field medical support to our combat troops. While the experience was invaluable not only in terms of my future medical career but also in terms of developing leadership and creative thinking skills, it put my undergraduate studies on hold for over two years. Consequently, my carefully-planned journey towards medical school and a medical career was thrown off course. Thus, while ten-year plans are valuable, I have learned from experience how easily such plans can dissolve in situations that are beyond one’s control, as well as the value of perseverance and flexibility.
Eventually, I returned to school. Despite my best efforts to graduate within two years, it took me another three years, as I suffered greatly from post-traumatic stress disorder following my time in Iraq. I considered abandoning my dream of becoming a physician altogether, since I was several years behind my peers with whom I had taken biology and chemistry classes before my deployment. Thanks to the unceasing encouragement of my academic advisor, who even stayed in contact with me when I was overseas, I gathered my strength and courage and began studying for the MCAT. To my surprise, my score was beyond satisfactory and while I am several years behind my original ten-year plan, I am now applying to Brown University’s School of Medicine.
I can describe my new ten-year plan, but I will do so with both optimism and also caution, knowing that I will inevitably face unforeseen complications and will need to adapt appropriately. One of the many insights I gained as a member of the National Guard and by serving in war-time was the incredible creativity medical specialists in the Armed Forces employ to deliver health care services to our wounded soldiers on the ground. I was part of a team that was saving lives under incredibly difficult circumstances—sometimes while under heavy fire and with only the most basic of resources. I am now interested in how I can use these skills to deliver health care in similar circumstances where basic medical infrastructure is lacking. While there is seemingly little in common between the deserts of Fallujah and rural Wyoming, where I’m currently working as a volunteer first responder in a small town located more than 60 miles from the nearest hospital, I see a lot of potential uses for the skills that I gained as a National Guardsman. As I learned from my father, who worked with Doctors Without Borders for a number of years, there is quite a bit in common between my field of knowledge from the military and working in post-conflict zones. I feel I have a unique experience from which to draw as I embark on my medical school journey, experiences that can be applied both here and abroad.
In ten years’ time, I hope to be trained in the field of emergency medicine, which, surprisingly, is a specialization that is actually lacking here in the United States as compared to similarly developed countries. I hope to conduct research in the field of health care infrastructure and work with government agencies and legislators to find creative solutions to improving access to emergency facilities in currently underserved areas of the United States, with an aim towards providing comprehensive policy reports and recommendations on how the US can once again be the world leader in health outcomes. While the problems inherent in our health care system are not one-dimensional and require a dynamic approach, one of the solutions as I see it is to think less in terms of state-of-the-art facilities and more in terms of access to primary care. Much of the care that I provide as a first responder and volunteer is extremely effective and also relatively cheap. More money is always helpful when facing a complex social and political problem, but we must think of solutions above and beyond more money and more taxes. In ten years I want to be a key player in the health care debate in this country and offering innovative solutions to delivering high quality and cost-effective health care to all our nation’s citizens, especially to those in rural and otherwise underserved areas.
Of course, my policy interests do not replace my passion for helping others and delivering emergency medicine. As a doctor, I hope to continue serving in areas of the country that, for one reason or another, are lagging behind in basic health care infrastructure. Eventually, I would also like to take my knowledge and talents abroad and serve in the Peace Corps or Doctors Without Borders.
In short, I see the role of physicians in society as multifunctional: they are not only doctors who heal, they are also leaders, innovators, social scientists, and patriots. Although my path to medical school has not always been the most direct, my varied and circuitous journey has given me a set of skills and experiences that many otherwise qualified applicants lack. I have no doubt that the next ten years will be similarly unpredictable, but I can assure you that no matter what obstacles I face, my goal will remain the same. I sincerely hope to begin the next phase of my journey at Brown University. Thank you for your kind attention.
Additional Tips for a Successful Medical School Essay
- Regardless of the prompt, you should always address the question of why you want to go to medical school in your essay.
- Try to always give concrete examples rather than make general statements. If you say that you have perseverance, describe an event in your life that demonstrates perseverance.
- There should be an overall message or theme in your essay. In the example above, the theme is overcoming unexpected obstacles.
- Make sure you check and recheck for spelling and grammar!
- Unless you’re very sure you can pull it off, it is usually not a good idea to use humor or to employ the skills you learned in creative writing class in your personal statement. While you want to paint a picture, you don’t want to be too poetic or literary.
- Turn potential weaknesses into positives. As in the example above, address any potential weaknesses in your application and make them strengths, if possible. If you have low MCAT scores or something else that can’t be easily explained or turned into a positive, simply don’t mention it.
Medical School Essay Three
The roots of my desire to become a physician are, thankfully, not around the bedside of a sick family member or in a hospital, but rather on a 10-acre plot of land outside of a small town in Northwest Arkansas. I loved raising and exhibiting cattle, so every morning before the bus arrived at 7 a.m. I was in the barn feeding, checking cattle for any health issues and washing the show heifers. These early mornings and my experiences on a farm not only taught me the value of hard work, but ignited my interest in the body, albeit bovine at the time. It was by a working chute that I learned the functions of reproductive hormones as we utilized them for assisted reproduction and artificial insemination; it was by giving vaccinations to prevent infection that I learned about bacteria and the germ theory of disease; it was beside a stillborn calf before the sun had risen that I was exposed to the frailty of life.
Facing the realities of disease and death daily from an early age, I developed a strong sense of pragmatism out of necessity. There is no place for abstractions or euphemisms about life and death when treating a calf’s pneumonia in the pouring rain during winter. Witnessing the sometimes harsh realities of life on a farm did not instill within me an attitude of jaded inevitability of death. Instead, it germinated a responsibility to protect life to the best of my abilities, cure what ailments I can and alleviate as much suffering as possible while recognizing that sometimes nothing can be done.
I first approached human health at the age of nine through beef nutrition and food safety. Learning the roles of nutrients such as zinc, iron, protein and B-vitamins in the human body as well as the dangers of food-borne illness through the Beef Ambassador program shifted my interest in the body to a new species. Talking with consumers about every facet of the origins of food, I realized that the topics that most interested me were those that pertained to human health. In college, while I connected with people over samples of beef and answered their questions, I also realized that it is not enough simply to have adequate knowledge. Ultimately knowledge is of little use if it is not digestible to those who receive it. So my goal as a future clinical physician is not only to illuminate the source of an affliction and provide treatment for patients, but take care to ensure the need for understanding by both patient and family is met.
I saw this combination of care and understanding while volunteering in an emergency room, where I was also exposed to other aspects and players in the medical field. While assisting a nurse perform a bladder scan and witnessing technicians carry out an echocardiogram or CT scan, I learned the important roles that other professionals who do not wear white coats have in today’s medical field. Medicine is a team sport, and coordinating the efforts of each of these players is crucial for the successful execution of patient care. It is my goal to serve as the leader of this healthcare unit and unify a team of professionals to provide the highest quality care for patients. Perhaps most importantly my time at the VA showed me the power a smile and an open ear can have with people. On the long walk to radiology, talking with patients about their military service and families always seemed to take their mind off the reason for their visit, if only for a few minutes. This served as a reminder that we are helping people with pasts and dreams, rather than simply remedying patients’ symptoms.
Growing up in a small town, I never held aspirations of world travel when I was young. But my time abroad revealed to me the state of healthcare in developing countries and fostered a previously unknown interest in global health. During my first trip abroad to Ghana, my roommate became ill with a severe case of traveler’s diarrhea. In the rural north of the country near the Sahara, the options for healthcare were limited; he told me how our professor was forced to bribe employees to bypass long lines and even recounted how doctors took a bag of saline off the line of another patient to give to him. During a service trip to a rural community in Nicaragua, I encountered patients with preventable and easily treatable diseases that, due to poverty and lack of access, were left untreated for months or years at a time. I was discouraged by the state of healthcare in these countries and wondered what could be done to help. I plan to continue to help provide access to healthcare in rural parts of developing countries, and hopefully as a physician with an agricultural background I can approach public health and food security issues in a multifaceted and holistic manner.
My time on a cattle farm taught me how to work hard to pursue my interests, but also fueled my appetite for knowledge about the body and instilled within me a firm sense of practicality. Whether in a clinic, operating room or pursuing public and global health projects, I plan to bring this work ethic and pragmatism to all of my endeavors. My agricultural upbringing has produced a foundation of skills and values that I am confident will readily transplant into my chosen career. Farming is my early passion, but medicine is my future.
Medical School Essay Four
I am a white, cisgender, and heterosexual female who has been afforded many privileges: I was raised by parents with significant financial resources, I have traveled the world, and I received top-quality high school and college educations. I do not wish to be addressed or recognized in any special way; all I ask is to be treated with respect.
As for my geographic origin, I was born and raised in the rural state of Maine. Since graduating from college, I have been living in my home state, working and giving back to the community that has given me so much. I could not be happier here; I love the down-to-earth people, the unhurried pace of life, and the easy access to the outdoors. While I am certainly excited to move elsewhere in the country for medical school and continue to explore new places, I will always self-identify as a Mainer as being from Maine is something I take great pride in. I am proud of my family ties to the state (which date back to the 1890’s), I am proud of the state’s commitment to preserving its natural beauty, and I am particularly proud of my slight Maine accent (we don’t pronounce our r’s). From the rocky coastline and rugged ski mountains to the locally-grown food and great restaurants, it is no wonder Maine is nicknamed, "Vacationland.” Yet, Maine is so much more than just a tourist destination. The state is dotted with wonderful communities in which to live, communities like the one where I grew up.
Perhaps not surprisingly, I plan to return to Maine after residency. I want to raise a family and establish my medical practice here. We certainly could use more doctors! Even though Maine is a terrific place to live, the state is facing a significant doctor shortage. Today, we are meeting less than half of our need for primary care providers. To make matters worse, many of our physicians are close to retirement age. Yet, according to the AAMC, only 53 Maine residents matriculated into medical school last year! Undoubtedly, Maine is in need of young doctors who are committed to working long term in underserved areas. As my primary career goal is to return to my much adored home state and do my part to help fill this need, I have a vested interest in learning more about rural medicine during medical school.
I was raised in Cumberland, Maine, a coastal town of 7,000 just north of Portland. With its single stoplight and general store (where it would be unusual to visit without running into someone you know), Cumberland is the epitome of a small New England town. It truly was the perfect place to grow up. According to the most recent census, nearly a third of the town’s population is under 18 and more than 75% of households contain children, two statistics which speak to the family-centric nature of Cumberland’s community. Recently rated Maine's safest town, Cumberland is the type of place where you allow your kindergartener to bike alone to school, leave your house unlocked while at work, and bring home-cooked food to your sick neighbors and their children. Growing up in such a safe, close-knit, and supportive community instilled in me the core values of compassion, trustworthiness, and citizenship. These three values guide me every day and will continue to guide me through medical school and my career in medicine.
As a medical student and eventual physician, my compassion will guide me to become a provider who cares for more than just the physical well-being of my patients. I will also commit myself to my patients’ emotional, spiritual, and social well-being and make it a priority to take into account the unique values and beliefs of each patient. By also demonstrating my trustworthiness during every encounter, I will develop strong interpersonal relationships with those whom I serve. As a doctor once wisely said, “A patient does not care how much you know until he knows how much you care.”
My citizenship will guide me to serve my community and to encourage my classmates and colleagues to do the same. We will be taught in medical school to be healers, scientists, and educators. I believe that, in addition, as students and as physicians, we have the responsibility to use our medical knowledge, research skills, and teaching abilities to benefit more than just our patients. We must also commit ourselves to improving the health and wellness of those living in our communities by participating in public events (i.e by donating our medical services), lobbying for better access to healthcare for the underprivileged, and promoting wellness campaigns. As a medical student and eventual physician, my compassion, trustworthiness, and citizenship will drive me to improve the lives of as many individuals as I can.
Cumberland instilled in me important core values and afforded me a wonderful childhood. However, I recognize that my hometown is not perfect. For one, the population is shockingly homogenous, at least as far as demographics go. As of the 2010 census, 97.2% of the residents of Cumberland were white. Only 4.1% of residents speak a language other than English at home and even fewer were born in another country. Essentially everybody who identified with a religion identified as some denomination of Christian. My family was one of maybe five Jewish families in the town. Additionally, nearly all the town’s residents graduated from high school (98.1%), are free of disability (93.8%), and live above the poverty line (95.8%). Efforts to attract diverse families to Cumberland is one improvement that I believe would make the community a better place in which to live. Diversity in background (and in thought) is desirable in any community as living, learning, and working alongside diverse individuals helps us develop new perspectives, enhances our social development, provides us with a larger frame of reference, and improves our understanding of our place in society.
Medical School Essay Five
“How many of you received the flu vaccine this year?” I asked my Bricks 4 Kidz class, where I volunteer to teach elementary students introductory science and math principles using Lego blocks. “What’s a flu vaccine?” they asked in confusion. Surprised, I briefly explained the influenza vaccine and its purpose for protection. My connection to children and their health extends to medical offices, clinics and communities where I have gained experience and insight into medicine, confirming my goal of becoming a physician.
My motivation to pursue a career in medicine developed when my mother, who was diagnosed with Lupus, underwent a kidney transplant surgery and suffered multiple complications. I recall the fear and anxiety I felt as a child because I misunderstood her chronic disease. This prompted me to learn more about the science of medicine. In high school, I observed patients plagued with acute and chronic kidney disease while briefly exploring various fields of medicine through a Mentorship in Medicine summer program at my local hospital. In addition to shadowing nephrologists in a hospital and clinical setting, I scrubbed into the operating room, viewed the radiology department, celebrated the miracle of birth in the delivery room, and quietly observed a partial autopsy in pathology. I saw many patients confused about their diagnoses. I was impressed by the compassion of the physicians and the time they took to reassure and educate their patients.
Further experiences in medicine throughout and after college shaped a desire to practice in underserved areas. While coloring and reading with children in the patient area at a Family Health Center, I witnessed family medicine physicians diligently serve patients from low-income communities. On a medical/dental mission trip to the Philippines, I partnered with local doctors to serve and distribute medical supplies to rural schools and communities. At one impoverished village, I held a malnourished two-year old boy suffering from cerebral palsy and cardiorespiratory disease. His family could not afford to take him to the nearest pediatrician, a few hours away by car, for treatment. Overwhelmed, I cried as we left the village. Many people were suffering through pain and disease due to limited access to medicine. But this is not rare; there are many people suffering due to inadequate access/accessibility around the world, even in my hometown. One physician may not be able to change the status of underserved communities, however, one can alleviate some of the suffering.
Dr. X, my mentor and supervisor, taught me that the practice of medicine is both a science and an art. As a medical assistant in a pediatric office, I am learning about the patient-physician relationship and the meaningful connection with people that medicine provides. I interact with patients and their families daily. Newborn twins were one of the first patients I helped, and I look forward to seeing their development at successive visits. A young boy who endured a major cardiac surgery was another patient I connected with, seeing his smiling face in the office often as he transitioned from the hospital to his home. I also helped many excited, college-bound teenagers with requests for medical records in order to matriculate. This is the art of medicine – the ability to build relationships with patients and have an important and influential role in their lives, from birth to adulthood and beyond.
In addition, medicine encompasses patient-centered care, such as considering and addressing concerns. While taking patient vitals, I grew discouraged when parents refused the influenza vaccine and could not understand their choices. With my experience in scientific research, I conducted an informal yet insightful study. Over one hundred families were surveyed about their specific reasons for refusing the flu vaccine. I sought feedback on patients’ level of understanding about vaccinations and its interactions with the human immune system. Through this project, I learned the importance of understanding patient’s concerns in order to reassure them through medicine. I also learned the value of communicating with patients, such as explaining the purpose of a recommended vaccine. I hope to further this by attending medical school to become a physician focused on patient-centered care, learning from and teaching my community.
Children have been a common thread in my pursuit of medicine, from perceiving medicine through child-like eyes to interacting daily with children in a medical office. My diverse experiences in patient interaction and the practice of medicine inspire me to become a physician, a path that requires perseverance and passion. Physicians are life-long learners and teachers, educating others whether it is on vaccinations or various diseases. This vocation also requires preparation, and I eagerly look forward to continually learning and growing in medical school and beyond.
To learn more about what to expect from the study of medicine, check out our Study Medicine in the US section.
Related Content:
Get the international student newsletter.

Great Medical School Personal Statement Examples (2024-2025) Insider’s Guide

A physician and former medical school admissions officer teaches you how to write your medical school personal statement, step by step. Read several full-length medical school personal statement examples for inspiration.
In this article, a former medical school admissions officer explains exactly how to write a stand-out medical school personal statement!
Our goal is to empower you to write a medical school personal statement that reflects your individuality, truest aspirations and genuine motivations.
This guide also includes:
- Real life medical school personal statement examples
- Medical school personal statement inventory template and outline exercise
- AMCAS , TMDSAS , and AACOMAS personal statement prompts
- Advanced strategies to ensure you address everything admissions committees want to know
- The secret to writing a great medical school personal statement
So, if you want your medical school personal statement to earn more more medical school interviews, you will love this informative guide.
Let’s dive right in.
Table of Contents
Medical School Personal Statement Fundamentals
If you are getting ready to write your medical school personal statement for the 2024-2025 application year, you may already know that almost 60% of medical school applicants are not accepted every year . You have most likely also completed all of your medical school requirements and have scoured the internet for worthy medical school personal statement examples and guidance.
You know the medical school personal statement offers a crucial opportunity to show medical schools who you are beyond your GPA and MCAT score .
It provides an opportunity to express who you are as an individual, the major influences and background that have shaped your interests and values, what inspired you to pursue medicine, and what kind of a physician you envision yourself becoming.
However, with so much information online, you are not sure who to trust. We are happy you have found us!
Insider Knowledge and Expertise
Because the vast majority of people offering guidance are not former admissions officers or doctors , you must be careful when searching online.
We are real medical school admissions insiders and know what goes on behind closed doors and how to ensure your medical school personal statement has broad appeal while highlighting your most crucial accomplishments, perspectives, and insights.
With tight limits on space, it can be tough trying to decide what to include in your medical school personal statement to make sure you stand out. You must think strategically about how you want to present your personal “big picture” while showing you possess the preprofessional competencies med schools are seeking.
When a medical school admissions reviewer finishes reading your medical school personal statement, ask yourself:
- What are the most important things you want that person to remember about you?
- Does your medical school personal statement sum up your personality, interests, and talents?
- Does your medical school personal statement sound as if it’s written from the heart? Is it authentic?
It’s pretty obvious to most admissions reviewers when applicants are trying too hard to impress them. Being authentic and upfront about who you are is the best way to be a memorable applicant.
“After sitting on a medical school admissions committee for many years, I can tell you, think strategically about how you want to present your personal “big picture.” We want to know who you are as a human being.”
The Biggest Medical School Personal Statement Mistakes
The most common medical school personal statement mistake we see students make is that they write about:
- What they have accomplished
- How they have accomplished it
By including details on what you have accomplished and how, you will make yourself sound like every other medical school applicant.
Most medical school applicants are involved in similar activities: research, clinical work, service, and social justice work.
To stand out, you must write from the heart making it clear you haven’t marched through your premedical years and checking boxes.
We also strongly discourage applicants from using ChatGPT or any AI bot to write their medical school personal statement. Writing in your own voice is essential and using anything automated will undermine success.
The Medical School Personal Statement Secret
MedEdits students stand out in the medical school personal statement because in their personal statements they address:
WHY they have accomplished what they have.
In other words, they write in more detail about their passions, interests, and what is genuinely important to them.
It sounds simple, we know, but by writing in a natural way, really zeroing in on WHY YOU DO WHAT YOU DO, you will appeal to a wide variety of people in a humanistic way.
Why? How is that possible? They all have a few things in common:
- They write a narrative that is authentic and distinctive to them.
- They write a medical school personal statement with broad appeal (many different types of people will be evaluating your application; most are not physicians).
- They don’t try too hard to impress; instead they write about the most impactful experiences they have had on their path to medical school.
- They demonstrate they are humble, intellectual, compassionate, and committed to a career in medicine all at the same time.
Keep reading for a step by step approach to write your medical school personal statement.
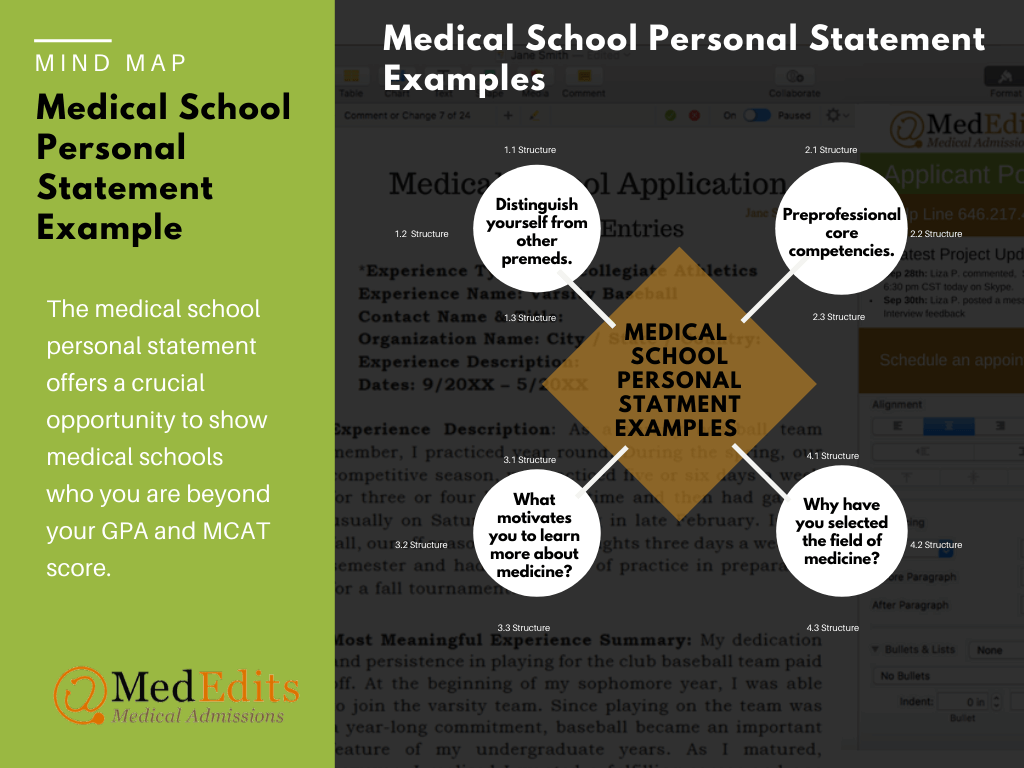
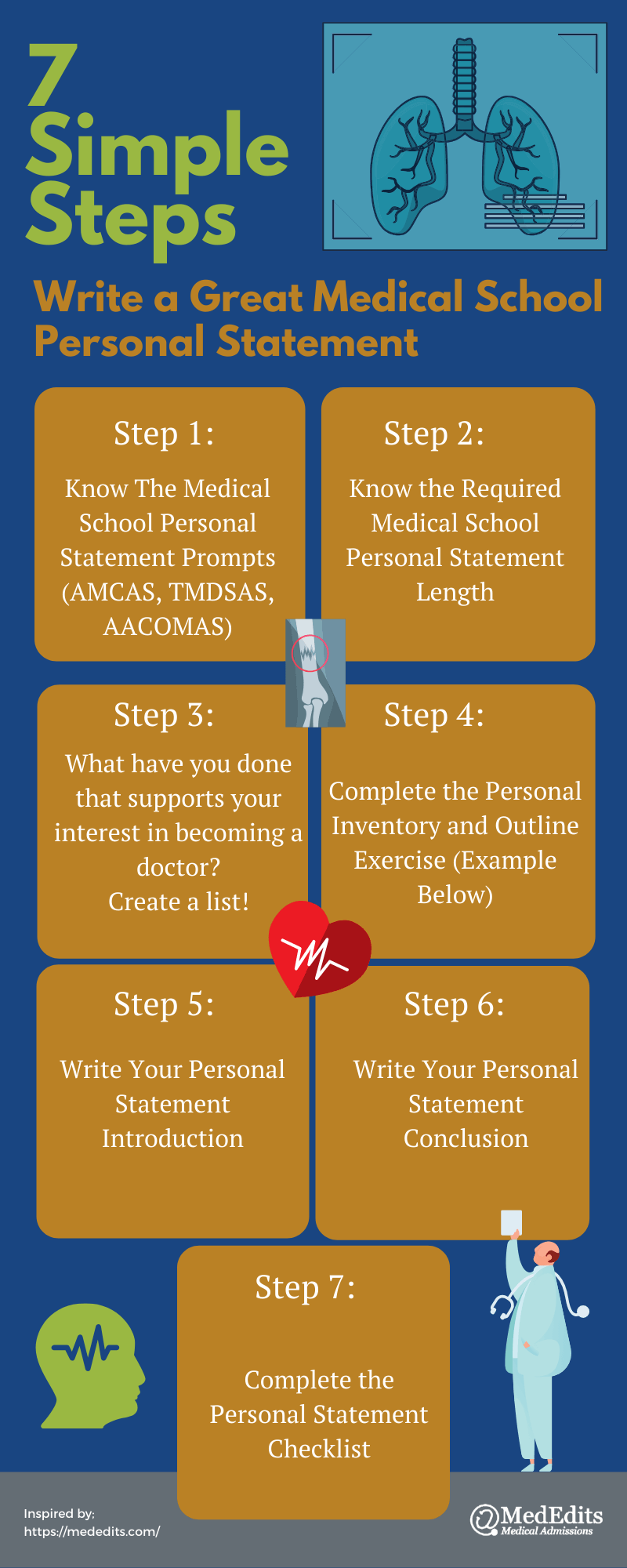
Learn the 2024-2025 Medical School Personal Statement Prompts ( AMCAS , TMDSAS , AACOMAS )
The personal statement is the major essay portion of your primary application process. In it, you should describe yourself and your background, as well as any important early exposures to medicine, how and why medicine first piqued your interest, what you have done as a pre med, your personal experiences, and how you became increasingly fascinated with it. It’s also key to explain why medicine is the right career for you, in terms of both personal and intellectual fulfillment, and to show your commitment has continued to deepen as you learned more about the field.
The personal statement also offers you the opportunity to express who you are outside of medicine. What are your other interests? Where did you grow up? What did you enjoy about college? Figuring out what aspects of your background to highlight is important since this is one of your only chances to express to the med school admissions committee before your interview what is important to you and why.
However, it is important to consider the actual personal statement prompt for each system through which you will apply, AMCAS, AACOMAS, and TMDSAS, since each is slightly different.
Need help with your Personal Statement?
Schedule a free 15 Minute Consultation with a MedEdits expert.
2024 AMCAS Personal Statement Prompt

The AMCAS personal statement instructions are as follows:
Use the Personal Comments Essay as an opportunity to distinguish yourself from other applicants. Consider and write your Personal Comments Essay carefully; many admissions committees place significant weight on the essay. Here are some questions that you may want to consider while writing the essay:
- Why have you selected the field of medicine?
- What motivates you to learn more about medicine?
- What do you want medical schools to know about you that hasn’t been disclosed in other sections of the application?
In addition, you may wish to include information such as:
- Unique hardships, challenges, or obstacles that may have influenced your educational pursuits
- Comments on significant fluctuations in your academic record that are not explained elsewhere in your application
As you can see, these prompts are not vague; there are fundamental questions that admissions committees want you to answer when writing your personal statement. While the content of your statement should be focused on medicine, answering the open ended third question is a bit trickier.
The AMCAS personal statement length is 5,300 characters with spaces maximum.
2024 TMDSAS Personal Statement Prompt

The TMDSAS personal statement is one of the most important pieces of your medical school application.
The TMDSAS personal statement prompt is as follows:
Explain your motivation to seek a career in medicine. Be sure to include the value of your experiences that prepare you to be a physician.
This TMDSAS prompt is very similar to the AMCAS personal statement prompt. The TMDSAS personal statement length is 5,000 characters with spaces whereas the AMCAS personal statement length is 5,300 characters with spaces. Most students use the same essay (with very minor modifications, if necessary) for both application systems.
2024 AACOMAS Personal Statement Prompt

The AACOMAS personal statement is for osteopathic medical schools specifically. As with the AMCAS statement, you need to lay out your journey to medicine as chronologically as possible in 5,300 characters with spaces or less. So you essentially have the same story map as for an AMCAS statement. Most important, you must show you are interested in osteopathy specifically. Therefore, when trying to decide what to include or leave out, prioritize any osteopathy experiences you have had, or those that are in line with the osteopathic philosophy of the mind-body connection, the body as self-healing, and other tenets.
Medical School Application Timeline and When to Write your Personal Statement
Most medical school personal statements can be used for AMCAS and AACOMAS.
Know the Required Medical School Personal Statement Length

Below are the medical schools personal statement length limits for each application system. As you can see, they are all very similar. When you start brainstorming and writing your personal statement, keep these limits in mind.
AMCAS Personal Statement Length : 5,300 characters with spaces.
As per the AAMC website : “The available space for this essay is 5,300 characters (spaces are counted as characters), or approximately one page. You will receive an error message if you exceed the available space.”
AACOMAS Personal Statement Length : 5,300 characters with spaces
TMDSAS Personal Statement Length : 5,000 characters with spaces
As per the TMDSAS Website (Page 36): “The personal essay asks you to explain your motivation to seek a career in medicine. You are asked to include the value of your experiences that prepare you to be a physician. The essay is limited to 5000 characters, including spaces.”
- Service Orientation
- Social Skills
- Cultural Competence
- Oral Communication
- Ethical Responsibility to Self and Others
- Reliability and Dependability
- Resilience and Adaptability
- Capacity for Improvement
- Critical Thinking
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Written Communication
- Scientific Inquiry
2. Why do you want to be a doctor?
This may seem pretty basic – and it is – but admissions officers need to know WHY you want to practice medicine. Many applicants make the mistake of simply listing what they have done without offering insights about those experiences that answer the question, “Why medicine?” Your reasons for wanting to be a doctor may overlap with those of other applicants. This is okay because the experiences in which you participated, the stories you can tell about those experiences, and the wisdom you gained are completely distinct—because they are only yours.
“In admissions committee meetings we were always interested in WHY you wanted to earn a medical degree and how you would contribute to the medical school community.”
Medical school admissions committees want to know that you have explored your interest deeply and that you can reflect on the significance of these clinical experiences and volunteer work. But writing only that you “want to help people” does not support a sincere desire to become a physician; you must indicate why the medical profession in particular—rather than social work, teaching, or another “helping” profession—is your goal.
3. How have your experiences influenced you?
It is important to show how your experiences are linked and how they have influenced you. What motivated you from your experiences? In what ways did they influence your other activities? How were your future goals shaped by these experiences? Medical school admissions committees like to see a sensible progression of involvements. While not every activity needs to be logically “connected” with another, the evolution of your interests and how your experiences have nurtured your future goals and ambitions show that you are motivated and committed.
4. Who are you as a person? What are your values and ideals?
Medical school admissions committees want to know about you as an individual beyond your interests in medicine, too. This is where answering that third open ended question in the prompt becomes so important. What was interesting about your background, youth, and home life? What did you enjoy most about college? Do you have any distinctive passions or interests? They want to be convinced that you are a good person beyond your experiences. Write about those topics that are unlikely to appear elsewhere in your statement that will offer depth and interest to your work and illustrate the qualities and characteristics you possess.
Related Articles:
- How to Get into Stanford Medical School
- How to Get into NYU Medical School
- How To Get Into Columbia Medical School
- How To Get Into UT Southwestern Medical School
- How To Get Into Harvard Medical School
Complete Your Personal Inventory and Outline (Example Below)
Highlighting valuable experiences, experience-based personal inventory exercise, creating your personal inventory.
- List Important Experiences: Write down a list of the most important experiences in your life and your development. The list should be all-inclusive and comprise those experiences that had the most impact on you. Put the list, which should consist of personal, extracurricular, and academic events, in chronological order.
- Identify Key Experiences: From this list, determine which experiences you consider the most important in helping you decide to pursue a career in medicine. This “experience-oriented” approach will allow you to determine which experiences best illustrate the personal competencies admissions committees look for in your written documents. Remember that you must provide evidence for your interest in medicine and for most of the personal qualities and characteristics that medical school admissions committees want to see.
- Reflect on Influences: After making your list, think about why each “most important” experience was influential and write that down. What did you observe? What did you learn? What insights did you gain? How did the experience influence your path and choices?
- Create Illustrations: Then think of a story or illustration for why each experience was important.
- Evaluate for Significance: After doing this exercise, evaluate each experience for its significance and influence and for its “story” value. Choose to write about those experiences that not only were influential but that also will provide interesting reading, keeping in mind that your goal is to weave the pertinent experiences together into a compelling story. In making your choices, think about how you will link each experience and transition from one topic to the next.
- Plan Your Outline: Decide which of your listed experiences you will use for your introduction first (see below for more about your introduction). Then decide which experiences you will include in the body of your personal statement, create a general outline, and get writing!
Crafting Your Narrative
Craft a compelling personal statement introduction and body.
You hear conflicting advice about application essays. Some tell you not to open with a story. Others tell you to always begin with a story. Regardless of the advice you receive, be sure to do three things:
- Be true to yourself. Everyone will have an opinion regarding what you should and should not write. Follow your own instincts. Your personal statement should be a reflection of you, and only you.
- Start your personal statement with something catchy. Think about the list of potential topics above.
- Don’t rush your work. Composing thoughtful documents takes time and you don’t want your writing and ideas to be sloppy and underdeveloped.
Most important is to begin with something that engages your reader. A narrative, a “story,” an anecdote written in the first or third person, is ideal. Whatever your approach, your first paragraph must grab your reader’s attention and motivate him to want to continue reading. I encourage applicants to start their personal statement by describing an experience that was especially influential in setting them on their path to medical school. This can be a personal or scholarly experience or an extracurricular one. Remember to avoid clichés and quotes and to be honest and authentic in your writing. Don’t try to be someone who you are not by trying to imitate personal statement examples you have read online or “tell them what you think they want to hear”; consistency is key and your interviewer is going to make sure that you are who you say you are!
When deciding what experiences to include in the body of your personal statement, go back to your personal inventory and identify those experiences that have been the most influential in your personal path and your path to medical school. Keep in mind that the reader wants to have an idea of who you are as a human being so don’t write your personal statement as a glorified resume. Include some information about your background and personal experiences that can give a picture of who you are as a person outside of the classroom or laboratory.
Ideally, you should choose two or three experiences to highlight in the body of your personal statement. You don’t want to write about all of your accomplishments; that is what your application entries are for!
Write Your Personal Statement Conclusion
In your conclusion, it is customary to “go full circle” by coming back to the topic—or anecdote—you introduced in the introduction, but this is not a must. Summarize why you want to be a doctor and address what you hope to achieve and your goals for medical school. Write a conclusion that is compelling and will leave the reader wanting to meet you.
Complete Personal Statement Checklist
When reading your medical school personal statement be sure it:
Shows insight and introspection
The best medical school personal statements tell a great deal about what you have learned through your experiences and the insights you have gained.
You want to tell your story by highlighting those experiences that have been the most influential on your path to medical school and to give a clear sense of chronology. You want your statement always to be logical and never to confuse your reader.
Is interesting and engaging
The best personal statements engage the reader. This doesn’t mean you must use big words or be a literary prize winner. Write in your own language and voice, but really think about your journey to medical school and the most intriguing experiences you have had.
Gives the reader a mental image of who you are
You want the reader to be able to envision you as a caregiver and a medical professional. You want to convey that you would be a compassionate provider at the bedside – someone who could cope well with crisis and adversity.

Not true. The vast majority of personal statements do not have themes. In fact, most are somewhat autobiographical and are just as interesting as those statements that are woven around a “theme.” It is only the very talented writer who can creatively write a personal statement around a theme, and this approach often backfires since the applicant fails to answer the three questions above.
Medical School Personal Statement Examples and Analysis for Inspiration

AMCAS Medical School Personal Statement Example and Analysis #1 with Personal Inventory
We will use Amy to illustrate the general process of writing an application to medical school, along with providing the resulting documents. Amy will first list those experiences, personal, extracurricular, and scholarly, that have been most influential in two areas: her life in general and her path to medical school. She will put this personal inventory in chronologic order for use in composing her personal statement.
She will then select those experiences that were the most significant to her and will reflect and think about why they were important. For her application entries, Amy will write about each experience, including those that she considers influential in her life but not in her choice of medicine, in her application entries. Experiences that Amy will not write about in her activity entries or her personal statement are those that she does not consider most influential in either her life or in her choice of medicine.
- Going with my mom to work. She is a surgeon — I was very curious about what she did. I was intrigued by the relationships she had with patients and how much they valued her efforts. I also loved seeing her as “a doctor” since, to me, she was just “mom.”
- I loved biology in high school. I started to think seriously about medicine then. It was during high school that I became fascinated with biology and how the human body worked. I would say that was when I thought, “Hmm, maybe I should be a doctor.”
- Grandmother’s death, senior year of high school. My grandmother’s death was tragic. It was the first time I had ever seen someone close to me suffer. It was one of the most devastating experiences in my life.
- Global Health Trip to Guatemala my freshman year of college. I realized after going to Guatemala that I had always taken my access to health care for granted. Here I saw children who didn’t have basic health care. This made me want to become a physician so I could give more to people like those I met in Guatemala.
- Sorority involvement. Even though sorority life might seem trivial, I loved it. I learned to work with different types of people and gained some really valuable leadership experience.
- Poor grades in college science classes. I still regret that I did badly in my science classes. I think I was immature and was also too involved in other activities and didn’t have the focus I needed to do well. I had a 3.4 undergraduate GPA.
- Teaching and tutoring Jose, a child from Honduras. In a way, meeting Jose in a college tutoring program brought my Guatemala experience to my home. Jose struggled academically, and his parents were immigrants and spoke only Spanish, so they had their own challenges. I tried to help Jose as much as I could. I saw that because he lacked resources, he was at a tremendous disadvantage.
- Volunteering at Excellent Medical Center. Shadowing physicians at the medical center gave me a really broad view of medicine. I learned about different specialties, met many different patients, and saw both great and not-so-great physician role models. Counselor at Ronald McDonald House. Working with sick kids made me appreciate my health. I tried to make them happy and was so impressed with their resilience. It made me realize that good health is everything.
- Oncology research. Understanding what happens behind the scenes in research was fascinating. Not only did I gain some valuable research experience, but I learned how research is done.
- Peer health counselor. Communicating with my peers about really important medical tests gave me an idea of the tremendous responsibility that doctors have. I also learned that it is important to be sensitive, to listen, and to be open-minded when working with others.
- Clinical Summer Program. This gave me an entirely new view of medicine. I worked with the forensics department, and visiting scenes of deaths was entirely new to me. This experience added a completely new dimension to my understanding of medicine and how illness and death affect loved ones.
- Emergency department internship. Here I learned so much about how things worked in the hospital. I realized how important it was that people who worked in the clinical department were involved in creating hospital policies. This made me understand, in practical terms, how an MPH would give me the foundation to make even more change in the future.
- Master’s in public health. I decided to get an MPH for two reasons. First of all, I knew my undergraduate science GPA was an issue so I figured that graduate level courses in which I performed well would boost my record. I don’t think I will write this on my application, but I also thought the degree would give me other skills if I didn’t get into medical school, and I knew it would also give me something on which I could build during medical school and in my career since I was interested in policy work.
As you can see from Amy’s personal inventory list, she has many accomplishments that are important to her and influenced her path. The most influential personal experience that motivated her to practice medicine was her mother’s career as a practicing physician, but Amy was also motivated by watching her mother’s career evolve. Even though the death of her grandmother was devastating for Amy, she did not consider this experience especially influential in her choice to attend medical school so she didn’t write about it in her personal statement.
Amy wrote an experience-based personal statement, rich with anecdotes and detailed descriptions, to illustrate the evolution of her interest in medicine and how this motivated her to also earn a master’s in public health.
Amy’s Medical School Personal Statement Example:
She was sprawled across the floor of her apartment. Scattered trash, decaying food, alcohol bottles, medication vials, and cigarette butts covered the floor. I had just graduated from college, and this was my first day on rotation with the forensic pathology department as a Summer Scholar, one of my most valuable activities on the path to medical school. As the coroner deputy scanned the scene for clues to what caused this woman’s death, I saw her distraught husband. I did not know what to say other than “I am so sorry.” I listened intently as he repeated the same stories about his wife and his dismay that he never got to say goodbye. The next day, alongside the coroner as he performed the autopsy, I could not stop thinking about the grieving man.
Discerning a cause of death was not something I had previously associated with the practice of medicine. As a child, I often spent Saturday mornings with my mother, a surgeon, as she rounded on patients. I witnessed the results of her actions, as she provided her patients a renewed chance at life. I grew to honor and respect my mother’s profession. Witnessing the immense gratitude of her patients and their families, I quickly came to admire the impact she was able to make in the lives of her patients and their loved ones.
I knew I wanted to pursue a career in medicine as my mother had, and throughout high school and college I sought out clinical, research, and volunteer opportunities to gain a deeper understanding of medicine. After volunteering with cancer survivors at Camp Ronald McDonald, I was inspired to further understand this disease. Through my oncology research, I learned about therapeutic processes for treatment development. Further, following my experience administering HIV tests, I completed research on point-of-care HIV testing, to be instituted throughout 26 hospitals and clinics. I realized that research often served as a basis for change in policy and medical practice and sought out opportunities to learn more about both.
All of my medically related experiences demonstrated that people who were ‘behind the scenes’ and had limited or no clinical background made many of the decisions in health care. Witnessing the evolution of my mother’s career further underscored the impact of policy change on the practice of medicine. In particular, the limits legislation imposed on the care she could provide influenced my perspective and future goals. Patients whom my mother had successfully treated for more than a decade, and with whom she had long-standing, trusting relationships, were no longer able to see her, because of policy coverage changes. Some patients, frustrated by these limitations, simply stopped seeking the care they needed. As a senior in college, I wanted to understand how policy transformations came about and gain the tools I would need to help effect administrative and policy changes in the future as a physician. It was with this goal in mind that I decided to complete a master’s in public health program before applying to medical school.
As an MPH candidate, I am gaining insight into the theories and practices behind the complex interconnections of the healthcare system; I am learning about economics, operations, management, ethics, policy, finance, and technology and how these entities converge to impact delivery of care. A holistic understanding of this diverse, highly competitive, market-driven system will allow me, as a clinician, to find solutions to policy, public health, and administration issues. I believe that change can be more effective if those who actually practice medicine also decide where improvements need to be made.
For example, as the sole intern for the emergency department at County Medical Center, I worked to increase efficiency in the ED by evaluating and mapping patient flow. I tracked patients from point of entry to point of discharge and found that the discharge process took up nearly 35% of patients’ time. By analyzing the reasons for this situation, in collaboration with nurses and physicians who worked in the ED and had an intimate understanding of what took place in the clinical area, I was able to make practical recommendations to decrease throughput time. The medical center has already implemented these suggestions, resulting in decreased length of stays. This example illustrates the benefit of having clinicians who work ‘behind the scenes’ establish policies and procedures, impacting operational change and improving patient care. I will also apply what I have learned through this project as the business development intern at Another Local Medical Center this summer, where I will assist in strategic planning, financial analysis, and program reviews for various clinical departments.
Through my mother’s career and my own medical experiences, I have become aware of the need for clinician administrators and policymakers. My primary goal as a physician will be to care for patients, but with the knowledge and experience I have gained through my MPH, I also hope to effect positive public policy and administrative changes.
Paragraphs 1 and 2: Amy started her personal statement by illustrating a powerful experience she had when she realized that medical caregivers often feel impotent, and how this contrasted with her understanding of medicine as a little girl going with her mother to work. Recognition of this intense contrast also highlights her maturity.
P-3: She then “lists” a few experiences that were important to her.
Paragraph 4: Amy describes the commonality in some of her experiences and how her observations were substantiated by watching the evolution of her mother’s practice. She then explains how this motivated her to earn an MPH so she could create change more effectively as a physician than as a layman.
P-5: Next, she explains how her graduate degree is helping her to better understand the “issues in medicine” that she observed.
Paragraph 6: Then, an exceptional accomplishment is described, highlighting what she has learned and how she has applied it.
P-7: Finally, she effectively concludes her personal statement and summarizes the major topics addressed in her essay.
As you can see, her statement has excellent flow, is captivating and unusual, and illustrates her understanding of, and commitment to, medicine. Throughout her application entries and statement, she exhibits the personal competencies, characteristics, and qualities that medical school admissions officers are seeking. Her application also has broad appeal; reviewers who are focused on research, cultural awareness, working with the underserved, health administration and policy, teaching, or clinical medicine would all find it of interest.

Osteopathic Medical School Personal Statement
Example and Analysis #2
Medical School Personal Statement Example Background: This is a nontraditional applicant who applied to osteopathic medical schools. With a 500 and a 504 on the MCAT , he needed to showcase how his former career and what he learned through his work made him an asset. He also needed to convey why osteopathic medicine was an ideal fit for him. The student does an excellent job illustrating his commitment to medicine and explaining why and how he made the well-informed decision to leave his former career to pursue a career in osteopathic medicine.
What’s Good About It: A nontraditional student with a former career, this applicant does a great job outlining how and why he decided to pursue a career in medicine. Clearly dedicated to service, he also does a great job making it clear he is a good fit for osteopathic medical school and understands this distinctions of osteopathic practice..
Working as a police officer, one comes to expect the unexpected, but sometimes, when the unexpected happens, one can’t help but be surprised. In November 20XX, I had been a police officer for two years when my partner and I happened to be nearby when a man had a cardiac emergency in Einstein Bagels. Entering the restaurant, I was caught off guard by the lifeless figure on the floor, surrounded by spilled food. Time paused as my partner and I began performing CPR, and my heart raced as I watched color return to the man’s pale face.
Luckily, paramedics arrived within minutes to transport him to a local hospital. Later, I watched as the family thanked the doctors who gave their loved one a renewed chance at life. That day, in the “unexpected,” I confirmed that I wanted to become a physician, something that had attracted me since childhood.
I have always been enthralled by the science of medicine and eager to help those in need but, due to life events, my path to achieving this dream has been long. My journey began following high school when I joined the U.S. Army. I was immature and needed structure, and I knew the military was an opportunity to pursue my medical ambitions. I trained as a combat medic and requested work in an emergency room of an army hospital. At the hospital, I started IVs, ran EKGs, collected vital signs, and assisted with codes. I loved every minute as I was directly involved in patient care and observed physicians methodically investigating their patients’ signs and symptoms until they reached a diagnosis. Even when dealing with difficult patients, the physicians I worked with maintained composure, showing patience and understanding while educating patients about their diseases. I observed physicians not only as clinicians but also as teachers. As a medic, I learned that I loved working with patients and being part of the healthcare team, and I gained an understanding of acute care and hospital operations.
Following my discharge in 20XX, I transferred to an army reserve hospital and continued as a combat medic until 20XX. Working as a medic at several hospitals and clinics in the area, I was exposed to osteopathic medicine and the whole body approach to patient care. I was influenced by the D.O.s’ hands-on treatment and their use of manipulative medicine as a form of therapy. I learned that the body cannot function properly if there is dysfunction in the musculoskeletal system.
In 20XX, I became a police officer to support myself as I finished my undergraduate degree and premed courses. While working the streets, I continued my patient care experiences by being the first to care for victims of gunshot wounds, stab wounds, car accidents, and other medical emergencies. In addition, I investigated many unknown causes of death with the medical examiner’s office. I often found signs of drug and alcohol abuse and learned the dangers and power of addiction. In 20XX, I finished my undergraduate degree in education and in 20XX, I completed my premed courses.
Wanting to learn more about primary care medicine, in 20XX I volunteered at a community health clinic that treats underserved populations. Shadowing a family physician, I learned about the physical exam as I looked into ears and listened to the hearts and lungs of patients with her guidance. I paid close attention as she expressed the need for more PCPs and the important roles they play in preventing disease and reducing ER visits by treating and educating patients early in the disease process. This was evident as numerous patients were treated for high cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, and diabetes, all conditions that can be resolved or improved by lifestyle changes. I learned that these changes are not always easy for many in underserved populations as healthier food is often more expensive and sometimes money for prescriptions is not available. This experience opened my eyes to the challenges of being a physician in an underserved area.
The idea of disease prevention stayed with me as I thought about the man who needed CPR. Could early detection and education about heart disease have prevented his “unexpected” cardiac event? My experiences in health care and law enforcement have confirmed my desire to be an osteopathic physician and to treat the patients of the local area. I want to eliminate as many medical surprises as I can.

Texas Medical School Personal Statement Example and Analysis #3
Medical School Personal Statement Example Background: This applicant, who grew up with modest means, should be an inspiration to us all. Rather than allowing limited resources to stand in his way, he took advantage of everything that was available to him. He commuted to college from home and had a part-time job so he was stretched thin, and his initial college performance suffered. However, he worked hard and his grades improved. Most medical school admissions committees seek out applicants like this because, by overcoming adversity and succeeding with limited resources, they demonstrate exceptional perseverance, maturity, and dedication. His accomplishments are, by themselves, impressive and he does an outstanding job of detailing his path, challenges, and commitment to medicine. He received multiple acceptances to top medical schools and was offered scholarships.
What’s Good About It: This student does a great job opening his personal statement with a beautifully written introduction that immediately takes the reader to Central America. He then explains his path, why he did poorly early in college, and goes on to discuss his academic interests and pursuits. He is also clearly invested in research and articulates that he is intellectually curious, motivated, hard working, compassionate and committed to a career in medicine by explaining his experiences using interesting language and details. This is an intriguing statement that makes clear the applicant is worthy of an interview invitation. Finally, the student expresses his interest in attending medical school in Texas.
They were learning the basics of carpentry and agriculture. The air was muggy and hot, but these young boys seemed unaffected, though I and my fellow college students sweated and often complained. As time passed, I started to have a greater appreciation for the challenges these boys faced. These orphans, whom I met and trained in rural Central America as a member of The Project, had little. They dreamed of using these basic skills to earn a living wage. Abandoned by their families, they knew this was their only opportunity to re-enter society as self- sufficient individuals. I stood by them in the fields and tutored them after class. And while I tried my best to instill in them a strong work ethic, it was the boys who instilled in me a desire to help those in need. They gave me a new perspective on my decision to become a doctor.
I don’t know exactly when I decided to become a physician; I have had this goal for a long time. I grew up in the inner city of A City, in Texas and attended magnet schools. My family knew little about higher education, and I learned to seek out my own opportunities and advice. I attended The University with the goal of gaining admission to medical school. When I started college, I lacked the maturity to focus on academics and performed poorly. Then I traveled to Central America. Since I was one of the few students who spoke Spanish, many of the boys felt comfortable talking with me. They saw me as a role model.
The boys worked hard so that they could learn trades that would help them to be productive members of society. It was then I realized that my grandparents, who immigrated to the US so I would have access to greater opportunities, had done the same. I felt like I was wasting what they had sacrificed for me. When I returned to University in the fall, I made academics my priority and committed myself to learn more about medicine.

Through my major in neuroscience, I strengthened my understanding of how we perceive and experience life. In systems neurobiology, I learned the physiology of the nervous system. Teaching everything from basic neural circuits to complex sensory pathways, Professor X provided me with the knowledge necessary to conduct research in Parkinson’s disease. My research focused on the ability of antioxidants to prevent the onset of Parkinson’s, and while my project was only a pilot study at the time, Professor X encouraged me to present it at the National Research Conference. During my senior year, I developed the study into a formal research project, recruiting the help of professors of statistics and biochemistry.
Working at the School of Medicine reinforced my analytical skills. I spent my summer in the department of emergency medicine, working with the department chair, Dr. Excellent. Through Dr. Excellent’s mentorship, I participated in a retrospective study analyzing patient charts to determine the efficacy of D-dimer assays in predicting blood clots. The direct clinical relevance of my research strengthened my commitment and motivated my decision to seek out more clinical research opportunities.
A growing awareness of the role of human compassion in healing has also influenced my choice to pursue a career in medicine. It is something no animal model or cell culture can ever duplicate or rival. Working in clinical research has allowed me to see the selflessness of many physicians and patients and their mutual desire to help others. As a research study assistant in the department of surgery, I educate and enroll patients in clinical trials. One such study examines the role of pre-operative substance administration in tumor progression. Patients enrolled in this study underwent six weeks of therapy before having the affected organ surgically excised. Observing how patients were willing to participate in this research to benefit others helped me understand the resiliency of the human spirit.
Working in clinical trials has enabled me to further explore my passion for science, while helping others. Through my undergraduate coursework and participation in volunteer groups I have had many opportunities to solidify my goal to become a physician. As I am working, I sometimes think about my second summer in Central America. I recall how one day, after I had turned countless rows of soil in scorching heat, one of the boys told me that I was a trabajador verdadero—a true worker. I paused as I realized the significance of this comment. While the boy may not have been able to articulate it, he knew I could identify with him. What the boy didn’t know, however, was that had my grandparents not decided to immigrate to the US, I would not have the great privilege of seizing opportunities in this country and writing this essay today. I look forward to the next step of my education and hope to return home to Texas where I look forward to serving the communities I call home.
Final Thoughts
Medical school personal statement help & consulting.
If all this information has you staring at your screen like a deer in the headlights, you’re not alone. Writing a superb medical school personal statement can be a daunting task, and many applicants find it difficult to get started writing, or to express everything they want to say succinctly. That’s where MedEdits can help. You don’t have to have the best writing skills to compose a stand-out statement. From personal-statement editing alone to comprehensive packages for all your medical school application needs, we offer extensive support and expertise developed from working with thousands of successful medical school applicants. We can’t promise applying to medical school will be stress-free, but most clients tell us it’s a huge relief not to have to go it alone.
MedEdits offers personal statement consulting and editing. Our goal when working with students is to draw out what makes each student distinctive. How do we do this? We will explore your background and upbringing, interests and ideals as well as your accomplishments and activities. By helping you identify the most distinguishing aspects of who you are, you will then be able to compose an authentic and genuine personal statement in your own voice to capture the admissions committee’s attention so you are invited for a medical school interview. Our unique brainstorming methodology has helped hundreds of aspiring premeds gain acceptance to medical school.

JESSICA FREEDMAN, M.D., is a former faculty member and admissions committee member at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. She is the founder and chair of MedEdits Medical Admissions and author of the MedEdits Guide to Medical Admissions and The Medical School Interview which you can find on Amazon . Follow Dr. Freedman and MedEdits on Facebook and YouTube.
- Website Disclaimer
- Terms and Conditions
- MedEdits Privacy Policy

Medical School Diversity Essay Examples and Tips
- Cracking Med School Admissions
Diversity secondary essay questions are a common prompt in secondary medical school applications. Diversity essays are extremely open-ended and broad. Many premedical students struggle with this secondary essay prompt because it is broad. Each year, our Cracking Med School Admissions team receives hundreds of questions from applicants about how to write about diversity in your secondary essays? Our Cracking Med School Admissions team thinks you can use the broad nature of diversity essay prompts to your advantage! Use your response to your diversity essays as a way to discuss an aspect of your application you have not been able to elaborate on already in your other secondary essays for that specific school. Additionally, you can use diversity secondary essays to augment your awesomeness to admissions officers through discussing your passions in medicine and conveying your leadership experiences! If you want to read medical school diversity essay examples , skip down below!
This diversity essay medical school essay blog post will cover:
- What are medical school diversity essays?
- Sample diversity essay prompts from various medical schools
- Tips on how to write about diversity in your secondary essays
- FAQs about medical school diversity essays
- * Medical school diversity essay examples*
What are Medical School Diversity Essays?
Medical school diversity essays are questions on medical school secondary applications that applicants write as part of the medical school application process. Medical schools value diversity in their student bodies because it leads to a more dynamic learning environment where students can learn from each other and benefit from diverse perspectives and experiences. Additionally, medical schools want to recruit students who aspire to improve healthcare in different ways. For examples, some applicants’ strengths lie in research. Other applicants thrive in creating public health programs to improve community health. Still other applicants are interested in narrative medicine and want to inspire others through future books they write about the human condition.
Diversity essays provide an opportunity for applicants to showcase their unique personal experiences, cultural background, educational experiences, extra-curricular activities, and perspectives. Applicants can express how they will contribute to the diversity of the medical school community.
As stated earlier, diversity essays are broad. Applicants are asked to describe how their culture background, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, race, gender, sexual orientation, religion, or any other characteristic that defines them has shaped their life experiences and perspective.
Topics you can discuss on your medical school diversity essay include:
- Personal background – ethnicity, socioeconomic status, race, gender, sexual orientation, or religion
- Perspectives from your cultural background
- Family background and life circumstances with regards to upbringing
- Adversity and challenges
- Healthcare experiences that reflect your motivation to pursue a career in medicine
- Unique non-healthcare passions and activities
- Courses that inspired you
- Majors and minors in college
- Summer internships
- Gap year activities
- Post-graduate degrees
- Personal qualities, including leadership skills and your personal strengths
Remember that secondary application essays should complement your primary application essays.
Medical School Diversity Essay Prompts
Diversity secondary essay questions may be phrased in a multitude of ways. Diversity essays have a wide range of character limit; some medical schools only allow 1,000 characters while other medical schools have no word limit. Additionally, some diversity secondary prompts are optional while other diversity secondary prompts are mandatory.
To better understand what diversity essays are and how broad they can be, let’s take a look a sample medical school diversity essay prompts.
Harvard Medical School Diversity Essay Prompt
- If there is an important aspect of your personal background or identity, not addressed elsewhere in the application, that you would like to share with the Committee, we invite you to do so here. Many applicants will not need to answer this question. Examples might include significant challenges in access to education, unusual socioeconomic factors, identification with a minority culture, religion, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation or gender identity. Briefly explain how such factors have influenced your motivation for a career in medicine.
As listed in the Harvard Medical School prompt, you can write about:
- Demographic variables, such as ethnic, racial, social, gender, religious, etc. diversity that have substantially shaped your life or your passion for medicine
- Personal circumstances/hardships that have shaped your growth
- A specific passion that you have cultivated and pursued over time (for example, sexual health, LGBTQ advocacy, etc.) You should further write about how this passion/activity that you have pursued has allowed you to develop qualities that you believe contribute to your individual diversity.
Note: You basically can write about anything.
In essence, these diversity secondary essay questions are asking you how your unique qualities/experiences will serve their medical community AND will help make you an excellent physician.
Let’s take a look and examine other medical school secondary essay prompts:
Yale School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Yale School of Medicine values diversity in all its forms. How will your background and experiences contribute to this important focus of our institution and inform your future role as a physician?
Read a Yale medical school diversity essay example below!

The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Optional: The (Johns Hopkins) Admissions Committee values hearing about each candidate for admission, including what qualities the candidate might bring to the School of Medicine if admitted. If you feel there is information not already addressed in the application that will enable the Committee to know more about you and this has influenced your desire to be a physician, feel free to write a brief statement in the space below. You may address any subject you wish, such as being a first generation college student, or being a part of a minority group (whether because of your sexual orientation, religion, economic status, gender identity, ethnicity) or being the child of undocumented immigrants or being undocumented yourself, etc. Please note that this question is optional and that you will not be penalized should you choose not to answer it.
A special point to notice here: This essay is optional. See our thoughts below in the FAQ section as to whether you should write this essay or not. Also, read an example Johns Hopkins diversity essay below!
And here are even more secondary essay prompts from various schools….
Baylor College of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Indicate any special experiences, unusual factors or other information you feel would be helpful in evaluating you, including, but not limited to, education, employment, extracurricular activities, prevailing over adversity. You may expand upon but not repeat TMDSAS or AMCAS application information. This section is mandatory. Please make sure you submit an essay or your application will not be reviewed by the committee.
Drexel University College of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- What else do you feel is important for us to know about you? You can use this space to highlight something not addressed in your application, including new experiences not in your AMCAS application. You can also talk about how COVID -19 impacted you. For example, it may have caused disruptions or changes in your plans. If there is something you would like to share regarding how this event impacted you, share that information here.
Duke University School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Tell us more about who you are. You may provide additional information that expands your self-identity where gender identification, racial and/or ethnic self description, geographic origin, socioeconomic, academic, and/or other characteristics that define who you are as you contemplate a career that will interface with people who are similar AND dissimilar to you. You will have the opportunity below to tell us how you wish to be addressed, recognized and treated.
- Optional: In addition to the broad categorization of race, ethnicity, geographic origin, socioeconomic status as provided through your AMCAS application, you may use the text box below to provide additional clarifying information that may reflect the impact of any of these parameters on your development thus far as well as the impact that these may have had on your path to a career in medicine and your plans for the future.
- No word limit & Optional: Please let us know of any additional information that you would like us to consider while reviewing your application.
Special note: Duke University School of Medicine has THREE diversity essays. Applicants can really leverage this an opportunity to give a holistic and varied view about themselves!
Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Please share with us something about yourself that is not addressed elsewhere in your application and which could be helpful to the Admissions Committee as we review your file.
Georgetown University School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Is there any further information that you would like the Committee on Admissions to be aware of when reviewing your file that you were not able to notate in another section of this or the AMCAS Application?
George Washington University School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- What makes you a unique individual? What challenges have you faced? How will these factors help you contribute to the diversity of the student body at GW?
Stanford University School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- The (Stanford) Committee on Admissions regards the diversity (broadly defined) of an entering class as an important factor in serving the educational mission of the school. The Committee on Admissions strongly encourages you to share unique, personally important and/or challenging factors in your background which may include such discussions as the quality of your early education, gender, sexual orientation, any physical challenges, and life or work experiences. Please describe how these factors have influenced your goals and preparation for a career in medicine and may help you to uniquely contribute to the Stanford learning environment.
- Optional: Please include anything else that will help us understand better how you may uniquely contribute to Stanford Medicine?
Note: Stanford University School of Medicine has multiple essays where you can write about your “diverse” experiences. Other than Stanford secondary essay questions about how you want to take advantage of Stanford’s curriculum, the rest of the Stanford University School of Medicine essay prompts are very open-ended!
The Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- How will your unique attributes (e.g., cultural or socioeconomic background, lifestyle, work experiences) add to the overall diversity of the Alpert Medical School community?
Tufts University School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Do you consider yourself a person who would contribute to the diversity of the student body of Tufts University School of Medicine ?
Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Feinberg’s mission is to train future leaders in medicine who will serve their patients, communities and society. Describe one specific interest in medicine and how FSM, located in Chicago which is one of the most culturally diverse cities in the country, will help you achieve this professional goal
- The Feinberg School of Medicine values diversity as a measure of excellence. We define diversity as the totality of the characteristics and experiences of our students. We believe that a diverse student body improves the educational environment and the ability of our graduates to serve an increasingly diverse patient population. Narrative Descriptions: Everyone has their own narrative. Please provide more detail about how your experiences would enrich the Northwestern community.
Note: Northwestern University has TWO diversity essays! In the first essay prompt, your essay topic should be more related to healthcare and medicine. But, in the second prompt, you can write about anything!
Washington University School of Medicine Secondary Application Diversity Essay Prompt
- Optional: Is there anything else you would like to share with the Committee on Admissions?
How to Write About Diversity in Your Secondary Essays
Our goal at Cracking Med School Admissions when helping students strategize and edit their secondary application essays is to always help students stand out. Yes, that means, we want students to stand out in every single essay, including this open-ended diversity essay question.
It is incredibly important to do THREE THINGS when it comes to your diversity essays:
1. Include anecdotes.
You want to make sure that you show your readers how specific experiences and demographic factors have shaped you as an individual, rather than tell them.
Examples of anecdotes include:
- Demographics – if you are going to discuss something from your demographic background, don’t just say where you are from. SHOW your culture through anecodotes and stories. For examples, premedical students in the past have talked about cooking a cultural meal with their grandparents. Other medical school applicants have talked about a grandparent’s or parent’s experience with the American healthcare systems.
- Challenges – Give specific instances where you faced a challenge. What was the challenge? How did you overcome the challenge?
- Patient care stories – Give anecodotes about memorable patient experiences. What were your interactions with a patient? Why was the patient in the hospital? What happened? What are your reflections about the human experience and human condition?
- Leadership – give a specific challenge you faced as a leader or a specific event that you organized. Alternatively, you can talk about a time when you led a team or founded an organization / initiatives.
2. Connect your stories to medicine.
How will your experiences help you become a better doctor? That is the question that is relevant to almost every single prompt regardless of if it is explicitly worded as such or not. You absolutely must discuss how your past experiences and the qualities you have cultivated through these experiences will help you in medicine. For example, you can illustrate how your experiences with patient advocacy or within medical teams will help you as a future doctor; it is a good idea to include particularly challenging patient encounters and how you grew from such experiences. You should further write about leadership, teamwork, resilience, and other qualities learned from your experiences—make the explicit connection to how you will use these qualities as a doctor.
3. Tailor your diversity essays TO EACH MEDICAL SCHOOL.
Connect your stories and experiences to what you will do at the medical school. You can talk about how you want to do research with a specific professor or work with a specific club to pioneer a new initiative. Talk about how your presence at the medical school will enhance the community.
Different schools have different strengths. You must do your research on each school that you are applying to, and try to connect your experiences to the schools’ strengths.
Moreover, different schools have different needs. If there is a specific problem in the regional community that the school belongs to that you feel you are poised to solve (for example, homeless health, refugee health, etc.), you can further tailor your essay to a medical school by making that connection.
Be creative to show EACH INDIVIDUAL medical school that you would be a standout contributor to their community.
Frequently Asked Questions about Diversity Secondaries
We want to share with you frequently asked questions about diversity secondaries. Our responses below are here to help you strategize your secondary essay topics.
Again, our goal is to help you STAND OUT in every single part of your application, including your secondary applications!
Remember, the point of the diversity essay is to help you discuss the strengths of your application. Whatever you write should complement the other responses and other essays in each school’s secondary application. Each applicant will have his or her own unique strengths, stories, and experiences, so if you have any questions, do not hesitate to contact Dr. Mediratta and Dr. Rizal , who literally read thousands of secondary essays each year!
What is the biggest mistake you’ve seen on diversity essays?
This is our biggest advice for medical school diversity essays:
Applicants often think that they have to write about their personal background, specifically culture, ethnicity, race, and/or socioeconomic status. While there are some secondary applications that ask for specifically those topics, most diversity essay prompts are broad. We often encourage students to talk about other extra-curricular activities and passions UNLESS they their cultural background plays a significant role in their pursuit towards a career in medicine.
You can think about the following questions:
- What will you bring to the medical school class?
- How will you change healthcare (and how have you already started on that journey)?
- What are your strengths as a person?
Can the topic of my secondary essay be the same as topics I wrote about in my primary application personal statement?
Yes! Absolutely! However, we would suggest that you write about a different angle.
For example, if in your primary application personal statement you talked about your research and what you did in your research, in your diversity essay medical school, talk about a challenge you faced in your research project. Or, talk about a different study or research lab your were involved with. Finally, premeds may write about teaching and mentoring younger individuals in their labs, again, to give a different angle in their diversity essays for medical school.
Can I “recycle” or “reuse” my diversity essay response for multiple schools?
Yes! What we typically advise students is to use most of the essay as a template or starting point. And then, tweak the essay as necessary based on the number of words or characters available. If applicable, you can tailor the diversity essay towards each school.
Many students will have 2-3 “diversity essay medical school topics and essays” that they draw from. And, depending on the medical school and other prompts, they will pick and choose which essay to use.
Can I talk about a challenge in my diversity essay?
Definitely. Make sure you did not use this essay for another essays like a “challenge” prompt for that specific school’s secondary. Discuss how overcoming the challenge has helped you grow, and what you will contribute to the medical school student body.
Can I talk about how COVID-19 impacted me and my application in my diversity essay?
Typically, talking about COVID-19 challenges isn’t the strongest topic for the diversity essay. But, if you faced a challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic and took action to improve society or healthcare, then you can definitely use those experiences! Also, another secondary application strategy to consider: make sure there is not another prompt that allows you to talk about COVID.
You can read about an ICU expererience during COVID down below in our diversity secondary essay examples!
Medical School Diversity Essay Examples
You can include multiple experiences in one diversity secondary essay, but make sure that your transitions are seamless. Furthermore, in such essays, you want to pay attention to your paragraph breaks to further communicate your strong attributes and diverse experiences with maximum impact. Remember—make it as easy as possible for your reader to understand your writing and to visualize you as a strong physician.
Below are 2 medical school diversity essay examples answers from a student who then received an interview at both Yale University School of Medicine and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Yale Medical School Diversity Essay Example
Prompt: Yale School of Medicine values diversity in all its forms. How will your background and experiences contribute to this important focus of our institution and inform your future role as a physician?
When I first arrived at UPenn, I was made acutely aware of an issue that plagued our campus community: an extensive culture of sexual assault. I felt compelled to act in opposition. I joined Abuse and Sexual Assault Prevention (ASAP) in my first semester and later became a Sexual Assault Counselor.
A lesson I learned as Co-Chair of ASAP is that leaders must critically examine their communities to meet unfulfilled needs. I transformed our programming to better serve survivors with an intersectional lens. I held a workshop at UPenn with a community leader from the Movement for Black Lives and discussed how racial justice must inform our advocacy. This focus was integrated into our Take Back the Night advocacy event, as we spoke at length about how to serve the needs of black and trans survivors. I piloted the expansion of this event to being held with eight other schools.
Moreover, the Title IX reporting process at UPenn is quite complex and not readily accessible. Given the number of sexual trauma survivors at our university, I worked to clarify this process for our student community by directing an educational campaign, to be released in the next academic year. I played the leading role in a meeting with the Title IX Coordinator and Associate Vice President for Equity, as well as Directors and Associate Directors from various UPenn Centers—we discussed my vision for the project and dove into specifics of the campaign. I enjoyed collaborating with individuals who direct initiatives and policy changes for the safety of our campus community of 25,000 students.
As a physician, I will continue to lead the movement to build a world free of sexual violence and gender inequity. I strive to integrate clinics that offer primary, psychiatric, and gynecological care for sexual trauma survivors into national healthcare. These clinics will also offer forensic examinations led by Sexual Assault Forensic Examiners (SAFE), as well as social and legal support. By providing a centralized location for all of the care needs of survivors, I want to limit the difficulties of navigating the healthcare system often faced by this vulnerable population. I would love to work with Dr. Jubanyik to drive this initiative forward and promote health equity for survivors at Yale. Furthermore, statewide tracking of SAFE centers is inconsistent. I want to generate a national database to consolidate these programs and help survivors better access them. I would love to extend my advocacy for survivors as a member of the student group, Prenatal Partners, to be able to advocate for a trauma-informed approach to medical care for expectant mothers.
As a medical student and physician, I am eager to leverage my skill in storytelling to inform and strengthen healthcare. I believe that compelling stories can be important catalysts for change, particularly in the context of my aspirations to serve women and survivors. I would love to work with Dr. Reisman to write a journalistic novel on women’s sexuality and resilience deriving from my longitudinal patient relationships.
Johns Hopkins Medical School Diversity Essay Example
Optional: The Admissions Committee values hearing about each candidate for admission, including what qualities the candidate might bring to the School of Medicine if admitted. If you feel there is information not already addressed in the application that will enable the Committee to know more about you and this has influenced your desire to be a physician, feel free to write a brief statement in the space below. You may address any subject you wish, such as being a first generation college student, or being a part of a minority group (whether because of your sexual orientation, religion, economic status, gender identity, ethnicity) or being the child of undocumented immigrants or being undocumented yourself, etc. Please note that this question is optional and that you will not be penalized should you choose not to answer it. 2500 characters
As a Neuro/COVID-19 ICU clinical volunteer operating at the center of the pandemic crisis, I encouraged patients who were suffering the worst of COVID-19 symptoms through our patient call bell system.
In public health emergencies, I understand how patients can feel detached from and misunderstood by their healthcare systems, causing them to refuse treatments or preventive measures like vaccines. I once had a conversation with an ICU patient who was approaching discharge and refusing to wear a mask. My team respectfully asked questions and listened to his supplication of answers and reasoning. I knew that convincing someone to let go of an entrenched opinion would be difficult. But I tried as hard as I could and felt him soften in conversation. He ultimately wore his mask. I left this interaction with a better understanding of how to approach and care for an individual with a radically different perspective from my own.
I take seriously my responsibility to listen carefully to my patient’s concerns and assure them that recommended measures are medically sound. To promote patient trust in medicine and to address health disparities exacerbated by the pandemic, I will work to leverage community partnerships, as I have done as an advocate for survivors. I will listen to what specific communities need and tailor health care delivery accordingly.
Throughout the coronavirus surge, I was able to have a more hands-on role with neurological care in the ICU. After caring for an unconscious patient with moyamoya disease and two ischemic strokes in the Neuro/COVID-19 ICU and learning of her poor prognosis from her physician, I pored through the medical literature. I hoped that studies would reveal something different. The patient’s antiplatelet therapy was proving ineffective. Yet surgery was not a safe option as her unstable moyamoya carried greater postoperative ischemic complication risk. I struggled, unable to find an alternative. Thereafter, I wrote “Between you and me,” excerpted below.
Her eyes are closed, a tube connecting her to her life.
They are draining her cerebrospinal fluid and it should
be yellow. But it’s pink. Like watermelon juice.
The act of writing brought me peace and helped me come to terms with my patient’s suffering.
Nikita’s work in the ICU was featured in U.S. News , “ What Premeds Can Learn in Intensive Care Units ”
We hope this blog post was a great starting point in giving you ideas for how to write a medical school diversity essay.
Check out our other helpful resources:
- COVID-19 Secondary Essay Prompts
- How to Write “Why This Medical School?” Secondary Essays
- Medical School Secondary Essay Editing
Contact Us. We're Excited to Help!
- Leave Us a Message or Question!
Start typing and press enter to search
Successful Harvard Medical School Essays | 2023
With a consistently competitive pool of applicants submitting essays to top medical schools each year, it is essential to gain a high-level understanding of what a successful application reads like. Browse through our list of successful medical school applications below from students who were accepted to elite universities and hear from expert college consultants on what made these pieces a success.

...and more!
Andrew's Essay

International Medical Aid (IMA) is a leading provider of pre-med shadowing study abroad programs and medical school admissions consulting services. Recognized for our unwavering commitment to student success, IMA helps aspiring doctors navigate the complex admissions process and offers invaluable, real-world clinical experience in diverse healthcare settings around the world.
Our pre-med shadowing study abroad programs offer students the unique opportunity to gain firsthand insights into global health, broaden their cultural competencies, and strengthen their medical school applications. These programs are designed to immerse students in foreign healthcare systems and give them a practical understanding of global medicine, all under the supervision of experienced professionals.
In addition to our study abroad programs, IMA offers comprehensive medical school admissions advising. Our team of seasoned consultants, including former admissions committee members from top medical schools, provides personalized guidance at every step of the application process. From crafting compelling personal statements to mastering medical school interviews, we equip students with the tools and strategies necessary to stand out in the highly competitive admissions landscape.
At International Medical Aid, we are passionate about helping the next generation of healthcare professionals reach their goals. With our global perspective, deep industry expertise, and commitment to each student's success, IMA is your partner on the journey to a fulfilling career in medicine.
Successful Harvard Medical School Essay
I vividly recall the surge of emotion and chills that ran down my spine as I wandered through the free health clinic in a rural, impoverished Salvadoran town. I met a kind nurse who cared for hundreds of patients by herself. She showed me her two tiny examination rooms, both littered with overly used equipment. It was sobering, but inspiring. No experience has been more impactful than witnessing the need for accessible, quality healthcare, especially in an area so close to my heart. Twenty-two years ago, my family adopted me from El Salvador. Over that time, they showed me how to care about people, keep a sharp focus on my goals, and always deliver on my word. Their teaching by example, coupled with the realization of just how fortunate I am, has led me to my passion. I want to spend the rest of my life helping others improve theirs, and believe that becoming a physician is how I’ll do it.
I want to spend the rest of my life helping others improve theirs, and believe that becoming a physician is how I'll do it.
My decision to pursue medicine began with a great deal of pain. It was the end of my eighth grade basketball season, in the semi-finals of a tournament. During the third quarter, I stole the ball from the other team, and dribbled up the court on a fast break. As I elevated for a layup, an opposing player charged into my body. SNAP! I immediately felt severe discomfort running up my leg, and knew something was very wrong. As the trainers helped me off the court, I watched the swelling around my ankle continue to grow. My first trip to the emergency room resulted in an inconclusive diagnosis, and a scheduled appointment with an orthopedic surgeon.
The next day, I was diagnosed with a fractured ankle, which unfortunately meant my season was over. The orthopedic surgeon’s vast knowledge of anatomy and physiology and explanation of my injury using X-rays captivated my attention, and sparked my interest in medicine. Over the next six weeks, I rehabilitated my ankle and returned to sports as healthy and quickly as possible. Grasping the impact of a medical profession, I set out to become a physician.
Setting goals was a habit growing up. Academics and sports were my primary focus, and in grade school, I dreamt of playing a varsity sport and set a goal in fourth grade to graduate as valedictorian of my class. These goals shaped the next eight years of my life, as I learned to balance schoolwork with playing sports. I was determined to excel inside and outside of the classroom, and worked very hard.
Throughout high school, I strove for academic and athletic excellence. Through dedication and perseverance, I started for three years in basketball and baseball, was named captain of both teams as a senior, led both teams to playoff appearances, and graduated as class valedictorian. While my academic and athletic experiences were very fulfilling, the highlight of my time in high school was sharing my love for sports and academics with children. Every summer, I volunteered to help my coaches run camps for kids in kindergarten through eighth grade. During these camps, I taught the fundamentals of the game and emphasized the importance of determination, commitment, and teamwork. Coaching the kids was extremely rewarding, and allowed me to develop an even temper and positive attitude, even in stressful situations. This experience also helped me discover a strong interest in teaching that I hope to develop as a physician.
In college, I’ve had extensive shadowing experience. One unforgettable moment came in the emergency room when a patient coded. I watched as physicians and nurses urgently tried to stabilize the patient, to no avail. I learned two challenging lessons from the patient’s passing: medicine affects patients, their families, and healthcare professionals equally, and witnessing death is unavoidable when working in medicine. These lessons, among many others learned through my shadowing experiences, have provided me with invaluable insight into the daily life of physicians and surgeons, as well as the demands and rewards medicine offers.
Medicine affects patients, their families, and healthcare professionals equally, and witnessing death is unavoidable when working in medicine.
Although my shadowing experience was enjoyable, I desired to learn more about the aspect of medicine that shapes clinical practice–research. Through my research experiences, I discovered the intricate relationship between research and clinical medicine. As I spent a summer studying tendon development with some of the world’s brightest minds in Boston, the importance of collaboration and perseverance in effectively translating research from bench to bedside became clear. Now, I hope to combine my love for medicine with my research interests to broaden the scope of my work. This approach will be personally fulfilling while enabling me to make a valuable contribution to biomedical science. Life experiences shape us as individuals. An unfortunate sports injury sparked my interest in medicine, while clinical and research experiences and a visit to a clinic in my birth country further strengthened my ambition. Ultimately, I hope to return to that Salvadoran clinic as a medical student and physician to provide quality healthcare to those in need. I’m excited about moving forward and the opportunities that lie ahead.
Professional Review by International Medical Aid
This great example of the AMCAS personal statement makes the thesis clear from the start which is that of the writer’s wish to ensure “good health” by “doing more”.
The narrative presents this thesis through specific examples that gradually broaden in scope: from “my little brother” to “the stranger in the grocery storey.” It also expands across social segments, when the writer finds myriad meanings for “good health” across “countries, cultures and individuals”.
Technical terms are used to show knowledge of medical practices while also revealing curiosity and aptitude for clinical research.
The second part of the thesis, which is to “do more”, is presented through two compelling arguments: that research and medicine are always evolving, and that there is always more to be done. Technical terms are used to show knowledge of medical practices while also revealing curiosity and aptitude for clinical research.
The essay then shifts to how being an ‘extraordinary physician’ involves being empathetic and paying attention to socioeconomic factors. The generalization that medicine is both a science and an art since it touches humans is well-situated in contextual examples of underrepresented groups in Guatemala and Kenya.
The wish to “do more” reveals the writer’s growth mindset as well as a passion for medicine in simple but effective words that befit the personal statement.
Keizra’s Essay

Every future doctor experiences some level of self-doubt when applying to medical school. We empower aspiring physicians to identify the unique qualities that make them great doctors of the future. Our MD admissions consultants help applicants like you weave these qualities into a compelling narrative in every aspect of the medical school application. Using a proven methodology that has been tried and tested over 15 years with more than 1000 successful applicants, we help you approach the admissions process with the confidence to get into your ideal medical school.
Interested in dental school or PA school instead? We can help you get there too.
I sat in the US Senate’s Hart Building, memo in hand, nervously awaiting my chance to explain the complexities of an FDA draft guidance to staffers working on the Senate counterpart to the 21st Century Cures bill. This FDA draft guidance would, if finalized, increase the regulatory burden on laboratories developing genetic tests. Although nearly all the scientists I interviewed felt this guidance would unreasonably slow the integration of Next Generation Sequencing genetic tests into diagnostics, I learned that their story ignored the many inadequacies which currently plague genetic testing.
As I began to explain my memo, I thought of the first time I watched a doctor offer a genetic test to a patient. Dr. Patel, a geriatric psychiatrist, was offering a test to help determine which drugs might be most effective for her schizophrenic patient. This test seemed to offer an alternative to a frustrating experience that many patients face: trying various medication regimens to see which works best. The patient’s excitement was palpable, but I couldn’t help but recognize the sad truth that for this patient, a person of color, the diagnostic tools could be less than perfectly reliable. In a world where 80% of the DNA in genetic databases is European, I struggled knowing that these tests are significantly less effective for people of color than for individuals of European descent.
These hidden inequalities in emerging diagnostic tools, when combined with existing inequalities in access to care, have solidified my desire to work as a physician to care for marginalized individuals. As a doctor, I hope to help vulnerable patients access the care they desire while treating them with the respect they deserve, a goal I have looked to advance prior to medical school. During my first two years at Duke, I had countless conversations with my peers about the pressure they felt to embody “effortless perfection.” This expectation, whether self or culturally imposed, created a stigma around speaking out about one’s struggles, fears, and insecurities, which in turn led to a wariness towards accessing campus mental health resources. While Vice President of Equity and Outreach on Duke Student Government, I made combating “effortless perfection” my priority. I felt it was time to give students a space to discuss their struggles and make mental health resources more accessible. These experiences led me to create Duke’s first Mental Health Awareness Month. One particular event, a panel for students suffering from mental illness to discuss their experiences, was attended by over 100 students. Through the month’s programming, students were able to find strength and support in the recognition that they were not alone in their struggles. As a physician, I hope to leverage this understanding to create a space in my exam room where I work to understand and affirm patients’ experiences in the hopes that I can make their illnesses less isolating.
I hope to leverage this understanding to create a space in my exam room where I work to understand and affirm patients' experiences.
Though it was extraordinarily fulfilling to create awareness of accessible mental health resources, I also sought to combat another impediment to care: access. This year, I have worked to provide abortion access to women who cannot afford their procedures through the DC Abortion Fund. As a case manager, I work with women in all stages of their abortion access process. For some, I simply help them close the gap in their funding. For others, I work with them from start, finding a clinic, all the way to finish, helping to fund the procedure. This work has revealed to me the mountain of circumstances that vulnerable women seeking funding for abortion face. Every time I call a patient, the first question I ask is, “Can I leave a voicemail on this phone and can I identify myself?” This question is a constant reminder that for many of these women, accessing this care is an act of resistance against circumstances outside of their control like homelessness, domestic abuse, and poverty.
One of the patients I aided, Ms. E, found out she was pregnant while at an urgent care appointment for debilitating anxiety. She only learned about the Fund because her physician sat with her in the exam room helping Google resources for abortion care. This physician recognized that without adequate resources, her patient would not have the agency to choose her next steps. As a physician, I will view it as my highest responsibility to understand patients’ lives and circumstances. Without understanding the systemic barriers many patients face, I do not believe one can optimally care for a patient. Even when a patient has access to care, I know that treating vulnerable patients demands cultural understanding. While shadowing Dr. Lo, a plastic surgeon in Philadelphia, I saw first-hand how physicians can utilize their knowledge to create a safe space. I watched Dr. Lo work with a transgender-identifying patient seeking cosmetic surgery as a part of her gender confirmation process. Dr. Lo treated this patient with dignity and respect through the simple act of using her correct pronoun, ignoring the fact that her birth name and gender were associated with her insurance. This simple act of recognizing a patient’s true identity reminded me of the vital need for good doctors: I can only hope to one day be among their number.
Professional Review by Admissions Helpers
Several features make Keizra’s essay strong and engaging. First, the essay contains a unifying theme that gives the reader a clear sense of the applicant’s motivations. Using different examples and anecdotes throughout the essay, Keizra demonstrates their commitment to working with “marginalized” and “vulnerable” individuals.
Keizra demonstrates their commitment to working with marginalized and vulnerable individuals.
This essay also demonstrates an awareness of some of the key challenges in today’s healthcare system. Specifically, Keizra discusses inequity in genetic testing for people of color, the impact of social determinants on access to critical healthcare services like abortion, and the need for inclusivity for diverse patients including members of the LGBTQIA+ community. The strength in this discussion is that Keizra directly connects each challenge to their lived experiences.
Finally, each of the different ideas presented in the essay are explicitly tied to the applicant’s desire to become a physician, allowing the reader to understand why and how their experiences have shaped their motivations. When writing about genetic testing, mental health services for college students, and caring for Ms. E, Keizra’s essay does an excellent job highlighting the kind of doctor they aspire to be.
While the essay is strong overall, there is opportunity for improvement. The explanation Keizra offers about why they want to be a physician (in the 3rd paragraph) could be further developed. In particular, one can’t help but wonder why Keizra wants to fight the inequalities as a physician and not through another career such as politics or public health? The reasons why Keizra wants to practice clinical medicine are not clearly articulated. The essay also ends fairly abruptly, failing to give the reader a cohesive and memorable closing argument. Ideally, a personal statement ends by providing reflections on the key ideas presented and pulling everything together with a powerful summative statement. This is difficult with limited space but could have nevertheless been achieved by rewording and omitting certain details in other areas of the essay.
Mark's Essay

Our Premedical Mentorship Program and Admissions Milestones serve as your personal roadmap to medical school, guiding you through the application process.
Our curriculum, divided into clear Milestones and specialized workshops, streamlines the extensive writing and high-pressure interviews intrinsic to medical school applications. We replace the cycle of writing and rewriting with a systematic framework, assisting you at every stage, from brainstorming to refining your final narrative.
Once enrolled in our programs, you gain access to our open booking system, allowing you to schedule one-on-one meetings with our Advocate Team at any time. We dedicate hundreds of hours to understanding your unique story, strengths, and aspirations, which informs our guidance and helps you craft a standout narrative for the competitive medical school admissions process. This approach has led to a 100% acceptance rate among our program graduates.
Ready to start your journey? Visit our website to schedule an introductory conversation.
“You have all the time.”
"Jay" was an advanced heart failure patient, unsure whether to continue treatment. But he needed to make a decision quickly. His EKG read “ventricular tachycardia.” Dr. D, though, saw the situation differently: Jay had “all the time.”
I analyze conversations like this in the LAB NAME Lab, where we study patient-physician communication, trying to understand what it means to provide patient-centered care. My research begins with the question: What is interesting in this encounter? In this interaction, Dr. D’s remark—“you have all the time”—caught my eye. It didn’t make sense. Jay’s arrhythmia was potentially life-threatening: he had no time. Surely, Dr. D, a cardiologist, knew this. And while Dr. D was personable in his other encounters with patients, he had never prioritized talking over treating. Why then, with Jay, did he ignore the “medical” side of medicine? At the time, I thought patient care revolved around somatic intervention. I was an EMT, after all. My job was to save people: if someone was bleeding, I didn’t stop to chat. I wrapped their bleed.
However, months later, my perception of medicine slowly began to change. Working as an EMT, I was dispatched to “Leo.” UNIVERSITY NAME staff had dialed 911 as he was heavily intoxicated. Immediately, Leo announced that he was fine; “You can leave,” he said to me. The situation seemed strange, though: alcohol by himself on a Monday afternoon? I thought: Should I ask Leo why he was drinking? But, perhaps, Leo was unable to be vulnerable around all the strangers in their uniforms. Hesitantly, I asked my partner and the mass of firefighters to step outside. I thought I could get Leo to open up. I recall sitting at eye level with him, considering what to say, aware of everyone outside, unsure if I was wasting their time. But in the end, I just talked—student to student. I described my life: how it felt to be away from family; how I missed home. Leo said nothing; so I kept speaking, conscious of myself. There was more silence, but then he replied, “I miss home too.” I waited for more; and Leo continued, “I need help.”
Our ability to talk—student to student, not EMT to student—allowed us to be honest with each other.
My interaction with Leo was at odds with my own understanding of medicine at that point; not once did I offer him an assessment of his blood pressure or his multicolored vomit. But had I done those things—focused on Leo’s physical condition—our encounter might have ended differently. I may never have discovered his intent to commit self-harm. Leo chose to be open with me, I think, because he trusted me, because I was open with him. Our ability to talk—student to student, not EMT to student—allowed us to be honest with each other. A disconnect between Leo and me would have failed both to address the root of his problem and to treat him as more than a brief emergency.
Now, I think that I better understand Dr. D’s remark to Jay. Maybe, he sought to humanize Jay, to reinforce his agency as a patient in a place that dealt with his physical ailments. Jay’s choice would have implications for the rest of his life. Perhaps, Dr. D wanted Jay to know that he was the decision-maker, that he controlled his own future. To Dr. D, the other aspect of medicine—the human side—was just as important as all the medications and IVs and drugs and shocks. I’ve begun to see that a physician’s work is stereoscopic. There is the intriguing and challenging human element, the opportunity to form meaningful relationships with patients. Then there is the somatic aspect, the chance to treat difficult medical conditions. I am drawn to medicine because of this duality.
As a physician, I’d like to develop my own ability to simultaneously practice the technical and personal elements of medicine. I think that patient-centered care might give my patients more than a fixed knee or a lower heart rate. Hopefully, they would feel healed, helped, respected—not as if I were just interested in fixing their physical ailments. I also think I’d enjoy medicine more if I could connect with my patients: talk to them as people, not just patients.
But, through the LAB NAME Lab, I’ve seen how difficult it can be to combine the objective and human sides of medicine. In patient-physician encounters, one of these two sides is often left out—it is hard to ask patients about their dogs when their livers are failing. Moreover, I’m not sure I can deconstruct Dr. D’s ability to communicate with patients like Jay: put it into a single competency that all doctors must master. It isn’t just empathy, honesty, or authenticity. I might describe it as humanity, the ability to talk to others without a machine-produced script. However, textbooks don’t feature a “How to Communicate Like Dr. D” section, and it isn’t a skill I imagine I will ever be done learning. The challenge of medicine appeals to me, though. I want a career in which I can constantly discover more.
Ultimately, I don’t expect to learn only in the clinic or hospital as a doctor. I will continue to do research on patient-physician communication. My work will likely inform my future medical practice, and, maybe, eventually I could teach what I’ve learned to residents and medical students.
As Dr. D has shown me, a physician’s work is complex and demanding. But the result can give patients like Jay “all the time.”
Professional Review by Premed Advocates
The compelling Personal Statement you've just read exemplifies the power of introspective storytelling. The author's reflection, highlighting his evolving understanding of medicine and future ambitions, led to acceptances and scholarships from prestigious medical schools like Johns Hopkins, Yale, Duke, UCLA, Mayo, Vanderbilt, Northwestern, and Mt Sinai.
At PreMed Advocates, we help create personal statements that keep the applicant as the central figure of the narrative. While many personal statements tend to recount the applicant's journey to medical school, often involving personal illness experiences or “inspirational” patient-doctor interactions, these narratives can inadvertently shift the focus onto the stories of others, and away from you—the main character.
Our reflective storytelling approach keeps your unique perspective at the heart of your personal statement.
Our reflective storytelling approach keeps your unique perspective at the heart of your personal statement. Through collaborative brainstorming, meticulous editing, and interview preparation, we guide applicants in transforming their experiences into a compelling narrative. Our method is also deeply rooted in our thorough understanding of medical school admissions rubrics and processes, which we've derived from extensive research and detailed profiling of each institution.
The PreMed Advocates difference lies in our unique approach. We equip our applicants with the tools they need to succeed, and supplement this with personalized, one-on-one guidance.
- Open access
- Published: 03 September 2024
Reliability of ChatGPT in automated essay scoring for dental undergraduate examinations
- Bernadette Quah 1 , 2 ,
- Lei Zheng 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Timothy Jie Han Sng 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Chee Weng Yong 1 , 2 na1 &
- Intekhab Islam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7754-0609 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 962 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
This study aimed to answer the research question: How reliable is ChatGPT in automated essay scoring (AES) for oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMS) examinations for dental undergraduate students compared to human assessors?
Sixty-nine undergraduate dental students participated in a closed-book examination comprising two essays at the National University of Singapore. Using pre-created assessment rubrics, three assessors independently performed manual essay scoring, while one separate assessor performed AES using ChatGPT (GPT-4). Data analyses were performed using the intraclass correlation coefficient and Cronbach's α to evaluate the reliability and inter-rater agreement of the test scores among all assessors. The mean scores of manual versus automated scoring were evaluated for similarity and correlations.
A strong correlation was observed for Question 1 ( r = 0.752–0.848, p < 0.001) and a moderate correlation was observed between AES and all manual scorers for Question 2 ( r = 0.527–0.571, p < 0.001). Intraclass correlation coefficients of 0.794–0.858 indicated excellent inter-rater agreement, and Cronbach’s α of 0.881–0.932 indicated high reliability. For Question 1, the mean AES scores were similar to those for manual scoring ( p > 0.05), and there was a strong correlation between AES and manual scores ( r = 0.829, p < 0.001). For Question 2, AES scores were significantly lower than manual scores ( p < 0.001), and there was a moderate correlation between AES and manual scores ( r = 0.599, p < 0.001).
This study shows the potential of ChatGPT for essay marking. However, an appropriate rubric design is essential for optimal reliability. With further validation, the ChatGPT has the potential to aid students in self-assessment or large-scale marking automated processes.
Peer Review reports
Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, LLaMA by META, and Google’s LaMDA (Language Models for Dialogue Applications), have demonstrated tremendous potential in generating outputs based on user-specified instructions or prompts. These models are trained using large amounts of data and are capable of natural language processing tasks. Owing to their ability to comprehend, interpret, and generate natural language text, LLMs allow human-like conversations with coherent contextual responses to prompts. The capability of LLMs to summarize and generate texts that resemble human language allows the creation of task-focused systems that can ease the demands of human labor and improve efficiency.
OpenAI uses a closed application programming interface (API) to process data. Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (OpenAI Inc., California, USA, https://chat.openai.com/ ) was introduced globally in 2020 as ChatGPT3, a generative language model with 175 billion parameters [ 1 ]. It is based on a generative AI model that can generate new content based on the data on which they have been trained. The latest version, ChatGPT-4, was introduced in 2023 and has demonstrated improved creativity, reasoning, and the ability to process even more complicated tasks [ 2 ].
Since its release in the public domain, ChatGPT has been actively explored by both healthcare professionals and educators in an effort to attain human-like performance in the form of clinical reasoning, image recognition, diagnosis, and learning from medical databases. ChatGPT has proven to be a powerful tool with immense potential to provide students with an interactive platform to deepen their understanding of any given topic [ 3 ]. In addition, it is also capable of aiding in both lesson planning and student assessments [ 4 , 5 ].
The potential of ChatGPT for assessments
Automated Essay Scoring (AES) is not a new concept, and interest in AES has been increasing since the advent of AI. Three main categories of AES programs have been described, utilizing regression, classification, or neural network models [ 6 ]. A known problem of current AES systems is their unreliability in evaluating the content relevance and coherence of essays [ 6 ]. Newer language models such as ChatGPT, however, are potential game changers; they are simpler to learn than current deep learning programs and can therefore improve the accessibility of AES to educators. Mizumoto and Eguchi recently pioneered the potential use of ChatGPT (GPT-3.5 and 4) for AES in the field of linguistics and reported an accuracy level sufficient for use as a supportive tool even when fine-tuning of the model was not performed [ 7 ].
The use of these AI-powered tools may potentially ease the burden on educators in marking large numbers of essay scripts, while providing personalized feedback to students [ 8 , 9 ]. This is especially crucial with larger class sizes and increasing student-to-teacher ratios, where it can be more difficult for educators to actively engage individual students. Additionally, manual scoring by humans can be subjective and susceptible to fatigue, which may put the scoring at risk of being unreliable [ 7 , 10 ]. The use of AI for essay scoring may thus help reduce intra- and inter-rater variability associated with manual scoring by providing a more standardized and reliable scoring process that eases the time- and labor-intensive scoring workload of human assessors [ 10 , 11 ].
The current role of AI in healthcare education
Generative AI has permeated the healthcare industry and provided a diverse range of health enhancements. An example is how AI facilitates radiographic evaluation and clinical diagnosis to improve the quality of patient care [ 12 , 13 ]. In medical and dental education, virtual or augmented reality and haptic simulations are some of the exciting technological tools already implemented to improve student competence and confidence in patient assessment and execution of procedures [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. The incorporation of ChatGPT into the dental curriculum would thus be the next step in enhancing student learning. The performance of ChatGPT in the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) was recently validated, with ChatGPT achieving a score equivalent to that of a third-year medical student [ 17 ]. However, no data are available on the performance of ChatGPT in the field of dentistry or oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMS). Furthermore, the reliability of AI-powered language models for the grading of essays in the medical field has not yet been evaluated; in addition to essay structure and language, the evaluation of essay scripts in the field of OMS would require a level of understanding of dentistry, medicine and surgery.
Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the reliability of ChatGPT for AES in OMS examinations for final-year dental undergraduate students compared to human assessors. Our null hypothesis was that there would be no difference in the scores between the ChatGPT and human assessors. The research question for the study was as follows: How reliable is ChatGPT when used for AES in OMS examinations compared to human assessors?
Materials and methods
This study was conducted in the Faculty of Dentistry, National University of Singapore, under the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. The study received ethical approval from the university’s Institutional Review Board (REF: IRB-2023–1051) and was conducted and drafted with guidance from the education interventions critical appraisal worksheet introduced by BestBETs [ 18 ].
Sample size calculation for this study was based on the formula provided by Viechtbauer et al.: n = ln (1-γ) / ln(1-π), where n, γ and π represent the sample size, significance level and level of confidence respectively [ 19 ]. Based on a 5% margin of error, a 95% confidence level and a 50% outcome response, it was calculated that a minimum sample size of 59 subjects was required. Ultimately, the study recruited 69 participants, all of whom were final-year undergraduate dental students. A closed-book OMS examination was conducted on the Examplify platform (ExamSoft Worldwide Inc., Texas, USA) as a part of the end-of-module assessment. The examination comprised two open-ended essay questions based on the topics taught in the module (Table 1 ).
Creation of standardized assessment
An assessment rubric was created for each question through discussion and collaboration of a workgroup comprising four assessors involved in the study. All members of the work group were academic staff from the faculty (I.I., B.Q., L.Z., T.J.H.S.) (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2) [ 20 ]. An analytic rubric was generated using the strategy outlined by Popham [ 21 ]. The process involved a discussion within the workgroup to agree on the learning outcomes of the essay questions. Two authors (I. I. and B. Q) independently generated the rubric criteria and descriptions for Question 1 (Infection). Similarly, for Question 2 (Trauma), the rubric criteria and descriptions were generated independently by two authors (I.I. and T.J.H.S.). The rubrics were revised until a consensus was reached between each pair. In the event of any disagreement, a third author (L.Z.) provided their opinion to aid in decision making.
Marking categories of Poor (0 marks), Satisfactory (2 marks), Good (3 marks), and Outstanding (4 marks) were allocated to each criterion, with a maximum of 4 marks attainable from each criterion. A criterion for overall essay structure and language was also included, with a maximum attainable 5 marks from this criterion. The highest score for each question was 40.
Model answers to the essays were prepared by another author (C.W.Y.), who did not participate in the creation of the rubrics. Using the rubrics as a reference, the author modified the model answer to create 5 variants of the answers such that each variant fell within different score ranges of 0–10, 11–20, 21–30, 31–40, 41–50. Subsequently, three authors (B. Q., L. Z., and T.J.H.S) graded the essays using the prepared rubrics. Revisions to the rubrics were made with consensus by all three authors, a process that also helped calibrate these three authors for manual essay scoring.
AES with ChatGPT
Essay scoring was performed using ChatGPT (GPT-4, released March 14, 2023) by one assessor who did not participate in the manual essay scoring exercise (I.I.). Prompts were generated based on a guideline by Giray, and the components of Instruction, Context, Input Data and Output Indication as discussed in the guideline were included in each prompt (Supplementary Tables 3 and 4) [ 22 ]. A prompt template was generated for each question by one assessor (I.I.) with advice from two experts in prompt engineering, based on the marking rubric. The criterion and point allocation were clearly written in prose and point forms. For the fine-tuning process, the prompts were input into ChatGPT using variants of the model answers provided by C.W.Y. Minor adjustments were made to the wording of certain parts of the prompts as necessary to correct any potential misinterpretations of the prompts by the ChatGPT. Each time, the prompt was entered into a new chat in the ChatGPT in a browser where the browser history and cookies were cleared. Subsequently, finalized prompts (Supplementary Tables 3 and 4) were used to score the student essays. AES scores were not used to calculate students’ actual essay scores.
Manual essay scoring
Manual essay scoring was completed independently by three assessors (B.Q., L.Z., and T.J.H.S.) using the assessment rubrics (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2). Calibration was performed during the rubric creation stage. The essays were anonymized to prevent bias during the marking process. The assessors recorded the marks allocated to each criterion, as well as the overall score of each essay, on a pre-prepared Excel spreadsheet. Scoring was performed separately and independently by all assessors before the final collation by a research team member (I.I.) for statistical analyses. The student was considered ‘able to briefly mention’ a criterion if they did not mention any of the keywords of the points within the criterion. The student was considered ‘able to elaborate on’ a point within the criterion if they were able to mention the keywords of that point as stated in the rubric, and were thus awarded higher marks in accordance with the rubric (e.g. the student was given a higher mark if they were able to mention the need to check for dyspnea and dysphagia, instead of simply mentioning a need to check the patient’s airway). Grading was performed with only whole marks as specified in the rubrics, and assessors were not allowed to give half marks or subscores.
Data synthesis
The scores given out of 40 per essay by each assessor were compiled. Data analyses were subsequently performed using SPSS® version 29.0.1.0(171) (IBM Corporation, New York, United States). For each essay question, correlations between the essay scores given by each assessor were analyzed and displayed using the inter-item correlation matrix. A correlation coefficient value ( r ) of 0.90–1.00 was indicative of a very strong, 0.70–0.89 indicative of strong, 0.40–0.69 moderate, 0.10–0.39 weak and < 0.10 negligible positive correlation between the scorers [ 23 ]. The cutoff p -value for the significance level was set at p < 0.05. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Cronbach's α were then calculated between all assessors to assess the inter-rater agreement and reliability, respectively [ 24 ]. The ICC was interpreted on a scale of 0 to 1.00, with a higher value indicating a higher level of agreement in scores given by the scorers to each student. A value less than 0.40 was indicative of poor, 0.40–0.59 fair, 0.60–0.74 good, and 0.75–1.00 excellent agreement [ 25 ]. Using Cronbach’s α, reliability was expressed on a range from 0 to 1.00, with a higher number indicating a higher level of consistency between the scorers in their scores given across the students. The reliability was considered ‘Less Reliable’ if the score was less 0.20, ‘Rather Reliable’ if the score was 0.20–0.40, ‘Quite Reliable’ if 0.40–0.60, ‘Reliable’ if 0.60–0.80 and ‘Very Reliable’ if 0.80–1.00 [ 26 ].
Similarly, the mean scores of the three manual scorers were calculated for each question. The mean manual scores were then analyzed for correlations with AES scores by using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Student’s t-test was also used to analyze any significant differences in mean scores between manual scoring and AES. A p -value of < 0.05 was required to conclude the presence of a statistically different score between the groups.
All final-year dental undergraduate students (69/69, 100%) had their essays graded by all manual scorers and AES as part of the study. Table 2 shows the mean scores for each individual assessor as well as the mean scores for the three manual scorers (Scorers 1, 2, and 3).
Analysis of correlation and agreement between all scorers
The inter-item correlation matrices and their respective p -values are listed in Table 3 . For Question 1, there was a strong positive correlation between the scores provided by each assessor (Scorers 1, 2, 3, and AES), with r -values ranging from 0.752–0.848. All p -values were < 0.001, indicating a significant positive correlation between all assessors. For Question 2, there was a strong positive correlation between Scorers 1 and 2 ( r = 0.829) and Scorers 1 and 3 ( r = 0.756). There was a moderate positive correlation between Scorers 2 and 3 ( r = 0.655), as well as between AES and all manual scores ( r -values ranging from 0.527 to 0.571). Similarly, all p -values were < 0.001, indicative of a significant positive correlation between all scorers.
For the analysis of inter-rater agreement, ICC values of 0.858 (95% CI 0.628 – 0.933) and 0.794 (95% CI 0.563 – 0.892) were obtained for Questions 1 and 2, respectively, both of which were indicative of excellent inter-rater agreement. Cronbach’s α was 0.932 for Question 1 and 0.881 for Question 2, both of which were ‘Very Reliable’.
Analysis of correlation between manual scoring versus AES
The results of the Student’s t-test comparing the test score values from manual scoring and AES are shown in Table 2 . For Question 1, the mean manual scores (14.85 ± 4.988) were slightly higher than those of the AES (14.54 ± 5.490). However, these differences were not statistically significant ( p > 0.05). For Question 2, the mean manual scores (23.11 ± 4.241) were also higher than those of the AES (18.62 ± 4.044); this difference was statistically significant ( p < 0.001).
The results of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient calculations are shown in Table 4 . For Question 1, there was a strong and significant positive correlation between manual scoring and AES ( r = 0.829, p < 0.001). For Question 2, there was a moderate and statistically significant positive correlation between the two groups ( r = 0.599, p < 0.001).
Qualitative feedback from AES
Figures 1 , 2 and 3 show three examples of essay feedback and scoring provided by ChatGPT. ChatGPT provided feedback in a concise and systematic manner. Scores were clearly provided for each of the criteria listed in the assessment rubric. This was followed by in-depth feedback on the points within the criterion that the student had discussed and failed to mention. ChatGPT was able to differentiate between a student who briefly mentioned a key point and a student who provided better elaboration on the same point by allocating them two or three marks, respectively.

Example #1 of a marked essay with feedback from ChatGPT for Question 1

Example #2 of a marked essay with feedback from ChatGPT for Question 1

Example #3 of a marked essay with feedback from ChatGPT for Question 1
One limitation of ChatGPT that was identified during the scoring process was its inability to identify content that was not relevant to the essay or that was factually incorrect. This was despite the assessment rubric specifying that incorrect statements should be given 0 marks for that criterion. For example, a student who included points about incision and drainage also incorrectly stated that bone scraping to induce bleeding and packing of local hemostatic agents should be performed. Although these statements were factually incorrect, ChatGPT was unable to identify this and still awarded student marks for the point. Manual assessors were able to spot this and subsequently penalized the student for the mistake.
Since its recent rise in popularity, many people have been eager to tap into the potential of large language models, such as ChatGPT. In their review, Khan et al. discussed the growing role of ChatGPT in medical education, with promising uses for the creation of case studies and content such as quizzes and flashcards for self-directed practice [ 9 ]. As an LLM, the ability of ChatGPT to thoroughly evaluate sentence structure and clarity may allow it to confront the task of automated essay marking.
Advantages of ChatGPT in AES
This study found significant correlations and excellent inter-rater agreement between ChatGPT and manual scorers, and the mean scores between both groups showed strong to moderate correlations for both essay questions. This suggests that AES has the potential to provide a level of essay marking similar to that of the educators in our faculty. Similar positive findings were reflected in previous studies that compared manual and automated essay scoring ( r = 0.532–0.766) [ 6 ]. However, there is still a need to further fine-tune the scoring system such that the score provided by AES deviates as little as possible from human scoring. For instance, the mean AES score was lower than that of manual scoring by 5 marks for Question 2. Although the difference may not seem large, it may potentially increase or decrease the final performance grade of students.
Apart from a decent level of reliability in manual essay scoring, there are many other benefits to using ChatGPT for AES. Compared to humans, the response time to prompts is much faster and can thus increase productivity and reduce the burden of a large workload on educational assessors [ 27 ]. In addition, ChatGPT can provide individualized feedback for each essay (Figs. 1 , 2 and 3 ). This helps provide students with comments specific to their essays, a feat that is difficult to achieve for a single educator teaching a large class size.
Similar to previous systems designed for AES, machine scoring is beneficial for removing human inconsistencies that can result from fatigue, mood swings, or bias [ 10 ]. ChatGPT is no exception. Furthermore, ChatGPT is more widely accessible than the conventional AES systems. Its software runs online instead of requiring downloads on a computer, and its user interface is simple to use. With GPT-3.5 being free to use and GPT-4 being 20 USD per month, it is also relatively inexpensive.
Marking the essay is only part of the equation, and the next step is to allow the students to know what went wrong and why. Nicol and Macfarlane described seven principles for good feedback. ChatGPT can fulfil most of these principles, namely, facilitating self-assessment, encouraging teacher and peer dialogue, clarifying what good performance is, providing opportunities to close the gap between current and desired performance, and delivering high-quality information to students [ 28 ]. In this study, the feedback given by ChatGPT was categorized based on the rubric, and elaboration was provided for each criterion on the points the student mentioned and did not mention. By highlighting the ideal answer and where the student can improve, ChatGPT can clarify performance goals and provide opportunities to close the gap between the student’s current and desired performance. This creates opportunities for selfdirected learning and the utilization of blended learning environments. Students can use ChatGPT to review their preparation on topics, self-grade their essays, and receive instant feedback. Furthermore, the simple and interactive nature of the software encourages dialogue, as it can readily respond to any clarification the student wants to make. The importance of effective feedback has been demonstrated to be an essential component in medical education, in terms of enhancing the knowledge of the student without developing negative emotions [ 29 , 30 ].
These potential advantages of engaging ChatGPT for student assessments play well into the humanistic learning theory of medical education [ 31 , 32 ]. Self-directed learning allows students the freedom to learn at their own pace, with educators simply providing a conducive environment and the goals that the student should achieve. ChatGPT has the potential to supplement the role of the educator in self-directed learning, as it can be readily available to provide constructive and tailored feedback for assignments whenever the student is ready for it. This removes the burden that assignment deadlines place on students, which can allow them a greater sense of independence and control over their learning, and lead to greater self-motivation and self-fulfillment.
Potential pitfalls of ChatGPT
Potential pitfalls associated with the use of ChatGPT were identified. First, the ability to achieve reliable scores relies heavily on a well-created marking rubric with clearly defined terms. In this study, the correlations between scorers were stronger for Question 1 compared to Question 2, and the mean scores between the AES and manual scorers were also significantly different for Question 2, but not for Question 1. The lower reliability of the AES for Question 2 may be attributed to its broader nature, use of more complex medical terms, and lengthier scoring rubrics. The broad nature of the question left more room for individual interpretation and variation between humans and AES. The ability of ChatGPT to provide accurate answers may be reduced with lengthier prompts and conversations [ 27 ]. Furthermore, with less specific instructions or complex medical jargon, both automated systems and human scorers may interpret rubrics differently, resulting in varied scores across the board [ 10 , 33 , 34 ]. The authors thus recommend that to circumvent this, the use of ChatGPT for essay scoring should be restricted to questions that are less broad (e.g. shorter essays), or by breaking the task into multiple prompts for each individual criterion to reduce variations in interpretation [ 27 , 35 ]. Furthermore, the rubrics should contain concise and explicit instructions with appropriate grammar and vocabulary to avoid misinterpretation by both ChatGPT and human scorers, and provide a brief explanation to specify what certain medical terms mean (e.g. writing ‘pulse oximetry (SpO2) monitoring’ instead of only ‘SpO2’) for better contextualization [ 35 , 36 ].
Second, prompt engineering is a critical step in producing the desired outcome from ChatGPT [ 27 ]. A prompt that is too ambiguous or lacks context can lead to a response that is incomplete, generic, or irrelevant, and a prompt that exhibits bias runs the risk of bias reinforcement in the given reply [ 22 , 34 ]. Phrasing the prompt must also be carefully checked for spelling, grammatical mistakes, or inconsistencies, since ChatGPT uses the prompt’s phrasing literally. For example, a prompt that reads ‘give 3 marks if the student covers one or more coverage points’ will result in ChatGPT only giving the marks if multiple points are covered, because of the plural nature of the word ‘points’.
Third, irrelevant content may not be penalized during the essay-marking process. Students may ‘trick’ the AES by producing a lengthier essay to hit more relevant points and increase their score. This may result in essays of lower quality with multiple incorrect or nonsensical statements still rewarded with higher scores [ 10 ]. Our assessment rubric attempts to penalize the student with 0 marks if incorrect statements on the criterion are made; however, none of the students were penalized. This issue may be resolved as ChatGPT rapidly and continuously gains more medical and dental knowledge. Although data to support the competence of AI in medical education are sparse, the quality of the medical knowledge that ChatGPT already has is sufficient to achieve a passing mark at the USMLE [ 5 , 37 ]. In dentistry, when used to disseminate information on endodontics to patients, ChatGPT was found to provide detailed answers with an overall validity of 95% [ 38 ]. Over time, LLMs such as ChatGPT may be able to identify when students are not factually correct.
Other comments
The lack of human emotion in machine scoring can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. AES can provide feedback that is entirely factual and less biased than humans, and grades are objective and final [ 39 ]. However, human empathy is an essential quality that ChatGPT does not possess. One principle of good feedback is to encourage and motivate students to provide positive learning experiences and build self-esteem [ 28 ]. While ChatGPT can provide constructive feedback, it will not be able to replace the compassion, empathy, or emotional intelligence possessed by a quality educator possesses [ 40 ]. In our study, ChatGPT awarded lower mean scores of 14.54/40 (36.4%) and 18.62/40 (46.5%) compared to manual scoring for both questions. Although objective, some may view automated scoring as harsh because it provided failing grades to an average student.
This study demonstrates the ability of GPT-4 to evaluate essays without any specialized training or prompting. One long prompt was used to score each essay. Although more technical prompting methods, such as chain of thought, could be deployed, our single prompt method makes the method scalable and easier to adopt. As discussed earlier, ChatGPT is the most reliable when prompts are short and specific [ 34 ]. Hence, each prompt should ideally task ChatGPT to score only one or two criteria, rather than the entire rubric of the 10 criteria. However, in a class of 70, the assessors are required to run 700 prompts per question, which is impractical and unnecessary. With only one prompt, a good correlation was still found between the AES and manual scoring. It is likely that further exploration and experimentation with prompting techniques can improve the output.
While LLMs have the potential to revolutionize education in healthcare, some precautions must be taken. Artificial Hallucination is a widely described phenomenon; ChatGPT may generate seemingly genuine but inaccurate information [ 41 , 42 , 43 ]. Hallucinations have been attributed to biases and limitations of training data as well as algorithmic limitations [ 2 ]. Similarly, randomness of the generated responses has been observed; while it is useful for generating creative content, this may be an issue when ChatGPT is employed for topics requiring scientific or factual content [ 44 ]. Thus, LLMs are not infallible and still require human subject matter experts to validate the generated content. Finally, it is essential that educators play an active role in driving the development of dedicated training models to ensure consistency, continuity, and accountability, as overreliance on a corporate-controlled model may place educators at the mercy of algorithm changes.
The ethical implications of using ChatGPT in medical and dental education also need to be explored. As much as LLMs can provide convenience to both students and educators, privacy and data security remain a concern [ 45 ]. Robust university privacy policies and informed consent procedures should be in place for the protection of student data prior to the use of ChatGPT as part of student assessment. Furthermore, if LLMs like ChatGPT were to be used for grading examinations in the future, issues revolving around fairness and transparency of the grading process need to be resolved [ 46 ]. GPT-4 may have provided harsh scores in this study, possibly due to some shortfall in understanding certain phrases the students have written; models used in assessments will thus require sufficient training in the field of healthcare to properly acquire the relevant medical knowledge and hence understand and grade essays fairly.
As AI continues to develop, ChatGPT may eventually replace human assessors in essay scoring for dental undergraduate examinations. However, given its current limitations and dependence on a well-formed assessment rubric, relying solely on ChatGPT for exam grading may be inappropriate when the scores can affect the student’s overall module scores, career success, and mental health [ 47 ]. While this study primarily demonstrates the use of ChatGPT to grade essays, it also points to great potential in using it as an interactive learning tool. A good start for its use is essay assignments on pre-set topics, where students can direct their learning on their own and receive objective feedback on essay structure and content that does not count towards their final scores. Students can use rubrics to practice and gain effective feedback from LLMs in an engaging and stress-free environment. This reduces the burden on educators by easing the time-consuming task of grading essay assignments and allows students the flexibility to complete and grade their assignments whenever they are ready. Furthermore, assignments repeated with new class cohorts can enable more robust feedback from ChatGPT through machine learning.
Study limitations
The limitations of this study lie in part of its methodology. The study recruited 69 dental undergraduate students; while this is above the minimum calculated sample size of 59, a larger sample size would help to increase the generalizability of the study findings to larger populations of students and a wide scope of topics. The unique field of OMS also requires knowledge of both medical and dental subjects, and hence the results obtained from the use of ChatGPT for essay marking in other medical or dental specialties may differ slightly.
The use of rubrics for manual scoring could also be a potential source of bias. While the rubrics provide a framework for objective assessment, they cannot eliminate the subjectiveness of manual scoring. Variations in the interpretation of the students’ answers, leniency errors (whereby one scorer marks more leniently than another) or rater drift (fatigue from assessing many essays may affect leniency of marking and judgment) may still occur. To minimize bias resulting from these errors, multiple assessors were recruited for the manual scoring process and the average scores were used for comparison with AES.
This study investigated the reliability of ChatGPT in essay scoring for OMS examinations, and found positive correlations between ChatGPT and manual essay scoring. However, ChatGPT tended towards stricter scoring and was not capable of penalizing irrelevant or incorrect content. In its present state, GPT-4 should not be used as a standalone tool for teaching or assessment in the field of medical and dental education but can serve as an adjunct to aid students in self-assessment. The importance of proper rubric design to achieve optimal reliability when employing ChatGPT in student assessment cannot be overemphasized.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Floridi L, Chiriatti M. GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Mind Mach. 2020;30(4):681–94.
Article Google Scholar
Abd-Alrazaq A, AlSaad R, Alhuwail D, Ahmed A, Healy PM, Latifi S, Aziz S, Damseh R, Alabed Alrazak S, Sheikh J. Large language models in medical education: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9:e48291.
Kasneci E, Sessler K, Küchemann S, Bannert M, Dementieva D, Fischer F, Gasser U, Groh G, Günnemann S, Hüllermeier E, et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn Individ Differ. 2023;103:102274.
Javaid M, Haleem A, Singh RP, Khan S, Khan IH. Unlocking the opportunities through ChatGPT Tool towards ameliorating the education system. BenchCouncil Transact Benchmarks Standards Eval. 2023;3(2): 100115.
Kung TH, Cheatham M, Medenilla A, Sillos C, De Leon L, Elepaño C, Madriaga M, Aggabao R, Diaz-Candido G, Maningo J, et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLOS Digit Health. 2023;2(2):e0000198.
Ramesh D, Sanampudi SK. An automated essay scoring systems: a systematic literature review. Artif Intell Rev. 2022;55(3):2495–527.
Mizumoto A, Eguchi M. Exploring the potential of using an AI language model for automated essay scoring. Res Methods Appl Linguist. 2023;2(2): 100050.
Erturk S, Tilburg W, Igou E: Off the mark: Repetitive marking undermines essay evaluations due to boredom. Motiv Emotion 2022;46.
Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT - Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci. 2023;39(2):605–7.
Hussein MA, Hassan H, Nassef M. Automated language essay scoring systems: a literature review. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2019;5:e208.
Blood I: Automated essay scoring: a literature review. Studies in Applied Linguistics and TESOL 2011, 11(2).
Menezes LDS, Silva TP, Lima Dos Santos MA, Hughes MM, Mariano Souza SDR, Leite Ribeiro PM, Freitas PHL, Takeshita WM: Assessment of landmark detection in cephalometric radiographs with different conditions of brightness and contrast using the an artificial intelligence software. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2023:20230065.
Bennani S, Regnard NE, Ventre J, Lassalle L, Nguyen T, Ducarouge A, Dargent L, Guillo E, Gouhier E, Zaimi SH, et al. Using AI to improve radiologist performance in detection of abnormalities on chest radiographs. Radiology. 2023;309(3): e230860.
Moussa R, Alghazaly A, Althagafi N, Eshky R, Borzangy S. Effectiveness of virtual reality and interactive simulators on dental education outcomes: systematic review. Eur J Dent. 2022;16(1):14–31.
Fanizzi C, Carone G, Rocca A, Ayadi R, Petrenko V, Casali C, Rani M, Giachino M, Falsitta LV, Gambatesa E, et al. Simulation to become a better neurosurgeon An international prospective controlled trial: The Passion study. Brain Spine. 2024;4:102829.
Lovett M, Ahanonu E, Molzahn A, Biffar D, Hamilton A. Optimizing individual wound closure practice using augmented reality: a randomized controlled study. Cureus. 2024;16(4):e59296.
Google Scholar
Gilson A, Safranek CW, Huang T, Socrates V, Chi L, Taylor RA, Chartash D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical licensing examination? the implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9:e45312.
Educational Intervention Worksheet, BestBets, Accessed 31/03/2024. https://bestbets.org/ca/pdf/educational_intervention.pdf .
Viechtbauer W, Smits L, Kotz D, Budé L, Spigt M, Serroyen J, Crutzen R. A simple formula for the calculation of sample size in pilot studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68(11):1375–9.
Cox G, Morrison J, Brathwaite B: The Rubric: An Assessment Tool to Guide Students and Markers; 2015.
Popham J. W: “What’s Wrong—And What’s Right—With Rubrics.” Educ Leadersh. 1997;55(2):72–5.
Giray L. Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT: A Guide for Academic Writers. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023;51:3.
Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(5):1763–8.
Liao SC, Hunt EA, Chen W. Comparison between inter-rater reliability and inter-rater agreement in performance assessment. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2010;39(8):613–8.
Cicchetti DV. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol Assess. 1994;6(4):284–90.
Hair J, Black W, Babin B, Anderson R: Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective; 2010.
Nazir A, Wang Z: A Comprehensive Survey of ChatGPT: Advancements, Applications, Prospects, and Challenges. Meta Radiol 2023;1(2).
Nicol D, Macfarlane D: Rethinking Formative Assessment in HE: a theoretical model and seven principles of good feedback practice. IEEE Personal Communications - IEEE Pers Commun 2004;31.
Spooner M, Larkin J, Liew SC, Jaafar MH, McConkey S, Pawlikowska T. “Tell me what is ‘better’!” How medical students experience feedback, through the lens of self-regulatory learning. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):895.
Kornegay JG, Kraut A, Manthey D, Omron R, Caretta-Weyer H, Kuhn G, Martin S, Yarris LM. Feedback in medical education: a critical appraisal. AEM Educ Train. 2017;1(2):98–109.
Mukhalalati BA, Taylor A. Adult learning theories in context: a quick guide for healthcare professional educators. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2019;6:2382120519840332.
Taylor DC, Hamdy H. Adult learning theories: implications for learning and teaching in medical education: AMEE Guide No. 83. Med Teach. 2013;35(11):e1561-1572.
Chakraborty S, Dann C, Mandal A, Dann B, Paul M, Hafeez-Baig A: Effects of Rubric Quality on Marker Variation in Higher Education. Studies In Educational Evaluation 2021;70.
Heston T, Khun C. Prompt engineering in medical education. Int Med Educ. 2023;2:198–205.
Sun GH: Prompt Engineering for Nurse Educators. Nurse Educ 2024.
Meskó B. Prompt engineering as an important emerging skill for medical professionals: tutorial. J Med Internet Res. 2023;25:e50638.
Sun L, Yin C, Xu Q, Zhao W. Artificial intelligence for healthcare and medical education: a systematic review. Am J Transl Res. 2023;15(7):4820–8.
Mohammad-Rahimi H, Ourang SA, Pourhoseingholi MA, Dianat O, Dummer PMH, Nosrat A: Validity and reliability of artificial intelligence chatbots as public sources of information on endodontics. Int Endodontic J 2023, n/a(n/a).
Peng X, Ke D, Xu B: Automated essay scoring based on finite state transducer: towards ASR transcription of oral English speech. In: Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Long Papers - Volume 1. Jeju Island, Korea: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2012:50–59.
Grassini S. Shaping the future of education: Exploring the Potential and Consequences of AI and ChatGPT in Educational Settings. Educ Sci. 2023;13(7):692.
Limitations. https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt .
Sallam M, Salim NA, Barakat M, Al-Tammemi AB. ChatGPT applications in medical, dental, pharmacy, and public health education: A descriptive study highlighting the advantages and limitations. Narra J. 2023;3(1):e103.
Deng J, Lin Y. The Benefits and Challenges of ChatGPT: An Overview. Front Comput Intell Syst. 2023;2:81–3.
Choi W. Assessment of the capacity of ChatGPT as a self-learning tool in medical pharmacology: a study using MCQs. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):864.
Medina-Romero MÁ, Jinchuña Huallpa J, Flores-Arocutipa J, Panduro W, Chauca Huete L, Flores Limo F, Herrera E, Callacna R, Ariza Flores V, Quispe I, et al. Exploring the ethical considerations of using Chat GPT in university education. Period Eng Nat Sci (PEN). 2023;11:105–15.
Lee H. The rise of ChatGPT: Exploring its potential in medical education. Anat Sci Educ. 2024;17(5):926–31.
Steare T, Gutiérrez Muñoz C, Sullivan A, Lewis G. The association between academic pressure and adolescent mental health problems: A systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2023;339:302–17.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to extend our gratitude to Mr Paul Timothy Tan Bee Xian and Mr Jonathan Sim for their invaluable advice on the process of prompt engineering for the effective execution of this study.
Author information
Lei Zheng, Timothy Jie Han Sng and Chee Weng Yong contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Faculty of Dentistry, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
Bernadette Quah, Lei Zheng, Timothy Jie Han Sng, Chee Weng Yong & Intekhab Islam
Discipline of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, National University Centre for Oral Health, 9 Lower Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
B.Q. contributed in the stages of conceptualization, methodology, study execution, validation, formal analysis and manuscript writing (original draft and review and editing). L.Z., T.J.H.S. and C.W.Y. contributed in the stages of methodology, study execution, and manuscript writing (review and editing). I.I. contributed in the stages of conceptualization, methodology, study execution, validation, formal analysis, manuscript writing (review and editing) and supervision. All authors provided substantial contributions to this manuscript in the following form:
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Intekhab Islam .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the university (REF: IRB-2023–1051). The waiver of consent from students was approved by the University’s Institutional Review Board, as the scores by ChatGPT were not used as the students’ actual grades, and all essay manuscripts were anonymized.
Consent for publication
All the authors reviewed the content of this manuscript and provided consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Quah, B., Zheng, L., Sng, T.J.H. et al. Reliability of ChatGPT in automated essay scoring for dental undergraduate examinations. BMC Med Educ 24 , 962 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05881-6
Download citation
Received : 04 February 2024
Accepted : 09 August 2024
Published : 03 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05881-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial intelligence
- Academic performance
- Educational
- Educational needs assessment
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]

“The Doctor as a Humanist”: The Viewpoint of the Students
Conference Report and Reflection by Poposki Ognen (University Pompeu Fabra); Castillo Gualda Paula (University of Balearic Islands); Barbero Pablos Enrique (University Autonoma de Madrid); Pogosyan Mariam (Sechenov University); Yusupova Diana (Sechenov University); and Ahire Akash (Sechenov University)

The practice of Medicine as a profession has become very technical; doctors rely on fancy investigations, treatment algorithms and standardized guidelines in treating patients. In a lot of universities, medical students and residents are trained without appreciating the importance of art and the humanities in delivering good care to patients and their families. Factual knowledge is imposed on us, as students, from scientific evidence delivered by highly specialized professionals: those who know more and more about niche subjects.
As a result, when someone decides to become a doctor , it seems that scientific training is the sole priority, with most attention being given to the disease-treatment model. As medical students, we are taught very specific subjects, leaving little or no space or time for any cultural enrichment programs. And yet, Personal growth as a doctor and a human being cannot be achieved unless one is exposed to the whole range of human experience. Learning from art and artists can be one such means of gaining these enriching experiences. We can learn from historians, and from eminent painters, sculptors, and writers, as well as from great scientists. How do we achieve these ends? The following essay summarizes and reviews one attempt at providing answers. The 2nd “Doctor as a Humanist” Symposium took place at Sechenov University in Moscow from the 1 st to the 3 rd of April, 2019, to explore the holistic perspective of interpersonal treatment.
To begin our essay, we would like to clarify some key concepts, such as culture, humanism and humanities, as they were employed at the conference. Culture is a complex phenomenon that includes knowledge, beliefs, artistic production, morals, customs and skills acquired by being part of a society, which can be transmitted consciously or unconsciously, by individuals to others and through different generations.
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the cultural aspects and frailties of being human, and use methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, which distinguish them from the approaches of the natural sciences. Humanism is the practice of making the human story central. Consequently, the studies of humanities, so invested in human stories, is one aspect of practicing humanism.
Technological and practical progress in medicine has been impressive in the past fifty years. Nevertheless, patients still suffer from chronic conditions such as heart failure, chronic lung disease, depression, and many others. These are conditions where technology cannot significantly change the outcomes or reverse the underlying condition. One of the ways to alleviate suffering is through compassion and empathy where the doctor is a professional who listens to, understands and comforts the patient, as well as engaging the patient as a fellow human being. We need arts and humanities as doctors’ tools to comfort and, perhaps, even to heal. We also need them to remind us that we are ‘merely human’ ourselves, and that we share our humanity with our patients, as equals.
Unquestionably, there are fundamental requirements that every physician must internalize; the conference goal was to explain that one such requirement is the humanistic view. Opera, poetry, philosophy, history, the study of dialectics, biographical readings, and even volunteering abroad can be means of engaging the world for positive change. Sometimes called “soft” skills, these are in fact necessary and valuable qualities to empower ourselves as persons, as well as doctors. The 2nd The Doctor as a Humanist Symposium placed the corner stone in a global project that aims to understand medicine as a multidisciplinary subject, and to establish the concept of humanistic medicine both as a science and an art where the patient and the doctor are human beings working together.

STUDENT PARTICIPATION
The event united experts in Medicine and the Humanities from all over the world. The speakers (doctors, nurses and students) were from Russia, the USA, the UK, Spain, Italy, Germany, Mexico and more. Each day’s program was both intense and diverse, and included plenary lectures and panel sessions. Medical students were highly involved in all parts of the conference, offering us a great chance to introduce our projects, share our opinions on various topics, and discuss our questions connected with the role of the humanities in medicine.We participated in roundtable discussions, which were chaired by experts from different countries. Even though this made us nervous, at the same time it was very important for us, as students, to be a part of it. We discussed the future of medical humanities from various perspectives, and above all our thoughts and ideas were listened to and commented on, on an equal basis with the world’s experts. For once, we could see that our views were being taken into consideration, and we hope that in the future this will be the norm and NOT the exception. We are the future of medicine, and our voices should be heard, too.
At the end of the first day there was a students’ session, where we gave our opinions on the relative importance of the medical humanities from a multicultural viewpoint, and on this particular roundtable there were students from Russia, Spain, Iran, Mexico, Italy, as well as a Nursing resident. One of the students during the session shared her view that “I would like to see medicine through the lens of humanism and empathy, and also implement all its principles in my professional life on a daily basis”. All participants agreed, and although we were representing different countries and cultures there was no disagreement about this. Even though we have not yet faced many of the obstacles of the world of medicine, we can see the role of compassion in clinical practice better perhaps than our seniors. We shared our points of view about this question and its relevance in the different countries. It was an incredible moment, as experts and professors demonstrated a great interest in our ideas.
The program was extremely diverse; however, the main idea that most speakers expressed was how to find, sustain and not lose humanist goals. Brandy Schillace gave an impressive presentation entitled “Medical Humanities today: a publisher’s perspective”, which studied the importance of writing and publishing not only clinical trials, but also papers from historians, literary scholars, sociologists, and patients with personal experiences. The nurses Pilar d’Agosto and Maria Arias made a presentation on the topic of the Nursing Perspective that is one of the main pillars of medical practice. Professor Jacek Mostwin (Johns Hopkins University) shared his thoughts on patients’ memoirs. An Italian student, Benedetta Ronchi presented the results of an interview on medical humanities posed to the participants and speakers during the symposium. The plurality of perspectives made this conference an enriching event and showed us how diverse ideas can help us become better doctors. More importantly, it reminded us of our common humanity.
A significant part of the symposium was dedicated to Medicine and Art. Prof Josep Baños and Irene Canbra Badii spoke about the portrayal of physicians in TV medical dramas during the last fifty years. The book “The role of the humanities in the teaching of medical students” was presented by these authors and then given to participants as gifts. Dr Ourania Varsou showed how Poetry can influence human senses through her own experience in communicating with patients. She believed that many of the opinions and knowledge that we have internalized should be unlearned in order to have a better understanding of the human mind. The stimulus of poetry makes this possible. Poetry allows us to find new ways to express ourselves, and thus increase our emotional intelligence and understanding of other people’s feelings.
One of the most impressive lectures was by Dr Joan.B Soriano, who spoke about “Doctors and Patients in Opera” and showed how the leading roles of physicians in opera have changed over the centuries. People used to consider the doctor as the antihero, but with time this view has transformed into a positive one that plays a huge role in history.
It is important to be professional in your medical career, but also to be passionate about the life surrounding you; for instance, Dr Soriano is also a professional baritone singer. For students, this Symposium was full of obvious and hidden messages, which gave us much lot of food for thought. As Edmund Pellegrino, the founding editor of the Journal of Medicine and Philosophy , said: “Medicine is the most humane of sciences, the most empiric of arts, and the most scientific of humanities.”

CHOOSING ONE WORD
To conclude our summary of the students’ viewpoint each of us chose One word to encapsulate our thoughts about the symposium.
|
| |||
| Medical students should widen their intellectual interests and activities beyond scientific evidence. | Consider Medicine as an art that cures the patient’s illness, and in which the doctor’s soul plays an important role. | To know how to empathize and treat adequately, the physician needs the ability to see things not only with a clinical eye. | |
| Medical students, as well as other university students, need to harmonize their career with their non-academic lives. | Motivate the students beyond formal education in order to become multidisciplinary. | Better trained “humanistic” medical students should become more balanced human beings and doctors; this would benefit both the patients and each Doctor. | |
| The human being is more than the coordinated work of billions of specialized cells | Listen to the patient, understand their suffering, integrate every aspect of their biography and, in this way, achieve the best or “least bad” solution. | Humanities are the only way to enable doctors try to reach this integrative manner to practice medicine.
| |
| Humanism enhances interpersonal awareness amongst people. | Cover a wide range of liberal arts topics related to the human condition, namely history, literature, fine arts, philosophy and ethics. | Forging healthy relationships, not only with the patient but also with work colleagues, family and friends, improves one’s ability to make sound judgements, empathize, listen, interact and ultimately communicate. |
The Doctor as a Humanist is a multicultural event where everyone can learn and contribute to this global necessity to put the heart and soul back into medicine. Of course, we are aware and delighted that other organizations are championing the cause of the Humanities in Medicine, and in some cases, such as https://www.dur.ac.uk/imh/ , they have been doing so for many years.
As medical students, we appreciate how we have been placed at the centre of the symposium, which we believe has made this new initiative rather special. We hope that students of Medicine and from other disciplines come and participate in future symposia.
If you want to learn more, and see how you can participate, please contact the International student representatives, Mariam ( [email protected] ) and David ( [email protected] ).
Acknowledgements
Assistance provided by Jonathan McFarland (c) and Joan B. Soriano (University Autonoma de Madrid) was greatly appreciated during the planning and the development of the article.
Analysis and discussion of research | Updates on the latest issues | Open debate
All BMJ blog posts are published under a CC-BY-NC licence
BMJ Journals

Aristotle credited Thespis with revolutionizing Greek drama in the Sixth Century, B.C., by introducing an actor in addition to the traditional chorus. The question has arisen, however, whether Thespis ever existed or, if he did, whether he was responsible for this radical change, which inspired Aeschylus and others to introduce additional actors, giving birth to Western theater as we know it. In Aristotle’s favor: someone must have introduced this change and many ancient Greeks believed it was Thespis, so why not? On the other side: believing does not make something so and it is unlikely that a single person could be responsible for an essential change to a long-standing ritual.
In the year 2000, nine years after the collapse of the Soviet Union and 43 after the publication in the West of Doctor Zhivago , I was studying in Russia and a literature professor told my class a story about the publication of this novel, an event that during the Cold War seemed of great symbolic importance. The professor’s story was that Boris Pasternak gave a copy of the manuscript to an Italian publisher, saying that he would send him a telegram stating whether or not to go ahead with publishing the novel. The idea was that Pasternak was still hoping to gain authorization to publish the novel in Russia, and he was not at all sure he wanted to have it published without the approval of his society and the Union of Soviet Writers. Some time after the publisher returned to Italy, Pasternak sent him a telegram saying, no, don’t publish the novel, but the Italian went ahead and published it anyway. (Among the less symbolic consequences: the publisher gained prominence and money, both of which he already had a great deal of; Pasternak was attacked by participants in the Soviet regime for having “fouled the spot where he ate and cast filth on those by whose labor he lives and breathes”. He won the Nobel Prize and was given the opportunity to leave Russia, but refused both, instead publicly apologizing to the Russian people for his work.)
To the professor the morals of the story were simple and clear: Pasternak, for all he was a Jew, an artist and critical of his society, was a loyal Russian first and foremost. He had been betrayed by a Western capitalist, or, more generally, by the immoral West, which values nothing so much as making money. (As Marx indicated: the capitalist manufacturer’s goal is to produce any article that can be sold for more than the production and sales costs. He does not produce either boots or books for their own sake.)
Yet even while the professor was still wrapping up the story I began to have doubts. Perhaps, I thought, the negative telegram was a positive signal that Pasternak and the publisher had agreed upon in advance? That is, perhaps “do not publish” in this case meant “do publish”? And was this a failed strategy? Had Russian spies failed to intercept the telegram and thus the Government had lacked the necessary “information” to conclude that Pasternak had opposed the publication of his novel in the West? Had he been punished—excoriated, dismissed from the Union of Soviet Writers, his mistress imprisoned—for his failure to pretend publicly enough that he was refusing to commit an antisocial act?
I asked the professor about this possibility, and she said there were Russians who believed that indeed the “no” telegram had meant yes, publish. Had anyone seen a copy of this telegram? I asked. In the West we have “critical editions” of literary works which include copies of pertinent historical documents.
The professor had never seen a copy of the telegram, nor had she heard of anyone seeing it, nor had she heard of it being kept in any archive. Was there ever any telegram? I wondered. My intuition—my character and my interpretation of experiences I had had up to that point—told me there wasn’t.
It seemed to me that this anecdote well portrayed the nature of much of Russians’ “knowledge”—about literary and political matters, medical treatments, child-rearing methods, Russian history, life in other countries. There were lots of bits of information floating around in the culture, but there was no way of being sure which bits were government lies, which were cherished fictions or popular superstitions, which something more reliable. Russians picked and chose among the bits based on their own characters and personal experiences. For one Russian the telegram existed and meant what it seemed on the surface to mean: don’t publish. For another, there never was any telegram, it was a government lie or popular fantasy. And yet all were as certain as we in the West about what they knew. The more sophisticated believers in the existence of a sincere “don’t publish” telegram understood that other intelligent Russians believed in different versions of the story, and they understood why these other people were wrong: they had gotten a little too caught up in conspiracy theorizing and cynicism. And similarly one might know whether a cancerous child had indeed been cured by psychic energy, or whether it had been Chechen terrorists or government agents who in 1999 had blown up apartment buildings in Moscow and Volgodonsk, reportedly killing hundreds of people, bolstering the government’s case to renew the military campaign against Chechen separatists. (A 2002 poll suggested that approximately 40 percent of Russians believed it likely that government agents were involved in the explosions, while another approximately 40 percent were sure they were not.)
It also seemed that all this baseless knowledge was the result of centuries of governments that sought to suppress dissent and relentlessly spied on their own people; of governments that in order to force people to do work that they otherwise would not do, accused and convicted people of crimes they did not commit and got the accused to confess publicly to having committed these crimes. (At the height of the Stalinist purges of the 1930s, Pasternak switched from publishing his own work to publishing translations, and not only of Shakespeare, Verlaine, Rilke, but also of poets from Stalin’s native Georgia. One theory is that on account of this latter work Stalin spared Pasternak’s life. However, why should this be the case? Georgian poets were among the targets of Stalin’s persecution. Alternatively, it has been said that in the 1930s Pasternak took steps to get himself denounced as an enemy of the people in order to avoid being called upon to serve as poet laureate for Stalin’s regime.)
It is plausible that since so many lies have been disseminated by Russian government authorities, be they ostensibly communist or otherwise, and since rarely have the sources of either government pronouncements or popular beliefs been able to be carefully examined, the people have lost interest in authoritative evidence, without losing interest in knowledge. Thus they embrace, interpret and imagine such evidence as seems necessary to support a set of beliefs that appears to be as comprehensive, coherent and seemingly well supported as Westerners’ sets. Further, since in their hearts they know that their evidence is unreliable, if not fanciful, Russians pay evidence in general little heed, preferring to theorize late into the night.
We might compare this situation to that of ancient Greek culture (which Russian culture resembles more than is noted, including in the power of the polis over the individual and the arbitrary way this power is often used). The Greeks too were little interested in evidence, in empirical data. A theory was credible if it organized bits of myth, folk beliefs, native prejudices and philosophical speculations in a logical fashion. Or as the Italians say, “ Si non è vero, è ben trovato .” Whether it’s true or not, it sure sounds good.
When we come in contact with or read about people who seem to live more limited or painful lives than we do, we have moments of appreciating that people and societies are not all the same. We may also have moments when we recognize that along with their disadvantages other peoples and cultures enjoy advantages that we do not. For example, notwithstanding our much-celebrated “free speech” and the independence of our media from government oversight, in my experience the intellectual level of discussion among middle-class Americans, and the quantity, scope and intellectual ambition of the books most Americans choose to read, is notably lower than that of Soviet-educated middle-class Russians. And if it has long been dangerous for Russians to criticize the existing government, they have also been free to criticize—they have luxuriated in criticizing—Russian life in general. Some might say that in the U.S. it is simply the other way round: one is free to criticize the existing government and constrained to sing the praises of the American system and way of life. Woe unto those who do not feel what a blessing it is to be an American, to those who—perhaps as a result of particular unpleasant experiences, say, in the American labor market—have forgotten that for Americans the glass is always at least half full. Such “losers” and “malcontents” are not merely criticized for having a bad attitude, they internalize this feeling and, inverting their personal histories, come to conclude that the fact that they are not financially successful or have not overcome some terrible disease is precisely because of their bad attitude; the system that needs reforming is their own internal one.
In any case, what certainly happens when we become acquainted with other cultures is that by focusing on particular limitations and sources of suffering of other peoples—and by defining these things as characteristics of these others—one disassociates oneself from these problems. In many cases we seize upon negative aspects of other cultures precisely because we do not wish to confront the fact that these are aspects of our own culture as well.
Thus reading about how the Russian government has spied on its own people allows Americans to enjoy moments of forgetting that their government has done and does the same. Reading about the role imprisonment played in the Russian economy, we forget about the use of imprisonment, and vigilante and police violence, in preserving an economically and politically useful black underclass in the decades after the Emancipation Proclamation and, less ferociously, in recent decades. Reading about the difficulties Russians face in trying to know what is going on in their country, and reading about how they turn to intuition, fantasy and what philosophers call the coherence theory of truth, we gain assurance that our knowledge is “the real thing”.
Which is also to say that we, or at least some of us, harbor suspicions that it may not be. Among the e-mails purportedly sent by Americans to the then-reigning Saddam Hussein via an Iraqi government website was one that concluded, “Oh well, what do I know. I am just an American citizen, which doesn’t entitle me to much in the way of knowledge.” The Harvard philosopher Willard Quine begins one of the great paragraphs in the history of epistemology: “The totality of our so-called knowledge or beliefs, from the most casual matters of geography and history to the profoundest laws of atomic physics or even of pure mathematics and logic, is a man-made fabric which impinges on experience only along the edges.”
In the political sphere, among the questions that for many years were not voiced regarding the Chechen separatists is how much covert support they may have been receiving from the American government or various oil interests. And what about our historical conundrums: Who was or was not behind the killing of John Kennedy? How much advance notice of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor did Franklin Roosevelt have? I read recently a reputable American source stating that at the end of the Second World War the Allies gave supplies to the German army fighting the Soviets. (To reduce the expanse of Central Europe that would come under Soviet influence or to reduce the credit the Soviets might receive for defeating Hitler? Or is the whole story apocryphal? That an event can be explained in no way implies that it occurred.)
Even before playwrights began turning doctors into staples of satire, medical information was being distorted by the pecuniary interests of medical specialists, and the intersection of capitalism and medicine seems to have magnified these distortions. In many cases the problem remains venality; in addition many medical specialists and consumers have been so brainwashed, let’s call it, that they rarely recognize the extent to which the profit motive is tainting the medical information and advice they are receiving. (In the U.S. the problem is compounded by the fact that the American media is beholden to business interests which, by buying advertising, provide most all the media’s income and which also reduce production costs by providing “information”, including whole stories ready to print.)
I once read some confused commentary from a renowned school of public health regarding the treatment for head lice. It seemed that an informal test conducted by the school had suggested that soaking one’s hair in olive oil might be an effective, low-risk and low-cost solution—and this while the toxic and rather expensive anti-lice pesticides were seeming to be of limited effectiveness. And yet the school on its website went to some lengths to deny that it was recommending olive oil and to point out disadvantages—e.g., the danger of slipping on spilt oil and the difficulty of getting the oil out of one’s hair (that is, of washing one’s hair?). Particularly given the extent to which knowledge is not an individual but a social construct, there is no reason to assume that my truth regarding this subject will prove more enduring than others’. Nonetheless, my hunch is that the companies that sell the anti-lice pesticides—or public relations companies in the pesticide companies’ employ—had lobbied the public-health school to make its website commentary on head lice “more objective”—that is, to make it say less about the problems with the pesticides and more about the problems of olive oil.
The situation is not all that different at American universities and with professors who via research grants, consulting contracts, donated facilities and the like enjoy a good deal of “corporate support”. For example, for many years while the previous generation of birth-control drugs was protected by patents, little innovation in the field was apparent in the West. At the beginning of the Twenty-First Century, when the patents were expiring and inexpensive “generic” versions would soon become available, drug companies began issuing new, patented drugs with all the usual claims of superiority. Does this in any way imply that these new drugs are not at least a little better? Before approving for sale a new drug, the U.S. government itself does not test the drug’s safety or effectiveness, let alone its superiority to existing, less-expensive products. Rather it requires the drug company in question to submit evidence from a few studies showing that the drug is safe and effective. It has been reported that before coming up with a few studies that “proved” the effectiveness of anti-depressant medications, drug companies did some 30 studies that suggested these drugs were no more effective than placebos. But for years this bit of information was withheld from the public.
Long ago my world view and my gratitude to aspirin for helping me through so many youthful migraines led me to suspect that aspirin had been condemned and acetaminophen and ibuprofen vaunted because the profit margins on sales of the latter were greater than those on aspirin sales. Recently I read of a study that gave credence to this suspicion, revealing that acetaminophen has serious side-effects that were previously “ignored” by the medical community. (That is, I suppose, information about these side-effects was suppressed.) So then one should go back to taking aspirin? The conducting and publication of this latest study could just be an indication that the profit margins on acetaminophen sales have dropped and drug companies have a new patent-protected product almost ready to go.
In 1956—the same year as a leading Moscow monthly rejected Doctor Zhivago , stating that the novel “represented in a libelous manner the October Revolution, the people who made it and social construction in the Soviet Union”—at the Soviet Communist Party congress Nikita Khrushchev rejected the notion that war between East and West was inevitable and denounced Stalin. This denouncement was made in a “secret speech” that like Zhivago was not published within the Soviet Union, but quickly became available to Russians via unofficial channels, including with the help of a Western publisher, in this case that of the U.S. Department of State. Perhaps like Stalin before it, in 2002 acetaminophen was in the process of being “secretly” denounced.
“Here’s what upsets me,” notes the badly hungover narrator of Venedikt Erofeev’s famous samizdat novel Moscow to the End of the Line (as the title has been translated). “I have just calculated that between Chekhov Street and the train station I drank another six rubles worth—but what did I drink where? and in what order? And did it help or hurt? No one knows, and now no one will ever know.”
William Eaton is an award-winning journalist, novelist, and writer of philosophical essays and dialogues. Surviving the Twenty-First Century , a collection of his essays from Montaigbakhtinian.com, was published last year by Serving House Books. One of Eaton’s dialogues, The Professor of Ignorance Condemns the Airplane , was staged in New York in 2014. He is editor of Zeteo , an online journal for generalists. (updated 4/2016)
William Eaton has also published in AGNI as William Eaton Warner.

Buy for others
Buying and sending ebooks to others.
- Select quantity
- Buy and send eBooks
- Recipients can read on any device
These ebooks can only be redeemed by recipients in the US. Redemption links and eBooks cannot be resold.
Sorry, there was a problem.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
On the Midnight Train: Moscow to Leningrad: Memoir, Essays, Psychology, Poetry, Theater - About profoundly deep--rooted conflict and an even more fundamental yearning for peace Kindle Edition
- Reading age 12 - 18 years
- Print length 166 pages
- Language English
- Grade level 11 - 12
- Publication date July 24, 2017
- Page Flip Enabled
- Word Wise Enabled
- Enhanced typesetting Enabled
- Sticky notes On Kindle Scribe
- See all details
Editorial Reviews
About the author, product details.
- ASIN : B07483BSLW
- Publication date : July 24, 2017
- Language : English
- File size : 888 KB
- Simultaneous device usage : Unlimited
- Text-to-Speech : Enabled
- Screen Reader : Supported
- Enhanced typesetting : Enabled
- X-Ray : Not Enabled
- Word Wise : Enabled
- Sticky notes : On Kindle Scribe
- Print length : 166 pages
- Page numbers source ISBN : 1532897227
Customer reviews
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 5 star 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 100%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 4 star 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 3 star 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 2 star 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 1 star 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Report an issue
- About Amazon
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell products on Amazon
- Sell on Amazon Business
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Become an Affiliate
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Make Money with Us
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Amazon and COVID-19
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

COMMENTS
REVIEW. In her essay for medical school, Morgan pitches herself as a future physician with an interdisciplinary approach, given her appreciation of how the humanities can enable her to better ...
Here are tips on writing a medical school personal statement and examples of essays that stood out.
As a medical school applicant, you've worked hard on your submitting the best AMCAS application you can. You've written a compelling medical school personal statement, a detailed AMCAS Work and Activities section, and more. Now med schools are sending you school-specific secondary applications that require you to write additional essays?
Successful Harvard Medical School Essays | 2024. With a consistently competitive pool of applicants submitting essays to top medical schools each year, it is essential to gain a high-level ...
220+ medical school personal statement examples, plus a step-by-step guide to writing a unique essay and an analysis of a top-5 medical school personal statement
Medical School Secondary Essay Prompts (2024-2025) August 30, 2024 / Dr. Shemmassian. A complete list of med school secondary prompts to help you get ahead and stay organized during your admissions process. We recommend using this resource alongside our Secondary Essay Premium Example Hub, which includes a sample essay in response to every ...
Secondary medical school essays should highlight why an applicant is a good fit. Applicants should submit the essays early without compromising quality. It's important to be authentic in essay ...
50 Successful Harvard Medical School Essays is the first in a new line of books published by the Staff of the Harvard Crimson. It includes fifty standout essays from students who successfully secured a spot at Harvard Medical School. Each student has a unique set of experiences that led them to medicine. Each essay includes analysis by Crimson ...
How to Answer Common Essay Prompts on Medical School Secondary Applications Coherently emphasize your unique persona, life journey, motivations and alignment with the medical profession.
Looking for inspiration for your medical school essay? Our blog provides examples, expert tips & common mistakes to avoid for helping you craft a winning essay.
SHARE: The Personal Comments Essay section of the American Medical College Application Service ® (AMCAS ®) application is your opportunity to tell medical school admissions officers who you are and what makes you unique. Here are some tips to help you as you write your essay.
Applying to medical school is a long stressful process, here are some sample medical school essays to help you get started.
A physician and former medical school admissions officer teaches you how to write your medical school personal statement, step by step. Read several full-length medical school personal statement examples for inspiration. In this article, a former medical school admissions officer explains exactly how to write a stand-out medical school personal statement!
How do you write strong diversity essays for medical school applications? Read our strategy tips, topics, and medical school diversity essays examples.
The Wakley Prize essay competition is open to people who use health services and to anyone working in medicine, research, or a health-related field. You can be at any career stage - just starting out in your studies, established in your specialty, or looking back over decades of service.
Successful Harvard Medical School Essay I vividly recall the surge of emotion and chills that ran down my spine as I wandered through the free health clinic in a rural, impoverished Salvadoran town.
Learn how to write college essays for BS/MD programs like Brown, Rice, or Villanova. Essay Examples + step-by-step guide for students applying to undergraduate medical programs.
Read the student essays about the promise of medicine featured in the 2017-2018 Dean's Report.
Medical Essays The essays below were written by students to help you with your own studies. If you are looking for help with your essay then we offer a comprehensive writing service, provided by fully qualified academics in your field of study. Essay Writing Service
Furthermore, the reliability of AI-powered language models for the grading of essays in the medical field has not yet been evaluated; in addition to essay structure and language, the evaluation of essay scripts in the field of OMS would require a level of understanding of dentistry, medicine and surgery.
The 2nd "Doctor as a Humanist" Symposium took place at Sechenov University in Moscow from the 1 st to the 3 rd of April, 2019, to explore the holistic perspective of interpersonal treatment. To begin our essay, we would like to clarify some key concepts, such as culture, humanism and humanities, as they were employed at the conference.
Even before playwrights began turning doctors into staples of satire, medical information was being distorted by the pecuniary interests of medical specialists, and the intersection of capitalism and medicine seems to have magnified these distortions.
In the form of essays, the authors of the book tried to convey to the reader the main historical milestones in the development of medical education at Moscow University. They give a brief overview of the development of university medical education and the historical origins of the first medical journals and societies.
On the Midnight Train: Moscow to Leningrad: Memoir, Essays, Psychology, Poetry, Theater - About profoundly deep-rooted conflict and an even more fundamental yearning for peace - Kindle edition by Robinson, Skip.