Jump to navigation
- Inside Writing
- Teacher's Guides
- Student Models
- Writing Topics
- Minilessons
- Shopping Cart
- Inside Grammar
- Grammar Adventures
- CCSS Correlations
- Infographics
Get a free Grammar Adventure! Choose a single Adventure and add coupon code ADVENTURE during checkout. (All-Adventure licenses aren’t included.)
Sign up or login to use the bookmarking feature.

7 Graphic Organizers for Critical Thinking

smit, 2015 / Shutterstock.com
We all want students to think critically about the subjects we teach, but how can we make it happen? What does deeper thinking look like in English language arts, science, social studies, and math?
One way to see students' thinking is to have them create graphic organizers. Each graphic organizer that follows requires your students to use different critical thinking skills (in parentheses). Read about each organizer and the thinking it creates, and then click to see minilesson activities you can present to your students to get them thinking deeply.
Time Lines (Sequencing)

When your students create time lines, they sort details in chronological order. Of course, time lines work well for historical events, like this time line of the life of Madame Curie. But they also work well for helping students understand the steps in a process or the sequence of events in a short story or novel.
Have students write the topic at the top and then draw a vertical line. On the left of the line, they write dates, numbers (1, 2, 3, 4 . . .), or even words like "First," "Next," and "Then." On the right of the line, students write events in time order. The minilesson activity has a document download that you can use as well.
View "Sequencing with a Timeline" Minilesson
Pro-Con Charts (Evaluation)

If you want students to evaluate the good and bad aspects of a topic, get them to create a pro-con chart. This chart explores the pros and cons of the Westward Expansion in U.S. history. You can also have students analyze a character from a novel or think deeply about an issue for an argument essay.
Have students write the topic at the top of a piece of paper and draw a large T shape under it. Afterward, they should label the left column "Pro" and use it for positives and label the right column "Con" and use it for negatives. If you would rather hand out a printout or have students work electronically, check out the document download in the minilesson activity.
View "Evaluating with a Pro-Con Chart" Minilesson
Cause-Effect Charts (Causation)
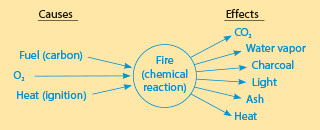
When students think about causes and effects, they tend to think in a very linear fashion: The bat hits the ball and sends it over the fence. But many topics have much more complex webs of cause and effect. A chart like this one, which analyzes the causes and effects of fire, helps students sort out those complexities. Imagine having students analyze the causes and effects of Katniss Everdeen's plight in The Hunger Games .
Have students write their topic in the middle of a page and circle it. Then have them write "Causes" above to the left and "Effects" above to the right. Under these labels, students list causes and effects and connect them to the topic using arrows. Or you can use the digital download available in the minilesson activity.
View "Analyzing with a Cause-Effect Chart" Minilesson
Venn Diagrams (Comparison and Contrast)
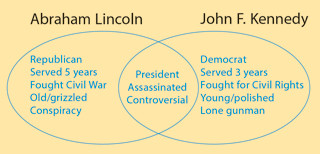
A good-old Venn diagram can help your students explore the ways that two topics are similar and the ways they are different. This diagram compares two American presidents who were assassinated. Your students can use the Venn diagram to compare two characters, two methods for doing a division problem, or any other topics with comparisons and contrasts.
Have students draw two overlapping circles (or ovals) and write one topic above each. Then have them list similarities in the overlapping section and differences in the outer parts. Encourage them to keep the differences parallel: When they write a detail in one side, they should write a contrasting detail in the other side. The minilesson activity includes a download of a Venn diagram template.
View "Comparing with a Venn Diagram" Minilesson
Line Diagrams (Classification)
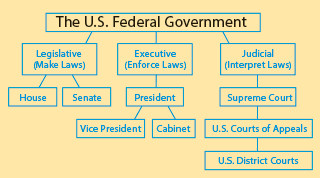
Creating a line diagram can help students analyze the parts of something and how those parts interconnect. This example shows the three branches of the U.S. federal government. Students could use line diagrams to analyze the structure of an organization, the relationships between members in a family, the taxonomy of a species, or even the different types of verbs (active, linking, and passive, with examples of each).
Have students write the topic at the top of the page in a centered box. Then have students break the topic into sub-categories by creating and connecting boxes beneath the first. Students can also have sub-sub-categories and so on. Or you can have students use the line diagram download in the minilesson activity.
View "Analyzing with a Line Diagram" Minilesson
Planning Sheets (Goal Setting)

Teachers are masters of planning, but we rarely teach students directly how to do it. This planning sheet brings all of the details together in one spot. By walking step by step through the process of planning a project or activity, your students can think deeply about their work. This planning sheet helped a student plan a video project about the U.S. Westward Expansion. You can use this sheet to help students plan research reports, Web sites, community projects, or any other complex student-centered activity.
Download the planning sheet in the minilesson activity and provide it to students either on paper or digitally. Then lead them through the minilesson for filling out the sheet. The sheet not only helps them think about the project in advance, but it also helps you track their progress and make sure they stay on target.
You can use the sheet in your own planning as well, outlining a complex project for your students so that they fully understand your expectations. And once you or your students create a planning sheet, you have the start of a rubric for the project (see below).
View "Creating a Plan" Minilesson
Rubrics (Evaluation)
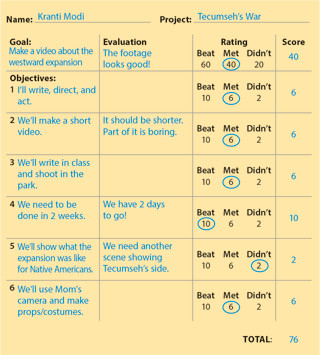
You can create a quick rubric for any project by writing the Goal (what students are doing and why) and creating Objectives (answering the 5 W's and H questions about the project: Who? What? Where? When? Why? and How? ). If you or your students have used the planning sheet to prepare for the project, you've already created a goal and objectives. You'll just copy them into the first column of the rubric template.
The first column in the example rubric was created from the goal and objectives outlined in the planning sheet for the Westward Expansion video project. In the second column, a student reflected on how well he had met the goal and objective. In the third column, the student circled whether he Beat, Met, or Didn't meet the goal and objectives. By adding up the weighted score, the student arrived at a percentage score of the project. (Note that simply meeting expectations results in an average score: C. If a student exceeds expectation for the goal and all objectives, he or she will score 120 points, an A+. Or you can convert the 20 points into extra credit on the project—a great incentive to excel.)
Get the rubric sheet download in the minilesson activity, and use the activity to teach your students the vital skill of evaluation.
View "Creating a Rubric to Evaluate Projects" Minilesson
Teacher Support:
Click to find out more about this resource.
Standards Correlations:
The State Standards provide a way to evaluate your students' performance.
- 110.6.b.11.B
- 110.6.b.12.B
- LAFS.4.W.1.2
- 110.6.b.11.A
- LAFS.4.W.2.4
- 110.6.b.11.C
- 110.6.b.11.D
- LAFS.4.W.2.5
- 110.6.b.11.E
- LAFS.4.W.2.6
- LAFS.4.W.3.7
- 110.7.b.12.B
- LAFS.5.W.1.2
- 110.7.b.11.A
- LAFS.5.W.2.4
- 110.7.b.11.C
- 110.7.b.11.D
- LAFS.5.W.2.5
- 110.7.b.11.E
- LAFS.5.W.2.6
- LAFS.5.W.3.7
- 110.22.b.10
- 110.22.b.11.B
- LAFS.6.W.1.2
- 110.22.b.10.A
- 110.22.b.10.B
- LAFS.6.W.2.4
- 110.22.b.10.C
- 110.22.b.10.D
- LAFS.6.W.2.5
- 110.22.b.10.E
- LAFS.6.W.2.6
- 110.22.b.12
- LAFS.6.W.3.7
- 110.23.b.10
- 110.23.b.11.B
- LAFS.7.W.1.2
- 110.23.b.10.A
- LAFS.7.W.2.4
- 110.23.b.10.C
- 110.23.b.10.D
- LAFS.7.W.2.5
- 110.23.b.10.E
- LAFS.7.W.2.6
- 110.23.b.12
- LAFS.7.W.3.7
- 110.24.b.10
- 110.24.b.11.B
- LAFS.8.W.1.2
- 110.24.b.10.A
- LAFS.8.W.2.4
- 110.24.b.10.C
- 110.24.b.10.D
- LAFS.8.W.2.5
- 110.24.b.10.E
- LAFS.8.W.2.6
- 110.24.b.12
- LAFS.8.W.3.7
Related Resources
All resources.
- Analyzing with a Line Diagram
- Sequencing with a Time Line
- Analyzing with a Cause-Effect Chart
- Comparing with a Venn Diagram
- Evaluating with a Pro-Con Chart
- Inquire Online Middle School Classroom Set
- Inquire Online Middle School Teacher's Guide
- Inquire Middle School Teacher's Guide
- Inquire Middle School
- Inquire Elementary Teacher's Guide
- Inquire Elementary
- Inquire High School Teacher's Guide

50 Super-Fun Critical Thinking Strategies to Use in Your Classroom
by AuthorAmy
Teaching students to be critical thinkers is perhaps the most important goal in education. All teachers, regardless of subject area, contribute to the process of teaching students to think for themselves. However, it’s not always an easy skill to teach. Students need guidance and practice with critical thinking strategies at every level.
One problem with teaching critical thinking is that many different definitions of this skill exist. The Foundation for Critical Thinking offers four different definitions of the concept. Essentially, critical thinking is the ability to evaluate information and decide what we think about that information, a cumulative portfolio of skills our students need to be successful problem solvers in an ever-changing world.
Here is a list of 50 classroom strategies for teachers to use to foster critical thinking among students of all ages.
1. Don’t give them the answers
Learning is supposed to be hard, and while it may be tempting to jump in and direct students to the right answer, it’s better to let them work through a problem on their own. A good teacher is a guide, not an answer key. The goal is to help students work at their “challenge” level, as opposed to their “frustration” level.
2. Controversial issue barometer
In this activity, a line is drawn down the center of the classroom. The middle represents the neutral ground, and the ends of the line represent extremes of an issue. The teacher selects an issue and students space themselves along the line according to their opinions. Being able to articulate opinions and participate in civil discourse are important aspects of critical thinking.
3. Play devil’s advocate
During a robust classroom discussion, an effective teacher challenges students by acting as devil’s advocate, no matter their personal opinion. “I don’t care WHAT you think, I just care THAT you think” is my classroom mantra. Critical thinking strategies that ask students to analyze both sides of an issue help create understanding and empathy.
4. Gallery walk
In a gallery walk, the teacher hangs images around the classroom related to the unit at hand (photographs, political cartoons, paintings). Students peruse the artwork much like they are in a museum, writing down their thoughts about each piece.
5. Review something
A movie, TV show , a book, a restaurant, a pep assembly, today’s lesson – anything can be reviewed. Writing a review involves the complex skill of summary without spoilers and asks students to share their opinion and back it up with evidence.
6. Draw analogies
Pick two unrelated things and ask students how those things are alike (for example, how is a museum like a snowstorm). The goal here is to encourage creativity and look for similarities.
7. Think of 25 uses for an everyday thing
Pick an everyday object (I use my camera tripod) and set a timer for five minutes. Challenge students to come up with 25 things they can use the object for within that time frame. The obvious answers will be exhausted quickly, so ridiculous answers such as “coatrack” and “stool” are encouraged.
8. Incorporate riddles
Students love riddles. You could pose a question at the beginning of the week and allow students to ask questions about it all week.
9. Crosswords and sudoku puzzles
The games section of the newspaper provides great brainteasers for students who finish their work early and need some extra brain stimulation.
10. Fine tune questioning techniques
A vibrant classroom discussion is made even better by a teacher who asks excellent, provocative questions. Questions should move beyond those with concrete answers to a place where students must examine why they think the way they do.
11. Socratic seminar
The Socratic seminar is perhaps the ultimate critical thinking activity. Students are given a universal question, such as “Do you believe it is acceptable to break the law if you believe the law is wrong?” They are given time to prepare and answer, and then, seated in a circle, students are directed to discuss the topic. Whereas the goal of a debate is to win, the goal of a Socratic discussion is for the group to reach greater understanding.
12. Inquiry based learning
In inquiry-based learning, students develop questions they want answers to, which drives the curriculum toward issues they care about. An engaged learner is an essential step in critical thinking.
13. Problem-based learning
In problem-based learning, students are given a problem and asked to develop research-based solutions. The problem can be a school problem (the lunchroom is overcrowded) or a global problem (sea levels are rising).
14. Challenge all assumptions
The teacher must model this before students learn to apply this skill on their own. In this strategy, a teacher helps a student understand where his or her ingrained beliefs come from. Perhaps a student tells you they believe that stereotypes exist because they are true. An effective teacher can ask “Why do you think that?” and keep exploring the issue as students delve into the root of their beliefs. Question everything.
15. Emphasize data over beliefs
Data does not always support our beliefs, so our first priority must be to seek out data before drawing conclusions.
16. Teach confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is the human tendency to seek out information that confirms what we already believe, rather than letting the data inform our conclusions. Understanding that this phenomenon exists can help students avoid it.
17. Visualization
Help students make a plan before tackling a task.
18. Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual way to organize information. Students start with a central concept and create a web with subtopics that radiate outward.
19. Develop empathy
Empathy is often cited as an aspect of critical thinking. To do so, encourage students to think from a different point of view. They might write a “con” essay when they believe the “pro,” or write a letter from someone else’s perspective.
20. Summarization
Summarizing means taking all the information given and presenting it in a shortened fashion.
21. Encapsulation
Encapsulation is a skill different from summarization. To encapsulate a topic, students must learn about it and then distill it down to its most relevant points, which means students are forming judgements about what is most and least important.
22. Weigh cause and effect
The process of examining cause and effect helps students develop critical thinking skills by thinking through the natural consequences of a given choice.
23. Problems in a jar
Perfect for a bell-ringer, a teacher can stuff a mason jar with dilemmas that their students might face, such as, “Your best friend is refusing to talk to you today. What do you do?” Then, discuss possible answers. This works well for ethical dilemmas, too.
24. Transform one thing into another
Give students an object, like a pencil or a mug. Define its everyday use (to write or to drink from). Then, tell the students to transform the object into something with an entirely separate use. Now what is it used for?
25. Which one doesn’t belong?
Group items together and ask students to find the one that doesn’t belong. In first grade, this might be a grouping of vowels and a consonant; in high school, it might be heavy metals and a noble gas.
26. Compare/contrast
Compare and contrast are important critical thinking strategies. Students can create a Venn diagram to show similarities or differences, or they could write a good old-fashioned compare/contrast essay about the characters of Romeo and Juliet .
27. Pick a word, find a related word
This is another fun bell-ringer activity. The teacher starts with any word, and students go around the room and say another word related to that one. The obvious words go quickly, meaning the longer the game goes on, the more out-of-the-box the thinking gets.
28. Ranking of sources
Give students a research topic and tell them to find three sources (books, YouTube videos, websites). Then ask them, what resource is best – and why.
29. Hypothesize
The very act of hypothesizing is critical thinking in action. Students are using what they know to find an answer to something they don’t know.
30. Guess what will happen next
This works for scientific reactions, novels, current events, and more. Simply spell out what we know so far and ask students “and then what?”
31. Practice inference
Inference is the art of making an educated guess based on evidence presented and is an important component of critical thinking.
32. Connect text to self
Ask students to draw connections between what they are reading about to something happening in their world. For example, if their class is studying global warming, researching how global warming might impact their hometown will help make their studies relevant.
33. Levels of questioning
There are several levels of questions (as few as three and as many as six, depending on who you ask). These include factual questions, which have a right or wrong answer (most math problems are factual questions). There are also inferential questions, which ask students to make inferences based on both opinion and textual evidence. Additionally, there are universal questions, which are “big picture” questions where there are no right or wrong answers.
Students should practice answering all levels of questions and writing their own questions, too.
34. Demand precise language
An expansive vocabulary allows a student to express themselves more exactly, and precision is a major tool in the critical thinking toolkit.
35. Identify bias and hidden agendas
Helping students to critically examine biases in sources will help them evaluate the trustworthiness of their sources.
36. Identify unanswered questions
After a unit of study is conducted, lead students through a discussion of what questions remain unanswered. In this way, students can work to develop a lifelong learner mentality.
37. Relate a topic in one subject area to other disciplines
Have students take something they are studying in your class and relate it to other disciplines. For example, if you are studying the Civil War in social studies, perhaps they could look up historical fiction novels set during the Civil War era or research medical advancements from the time period for science.
38. Have a question conversation
Start with a general question and students must answer your question with a question of their own. Keep the conversation going.
39. Display a picture for 30 seconds, then take it down
Have students list everything they can remember. This helps students train their memories and increases their ability to notice details.
40. Brainstorm, free-write
Brainstorming and freewriting are critical thinking strategies to get ideas on paper. In brainstorming, anything goes, no matter how off-the-wall. These are great tools to get ideas flowing that can then be used to inform research.
41. Step outside your comfort zone
Direct students to learn about a topic they have no interest in or find particularly challenging. In this case, their perseverance is being developed as they do something that is difficult for them.
42. The answer is, the question might be
This is another bell-ringer game that’s great for engaging those brains. You give students the answer and they come up with what the question might be.
43. Cooperative learning
Group work is a critical thinking staple because it teaches students that there is no one right way to approach a problem and that other opinions are equally valid.
44. What? So what? Now what?
After concluding a unit of study, these three question frames can be used to help students contextualize their learning.
45. Reflection
Ask students to reflect on their work – specifically, how they can improve moving forward.
46. Classify and categorize
These are higher level Bloom’s tasks for a reason. Categorizing requires students to think about like traits and rank them in order of importance.
47. Role play
Roleplay allows students to practice creative thinking strategies. Here, students assume a role and act accordingly.
48. Set goals
Have students set concrete, measurable goals in your class so they understand why what they do matters.
No matter your subject area, encourage students to read voraciously. Through reading they will be exposed to new ideas, new perspectives, and their worlds will grow.
50. Cultivate curiosity
A curious mind is an engaged mind. Students should be encouraged to perform inquiry simply for the sake that it is a joy to learn about something we care about.

TREAT YO' INBOX!
All the trending teacher stories, resources, videos, memes, podcasts, deals, and the laughter you need in your life!
Educationise
11 Activities That Promote Critical Thinking In The Class
Ignite your child’s curiosity with our exclusive “Learning Adventures Activity Workbook for Kids” a perfect blend of education and adventure!
Critical thinking activities encourage individuals to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to develop informed opinions and make reasoned decisions. Engaging in such exercises cultivates intellectual agility, fostering a deeper understanding of complex issues and honing problem-solving skills for navigating an increasingly intricate world.
Through critical thinking, individuals empower themselves to challenge assumptions, uncover biases, and constructively contribute to discourse, thereby enriching both personal growth and societal progress.
Critical thinking serves as the cornerstone of effective problem-solving, enabling individuals to dissect challenges, explore diverse perspectives, and devise innovative solutions grounded in logic and evidence. For engaging problem solving activities, read our article problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest.
52 Critical Thinking Flashcards for Problem Solving
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a 21st-century skill that enables a person to think rationally and logically in order to reach a plausible conclusion. A critical thinker assesses facts and figures and data objectively and determines what to believe and what not to believe. Critical thinking skills empower a person to decipher complex problems and make impartial and better decisions based on effective information.
More Articles from Educationise
- 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
- How to Foster Critical Thinking Skills in Students? Creative Strategies and Real-World Examples
- 9 Must-Have AI Tools for Teachers to Create Interactive Learning Materials
- The Future of Education: 8 Predictions for the Next Decade
- The Latest in EdTech: 5 Innovative Tools and Technologies for the Classroom
- 8 Free Math Problem Solving Websites and Applications
Importance of Acquiring Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking skills cultivate habits of mind such as strategic thinking, skepticism, discerning fallacy from the facts, asking good questions and probing deep into the issues to find the truth. Acquiring critical thinking skills was never as valuable as it is today because of the prevalence of the modern knowledge economy.
Today, information and technology are the driving forces behind the global economy. To keep pace with ever-changing technology and new inventions, one has to be flexible enough to embrace changes swiftly.
Today critical thinking skills are one of the most sought-after skills by the companies. In fact, critical thinking skills are paramount not only for active learning and academic achievement but also for the professional career of the students.
The lack of critical thinking skills catalyzes memorization of the topics without a deeper insight, egocentrism, closed-mindedness, reduced student interest in the classroom and not being able to make timely and better decisions.
Incorporating critical thinking lessons into the curriculum equips students with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of the modern world, fostering a mindset that is adaptable, inquisitive, and capable of discerning truth from misinformation.
Benefits of Critical Thinking for Students
Certain strategies are more eloquent than others in teaching students how to think critically. Encouraging critical thinking in the classroom is indispensable for the learning and growth of the students. In this way, we can raise a generation of innovators and thinkers rather than followers. Some of the benefits offered by thinking critically in the classroom are given below:
- It allows a student to decipher problems and think through the situations in a disciplined and systematic manner
- Through a critical thinking ability, a student can comprehend the logical correlation between distinct ideas
- The student is able to rethink and re-justify his beliefs and ideas based on facts and figures
- Critical thinking skills make the students curious about things around them
- A student who is a critical thinker is creative and always strives to come up with out of the box solutions to intricate problems
Read our article: How to Foster Critical Thinking Skills in Students? Creative Strategies and Real-World Examples
- Critical thinking skills assist in the enhanced student learning experience in the classroom and prepares the students for lifelong learning and success
- The critical thinking process is the foundation of new discoveries and inventions in the world of science and technology
- The ability to think critically allows the students to think intellectually and enhances their presentation skills, hence they can convey their ideas and thoughts in a logical and convincing manner
- Critical thinking skills make students a terrific communicator because they have logical reasons behind their ideas
Critical Thinking Lessons and Activities
11 Activities that Promote Critical Thinking in the Class
We have compiled a list of 11 critical thinking activities for students that will facilitate you to promote critical thinking abilities in the students. By incorporating these activities, educators can introduce real-world examples of critical thinking in the classroom, empowering students to apply these skills in everyday situations.
We have also covered problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest in our another article. Click here to read it.
1. Worst Case Scenario
Divide students into teams and introduce each team with a hypothetical challenging scenario. Allocate minimum resources and time to each team and ask them to reach a viable conclusion using those resources.
The scenarios can include situations like stranded on an island or stuck in a forest. Students will come up with creative solutions to come out from the imaginary problematic situation they are encountering. Besides encouraging students to think critically, this activity will enhance teamwork, communication and problem-solving skills of the students.
This critical thinking activity not only pushes students to devise innovative solutions in challenging scenarios but also strengthens their teamwork, communication, and problem-solving abilities, making it an engaging and educational experience.
Read our article: 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
2. If You Build It
It is a very flexible game that allows students to think creatively. To start this activity, divide students into groups. Give each group a limited amount of resources such as pipe cleaners, blocks, and marshmallows etc.
Every group is supposed to use these resources and construct a certain item such as building, tower or a bridge in a limited time. You can use a variety of materials in the classroom to challenge the students. This activity is helpful in promoting teamwork and creative skills among the students.
Incorporating critical thinking games like this into your classroom not only promotes teamwork and creativity but also challenges students to think outside the box as they work together to build their structures.
It is also one of the classics which can be used in the classroom to encourage critical thinking. Print pictures of objects, animals or concepts and start by telling a unique story about the printed picture. The next student is supposed to continue the story and pass the picture to the other student and so on.
This engaging exercise is one of the most effective critical thinking activities for kids, as it encourages them to use their creativity and problem-solving skills while working together to construct innovative structures with limited resources.
4. Keeping it Real
In this activity, you can ask students to identify a real-world problem in their schools, community or city. After the problem is recognized, students should work in teams to come up with the best possible outcome of that problem.
5. Save the Egg
Make groups of three or four in the class. Ask them to drop an egg from a certain height and think of creative ideas to save the egg from breaking. Students can come up with diverse ideas to conserve the egg like a soft-landing material or any other device. Remember that this activity can get chaotic, so select the area in the school that can be cleaned easily afterward and where there are no chances of damaging the school property.
6. Start a Debate
In this activity, the teacher can act as a facilitator and spark an interesting conversation in the class on any given topic. Give a small introductory speech on an open-ended topic. The topic can be related to current affairs, technological development or a new discovery in the field of science. Encourage students to participate in the debate by expressing their views and ideas on the topic. Conclude the debate with a viable solution or fresh ideas generated during the activity through brainstorming.
7. Create and Invent
This project-based learning activity is best for teaching in the engineering class. Divide students into groups. Present a problem to the students and ask them to build a model or simulate a product using computer animations or graphics that will solve the problem. After students are done with building models, each group is supposed to explain their proposed product to the rest of the class. The primary objective of this activity is to promote creative thinking and problem-solving skills among the students.
8. Select from Alternatives
This activity can be used in computer science, engineering or any of the STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) classes. Introduce a variety of alternatives such as different formulas for solving the same problem, different computer codes, product designs or distinct explanations of the same topic.
Form groups in the class and ask them to select the best alternative. Each group will then explain its chosen alternative to the rest of the class with reasonable justification of its preference. During the process, the rest of the class can participate by asking questions from the group. This activity is very helpful in nurturing logical thinking and analytical skills among the students.
9. Reading and Critiquing
Present an article from a journal related to any topic that you are teaching. Ask the students to read the article critically and evaluate strengths and weaknesses in the article. Students can write about what they think about the article, any misleading statement or biases of the author and critique it by using their own judgments.
In this way, students can challenge the fallacies and rationality of judgments in the article. Hence, they can use their own thinking to come up with novel ideas pertaining to the topic.
10. Think Pair Share
In this activity, students will come up with their own questions. Make pairs or groups in the class and ask the students to discuss the questions together. The activity will be useful if the teacher gives students a topic on which the question should be based.
For example, if the teacher is teaching biology, the questions of the students can be based on reverse osmosis, human heart, respiratory system and so on. This activity drives student engagement and supports higher-order thinking skills among students.
11. Big Paper – Silent Conversation
Silence is a great way to slow down thinking and promote deep reflection on any subject. Present a driving question to the students and divide them into groups. The students will discuss the question with their teammates and brainstorm their ideas on a big paper.
After reflection and discussion, students can write their findings in silence. This is a great learning activity for students who are introverts and love to ruminate silently rather than thinking aloud.
Incorporating critical thinking activities for high school students, like silent reflection and group brainstorming, encourages deep thought and collaboration, making it an effective strategy for engaging both introverted and extroverted learners.
Finally, for students with critical thinking, you can go to GS-JJ.co m to customize exclusive rewards, which not only enlivens the classroom, but also promotes the development and training of students for critical thinking.
Share this:
Discover more from educationise.
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
4 thoughts on “ 11 Activities That Promote Critical Thinking In The Class ”
- Pingback: What is Growth Mindset? 50+ Motivational Quotes on Growth Mindset - Educationise
- Pingback: 6 Steps To Implement Project-Based Learning In The Classroom - Educationise
- Pingback: Engaging Problem-Solving Activities That Spark Student Interest - Educationise
Thanks for the great article! Especially with the post-pandemic learning gap, these critical thinking skills are essential! It’s also important to teach them a growth mindset. If you are interested in that, please check out The Teachers’ Blog!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Picture Prompts
145 Picture Prompts to Inspire Student Writing
A school year’s worth of short, accessible image-driven posts that invite a variety of kinds of writing.

By The Learning Network
Image from our related Picture Prompt “ Creative Juices .”
We’ve been publishing our Picture Prompts series four days a week since 2016. Below, we’ve rounded up all the prompts we published for the 2021-22 school year.
These short, accessible, image-driven prompts invite students to pen short stories, poems and memoirs; share experiences from their lives; analyze illustrations, graphs and charts; and tell us their opinions on hot-button issues.
You can find even more in our roundups for the 2016-17 , 2017-18 , 2018-19 , 2019-20 and 2020-21 school years. That’s nearly 900 prompts, many still open for comment by students 13 and up. We have also published a short, visual post highlighting four popular prompts from this school year.
To learn how you can use Picture Prompts to build literacy skills, promote critical thinking, inspire discussion and foster creativity in your classroom, watch our three-minute tutorial video or our on-demand webinar . For dozens more ideas, see our lesson plan, “ How to Teach With Our Picture Prompts (and Other Times Images) .”
If you use this feature with your students, or if you have other ideas for how to use photos, illustrations and graphics to encourage writing, let us know in the comments.
What story does this image inspire for you?

Phone Booth in the Wilderness Roller Coasters In the Waves In the Lunchroom Den of Toys Butterflies Flight Delays Two Roads Dog Park Friendship Under the Sea Found in the Crowd Under the Desk Barren Landscape Park Bench Other Selves On the Court Holiday Party Little Red House Candy Cornucopia Doors Mystery Money Royal Dining Up in a Tree Around the Fire Galaxy Plundered Shelves Confetti Solo Climb At the Fountain Heated Conversation Yellow Creatures Meadow in Starlight Storm On the Subway Giant Jar Family
Share experiences from your own life.
Pet Ownership Creative Juices Horror Stories One Great Summer Memory Dining Out Riddle Me This Your Go-To Recipes Hitting the Road Comic Con Craze October Thrifting Harry Potter Self-Compassion Holiday Shopping Giving Gratitude Festive Wear Measuring Time Winter TV Shows Sacred Spaces Your Tech Local Celebrities Winter Olympics Wildlife in Winter Group Chat Winter Getaways D.I.Y. Taste Test Spring Fashion March Madness Mask Withdrawal Your Favorite Tree Rites of Spring Fortuitous Finds Hanging Out Heartbroken Best Pizza? Everyday Pleasures Musical Instruments
What do you think this image, chart or cartoon is saying?
Hands Blasting Out of a Phone Dings and Pings Pulling at a Reflection Memorial Twisting Track Elephant and Donkey Tiny Dollar Clouds Vision Test The Whole World Work and Home Bedroom Staring Crossed-Out Words Clicking Her Heels Weapon Burger Quitting Spoonfed Brady Mesmerized Skates Melting Man Lit-Up Landmarks Literary Allusions A Brick on an Egg Listening and Clapping Between the Ears Smiling X’s on Bubbles Eyeballs Inside Vs. Outside Amazon Boxes Area Closed High Wire Very, Very Tired
What’s your opinion on this issue?
A New Social App Morality Plays Flamboyant Fashion Home Games Powering Down Facebook Outage Old Glory Custom Cars Tourist Surveillance E-Scooters, E-Bikes Motorcycle Adventures Veterans Day Book Lovers Speed Skydiving Gift-Giving, Gift-Getting Solstice Favorite Moments in Sports Your Word of the Year Guilty Pleasures Smart Watch Wordle True Love? Prized Possessions Audiobooks Separate Together TV-Themed Trips Forgiveness Life at Sea Constructive Criticism Electric Cars Little Free Libraries Met Gala #VanLife Responding to the Shooting in Uvalde
- Description Generator
Child Report Generator
- Marking and Grading Assistant
- Lesson Plans
- Lesson Plan Power Points
Email & Message Reply Generator
- Story Writer
Question Generator
- Multi Choice Generator
- Long Form Question Generator
- All Articles
- Effective Feedback
- Future Classrooms
- Lesson Planning Evolution
- Collaborative Learning with AI
- Digital Literacy
- English Language
- English Literature
- Religious Studies
- Phonics and Reading
- Get Started in Seconds
Revolutionize Your Teaching with AI
Planit Teachers offers cutting-edge AI tools to supercharge your teaching productivity.
Boost Productivity
AI-Powered Planning
Use code "GETSTARTED" for 50% off your first month!
10 Fun Classroom Activities to Promote Critical Thinking
As a teacher, it's important to promote critical thinking skills in your students. Critical thinking is a valuable skill that helps students analyze information, solve problems, and make decisions. In this blog post, we'll explore 10 fun classroom activities that promote critical thinking.
Here are 10 fun classroom activities that promote critical thinking:
1. Problem-Solving Scenarios: Provide students with real-life scenarios and ask them to come up with solutions. This activity encourages students to think critically and creatively to solve problems. 2. Group Discussions: Encourage students to discuss and debate topics in groups. This activity helps students develop their communication and critical thinking skills. 3. Brainstorming: Ask students to brainstorm ideas for a project or assignment. This activity helps students develop their creativity and critical thinking skills. 4. Role-Playing: Assign students roles and ask them to act out a scenario. This activity helps students develop their empathy and critical thinking skills. 5. Analyzing Texts: Provide students with texts and ask them to analyze and interpret them. This activity helps students develop their analytical and critical thinking skills. 6. Debate: Assign students a topic and ask them to debate it. This activity helps students develop their communication and critical thinking skills. 7. Mind Mapping: Ask students to create a mind map of a topic. This activity helps students develop their organizational and critical thinking skills. 8. Creative Writing: Ask students to write a story or poem. This activity helps students develop their creativity and critical thinking skills. 9. Problem-Solving Games: Provide students with problem-solving games and ask them to solve them. This activity helps students develop their problem-solving and critical thinking skills. 10. Reflection: Ask students to reflect on their learning and identify areas for improvement. This activity helps students develop their self-awareness and critical thinking skills.
These activities are just a few examples of how you can promote critical thinking in your classroom. By incorporating these activities into your lessons, you can help your students develop their cognitive abilities and become better problem-solvers and decision-makers.
It's important to remember that critical thinking is a skill that takes time and practice to develop. By providing your students with opportunities to think critically, you can help them build this valuable skill.
In conclusion, promoting critical thinking in your classroom is essential for your students' success. By using these 10 fun classroom activities, you can engage your students and help them develop their critical thinking skills.
So, what are you waiting for? Try these activities in your classroom today and watch your students' critical thinking skills soar!
Transform Your Grading with AI Teacher Marking
Revolutionize your grading process with our advanced AI Teacher Marking tool. Our AI algorithms can efficiently grade a variety of assignments, providing detailed feedback and insights.
AI Teacher Marking doesnt just grade; it provides constructive criticism, pinpoints errors, identifies model answers, and references the mark scheme for a holistic evaluation.
By automating the grading process, AI Teacher Marking frees up valuable time for educators, allowing them to focus more on student engagement and personalized teaching.
AI Teacher Marking revolutionizes workflow efficiency for educators. The tool's capability to quickly process and grade student submissions in bulk significantly reduces the time spent on manual marking.
Beyond just grading, AI Teacher Marking offers deep analytical insights into student performance. It provides educators with detailed reports highlighting class trends, common misconceptions, and areas needing more focus.
Revolutionize Your Teaching with AI-Powered Lesson Plans
Welcome to the future of education! Planit Teachers brings you AI-powered lesson plans, tailored for any subject and age group. Just describe your topic and age group, and our advanced AI will craft a bespoke, unique lesson plan designed specifically for your needs.
Our AI-driven lesson plans are not just about convenience, they're about quality. Each plan is meticulously crafted to ensure it meets the highest educational standards. Plus, with our AI's ability to learn and adapt, your lesson plans will only get better over time.
But that's not all! With each lesson plan, you'll also receive a comprehensive list of resources to aid your teaching. And the best part? You can save your plan to your account, edit it as you see fit, and even generate a PDF for offline use or printing.
Innovative Long Form Question Generator
Transform the way you create quizzes with our state-of-the-art Long Form Question Generator. Designed for educators, this revolutionary tool crafts unlimited, expertly written questions tailored to any topic or age group, all powered by advanced AI.
Experience the freedom to customize your quizzes to align perfectly with your educational goals. Our generator allows for unparalleled customization of topics, difficulty levels, and more, enabling you to craft the perfect questions for your students in mere minutes.
Elevate your teaching and engage your students like never before. Save time, enhance learning, and ensure your quizzes are always fresh and relevant. Our Long Form Question Generator is your ultimate partner in creating dynamic, impactful educational content.
End of term reports are a time consuming and stressful task for any teacher. We've built a tool to help you save time and effort when writing reports. Simply describe the child and we'll generate a report for you. You can then edit the report to make it perfect and download it as a PDF. Your report can be tailored using tone, length and complexity settings.
Get back control of your free time using our Child Report Generator. Instant report generation for any child. Happy, angry, concerned and comedic reports generated instantly to your exact specifications.
Crafting quizzes and question sheets for your class is a problem of the past with our Question Generator. Simply describe the topic and age group and we'll do the rest, crafting you a bespoke and totally unique set of questions built exactly for your needs.
With your new quiz, you'll also get a list of resources to help as well as the ability to save your quiz to your account and edit it later. You can then generate a PDF from your quiz, download it for offline use and print for your class.
Get back control of your free time using our Question Generator. Instant quiz and question generation for any topic and age group.
Subject Description Generator
When teaching English, Teachers often need to spend time crafting complex subject, landscape, setting and character descriptions. With our Subject Description Generator, you can instantly generate a description for any subject, landscape, setting or character. Simply describe the subject, landscape, setting or character and we'll do the rest, crafting you a bespoke and totally unique description built exactly for your needs.
We even tailor the description to your exact specifications, allowing you to choose the length, complexity and tone of the description. We then craft the wording to perfectly match your age group and child level.
Multiple Choice Question Generator
Say goodbye to the hassle of creating quizzes manually. Our innovative Multiple Choice Question Generator empowers teachers to generate unlimited questions with 4 multiple choice answers on any topic for any age group, all powered by AI.
Tailor your quizzes to perfectly match your teaching needs. With the ability to customize topics, difficulty levels, and more, you can create the ideal quiz for your class in minutes. Plus, save your quizzes for future use, edit them as needed, and even generate PDFs for easy sharing and printing.
Reclaim your free time and enhance your teaching with quizzes that engage and challenge your students. Our Multiple Choice Question Generator is the ultimate tool for instant, hassle-free quiz creation for any subject and age group.
AI-powered instant replies for emails and messages. Everyone knows that teachers already have enough on their plate, so we've built a tool to help you save time and effort when replying to emails and messages from parents, students and colleagues. Simply describe the topic of the email and we'll generate a reply for you. You can then edit the reply to make it perfect and send it off. If it totally misses the mark, you can instantly regenerate a new reply and try again.
Get back control of your free time using our Email, Message, Class Dojo Reply Generator. Instant message generation for any usage.
Related Articles
- The Maker Movement in Education: Fostering Creativity and Innovation
- The Power of Project-Based Learning: Inspiring Creativity and Critical Thinking in Education
- The Teacher as a Cognitive Coach: Nurturing Metacognition in the Classroom
- The Neuroscience of Creativity: Fostering Innovation in Education | Planit Teachers
- Empowering Students Through Project-Based Learning
- The Power of Play: Incorporating Play-Based Learning in the Classroom
- The Impact of Outdoor Education: Fostering Exploration and Environmental Awareness
- The Magic of Mind Mapping: Boosting Creativity and Critical Thinking in Students
- The Power of Peer Collaboration: Fostering Student Engagement
- The Benefits of Project-Based Learning: Engaging Students Through Real-World Experiences
- The Art of Reflection: Fostering Metacognitive Skills in Students
- AI and Creativity: Fostering Innovation and Critical Thinking in the Classroom
- AI and Student Engagement: Enhancing Learning Motivation with Interactive Technology
- The Art of AI-Powered Creativity: Inspiring Innovation and Critical Thinking in Students
- The Benefits of Project-Based Learning: Engaging Students Through Real-World Applications
- Fostering Creativity in the Classroom: Strategies for Inspiring Student Innovation
- The Role of Play in Learning: Enhancing Creativity and Imagination in the Classroom
- Promoting Creativity and Innovation in the Classroom - Inspiring Student Growth
- The Benefits of Project-Based Learning for Student Success
- Cultivating 21st Century Skills in Students: Preparing for the Future
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Subjects all subjects all subjects the arts all the arts visual arts performing arts value of the arts back business & economics all business & economics global economics macroeconomics microeconomics personal finance business back design, engineering & technology all design, engineering & technology design engineering technology back health all health growth & development medical conditions consumer health public health nutrition physical fitness emotional health sex education back literature & language all literature & language literature linguistics writing/composition speaking back mathematics all mathematics algebra data analysis & probability geometry measurement numbers & operations back philosophy & religion all philosophy & religion philosophy religion back psychology all psychology history, approaches and methods biological bases of behavior consciousness, sensation and perception cognition and learning motivation and emotion developmental psychology personality psychological disorders and treatment social psychology back science & technology all science & technology earth and space science life sciences physical science environmental science nature of science back social studies all social studies anthropology area studies civics geography history media and journalism sociology back teaching & education all teaching & education education leadership education policy structure and function of schools teaching strategies back thinking & learning all thinking & learning attention and engagement memory critical thinking problem solving creativity collaboration information literacy organization and time management back, filter by none.
- Elementary/Primary
- Middle School/Lower Secondary
- High School/Upper Secondary
- College/University
- TED-Ed Animations
- TED Talk Lessons
- TED-Ed Best of Web
- Under 3 minutes
- Under 6 minutes
- Under 9 minutes
- Under 12 minutes
- Under 18 minutes
- Over 18 minutes
- Algerian Arabic
- Azerbaijani
- Cantonese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Singapore)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese Simplified
- Chinese Traditional
- Chinese Traditional (Taiwan)
- Dutch (Belgium)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- Kurdish (Central)
- Luxembourgish
- Persian (Afghanistan)
- Persian (Iran)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Spanish (Argentina)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (United States)
- Western Frisian
sort by none
- Longest video
- Shortest video
- Most video views
- Least video views
- Most questions answered
- Least questions answered

How could so many people support Hitler?
Lesson duration 05:10
687,504 Views

Can you solve the magical maze riddle?
Lesson duration 04:51
479,863 Views

How to make smart decisions more easily
Lesson duration 05:16
1,346,258 Views

Can you solve a mystery before Sherlock Holmes?
Lesson duration 05:17
530,114 Views

Can you solve the secret assassin society riddle?
Lesson duration 05:01
908,842 Views

How to overcome your mistakes
Lesson duration 04:52
1,040,056 Views

Can you solve the cursed dice riddle?
Lesson duration 04:31
802,739 Views

Why some people don't have an inner monologue
Lesson duration 12:03
2,913,465 Views

Science vs. Pseudoscience
Lesson duration 05:48
370,757 Views
Can you solve the time traveling car riddle?
Lesson duration 05:18
700,213 Views

This one weird trick will get you infinite gold
Lesson duration 05:08
1,172,764 Views

How to quit your job — without ruining your career - Gala Jackson
Lesson duration 06:13
117,018 Views

What if you experienced every human life in history?
Lesson duration 05:21
3,004,199 Views

How to design climate-resilient buildings - Alyssa-Amor Gibbons
Lesson duration 14:12
46,393 Views

The case for free, universal basic services - Aaron Bastani
Lesson duration 19:09
82,191 Views

Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world?
Lesson duration 05:20
834,746 Views

History vs. Thomas Jefferson
494,585 Views

The best way to apologize (according to science)
Lesson duration 05:06
1,571,275 Views

How do we determine the value of a life?
Lesson duration 06:06
819,373 Views

What’s the smartest age?
Lesson duration 04:53
1,717,111 Views

The Boltzmann brain paradox
Lesson duration 05:40
1,231,950 Views

The 4 greatest threats to the survival of humanity
Lesson duration 05:24
496,401 Views

Can you outsmart the college admissions fallacy?
Lesson duration 06:17
838,744 Views

Can you solve the fortress riddle?
Lesson duration 05:23
1,310,347 Views
Fun Critical Thinking Activities

Learning to evaluate information, find credible sources, and prepare for counterarguments is an important skill for people to learn, especially in the modern age of information. Here are 10 great critical thinking activities designed to develop your critical thinking skills.
With so much information on the internet, parsing through what’s true and what isn’t can be a difficult challenge that relies heavily on your ability to think critically . The rest of this article will discuss 10 fun activities to improve your critical thinking skills.
Worst Case Scenario
In this first scenario, you’ll want a group of friends to bounce ideas around. The premise works by assuming that you and a group of friends are in a worst-case scenario. This might be the classic stranded on a desert island trope, but you can also change it up with something like being trapped in a spaceship with hostile aliens aboard.
In this exercise, you’ll be required to think both creatively and critically to evaluate what your best course of action is, how to allocate resources, and who should take on what roles and responsibilities.
Creative Construction
This exercise works your critical thinking muscles by forcing you to evaluate the resources you have on hand, what you can build out of them, and how you’re going to go about constructing it with the tools you have.
Story Telling
A very popular game that’s still worth its salt for adults, this activity starts with a series of random images. You can pull these straight from pictures on a browser and put them into a slideshow. Get a group together for your favorite storytime.
Not only does this create some hilarious stories, but it allows you to develop your critical thinking skills by evaluating how the image you’re given and the story might pair up.
Pragmatic Problem Solving
Where applicable, you can convert this idea into action by sharing your plan with public officials or starting a petition to inspire the change you want to see. Considering how different perspectives and resources play into this quandary is a powerful thought exercise that can help you develop your critical thinking skills.
Critical Analysis
Another great and dead simple exercise to develop your critical thinking skills is analyzing a popular piece of literature. Read it carefully and evaluate the author’s opinion, the biases behind them, and how you would either agree or contradict their viewpoints.
Controversy Conundrum
Not only do you have to present and uphold your viewpoint, but you’ll be obligated to address and respond to opposing viewpoints. To make this a twist, consider which side you’d take in the question and force yourself (and all participants) to defend their opponents’ points of view.
Alien Vacation
An entertaining premise puts you in the role of a tour guide for an alien on vacation. Evaluate something you take for granted, like a baseball game, and try to explain every aspect about it in a way that an alien would be able to comprehend. To add some humor, take turns on this exercise and have a friend play the alien to ask those probing questions.
Prison Promises
Competitor compromises.
Not only is this exercise good for developing critical thinking , but it’s a good way to think about your business. Consider your greatest business rival and assess how you could help them succeed further in their business without detrimentally affecting your own.
Final Thoughts on Fun Critical Thinking Activities
There are lots of great critical thinking exercises you can partake in, whether you want to get a group of friends together or just sit down with a pen and a pencil. Developing these skills is a dynamic and valuable way of improving your ability to solve problems.
You may also like
The relationship between empathy and critical thinking: a balanced approach, debate & critical thinking, when to use critical thinking – what you need to know.

How to Evaluate Sources Using Critical Thinking: A Concise Guide to Informed Research
Download this free ebook.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Have you seen our latest free teacher workshop?
5 Critical Thinking Activities That Get Students Up and Moving
More movement means better learning.

It’s easy to resort to having kids be seated during most of the school day. But learning can (and should) be an active process. Incorporating movement into your instruction has incredible benefits—from deepening student understanding to improving concentration to enhancing performance. Check out these critical thinking activities, adapted from Critical Thinking in the Classroom , a book with over 100 practical tools and strategies for teaching critical thinking in K-12 classrooms.
Four Corners
In this activity, students move to a corner of the classroom based on their responses to a question with four answer choices. Once they’ve moved, they can break into smaller groups to explain their choices. Call on students to share to the entire group. If students are persuaded to a different answer, they can switch corners and further discuss.
Question ideas:
- Which president was most influential: George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, or Abraham Lincoln?
- Is Holden Caulfield a hero: Strongly Agree, Agree, Disagree, or Strongly Disagree?
Gallery Walk
This strategy encourages students to move around the classroom in groups to respond to questions, documents, images, or situations posted on chart paper. Each group gets a different colored marker to record their responses and a set amount of time at each station. When groups move, they can add their own ideas and/or respond to what prior groups have written.
Gallery ideas:
- Political cartoons
Stations are a great way to chunk instruction and present information to the class without a “sit and get.” Group desks around the room or create centers, each with a different concept and task. There should be enough stations for three to five students to work for a set time before rotating.
Station ideas:
- Types of rocks
- Story elements
- Literary genres
Silent Sticky-Note Storm
In this brainstorming activity, students gather in groups of three to five. Each group has a piece of chart paper with a question at the top and a stack of sticky notes. Working in silence, students record as many ideas or answers as possible, one answer per sticky note. When time is up, they post the sticky notes on the paper and then silently categorize them.
- How can you exercise your First Amendment rights?
- What are all the ways you can divide a square into eighths?
Mingle, Pair, Share
Take your Think, Pair, Share to the next level. Instead of having students turn and talk, invite them to stand and interact. Play music while they’re moving around the classroom. When the music stops, each student finds a partner. Pose a question and invite students to silently think about their answer. Then, partners take turns sharing their thoughts.
- How do organisms modify their environments?
- What is the theme of Romeo and Juliet ?
Looking for more critical thinking activities and ideas?

Critical Thinking in the Classroom is a practitioner’s guide that shares the why and the how for building critical thinking skills in K-12 classrooms. It includes over 100 practical tools and strategies that you can try in your classroom tomorrow!
Get Your Copy of Critical Thinking in the Classroom

You Might Also Like

10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers
Help students dig deeper! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
- Members Newsfeed
20 Critical Thinking Activities for Elementary Classrooms
- Elementary Education

Introduction:
In today’s fast-paced world, instilling critical thinking skills in young minds is more important than ever. By nurturing these skills, teachers are laying the foundation for a lifetime of learning, problem-solving, and creativity. Here are 20 critical thinking activities that can be easily incorporated into any elementary classroom setting.
1. Think-Pair-Share
This simple activity encourages students to think about a question or problem individually first and then discuss with a partner before sharing their thoughts with the entire class.
2. Brainstorming Sessions
Encourage students to throw out ideas and suggest solutions within a given time frame on a specific topic without judgment or criticism.
3. Fact vs. Opinion
Prompt students to analyze the statements in this activity and decide which ones are facts and which are opinions.
4. The “Why” Chain
Ask students to continuously inquire ‘Why?’ to any given event, encouraging them to think deeply about cause-and-effect relationships.
5. Comparing Perspectives
Given two or more characters from a story, have students compare and contrast their different perspectives on a particular issue.
6. Classification Activities
Challenge students to classify objects or ideas into specific categories based on their characteristics, fostering organizational thinking.
7. Similes and Metaphors
Encourage imaginative thinking by having students create similes and metaphors to describe various objects or situations.
8. Storytelling Circles
Students take turns adding onto a collective story that promotes creative thinking and collaboration skills.
9. Mind Mapping
Guide students through creating visual diagrams that highlight connections between ideas in an organized fashion.
10. Analogy Activities
Students use analogies to explore connections between seemingly unrelated concepts or ideas.
11. Socratic Seminars
The class engages in group discussions using the Socratic method where they answer open-ended questions and challenge each other’s viewpoints respectfully.
12. Create Your Own Country
In this creative activity, students develop the governance, geography, culture, and history of a fictional country.
13. Problem-Solving Challenges
Present students with real-life scenarios and ask them to brainstorm potential solutions as a group.
14. Peer Review Sessions
Students exchange their work and provide feedback on each other’s assignments, fostering critical assessment.
15. Inquiry-Based Science Experiments
Students participate in hands-on experiments that allow them to develop their own hypotheses and draw conclusions based on observations.
16. Optical Illusions
Examine various optical illusions and discuss as a class how our minds can be tricked into perceiving things differently.
17. What Would You Do?
Pose hypothetical situations to students requiring them to think about what they would do in those circumstances.
18. 4 Corners Debate
Assign the corners of your classroom as “Agree,” “Disagree,” “Strongly Agree,” or “Strongly Disagree.” Pose a statement and have students move to a corner based on their opinion, encouraging them to defend their stance.
19. Creating Advertisements
Guide students through the creation of advertisements for different products, promoting persuasive thinking and communication skills.
20. KWL Chart
Use KWL charts (What I Know; What I Want to Know; What I Learned) to encourage reflection on topics or concepts before, during, and after your lesson.
Conclusion:
The incorporation of these 20 critical thinking activities into your elementary classroom can pave the way for the development of vital skills in problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity, positioning children for future success in academics and life beyond school.
Related Articles

As summer ends and the new school year beckons, educators from preschool…

On Inauguration Day, educators have a unique opportunity to engage children in…

Unit Introduction: Understanding time is a critical skill that students need to…

Pedagogue is a social media network where educators can learn and grow. It's a safe space where they can share advice, strategies, tools, hacks, resources, etc., and work together to improve their teaching skills and the academic performance of the students in their charge.
If you want to collaborate with educators from around the globe, facilitate remote learning, etc., sign up for a free account today and start making connections.
Pedagogue is Free Now, and Free Forever!
- New? Start Here
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Registration
Don't you have an account? Register Now! it's really simple and you can start enjoying all the benefits!
We just sent you an Email. Please Open it up to activate your account.
I allow this website to collect and store submitted data.
7 Fun Critical Thinking Activities to Train Your Brain to Think More Clearly
- Post author: Sherrie Hurd, A.A.
- Post published: August 9, 2018
- Reading time: 8 mins read
- Post category: Brain Power / Personal Development / Self-Improvement
Critical thinking activities not only help us develop a sharper mind, but they also help us develop a consistent mindset and way of thinking.
While thinking is easy, critical thinking, on a consistent basis, takes some skill . Improving it helps us develop a healthy way of reasoning, analyzing and empathizing that helps us take the right actions and perform the right deeds.
Yes, we can think about helping someone make a decision, but can we truly help them make the best one for their given situation ?
How to Improve Your Critical Thinking with These Activities
And what about our own issues? Can we clearly and concisely make the best possible decision each and every day according to the experience we have? This is where critical thinking comes in.
There are actually ideas which can vastly improve our critical thinking skills and help us create a better long-term outcome .
Maybe we can try these fun critical thinking activities to train our brain to be the best it can be.
1. stay on topic.
How easy is it for you to lose your concentration during a discussion? For me, it seems pretty easy, but the truth is, sometimes when you communicate, it’s easy to take, what I call, “tangents”.
For example, if I’m planning a way to complete a task, but yet I start talking about something else that needs to get done, I am going off topic . Every time I go off topic, I take the focus off the present issue.
One of the best activities to improve your critical thinking is practicing the incredibly hard objective of staying on task . Try it and see just how difficult it can sometimes be. It will be challenging to stay focused , but it will also be fun learning how to train your brain on a thinking “tightrope”.
The good news is, it does help improve the quality of your thought patterns.
2. Understand true motives
This is just smart thinking if you ask me. There are times when, during a conversation, someone will present an idea that supports their cognitive bias . It’s not easy to catch sometimes, but if you are good at critical thinking, you will notice the indicators. Pay attention to the details of the argument and understand how these details apply to the ones who are talking.
Unfortunately, some people have selfish motives and you will want to become familiar with the telltale signs. As you practice filtering out the true motives, it will become easier overtime to do so. Here’s the interesting part: you will also notice biases in yourself as well. Practice seeing things from a neutral position instead.
3. Character improvements
Now, take a look at your good and bad traits. When arguments arise, how often do you admit you’re wrong? How often do you turn to introspection? It’s important to regularly do an inventory of your own character . It’s also important to gauge just how much you are willing to learn from others .
Maybe you are truly right most of the time, but is it wise to remain steadfast in your beliefs ? Could it be more important to bend toward someone else’s opinion of the situation at hand? These are good questions to ask yourself as you examine who you really are.
After a rather heated argument , rehash the debate and come from your partner’s standpoint instead. Try to understand things from their point of view and decide to agree the next time to see what transpires. Maybe change is good for you.
4. One thing at a time
It also benefits you to take one problem at a time when working through various life circumstances. A good way to do this is by taking steps. First, identify the problem. Then decide whether you have a solution or not. I found out long ago that some problems require a number of steps instead of one big solution.
Sometimes these steps turn into smaller problems which must be solved before tackling the larger problem. This has to be discovered by careful analyzation of each step.
Practicing this technique of solving problems will help you stay patient in the future instead of getting irritable and overwhelmed when things take a turn for the worst.
Here’s a fun twist. Take a simple problem, for practice, and break it down into increments. Make different decisions on smaller portions of the problem to see where those decisions lead you.
5. Review your day
Wasted time is one of the biggest obstacles to productive thinking, and another culprit is procrastination, as you already know. So, first off, you must try to perform better during the day. Then, you need to practice doing a recap of what you’ve accomplished.
At the end of your workday, instead of watching television, try going back over all the things you got done. Think of your conversations , your errands, and even your thinking. Was it time well spent, or did you procrastinate and worry most of the day? Maybe you thought too long on the past.
Each evening, take time to recap your day and take note of any wasted time. This will help you improve in that area .
6. Journal your actions and reactions
At the end of each day or week, write down certain notable happenings in your day to day life. Write about the event and how it made you feel. Talk honestly about how you reacted to the situation. Do you feel good about what you said or did?
Now, analyze your response in this way. If you feel as though you could have reacted differently, then how do you plan to do that? Keep these journal entries so you can learn how to better respond to situations and eliminate instances of making rash decisions.
7. Illustrations
When debating something, it can get hard to convey a moral or standard that’s important to you. Illustrations can provide a story that helps the other person see how your argument works.
For instance, if you’re trying to help someone and they refuse to accept or understand your gesture, then talk to them about how your offer is similar to saving someone from having a physical accident (like an illustration of you pulling them out of the way or a speeding automobile.)
Maybe your gesture of help will eliminate a bad consequence by sharing an unrelated illustration or story. So, in your mind, practice placing ideas in story form for better understanding. When real problems come, you will have easy to understand illustrations in case you’re struggling with a solution.
Final words
The reason why improving critical thinking is so important is that activities like the above ones help us train our brain to stretch to new limits. Our simple thinking can be transformed into a well-informed intellect, paired with the ability to feel and reason productively. Critical thinking can actually improve our quality of life and the life of the ones we love.
To take advantage of the best the world has to offer, you must activate your brain’s powers. Once you start to practice the above activities, you will be surprised by your own critical thinking skills. Let’s do this together and enjoy the process of learning.
References :
- https://www.lifehack.org
- https://www.thebalancecareers.com
Like what you are reading? Subscribe to our newsletter to make sure you don’t miss new thought-provoking articles!
Share this story share this content.
- Opens in a new window Facebook
- Opens in a new window X
- Opens in a new window LinkedIn
- Opens in a new window Reddit
- Opens in a new window Tumblr
This Post Has 2 Comments
Thanks for reading!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

7 Puzzles to Challenge Your Critical Thinking
Can you spot the connections and sort these items.
Posted March 5, 2015 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan

The theme of this post is critical thinking—and the kinds of puzzles that can be constructed around it. This term is used frequently in psychology and education . There are various definitions, but the one that best suits our purpose and which is, in the end, perhaps the best, is the ability to comprehend the logical connections among ideas, words, phrases, and concepts . In the relevant scientific literature, of course, the term is used much more broadly as a framework for understanding human cognition . But in my opinion, the best way to understand things is to construct puzzles to illustrate their basic essence.
Critical thinking involves skill at recognizing a pattern in given information and especially recognizing how the information is connected to the real world. Here are a couple of very simple examples. First, consider the five words below:
- Cruise ship
- Walking on foot
- Automobile (not a race car)
Now, put them in order from the slowest to the fastest, when they are going at maximum speed. The solution, of course, is: 4-2-5-1-3.
As with all such puzzles, there might be slightly different solutions—one could claim that some automobiles go faster than cruise ships. This “indeterminacy” characterizes this kind of thinking. However, some puzzles are straightforward. For instance, what do the following five things have in common?
The answer? These are all words referring to shades of blue.
The seven puzzles below are to the ones above, though hopefully more challenging. Some involve knowledge of facts, but critical thinking is still involved in such cases because the organization of the facts according to some principle is always involved—for example, a puzzle may ask you to put five items in order of their dates of invention.
The following tongue-in-cheek definition of critical thinking by Richard W. Paul, a leading expert on critical thinking theory, says it all: “Critical thinking is thinking about your thinking while you’re thinking in order to make your thinking better.”
I. What do the following 5 things have in common?
- Orange juice
II. Put the following buildings or structures in order of height, from the shortest to the tallest.
- Typical camping tent
III. What do the following animals have in common?
IV. Put the following inventions in order from earliest to most recent.
V. What feature do the following words have in common?
- Imagination
VI. Put these bodies of water in order in terms of volume, from smallest to largest .
VII. What do the following landmasses have in common?
I. They are all drinkable liquids. II. 5-1-4-3-2 III. They all have a tail. They are also all quadrupeds. IV. To the best of my knowledge: 5-4-3-1-2 V. They start with a vowel: a, e, i, o, u VI. 4-2-1-5-3 VII. They are all peninsulas.

Marcel Danesi, Ph.D. , is a professor of semiotics and anthropology at Victoria College, University of Toronto. His books include The Puzzle Instinct and The Total Brain Workout .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

It’s increasingly common for someone to be diagnosed with a condition such as ADHD or autism as an adult. A diagnosis often brings relief, but it can also come with as many questions as answers.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

The Critical Thinking Workbook - Games and Activities for Developing CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS - Free Printable PDF Workbook
Download The Critical Thinking Workbook - Games and Activities for Developing CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS - Free Printable PDF Workbook
Jump start your critical thinking skills by using this handy free printable PDF workbook. Our friends over at Global Digital Citizen Foundation have provided this free learning resource for your education and enjoyment. With lessons, exercises and activities to keep you on track, you'll be able to gain powerful critical thinking skills and begin your transformation!
The activity pages in the Critical Thinking Workbook are meant to be shared and explored. Use it as an electronic document or as worksheets. You can either print off the pages and use them as activity sheets, or you can edit them directly right in the document on your computer. There are also Answer Keys for the activities that need them provided at the back of the book. Now, go get thinking!
This Printable PDF Workbook is immediately available for FREE download.
By downloading and using this product, you understand and agree to the following terms of use. The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained in this product are for educational, informational and entertainment purposes only.
No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical or mental health advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read or seen on this website.
This is not a physical printed product and is not physically shipped. “Shipped” on the product email means virtually shipped and available for download. You have an implied license to print this digital file and use it for your own personal purpose. Commercial reselling or distribution of this product is strictly prohibited.
http://www.leapfroggingsuccess.com website is currently under development and will be relaunched soon. Any references made to this website can be redirected to https://critical3academy.teachable.com .
If you have any issues with downloading your product, please email leapfroggingsuccess [!at] gmail.com and we will resolve your issue right away.
Explore related searches
#criticalthinking
#criticalspeaking
#criticallearning
#cognitivebias
#cognitivedistortions
#conspiracytheories
#defensemechanisms
#logicalfallacies
#superstitions
#intelligence
#personalities
#psychology
#philosophy
#flashcards

Choose a Pricing Option
Teachers Toolkit Blog
Encourage Critical Thinking with Puzzles, Games, and Activities
Resources · Thematic · Thinking Skills
Critical thinking is a necessary skill that all students need. Even students as young as kindergarten or first grade can start to learn this skill. Encourage critical thinking with fun, engaging activities that make your students think! To see more tips on teaching critical thinking, check out my earlier blog post.

how to encourage critical thinking
Critical thinking is being able to see and understand the logical connections between ideas, identify inconsistencies, and solve problems. This might seem like a tall order for our littlest students. There are activities that will encourage critical thinking while still keeping the learning fun.
- Fill in the Gaps – this activity requires students to use evidence and prior knowledge. Project a picture on the board. Then at the top of a piece of paper, students will write “What is happening in this picture?” At the bottom of the page, they can write their answer. In the middle of the paper, students should write down the evidence they see in the picture that led them to their answer.
- Build It – do this flexible team-building activity at any age level. Give the teams some simple building materials in equal amounts, such as pipe cleaners, gum drops, marshmallows, spaghetti, blocks, etc. Then give them something specific to construct with the materials. In addition to critical thinking skills, students will practice teamwork and collaboration.
- Open-Ended Questions – Read a story to your students and ask them questions that can’t be answered with a simple one or two-word answer. First, ask them to predict what will happen next or at the end of the story. Next, practice inference with questions that are not explicitly answered in the story. For example, show them a page in the story that shows the sun shining with leafy trees and ask what time of year it is. Third, have students tell you what the story is about in one sentence. This is a great way for them to start thinking about the main ideas of stories.
higher-order thinking with games and puzzles
Playing games and solving puzzles are fun ways to encourage critical thinking skills. Math puzzles, mazes, and jigsaw puzzles all require students to use higher-order thinking.
It’s fairly easy to incorporate this skill into your everyday teaching. Bellwork is a perfect time! I’ve created Critical Thinking Activities Task Cards for quick ways to let your students practice different types of critical thinking.
These Critical Thinking Activities Task Cards provide teachers with activities and puzzles to help students develop critical thinking skills . In this pack, you will find 80 quick start task cards – 4 cards per page. Your elementary students will love trying to figure out the puzzle or challenge and you will love knowing that they are using higher order thinking skills!
These ‘quick starts’ are ideal warm-up activities for the beginning of a lesson. Use them flexibly in any order, at any time. I would suggest laminating them for durability.
Today’s students are the problem-solvers of the future. If they are taught factual knowledge only, they tend to respond with conventionally correct answers rather than exploring creative solutions. All students can learn to think critically and creatively.
See my other resources for critical thinking:
- Think Outside of the Box Series: Surprising Shapes
- Thinking Skills Think Outside of the Box Series: Activities
- Thinking Skills Think Outside of the Box Series: Bundle
Related posts:

- Privacy Policy
- VIP Resource Library
- Cookie Policy (EU)
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Teaching Expertise
- Classroom Ideas
- Teacher’s Life
- Deals & Shopping
- Privacy Policy
20 Critical Thinking Activities For Elementary Classrooms: Navigating Fact And Fiction (+Resources)
December 1, 2023 // by Seda Unlucay
With the barrage of mainstream news, advertising, and social media content out there, it’s vital for students to think independently and learn to differentiate between fact and fiction.
This series of critical thinking activities, STEM-based design challenges, engaging Math puzzles, and problem-solving tasks will support students in thinking rationally and understanding the logical connection between concepts.
1. Teach Students How to Obtain Verifiable News
There’s probably no 21st-century skill more important than differentiating between real and fake sources of news. This editable PowerPoint bundle covers traditional media, social networks, and various target audiences and teaches students how to find verifiable facts.
Learn More: Teachers Pay Teachers
2. Watch and Discuss a Critical Reasoning Video

This kid-friendly video teaches students to break arguments down into claims, evidence, and reasoning. Armed with this lifelong learning tool, they will be able to make more informed decisions when consuming all types of information.
Learn More: Brain Pop
3. Complete a Critical Design Challenge
This science and designed-based classroom activity challenges students to find ways to prevent a falling egg from breaking. Pairing it with the classic Humpty Dumpty nursery rhyme is sure to inspire many creative ideas.
Learn More: Education
4. Critical Community Engagement Activity
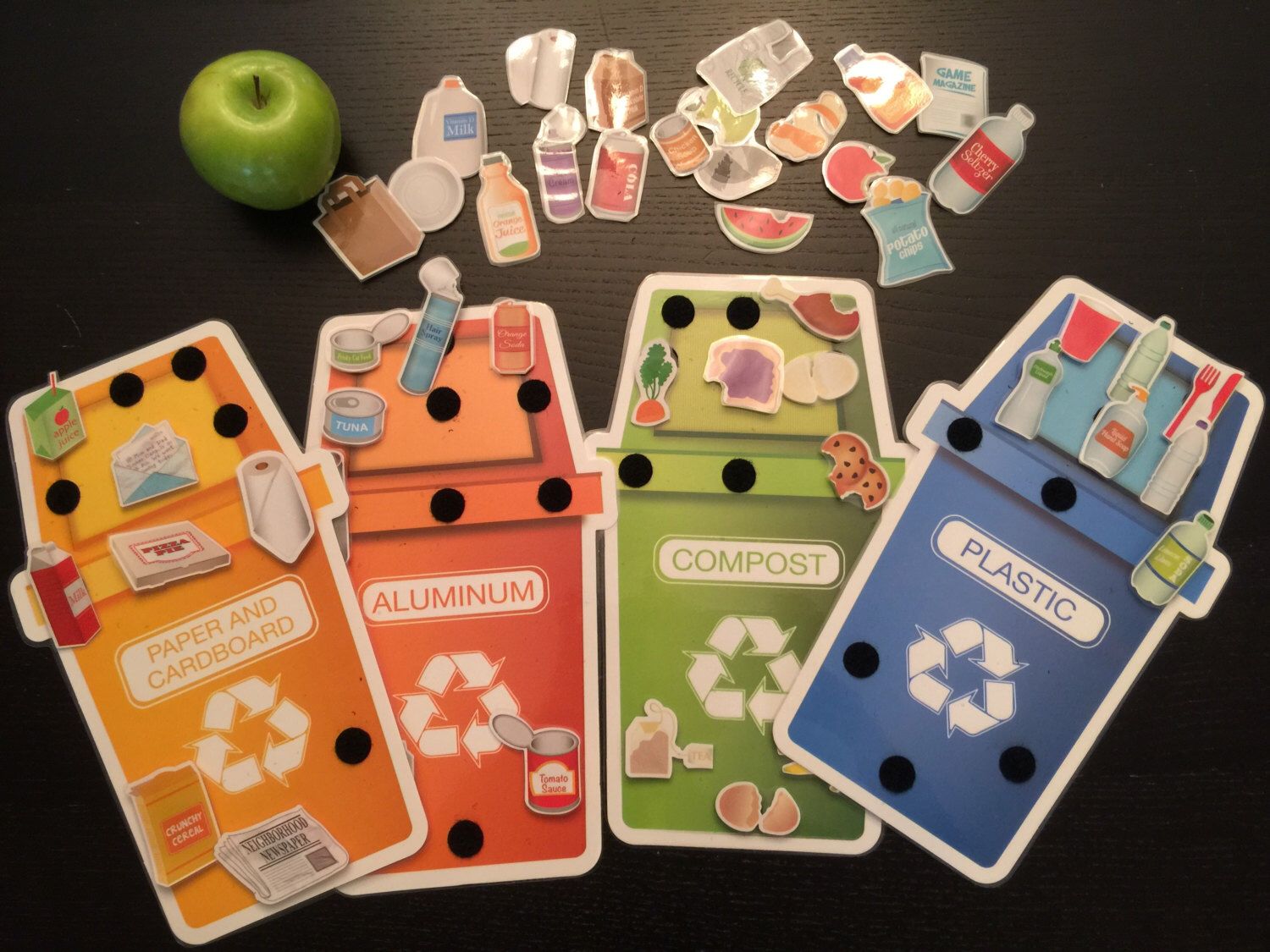

This community engagement activity requires analytical skills to determine what items can be recycled in the classroom and in their neighborhood. By creating recycling bins from reusable cardboard boxes, students have an opportunity to contribute to the environmental well-being of their community while practicing social responsibility.
Learn More: Kaboom
5. Develop Logical Skills with a Then and Now Activity
We may no longer use candles for reading or quill pens for writing, but can your students identify the objects that have replaced them? This activity engages their writing, drawing, and logical skills while giving them a chance to reflect on all the changes in our modern world.
Learn More: Education
6. Play a Critical Thinking Game
This active learning activity requires students to use their critical thinking skills to make comparisons and create meaningful analogies. The fun animal safari theme is sure to inspire many funny and creative ideas!

7. Develop Social-Emotional Problem-Solving Skills
Through this lesson, students will understand that while conflicts are a normal part of life, it’s vital to have problem-solving skills to resolve them. This is also an excellent opportunity for developing their social awareness and relationship skills.
Learn More: ED Foundations
8. Desert Island Survival Game

This classic game is sure to inspire student engagement, as they use their critical thinking skills to survive being stranded on a desert island. Students have to watch out for ideological assumptions and question ideas in order to determine the appropriate items to bring.
9. Play a Problem-Solving Treasure Hunt Game
This exciting game for kids requires them to use key math skills to break a series of codes. With ample time, designated progress monitors, and sharp critical thinking skills, students are sure to find the hidden treasure.
Learn More: Twinkl
10. Use Writing to Increase Critical Empathy

This activity builds writing fluency while giving students a chance to show appreciation for each other. As they reflect emphatically on their classmates’ contributions and character, their base level of kindness and sense of ethical responsibility is bound to increase.
Learn More: Edutopia
11. Learn How to Make Logical Inferences

This activity for kids teaches the critical academic skill of making inferences from a series of texts. Students will surely enjoy playing the role of detective in order to draw their own logical conclusions.
Learn More: Study
12. Think Critically About Cultural Assumptions

This engaging activity for students challenges them to think critically about why people from a variety of cultures decorate their bodies. It helps them to break through cultural assumptions while comparing and contrasting the different forms of hand and body painting around the world.
Learn More: Harmony
13. Big Paper Silent Reflection Activity

After posing some open-ended questions, students silently write their responses with colored markers on large chart paper. After each group has circulated around the room, students can share their critical reflections and learn from the various perspectives of their classmates.
Learn More: Slideshare
14. Watch a TED Video About the Socratic Method

Socrates is one of the forefathers of critical thinking, who focused on making his students thinking visible by questioning their logic and reasoning. The accompanying quiz and discussion questions are an excellent way to reinforce student learning.
Learn More: Ted Ed
15. Brainstorm Ways to Help a Homeless Person

This lesson in civic responsibility teaches students about the causes of homelessness and guides them to find ways to help the homeless in their communities. It develops key problem-solving skills while building critical empathy.
Learn More: National Homeless.org
16. Guess the Object Game
This video features a series of twenty zoomed-in mystery objects. Students will love using their critical thinking skills to guess each one!
Learn More: Andy – The ESL Guy
17. Solve Some Challenging Math Brain Teasers
This abundant series of brain teasers is the perfect choice if you’re looking to test your children’s memory and problem-solving skills. Encourage them to use their knowledge of numbers to complete these tricky math problems that are not only designed to challenge your little brainiacs but are also compiled in an easy-to-use format.
Learn More: Mental Up
18. Complete a STEM Elevator Challenge
In this design and engineering-based lesson, students have to build a functional elevator that can carry an object to the top of a structure. It’s a terrific way to encourage cooperative learning while sharpening their problem-solving skills.
Learn More: Georgia Youth Science and Technology Centers
19. Create the Perfect Farm

There’s no better way to develop critical thinking skills than by solving real-world problems. This video encourages students to think about ways to feed a growing global population in an environmentally sustainable way.
20. Solve Logic Grid Puzzles
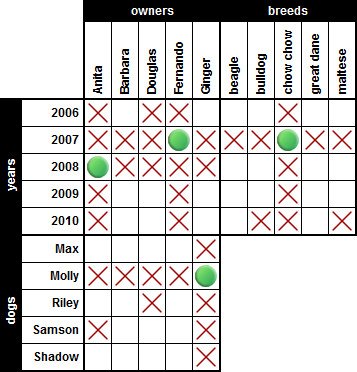
These logic grid puzzles will motivate students to use logical reasoning skills and the process of elimination to solve a series of clues. But be warned, they are highly addictive and difficult to put down once you get started!
Learn More: Puzzle Baron’s Logic Puzzles
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Critical thinking with pictures

Making Inferences With Pictures - Critical Thinking - Google Slides Included

Fun ESL & ELA Games with Pictures | Critical Thinking Activities | Speaking

Boosting Critical Thinking with Halloween Picture Books: A GATE Resource

Halloween Book Twists: Elevating Critical Thinking with Picture Books (GATE)

PRODUCT PAIR Critical Thinking with Picture Books Extension Activities (GATE)

Describing & Inferring Details with Picture of the Day: Reading Photos "Closely"

Depth and Complexity Critical Thinking Task Cards for Literature

Sequencing Stories With Pictures Kindergarten Literacy Center Sequence of Events

Book Report Foldable Project: Pop-Up Picture Book with Editable Rubrics

Describing & Inferring with Picture of the Day - Vol. 3 #hellopotd

Ultimate Response to Reading Bundle-Use with any fiction text!

Activities for Making Inferences With Pictures : Bundle of Fiction Reading Skills

Winter Activities Sequencing Stories with Pictures Small Group Reading

Describing & Inferring with Picture of the Day - Vol. 2 #hellopotd

Depth and Complexity Critical Thinking Task Cards Bundle

Sequencing Stories with Pictures Fall Activities - Sequencing of Events Autumn

Mystery Problem Solving Activities: Critical Thinking Fun

Algebra Critical Thinking Logic Puzzles Can You Solve This Emoji Puzzles

Daily ELA Bell Ringers - Warm Ups: Writing & Reading Comprehension with Pictures

Year-long Making Inferences Comprehension Bundle - with pictures

Algebra Critical Thinking Winter Christmas Logic Puzzles

What's Wrong with this Picture ? Adventure Kids Boom Cards | Language

Making Inferences With Pictures : Teaching Theme
Modeling Mitosis & Meiosis with Jelly Beans Lab

- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

19 Short Stories and Questions For Critical Thinking
Apr 2, 2024
There have been rumblings in different online teacher groups recently about replacing novels with short stories and informational articles in middle and high school English classrooms. I have to admit I was shocked when I first read the comments because I am a book lover at heart, but since then, I’ve considered that there are several pros and cons to this approach.
Short stories and other smaller texts can provide a briefer timeline to complete tasks, and this process is helpful when there is already SO MUCH curriculum to cover. Short stories and related activities can also be more engaging for our students because of the exposure to diverse voices and themes! Using short stories and lessons provides students with amazing choices to meet their needs and preferences!
On the other hand, incorporating mainly short stories and other shorter passages means students’ already-pressed attention spans (as a result of social media influences and pervasive sources of technology) are reinforced. Plus, students miss out on the more complex stories within longer pieces of fiction that are, dare I say, life-altering! A novel can provide opportunities for sustained reading and layers for analysis that shorter pieces of literature like short stories and related texts cannot offer.
Ultimately, no matter where you find yourself on the issue, I think we can all agree that short stories and their counterparts can be vital, effective, and helpful in the modern classroom!
Continue reading for 19 Short Stories and Questions For Critical Thinking!!
Need help with Test Prep ? Check out this FREE Pack of 3 Test Prep Activities to help students achieve success on standardized tests!

Table of Contents
19 Short Stories and Questions – Suggestions for Teaching Them
You don’t need to remove all novels to be able to include short stories and smaller passages like vignettes, articles, and narratives; there’s a time and place for all genres! But if you’re thinking about ways to include more short stories and fun activities, check out this list of 19 varied short stories and critical thinking questions as well as suggestions for teaching them in middle school and high school.
1. “The Most Dangerous Game”
“The Most Dangerous Game” is one of my absolute favorite short stories and overall plots to teach! This suspenseful short story by Richard Connell follows the harrowing ordeal of Sanger Rainsford, a skilled hunter who becomes the prey of a deranged aristocrat named General Zaroff. Stranded on Zaroff’s secluded island, Rainsford must outwit the cunning general in a deadly game of survival, where the stakes are life and death.

SUGGESTIONS FOR TEACHING:
- You could focus on the setting (description of time and place) and examine how the setting changes throughout the story.
- Students could learn about the plot (major events in the story) and list the major events and evidence as they read.
- Define foreshadowing (hints for what will happen by the end of the story) and encourage students to hypothesize about what will happen after every page.
- Analyze the character development (how a character changes over time) of Rainsford and highlight his traits/actions as you read along.
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS:
- How does the setting contribute to the tension and suspense in the story?
- How does the author use foreshadowing? How does the author hint at the danger Rainford is facing?
- What inferences can you make about the main character and the changes he undergoes from the beginning to the end of the story?
If you want to teach plot elements and plot analysis , check out this lesson bundle for the story , which includes comprehension quizzes and a variety of activities!
2. “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge”
Ambrose Bierce’s story is a gripping tale set during the American Civil War, where a Southern civilian named Peyton Farquhar faces execution by hanging after attempting to sabotage a Union railroad bridge. As Farquhar falls through the trapdoor, time seems to stretch, and he experiences a surreal moment, only to realize his grim reality.
Integrating historical texts with other short stories and passages like “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge” will make history come more alive and relevant for our students!
- Teach about irony (when the opposite occurs from what is expected) and how it plays a role throughout the story.
- Explain the term characterization (how a character is depicted) by looking at direct and indirect references while reading with your students.
- Discuss the major themes (messages) of the story and how they connect to our modern era within a Socratic Seminar.
- How does the author use characterization to convey Peyton Farquhar’s thoughts, emotions, and motivations?
- What is the purpose of irony in this story? How does its use affect the reader’s interpretation and understanding of events?
- What is the significance in our contemporary/real world of the themes of the story, including reality and fantasy, the passage of time, and the consequences of actions?
Ensure students’ understanding of the story with this set of reading questions that are perfect for state test prep, too !

3. “The Masque of the Red Death”
This chilling tale from Edgar Allan Poe is set in a secluded abbey where Prince Prospero and his wealthy guests attempt to escape a deadly plague known as the Red Death. Despite their isolation efforts, the guests are confronted with their own mortality as a mysterious figure in a blood-red mask appears.
If you have not read any short stories and poems from Poe, this story is a perfect journey into the horror genre!
- The setting (description of time and place) plays a MAJOR role in the story, so following the Prince from room to room and highlighting the imagery (description that connects to the five senses) is very important when reading.
- If you have not introduced mood (emotion intended for the reader to experience), this story is PERFECT for delineating its progression from start to finish.
- As students read, you might guide them through identifying various examples of symbolism (object, person, or place that represents something else); each room, objects within, and the “antagonist” is symbolic in some way!
- How does the author convey the tone of the story? How would you, as the reader, describe the story’s mood?
- What role does the plot structure (focus on the different rooms) play in shaping the reader’s understanding of the story?
- What is the purpose of the symbolism in the story such as the clock and the masked figure?
Check out this EASY-TO-TEACH bundle , you can practice with your students, so they will feel more confident analyzing higher-level language in “The Masque of the Red Death!”
4. “The Cask of Amontillado”
Another chilling tale from Poe is the classic story “The Cask of Amontillado.” This one is set during Carnival in an unnamed Italian city. The plot centers on a man seeking revenge on a ‘friend’ he believes has insulted him. If your students are anything like mine, they will relish the ending particularly!
This is just one more of Poe’s short stories and tales that will capture the mind of every reader!
- As you plan for this short story, be sure to encourage your students to analyze the changing setting (description of time and place); following Fortunato from scene to scene will help your students track what is really going on.
- This story is the perfect moment to teach about dialogue (conversation within someone=internal and/or between someone and someone/thing else=external); Montresor certainly means more than what he SEEMS to say!
- You might also offer a mini-lesson on the 3 types of irony and how each plays a role in the story: verbal (when a person says the opposite of what is really intended), situational (an action occurs that is the opposite from what the reader expects), and dramatic (a character expects a result, but the opposite occurs and the audience can tell what will happen)!
- Describe Montresor. What are his motives and personality?
- What inferences can you make about Montresor’s mindset based on his dialogue?
- What is the purpose of the family’s motto and the carnival atmosphere?
Check out this Short Story Activity & Quiz Bundle for Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Cask of Amontillado,” which contains questions and answers modeled after various reading standardized tests as well as pre-quiz reading comprehension questions, graphic organizers, and a writing activity to get students thinking critically about this classic short story involving REVENGE!
Want 7 more teaching ideas for one of Poe’s epic short stories and questions to go with it? Click below!

5. “To Build a Fire”
This story by Jack London describes the treacherous journey of a man through the harsh Yukon wilderness during extreme cold. Despite warnings and the company of a loyal dog, the man’s arrogance and underestimation of nature’s power lead to a tragic end.
Short stories and ideas related to survival in nature are still relevant today! Who knows when you might get lost on a hike or crashland in no man’s land?
- This story is PERFECT for a bit of literary analysis (examining the impact of various ideas, elements, or themes within a piece of literature); you could hone in on literary devices, characterization, theme, etc.!
- Integrating clips from survival shows will help students see connections to the world and extend their thinking by comparing (recognizing similarities) and contrasting (recognizing differences) varied experiences!
- Write a short narrative about surviving 24 hours in a different setting (description of time and place).
- How does the author use irony? Provide an example and explain.
- What real-world connections can be made between this story and our contemporary life?
- What is the story’s message about preparedness and respecting nature?
Grab these engaging short stories and activities to make teaching this Jack London story stress-free!
6. “The Cactus”
Told from the point of view of a young man at his former lover’s wedding, the narrator retells their story. Like most of O. Henry’s short stories and texts, this one has a twist that involves the titular cactus plant.
The ending will end in a bit of fun for your students!
- Introduce diction (word choice) and its impact within the story by hyperfocusing on specific words within the story . Students can look up definitions, locate synonyms, create their own sentences, replace the words, etc.
- Investigate twist endings (unexpected finish to a story); before reading the end of the story, ask students to guess why the girl “rejected” him. Some students may know the answer before reading it!
- Describe the main characters. What similarities and differences are evident? How does this affect the story’s action?
- What inferences can you make about Trysdale and his feelings about love and marriage?
- What are the real and symbolic meanings of the cactus?
This resource packed with questions and answers, graphic organizers, and writing activities is sure to get your students thinking about this love story driven by misconceptions.

7. “After Twenty Years”
This tale of friendship and betrayal focuses on the reunion of two old friends after twenty years apart on a New York City street corner. As they reminisce, something is revealed that demonstrates the reality of their bond as well as the choices they’ve made in life.
If you have not read O. Henry’s short stories and incorporated character analysis yet, this is your chance! The story is not long and can be completed in one to two class periods!
- Sometimes, we ask students to visualize (create a picture) in their minds, but why not give them the opportunity to use their artistic skills to draw the two characters?
- As students read, annotate for a description of each character; then, students can do a character analysis (investigation of the characters’ similarities and differences).
- What type of irony is used in the story? How does its use affect your interpretation and understanding of the story?
- How does the urban setting contribute to the mood of the story?
- What is the story’s message about friendship and loyalty?
Examine the links between loyalty and duty with this set of resources designed specifically for this O. Henry story.
8. “The Lottery”
“The Lottery” is the quintessential short story for middle school or high school English! Shirley Jackson’s “The Lottery” tells the story of an annual ritual that takes place in a seemingly idyllic town. When the townsfolk gather for the lottery drawing, a shocking turn of events demonstrates the dark side of human nature and their ties to (outdated) traditions.
- Introduce the terms suspense (uncertainty and/or excitement leading up to a major event) and tension (anxiety or uneasy feelings experienced by characters). While reading, identify evidence that relates to each of these concepts and chat/write about their impact on meaning and plot.
- Teach title (the name of the text) analysis. The title of “The Lottery” is perfect for teaching the impact of the title and audience expectations. Before reading, students may write what they believe the story will be about based on the title. After reading, students can complete a quick write responding to their previous expectations! You can do a text analysis for all short stories and poems!
- What role does the plot structure play in building suspense and tension? (Consider the revelation of the lottery’s ‘prize’ in particular.)
- What social commentary is being made through the story and its characters?
- Describe Mr. Summers, Tessie, and Old Man Warner. What does the story reveal about their role in the community and their feelings about the lottery?
Give yours elf a breath of fresh air with this NO PREP curriculum that integrates test prep within the teaching of literature by using Shirley Jackson’s quintessential story!

9. “The Pedestrian”
This Ray Bradbury story follows a lone walker in a futuristic society in which everyone else is consumed by technology, particularly the television. One evening, the walker encounters a police car that questions his unusual behavior and the end is quite unexpected! (Most of Bradbury’s short stories and texts connect to the future and technology in some way!)
- This story exemplifies Dystopian Literature (texts that include a supposedly perfect future society marred in some way by governmental or societal oppression). Using this story to introduce this type of literature is always fun for students because they will easily make connections to other dystopic short stories and poems!
- Teach about mood (the emotional impact of a story’s description/action). The goal is to get students to deepen their critical thinking skills by recognizing how the mood changes and the purpose for that change!
- How does the author use foreshadowing and suspense to build the mood of the story?
- What is the central theme of the story? How might it connect with our current world?
- What similes and metaphors does Bradbury use to describe the community and its members? What is notable about these comparisons?
With this resource about Bradbury’s “The Pedestrian,” you can just print and teach the lesson and activities with EASE!
10. “The Gift of the Magi”
This 1905 story by O. Henry relays a tale about a couple struggling to make ends meet. Throughout the story, they both figure out gifts to buy one another for Christmas and realize what love truly means!
- Review character traits (how a character is depicted internally and externally). Log the traits of each character within the story and how they are important to the meaning of the story.
- Extend (move beyond the text) critical thinking skills by encouraging students to think and write about other people. If they had $1,000 to spend on someone else, how would they spend the money and why?

- How would you describe Della and Jim, and their relationship?
- What values do the characters have, when you consider their actions and decisions?
- Explain how dramatic irony is used in the story. Is it necessary? Is it effective? Why or why not?
This tale is a great addition to your short stories and questions unit around the winter holidays! Save yourself time at that time of the year with this lesson bundle .
11. “The Monkey’s Paw”
“The Monkey’s Paw” is a classic horror story about the White family who come into possession of a mystical monkey’s paw that grants three wishes. Despite warnings, they use it and then face devastating consequences as a result.
- Teach about the elements of the horror/suspense genre (Ex. Scary movies are typically dark, stormy, surprising, morbid, etc.).
- Create a thematic statement (message relayed by the text in a complete sentence). There is no perfectly created theme (message) unless it is directly stated by the author; however, students can create a theme by supporting their ideas with evidence from the story!
- What is the main theme of the story? Or how does the author communicate the themes of greed or fate? Is one stronger than the other?
- Are Mr. and Mrs. White more alike or different from one another? How do you know?
- Should we be afraid of the unknown? What message does the story share? Do you agree or disagree?
Examine W.W. Jacobs’ classic story with this set of questions and answers along with rigorous reading and writing activities . While it is ideal for a spooky season, the story is valuable for its ability to hook readers any time of year!
12. “Lamb to the Slaughter”
This classic story with a killer plot twist is about a woman who kills her husband and gets away with murder thanks to cooking a leg of lamb!
- You could introduce the plot elements (exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution), encourage students to identify major events to fit each element and write down textual evidence to support their ideas.
- Complete a film analysis (examination of film techniques and their effects) to compare/contrast the short story with the classic Alfred Hitchcock television episode.
- What is Mary Maloney’s state of mind? Does it remain the same or does it change throughout the story? Explain.
- Is the resolution of the story satisfying? Why or why not? Why do you think the author ended it as he did?
- How does irony contribute to the theme of deception in the story? Explain.
Spice up your middle school English or high school English class with this short stories and activities bundle for Dahl’s famous story!
13. “The Tell-Tale Heart”
Poe’s classic psychological thriller is narrated by an unnamed protagonist who insists on their sanity while recounting how they murdered an old man. The narrator is haunted by the sound of the victim’s beating heart, which ultimately drives him to confess to the crime despite not originally being a suspect.
- Teach symbolism (object, person, or place that represents something else) by focusing on the heart and eye . The author used these symbols in various ways!
- Investigate psychology (the study of the human mind) as a part of the story. Determine what is fact and what is fiction within the narrator’s mind.
- What does the story reveal about the human psyche?
- What is the deeper meaning of the two key symbols in the story – the beating heart and the eye of the old man?
- What role do the narrator’s inner thoughts play in the development of the plot?

This Short Story Comprehension Bundle offers quick (and effective!) ways to assess students’ learning and understanding of the story. It’s easy to use and will no doubt save you time too!
14. “The Scarlet Ibis”
Emotional short stories and their counterparts have a place as well in English classrooms! This short story by James Hurst about two brothers is a heartbreaking must-read. Through flashbacks, the unnamed narrator tells the life story of his younger sickly brother William Armstrong, who is nicknamed Doodle. And the end…well, you’ll see.
- Define and explain the purpose of a flashback (referring back to the past within a story). Think about the implications of never thinking back on the past or always thinking about the past.
- Complete a comparison chart between Doodle and the Ibis as you read along. Then, students can create a visual of each after they have ready by using their own evidence!
- What is the meaning of the story’s title and the presence of a scarlet ibis in the story?
- What is the central theme of the story? How do the events of the story support this chosen theme?
- How does the author use personification for the storm? What effect does this have on the story?
This flexible resource features critical thinking questions and answers as well as writing and reading activities for students to explore Hurst’s heartbreaking story.
15. “The Veldt”
This science fiction story by Ray Bradbury was first published as “The World the Children Made” and it is quite fitting as a title! The story focuses on a futuristic world in which a video screen can be controlled and it turns out to be more than simple virtual reality! By the story’s conclusion, the world the children made is the downfall of their parents.
- Compare and contrast “The Veldt” with “The Pedestrian,” two short stories and dystopic texts by Ray Bradbury. Analyze the similarities and differences of both short stories and create a thematic statement that connects to both texts!
- Make connections to our current reality in the 21st century. Locate research about the implications of technology on young people and integrate this information as you discuss this short story.
- How does the author address the theme of technology versus humanity in the story? Do you agree with this commentary? Why or why not?
- How does the nursery reflect the personalities of Wendy and Peter in this story?
- Do you know the story of Peter Pan and his friend Wendy? What connections can you make between it and this story by Ray Bradbury?
Ray Bradbury’s classic short stories and similar passages are the BEST to teach in middle and high school English! With so much to dive into, they are sure to be a hit with your students. Grab this set of activities to extend your students’ engagement with rigorous reading and writing activities about “The Veldt.”
16. “The Necklace”
A woman who longs for a life of luxury and elegance beyond her means faces consequences when she loses a borrowed necklace. Guy de Maupassant’s story ends with a twist that has the reader question the value of material possessions.
- I love comparing this short story with O. Henry’s “The Gift of the Magi.” You might choose to focus on the theme, characterization, setting, etc.
- Summarize (writing about the main idea with details) each chunk of the story as you read with your students. Instead of asking students to write a paragraph, you could ask students to create each summary in only one sentence.
- The story explores vanity, deception, and the consequences of striving for social status. Which theme do you think is the most important? Explain with support from the story.
- Is Mathilde Loisel a likable character? Does this change during the story? Does it matter if the reader likes her? Why or why not?
- What clues does the author provide throughout the story that foreshadow the twist at the story’s end?
Focus on the standards with this Short Story Lesson Bundle for “The Necklace” by Guy de Maupassant!
Need help with implementing activities for “The Necklace?” See below!

17. “A Vendetta”
Guy de Maupassant’s late-19th-century story is all about REVENGE. A mother is obsessed with creating a plan to avenge her son’s murder and she then puts the plan into action with a morbid outcome.
- There are so many texts that involve REVENGE! Why not use this concept as a focus for a thematic unit (texts linked to a similar concept and/or message)? You could read “A Poison Tree,” “The Cask of Amontillado,” and “Lamb to the Slaughter” as well as “A Vendetta” with the intention of writing about all 4 for a comparison/contrast paper, presentation, or seminar.
- Analyze the development (how a character changes over time) of the mother and the dog throughout the story; you might annotate for similarities and differences as well as their motivations!
- What comment is the story making about the nature (or need) for justice? Do you agree or disagree? Why or why not?
- What similes and metaphors does the author use to communicate the main character’s feelings about the vendetta?
- How does the author use details to explain the main character’s thoughts, feelings, and motivation?
Add these activities for this lesser-known work to your short story plans. It’s sure to keep things fresh for your short stories and activities unit!
18. “Thank You, Ma’am” (also known as “Thank You, M’am”)
This heartfelt story by Langston Hughes tells the story of Luella, an older woman in the neighborhood, who is nearly robbed by a young man named Roger. In response to Roger, Luella brings him back to her home and treats him with an abundance of kindness, which has a profound effect on Roger.
This tale is at the top of the list for the BEST short stories and passages for upper middle and younger high school students!
- Introduce perspective and/or point of view (how a story is told: 1st, 2nd, 3rd omniscient, 3rd limited, 3rd objective). Students might rewrite the story from another perspective or extend the story using the perspective of one of the main characters.
- Review plot elements with a focus on the exposition (introduction to the characters, setting, and conflict), climax (highest point of interest/turning point of the story), and resolution (how the story is concluded and/or resolved in some way.) You could assign an activity surrounding each concept: visualization of the scene, a journal response to the event, or a short response focused on how the element is important to the overall theme!

- Do you believe in second chances? What does the story say about second chances?
- How might the climax of the story also be seen as the turning point in Roger’s life?
- How would you describe Mrs. Luella Bates Washington Jones? Are her actions expected or unexpected in the story? Consider from Roger’s and the reader’s point of view.
Click to check out all of the details for this BUNDLE with differentiated options , which includes a Test Prep Quiz (with varied options), Venn Diagrams, Graphic Organizers, and Writing Responses!!
19. “Click Clack the Rattle Bag”
This short story by Neil Gaiman is creepy and fun in the best ways possible! The narrator is taking care of his girlfriend’s little brother and walking him to bed when the child asks for a story. Instead of the narrator sharing a story, the boy shares about the Click Clacks who drink their prey and leave behind rattling bodies. The end is too good to be missed!
Short stories and plots like those in “Click Clack the Rattle Bag” will most certainly engage even your most struggling learners!
- We all know that test prep can be tough as many reading passages are, well, boring! Why not accomplish some test prep with your students and incorporate 5 standardized test-related questions ? You could focus on theme, structure, order of events, characterization, etc.!
- Help students make inferences (acknowledging and hypothesizing about the impact of details that are not directly referenced or stated) as the scene moves along. Students can analyze the change in the setting, the little boy himself, the story the boy is telling, and specific phrases from the story.
- What details in the story contribute to its eerie atmosphere or mood? Or what figurative language devices does Neil Gaiman use to create a sense of suspense in the story?
- How does the author use ambiguity in the story? Is it effective or not? Explain.
- What inferences can you make about the relationship between the narrator and the young boy?

This “Click Clack the Rattle Bag” Quiz Pack for middle and high school students uses the Common Core standards and contains questions and answers modeled after various state standardized tests! Make teaching this amazing short story by Neil Gaiman SIMPLE & EASY!
Why should we incorporate more short stories and activities in our teaching?
While I would never advocate replacing all novels with short stories and smaller texts, there is still something to be said about spending quality time with short stories and excerpts.
Including short stories and standards-based activities is an ideal option to improve reading comprehension and develop skills, especially in middle and high school English classes!
SHORT STORIES AND ACTIVITIES RESOURCES:

This Short Stories and Test Prep Questions ULTIMATE BUNDLE with Lessons, Quizzes, and Activities uses the Common Core standards with reading comprehension QUESTIONS and ANSWERS for 18 short stories such as “The Most Dangerous Game,” “The Monkey’s Paw,” “The Tell-Tale Heart,” “After Twenty Years,” “The Gift of the Magi,” “The Veldt,” “The Lottery,” “The Pedestrian,” etc. modeled after various state reading exams.
Make teaching short stories and activities SIMPLE & EASY!
Just PRINT & TEACH with engaging short stories and lessons!!
Need more fun ideas for teaching short stories and corresponding activities? Check out my store Kristin Menke-Integrated ELA Test Prep !

Hi, I’m KRISTIN!
I primarily focus on integrating multiple disciplines and subjects. The goal is to make teaching simplified and effective!
Let's Connect
- Follow Follow
Click below to download “13 Simple Strategies to make test prep a breeze!”
41+ Critical Thinking Examples (Definition + Practices)

Critical thinking is an essential skill in our information-overloaded world, where figuring out what is fact and fiction has become increasingly challenging.
But why is critical thinking essential? Put, critical thinking empowers us to make better decisions, challenge and validate our beliefs and assumptions, and understand and interact with the world more effectively and meaningfully.
Critical thinking is like using your brain's "superpowers" to make smart choices. Whether it's picking the right insurance, deciding what to do in a job, or discussing topics in school, thinking deeply helps a lot. In the next parts, we'll share real-life examples of when this superpower comes in handy and give you some fun exercises to practice it.
Critical Thinking Process Outline
Critical thinking means thinking clearly and fairly without letting personal feelings get in the way. It's like being a detective, trying to solve a mystery by using clues and thinking hard about them.
It isn't always easy to think critically, as it can take a pretty smart person to see some of the questions that aren't being answered in a certain situation. But, we can train our brains to think more like puzzle solvers, which can help develop our critical thinking skills.
Here's what it looks like step by step:
Spotting the Problem: It's like discovering a puzzle to solve. You see that there's something you need to figure out or decide.
Collecting Clues: Now, you need to gather information. Maybe you read about it, watch a video, talk to people, or do some research. It's like getting all the pieces to solve your puzzle.
Breaking It Down: This is where you look at all your clues and try to see how they fit together. You're asking questions like: Why did this happen? What could happen next?
Checking Your Clues: You want to make sure your information is good. This means seeing if what you found out is true and if you can trust where it came from.
Making a Guess: After looking at all your clues, you think about what they mean and come up with an answer. This answer is like your best guess based on what you know.
Explaining Your Thoughts: Now, you tell others how you solved the puzzle. You explain how you thought about it and how you answered.
Checking Your Work: This is like looking back and seeing if you missed anything. Did you make any mistakes? Did you let any personal feelings get in the way? This step helps make sure your thinking is clear and fair.
And remember, you might sometimes need to go back and redo some steps if you discover something new. If you realize you missed an important clue, you might have to go back and collect more information.
Critical Thinking Methods
Just like doing push-ups or running helps our bodies get stronger, there are special exercises that help our brains think better. These brain workouts push us to think harder, look at things closely, and ask many questions.
It's not always about finding the "right" answer. Instead, it's about the journey of thinking and asking "why" or "how." Doing these exercises often helps us become better thinkers and makes us curious to know more about the world.
Now, let's look at some brain workouts to help us think better:
1. "What If" Scenarios
Imagine crazy things happening, like, "What if there was no internet for a month? What would we do?" These games help us think of new and different ideas.
Pick a hot topic. Argue one side of it and then try arguing the opposite. This makes us see different viewpoints and think deeply about a topic.
3. Analyze Visual Data
Check out charts or pictures with lots of numbers and info but no explanations. What story are they telling? This helps us get better at understanding information just by looking at it.
4. Mind Mapping
Write an idea in the center and then draw lines to related ideas. It's like making a map of your thoughts. This helps us see how everything is connected.
There's lots of mind-mapping software , but it's also nice to do this by hand.
5. Weekly Diary
Every week, write about what happened, the choices you made, and what you learned. Writing helps us think about our actions and how we can do better.
6. Evaluating Information Sources
Collect stories or articles about one topic from newspapers or blogs. Which ones are trustworthy? Which ones might be a little biased? This teaches us to be smart about where we get our info.
There are many resources to help you determine if information sources are factual or not.
7. Socratic Questioning
This way of thinking is called the Socrates Method, named after an old-time thinker from Greece. It's about asking lots of questions to understand a topic. You can do this by yourself or chat with a friend.
Start with a Big Question:
"What does 'success' mean?"
Dive Deeper with More Questions:
"Why do you think of success that way?" "Do TV shows, friends, or family make you think that?" "Does everyone think about success the same way?"
"Can someone be a winner even if they aren't rich or famous?" "Can someone feel like they didn't succeed, even if everyone else thinks they did?"
Look for Real-life Examples:
"Who is someone you think is successful? Why?" "Was there a time you felt like a winner? What happened?"
Think About Other People's Views:
"How might a person from another country think about success?" "Does the idea of success change as we grow up or as our life changes?"
Think About What It Means:
"How does your idea of success shape what you want in life?" "Are there problems with only wanting to be rich or famous?"
Look Back and Think:
"After talking about this, did your idea of success change? How?" "Did you learn something new about what success means?"
8. Six Thinking Hats
Edward de Bono came up with a cool way to solve problems by thinking in six different ways, like wearing different colored hats. You can do this independently, but it might be more effective in a group so everyone can have a different hat color. Each color has its way of thinking:
White Hat (Facts): Just the facts! Ask, "What do we know? What do we need to find out?"
Red Hat (Feelings): Talk about feelings. Ask, "How do I feel about this?"
Black Hat (Careful Thinking): Be cautious. Ask, "What could go wrong?"
Yellow Hat (Positive Thinking): Look on the bright side. Ask, "What's good about this?"
Green Hat (Creative Thinking): Think of new ideas. Ask, "What's another way to look at this?"
Blue Hat (Planning): Organize the talk. Ask, "What should we do next?"
When using this method with a group:
- Explain all the hats.
- Decide which hat to wear first.
- Make sure everyone switches hats at the same time.
- Finish with the Blue Hat to plan the next steps.
9. SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is like a game plan for businesses to know where they stand and where they should go. "SWOT" stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
There are a lot of SWOT templates out there for how to do this visually, but you can also think it through. It doesn't just apply to businesses but can be a good way to decide if a project you're working on is working.
Strengths: What's working well? Ask, "What are we good at?"
Weaknesses: Where can we do better? Ask, "Where can we improve?"
Opportunities: What good things might come our way? Ask, "What chances can we grab?"
Threats: What challenges might we face? Ask, "What might make things tough for us?"
Steps to do a SWOT Analysis:
- Goal: Decide what you want to find out.
- Research: Learn about your business and the world around it.
- Brainstorm: Get a group and think together. Talk about strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Pick the Most Important Points: Some things might be more urgent or important than others.
- Make a Plan: Decide what to do based on your SWOT list.
- Check Again Later: Things change, so look at your SWOT again after a while to update it.
Now that you have a few tools for thinking critically, let’s get into some specific examples.
Everyday Examples
Life is a series of decisions. From the moment we wake up, we're faced with choices – some trivial, like choosing a breakfast cereal, and some more significant, like buying a home or confronting an ethical dilemma at work. While it might seem that these decisions are disparate, they all benefit from the application of critical thinking.
10. Deciding to buy something
Imagine you want a new phone. Don't just buy it because the ad looks cool. Think about what you need in a phone. Look up different phones and see what people say about them. Choose the one that's the best deal for what you want.
11. Deciding what is true
There's a lot of news everywhere. Don't believe everything right away. Think about why someone might be telling you this. Check if what you're reading or watching is true. Make up your mind after you've looked into it.
12. Deciding when you’re wrong
Sometimes, friends can have disagreements. Don't just get mad right away. Try to see where they're coming from. Talk about what's going on. Find a way to fix the problem that's fair for everyone.
13. Deciding what to eat
There's always a new diet or exercise that's popular. Don't just follow it because it's trendy. Find out if it's good for you. Ask someone who knows, like a doctor. Make choices that make you feel good and stay healthy.
14. Deciding what to do today
Everyone is busy with school, chores, and hobbies. Make a list of things you need to do. Decide which ones are most important. Plan your day so you can get things done and still have fun.
15. Making Tough Choices
Sometimes, it's hard to know what's right. Think about how each choice will affect you and others. Talk to people you trust about it. Choose what feels right in your heart and is fair to others.
16. Planning for the Future
Big decisions, like where to go to school, can be tricky. Think about what you want in the future. Look at the good and bad of each choice. Talk to people who know about it. Pick what feels best for your dreams and goals.
Job Examples
17. solving problems.
Workers brainstorm ways to fix a machine quickly without making things worse when a machine breaks at a factory.
18. Decision Making
A store manager decides which products to order more of based on what's selling best.
19. Setting Goals
A team leader helps their team decide what tasks are most important to finish this month and which can wait.
20. Evaluating Ideas
At a team meeting, everyone shares ideas for a new project. The group discusses each idea's pros and cons before picking one.
21. Handling Conflict
Two workers disagree on how to do a job. Instead of arguing, they talk calmly, listen to each other, and find a solution they both like.
22. Improving Processes
A cashier thinks of a faster way to ring up items so customers don't have to wait as long.
23. Asking Questions
Before starting a big task, an employee asks for clear instructions and checks if they have the necessary tools.
24. Checking Facts
Before presenting a report, someone double-checks all their information to make sure there are no mistakes.
25. Planning for the Future
A business owner thinks about what might happen in the next few years, like new competitors or changes in what customers want, and makes plans based on those thoughts.
26. Understanding Perspectives
A team is designing a new toy. They think about what kids and parents would both like instead of just what they think is fun.
School Examples
27. researching a topic.
For a history project, a student looks up different sources to understand an event from multiple viewpoints.
28. Debating an Issue
In a class discussion, students pick sides on a topic, like school uniforms, and share reasons to support their views.
29. Evaluating Sources
While writing an essay, a student checks if the information from a website is trustworthy or might be biased.
30. Problem Solving in Math
When stuck on a tricky math problem, a student tries different methods to find the answer instead of giving up.
31. Analyzing Literature
In English class, students discuss why a character in a book made certain choices and what those decisions reveal about them.
32. Testing a Hypothesis
For a science experiment, students guess what will happen and then conduct tests to see if they're right or wrong.
33. Giving Peer Feedback
After reading a classmate's essay, a student offers suggestions for improving it.
34. Questioning Assumptions
In a geography lesson, students consider why certain countries are called "developed" and what that label means.
35. Designing a Study
For a psychology project, students plan an experiment to understand how people's memories work and think of ways to ensure accurate results.
36. Interpreting Data
In a science class, students look at charts and graphs from a study, then discuss what the information tells them and if there are any patterns.
Critical Thinking Puzzles
Not all scenarios will have a single correct answer that can be figured out by thinking critically. Sometimes we have to think critically about ethical choices or moral behaviors.
Here are some mind games and scenarios you can solve using critical thinking. You can see the solution(s) at the end of the post.
37. The Farmer, Fox, Chicken, and Grain Problem
A farmer is at a riverbank with a fox, a chicken, and a grain bag. He needs to get all three items across the river. However, his boat can only carry himself and one of the three items at a time.
Here's the challenge:
- If the fox is left alone with the chicken, the fox will eat the chicken.
- If the chicken is left alone with the grain, the chicken will eat the grain.
How can the farmer get all three items across the river without any item being eaten?
38. The Rope, Jar, and Pebbles Problem
You are in a room with two long ropes hanging from the ceiling. Each rope is just out of arm's reach from the other, so you can't hold onto one rope and reach the other simultaneously.
Your task is to tie the two rope ends together, but you can't move the position where they hang from the ceiling.
You are given a jar full of pebbles. How do you complete the task?
39. The Two Guards Problem
Imagine there are two doors. One door leads to certain doom, and the other leads to freedom. You don't know which is which.
In front of each door stands a guard. One guard always tells the truth. The other guard always lies. You don't know which guard is which.
You can ask only one question to one of the guards. What question should you ask to find the door that leads to freedom?
40. The Hourglass Problem
You have two hourglasses. One measures 7 minutes when turned over, and the other measures 4 minutes. Using just these hourglasses, how can you time exactly 9 minutes?
41. The Lifeboat Dilemma
Imagine you're on a ship that's sinking. You get on a lifeboat, but it's already too full and might flip over.
Nearby in the water, five people are struggling: a scientist close to finding a cure for a sickness, an old couple who've been together for a long time, a mom with three kids waiting at home, and a tired teenager who helped save others but is now in danger.
You can only save one person without making the boat flip. Who would you choose?
42. The Tech Dilemma
You work at a tech company and help make a computer program to help small businesses. You're almost ready to share it with everyone, but you find out there might be a small chance it has a problem that could show users' private info.
If you decide to fix it, you must wait two more months before sharing it. But your bosses want you to share it now. What would you do?
43. The History Mystery
Dr. Amelia is a history expert. She's studying where a group of people traveled long ago. She reads old letters and documents to learn about it. But she finds some letters that tell a different story than what most people believe.
If she says this new story is true, it could change what people learn in school and what they think about history. What should she do?
The Role of Bias in Critical Thinking
Have you ever decided you don’t like someone before you even know them? Or maybe someone shared an idea with you that you immediately loved without even knowing all the details.
This experience is called bias, which occurs when you like or dislike something or someone without a good reason or knowing why. It can also take shape in certain reactions to situations, like a habit or instinct.
Bias comes from our own experiences, what friends or family tell us, or even things we are born believing. Sometimes, bias can help us stay safe, but other times it stops us from seeing the truth.
Not all bias is bad. Bias can be a mechanism for assessing our potential safety in a new situation. If we are biased to think that anything long, thin, and curled up is a snake, we might assume the rope is something to be afraid of before we know it is just a rope.
While bias might serve us in some situations (like jumping out of the way of an actual snake before we have time to process that we need to be jumping out of the way), it often harms our ability to think critically.
How Bias Gets in the Way of Good Thinking
Selective Perception: We only notice things that match our ideas and ignore the rest.
It's like only picking red candies from a mixed bowl because you think they taste the best, but they taste the same as every other candy in the bowl. It could also be when we see all the signs that our partner is cheating on us but choose to ignore them because we are happy the way we are (or at least, we think we are).
Agreeing with Yourself: This is called “ confirmation bias ” when we only listen to ideas that match our own and seek, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms what we already think we know or believe.
An example is when someone wants to know if it is safe to vaccinate their children but already believes that vaccines are not safe, so they only look for information supporting the idea that vaccines are bad.
Thinking We Know It All: Similar to confirmation bias, this is called “overconfidence bias.” Sometimes we think our ideas are the best and don't listen to others. This can stop us from learning.
Have you ever met someone who you consider a “know it”? Probably, they have a lot of overconfidence bias because while they may know many things accurately, they can’t know everything. Still, if they act like they do, they show overconfidence bias.
There's a weird kind of bias similar to this called the Dunning Kruger Effect, and that is when someone is bad at what they do, but they believe and act like they are the best .
Following the Crowd: This is formally called “groupthink”. It's hard to speak up with a different idea if everyone agrees. But this can lead to mistakes.
An example of this we’ve all likely seen is the cool clique in primary school. There is usually one person that is the head of the group, the “coolest kid in school”, and everyone listens to them and does what they want, even if they don’t think it’s a good idea.
How to Overcome Biases
Here are a few ways to learn to think better, free from our biases (or at least aware of them!).
Know Your Biases: Realize that everyone has biases. If we know about them, we can think better.
Listen to Different People: Talking to different kinds of people can give us new ideas.
Ask Why: Always ask yourself why you believe something. Is it true, or is it just a bias?
Understand Others: Try to think about how others feel. It helps you see things in new ways.
Keep Learning: Always be curious and open to new information.
In today's world, everything changes fast, and there's so much information everywhere. This makes critical thinking super important. It helps us distinguish between what's real and what's made up. It also helps us make good choices. But thinking this way can be tough sometimes because of biases. These are like sneaky thoughts that can trick us. The good news is we can learn to see them and think better.
There are cool tools and ways we've talked about, like the "Socratic Questioning" method and the "Six Thinking Hats." These tools help us get better at thinking. These thinking skills can also help us in school, work, and everyday life.
We’ve also looked at specific scenarios where critical thinking would be helpful, such as deciding what diet to follow and checking facts.
Thinking isn't just a skill—it's a special talent we improve over time. Working on it lets us see things more clearly and understand the world better. So, keep practicing and asking questions! It'll make you a smarter thinker and help you see the world differently.
Critical Thinking Puzzles (Solutions)
The farmer, fox, chicken, and grain problem.
- The farmer first takes the chicken across the river and leaves it on the other side.
- He returns to the original side and takes the fox across the river.
- After leaving the fox on the other side, he returns the chicken to the starting side.
- He leaves the chicken on the starting side and takes the grain bag across the river.
- He leaves the grain with the fox on the other side and returns to get the chicken.
- The farmer takes the chicken across, and now all three items -- the fox, the chicken, and the grain -- are safely on the other side of the river.
The Rope, Jar, and Pebbles Problem
- Take one rope and tie the jar of pebbles to its end.
- Swing the rope with the jar in a pendulum motion.
- While the rope is swinging, grab the other rope and wait.
- As the swinging rope comes back within reach due to its pendulum motion, grab it.
- With both ropes within reach, untie the jar and tie the rope ends together.
The Two Guards Problem
The question is, "What would the other guard say is the door to doom?" Then choose the opposite door.
The Hourglass Problem
- Start both hourglasses.
- When the 4-minute hourglass runs out, turn it over.
- When the 7-minute hourglass runs out, the 4-minute hourglass will have been running for 3 minutes. Turn the 7-minute hourglass over.
- When the 4-minute hourglass runs out for the second time (a total of 8 minutes have passed), the 7-minute hourglass will run for 1 minute. Turn the 7-minute hourglass again for 1 minute to empty the hourglass (a total of 9 minutes passed).
The Boat and Weights Problem
Take the cat over first and leave it on the other side. Then, return and take the fish across next. When you get there, take the cat back with you. Leave the cat on the starting side and take the cat food across. Lastly, return to get the cat and bring it to the other side.
The Lifeboat Dilemma
There isn’t one correct answer to this problem. Here are some elements to consider:
- Moral Principles: What values guide your decision? Is it the potential greater good for humanity (the scientist)? What is the value of long-standing love and commitment (the elderly couple)? What is the future of young children who depend on their mothers? Or the selfless bravery of the teenager?
- Future Implications: Consider the future consequences of each choice. Saving the scientist might benefit millions in the future, but what moral message does it send about the value of individual lives?
- Emotional vs. Logical Thinking: While it's essential to engage empathy, it's also crucial not to let emotions cloud judgment entirely. For instance, while the teenager's bravery is commendable, does it make him more deserving of a spot on the boat than the others?
- Acknowledging Uncertainty: The scientist claims to be close to a significant breakthrough, but there's no certainty. How does this uncertainty factor into your decision?
- Personal Bias: Recognize and challenge any personal biases, such as biases towards age, profession, or familial status.
The Tech Dilemma
Again, there isn’t one correct answer to this problem. Here are some elements to consider:
- Evaluate the Risk: How severe is the potential vulnerability? Can it be easily exploited, or would it require significant expertise? Even if the circumstances are rare, what would be the consequences if the vulnerability were exploited?
- Stakeholder Considerations: Different stakeholders will have different priorities. Upper management might prioritize financial projections, the marketing team might be concerned about the product's reputation, and customers might prioritize the security of their data. How do you balance these competing interests?
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term Implications: While launching on time could meet immediate financial goals, consider the potential long-term damage to the company's reputation if the vulnerability is exploited. Would the short-term gains be worth the potential long-term costs?
- Ethical Implications : Beyond the financial and reputational aspects, there's an ethical dimension to consider. Is it right to release a product with a known vulnerability, even if the chances of it being exploited are low?
- Seek External Input: Consulting with cybersecurity experts outside your company might be beneficial. They could provide a more objective risk assessment and potential mitigation strategies.
- Communication: How will you communicate the decision, whatever it may be, both internally to your team and upper management and externally to your customers and potential users?
The History Mystery
Dr. Amelia should take the following steps:
- Verify the Letters: Before making any claims, she should check if the letters are actual and not fake. She can do this by seeing when and where they were written and if they match with other things from that time.
- Get a Second Opinion: It's always good to have someone else look at what you've found. Dr. Amelia could show the letters to other history experts and see their thoughts.
- Research More: Maybe there are more documents or letters out there that support this new story. Dr. Amelia should keep looking to see if she can find more evidence.
- Share the Findings: If Dr. Amelia believes the letters are true after all her checks, she should tell others. This can be through books, talks, or articles.
- Stay Open to Feedback: Some people might agree with Dr. Amelia, and others might not. She should listen to everyone and be ready to learn more or change her mind if new information arises.
Ultimately, Dr. Amelia's job is to find out the truth about history and share it. It's okay if this new truth differs from what people used to believe. History is about learning from the past, no matter the story.
Related posts:
- Experimenter Bias (Definition + Examples)
- Hasty Generalization Fallacy (31 Examples + Similar Names)
- Ad Hoc Fallacy (29 Examples + Other Names)
- Confirmation Bias (Examples + Definition)
- Equivocation Fallacy (26 Examples + Description)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
Critical Thinking Exercises
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Critical thinking is a skill that students develop gradually as they progress in school. While the skill becomes more important in higher grades, some students find it difficult to understand the concept of critical thinking .
The reason critical thinking can be difficult to grasp is because it requires students to set aside assumptions and beliefs to learn to think without bias or judgment.
Critical thinking involves suspending your beliefs to explore and question topics from a "blank page" point of view. It also involves the ability to distinguish fact from opinion when exploring a topic.
These exercises are designed to help develop critical thinking skills.
Critical Thinking Exercise 1: Tour Guide for an Alien
This exercise provides an opportunity to think outside your normal way of thinking.
Pretend that you have been assigned the task of conducting a tour for aliens who are visiting the earth and observing human life. You're riding along in a blimp, viewing the landscape below, and you float over a professional baseball stadium. One of the aliens looks down and is very confused by what he sees. You explain that there is a game going on and he asks several important questions.
- What is a game?
- Why are there no female players?
- Why do people get so excited about watching other people play games?
- What is a team?
- Why can't the people in the seats go down on the field and join in?
If you try to answer these questions fully, it will quickly become apparent that we carry around certain assumptions and values. We support a certain team, for instance, because it makes us feel like we're a part of a community. This sense of community is a value that matters to some people more than others.
Furthermore, when trying to explain team sports to an alien, you have to explain the value we place on winning and losing.
When you think like an alien tour guide, you are forced to take a deeper look at the things we do and things we value. Sometimes they don't sound logical from the outside looking in.
Critical Thinking Exercise 2: Fact or Opinion
Do you think you know the difference between fact and opinion? It's not always easy to discern. When you visit websites, do you believe everything you read? The abundance of available information makes it more important than ever for students to develop critical thinking skills. Additionally, it's an important reminder that you must use trustworthy sources in your school work.
If you don't learn the difference between fact and opinion, you may end up reading and watching things that continue to reinforce beliefs and assumptions you already own.
For this exercise, read each statement and try to determine whether it sounds like a fact or an opinion. This can be completed alone or with a study partner .
- My mom is the best mom on earth.
- My dad is taller than your dad.
- My telephone number is difficult to memorize.
- The deepest part of the ocean is 35,813 feet deep.
- Dogs make better pets than turtles.
- Smoking is bad for your health.
- Eighty-five percent of all cases of lung cancer in the U.S. are caused by smoking.
- If you flatten and stretch out a Slinky toy it will be 87 feet long.
- Slinky toys are fun.
- One out of every one hundred American citizens is color blind.
- Two out of ten American citizens are boring.
You will probably find some of the statements easy to judge but other statements difficult. If you can effectively debate the truthfulness of a statement with your partner, then it's most likely an opinion.
- Research Note Cards
- How Can You Stretch a Paper to Make it Longer?
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- Understanding the Progressive Era
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- How to Write a News Article That's Effective
- How Long Should My Paper Be?
- When to Cite a Source in a Paper
- Tips for Typing an Academic Paper on a Computer
- How to Narrow the Research Topic for Your Paper
- Unreliable Sources for Your Research Project
- Creating a Table of Contents
- Finding Sources for Death Penalty Research
- How to Write a 10-Page Research Paper
- What Is an Autobiography?
- Your Personal Essay Thesis Sentence
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
Best Critical Thinking Activities & Games for Employees
8 mins read
by Pete Ford
Updated On Aug 30, 2024
Critical thinking is a valuable skill that can make all the difference in an employee's success. It enables individuals to analyze information, evaluate evidence, and form sound judgments.
Furthermore, it's an essential skill an employee needs to perform excellently in the workplace. For a company to grow and develop, employees need to think of how and what to do to ensure the company grows and moves forward.
In his 1910 book How We Think, Dewey described reflective thinking as an active, persistent, and careful consideration of beliefs or supposed forms of knowledge in light of the grounds that support them and the further conclusions to which they tend. This is closely related to what we now call critical thinking.
A survey by the American Association of Colleges and Universities found that 75% of employers want colleges to emphasize critical thinking, real-world problem-solving, communication, and creativity.
Why Critical Thinking Matters
Critical thinking is crucial in the workplace because it enables employees to:
1. Make Informed Decisions: Provides employees with the skills to analyze data and information thoroughly. This process involves assessing the credibility of sources, weighing evidence, and considering various perspectives. By doing so, employees can avoid hasty judgments and ensure their decisions are based on solid reasoning and facts. This leads to more effective and strategic outcomes, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing overall organizational performance.
2. Identify Biases and Assumptions: Critical thinkers are adept at recognizing their own biases and assumptions, as well as those of others. This self-awareness allows them to approach situations more objectively, leading to fairer and more balanced decisions. It also helps in mitigating the influence of personal prejudices on professional judgments.
3. Solve Complex Problems: Identifies underlying issues, breaks complex problems down into manageable parts, and develops innovative solutions. This systematic approach helps in addressing challenges more efficiently and effectively, fostering a culture of problem-solving within the organization.
4. Evaluate Information and Sources: Employees skilled in critical thinking can discern the reliability and relevance of information from various sources. This ability is crucial in an age of information overload, where distinguishing between credible data and misinformation can significantly impact decision-making and strategic planning.
14 Critical Thinking Activities, Games & Exercises for Employees
1. egg drop.
Many people may have encountered this activity in science class. As it turns out, it is also a great way to help coworkers bond and grow their problem-solving and critical-thinking skills. For this activity, members can split into small teams of three to six people. The goal is to create a contraption that will secure and protect the egg from breaking.

Via Edstellar
It has to be effective in case the egg is dropped from a desk or the top of a building. Each team can use any material available around the workplace. Some of the materials include newspapers, paper clips, straws, tape, cotton balls, balloons, etc. Teams have 15 minutes to decide on the best strategy and building materials.
How to Play The Game
1. Preparation
- Materials: Gather materials like eggs, straws, tape, rubber bands, paper, plastic bags, and other office supplies that can be used for constructing a protective device.
- Set a Time Limit: Decide on a time limit for the activity, typically 30-60 minutes, depending on the complexity you want to introduce.
2. Group Formation
- Divide employees into small teams of 3-5 members each. This ensures that everyone can participate and contribute to the design process.
3. Explanation of Rules
- Objective: Each team must design and build a structure that can protect an egg from breaking when dropped from a predetermined height.
- Constraints: Set any specific rules, such as limiting the materials they can use or requiring the structure to fit within certain dimensions.
4. The Building Process
- Teams brainstorm, design, and construct their egg-protection devices within the allotted time. Encourage creativity and teamwork during this phase.
5. Drop Test
- Once the time is up, gather all teams and conduct the drop test from the designated height. You can use a ladder, a balcony, or a raised platform for this.
- Each team drops its egg, and the group observes whether the egg survives the fall intact.
6. Evaluation
- Assess which designs successfully protected the egg and discuss what worked and what didn’t. You can award points for creativity, durability, and teamwork.
- Consider holding a debrief session where teams can share their design processes and the thinking behind their approaches.
7. Conclude
- Conclude by highlighting the lessons learned, such as the importance of collaboration, creative problem-solving, and strategic planning.
- Recognize the winning team(s) and acknowledge the effort of all participants.
Review and Reflection of the Game
Here are three key review and reflection points for the Egg Drop activity:
1. Team Collaboration and Communication: Reflect on how effectively the teams worked together. Consider the quality of communication, how tasks were divided, and how decisions were made. What contributed to strong teamwork, and where could collaboration be improved?
2. Problem-Solving and Creativity: Review the problem-solving strategies and creative approaches teams used. What innovative designs emerged, and what made them successful? Analyze any failed attempts to understand what could be done differently next time.
3. Application to Workplace Skills: Reflect on how the activity relates to real workplace scenarios. How can the teamwork, creativity, and problem-solving skills demonstrated in the Egg Drop challenge be applied to everyday tasks and projects at work?
Key Takeaway
Employees must collaborate to design a structure that protects an egg from breaking when dropped from a height. The challenge requires them to think critically about materials, design, and physics, testing and refining their ideas. It highlights the importance of planning, innovative thinking, and learning from failure, all of which are crucial skills in the workplace.
Through improv activities, teams can improve their rapid problem-solving and critical thinking skills . Start by giving them a problem or scenario to solve together. Next, each participant builds on the preceding response by adding one sentence in turn. The scenario changes and gets more challenging with every new sentence. When the group responds to all the questions and comes up with a workable solution, the activity is over.

How to Conduct the Activity
1. Set the scenario: Provide the team with a question or scenario to resolve together.
2. Take Turns: Participants take turns adding one sentence to build on the previous response, evolving the scenario.
3. Encourage Creativity: Each new sentence should creatively change the situation, challenging the team to adapt quickly.
4. Conclude: The activity ends when the team completes the story or reaches a solution.
Review and Reflection of the Activity
1. Team Adaptability : Reflect on how well the team adapted to the constantly changing scenario. Did participants remain flexible and build on each other’s ideas effectively?
2. Creative Problem-Solving: Consider the level of creativity in the responses. How did the team use their imagination to navigate the evolving scenario? Were they able to think on their feet?
3. Communication and Collaboration : Assess how well team members communicated and collaborated. Was there a smooth flow of ideas? Did everyone contribute equally?
3. Escape Room
Escape Room Challenge is one of the best critical thinking games for team building that encourages problem-solving, communication, and teamwork.

To "escape" from a themed room, employees must solve puzzles and riddles within a predetermined amount of time. This team-building activity improves communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities by forcing participants to think critically and work under pressure. It's an exciting way to foster strategic thinking in a light-hearted, immersive setting.
How to Play the Game
1. Preparation: Create or select a themed room with a series of puzzles, riddles, and challenges. Ensure the setup is safe, and the puzzles are varied to engage different skill sets.
2. Gather Materials: Collect necessary items such as locks, keys, clues, and props related to the theme.
3. Form Teams: Divide participants into small teams of 4–6 people to encourage collaboration and maximize participation.
4. Set the Scene: Explain the objective: Brief the teams on the scenario, the backstory, and their goal to solve all the puzzles within a set time (usually 60 minutes) to "escape" the room.
5. Review the Rules: Outline any specific rules, such as not forcing open locks or damaging props, and explain how they can ask for hints if needed.
6. Gameplay: Start the timer. Begin the activity and let the teams work together to find clues, solve puzzles, and unlock the final solution.
7. Monitor Progress: Observe the teams as they play, providing hints if requested, and ensuring the game flows smoothly.
8. Debrief and Reflect: After the time is up, gather everyone to discuss what worked, what didn’t, and the strategies used. Highlight the importance of teamwork, communication, and creative problem-solving.
9. Celebrate Success: Recognize the efforts of all teams, whether they escaped or not, and celebrate the collaboration and critical thinking demonstrated during the activity.
Reviews and Reflection of the Game
1. Team Dynamics and Communication: Reflect on how well the team members communicated and collaborated. Did everyone contribute ideas, and was there effective coordination in solving the puzzles?
2. Problem-Solving Approaches: Consider the strategies the teams used to tackle the challenges. Were they able to think critically and creatively under pressure? How did they handle setbacks or difficult puzzles?
3. Time Management : Evaluate how the teams managed their time during the activity. Did they prioritize tasks effectively and work efficiently within the time limit? What could be improved in future scenarios?
The Escape Room activity emphasizes the importance of effective teamwork, communication, and creative problem-solving under pressure in the workplace. It highlights how working together and managing time efficiently are crucial for overcoming challenges, achieving goals, and meeting standards set by the company.
4. Murder Mystery
A Murder Mystery game is a critical thinking activity where employees work together to solve a fictional crime. It involves analyzing clues, collaborating, and deducing the perpetrator's identity based on evidence and logical reasoning. This exercise enhances critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and teamwork, as employees must communicate effectively and use their analytical skills to uncover the solution.

1. Preparation: Choose or create a murder mystery scenario, assign roles to participants, and distribute character information.
2. Gameplay: Set the scene and rules, then let participants interact, gather clues, and work together to solve the mystery.
3. Debrief and Reveal: Reveal the solution, discuss how clues led to the conclusion, and acknowledge participants’ efforts and teamwork.
1. Engagement and Role-Playing: Reflect on how engaged participants were with their roles and the storyline. Did they fully immerse themselves in their characters and contribute to the narrative effectively?
2. Clue Gathering and Deduction: Consider how well teams gathered and analyzed clues. Were they able to piece together information and make logical deductions to identify the "murderer"? How effective were their investigative strategies?
3. Team Collaboration: Assess the level of collaboration and communication among team members. Did they work together cohesively to solve the mystery, or were there challenges in sharing information and coordinating efforts?
The Murder Mystery activity highlights the value of teamwork, effective communication, and critical thinking. It demonstrates how collaborative problem-solving and role-playing can enhance investigative skills and foster a deeper understanding of team dynamics in a fun and engaging way.
5. Puzzle-Solving Relay
A team-building exercise called the Puzzle Solving Relay aims to improve problem-solving and collaboration. In a relay-style setting, teams solve puzzles individually before moving on to the next member. Critical thinking abilities can be improved individually and as a team using this exercise.

1. Setup: Prepare a series of puzzles (e.g., logic puzzles, crosswords, riddles) and divide participants into teams. Each team will work on the puzzles in a relay format.
2. Relay Play: Each team member solves one puzzle before passing it to the next person. Teams continue this process until all puzzles are completed.
1. Evaluate Team Performance: Assess how well teams communicated and collaborated during the relay. Were they efficient and supportive of each other?
2. Analyze Problem-Solving Strategies: Reflect on the strategies used to solve the puzzles. What methods were effective, and where did teams face challenges?
3. Discuss Lessons Learned: Discuss to share insights and feedback. Highlight what worked well and areas for improvement in teamwork and problem-solving skills.
The Puzzle Solving Relay activity emphasizes the importance of teamwork, effective communication, and strategic problem-solving. It demonstrates how working collaboratively and leveraging each team member’s strengths can lead to successful outcomes and improved team dynamics.
6. Role-Playing Activities
Role-playing exercises, such as scenario-based training exercises, are effective critical thinking exercises for teams. Real-world scenarios are utilized to enhance employees' skills and knowledge. This approach involves creating scenarios that closely mimic the challenges and expectations employees face in their roles. For example, Walmart uses role-playing games to train employees in customer service, where they practice handling various scenarios such as resolving complaints and providing assistance. Similarly, Lockheed Martin employs virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences to train employees in assembling spacecraft and aircraft, allowing them to practice complex tasks in a controlled, realistic environment.

Role-playing activities in scenario-based training emphasize the importance of practical, hands-on learning. By simulating real-world challenges, employees can develop critical skills, improve their problem-solving abilities, and enhance their overall job performance. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of their roles and prepares them for real-life situations, ultimately leading to more effective and confident employees.
How to Conduct the “Role Playing” Activity
1. Define the Scenario
- Choose or create a relevant workplace scenario or issue for participants to role-play.
- Clearly explain the context, objectives, and roles each participant will assume.
2. Conduct the Role Play
- Have participants act out their roles and interact according to the scenario.
- Allow them time to address the situation and make decisions based on their characters’ perspectives.
3. Debrief and Discuss
- After the role play, gather everyone to discuss the experience.
- Reflect on the strategies used, the effectiveness of communication, and how the scenario relates to real workplace situations.
1. Assess Role Performance : Evaluate how well participants embodied their roles and handled the scenario. Did they stay true to their characters and effectively address the situation?
2. Analyze Communication and Problem-Solving : Reflect on the communication strategies and problem-solving approaches used during the role play. How did participants collaborate and resolve issues?
3. Discuss Lessons Learned : Share insights and feedback. Highlight what participants learned about handling similar situations in real life and how role play can improve workplace interactions and decision-making.
The key takeaway is that it helps enhance critical thinking by allowing participants to explore various perspectives, practice problem-solving, and improve communication skills in a dynamic, interactive environment.
7. Reverse Brainstorming
Teams that participate in the Reverse Brainstorming challenge begin by generating ideas for ways to exacerbate an issue rather than find a solution. After listing all the bad ideas, they reverse these concepts to come up with possible fixes. By taking a novel perspective on the problem, this exercise promotes innovative problem-solving and helps teams look beyond the box.

1. Define the Problem : Clearly state the problem or challenge you want to address. Make sure everyone understands the issue before starting.
2. Reverse Brainstorming : Ask participants to brainstorm ways to make the problem worse rather than solving it. Encourage them to think creatively about actions or strategies that would exacerbate the issue.
3. Generate Solutions : Reverse the negative ideas into positive solutions. Discuss how the actions that would worsen the problem can be flipped to create effective solutions. Reflect on the insights gained from this approach.
1. Evaluate Idea Generation : Assess the creativity and range of ideas generated for worsening the problem. Did participants think broadly and consider various aspects of the issue?
2. Analyze Solution Development : Reflect on how effectively the negative ideas were transformed into positive solutions. Were the solutions practical and innovative?
3. Discuss Insights and Learning : Discuss the overall process. What did participants learn about problem-solving and creativity? How did the reverse approach influence their understanding of the original problem?
Critical thinking activities like reverse brainstorming illustrate how innovative solutions can be found by taking a different approach to a problem. By first considering how to worsen the issue, teams gain new perspectives that can be flipped to develop creative and effective strategies for solving the original problem.
8. The Marshmallow Challenge
In the Marshmallow Challenge, teams are given a set amount of time to build the tallest freestanding structure using only spaghetti, tape, string, and a marshmallow. The catch is that the marshmallow must be placed on top of the structure. It enhances critical thinking by fostering problem-solving, creativity, collaboration, and iterative learning. Teams design and build a structure with limited resources, learning to adapt and refine their strategies in real time.

1. Distribute Materials : Provide each team with a set of materials (e.g., spaghetti, tape, string, and a marshmallow). Ensure all teams have the same resources.
2. Build the Structure : Challenge teams to build the tallest freestanding structure they can using the materials provided, with the marshmallow placed on top. Set a time limit (typically 18–30 minutes).
3. Evaluate and Reflect : Measure the height of each structure and check if the marshmallow is on top. Discuss the design approaches, teamwork, and problem-solving strategies used during the challenge.
Assess Design and Execution: Evaluate how well each team’s structure was built and the effectiveness of their design. Did the structures achieve the goal of being the tallest and holding the marshmallow?
Analyze Team Collaboration: Reflect on how teams worked together. Were roles and tasks divided effectively? Did team members communicate and collaborate well
Discuss Lessons Learned: Review the key insights gained from the challenge. What did teams learn about planning, prototyping, and adjusting their approach? How can these lessons be applied to workplace projects and problem-solving?
The Marshmallow Challenge highlights the importance of prototyping, iterative design, and teamwork. It demonstrates how rapid experimentation and collaboration can lead to successful outcomes, emphasizing the need for adaptability and creativity in problem-solving.
9. Two Truths and A Lie
The first task involves one individual making three assertions about themselves, two of which are true and one of which is false. The other participants must then determine which of the three statements about the person were true and which were lies.

Two Truths and a Lie helps employees with critical thinking by:
- Enhancing Observation : Participants must discern truth from deception.
- Improving Communication: It encourages clear and thoughtful sharing of information.
- Fostering Insight: Employees learn to read cues and understand underlying motives.
1. Explain the Rules : Each participant takes turns sharing three statements about themselves: two that are true and one that is a lie. The rest of the team must guess which statement is a lie.
2. Take Turns : Allow each participant to present their three statements. After each person shares, the team discusses and votes on which statement they think is false.
3. Reveal and Discuss : After guesses are made, the participant reveals which statement was the lie. Discuss the truths behind the statements, fostering conversation and helping team members learn more about each other.
1. Evaluate Participation and Engagement : Reflect on how actively participants engaged with the activity. Did everyone take part and contribute to guessing and revealing the statements?
2. Analyze Communication and Interaction : Assess the quality of interaction and communication during the activity. How well did team members discuss their guesses and share their thoughts?
3. Discuss Insights and Team Building : Review what participants learned about each other and how the activity helped in team bonding. Discuss any new insights gained and how the activity might improve team dynamics and understanding.
The "Two Truths and a Lie" activity fosters team bonding and improves communication by encouraging employees to share personal insights and engage in light-hearted interaction. It helps team members learn more about each other, build relationships, and enhance trust in a fun and informal setting.
10. Silent Line-Up
In just five minutes, you may finish the non-verbal game called Silent Line-Up. This exercise aims to promote problem-solving, cooperation, and communication abilities without the use of words.

Team members must form a line and silently arrange themselves according to a predetermined criterion to participate in the silent line-up.
How to play the Game
1. Explain the Objective : Inform participants that the goal is to line up in a specific order (e.g., by birthdate, height, or years of experience) without speaking. Clearly state the criteria for the lineup.
2. Initiate the Activity : Start the activity and let participants begin organizing themselves according to the specified criteria. Ensure they understand they must use non-verbal communication and gestures to coordinate.
Once the lineup is complete, check if the order is correct. Discuss the experience, focusing on the strategies used, the effectiveness of non-verbal communication, and how the activity can enhance teamwork and problem-solving skills.
The silent line-up activity emphasizes the importance of non-verbal communication and teamwork. It demonstrates how effective coordination and understanding can be achieved through gestures and teamwork without relying on verbal instructions, fostering stronger collaboration and problem-solving skills.
11. Tower of Hanoi
The Tower of Hanoi is a straightforward mathematical puzzle that can be effectively used to evaluate and enhance employees’ problem-solving skills. This puzzle involves moving a series of disks from one peg to another, following specific rules, and is a popular tool for assessing working memory and planning abilities. By incorporating the Tower of Hanoi into training programs, companies can help employees develop critical thinking skills, as the puzzle requires careful planning and strategic thinking to solve.

Additionally, the complexity of the puzzle can be easily adjusted by adding more disks or pegs, making it suitable for various skill levels. Incorporating the Tower of Hanoi into employee training not only fosters critical thinking but also provides a fun and engaging way to improve cognitive abilities. Employees can work individually or in teams to solve the puzzle, promoting collaboration and communication.
This activity can also serve as a diagnostic tool to identify areas where employees may need further development, particularly in their planning and problem-solving skills. By challenging employees with the Tower of Hanoi, companies can create a dynamic learning environment that encourages continuous improvement and innovation.
1. Objective : Move all disks from the starting peg to the target peg, following the rules.
- Only one disk can be moved at a time.
- A disk can only be placed on a larger disk or an empty peg.
- Move the top (n−1)(n−1)(n−1) disks to the auxiliary peg.
- Move the largest disk to the target peg.
- Move the (n−1)(n−1)(n−1) disks from the auxiliary peg to the target peg.
The challenge involves strategic planning and problem-solving to achieve the goal efficiently.
1. Assess Strategy and Execution : Evaluate the strategies used to solve the Tower of Hanoi. How effectively did participants plan their moves and manage the constraints? Were there any common strategies or approaches?
2. Analyze Problem-Solving Skills : Reflect on how participants approached problem-solving. Did they demonstrate effective planning and foresight? How did they handle challenges or mistakes?
3. Discuss Lessons Learned : Hold a discussion on the insights gained from the activity. What did participants learn about strategic thinking, patience, and perseverance? How can these lessons be applied to workplace problem-solving and project management?
The Tower of Hanoi activity highlights the importance of strategic planning , patience, and problem-solving. It demonstrates how methodical thinking and careful execution can lead to successful outcomes, reinforcing skills that are valuable for tackling complex tasks and managing projects in the workplace.
12. Rebus Puzzle
For a rebus puzzle, every component of a jigsaw puzzle represents a member of your team. It is distinct from every other piece in terms of shape and function. Because of this, an effective team leader will learn about their needs and handle each member uniquely. Every component of a jigsaw puzzle fits into the overall design.

Basically, it uses pictures and symbols to represent words or phrases. It enhances workplace critical thinking by promoting problem-solving, creativity, and teamwork through decoding visual clues.
How to Play the Rebus Puzzle
1. Receive the Puzzle : Obtain the visual representation of words or phrases. This could be a printed sheet, a digital image, or a projected slide.
2. Analyze the Clues : Examine the pictures, symbols, or letters presented in the puzzle. Look for familiar shapes, objects, or patterns that might hint at a word or phrase.
3. Interpret the Symbols : Break down the visual elements into parts that could represent sounds, words, or phrases. For example, a picture of an eye might represent the word “I,” and a picture of a bee might represent the sound “B.”
4. Combine Interpretations : Piece together the individual interpretations to form a coherent phrase or solution. This step often requires creative thinking and the ability to see connections between different elements.
5. Verify the Answer : Check if your solution makes sense and matches the intended message. If the phrase or word seems logical and fits the clues provided, you have likely solved the puzzle correctly.
1. Evaluate the Problem-Solving Approach : Assess how participants approached solving the puzzle. Did they use effective strategies and collaborate well? How did they interpret and piece together the visual clues?
2. Analyze Communication and Teamwork : Reflect on how well participants communicated and worked together (if in teams). Was there effective sharing of ideas and feedback?
3. Discuss Insights and Learning : Discuss what participants learned from the activity. How did it enhance their ability to think creatively and solve problems? What insights can be applied to other problem-solving scenarios in the workplace?
The Rebus Puzzle activity emphasizes the importance of creative thinking and collaborative problem-solving. It shows how interpreting visual clues can enhance lateral thinking skills and teamwork, providing valuable insights into how diverse approaches can be applied to solving complex problems in the workplace.
13. Socrates Circle
Socrates Circle is a critical thinking game where participants discuss a topic in a structured dialogue, encouraging deep questioning and reflection. It helps employees enhance their analytical skills , communication, and collaborative problem-solving.

1. Define the Topic : Select a topic or question for discussion that is relevant to the workplace or team dynamics. Ensure it is open-ended and thought-provoking.
2. Facilitate the Discussion :
- Arrange Participants : Set up a circle or virtual meeting where everyone can see each other.
- Start the Discussion : Ask the chosen question and encourage participants to share their thoughts and perspectives.
3. Use Socratic Questioning Techniques : Ask probing questions that challenge assumptions and encourage deeper thinking. For example, "What is the underlying reason for this issue?" or "How might this perspective change our approach?"
4. Summarize and Reflect : Conclude the discussion by summarizing the key points and insights gained. Reflect on the different viewpoints shared and how they might influence future actions or decisions. Encourage participants to consider how the discussion can impact their work and interactions.
1. Evaluate Participation and Engagement : Assess how actively participants engaged in the discussion. Did they contribute thoughtfully and consider different perspectives?
2. Analyze the Depth of Discussion : Reflect on how effectively the Socratic questioning deepened the discussion. Did it challenge assumptions and lead to meaningful insights?
3. Discuss Lessons Learned : Review the key insights and understanding gained from the discussion. How did the activity enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills? What new perspectives or solutions emerged?
The Socrates Circle fosters deep critical thinking and open dialogue by encouraging participants to explore different viewpoints and challenge assumptions. It enhances understanding and decision-making by promoting thoughtful questioning and reflection on complex issues.
14. Paper Tower Challenge
The Paper Town Challenge is a critical thinking game where employees use only paper to create a model of a town or structure. Participants must plan, design, and construct their models while adhering to specific constraints.

Here’s the formatted version with bold subheadings:
For the Workplace, This Game Fosters Critical Thinking by
1. Encouraging Creativity : Requires innovative use of limited resources.
2. Enhancing Problem-Solving : Involves overcoming design and construction challenges.
3. Promoting Teamwork : Requires collaboration and communication to build the model.
1. Distribute Materials : Provide paper and basic tools.
2. Define Objectives : Set guidelines for what to build (e.g., a town or structure).
3. Design and Build : Teams plan and construct their models using only paper.
4. Present and Review : Share and evaluate each model based on creativity and adherence to guidelines.
This game enhances creativity, problem-solving, and teamwork.
1. Evaluate Creativity and Design : Assess how creatively and effectively participants designed their paper towns. Did they use the materials in innovative ways and incorporate various elements into their designs?
2. Analyze Teamwork and Execution : Reflect on how well teams worked together during the challenge. Was there clear communication and collaboration? How did they handle any obstacles or constraints?
3. Discuss Learning and Application : Review the key takeaways from the activity, including insights into planning, resource management, and teamwork. How can the experience be applied to real-world projects and problem-solving scenarios?
The Paper Town Challenge emphasizes the importance of creativity, collaboration, and resource management. It shows how working together to create a complex design with limited materials can enhance problem-solving skills, encourage innovative thinking, and improve team dynamics. Games for critical thinking in the workplace are crucial because they foster essential skills such as problem-solving, creativity, and effective communication.
By engaging in these activities, employees enhance their ability to think analytically, collaborate effectively, and approach challenges with innovative solutions. These skills contribute to a more dynamic, adaptable, and resilient workforce, ultimately driving greater organizational success.
The 14 critical thinking activities for employees in the workplace are outlined, and they offer proper insight to help employees in the workplace develop strong hindsight in their day-to-day activities.
Edstellar , a global training platform, provides a wealth of additional team-building activities to provide a wide range of critical thinking activities, as mentioned, to help build better employees in the workplace.
Ultimately, it’s going to provide an amazing method for organizations that need employees to think far and wide to better themselves for the organization's growth and development.

By Pete Ford
Explore High-impact instructor-led training for your teams.
#On-site #Virtual #GroupTraining #Customized
Edstellar Training Catalog
Explore 2000+ industry ready instructor-led training programs.
Have a Training Requirement?
Coaching that unlocks potential.
Create dynamic leaders and cohesive teams. Learn more now!

Want to evaluate your team’s skill gaps?
Do a quick Skill gap analysis with Edstellar’s Free Skill Matrix tool
Related Posts

Stay informed on L&D best practices
Get periodic updates on learning and development industry trends, expert insights, success stories and innovative training practices from Edstellar.
Featured Post
10 reasons why cultural sensitivity is essential in today’s workplace, top 10 in-demand skills in belgium, 9 leadership conferences to attend in australia in 2025, upcoming l&d international conferences in europe 2025, top 10 in-demand skills in austria, top 4 corporate training companies in china, blog categories, related corporate training programs.
.webp)
Submit your Training Requirements below and We'll get in touch with you shortly.
Tell us about your requirements
Edstellar is a one-stop instructor-led corporate training and coaching solution that addresses organizational upskilling and talent transformation needs globally. Edstellar offers 2000+ tailored programs across disciplines that include Technical, Behavioral, Management, Compliance, Leadership and Social Impact.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writing (or drawing) and silence are used as tools to slow down thinking and allow for silent reflection, unfiltered. By using silence and writing, learners can focus on other viewpoints. This activity uses a driving question, markers, and Big Paper (poster-sized is best).
One way to see students' thinking is to have them create graphic organizers. Each graphic organizer that follows requires your students to use different critical thinking skills (in parentheses). Read about each organizer and the thinking it creates, and then click to see minilesson activities you can present to your students to get them ...
26. Compare/contrast. Compare and contrast are important critical thinking strategies. Students can create a Venn diagram to show similarities or differences, or they could write a good old-fashioned compare/contrast essay about the characters of Romeo and Juliet. 27. Pick a word, find a related word.
6. Start a Debate. In this activity, the teacher can act as a facilitator and spark an interesting conversation in the class on any given topic. Give a small introductory speech on an open-ended topic. The topic can be related to current affairs, technological development or a new discovery in the field of science.
This arrangement will help you and your students more clearly understand and identify the specific critical-thinking skills they are using. For each thinking skill in this book, there are two kinds of activities: (1) those that you, as the teacher, will lead, and (2) student reproducibles for indepen-dent work.
These short, accessible, image-driven prompts invite students to pen short stories, poems and memoirs; share experiences from their lives; analyze illustrations, graphs and charts; and tell us ...
3. Brainstorming: Ask students to brainstorm ideas for a project or assignment. This activity helps students develop their creativity and critical thinking skills. 4. Role-Playing: Assign students roles and ask them to act out a scenario. This activity helps students develop their empathy and critical thinking skills.
TED-Ed lessons on the subject Critical Thinking. TED-Ed celebrates the ideas of teachers and students around the world. Discover hundreds of animated lessons, create customized lessons, and share your big ideas. ... Thinking & Learning Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world? Lesson duration 05:20 834,454 Views. 06:13 ...
The rest of this article will discuss 10 fun activities to improve your critical thinking skills. Contents. 1 Worst Case Scenario. 2 Creative Construction. 3 Story Telling. 4 Pragmatic Problem Solving. 5 Egg Rescue. 6 Critical Analysis. 7 Controversy Conundrum.
Check out these critical thinking activities, adapted from Critical Thinking in the Classroom , a book with over 100 practical tools and strategies for teaching critical thinking in K-12 classrooms. Four Corners. In this activity, students move to a corner of the classroom based on their responses to a question with four answer choices.
Here are 20 critical thinking activities that can be easily incorporated into any elementary classroom setting. 1. Think-Pair-Share. This simple activity encourages students to think about a question or problem individually first and then discuss with a partner before sharing their thoughts with the entire class. 2.
7 FREE Creative and Critical Thinking Activities. Looking for some fun after-testing creative and critical thinking activities? Try these seven ready-to-use printables! This is actually a mini-sampler, as each activity has been pulled from one of my other critical and creative thinking skills products.
Take a simple problem, for practice, and break it down into increments. Make different decisions on smaller portions of the problem to see where those decisions lead you. 5. Review your day. Wasted time is one of the biggest obstacles to productive thinking, and another culprit is procrastination, as you already know.
First, consider the five words below: Cruise ship. Bicycle. Airplane. Walking on foot. Automobile (not a race car) Now, put them in order from the slowest to the fastest, when they are going at ...
The activity pages in the Critical Thinking Workbook are meant to be shared and explored. Use it as an electronic document or as worksheets. You can either print off the pages and use them as activity sheets, or you can edit them directly right in the document on your computer. There are also Answer Keys for the activities that need them ...
These Critical Thinking Activities Task Cards provide teachers with activities and puzzles to help students develop critical thinking skills.In this pack, you will find 80 quick start task cards - 4 cards per page.Your elementary students will love trying to figure out the puzzle or challenge and you will love knowing that they are using higher order thinking skills!
With the barrage of mainstream news, advertising, and social media content out there, it's vital for students to think independently and learn to differentiate between fact and fiction. This series of critical thinking activities, STEM-based design challenges, engaging Math puzzles, and problem-solving tasks will support students in thinking rationally and understanding the logical ...
Making Inferences with Pictures is a fun way to teach the concept of inferring. This 35 page activity helps students develop important skills needed in reading. (observing details, describing, and using prior knowledge) Students will be presented with part of a eye-catching photo. Students will study the photo and use their own knowledge to infer what the complete photo is.
Table of Contents. 19 Short Stories and Questions - Suggestions for Teaching Them. 1. "The Most Dangerous Game". 2. "An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge". 3. "The Masque of the Red Death". 4.
There are many resources to help you determine if information sources are factual or not. 7. Socratic Questioning. This way of thinking is called the Socrates Method, named after an old-time thinker from Greece. It's about asking lots of questions to understand a topic.
Critical Thinking Exercise 1: Tour Guide for an Alien. This exercise provides an opportunity to think outside your normal way of thinking. Pretend that you have been assigned the task of conducting a tour for aliens who are visiting the earth and observing human life. You're riding along in a blimp, viewing the landscape below, and you float ...
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...
Critical thinking activities like reverse brainstorming illustrate how innovative solutions can be found by taking a different approach to a problem. By first considering how to worsen the issue, teams gain new perspectives that can be flipped to develop creative and effective strategies for solving the original problem. 8. The Marshmallow ...