11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.

Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Company summary | Brief overview (one to two paragraphs) of the problem, solution, and potential customers |
| Customer analysis | Description of potential customers and evidence they would purchase product |
| Market analysis | Size of market, target market, and share of market |
| Product or service | Current state of product in development and evidence it is feasible |
| Intellectual property | If applicable, information on patents, licenses, or other IP items |
| Competitive differentiation | Describe the competition and your competitive advantage |
| Company founders, management team, and/or advisor | Bios of key people showcasing their expertise and relevant experience |
| Financials | Projections of revenue, profit, and cash flow for three to five years |
| Amount of investment | Funding request and how funds will be used |
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Executive Summary Component | Content |
|---|---|
The Concept | La Vida Lola is a food truck serving the best Latin American and Caribbean cuisine in the Atlanta region, particularly Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes, with a festive flair. La Vida Lola offers freshly prepared dishes from the mobile kitchen of the founding chef and namesake Lola González, a Duluth, Georgia, native who has returned home to launch her first venture after working under some of the world’s top chefs. La Vida Lola will cater to festivals, parks, offices, community and sporting events, and breweries throughout the region. |
Market Advantage | Latin food packed with flavor and flair is the main attraction of La Vida Lola. Flavors steeped in Latin American and Caribbean culture can be enjoyed from a menu featuring street foods, sandwiches, and authentic dishes from the González family’s Puerto Rican and Cuban roots. craving ethnic food experiences and are the primary customers, but anyone with a taste for delicious homemade meals in Atlanta can order. Having a native Atlanta-area resident returning to her hometown after working in restaurants around the world to share food with area communities offers a competitive advantage for La Vida Lola in the form of founding chef Lola González. |
Marketing | The venture will adopt a concentrated marketing strategy. The company’s promotion mix will comprise a mix of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Much of the promotion mix will center around dual-language social media. |
Venture Team | The two founding members of the management team have almost four decades of combined experience in the restaurant and hospitality industries. Their background includes experience in food and beverage, hospitality and tourism, accounting, finance, and business creation. |
Capital Requirements | La Vida Lola is seeking startup capital of $50,000 to establish its food truck in the Atlanta area. An additional $20,000 will be raised through a donations-driven crowdfunding campaign. The venture can be up and running within six months to a year. |
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Business Description | La Vida Lola will operate in the mobile food services industry, which is identified by SIC code 5812 Eating Places and NAICS code 722330 Mobile Food Services, which consist of establishments primarily engaged in preparing and serving meals and snacks for immediate consumption from motorized vehicles or nonmotorized carts. Ethnically inspired to serve a consumer base that craves more spiced Latin foods, La Vida Lola is an Atlanta-area food truck specializing in Latin cuisine, particularly Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes native to the roots of the founding chef and namesake, Lola González. La Vida Lola aims to spread a passion for Latin cuisine within local communities through flavorful food freshly prepared in a region that has embraced international eats. Through its mobile food kitchen, La Vida Lola plans to roll into parks, festivals, office buildings, breweries, and sporting and community events throughout the greater Atlanta metropolitan region. Future growth possibilities lie in expanding the number of food trucks, integrating food delivery on demand, and adding a food stall at an area food market. After working in noted restaurants for a decade, most recently under the famed chef José Andrés, chef Lola González returned to her hometown of Duluth, Georgia, to start her own venture. Although classically trained by top world chefs, it was González’s grandparents’ cooking of authentic Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes in their kitchen that influenced her profoundly. The freshest ingredients from the local market, the island spices, and her attention to detail were the spark that ignited Lola’s passion for cooking. To that end, she brings flavors steeped in Latin American and Caribbean culture to a flavorful menu packed full of street foods, sandwiches, and authentic dishes. Through reasonably priced menu items, La Vida Lola offers food that appeals to a wide range of customers, from millennial foodies to Latin natives and other locals with Latin roots. |
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategy | According to ’ first annual report from the San Francisco-based Off The Grid, a company that facilitates food markets nationwide, the US food truck industry alone is projected to grow by nearly 20 percent from $800 million in 2017 to $985 million in 2019. Meanwhile, an report shows the street vendors’ industry with a 4.2 percent annual growth rate to reach $3.2 billion in 2018. Food truck and street food vendors are increasingly investing in specialty, authentic ethnic, and fusion food, according to the report. Although the report projects demand to slow down over the next five years, it notes there are still opportunities for sustained growth in major metropolitan areas. The street vendors industry has been a particular bright spot within the larger food service sector. The industry is in a growth phase of its life cycle. The low overhead cost to set up a new establishment has enabled many individuals, especially specialty chefs looking to start their own businesses, to own a food truck in lieu of opening an entire restaurant. Off the Grid’s annual report indicates the average typical initial investment ranges from $55,000 to $75,000 to open a mobile food truck. The restaurant industry accounts for $800 billion in sales nationwide, according to data from the National Restaurant Association. Georgia restaurants brought in a total of $19.6 billion in 2017, according to figures from the Georgia Restaurant Association. There are approximately 12,000 restaurants in the metro Atlanta region. The Atlanta region accounts for almost 60 percent of the Georgia restaurant industry. The SAM is estimated to be approximately $360 million. The mobile food/street vendor industry can be segmented by types of customers, types of cuisine (American, desserts, Central and South American, Asian, mixed ethnicity, Greek Mediterranean, seafood), geographic location and types (mobile food stands, mobile refreshment stands, mobile snack stands, street vendors of food, mobile food concession stands). Secondary competing industries include chain restaurants, single location full-service restaurants, food service contractors, caterers, fast food restaurants, and coffee and snack shops. The top food truck competitors according to the , the daily newspaper in La Vida Lola’s market, are Bento Bus, Mix’d Up Burgers, Mac the Cheese, The Fry Guy, and The Blaxican. Bento Bus positions itself as a Japanese-inspired food truck using organic ingredients and dispensing in eco-friendly ware. The Blaxican positions itself as serving what it dubs “Mexican soul food,” a fusion mashup of Mexican food with Southern comfort food. After years of operating a food truck, The Blaxican also recently opened its first brick-and-mortar restaurant. The Fry Guy specializes in Belgian-style street fries with a variety of homemade dipping sauces. These three food trucks would be the primary competition to La Vida Lola, since they are in the “ethnic food” space, while the other two offer traditional American food. All five have established brand identities and loyal followers/customers since they are among the industry leaders as established by “best of” lists from area publications like the . Most dishes from competitors are in the $10–$13 price range for entrees. La Vida Lola dishes will range from $6 to $13. One key finding from Off the Grid’s report is that mobile food has “proven to be a powerful vehicle for catalyzing diverse entrepreneurship” as 30 percent of mobile food businesses are immigrant owned, 30 percent are women owned, and 8 percent are LGBTQ owned. In many instances, the owner-operator plays a vital role to the brand identity of the business as is the case with La Vida Lola. Atlanta has also tapped into the nationwide trend of food hall-style dining. These food halls are increasingly popular in urban centers like Atlanta. On one hand, these community-driven areas where food vendors and retailers sell products side by side are secondary competitors to food trucks. But they also offer growth opportunities for future expansion as brands solidify customer support in the region. The most popular food halls in Atlanta are Ponce City Market in Midtown, Krog Street Market along the BeltLine trail in the Inman Park area, and Sweet Auburn Municipal Market downtown Atlanta. In addition to these trends, Atlanta has long been supportive of international cuisine as Buford Highway (nicknamed “BuHi”) has a reputation for being an eclectic food corridor with an abundance of renowned Asian and Hispanic restaurants in particular. The Atlanta region is home to a thriving Hispanic and Latinx population, with nearly half of the region’s foreign-born population hailing from Latin America. There are over half a million Hispanic and Latin residents living in metro Atlanta, with a 150 percent population increase predicted through 2040. The median age of metro Atlanta Latinos is twenty-six. La Vida Lola will offer authentic cuisine that will appeal to this primary customer segment. La Vida Lola must contend with regulations from towns concerning operations of mobile food ventures and health regulations, but the Atlanta region is generally supportive of such operations. There are many parks and festivals that include food truck vendors on a weekly basis. |
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
| Operations and Management Plan Category | Content |
|---|---|
Key Management Personnel | The key management personnel consist of Lola González and Cameron Hamilton, who are longtime acquaintances since college. The management team will be responsible for funding the venture as well as securing loans to start the venture. The following is a summary of the key personnel backgrounds. Chef Lola González has worked directly in the food service industry for fifteen years. While food has been a lifelong passion learned in her grandparents’ kitchen, chef González has trained under some of the top chefs in the world, most recently having worked under the James Beard Award-winning chef José Andrés. A native of Duluth, Georgia, chef González also has an undergraduate degree in food and beverage management. Her value to the firm is serving as “the face” and company namesake, preparing the meals, creating cuisine concepts, and running the day-to-day operations of La Vida Lola. Cameron Hamilton has worked in the hospitality industry for over twenty years and is experienced in accounting and finance. He has a master of business administration degree and an undergraduate degree in hospitality and tourism management. He has opened and managed several successful business ventures in the hospitality industry. His value to the firm is in business operations, accounting, and finance. |
Advisory Board | During the first year of operation, the company intends to keep a lean operation and does not plan to implement an advisory board. At the end of the first year of operation, the management team will conduct a thorough review and discuss the need for an advisory board. |
Supporting Professionals | Stephen Ngo, Certified Professional Accountant (CPA), of Valdosta, Georgia, will provide accounting consulting services. Joanna Johnson, an attorney and friend of chef González, will provide recommendations regarding legal services and business formation. |
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
| Marketing Plan Category | Content |
|---|---|
Overview | La Vida Lola will adopt a concentrated marketing strategy. The company’s promotion mix will include a mix of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Given the target millennial foodie audience, the majority of the promotion mix will be centered around social media platforms. Various social media content will be created in both Spanish and English. The company will also launch a crowdfunding campaign on two crowdfunding platforms for the dual purpose of promotion/publicity and fundraising. |
Advertising and Sales Promotion | As with any crowdfunding social media marketing plan, the first place to begin is with the owners’ friends and family. Utilizing primarily Facebook/Instagram and Twitter, La Vida Lola will announce the crowdfunding initiative to their personal networks and prevail upon these friends and family to share the information. Meanwhile, La Vida Lola needs to focus on building a community of backers and cultivating the emotional draw of becoming part of the La Vida Lola family. To build a crowdfunding community via social media, La Vida Lola will routinely share its location, daily if possible, on both Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Inviting and encouraging people to visit and sample their food can rouse interest in the cause. As the campaign is nearing its goal, it would be beneficial to offer a free food item to backers of a specific level, say $50, on one specific day. Sharing this via social media in the day or two preceding the giveaway and on the day of can encourage more backers to commit. Weekly updates of the campaign and the project as a whole are a must. Facebook and Twitter updates of the project coupled with educational information sharing helps backers feel part of the La Vida Lola community. Finally, at every location where La Vida Lola is serving its food, signage will notify the public of their social media presence and the current crowdfunding campaign. Each meal will be accompanied by an invitation from the server for the patron to visit the crowdfunding site and consider donating. Business cards listing the social media and crowdfunding information will be available in the most visible location, likely the counter. Before moving forward with launching a crowdfunding campaign, La Vida Lola will create its website. The website is a great place to establish and share the La Vida Lola brand, vision, videos, menus, staff, and events. It is also a great source of information for potential backers who are unsure about donating to the crowdfunding campaigns. The website will include these elements: . Address the following questions: Who are you? What are the guiding principles of La Vida Lola? How did the business get started? How long has La Vida Lola been in business? Include pictures of chef González. List of current offerings with prices. Will include promotional events and locations where customers can find the truck for different events. Steps will be taken to increase social media followers prior to launching the crowdfunding campaign. Unless a large social media following is already established, a business should aggressively push social media campaigns a minimum of three months prior to the crowdfunding campaign launch. Increasing social media following prior to the campaign kickoff will also allow potential donors to learn more about La Vida Lola and foster relationship building before attempting to raise funds. |
Facebook Content and Advertising | The key piece of content will be the campaign pitch video, reshared as a native Facebook upload. A link to the crowdfunding campaigns can be included in the caption. Sharing the same high-quality video published on the campaign page will entice fans to visit Kickstarter to learn more about the project and rewards available to backers. |
Crowdfunding Campaigns | Foodstart was created just for restaurants, breweries, cafés, food trucks, and other food businesses, and allows owners to raise money in small increments. It is similar to Indiegogo in that it offers both flexible and fixed funding models and charges a percentage for successful campaigns, which it claims to be the lowest of any crowdfunding platform. It uses a reward-based system rather than equity, where backers are offered rewards or perks resulting in “low-cost capital and a network of people who now have an incentive to see you succeed.” Foodstart will host La Vida Lola’s crowdfunding campaigns for the following reasons: (1) It caters to their niche market; (2) it has less competition from other projects which means that La Vida Lola will stand out more and not get lost in the shuffle; and (3) it has/is making a name/brand for itself which means that more potential backers are aware of it. La Vida Lola will run a simultaneous crowdfunding campaign on Indiegogo, which has broader mass appeal. |
Publicity | Social media can be a valuable marketing tool to draw people to the Foodstarter and Indiegogo crowdfunding pages. It provides a means to engage followers and keep funders/backers updated on current fundraising milestones. The first order of business is to increase La Vida Lola’s social media presence on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Establishing and using a common hashtag such as #FundLola across all platforms will promote familiarity and searchability, especially within Instagram and Twitter. Hashtags are slowly becoming a presence on Facebook. The hashtag will be used in all print collateral. La Vida Lola will need to identify social influencers—others on social media who can assist with recruiting followers and sharing information. Existing followers, family, friends, local food providers, and noncompetitive surrounding establishments should be called upon to assist with sharing La Vida Lola’s brand, mission, and so on. Cross-promotion will further extend La Vida Lola’s social reach and engagement. Influencers can be called upon to cross promote upcoming events and specials. The crowdfunding strategy will utilize a progressive reward-based model and establish a reward schedule such as the following: In addition to the publicity generated through social media channels and the crowdfunding campaign, La Vida Lola will reach out to area online and print publications (both English- and Spanish-language outlets) for feature articles. Articles are usually teased and/or shared via social media. Reaching out to local broadcast stations (radio and television) may provide opportunities as well. La Vida Lola will recruit a social media intern to assist with developing and implementing a social media content plan. Engaging with the audience and responding to all comments and feedback is important for the success of the campaign. Some user personas from segmentation to target in the campaign: |
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jun 26, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Simple Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | April 2, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve compiled a variety of simple business plan templates, all of which are free to download in PDF, Word, and Excel formats.
On this page, you’ll find a one-page business plan template , a simple business plan for startups , a small-business plan template , a business plan outline , and more. We also include a business plan sample and the main components of a business plan to help get you started.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Word | PDF
This simple business plan template lays out each element of a traditional business plan to assist you as you build your own, and it provides space to add financing information for startups seeking funding. You can use and customize this simple business plan template to fit the needs for organizations of any size.
One-Page Business Plan Template
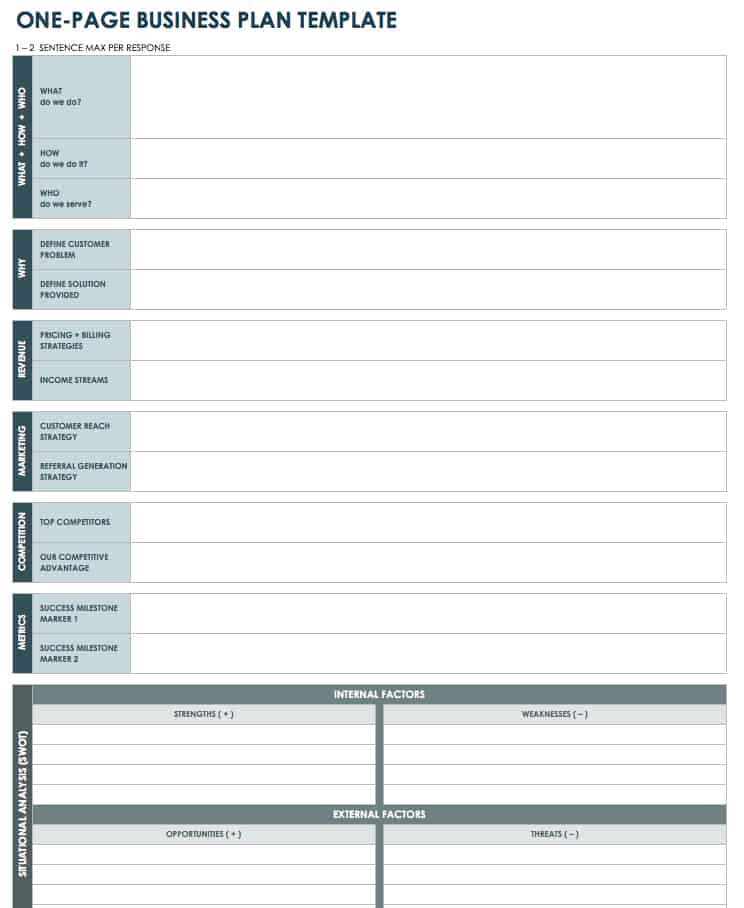
Download One-Page Business Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Use this one-page business plan to document your key ideas in an organized manner. The template can help you create a high-level view of your business plan, and it provides easy scannability for stakeholders. You can use this one-page plan as a reference to build a more detailed blueprint for your business.
For additional single page plans, take a look at " One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
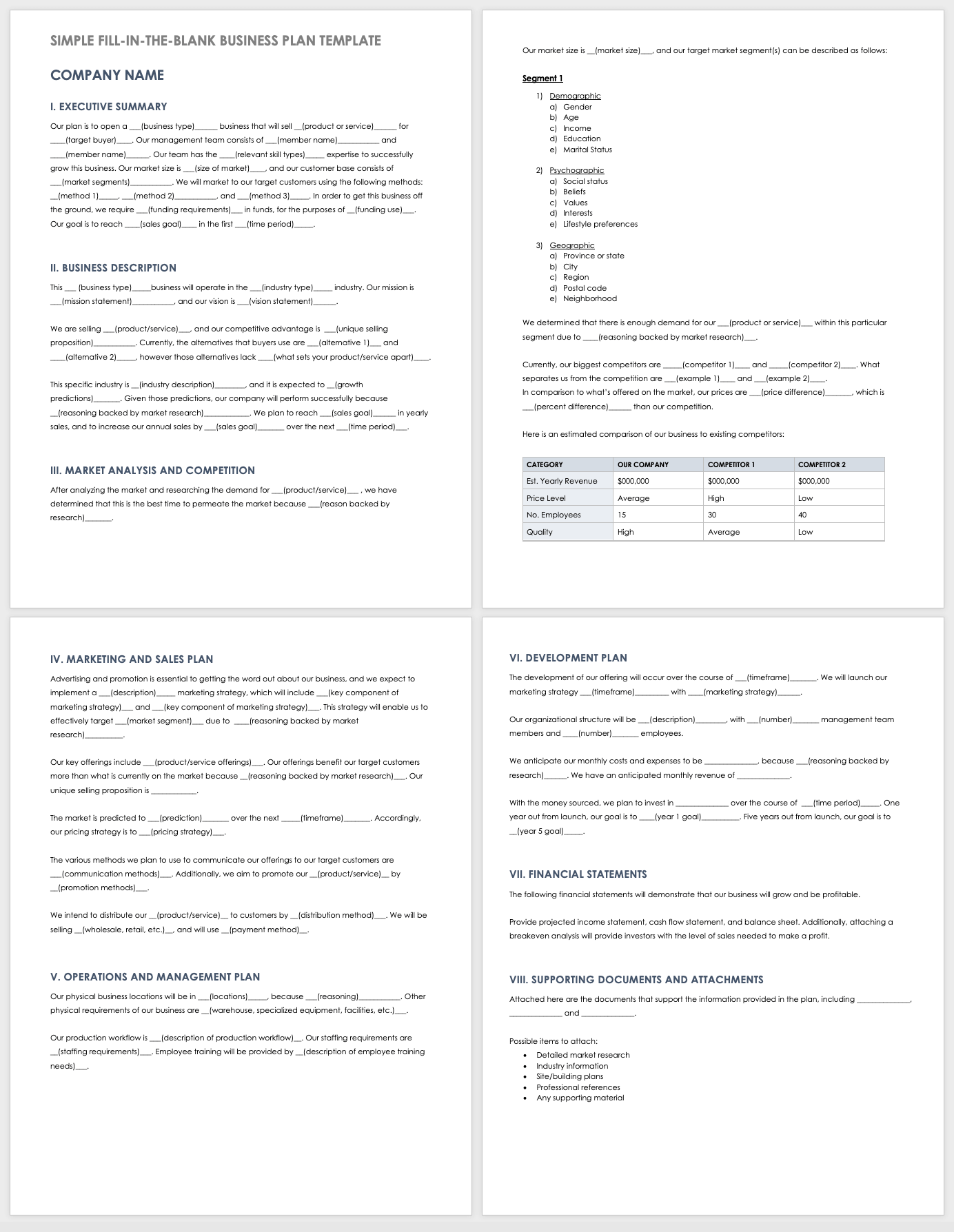
Download Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
Use this fill-in-the-blank business plan template to guide you as you build your business plan. Each section comes pre-filled with sample content, with space to add customized verbiage relevant to your product or service.
For additional free, downloadable resources, visit " Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates ."
Simple Business Plan for Startup

Download Startup Business Plan Template — Word
This business plan template is designed with a startup business in mind and contains the essential elements needed to convey key product or service details to investors and stakeholders. Keep all your information organized with this template, which provides space to include an executive summary, a company overview, competitive analysis, a marketing strategy, financial data, and more. For additional resources, visit " Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples ."
Simple Small-Business Plan Template

Download Simple Small-Business Plan Template
This template walks you through each component of a small-business plan, including the company background, the introduction of the management team, market analysis, product or service offerings, a financial plan, and more. This template also comes with a built-in table of contents to keep your plan in order, and it can be customized to fit your requirements.
Lean Business Plan Template

Download Lean Business Plan Template
This lean business plan template is a stripped-down version of a traditional business plan that provides only the most essential aspects. Briefly outline your company and industry overview, along with the problem you are solving, as well as your unique value proposition, target market, and key performance metrics. There is also room to list out a timeline of key activities.
Simple Business Plan Outline Template

Download Simple Business Plan Outline Template
Use this simple business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains 11 sections, including a title page and a table of contents, which details what each section should cover in a traditional business plan. Simplify or expand this outline to create the foundation for a business plan that fits your business needs.
Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
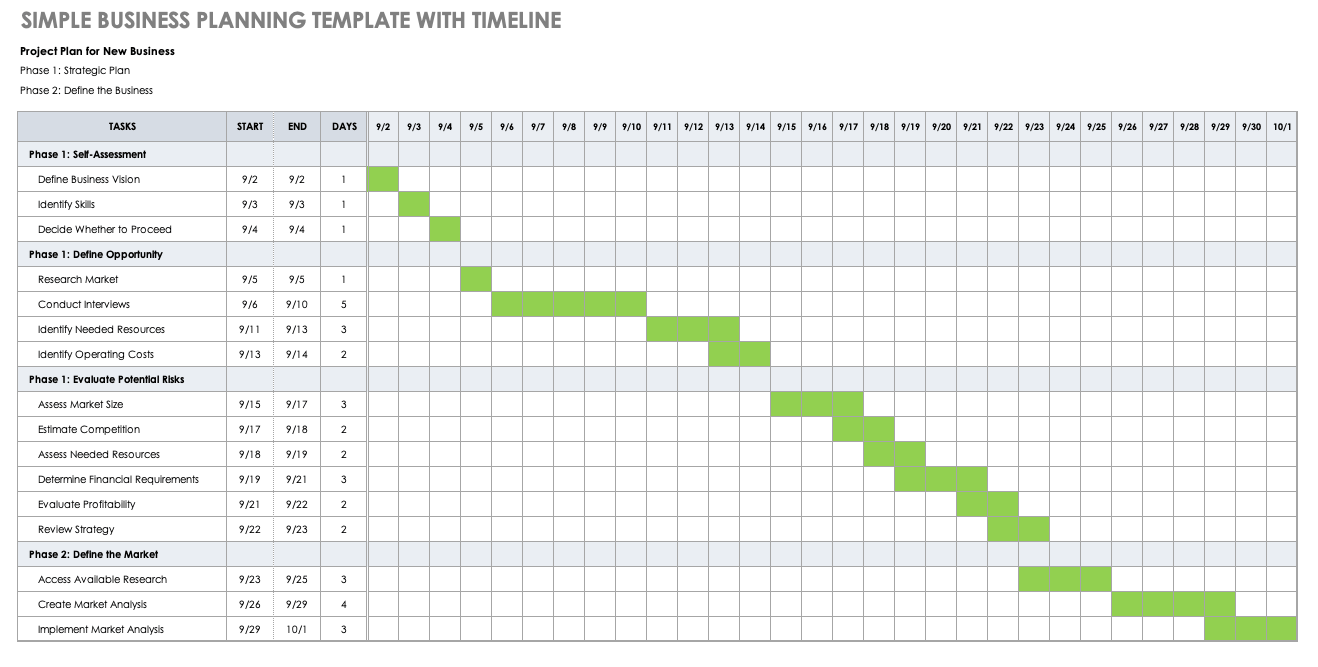
Download Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
This template doubles as a project plan and timeline to track progress as you develop your business plan. This business planning template enables you to break down your work into phases and provides room to add key tasks and dates for each activity. Easily fill in the cells according to the start and end dates to create a visual timeline, as well as to ensure your plan stays on track.
Simple Business Plan Rubric Template
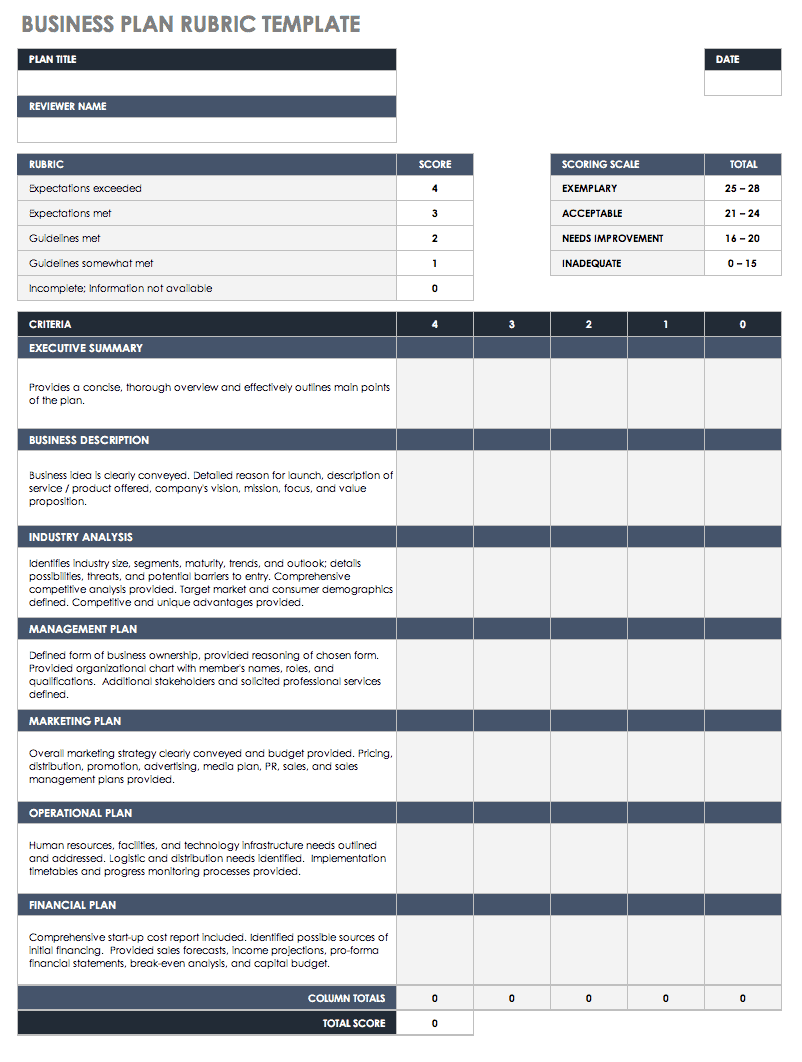
Download Simple Business Plan Rubric
Once you complete your business plan, use this business plan rubric template to assess and score each component of your plan. This rubric helps you identify elements of your plan that meet or exceed requirements and pinpoint areas where you need to improve or further elaborate. This template is an invaluable tool to ensure your business plan clearly defines your goals, objectives, and plan of action in order to gain buy-in from potential investors, stakeholders, and partners.
Basic Business Plan Sample
Download Basic Business Plan Sample
This business plan sample serves as an example of a basic business plan that contains all the traditional components. The sample provides a model of what a business plan might look like for a fictional food truck business. Reference this sample as you develop your own business plan.
For additional resources to help support your business planning efforts, check out “ Free Strategic Planning Templates .”
Main Components of a Business Plan
The elements you include in your business plan will depend on your product or service offerings, as well as the size and needs of your business.
Below are the components of a standard business plan and details you should include in each section:
- Company name and contact information
- Website address
- The name of the company or individual viewing the presentation
- Table of Contents
- Company background and purpose
- Mission and vision statement
- Management team introduction
- Core product and service offerings
- Target customers and segments
- Marketing plan
- Competitive analysis
- Unique value proposition
- Financial plan (and requirements, if applicable)
- Business and industry overview
- Historical timeline of your business
- Offerings and the problem they solve
- Current alternatives
- Competitive advantage
- Market size
- Target market segment(s)
- Projected volume and value of sales compared to competitors
- Differentiation from competitors
- Pricing strategy
- Marketing channels
- Promotional plan
- Distribution methods
- Legal structure of your business
- Names of founders, owners, advisors, etc.
- Management team’s roles, relevant experience, and compensation plan
- Staffing requirements and training plans
- Physical location(s) of your business
- Additional physical requirements (e.g., warehouse, specialized equipment, facilities, etc.)
- Production workflow
- Raw materials and sourcing methods
- Projected income statement
- Projected cash flow statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Break-even analysis
- Charts and graphs
- Market research and competitive analysis
- Information about your industry
- Information about your offerings
- Samples of marketing materials
- Other supporting materials
Tips for Creating a Business Plan
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed at the thought of putting together a business plan. Below, you’ll find top tips to help simplify the process as you develop your own plan.
- Use a business plan template (you can choose from the variety above), or refer to the previous section to create a standard outline for your plan.
- Modify your outline to reflect the requirements of your specific business. If you use a standard business plan outline, remove sections that aren’t relevant to you or aren’t necessary to run your business.
- Gather all the information you currently have about your business first, and then use that information to fill out each section in your plan outline.
- Use your resources and conduct additional research to fill in the remaining gaps. (Note: It isn’t necessary to fill out your plan in order, but the executive summary needs to be completed last, as it summarizes the key points in your plan.)
- Ensure your plan clearly communicates the relationship between your marketing, sales, and financial objectives.
- Provide details in your plan that illustrate your strategic plan of action, looking forward three to five years.
- Revisit your plan regularly as strategies and objectives evolve.
- What product or service are we offering?
- Who is the product or service for?
- What problem does our product or service offering solve?
- How will we get the product or service to our target customers?
- Why is our product or service better than the alternatives?
- How can we outperform our competitors?
- What is our unique value proposition?
- When will things get done, and who is responsible for doing them?
- If you need to obtain funding, how will you use the funding?
- When are payments due, and when do payments come in?
- What is the ultimate purpose of your business?
- When do you expect to be profitable?
To identify which type of business plan you should write, and for more helpful tips, take a look at our guide to writing a simple business plan .
Benefits of Using a Business Plan Template
Creating a business plan can be very time-consuming, especially if you aren’t sure where to begin. Finding the right template for your business needs can be beneficial for a variety of reasons.
Using a business plan template — instead of creating your plan from scratch — can benefit you in the following ways:
- Enables you to immediately write down your thoughts and ideas in an organized manner
- Provides structure to help outline your plan
- Saves time and valuable resources
- Helps ensure you don’t miss essential details
Limitations of a Business Plan Template
A business plan template can be convenient, but it has its drawbacks — especially if you use a template that doesn’t fit the specific needs of your business.
Below are some limitations of using a business plan template:
- Each business is unique and needs a business plan that reflects that. A template may not fit your needs.
- A template may restrict collaboration with other team members on different aspects of the plan’s development (sales, marketing, and accounting teams).
- Multiple files containing different versions of the plan may be stored in more than one place.
- You still have to manually create charts and graphs to add to the plan to support your strategy.
- Updates to the plan, spreadsheets, and supporting documents have to be made in multiple places (all documents may not update in real time as changes are made).
Improve Your Business Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Business Plan Example
Writing the plan, what goes in a business plan, sample plans.
One of the best ways to learn about writing a business plan is to study the plans of established businesses in your industry.
http://www.bplans.com/sp/businessplans.cfm
Develop a Business Plan Worksheet
This worksheet describes the basic components of any business plan. Please note that every plan will be unique to its particular company.
The Executive Summary
Include crisp, clear descriptions of the following elements:
- Company history
- Company objectives
- Product/service offerings
- Competitive advantage (A persuasive statement of why and how the business will succeed)
- Projected growth for the company and the market
- Key management team members
- Funding requirements, including a timeline and details on how the funds will be used
The Products and Services
Answer the following questions in this section:
- Why is there a need for your offering?
- Is your product or service already on the market, or is it still in the research and development stage? If you are still in the development stage, what is the rollout strategy or timeline to bring the product to market?
- What makes your product or service unique? What competitive advantage does the product or service have over its competition?
- Can you price the product or service competitively and still maintain a healthy profit margin?
- What patents, copyrights and trademarks does your company currently own or plan to obtain?
- What confidential and non-disclosure protection have you secured?
- What barriers do you face in bringing the product to market, such as government regulations, competing products, high product-development costs, the need for manufacturing materials, etc.?
Include the following elements:
- A detailed description of your market
- A detailed description of your niche and why you chose it
- An explanation of the market demand for your product or service offering (Requires supporting documentation)
- What percentage of market share do you project you can capture?
- What is the growth potential of the market? (Requires supporting documentation)
- Will your share of the market increase or decrease as the market grows?
- How will you satisfy market growth?
- How will you price your goods or services to remain competitive in a growing market?
Note: If you are launching a new product, include your market research data. Likewise, if you have existing customers, provide a customer profile, detailing their purchasing habits and their buying cycle.

The Marketing Strategy
The following are some promotional options to consider:
- Social Media
- Direct mail
- Trade shows
- Public relations
- Promotional materials
- Telephone sales
- One-on-one sales
- Strategic alliances
If you have current samples of marketing materials or strategies that have proven successful for you, include them with your plan.
Discuss your distribution strategy:
- Will you mail order, personally deliver, hire sales reps, contract with distributors or resellers, or use some other method?
- What are the costs associated with your proposed delivery methods?
- How will you track the effectiveness of the methods you choose?
The Competition
Specific areas to address in this section are:
- Who are your closest competitors and what are their product/service offerings?
- Where are they located?
- What are their revenues?
- How long have they been in business?
- Who is their target market?
- What percentage of market share do they currently hold?
- Do they service a local, geographic market or a national customer base? Is that the same or different from your approach?
- In what other ways do your operations differ from each of them? How are they similar?
- What do your rivals do well? Where is there room for improvement?
- In what ways is your business superior to the competition?
- How is their business doing? Is it growing, declining or stable?
- Are there certain areas of the business where the competition surpasses you (management team, economies of scale, better distribution, volume discounts, etc.)? If so, what are those areas, and how do you plan on compensating for them?
This section of the plan should describe the following requirements of your business:
- Manufacturing
Note: Provide a rollout strategy as to when these requirements need to be purchased and implemented. In addition, describe the vendors you will need to build the business. Do you have current relationships, or do you need to establish new ones? Who will you choose and why?
The Management Team
When preparing this section of the business plan, you should address the following five areas:
- Business background of the principals
- Past experience — tracking successes, responsibilities and capabilities
- Educational background (formal and informal)
- Personal data: age, current address, past addresses, interests, education, special abilities, reasons for entering into business
- Personal financial statements with supporting documentation
- Direct operational and managerial experience in related businesses
- Indirect managerial experiences
- Who will do what and why? Who is responsible for final decisions?
- Organizational chart with chain of command and listing of duties
- A simple statement of what management members will be paid, by position
- Listing of bonuses in realistic terms
- Benefits (medical, life insurance, disability, etc.)
- Insurance brokers
- Accountants
- Consulting groups
- Small Business Association
- Local business information centers
- Chambers of Commerce
- Local colleges and universities
- Federal, state and local agencies
- Board of Directors
- World Wide Web (various search engines)
Consider the following questions in completing this section of the business plan:
- What are your current personnel needs (full- and/or part-time)? How many employees do you envision in the near future, and then in the next three to five years?
- What skills must your employees have?
- What will their job descriptions be?
- Are the people you need readily available? If not, how will you attract them?
- Will you pay salaries or hourly wages?
- Will you provide benefits? If so, what will they be, and at what cost?
- Will you pay overtime?
Financial Data
Have a certified public accountant establish your accounting system before the start of business to provide you with data in the following four areas:
- Balance Sheet – indicates what the cash position of the business is and what the owner’s equity is at any given point (the balance sheet will show assets, liabilities and retained earnings).
- Break-Even Analysis – Shows the volume of revenue from sales that are needed to balance the fixed and variable expenses. Without exception, all businesses should perform this analysis, which is based on the income statement and cash flow.
- Income Statement (also called the profit and loss statement) – Indicates how well the company is managing its cash, by subtracting disbursements from receipts.
- Cash Flow – Projects all cash receipts and disbursements. Healthy cash flow is critical to the survival of any business.
Supporting Documentation
You will need to include all documents that lend support to statements made in the body of your company’s business plan. Please be aware that this list is not complete and may vary depending on the stage of development of your business.
- Credit information (include in appendix)
- Quotes or estimates
- Letters of intent from prospective customers
- Letters of support from credible personal references
- Leases or buy/sell agreements
- Legal documents relevant to the business
- Census/demographic data
- No category
SAMPLE-BUSINESS-PLAN-FULL
Related documents.

Study collections
- Business plan
Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

FINAL OUTPUT in ENTREPRENEURSHIP "BUSINESS PLAN" Of ALBERJ'S EATS-TIME RESTAURANT XII-CAPARAS (HUMSS

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Educational Software K-12 Business Plan
Start your own educational software k-12 business plan
Curriculum Companion Suites
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Introduction Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS) is a medium-sized software development and consulting firm focused on making the educational process more efficient and effective for K-12 schools. CCS software serves as a virtual teaching assistant for the educational process. Students can follow along with curriculum electronically through a central computer terminal at the front of the classroom.
The Company CCS keys to success are the company’s commitment to market awareness and future potential direction of the educational process, and CCS’ relationships with a large number of educational institutions and districts.
Curriculum Companion Suites is a start-up company comprised of six executives and seventy-six employees. The executives represent all functional areas, with 70 years of combined experience in the software development industry. Two majority shareholders, Andrew Christiansen and David Fields, own 80% of the company. Other investors own a minority stake. At the moment, the company does not have plans for going public, as most of the financing is raised internally. CSS is incorporated in the state of Oregon by the two majority shareholders.
Products CCS offers a suite of educational software for each grade level, from kindergarten through 12th grade. These suites are developed in collaboration with major curriculum publishers with whom CCS has established strategic partnerships.
CCS provides full installation, initial and ongoing consulting support. These services are provided as part of each software package purchase.
The Market The competitive marketplace includes only a handful of direct competitors within the learning information systems vendors segment, providing software products and installation and systems integration services to kindergarten through senior high (K-12) schools in the United States. CCS competes primarily against more traditional methods of education, training and testing, including pencil and paper testing. In addition, CCS competes with other companies offering educational software products to schools, such as International Business Machines Corporation, Apple Computer, Inc., and Mattel, Inc.
Educational institutions and school districts have not been active in searching out technical enhancements to the educational process. Rather, companies such as CCS have often utilized a more “push” type of marketing strategy. The educational community has had to be “educated” themselves on the opportunities of utilizing technical infrastructures to enhance learning processes.
Since only a handful of other companies are competing directly with CCS in this market, the company plans to develop a healthy level of market share, with a goal of 10% at the end of three years.
The target market for CCS is the urban/metropolitan educational market, as this market presents the highest level of opportunity in terms of revenues. Additionally, software installations and customizations in this market are much more feasible in terms of technical logistics and efficiencies. Thus, profitability is by far more likely in this market.
Relationships have been established with a large number of educational institutions and school districts across the U.S. Significant investments have been made by CCS to research and understand the specific needs and potential enhancements to the current educational process.
Financial Considerations CCS expects to raise a substantial amount of owner capital, and borrow a comparable amount in a guaranteed SBA 10-year loan. This provides the bulk of the current financing required.
CCS intends to deliver generous sales in the first year, with steady grown in the second and third years of the plan.
1.1 Mission
Curriculum Companion Suites aims to offer software curriculum suites to K-12 schools within the U.S. market. CCS will focus on providing solutions to enhance the educational capabilities of schools.

1.2 Keys to Success
CCS keys to success include:
- The company’s commitment to being keenly alert to the current educational environment and future potential direction of the educational process.
- CCS’ relationships with a large number of educational institutions and districts.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Curriculum Companion Suites is a start-up comprised of six executives. These executives represent all functional areas, with 70 years of combined experience in the software development industry. Two majority shareholders, Andrew Christiansen and David Fields, own 80% of the company. The bulk of outside financing will come from a 10-year Small Business Administration (SBA) loan.
2.1 Company Ownership
CSS is incorporated in the state of Oregon by Andrew Christiansen and David Fields. Other investors own a minority stake. At the moment, the company does not have plans for going public, as most of the financing is raised internally.
CSS is a start-up company that was registered in the year 2000.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Of the total start-up expenses, the lion’s share has been spent on software licenses. Estimated start-up cash requirements should be sufficient to cover ongoing expenses in the first months of operation. Christiansen and Fields have each invested heavily, with the rest of investment coming from minority shareholders. The company has also secured a 10-year SBA loan and a one-year loan from its bank. Following is a chart and table summarizing projected initial start-up costs.

| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $3,000 |
| Software Licenses | $20,000 |
| Other | $1,000 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $24,000 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $180,000 |
| Other Current Assets | $75,000 |
| Long-term Assets | $100,000 |
| Total Assets | $355,000 |
| Total Requirements | $379,000 |
| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $24,000 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $355,000 |
| Total Funding Required | $379,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $175,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $180,000 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $180,000 |
| Total Assets | $355,000 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $50,000 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $150,000 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $1,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $201,000 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Andrew Christiansen | $60,000 |
| David Fields | $60,000 |
| Other | $58,000 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $178,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($24,000) |
| Total Capital | $154,000 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $355,000 |
| Total Funding | $379,000 |
CCS offers a suite of educational software for each grade level, from Kindergarten through 12th grade. These suites are developed in collaboration with major curriculum publishers with whom CCS has established strategic partnerships.
CCS provides full installation, initial, and ongoing consulting support. These services are provided as part of each software package purchase.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
CCS has a focus on K-12 schools within the U.S. market, especially schools who:
- already own educational packages from large curriculum publishers who are CCS strategic partners
- owns software that has been recently developed by CSS.
The following chart and table summarize the total market potential for CSS products.

| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Urban K-12 Schools | 5% | 2,500 | 2,625 | 2,756 | 2,894 | 3,039 | 5.00% |
| Rural K-12 Schools | 5% | 1,500 | 1,575 | 1,654 | 1,737 | 1,824 | 5.01% |
| Total | 5.01% | 4,000 | 4,200 | 4,410 | 4,631 | 4,863 | 5.01% |
4.1 Market Segmentation
Metropolitan Schools
Metropolitan schools often have larger student populations, with more classes, requiring more extensive and comprehensive software packages. The installations are consequently more extensive in nature.
Rural Schools
Rural schools often have relatively smaller student populations, and fewer classes. Additional customization during installations is usually necessary, as the infrastructure for computer networks is either substandard or nonexistent.
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy

4.3 Market Needs
CCS’s research has found that educators, as well as parents of K-12 children believe that the educational process is in need of significant improvements. Children, for the most part, have been found to strongly prefer an educational environment where they can learn “hands on” using the computer in conjunction with teacher facilitation, as opposed to teacher facilitation only.
4.4 Service Business Analysis
Major competition to CSS comes not from other software developers but from traditional book publishers. In fact, one of the goals of the company is to educate its clientele about the possibilities and features of the specially-designed software that assists in the educational process. The tool CSS provides teachers with will help them become more effective and efficient in classrooms. The company believes that the novelty and added value its products provide to educators will be key buying decision criteria for the customers.
4.5 Competition and Buying Patterns
Only a handful of other companies are competing directly with CCS in this market. CCS plans to develop a healthy level of market share, with a goal of 10% at the end of three years. With the exponential increase in computer and Internet usage among the public in the last five years, this is a relatively new market. CCS has taken a lead primarily due to its intense efforts both in research and development, as well as in establishing relationships in the educational community.
The competitive marketplace includes only a handful of direct competitors within the learning information systems vendors segment, providing software products and installation and systems integration services to kindergarten through senior high (K-12) schools in the United States. Typical learning information systems consist of computer software and related training designed to improve student academic performance by increasing the quality, quantity, and timeliness of performance data available to educators and by facilitating increased student practice of essential skills.
There are a number of competing products covering a wide range of educational requirements. These include:
- Accelerated reading products–software for motivating and monitoring increased literature-based reading practice.
- Accelerated math–software aimed to increase a student’s competency across this discipline utilizing the latest techniques.
- Professional development training for educators.
- Test-generation software.
Software products offered by competitors also aim to improve student academic performance by intensifying skills practice and increasing the quality, quantity and timeliness of information available to educators.
CCS competes primarily against more traditional methods of education, training and testing, including pencil and paper testing. In addition, CCS competes with other companies offering educational software products to schools, such as International Business Machines Corporation, Apple Computer, Inc., and Mattel, Inc. Many other companies, including Microsoft Corporation and Walt Disney Company, provide educational software products.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
CCS intends to succeed by offering K-12 schools a technological tool to assist teachers in making the educational process more efficient and effective.
5.1 Competitive Edge
CCS’ competitive edge is its new ideas and first to market technologies.
5.2 Sales Strategy
The table and charts shows the level of sales CCS intends to deliver in the first year through the third year of the plan. Detailed monthly sales for the first year are in the appendix.

| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Unit Sales | |||
| Software Systems | 240 | 276 | 317 |
| Installation & Customization | 240 | 276 | 317 |
| Other Consulting | 120 | 138 | 159 |
| Total Unit Sales | 600 | 690 | 794 |
| Unit Prices | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Software Systems | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 |
| Installation & Customization | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 |
| Other Consulting | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 |
| Sales | |||
| Software Systems | $6,000,000 | $6,900,000 | $7,935,000 |
| Installation & Customization | $3,600,000 | $4,140,000 | $4,761,000 |
| Other Consulting | $600,000 | $690,000 | $793,500 |
| Total Sales | $10,200,000 | $11,730,000 | $13,489,500 |
| Direct Unit Costs | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Software Systems | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Installation & Customization | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 |
| Other Consulting | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | |||
| Software Systems | $480,000 | $552,000 | $634,800 |
| Installation & Customization | $2,400,000 | $2,760,000 | $3,174,000 |
| Other Consulting | $240,000 | $276,000 | $317,400 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $3,120,000 | $3,588,000 | $4,126,200 |
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Andrew B. Christiansen has extensive experience in business planning and finance, including tenures as chief financial officer with ABC Conglomerate and DEF International. David E. Fields brings in experience in the area of marketing, advertising, and communications.
6.1 Personnel Plan
CSS will focus on strong product development and marketing. These are the areas where most of the investments and training will go. The table below, and in the appendix, outlines the company’s personnel plan for the next years.
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Product Development | $900,000 | $945,000 | $992,250 |
| Installation Technicians | $875,000 | $918,750 | $964,688 |
| Administrative | $595,000 | $624,750 | $655,988 |
| Sales & Marketing | $900,000 | $945,000 | $992,250 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total People | 82 | 86 | 90 |
| Total Payroll | $3,270,000 | $3,433,500 | $3,605,175 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
CCS expects to raise its own capital, and to acquire a guaranteed the SBA 10-year loan. This provides the bulk of the current financing required.
7.1 Break-even Analysis
CCS’s Break-even Analysis is based on the average of the first-year figures for total sales by units, and by operating expenses. These are presented as per-unit revenue, per-unit cost, and fixed costs. These conservative assumptions make for a more accurate estimate of real risk.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Units Break-even | 27 |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $466,023 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Per-Unit Revenue | $17,000.00 |
| Average Per-Unit Variable Cost | $5,200.00 |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $323,475 |
7.2 Projected Profit and Loss
The projected Profit and Loss for CCS is presented in the accompanying table. The three yearly totals are shown here, with year one monthlies in the appendix.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $10,200,000 | $11,730,000 | $13,489,500 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $3,120,000 | $3,588,000 | $4,126,200 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $3,120,000 | $3,588,000 | $4,126,200 |
| Gross Margin | $7,080,000 | $8,142,000 | $9,363,300 |
| Gross Margin % | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $3,270,000 | $3,433,500 | $3,605,175 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $96,000 | $150,000 | $265,000 |
| Depreciation | $24,000 | $27,600 | $31,740 |
| Utilities | $1,200 | $1,500 | $1,700 |
| Payroll Taxes | $490,500 | $515,025 | $540,776 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $3,881,700 | $4,127,625 | $4,444,391 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $3,198,300 | $4,014,375 | $4,918,909 |
| EBITDA | $3,222,300 | $4,041,975 | $4,950,649 |
| Interest Expense | $18,700 | $16,400 | $14,000 |
| Taxes Incurred | $808,144 | $999,494 | $1,246,664 |
| Net Profit | $2,371,456 | $2,998,481 | $3,658,244 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 23.25% | 25.56% | 27.12% |
7.3 Projected Cash Flow
The cash flow projection shows that provisions for ongoing expenses are adequate to meet CCS’s needs as the business generates cash flow sufficient to support operations.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $3,468,000 | $3,988,200 | $4,586,430 |
| Cash from Receivables | $5,628,700 | $7,576,305 | $8,712,751 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $9,096,700 | $11,564,505 | $13,299,181 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $190,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $9,286,700 | $11,564,505 | $13,299,181 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $3,270,000 | $3,433,500 | $3,605,175 |
| Bill Payments | $4,171,394 | $5,201,383 | $6,118,402 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $7,441,394 | $8,634,883 | $9,723,577 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $12,000 | $12,000 | $12,000 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $12,000 | $12,000 | $12,000 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $135,000 | $225,000 | $295,000 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $7,600,394 | $8,883,883 | $10,042,577 |
| Net Cash Flow | $1,686,306 | $2,680,622 | $3,256,604 |
| Cash Balance | $1,866,306 | $4,546,928 | $7,803,532 |
7.4 Projected Balance Sheet
Following is the projected Balance Sheet for CCS. Again, three years of annuals are shown below, with first year monthlies in the appendix.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $1,866,306 | $4,546,928 | $7,803,532 |
| Accounts Receivable | $1,103,300 | $1,268,795 | $1,459,114 |
| Other Current Assets | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $3,044,606 | $5,890,723 | $9,337,646 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $235,000 | $460,000 | $755,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $24,000 | $51,600 | $83,340 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $211,000 | $408,400 | $671,660 |
| Total Assets | $3,255,606 | $6,299,123 | $10,009,306 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $364,149 | $433,185 | $509,124 |
| Current Borrowing | $38,000 | $26,000 | $14,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $402,149 | $459,185 | $523,124 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $138,000 | $126,000 | $114,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $540,149 | $585,185 | $637,124 |
| Paid-in Capital | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($24,000) | $2,347,456 | $5,345,938 |
| Earnings | $2,371,456 | $2,998,481 | $3,658,244 |
| Total Capital | $2,715,456 | $5,713,938 | $9,372,182 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $3,255,606 | $6,299,123 | $10,009,306 |
| Net Worth | $2,715,456 | $5,713,938 | $9,372,182 |
7.5 Business Ratios
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 15.00% | 15.00% | 9.70% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 33.89% | 20.14% | 14.58% | 21.50% |
| Other Current Assets | 2.30% | 1.19% | 0.75% | 45.70% |
| Total Current Assets | 93.52% | 93.52% | 93.29% | 70.20% |
| Long-term Assets | 6.48% | 6.48% | 6.71% | 29.80% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 12.35% | 7.29% | 5.23% | 42.40% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 4.24% | 2.00% | 1.14% | 19.20% |
| Total Liabilities | 16.59% | 9.29% | 6.37% | 61.60% |
| Net Worth | 83.41% | 90.71% | 93.63% | 38.40% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 100.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 46.04% | 43.87% | 42.17% | 79.40% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.59% | 0.85% | 1.48% | 1.30% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 31.36% | 34.22% | 36.46% | 2.20% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 7.57 | 12.83 | 17.85 | 1.51 |
| Quick | 7.57 | 12.83 | 17.85 | 1.16 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 16.59% | 9.29% | 6.37% | 61.60% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 117.09% | 69.97% | 52.33% | 3.50% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 97.67% | 63.47% | 49.00% | 9.20% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 23.25% | 25.56% | 27.12% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 87.33% | 52.48% | 39.03% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 6.10 | 6.10 | 6.10 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 57 | 56 | 56 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 12.45 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 28 | 28 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 3.13 | 1.86 | 1.35 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.07 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.82 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $2,642,456 | $5,431,538 | $8,814,522 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 171.03 | 244.78 | 351.35 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.32 | 0.54 | 0.74 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 12% | 7% | 5% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 4.83 | 10.07 | 15.06 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 3.76 | 2.05 | 1.44 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Unit Sales | |||||||||||||
| Software Systems | 0% | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Installation & Customization | 0% | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Other Consulting | 0% | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Total Unit Sales | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| Unit Prices | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Software Systems | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | |
| Installation & Customization | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | |
| Other Consulting | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | |
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Software Systems | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | |
| Installation & Customization | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | |
| Other Consulting | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | |
| Total Sales | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Direct Unit Costs | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Software Systems | 0.00% | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Installation & Customization | 0.00% | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 |
| Other Consulting | 0.00% | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | |||||||||||||
| Software Systems | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | |
| Installation & Customization | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | |
| Other Consulting | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Product Development | 0% | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Installation Technicians | 0% | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 |
| Administrative | 0% | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 |
| Sales & Marketing | 0% | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Other | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total People | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | |
| Total Payroll | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 30.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | |
| Gross Margin | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | |
| Gross Margin % | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Depreciation | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | |
| Utilities | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | |
| EBITDA | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | |
| Interest Expense | $1,650 | $1,633 | $1,617 | $1,600 | $1,583 | $1,567 | $1,550 | $1,533 | $1,517 | $1,500 | $1,483 | $1,467 | |
| Taxes Incurred | $79,463 | $66,223 | $66,227 | $66,231 | $66,235 | $66,240 | $66,244 | $66,248 | $66,252 | $66,256 | $66,260 | $66,265 | |
| Net Profit | $185,413 | $198,669 | $198,681 | $198,694 | $198,706 | $198,719 | $198,731 | $198,744 | $198,756 | $198,769 | $198,781 | $198,794 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | 21.81% | 23.37% | 23.37% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.39% | 23.39% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | |
| Cash from Receivables | $0 | $18,700 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $289,000 | $307,700 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $190,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $289,000 | $497,700 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | |
| Bill Payments | $14,003 | $389,646 | $376,831 | $376,818 | $376,806 | $376,793 | $376,781 | $376,768 | $376,756 | $376,743 | $376,731 | $376,718 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $286,503 | $662,146 | $649,331 | $649,318 | $649,306 | $649,293 | $649,281 | $649,268 | $649,256 | $649,243 | $649,231 | $649,218 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $288,503 | $664,146 | $651,331 | $666,318 | $666,306 | $666,293 | $666,281 | $666,268 | $666,256 | $666,243 | $666,231 | $666,218 | |
| Net Cash Flow | $497 | ($166,446) | $198,669 | $183,682 | $183,694 | $183,707 | $183,719 | $183,732 | $183,744 | $183,757 | $183,769 | $183,782 | |
| Cash Balance | $180,497 | $14,051 | $212,721 | $396,402 | $580,096 | $763,803 | $947,522 | $1,131,254 | $1,314,998 | $1,498,755 | $1,682,524 | $1,866,306 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $180,000 | $180,497 | $14,051 | $212,721 | $396,402 | $580,096 | $763,803 | $947,522 | $1,131,254 | $1,314,998 | $1,498,755 | $1,682,524 | $1,866,306 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $561,000 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 |
| Other Current Assets | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $255,000 | $816,497 | $1,192,351 | $1,391,021 | $1,574,702 | $1,758,396 | $1,942,103 | $2,125,822 | $2,309,554 | $2,493,298 | $2,677,055 | $2,860,824 | $3,044,606 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $100,000 | $100,000 | $100,000 | $100,000 | $115,000 | $130,000 | $145,000 | $160,000 | $175,000 | $190,000 | $205,000 | $220,000 | $235,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $2,000 | $4,000 | $6,000 | $8,000 | $10,000 | $12,000 | $14,000 | $16,000 | $18,000 | $20,000 | $22,000 | $24,000 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $100,000 | $98,000 | $96,000 | $94,000 | $107,000 | $120,000 | $133,000 | $146,000 | $159,000 | $172,000 | $185,000 | $198,000 | $211,000 |
| Total Assets | $355,000 | $914,497 | $1,288,351 | $1,485,021 | $1,681,702 | $1,878,396 | $2,075,103 | $2,271,822 | $2,468,554 | $2,665,298 | $2,862,055 | $3,058,824 | $3,255,606 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $1,000 | $377,085 | $364,270 | $364,258 | $364,246 | $364,234 | $364,222 | $364,210 | $364,198 | $364,186 | $364,174 | $364,161 | $364,149 |
| Current Borrowing | $50,000 | $49,000 | $48,000 | $47,000 | $46,000 | $45,000 | $44,000 | $43,000 | $42,000 | $41,000 | $40,000 | $39,000 | $38,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $51,000 | $426,085 | $412,270 | $411,258 | $410,246 | $409,234 | $408,222 | $407,210 | $406,198 | $405,186 | $404,174 | $403,161 | $402,149 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $150,000 | $149,000 | $148,000 | $147,000 | $146,000 | $145,000 | $144,000 | $143,000 | $142,000 | $141,000 | $140,000 | $139,000 | $138,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $201,000 | $575,085 | $560,270 | $558,258 | $556,246 | $554,234 | $552,222 | $550,210 | $548,198 | $546,186 | $544,174 | $542,161 | $540,149 |
| Paid-in Capital | $178,000 | $178,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) |
| Earnings | $0 | $185,413 | $384,081 | $582,763 | $781,456 | $980,163 | $1,178,881 | $1,377,613 | $1,576,356 | $1,775,113 | $1,973,881 | $2,172,663 | $2,371,456 |
| Total Capital | $154,000 | $339,413 | $728,081 | $926,763 | $1,125,456 | $1,324,163 | $1,522,881 | $1,721,613 | $1,920,356 | $2,119,113 | $2,317,881 | $2,516,663 | $2,715,456 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $355,000 | $914,497 | $1,288,351 | $1,485,021 | $1,681,702 | $1,878,396 | $2,075,103 | $2,271,822 | $2,468,554 | $2,665,298 | $2,862,055 | $3,058,824 | $3,255,606 |
| Net Worth | $154,000 | $339,413 | $728,081 | $926,763 | $1,125,456 | $1,324,163 | $1,522,881 | $1,721,613 | $1,920,356 | $2,119,113 | $2,317,881 | $2,516,663 | $2,715,456 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This is a sample of our proposed business plan in S.Y. 2021-2022. snack attack business plan prepared : cinco, mark owen cobosa, annabel gisolga, wilchina. Skip to document. ... Business Plan Correct Format Grade 12. This is a sample of our proposed business plan in S.Y. 2021-2022. Subject. English. 181 Documents.
She is currently a Grade 12 student taking up the Accountancy, Business and Management ABM. Her dream job is to become a Manager. Kylene P. Daño. She was born on August 18, 2002. She is the daughther of Ma. Bella Amaro and Samson Berdigan. She is currently a Grade 12 student taking up the Accountancy, Business and Management ABM. She wants to ...
SAMPLE-ONLY-BUSINESS-PLAN-for-Grade-12-1 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document summarizes a business proposal for Yummango Panna Cotta, a company that produces mango panna cotta. It will be located in La Union, Philippines and led by CEO Lianne Janel Fabila. The proposal outlines the company's vision, product, organizational structure, and ...
Quarter 2 - Module 9. Second Edition, 2021. copyright shall subsist in any. work of theGovernment of the Philippines. However, prior. pproval of the government agency or officewherein the work is created shall be necessar. for. exploitation of such work for profit. Suchagency or office may, among other things, im.
AP8 Q1 SEPT-18-2023 - aaaa. AP9-Q1 August-15-20241. AP9-Q1 August-15-20241. Pdfcoffee - aaaaaaaaaaa. AP9-Q1 August-15-2024-1. Sample Business Plan mindanao state university iligan institute of technology college of business administration and accountancy department of marketing alibata.
Rice University's Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51, 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2.
rk in small groups to brainstorm ideas. (15 min)4. As the class comes back, the teacher writes the words "Business Plan" on the board, and asks the class what they thi. k. eeds to be included in a business plan. (5 min)5. From there the teacher will pass out copies of the first part of a transcript from the article Ho.
Download Simple Business Plan Outline Template. Word | PDF. Use this simple business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains 11 sections, including a title page and a table of contents, which details what each section should cover in a traditional business plan.
entrepreneurship12_q1_mod3_jdRivero - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
business plan grade 12.pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Job Description: Assist the overall operation of the business. Job Specification: At least Senior High School student. Flexible. All positions are voluntary and will be rotated every month.
Business plans are crucial for entrepreneurial ventures. It helps businesses to identify possible problems and design practical solutions. It helps in critical decision-making. This is a pragmatic approach and helps the business in the long run. Another critical aspect of a business plan is it helps in identifying short-term goals and long-term ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
business plan for entrepreneur about opening a book store. Course. Grade 12 HUMSS. 42 Documents. Students shared 42 documents in this course. University New Era University. Academic year: 2021/2022. Uploaded by: Bea Nicole Aguilan. New Era University. 0 followers. 4 Uploads. 7 upvotes.
This section of the plan should describe the following requirements of your business: Manufacturing. R&D. Purchasing. Staffing. Equipment. Facilities. Note: Provide a rollout strategy as to when these requirements need to be purchased and implemented. In addition, describe the vendors you will need to build the business.
Name of the Business: Maffle House. Location of the Business: Maffle House is located at the 2nd Floor of Mayfair Plaza, 12th St, Bacolod City, 6100. Negros Occidental, Philippines. Bacolod is known to be one of the most business-friendly cities in the Visayas. (PhilStar, 2017).
Viand Business Plan Grade 12 Abm b - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document contains a business plan for VIAND Dining Restaurant. The business plan outlines the vision, mission and values of the restaurant which is to share joy through fine culinary meals and heartfelt service.
Business Floor Plan Figure No.2 Dining Department Flow of Operaiion Figure No.3 Flow of Operation for HR Department Figure No.4 Inventory Department Flow of Operation Figure No.5 Accounting Department Flow of Operation Figure No.6 Alberj's Eats-Time Restaurant Paper Bags C E O ORGANIZATIONAL PLAN SECRETARY ATTORNEY/ LAWYER EXTERNAL AUDITOR ...
Its a sample business plan for grade 11 or 12 executive summary this business plan is based on studies and surveys, and is highly focused and promises to follow. Skip to document. University; High School; Books; ... Its a sample business plan for grade 11 or 12. Course. Industrial Technology (PE 110) 26 Documents. Students shared 26 documents ...
Introduction. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS) is a medium-sized software development and consulting firm focused on making the educational process more efficient and effective for K-12 schools. CCS software serves as a virtual teaching assistant for the educational process. Students can follow along with curriculum electronically through a ...
3 Sample SHS G12 Business Plan - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Kemvet Trading is an agricultural trading business in Silang, Cavite that distributes affordable quality agricultural products, veterinary medicines, and feed additives to farms and retailers in the region. It aims to empower farmers and others in agriculture ...