
200 Best Position Paper Topics and Ideas to Consider
Table of Contents
What are the best Position Paper Topics? Do you want to write a persuasive position paper? No worries! We are here to help you. In this blog post, we have shared a list of the top position paper topics from different fields of study. Continue reading this blog post and get interesting ideas that will help you fetch an A+ grade. Also, learn how to write a position paper effectively.
What is a Position Paper?
A position paper is a kind of essay that clearly focuses on one side of an arguable point about an issue. It is similar to a debate and can also be identified as an argumentative paper. The main aim of the position paper is to persuade the audience that your argument or opinion is valid. Convincing the audience is not a piece of cake. For writing a position paper, you must have a strong topic.
Position Paper Topic Selection Tips
One of the simplest ways to select good position paper topics is to consider popular subjects that excite you. Mainly, in order to create a compelling argument, you can choose subjects that are against common values, contrasting mass opinions, or any social taboos.

In specific, ask yourself the following question during the topic selection.
- Is your topic a real issue with uncertainty and controversy?
- Can you find out at least two distinctive positions?
- Are you interested in supporting one of the identified distinctive positions?
- Is the scope of the issue narrow enough to be feasible?
Finalize the topic only if you can present a strong argument. Remember, the topic you select should be original and interesting. It should match your area of interest. Most importantly, your selected topic should have enough evidence or proof to support your opinion. Additionally, the topic should help you to prepare a position paper as per your instructor’s specifications.
Know How to Write a Position Paper
After you have selected a topic, analyze the issue and come up with a valid argument. When determining your viewpoint, make sure to consider your audience. Also, prepare a list of the pros and cons of your topic. The pros and cons will assist you to evaluate your potential to support your counterclaims, with the necessary pieces of evidence.
If you are clear with your viewpoint, prepare a well-structured outline that includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. In the introductory paragraph, introduce the topic, provide brief background information on the topic, and specify a strong thesis statement. Next, generate counterarguments in the body paragraphs. For each argument, submit relevant proof from a credible source. Finally, conclude the paper by restating your arguments and giving a call to action.
The position paper you have prepared should be understandable to your readers. After you have completed preparing the argumentative paper, do a complete revision. Proofreading the paper will help you spot and rectify the errors in your content.

List of Position Paper Topics and Ideas
In general, there are numerous position paper topics available in various fields of study. But searching them all and finding one good topic is a time-consuming process. So, to help you, here, we have categorized and listed a few best argumentative paper help in some interesting areas such as health, sports, criminal justice, etc.

Right now, are you searching for the top position paper topics for your assignment? If yes, then refer to the list of ideas suggested below and identify a topic of your choice.
Position Paper Topics on Health
- Is drug addiction a disease?
- Is it necessary to permit euthanasia?
- Should doctors be allowed to advertise certain medications?
- Pros and cons of the electronic health record system.
- Is it necessary to give stringent punishment for medical malpractice?
- Should the government support independent medical research?
- The pros and cons of cosmetic surgery.
- Should HIV testing before marriage be made mandatory?
- Do race and ethnicity have an impact on the health of individuals?
- Is online medical consultation a good idea?
- Should healthcare insurance be mandatory?
- Write a position paper on the legalization of abortion.
- How can you best help a family member or friend who is depressed?
- Do laws that make abortions harder to obtain decrease the abortion rate?
- Is a nursing home the best choice for elderly people?
Additional Position Paper Ideas on Health
- How does depression affect the workplace?
- Write a position paper on alleviating global hunger.
- Is a medical experiment on animals ethical? Justify your position.
- What causes postpartum depression?
- Should healthcare services be free for anyone?
- Is a medical experiment on animals ethical?
- Is it a good idea to use the medical knowledge that was gained by experiments in Nazi camps in modern medicine?
- Should forcible quarantining of individuals with STDs like HIV aids be imposed?
- How can you beat a teenage girl who is suffering from depression, anxiety, and stress?
- Why do you believe that every country needs to allow healthcare professionals to help patients suffering from life-threatening diseases with assisted suicide?
- What causes self-treatment without professional supervision risky?
- Withholding health-related information from patients and their family create an ethical dilemma for healthcare professionals
- People should take the required measures to prevent diseases because prevention is better than cure
Position Paper Topics on Psychology
- Geniuses are always eccentric.
- Mental health education in school is mandatory.
- How can schools equip students better to deal with mental health issues?
- Counseling in schools should be mandatory.
- The government should invest in providing better mental health facilities.
- Personality and psychology are related to each other.
- People who are addicted to substances have an inherent addictive personality.
- Trauma or poor upbringing is responsible for the sexual orientation of an individual.
- Cyberbullying should be a punishable offense.
- Mental health issues should not be grounds for termination of employment.
- People with mental health issues should be provided with employment opportunities too.
- Behavioral psychology should be understood and studied by HR personnel.
- Do mental health issues affect a relationship?
- Mental health disorders can be treated at home by making small changes in routines and habits.
- Impulsive decisions should not be viewed as negative.
- Mental health issues are responsible for substance abuse.
- There should be more stringent tests to evaluate the qualification of mental health professionals.
- Teachers should be taught the basics of child development and psychology.
- Is food addiction a cause for concern?
- Freudian principles and their relevance in modern society.
- Should complications arising from self-treatment be covered under insurance?
- Should the punishment for medical malpractice be more stringent?
- Should vaccination be obligatory?
Position Paper Topics on Criminal Justice
- Freedom of speech represents a double standard by law.
- Improving juvenile prison systems benefits society.
- White-collar criminals should face the same prosecution as other criminals.
- Building more prisons can curb the increase in crime rates.
- Media coverage can influence the outcome of criminal justice.
- Holistic practices like yoga and meditation can improve the mindset of prison inmates.
- Banning illegal drugs will reduce dependency.
- Police officers must have stricter ethical codes.
- Domestic violence must not be limited to women.
- Women misuse sexual violence laws.
- Consuming drugs should remain a criminal offense.
- Providing vocational training to inmates can reduce the rate of crime when they are released.
- Minors committing heinous crimes should be tried as adults instead of juveniles.
- Capital punishment should be abolished.
- Is there a relationship between socioeconomic status and crime?
- Should healthcare be a public sector or a private sector?
- Student-centered education or teacher-centered education, which one is better?
- Every nation should abolish the death penalty and strengthen its criminal law to create fear among people to restrict them from committing a crime
- A sick person should not be punished if he/she violates the law due to a poor mental condition
- Moral policing is ineffective in terms of reducing the rate of crime among the young generation
Outstanding Claim of Facts Topics
- Liberty is freedom.
- Medical research can be threatening to society.
- The plea bargaining system is flawed.
- The rights of artists are protected on the internet
- Diversity in the workplace improves productivity
- Online technologies are changing the way we live.
- Unemployment leads to a surge in crime rates.
- Religious persecution exists even in the modern world.
- Media can influence election results.
- Computers are changing the way people think.
- Women are safer when they dress more conservatively.
- The progress of a country can be determined by the status of women in society.
- The loyalty of employees is determined by HR policies.
- Pursuing arts can improve the longevity of an individual
- Freedom of the press is necessary for the development of our civilization
- Should children be given more time for free play or should they have scheduled activities?
- Is equal gender representation in political office important?
- Should you pay for music or should it be free?
- Marijuana is less harmful compared to tobacco smoking
- Changes in land use patterns in southern California over the past five decades have rendered the Salton Sea the single most important gateway in the West for migrating waterfowl
- Public school performance in the USA has plummeted over the past 10 years
- Public funded art and craft offer the most expensive piece of art and craft in the world
Amazing Claim of Value Topics
- Video games versus traditional games.
- Should concepts of nutrition be taught at home or at school?
- Classical education versus modern education
- Have cell phones changed the way we relate to each other?
- Are virtual classes better than in-person classes?
- Write about conducting experiments on human embryos.
- Are liberal arts in education important?
- Is it necessary to conduct beauty contests for young girls?
- Is it important to give enormous incomes to elite athletes?
- Nuclear families versus traditional joint families. Which is better for children?
- Is the use of biological mutation in warfare morally acceptable?
- Is private tuition worth the high costs?
- Does the racial background of police officers determine how well they do their jobs?
- Discuss the concept of “designer babies”
- Texts and emails versus talking face-to-face.
- Should parents use an authoritative approach to parenting or a liberal one?
- Is it important to ban Barbie dolls?
- “The Wizard of Oz is the greatest movie of all time”: Why or why not
- Should Snowboarding be considered one of the greatest ways to spend a vacation?
- Write about companies hiring human workers over the usage of autonomous machines.
- “In one study, 37% of eighth-grade females who drank heavily reported attempting suicide, compared with 11% who did not drink” (NIH)
- The death penalty is an inequitable, unjust capital punishment and does not deter crime
Position Paper Topics on Sports
- College coaches have unreasonably high fees. Justify your opinion.
- Write about the involvement of children in competitive sports.
- Are overbearing sports parents helpful or harmful?
- Is it important to grant compensation to college athletes in case of injury?
- Write about the participation of female students in sports at schools and colleges.
Position Paper Topics on Economics
- Banks are necessary. Share your views
- Should we care more about global poverty?
- Do you agree that “market force” leads to good outcomes?
- Is it essential to limit the ownership of private property?
- How do economic strategies like a “trade war” affect global stability?
Read more: Top 100 Excellent Economics Research Topic
Position Paper Topics on Technology and Social Media
- Are the effects of living in a technological world positive or negative?
- What role should technology play in education?
- Is it necessary to replace Textbooks with i-Pads and online resources?
- What are the applications of nanotechnology and its possible uses in the future?
- What privacy policies should social media companies uphold?
- Are social media memes ethical?
- Should parents limit teenagers’ use of social media?
- How is social media changing family relationships?
- Depression and anxiety are the results of enhanced social media engagement.
- What people should and should not post on social media?
Environmental Topic Ideas for Position Paper
- What is the relationship between pollution and health ?
- How can citizens be responsible for their local environment?
- How does the current trend of species extinction compare to the past?
- What can manufacturers do to help clean up the earth?
- How can we encourage people to recycle more?
- Is global warming a problem and if so, what can we do about it?
- How can we be sure to provide clean water for everyone?
- Should hunting be allowed?
- How can we resolve the economy versus environment debate?
- Explain how to stop the poaching of species that are about to extinct.
Position Paper Topics on Identity, Race, and Culture
- Should churches work harder to be multi-racial?
- What is the value of knowing your racial and cultural heritage?
- How can parents help raise their children to be appreciative of other cultures?
- Should schools teach multiculturalism?
- Is it a good idea for people to adopt children from another ethnic group?
- How does immigration from Latin America affect the culture of America?
- To what extent does individual identity depend on ethnic affiliation?
- What is the role of culture in the shaping of an identity?
- Do you believe that reverse discrimination is a problem in the American community?
Position Paper Topics on Military
- Is drone warfare ethical?
- Should military spending in the U.S. increase or decrease?
- How is cyber warfare becoming more important?
- How do people justify war?
- Is war inevitable?
- How should the United States defend itself against terrorism?
- Is the U.S. engaging in cyber-attacks on other countries?
- Should the U.S. continue to act as a policeman for other countries?
- How did 9/11 change the way Americans feel about themselves as a world power?
- What might help establish peace?
Ideas Based on Immigration for Position Paper
- What causes people to immigrate illegally?
- How should we respond to the global problem of illegal immigration?
- Should the U.S. have a visitor work program?
- How to streamline legal immigration.
- Who should and should not be allowed to immigrate?
- Would a border fence solve the immigration problem in the U.S.A?
- Should all states have laws giving policemen the right to require people to prove their legal status?
- How has immigration affected the history of the U.S.A?
- Should there be a path to citizenship for illegal immigrants currently in the U.S.A?
- What is the relationship between immigration and nationality?
- How to treat people with mental health problems.
- Medical help is preferable to medical insurance for societies with limited resources.
- Does it make more sense to teach nutrition lessons in the classroom or at home?
- Which position is preferable, support for the unborn or support for life?
- traditional games versus video games.
- Should parents adopt a liberal or an authoritative style of parenting?
- Should the healthcare industry be in the public or private sector?
- Which is better: education focused on the student or education focused on the teacher?
- Is it essential to ban Fast food commercials on TV to help people make better dietary decisions?
- The tests used to determine whether mental health professionals are qualified need to be more demanding.
Position Paper Topics to Ace an A+ Grade
- Progressive tax or proportional tax: what is better?
- Does class size matter for the achievement of students?
- How can pro-life and pro-choice organizations work together?
- Is Barbie to blame for setting high beauty standards?
- Why are organizations investing in corporate well-being programs in their workplace?
- Discuss the psychology of xenophobic attitudes.
- Is it possible to reduce abortions without passing laws?
- Should schools start giving cash credits to students with high test scores?
- Explain the impact of demonetization on the Indian economy
- Do GMOs harm human health?
For writing a brilliant position paper, make use of the list of the best position paper topics suggested above. If you find the position paper topic selection and writing process tougher, feel free to call us.

Related Post

110 Hard Words to Spell for Students and Adults

Learn How to Avoid Passive Voice in 3 Simple Steps

117 Best Greek Mythology Essay Topics For Students
About author.
Jacob Smith
I am an Academic Writer and have affection to share my knowledge through posts’. I do not feel tiredness while research and analyzing the things. Sometime, I write down hundred of research topics as per the students requirements. I want to share solution oriented content to the students.
Comments are closed.
- Featured Posts
140 Unique Geology Research Topics to Focus On
200+ outstanding world history topics and ideas 2023, 190 excellent ap research topics and ideas, 150+ trending group discussion topics and ideas, 170 funny speech topics to blow the minds of audience, who invented exams learn the history of examination, how to focus on reading 15 effective tips for better concentration, what is a rhetorical analysis essay and how to write it, primary school teacher in australia- eligibility, job role, career options, and salary, 4 steps to build a flawless business letter format, get help instantly.
Raise Your Grades with Assignment Help Pro
- Privacy Policy

Home » Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Position Paper
Definition:
Position paper is a written document that presents an argument or stance on a particular issue or topic. It outlines the author’s position on the issue and provides support for that position with evidence and reasoning. Position papers are commonly used in academic settings, such as in Model United Nations conferences or debates, but they can also be used in professional or political contexts.
Position papers typically begin with an introduction that presents the issue and the author’s position on it. The body of the paper then provides evidence and reasoning to support that position, often citing relevant sources and research. The conclusion of the paper summarizes the author’s argument and emphasizes its importance.
Types of Position Paper
There are several types of position papers, including:
- Advocacy Position Paper : This type of position paper presents an argument in support of a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to persuade the reader to take a particular action or adopt a particular perspective.
- Counter-Argument Position Paper: This type of position paper presents an argument against a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to convince the reader to reject a particular perspective or course of action.
- Problem-Solution Position Paper : This type of position paper identifies a problem and presents a solution to it. It seeks to convince the reader that the proposed solution is the best course of action to address the identified problem.
- Comparative Position Paper : This type of position paper compares and contrasts two or more options, policies, or proposals. It seeks to convince the reader that one option is better than the others.
- Historical Position Paper : This type of position paper examines a historical event, policy, or perspective and presents an argument based on the analysis of the historical context.
- Interpretive Position Paper : This type of position paper provides an interpretation or analysis of a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to persuade the reader to adopt a particular perspective or understanding of the topic.
- Policy Position Paper: This type of position paper outlines a specific policy proposal and presents an argument in support of it. It may also address potential objections to the proposal and offer solutions to address those objections.
- Value Position Paper: This type of position paper argues for or against a particular value or set of values. It seeks to convince the reader that a particular value or set of values is more important or better than others.
- Predictive Position Paper : This type of position paper makes predictions about future events or trends and presents an argument for why those predictions are likely to come true. It may also offer suggestions for how to prepare for or respond to those events or trends.
- Personal Position Paper : This type of position paper presents an individual’s personal perspective or opinion on a particular issue. It may draw on personal experiences or beliefs to support the argument.
Position Paper Format
Here is a format you can follow when writing a position paper:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide a brief overview of the topic or issue being discussed. It should also provide some background information on the issue and state the purpose of the position paper.
- Definition of the problem : This section should describe the problem or issue that the position paper addresses. It should explain the causes and effects of the problem and provide evidence to support the claims made.
- Historical perspective : This section should provide a historical perspective on the issue or problem, outlining how it has evolved over time and what previous attempts have been made to address it.
- The organization’s stance : This section should present the organization’s stance on the issue or problem. It should provide evidence to support the organization’s position and explain the rationale behind it. This section should also address any counterarguments or alternative perspectives.
- Proposed solutions: This section should provide proposed solutions or recommendations to address the problem or issue. It should explain how the proposed solutions align with the organization’s stance and provide evidence to support their effectiveness.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the organization’s position on the issue or problem and restate the proposed solutions or recommendations. It should also encourage further discussion and action on the issue.
- References: Include a list of references used to support the claims made in the position paper.
How to Write Position Paper
Here are the steps to write a position paper:
- Choose your topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about or have knowledge of. It could be related to social, economic, environmental, political, or any other issues.
- Research: Conduct thorough research on the topic to gather relevant information and supporting evidence. This could include reading scholarly articles, reports, books, and news articles.
- Define your position: Once you have gathered sufficient information, identify the main arguments and formulate your position. Consider both the pros and cons of the issue.
- Write an introduction : Start your position paper with a brief introduction that provides some background information on the topic and highlights the key points that you will discuss in the paper.
- Present your arguments: In the body of your paper, present your arguments in a logical and coherent manner. Each argument should be supported by evidence from your research.
- Address opposing views : Acknowledge and address the opposing views on the issue. Provide counterarguments that refute these views and explain why your position is more valid.
- Conclusion : In the conclusion, summarize your main points and reiterate your position on the topic. You can also suggest some solutions or actions that can be taken to address the issue.
- Edit and proofread : Finally, edit and proofread your position paper to ensure that it is well-written, clear, and free of errors.
Position Paper Example
Position Paper Example structure is as follows:
- Introduction:
- A brief overview of the issue
- A clear statement of the position the paper is taking
- Background:
- A detailed explanation of the issue
- A discussion of the history of the issue
- An analysis of any previous actions taken on the issue
- A detailed explanation of the position taken by the paper
- A discussion of the reasons for the position taken
- Evidence supporting the position, such as statistics, research, and expert opinions
- Counterarguments:
- A discussion of opposing views and arguments
- A rebuttal of those opposing views and arguments
- A discussion of why the position taken is more valid than the opposing views
- Conclusion:
- A summary of the main points of the paper
- A call to action or recommendation for action
- A final statement reinforcing the position taken by the paper
- References:
- A list of sources used in the paper, cited in an appropriate citation style
Purpose of Position Paper
Here are some of the most common purposes of position papers:
- Advocacy: Position papers are often used to promote a particular point of view or to advocate for a specific policy or action.
- Debate : In a debate, participants are often required to write position papers outlining their argument. These papers help the debaters clarify their position and provide evidence to support their claims.
- Negotiation : Position papers can be used as part of negotiations to establish each party’s position on a particular issue.
- Education : Position papers can be used to educate the public, policymakers, and other stakeholders about complex issues by presenting a clear and concise argument supported by evidence.
- Decision-making : Position papers can be used by decision-makers to make informed decisions about policies, programs, or initiatives based on a well-reasoned argument.
- Research : Position papers can be used as a starting point for further research on a particular topic or issue.
When to Write Position Paper
Here are some common situations when you might need to write a position paper:
- Advocacy or lobbying : If you are part of an organization that is advocating for a specific policy change or trying to influence decision-makers, a position paper can help you articulate your organization’s position and provide evidence to support your arguments.
- Conferences or debates: In academic or professional settings, you may be asked to write a position paper to present your perspective on a particular topic or issue. This can be a useful exercise to help you clarify your thoughts and prepare for a debate or discussion.
- Public relations: A position paper can also be used as a tool for public relations, to showcase your organization’s expertise and thought leadership on a particular issue.
- Internal communications: Within an organization, a position paper can be used to communicate a particular stance or policy to employees or stakeholders.
Advantages of Position Paper
There are several advantages to writing a position paper, including:
- Organizing thoughts : Writing a position paper requires careful consideration of the issue at hand, and the process of organizing thoughts and arguments can help you clarify your own position.
- Demonstrating expertise: Position papers are often used in academic and professional settings to demonstrate expertise on a particular topic. Writing a well-researched and well-written position paper can help establish your credibility and expertise in a given field.
- Advocacy: Position papers are often used as a tool for advocacy, whether it’s advocating for a particular policy or for a specific point of view. Position papers can help persuade others to adopt your position on an issue.
- Facilitating discussion : Position papers can be used to facilitate discussion and debate on a particular issue. By presenting different perspectives on an issue, position papers can help foster dialogue and lead to a better understanding of the topic at hand.
- Providing a framework for action: Position papers can also be used to provide a framework for action. By outlining specific steps that should be taken to address an issue, a position paper can help guide decision-making and policy development.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

What is Literature – Definition, Types, Examples

What is Biology – Definition, Concepts

Evolution – Definition, Types and Example

Research – Types, Methods and Examples

What is Sociology – Definition and Overview

Concept – Definition, Types and Examples
- Other Guides
- How to Write a Position Paper: Definition, Outline & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Position Paper: Definition, Outline & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A position paper is a written statement that presents a particular perspective on any issue or topic. It typically argues a specific point of view and presents evidence to support that position. To write a position paper, you need to research and understand the topic, develop a supported argument, and address opposing viewpoints.
In this comprehensive guide, you will find all important information that will help you prepare this type of assignment. More specifically we will talk about:
- What is a position paper?
- How to write a position paper?
- Position paper example you could use for inspiration.
As an experienced paper writer team, we always come to support fellow students by providing them with helpful information and tips. Our readers can find detailed definitions and high-quality supporting materials on this website – all of that available for free!
What Is a Position Paper: Definition
First of all, let’s define it. Your position paper should clearly display and support your own view of a specific problem. Typically, position papers explore more or less controversial questions, which is why they must include argumentation supported by valid data. Providing evidence to the readers is the main distinctive feature of such an essay. Your work should demonstrate your ability to put up a strong case, not just describe your beliefs. Before you write a position paper, think it through and start with understanding your purpose. What do you try to tell your audience, and what is the best way to convey it? This helps with building good argumentation and structuring your essay.

Keep in mind that unlike a persuasive essay , convincing your readers to accept your point isn’t your primary task. Your piece should mainly focus on information that makes an argument strong. That’s why you should use supportive evidence that backs up your viewpoints.
Purpose of a Position Paper
Why do you need a position paper? First of all, it serves as great supporting material when talking about your viewpoint in front of an audience. Writing a position paper beforehand helps to organize your thoughts on the topic and set your defenses properly. Besides, you can use it when speaking to ensure you haven’t forgotten to mention something important. You might also be required to submit your paper before or after your speech. If it is your college or university assignment, this document will be your main output, which is why its structure and format are so important.
Position Paper Outline
One of the main first steps is preparing an outline for a position paper. After you’ve done some research and gathered enough data on your topic, spend additional time and create a concise draft. It should display your paper’s entire structure, including the key arguments, without going into much details. Your writing should follow a basic 5 paragraph essay outline . Once done with your plan, you can review it and easily spot major gaps or inconsistencies. Checking your work at this stage is typically much more productive than after writing the full text. Here is an example of position paper outline:
- Hook the reader with stats, numbers or facts
- Introduce the issue
- Include a thesis statement presenting your central idea and stand on the problem
- Present counterclaims
- Offer evidence that backs up counterarguments
- Refute the counter arguments using examples
- Strong opinion
- Supporting examples
- Restate your main claim
- Offer a course of action
Hopefully, this position paper template will speed up your progress with your own work. Check the attachments below – complete sample papers along with outlines are available there.

Position Paper Structure
What exactly does the structure of a position paper include? This is quite easy: similarly to any other scholarly essay, your position paper should contain three main parts:
Introduction
- Main body part
- Conclusion.
You’ll write a good position paper if you make it readable and concise in addition to preparing string argumentation backed by valid evidence. Otherwise, your poorly structured text won’t impress your readers. We’ve prepared more helpful information on how you should compose each of these sections. You can find it below, so please read it attentively. Also, check out the sample position papers available on this page. You can find more tips and ideas below.
Good introduction for a position paper should make your reader well familiar with the problem you are arguing about. This typically involves explaining why it is important for everyone or why you’ve decided to discuss it. Besides, the introduction must engage your audience so that they would be interested in hearing more about your position and evaluating its validity. This is how to start writing a position paper:
- Clearly state your position, giving the thesis statement.
- Give enough context about the problem and its background, explaining why you stand this ground.
- ‘Hook’ your readers by making it sound interesting.
The latter can be achieved by making some hints about upcoming evidence, using some kind of wordplay, or just making a suitable joke.
Body of a position paper is where its argumentation should be placed. When you make a position paper, be sure to divide it into logically interconnected paragraphs – each one for one of your major arguments expressed in the topic sentence . Make proper transitions between them. Leave at least one paragraph for the counter argumentation you may have faced and for its rebuttal. The evidence you’ve collected to support your claim should also be presented in the main body, together with quotes and references (if any). Remember to use solid and relevant data and avoid unnecessary facts, as they don’t bring value and may just make the text less readable. Pay attention to the consistency and readability of this section. Its structure and contents show how well you’ve built your argumentation. And that is what makes position papers persuasive.
This is how to write a conclusion for a position paper that adds real value to it:
- Properly summarize your argumentation, showing how it supports your take.
- Make it sound strong; ensure that it is logical and well-readable.
- Keep it brief, don’t repeat anything from the main part.
Remember that your proposition paper conclusion will be the last thing your audience reads, so making a strong and persuasive ending would help with leaving a good impression on it. You’ll find a conclusion template in one of the sections below.
How to Write a Position Paper in 9 Steps
Let’s get to the point – you must write a good position paper, and now you’re looking for some helpful tips on that. We’ve got your back! First and foremost, the best beginning is to set up a strong position. Otherwise, your essay will simply be uninteresting. Now make sure you can actually prove what it states. But that’s just the beginning: think about captivating headings, add some clever techniques and diligent work to that, keeping focus on your goal – and you’ll get an excellent paper. What should be added? Just keep reading. We’ve prepared an elaborate guide on how to write a position paper step by step. Let’s go and check it!
1. Choose a Topic
Creating position papers requires some hard work, but choosing a proper subject may save a lot of time and effort. If it is uninteresting or too narrow, that might result in an issue. Better to choose a topic that:
- Is relevant and controversial: this will draw your readers’ interest.
- Is understandable for you, so it would be easier for you to discuss some points about it.
- Has received some coverage in news, books, or other sources, making it simpler to find enough evidence about it.
Before commencing the writing process, search among good topics for position papers and select one most suitable for taking a point around it.
2. Do Research Before Writing a Position Paper
Conducting preliminary research for position papers is a key step before starting with actual writing. This is where you can collect evidence about your subject:
- Google it This is easier but remember to filter out results with low credibility.
- Media If this is a recent and big event, it should be mentioned in the news; make sure to pick the most credible resources.
- Check the sources used by books or articles written on the subject This way, you might find some ‘hidden gems’ that are difficult to google.
Don’t know if you’ll write a winning position paper? Follow the next steps closely. And don’t forget to explore the free samples available on this page, check their structure and style.
3. Draft a Position Paper Thesis
Thesis of a position paper is basically its foundation. Make it strong, and you’ll ensure your success. Don’t be too wordy. One sentence is enough to deliver your thesis and summarize your position on the topic. You can put it closer to the start or put it at the end of your introduction so that it summarizes the explanations you would give about the problem. Examples of a position paper thesis:
4. Create an Outline
Once you have decided about the direction you’re taking with your essay, proceed with the position essay outline. This step is often overlooked, but it will be much easier to find and correct mistakes and gaps at this early stage. So, writing a position paper outline actually saves you time. This is how to write a position paper outline:
- Keep it brief, just one sentence per idea. No need to always use full sentences, just make them readable.
- Include your thesis, mention the context, then write one sentence per each argument.
- Briefly summarize it, one sentence will suffice as well.
Don’t forget to review your outline carefully.
5. Begin Writing Your Position Paper
Once you’ve ensured the outline of an essay doesn’t have any gaps or logical flaws, go ahead and complete the full-text version. If you wonder how to start a position paper at this stage, begin with the introduction. You already have its shortened draft, so just add necessary details and list explanations if needed. But don’t give particular arguments or refute opposing opinions yet, those should come in the main body part. See how to write an introductory paragraph for a position paper in the next section.
Position Paper Introduction Example
Looking for introduction position paper examples? We’ve got one for you. Here’s how you can start your essay:
Check our sample position paper for introduction examples. They are available for free download.
6. Include Evidence in Your Position Paper
As we’ve already explained, position papers must be backed by solid evidence. You have to prove your point, and that requires addressing it with data, not just stating it with confidence. When you write your position paper, there are two main requirements for backing your claim:
- collect valid and relevant data;
- present it in your text properly.
Here’s an example of evidence in a position paper:
7. Provide Counterarguments and Refute Them
Still learning how to write position paper? If it is your first one, consider an important fact: ignoring evident contradictions to your claim doesn’t add credibility. Instead, you must work with counter arguments which is similar to writing an argumentative essay . You may be aware of the opposite opinions or think and assume which objections your opponents would make. Better mention them in your essay and show how you counter these claims. Here are some examples of counterarguments for position papers:
8. Summarize Your Position
When writing your position paper, it is important that you make it sound impressive in the end. Your position paper conclusion should properly summarize all arguments and rebuttal of counterarguments . Keep it brief, without repeating much, just highlight how all your findings support the claim. You can also add some extra notes, e.g., making additional assumptions, different predictions about this problem’s impact in the future, or hints about extra evidence you haven’t mentioned before to keep your text brief. This may help to make a lasting impression on your audience. Finally, review your conclusion once again, ensuring that it is logical and doesn’t contradict any claims, arguments, or assumptions provided above. Check the next section for an example of how to write a position paper conclusion.
Example of a Position Paper Conclusion
Need an actual conclusion for a position essay example? It can be something like this:
You can also find the conclusion of a position paper essay example if you check the free samples that are available on this page.
9. Proofread Your Position Paper
After your position essay is complete, you absolutely should spend some extra time and review it again. Try adopting a critical view, putting yourself in your potential opponent’s shoes. Are there any logical gaps or grammar mistakes left? Paper position is not clear enough? Wrong source mentioned? Nearly every text has some issues to correct. Sometimes even evident typos are left overlooked when writing. It is best to have someone else review a position paper since its writer may be biased toward their own text. Another way is reading it aloud to yourself prior to submission. Some flaws may be uncovered this way too.
Position Paper Format
Your position papers format is another element that shouldn’t be overlooked. Proper headline and paragraph styles make your text more readable. Also, there might be specific requirements for making citations. All your evidence must be presented correctly so that it doesn’t get mixed with your own opinions. Format depends on the discipline. You might need to use one of the popular styles: MLA, APA, or Chicago. If you don’t see which one of them is required, better ask your tutor. You can find some position paper format sample in our free attachments, available below.
Position Paper Examples
Need an example of a position paper so that you could learn how all these recommendations can be implemented? We’ve got some for you! Scroll down to the bottom of the page, and you’ll find sample of position papers available for free download. Each position paper example essay has been written by professional research writers and can be used for inspiration or as a reference. Just don’t copy any of those materials in your own text, as you should only submit 100% original works. Position paper example 1
Position paper example 2
Position paper example 3
Position Paper Sample 4
Tips for Writing a Position Paper
Finally, some extra tips on writing a position paper that is really persuasive:
- Choose topics that are interesting for you. This will motivate you to discuss them.
- Plan ahead and consider your deadlines. Don’t spend too much time conducting the preliminary research or perfecting your argumentation if it is already valid.
- Pay attention to your sources. Some books or research might be considered dubious by your opponents or might have some obvious gaps.
- Review your position papers as many times as possible. Ideally, ask a person with an opposite side on this issue to read and refute it.
- Keep it professional. Maintain a confident tone but stay logical and correct, avoid emotional or derogatory remarks.
More examples of position papers are available here – you can check them below.
Final Thoughts on How to Write a Position Paper
So, in order to write a position paper, you need to choose an appropriate topic and elaborate on your position regarding the specific problem. Then you should defend it using logic, facts, and confidence. Still not clear what are position papers and how one should write them? Check out this sample position paper for students available below, and you’ll find all our tips illustrated there. Follow its structure and style, just don’t copy anything to avoid plagiarizing.
If you are stuck in any stage of the writing process, don’t hesitate to use professional academic writing services. StudyCrumb is always here for you to solve any academic challenge you may have. Let us know your task, and we will match you with the most fitting expert who can write an excellent position paper for you.
FAQ About a Position Paper
1. how long should a position paper be.
The length of a position paper is usually limited to one page and a half (up to 350 words). Don’t make it too long, stick to the facts and brief statements. When given with confidence, concise claims are more persuasive. At the same time better include all necessary evidence, not rely just on confidence. So don’t make it less than one page.
2. What are the kinds of support in a position paper?
You can use these support types in your position paper:
- Factual knowledge: either well-known facts (e.g., historical or biological) or data retrieved from credible sources;
- Statistical trends: always helpful for making assumptions but also need to be backed by sources;
- Informed opinion: citations from renowned specialists in fields related to your topic.
3. What is forbidden in a position paper?
When writing a position paper, avoid the following:
- Taking opinions for facts.
- Using threats or derogatory language as a means of persuasion.
- Comparing unrelated situations and making some conclusions from that.
- Copying other works without citing them.

Rachel R. Hill is a real educational devotee. She prides in writing exceptional general guides while listening to every need of students.
You may also like

• Online education is cost-effective, being more affordable for both students and educational institutions. • Schools should offer low-income pupils summertime educational resources.
Traditional education is commonly regarded as a better alternative since live interaction with teachers often facilitates the learning process. However, given the ever-growing problem with student loans, the affordability of online education has become an important factor. Additionally, when studying online, people don’t have to commute, thus saving extra time and money. So, we can see that online education is more effective for common students.
As shown by many researchers (particularly by Kim and Norton in their work, 2018), more than 60% of students in the US attend online courses on a regular basis.
Evidently, e-learning doesn’t allow face-to-face interaction with your tutor, which may make it harder to exchange experience. However, the affordability factor still makes it a better choice, especially for motivated students. The price difference between traditional and online education might not be that big. But if we add the price of commuting and time spent on that, this difference becomes much bigger.
According to the statistical data presented above, e-learning is already gaining increasing popularity among students below 25 ages all over the globe. Since it is better compatible with the part-time work schedule most students have to follow, this format has actually proven its efficiency in recent years. And it is quite safe to assume it will become a new dominant way of education within the next decade or two.
A Guide to Writing a Compelling Position Paper
Table of contents
- 1 What is a Position Paper?
- 2 An Effective Position Paper Format To Follow
- 3 Position Paper Outline Example
- 4.1 Articulate Your Central Thesis Clearly
- 4.2 Examine a Topic and Gather Supporting Evidence
- 4.3 Construct Supporting Claims For The Positioning Statement
- 4.4 Anticipate and Study the Opposing Views
- 4.5 Construct Supporting Claims For The Positioning Statement
- 4.6 Ensure a Coherent Organisation and Structure Of your Paper
- 5 Position Paper Example Topics
- 6 Template For Writing a Position Essay
- 7.1 “Should video games be used in education?”
- 8.1 How long should a position paper be?
- 8.2 How many paragraphs are in a position paper?
- 8.3 What should a position paper include?
- 8.4 What is the difference between a position paper and an argumentative essay?
Writing can be tough at times, especially when you have to express your opinion on a controversial issue, especially if such an opinion is an unconventional one. Such a piece of writing is called a position paper. It may seem that to speak your opinion out loud is a lot harder than to do the same, but in writing. The reality is that even when you prepare a speech for some debates, you have to write it down first.
Moreover, it gets easier as you speak, as no one requires you to say precisely what you’ve written down, but when it comes to writing, readers only get to know what you’ve put down and nothing more. Nothing can be changed as soon as you submit your work. So, let’s break down a universal position paper you could use for pretty much any topic.
Position essays serve as a tool to inform and educate the relevant audience and stakeholders. Here are some essay tips you can use to ensure that you are writing an effective position statement.
What is a Position Paper?
A position paper is an argument representing an organization or individual’s stand on an issue or problem in writing. This viewpoint is in opposition to another opinion. The content outlines beliefs, arguments, and evidence in support of their view. A position piece is to convince others to adopt a similar perspective or understand and recognize the reasoning behind an idea. Knowing how to write a good position statement and back your argument with statistics and evidence is important.
An Effective Position Paper Format To Follow

Suppose you are wondering how to write a position paper. A good position article begins with a well-crafted title. Once you have decided on the position paper title, start with the position paper outline . A typical position paper structure starts to introduce your topic and your stance on a topic, it is then followed by the body of position paper that includes counterarguments and claims that reinforce your position. It is then followed by a conclusion that reinforces your claim.
There are different types of research papers . The notable difference in an opinion piece is that two opposing viewpoints are presented without any one opinion being endorsed. However, in a position article you need to give your belief which is in opposition to another idea.
Writing position papers is different compared to other formats, and you want to set up a strong position. Here are five key differences in the form you should note if you are wondering how to write a position paper.
The best research paper writers will use the following components:
- The main goal while writing a position paper is to argue a specific view and convince the reader to adopt the same idea.
- It requires the writer to take a clear stand and defend it with solid reasoning and evidence.
- The text should incorporate research and sources to back what you are arguing throughout the parts of the position paper.
- The tone of the content needs to be formal and persuasive, which is different from other types of documents, for example, descriptive and narrative.
- The structure is also different, and a good system needs to be followed to set up a solid position.
Position Paper Outline Example
Every good position paper outline should start with writing a title for a research paper . Having done that, you can proceed with the outline. Notably, this kind of paper resembles an opinion essay, though, in the latter, you had to present two opposing opinions without necessarily sharing one of them. In the position paper, you need to counter an idea with that one of your own. So, a simple position paper outline example would look as follows:

As you see, this position paper sample outline can be applied to pretty much any topic.
Tips For Creating an Effective Position Paper
If you want to write an effective and well-crafted position paper, make sure that your writing is clear and persuasive, supported by robust research and evidence. Here are some tips for creating a paper that conveys your viewpoint most effectively.
Articulate Your Central Thesis Clearly
When articulating your position and the central statement, make sure it is clear and precise. The thesis should be stated concisely and in the introduction of position paper. To ensure that it is clear what side you are taking on the issue under discussion. It serves as the foundation for the complete paper. Once you have effectively positioned yourself while writing the introduction, the rest can focus on the supporting facts.
Examine a Topic and Gather Supporting Evidence
The first step in building a cohesive argument is to examine the topic and gather evidence. Start by carefully analyzing the issue and understanding the counter-arguments surrounding the case. In this way, you can formulate a well-informed position. The second step is to collect and review all evidence and facts; these should be extracted from reputable sources such as case studies, research papers, expert opinions, and statistics.
All the data that you gather needs to be relevant. With a solid foundation of your evidence, you can make a foolproof position statement and build superior quality paper.
Construct Supporting Claims For The Positioning Statement
To enhance your claim, it is crucial to build proofs that are logical. Introduce evidence to make your claims credible. When you write an essay stating your position, make sure you present each argument clearly and link it to your stance on the topic. Additionally, construct evidence to back your claim and make sure that you are also considering the opposing points.
Anticipate and Study the Opposing Views
To ensure that your paper is sturdy, anticipate and study the opposing points. By considering all opposing views, you are more prepared for the objections to your supporting claims and can address them in the paper. This displays your commitment to your claim.
It also proves that you have gone through all the alternative perspectives before making a decision. It also strengthens your paper by showing that it is well-researched. So, whenever you start, research both sides. Then, make a list of all the counterclaims made by those who disagree with your position.
Your writing style can make or break the paper. With a clear and straightforward manner, you can let your research be the highlight. This will help you avoid anything that may need to be clarified for the reader. Even if you pay for an essay to be written , avoid complex language and use shorter sentences with simple vocabulary.
Also, remove any unnecessary words and details that are irrelevant. Stay focused on the main point to make your position unchallengeable. This will help the reader follow your line of reasoning without any distractions.
Ensure a Coherent Organisation and Structure Of your Paper
If you want to communicate your argument while also persuading the audience effectively, it’s important to focus on the structure of your writing. A well-structured paper helps present your idea clearly and cohesively. Usually, academic essay writers start with the outline of the main points you would like to cover in the article.
From the beginning to the conclusion, ensure that the content flows seamlessly from one point to the next. The transition between sections also needs to be smooth. Also, use headings and subheadings to divide the text into paragraphs. These sections are then easy to navigate and comprehend.
Position Paper Example Topics
If you are wondering how to start a position paper, here are some example topics and titles you can take inspiration from:
- The benefits and uses of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Gig Economy and its benefits or drawbacks
- What is the future of work, and how will it impact our society?
- How is social media affecting our mental health?
- Generally modified crops; are they ethical or not?
- Does technology play a positive role in educating and education?
- The impact of climate change on wildlife and biodiversity
- The advantages and obstacles that we face due to urbanisation.
- Government and its role in protecting privacy rights.
- What will be the impact of automation and artificial intelligence on employees?
- Cruelty-free products; a positive step or a hoax?
- How does increasing income disparities result in an increased crime rate?
- Is virtual reality a way to overcome distances?
- Drones for military and civilian applications.
- Is work-from-home the new way forward?
Writing a position paper requires a lot of research and analysis of the current literature on the given topic. It’s necessary to understand the opinions of different stakeholders and take into account all the facts before making a decision. To make the task easier, you can find services like PapersOwl who can write papers for you . With their help, you can get quality assistance with research, writing and editing your position paper. They will provide you with the necessary support and guidance to make your position paper stand out among others. -rewrite this paragraph as a human. First sentence can’t be about how the writing is challenging task. Do not write obvious sentences and act like a pro writer in this paper type
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Template For Writing a Position Essay
Here is a sample position essay outline you can use
Introduction
- Define the issue and why it’s worth discussing
- Introduce your topic
- Discuss the background and controversies
- Choose a position
- Present your thesis statement and opinion in one sentence
- Present the counterclaims and the evidence supporting them.
- Refute the opposing claims by stating your position. Ensure you reinforce your argument with data and statistics to set up a well-rooted claim.
- Ensure that the counter-arguments are equal to the pro-arguments: for example, for four counter-arguments, give four statements that back your viewpoint.
- Restate both viewpoints, and summarise the side you are arguing for.
- Provide a plan of action with a suggested resolution.
Position Paper Example
“should video games be used in education”.
As a student at a medical university studying surgery, I strongly believe that video games have a valuable role to play in education. While they should not be the sole source of learning, they can provide valuable benefits.
Statistics show that video games increase engagement, develop critical thinking and problem-solving. Additionally, the interactive nature of video games can help students retain information better. This can be especially important in fields like medicine. Where it is important to remember complex procedures and concepts. For instance, in the field of surgery, video games can serve as a valuable tool for teaching anatomy and surgical procedures.
They allow students to practice and experiment in a safe, low-stakes environment. This can help to build their confidence and improve their understanding of complex concepts. Also, it can help to reduce the risk of mistakes during real-life surgeries.
In conclusion, video games can be a valuable addition to the educational toolkit. However, they should be used in conjunction with other methods to provide a well-rounded education for students. Using video games thoughtfully has the potential to enhance students’ learning and prepare them for success in their chosen fields.
How long should a position paper be?
How many paragraphs are in a position paper, what should a position paper include.
It typically includes the following:
- Introduction with background info on the topic.
- A clear thesis statement stating a position.
- Evidence from facts, data, and statistics supports the argument.
- Examination of opposing viewpoints and counter-arguments.
- Conclusion reiterating position and its significance.
What is the difference between a position paper and an argumentative essay?
Readers also enjoyed.

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
A Brief Guide to Writing a Position Paper
13 July, 2020
13 minutes read
Author: Mathieu Johnson
Speaking your thoughts out loud happens to be easier than doing the same in writing. Why is that so? Every time you prepare a speech, you need to write it down first. And your writing needs to be precise because readers are about to know what you’ve put down on a paper. When it comes to a position paper, your mission is to express your opinion on a controversial topic. You will have to take a side on a specific topic and make up a case based on your opinion. To succeed in this writing task, you may need some guidelines.

What Is Position Paper?
A position paper is a kind of essay in which you express your opinion or position regarding a particular subject matter. It can be used for different purposes, from a discussion of international challenges to an analysis of business strategies. As a result, a position paper format is widely used in business and politics. Also, it can take a form of a report revealing your plans for the subject matter at hand. A position paper should contain a smooth flow of thoughts and ideas that provide a rock-solid evidence for your line of reasoning.

What Are The 3 Parts of a Position Paper?
A position paper consists of three main parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. Here is an explanation of what you can write in each part:
Introduction
The introductory part aims to attract the reader’s attention to the covered subject matter. Ideally, you should begin with several opening sentences about the specific issue to hook the reader.
The body part involves background information, evidence to back up your opinion, and analysis of both sides of the subject matter. By conducting thorough research, you will collect enough data to support your claims. The main point is to address both aspects of the argument. That way, you will show the reader that you are objective in your statements.
In the conclusion part, you need to restate the key points of your essay without adding anything new. Depending on your topic, it makes sense to suggest a solution to the problem.
How to Write a Position Paper?
To start writing a position paper , you should have a clearly stated topic that is debatable with logical details. While writing a paper, you should examine your vision of the problem through the prism of available arguments. Consider practicability, cost-effectiveness, and local environment when evaluating possible solutions and necessary actions. In other words, you should express, explain, and back up your opinion. And don’t forget to be specific in stating and supporting your arguments.
Select a Position Paper Topic
If you want to create a good position paper, you should focus on a subject matter that has enough findings to support it as well as some controversy to produce an argument. If you are dealing with a position paper assignment, you will want to skip your personal values and focus on something that can get you the highest grade. Here are some of the position paper topics to consider:
- Should reality TV shows be regulated?
- What are the positive and negative sides of video gaming?
- Are there any parallels between video gaming and addiction?
- Can beauty contests have a positive impact on women?
- Should children have a schedule for school and after-school activities or be given more free time for playing?
- What affects the rapid increase in child obesity?
- How to reduce the number of abortions without legislation?
- How can pro-life and pro-choice groups cooperate?
- Should the production of Barbie dolls be banned?
- What is the meaning of true beauty?
- Should young children be forced to compete at athletics?
- What are the reasons for blood cancer?
- How does COVID-19 pandemic affect the business sector?
- Is COVID-19 a real problem or a huge fake?
- How does COVID-19 affect our lives?
- Should media coverage be taken under control?
- Is private school tuition really worth it?
- How can the country’s school system be amended?
- What role should technology play in the business sector?
- Should college athletes receive a salary?
- Should college athletes be allowed to skip classes?
- Technologies are changing the way people think.
- How are online technologies affecting the way we live?
- What laws should regulate the use of cell phones in cars?
- Should parents limit teenagers’ use of social media?
- Should scientists be allowed to experiment on human embryos?
- What causes people to immigrate illegally?
- Is there any way to reduce the immigration rate?
- Can illegal immigration be justified?
- How do people justify war?
- How significant is race to American identity?
- What is the world culture?
- What is the value of knowing your cultural background?
- Should schools teach multiculturalism?
- Is global warming a problem?
- Is racism the problem of the modern community?
- How can clean water be provided to everyone?
- Is the problem of air pollution exaggerated?
- What needs to be done to reduce the level of air pollution?
- Who should take responsibility for air pollution?
- Will the worldwide population increase?
- What needs to be done to stop poaching of endangered species?
- Is hunting good for the environment?
- Are citizens responsible for their local environment?
- What can manufacturers do to reduce the air and water pollution across the world?
- What is the real importance of clean water?
- Is there any connection between health and pollution?
- What can people do to stop global pollution?
- How can people be encouraged to recycle more?
- How does global warming increase?
Preliminary Research
How do you write a position paper? Where to start from? Preliminary research requires you to find sufficient evidence for the covered subject matter. At the same time, you don’t need to rely on a subject matter that falls apart under a challenge of hefty research. You will also need to specify the sources you are planning to use. Follow them in bibliography and make some notes about every particular book, journal, or document you take information from. Thus, you will save a lot of time in the writing process.
By searching a couple of education and social sites, you will be able to find professional research data. Our professional essay writer recommends to narrow your focus, you will develop a list of questions that you have to answer in your paper. If you find no valuable information after spending several hours on research, you should understand that your position cannot be supported by sufficient findings on trustworthy sites.
Challenge Your Topic and Collect Supporting Evidence
You will need to dispute the truth or validity of your topic by finding supporting evidence. If you have some doubts, you may need some time to identify all the possible challenges that you have to deal with. Your position paper will address the opposing view and address it with counterevidence. It will make sense to have some discussions with friends, colleagues, or family about the topic. That way, you will be able to learn some additional thoughts and ideas that can be used for further research. As soon as you find some counterarguments, you will need to analyze them. Once it is done, you will see whether they are sound or not.
Another useful approach to challenging the topic requires you to mention your arguments on one side and opposing arguments on the other one. In which part of the paper do you have more points collected? Which points are stronger? If counterarguments seem to outnumber your arguments, you will have to reconsider your subject matter or your opinion on it .
Position Paper Outline
Before taking action, you’ll need to develop a position paper outline to organize your thoughts and ideas. With an outline, you will find it easier to write a position paper. So how will you do that? It depends on your personal preferences. Some writers find it easier to apply pictures and diagrams, others just follow a template offered by the teacher. If you feel like writing an outline yourself from scratch, don’t hesitate to do so. You can create it on your computer or write it down in your notebook. After all, there is no right or wrong approach to developing an outline. The main point is that an outline contains all the key points that you have to add to your position paper. You may want to look at a position paper sample before starting the writing process. Here is the format to be followed:
Decide on your topic with some background details. Develop a thesis sentence that addresses your position. Some examples are as follows:
- Smoking is a bad habit causing breathing problems.
- Fast food packages should be marked with health warnings .
- Air pollution requires certain actions from the national governments.
Decide on potential contradictions to your position. Here are some examples: :
- A medical examination needs to be conducted on an annual basis to monitor the possible negative health conditions .
- Health warnings can affect the companies’ revenues.
- The national program can be quite costly.
Cover the opposing points. Make sure that you aren’t contradicting your own thoughts and ideas. Sample points are as follows:
- It can be hard to determine the monitoring process.
- Citizens don’t want their government to abuse its power.
- Program funding will fall on the shoulders of average taxpayers.
Explain your position through the prism of counterarguments. This is how you can contradict some of the counterarguments and back up your own one. Sample points are as follows:
- The government has already tried to reduce smoking statistics in the country.
- Restaurants will enhance the quality of food in case of using health warnings .
- The government’s primary role is to protect citizens.
Sum up your arguments and express your opinion in different words. You should finish your paper by focusing on your arguments and responding to the counterarguments. You need your reader to understand and accept your opinion on the covered subject matter.
When you create a position paper, you should act with confidence. In the end, your mission is to reveal your position from the best side.
Tips on Writing a Position Paper from Our Experts
Even if you have a position paper example, you still may need some practical recommendations to make things easier for you. Here are some tips you need to follow during the writing process:
- Decide on a topic. While choosing the topic for discussion, you should find the one you have a clear idea of. You can broaden your outlook by reading some literature on the desired subject matter. Ideally, you should embark on different viewpoints to consider them for further analysis.
- Express your position idea. Focus on one specific aspect of the topic in order to express it in a one-sentence opinion. Make sure you have found a really arguable idea. If the topic cannot be debated, then it can hardly be used for writing a good position paper.
- Be precise in your statement. Try to express your opinion briefly and clearly. A position paper is not meant to be vague.
- Lead the narrative in the present tense. You are discussing the topic here and now, so the use of the past tense is quite inappropriate.
- Minimize the use of superlatives . Avoid using superlatives such as biggest, major, extremely, and so on because they make the context sound exaggerated.
- Use frequently used terms. To make the content look appealing and well-written , you should use the most common thematic terms such as world community, member states, recommendations, development, realization, regulations, international, and so on.
- Use commonly used verbs . You should include some commonly used verbs such as comprehend, enable, recognize, acknowledge, believe, suggest, consider, addresse, highlight, and so on.
- Proceed with final proofreading . You cannot consider your position paper as completed unless a successful spelling and grammar check is done. To achieve the maximum result, you should read your paper aloud a couple of times. That way, you will find it easier to indicate and fix mistakes.
While there is no universal formula for writing a perfect position paper, you can still follow some simple tips that’ll make you closer to the desired result. Just think analytically and act logically throughout the writing process.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]


Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
In a position paper assignment, your charge is to choose a side on a particular topic, sometimes controversial, and build up a case for your opinion or position. You will use facts, opinion, statistics, and other forms of evidence to convince your reader that your position is the best one. To do this, you'll collect research and craft an outline in order to create a well-constructed argument. Need an easy guide for how to write a position paper? Read on for five important steps.
Select a Topic for Your Position Paper
Your position paper centers around a topic that is supported by research. Your topic and position have to hold up when challenged, so it's helpful to research a few topics and pick the one you can best argue, even if it may not reflect your personal beliefs. In many cases, the subject matter and your topic are not as important as your ability to make a strong case. Your topic can be simple or complex, but your argument must be sound and logical.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Preliminary research is necessary to determine whether sufficient evidence is available to back up your stance. You don’t want to get too attached to a topic that falls apart under a challenge.
Search a few reputable sites, like education (.edu) sites and government (.gov) sites, to find professional studies and statistics. If you come up with nothing after an hour of searching, or if you find that your position doesn’t stand up to the findings on reputable sites, choose another topic. This could save you from a lot of frustration later.
Challenge Your Own Topic
You must know the opposite view as well as you know your own stance when you take a position. Take the time to determine all the possible challenges that you might face as you support your view. Your position paper must address the opposing view and chip away at it with counter-evidence. Consider having friends, colleagues, or family debate the topic with you to get alternative points of view that you might not have readily considered yourself. When you find arguments for the other side of your position, you can address them in a fair manner, and then state why they are not sound.
Another helpful exercise is to draw a line down the middle of a plain sheet of paper and list your points on one side and list opposing points on the other side. Which argument is really better? If it looks like your opposition might outnumber you with valid points, you should reconsider your topic or your stance on the topic.
Continue to Collect Supporting Evidence
Once you’ve determined that your position is supportable and the opposite position is (in your opinion) weaker than your own, you are ready to branch out with your research. Go to a library and conduct a search, or ask the reference librarian to help you find more sources. You can, of course, conduct online research as well, but it's important to know how to properly vet the validity of the sources you use . Ensure that your articles are written by reputable sources, and be wary of singular sources that differ from the norm, as these are often subjective rather than factual in nature.
Try to collect a variety of sources, and include both an expert’s opinion (doctor, lawyer, or professor, for example) and personal experience (from a friend or family member) that can add an emotional appeal to your topic. These statements should support your own position but should read differently than your own words. The point of these is to add depth to your argument or provide anecdotal support.
Create a Position Paper Outline
A position paper can be arranged in the following format:
1. Introduce your topic with some basic background information. Build up to your thesis sentence , which asserts your position. Sample points:
- For decades, the FDA has required that warning labels should be placed on certain products that pose a threat to public health.
- Fast food restaurants are bad for our health.
- Fast food packages should contain warning labels.
2. Introduce possible objections to your position. Sample points:
- Such labels would affect the profits of major corporations.
- Many people would see this as overreaching government control.
- Whose job is it to determine which restaurants are bad? Who draws the line?
- The program would be costly.
3. Support and acknowledge the opposing points. Just be sure you aren't discrediting your own views. Sample points:
- It would be difficult and expensive for any entity to determine which restaurants should adhere to the policy.
- Nobody wants to see the government overstepping its boundaries.
- Funding would fall on the shoulders of taxpayers.
4. Explain that your position is still the best one, despite the strength of counter-arguments. This is where you can work to discredit some of the counter-arguments and support your own. Sample points:
- The cost would be countered by the improvement of public health.
- Restaurants might improve the standards of food if warning labels were put into place.
- One role of the government is to keep citizens safe.
- The government already does this with drugs and cigarettes.
5. Summarize your argument and restate your position. End your paper focusing on your argument and avoid the counter-arguments. You want your audience to walk away with your view on the topic being one that resonates with them.
When you write a position paper, write with confidence and state your opinion with authority. After all, your goal is to demonstrate that your position is the correct one.
- Words, Phrases, and Arguments to Use in Persuasive Writing
- How Can You Stretch a Paper to Make it Longer?
- Research Paper Writing Checklist
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography for a Paper
- Revising a Paper
- Strategies for Writing a 20-Page Paper
- How to Write a Paper at the Last Minute
- Tips for Typing an Academic Paper on a Computer
- Creating a Table of Contents
- How Long Should My Paper Be?
- What Is a Bibliography?
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- How to Write a 10-Page Research Paper
- Research Note Cards
How To Write the Perfect Position Paper
Opinions are like cars. Lots of people have them, but very few know how they actually work. At some point in high school, or college, you will be required to have an opinion on something. That’s the easy part. The hard part is providing that your opinion has merit. That’s the basic premise behind writing a position paper, or a persuasive essay. This is the time-tested academic tradition where you are required to stake out a meaningful position on an important subject and, subsequently, to provide relevant and verifiable evidence that your position is grounded in solid fact.

This is an important skill, not just in school or on social media, but in real life. So if you’re on the hunt for solid facts, check out our constantly growing library of The Most Controversial Topics For Your Position Paper .
We recognize, however, that knowing a lot of facts isn’t the same as being able to write about these facts in a convincing or authoritative way. Writing an excellent position paper is a multi-step process that requires you to integrate both fact and opinion into a coherent and compelling essay. Lucky for you, we’ve got a handy step-by-step guide on how to do this.
Read on to find how you can write the perfect position paper in 10 steps...
How To Write a Position Paper
1. choose a topic that interests you.
Start with something you actually care about. If given the freedom, choose a subject that has personal meaning for you. Having real passion for the subject matter can be energizing as you dive into the research and it can infuse your writing with authenticity.
Many students like to write about controversial topics. Our study starters cover the top 25 controversial topics today .
2. Develop a Thesis Statement
Once you’ve got a subject, it’s time to define exactly where you stand on the issue. What is the point you hope to prove in your position paper? And how do you plan to prove it? If you’re not sure exactly where you stand, this is the starting point in your research. Find out what some of the leading thinkers, journalists, and public figures are saying on the subject. Which viewpoint resonates most with you? You should come away from this process with a thesis statement that both indicates your viewpoint and lays out the supporting points that will ultimately shape your essay. For instance, if you’re writing about a policy issue, your thesis might say something like “The newly proposed policy to ______ would be beneficial to the general public because it would ______, _________, and ________.
3. Identify Credible Sources
As you begin your research, it is absolutely critical that you identify only credible sources including primary sources, scholarly journals, and articles from legitimate news outlets. Of course, every source has its own implicit biases. But as you identify and use these sources, it’s your job to identify and recognize those biases. You can use a source provided by a politically biased think tank as long as you explicitly identify that bias. The most important thing you can do, as you gather resources, is ensure that they come from valid outlets , that you recognize any affiliations that might shape their perspective, and that you eliminate any sources that peddle in disinformation.
For more tips on how to do this, check out our article on How Students Can Spot Fake News .
4. Build Your Reference List
Now that you’ve identified credible resources, create your reference list. Citation is a building block of both the research process and the broader concept of academic integrity. As a student, you are expected to draw on the findings of those who came before you. But you have to credit those scholars in order to do so. Make sure you adhere to the formatting style indicated by your academic institution, course, and instructor , whether you are required to write in MLA, APA, Chicago, or its exotic-sounding twin, Turabian. Purdue’s website provides one of the more reliable style guides for your formatting reference needs .
We have a database to help you find influential scholars in a variety of subjects. We also point out influencers related to nearly 30 of the most controversial topics
5. Do Your Research
This step is all about gathering information. Now that you’ve locked in your sources, it’s time to dive deeper. If you enjoy learning new things, this is the fun part. Get comfortable and start reading. Research is the process of discovery, so take your time. Allow yourself to become absorbed in the subject matter, to be immersed, to lose yourself in the information. But come up for air every once in a while so you can take notes. Gather the ideas, statistics, and direct quotes from your research that ultimately strengthen your argument. And don’t shy away from information that contradicts your argument either. This is meant to be a learning process, so allow your position on the subject to evolve as you are presented with new information. The thesis that you’ve written is a starting point, but it’s not set in stone. If your research leads you in a different direction, don’t be afraid to refine or even revise your thesis accordingly.
6. Outline Your Position Paper
Now that your thesis has been reinforced by research, create a basic outline for what you’ll be writing . If you do this part correctly, the rest should simply be a process of filling in the blanks. Below is a basic framework for how you might structure a position paper:
- Introduction
- Setting up the subject
- Thesis Statement
- Basic Argument
- Identification of Supporting Evidence
- Supporting Evidence 1
- Explanation
- Supporting Evidence 2
- Supporting Evidence 3
- Counterpoint
- Identification of Opposing Viewpoint(s)
- Refutation of Opposing Viewpoint(s)
- Reiterate Thesis
- Tie Together Supporting Arguments
7. Build Your Argument
The outline above is merely a framework. Now it’s up to you to infuse that framework with your personality, your perspective and your voice. Your thesis and supporting quotes are the bones of your essay, but you’ll be adding the flesh to those bones with your set ups and explanations. This is your chance to explain why the evidence located in your research makes you feel the way you do. Remember, you are writing a fact-based essay on something that should trigger emotions in both you and the reader. Do not be afraid to lean into these feelings for your writing, as long as you keep those feelings strongly grounded in the facts of the case.
8. Address the Counterpoint
No argument is complete without recognition of its counterpart. Your willingness to acknowledge opposing viewpoints is a show of faith in your own argument. This gives you a chance to provide an honest appraisal of an opposing viewpoint and to confront this appraisal with fact-based refutation.
9. Tie It All Together
Now that you’ve spent your time fully immersed in the argument, it’s time to pull the pieces together. Revisit your introduction. Your opening paragraph should be crisp, engaging, and straight to the point. Don’t bury the lead. The purpose of your essay should be stated early and clearly. Likewise, build a concluding section that offers a compelling way of restating the thesis while incorporating some of the new things we’ve learned from reading your essay. Tie your various supporting arguments together to illustrate that we have all learned enough to agree with your initial position. And revisit each of your supporting paragraphs to ensure that each idea logically flows into the next. Write natural segue sentences between paragraphs and ensure that the connection between each supporting argument and your thesis is clear .
10. Proof, Edit, Revise, Repeat
Now you’ve assembled an essay, but it needs work. That’s not an insult. Anything ever written always needs work. Start with proofing. Look for typos, grammatical errors and incomplete sentences. Give your essay a technical cleaning. But you should also read for style, tone and substance. Does your argument hang together? Is it compelling? Do you adequately prove your point? You may find that this is an opportunity to trim gratuitous information or to add supporting information that might strengthen your argument. And as you revise your essay, try reading your work out loud. Hearing your own words out loud can reveal areas where your point might not come across as clearly. Spend as much time as you need on this step. Don’t be afraid to make substantive changes during this process. Invariably, your final draft will be significantly stronger than your rough draft.
And I’ll leave you with just one more thought-one that has always helped me as a writer. This tip comes from author Henry Miller’s famous 11 Commandments of Writing . Among the numerous valuable tips you can draw from his list, my personal favorite says “Don’t be nervous. Work calmly, joyously, recklessly on whatever is in hand.”
This is great advice at any stage in your writing career. Dive in and write fearlessly.
And now that you’ve got a step-by-step roadmap for attacking your position paper, get more valuable tips, tricks, and hacks from our comprehensive collection of Study Guides and Study Starters .
And if you are struggling with how to take effective notes in class, check out our guide on note taking .
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Write a Position Paper
Last Updated: March 22, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Emily Listmann is a Private Tutor and Life Coach in Santa Cruz, California. In 2018, she founded Mindful & Well, a natural healing and wellness coaching service. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. Emily also received her Wellness Coach Certificate from Cornell University and completed the Mindfulness Training by Mindful Schools. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 258,387 times.
Just like an argument paper, a position paper supports one side of an issue, similar to in a debate. Your goal will be to provide convincing evidence to the reader that your position is the correct stance to take on an issue. You can write a great position paper by choosing your position carefully, developing your argument, drafting your paper, and revising and editing your work.
Position Paper Outline and Example

Choosing Your Position

- For example, you wouldn’t want to write a paper arguing that children need proper care, as no one would disagree with that stance.
- A better topic may be taking a stance on what should be done if children are not receiving proper care.

- Visit your local library to find books, journals, and newspapers.
- Access online databases, credible websites, and news sources.
- To decide if a source is credible , look for peer-reviewed journals, check the credentials of the author, locate the information in two separate sources, and check the date to make sure the information is the most recent available. You should also avoid self-published sources.

- Looking at both sides not only helps you pick the best position, it will also help you choose a good counterargument. [3] X Research source
- For example, if you are writing a paper about whether or not your community should invest in new park equipment, your two sides would be either in favor of the new park equipment or against it. A pro of buying new equipment might be purchasing safer equipment, while a con would be the expense of the purchase.

- In some cases, it’s easier to argue a position if you don’t have strong opinions either way. This is because you can focus on the evidence, not on your personal views.

- While you don’t have to change your position to fit your audience, you may want to adjust your reasons behind the position or the counter-argument you choose.
Building Your Argument

- If possible, look for supporting reasons that are shown through 2 or more different pieces of evidence, as this will make your argument stronger.
- Use your assignment sheet or the parameters of your paper to determine how many supporting reasons you should include. For many academic papers, you will use 2 to 3 reasons.

- Use an organizing strategy that works for you.
- Compiling your evidence now will help you more easily write your paper.
- Keep in mind that it is important to cite your sources. If you use a direct quote from a source, then put it into quotation marks and identify the author when you use it. If you paraphrase or summarize something from a source, give credit to the author for the ideas.
- Don’t go overboard on including evidence! Remember that most of the ideas in the paper should be your own. It’s good to quote sources, but avoid quoting entire paragraphs from other sources. Keep your quotes to a sentence or two and try to avoid including more than one quote per paragraph.

- For example, if you are writing a position paper arguing that your community should purchase new playground equipment, your counter-argument could be that the purchase will be too expensive. To strengthen your argument, you would cite this possible point against you but show why it's not a valid reason to dismiss your position. A good way to do that would be to show that the equipment is worth the expense or that there is outside funding to pay for it.
- You will also want a piece of evidence that supports your counter-argument. This evidence, which should be easy to dismiss, will be included in your paper.
Drafting Your Paper

- One easy way to set up your argument in your thesis is to include both your counter-argument and claim, preceded by the word “although.” For example, “Although installing new playground equipment in the park will be expensive, new playground equipment would provide a safe play area for children and offer options for special needs children.”
- If you’re an expert writer, you may not need to include supporting reasons in your thesis. For example, “As parents learn the benefits and dangers of outside play, communities across the nation are turning their eyes toward their parks, making safe, accessible equipment a public necessity.” [11] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Start with a hook that introduces your topic. For example, you could provide a statistic of how many children are injured on old playground equipment every year.
- Include a few sentences that provide more information on your topic, narrowing down toward your stance.
- End your introduction with your thesis.

- Follow the requirements for your paper, which may state how many paragraphs you should include.

- For example, you could write: “Installing new playground equipment would make the park more inclusive for special needs children because updated designs are accessible to those who are disabled.”

- Documented stories

- Without commentary, there is no link between your evidence and your position, leaving your argument weak.

- Restate your thesis. For example, "While new playground equipment is expensive, it's worth the investment because it serves the best interests of the community by providing children with a safe area to play and making the park more accessible for special needs children."
- Sum up your argument.
- End on a high note with a call to action. For example, "Children need a safe, accessible place to play, so the only choice is to install new park equipment in Quimby Park."

- If you don’t cite your sources, then you will be guilty of plagiarism. You could lose credit or face harsher penalties if you are caught stealing someone else’s words or ideas.
Revising and Editing Your Paper

- Before you change a word, re-read the sentence to make sure that the new suggestion fits. The spell checker may think that you mean one thing, while you really mean something else.

- Waiting at least a day is best. If you are short on time, wait at least 30 minutes before reviewing what you’ve written.

- If possible, have a friend or mentor read your paper and suggest edits or revisions.

- Combine short, choppy sentences, and break up long sentences.
- Fix sentence fragments and run-ons.

- If possible, ask a friend or mentor to proofread your final draft. They may be able to spot errors that you don’t see.

- If you are presenting or turning in a printed paper, check to see if you should place it in a presentation folder.
Community Q&A
- Avoid using the words “I” and “you” in your thesis. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 0
- Make sure that you stay focused on your claim throughout your paper and that all of the evidence you present in the paper is supporting your claim. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0

- Give credit when you use someone else's opinion, statistics, facts or quotations. Avoid plagiarism by referencing and citing your sources. Thanks Helpful 10 Not Helpful 3
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-position-paper
- ↑ https://www.cs.rutgers.edu/~rmartin/teaching/fall15/Writing_a_Position_Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://www.nmun.org/assets/documents/nmun-pp-guide.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://bowiestate.libguides.com/c.php?g=442189&p=3014828
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-12-peer-review-and-final-revisions/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/proofreading
About This Article

If you need to write a position paper, choose a topic that has at least 2 clear sides, then pick one of those sides as your position. Gather research from books, newspapers, academic journals, online databases, and other credible sources, making sure to cover your own position and at least one opposing side. Open your paper by stating your claim, or the position you have taken, then offer at least 2 pieces of evidence to support that stance. Identify and dismiss a counter-argument to your position as well. For tips on how to use topic sentences to link your paragraphs to your thesis, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Hannah Curry
May 22, 2018
Did this article help you?

Aug 17, 2016
Mitra Mohamadzadeh
Jan 30, 2018
Jul 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
What Is a Position Paper – Free Writing Guide for Beginners

Academic writing covers all course units in the form of different essay types. A position paper is a type of essay where the writer provides concrete opinions relating to a certain study. The writer can express their own opinion or from another credible source. These essays are applicable in various fields such as academics, law, and political affairs, among other disciplines.
Since this assignment focuses on argumentation, most students might find it challenging to develop exceptional essays. Writing it well needs intense planning, research, and meticulous writing skills. That is why college students turn to professional services to get expert assistance.
This article discusses essential aspects that offer insight into how to write a position paper and things to consider to get remarkable results.
Table of Contents
5 Things to Consider Before Writing a Paper
What is a position paper ? It is imperative to comprehend its definition before we embark on the writing phase. Learners often think that a position paper is a regular report, but it comprises one-sided argumentation from the writer’s perspective.
Express your standpoint to the readers through adequate research and presentation of findings from other published works.
However, before you embark on the writing phase, below are a few factors you must consider to compose a remarkable product.
Understand the Topic
Read the essay question carefully to understand the paper’s expectations. Ensure you comprehend the topic before you pick an argumentative side. If you don’t understand the topic, you might argue irrelevant points that might jeopardize your entire paper.
Research Sources
Conducting extensive research is a crucial aspect that allows you to get relevant resources. It is essential to have an arguable topic with a broad perspective. You can use online sites, the public library, or other available resources.
Intend Audience
Who are the target readers? Having the audience in mind will help you compose relevant opinions that will convince them to back your perspective. Make sure you also know where the audience stands.
Pick Your Standpoint
It is essential to choose a standpoint after reading through the essay question. Picking a stand will allow you to organize your thoughts and see whether they are sufficient to back your arguments.
Deliberate Arguments
Evaluate the argument thoroughly and weigh the upsides and downsides. Make sure your stand has strong arguments to give you the upper hand in persuading the audience.
Position Paper Example – Get Creative First
A position paper example, in this case, will help you learn more about the contents of each section. It would help if you organized you articulated your thoughts in a logical and transitional flow to ensure your readers follow through with the entire text.
Below is a guideline to use as an example when composing a position paper.
1. Introduction
- Topic introduction
- Background information
- Thesis statement
2. Body Paragraphs
- Counter argument
– Supporting evidence
– Refute counter-claims
– State your argument with evidence
- Your perspective
– Present your opinion
– Evidence
– Reliable resources
3. Conclusion
- Summarize main arguments
- Offer solutions
- Avoid adding new information
Position Paper Format: APA, MLA, and Other Styles Explained
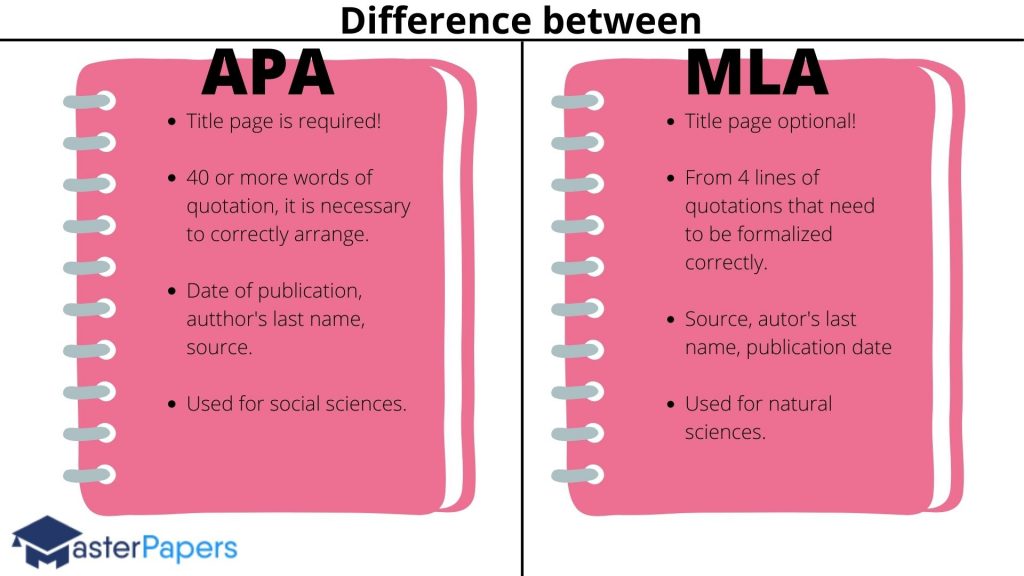
Academic writing has various formatting styles that students must learn to incorporate in the various essays. How do you know the required style? Usually, the essay instructions have the specified format expected from the students. Therefore, if you are unsure, you can consult with your tutor on the required formatting style. The most common styles are APA, MLA, and Chicago formatting styles. Each style is unique and has subtle differences from the rest.
When citing a position paper, format APA is usually recommended by scholars. In this style, you start with the author’s name, publication year, title name, location, and publisher’s name. You must note the comma, full stop, and semi-colon placements to avoid compromising the citation rules.
It is imperative to learn more about the formatting styles to know which style is the best for a particular essay.
How to Start a Position Paper Like a PRO
Starting any academic paper is a tricky section since it is critical to determining its direction. Therefore, students must know how to start a position paper to capture to keep it interesting.
The first step is to introduce your topic with captivating hook sentences that inform the audience about the topic. Research comprehensively and come up with background information about the research issue and explain why the investigation is essential. Not forgetting to formulate a relevant thesis statement to guide the audience.
To engage readers, your introduction sentence can be in a question form that invokes curiosity. You can also add a thought-provoking statement that leaves the reader with an excellent first impression. Or a quote from a reputable scholar that relates to the research topic.
The body comprises three to five paragraphs with the arguments. You can start the body paragraph by generating the counter-arguments first. You can do this by stating what people who disagree might say about your position. Present your arguments and disprove the counter-claims objectively with factual information. For each argument, ensure you provide supporting evidence from reliable sources.
Finally, compose a conclusion paragraph that reiterates your main argument and offers a recommendation. However, don’t introduce new ideas or arguments in this section.
If you are still stuck and don’t know how to write a position paper , you can seek professional help from our academic experts. We guarantee you top-notch essays that will score you top-of-the-class grades.
FAQ on How to Write a Position Paper
Read the detailed FAQs below to help you make an informed decision about our writing services.
How do you start an introduction for a position paper?
Make sure you capture the readers’ interest by using hook sentences. You can pose a captivating question, interesting quote, or introduce a strong declaration that will evoke curiosity to continue reading the essay.
How do you outline a position paper?
A position paper is similar to a standard academic paper. It has an introduction section that reveals your position, which captures several arguments, and the conclusion section summarizes the major research points.
How important is the position paper in an academic setting?
Position papers are significant in academics because it helps students discuss different topics without having the original research. It presents various opinions and perspectives with supporting evidence of the subject matter.
Why is it essential to make a reliable position paper?
It is vital to craft an accurate paper with factual information because the primary purpose is to persuade the readers to understand your opinion through your arguments.
Don’t Understand a Thing? Contact Us for Help!
Need help to write an outstanding position paper? You are on the right platform. We have dedicated experts working round the clock read to deliver flawless papers. Excellence is a paramount aspect of our service since we guarantee exceptional essays that will score you super grades.
If you are still asking yourself, “what is the purpose of a position paper?” then you need immediate academic assistance. Why stress yourself with detailed research and argument presentation? We hire skilled authors with years of experience in the academic writing industry. Each writer writes the orders from scratch without lifting content online. Therefore, you will submit 100% original essays without a doubt.
All you have to do is reach out to us, and we will match you with a qualified writer to help you compose a top-notch paper. Contact us now and transform your grades.

15% OFF Your first order!
Aviable for the first 1000 subscribers, hurry up!
You might also like:

150 Qualitative and Quantitative Nursing Research Topics for Students

Why You Should Read a Data Gathering Procedure Example

What Is Culture and What Are Some Popular Culture Essay Topics?
Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Paper titles: inform by stating your topic and position; grab the reader’s interest if you can.
Jerz > Writing > Academic [ Argument | Title | Thesis | Blueprint | Pro/Con | Quoting | MLA Format ]
An effective research paper title will
- identify the limited subject of the essay, and
- the position the paper takes on the subject.

Your title is your first opportunity to persuade your reader. Don’t waste it.
| Essay 1 | |
| That’s not a paper title, it’s just a label. Your instructor already knows what the homework is; your instructor will be reading the title to find out what position your paper is doing to defend. | |
| The Social Value of Television | |
| The above at least identifies the topic, but it’s weak because it doesn’t identify the position the author is going to take. | |
| The Social Value of Television: Smith’s Microcommunities from “Appointment TV” to “Binge-watching” | |
| This title is more informative; if your instructor simply wants you to list what you’ve learned, then this title might be fine. But if your instructor has asked you to defend a position, this title doesn’t even hint at what position this paper will take. (On the most basic level, will this paper or with Smith’s position on the relationship between microcommunities and the social value of television?) | |
| How Smith’s Microcommunities Elevated the Social Value of Television (1980s-2010s) | |
| Television’s Surprising Endurance Disproves Smith’s Microcommunity Model | |
| Either of these will work. Note that simply mentioning that the paper will talk about the social value of television and Smith’s concept of microcommunities is vague; there are a limitless number of creative ways that an intelligent student could work with those two subjects. | |
| Hamlet and Macbeth: Similarities and Differences | |
| My freshman year in college, I actually turned this in as the title of a paper. My argument was that as Hamlet’s plot descended into tragedy, Hamlet became more human, while as Macbeth’s plot unfolded, Macbeth became less human. | |
| Tragic reversal: Macbeth’s tragic fall mirrors Hamlet’s tragic ascent | |
| That would have been a much better title for the paper I described above. | |
6 thoughts on “ Paper Titles: Inform by Stating your Topic and Position; Grab the Reader’s Interest If You Can ”
Our topic is “Euthanasia should be legal”. What could be title for this?
Our topic is about Complicated Pregnancy. How can we title this?
That depends on what your assignment is. I won’t be grading your paper, so I’m not in a position to give you specific advice. If your instructor simply wants you to summarize information accurately, then simply stating the topic is fine. I expect my students to do more than summarize the “correct answer”. I expect them to take a position on a topic worth debating, and use evidence to defend a particular position. So I would ask my students to write a title that specifies what position they are taking on their stated topic.
AJ, take a look at the title of this page and give it a try.
My topic is about legalizing divorce because here in our cuontry we don’t have divorce, What would be a good title for this?
RT @DennisJerz: Essay Paper Titles: Inform by Stating your Topic and Position; Grab the Reader’s Interest If You Can https://t.co/Qr1jpo9Ccj
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Title Page Setup
A title page is required for all APA Style papers. There are both student and professional versions of the title page. Students should use the student version of the title page unless their instructor or institution has requested they use the professional version. APA provides a student title page guide (PDF, 199KB) to assist students in creating their title pages.
Student title page
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
Title page setup is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 2.3 and the Concise Guide Section 1.6
Related handouts
- Student Title Page Guide (PDF, 263KB)
- Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3MB)
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names | Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Cecily J. Sinclair and Adam Gonzaga |
| Author affiliation | For a student paper, the affiliation is the institution where the student attends school. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author name(s). | Department of Psychology, University of Georgia |
| Course number and name | Provide the course number as shown on instructional materials, followed by a colon and the course name. Center the course number and name on the next double-spaced line after the author affiliation. | PSY 201: Introduction to Psychology |
| Instructor name | Provide the name of the instructor for the course using the format shown on instructional materials. Center the instructor name on the next double-spaced line after the course number and name. | Dr. Rowan J. Estes |
| Assignment due date | Provide the due date for the assignment. Center the due date on the next double-spaced line after the instructor name. Use the date format commonly used in your country. | October 18, 2020 |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Professional title page
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the professional title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names
| Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Francesca Humboldt |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals after author names to connect the names to the appropriate affiliation(s). If all authors have the same affiliation, superscript numerals are not used (see Section 2.3 of the for more on how to set up bylines and affiliations). | Tracy Reuter , Arielle Borovsky , and Casey Lew-Williams | |
| Author affiliation
| For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author names; when there are multiple affiliations, center each affiliation on its own line.
| Department of Nursing, Morrigan University |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals before affiliations to connect the affiliations to the appropriate author(s). Do not use superscript numerals if all authors share the same affiliations (see Section 2.3 of the for more). | Department of Psychology, Princeton University | |
| Author note | Place the author note in the bottom half of the title page. Center and bold the label “Author Note.” Align the paragraphs of the author note to the left. For further information on the contents of the author note, see Section 2.7 of the . | n/a |
|
| The running head appears in all-capital letters in the page header of all pages, including the title page. Align the running head to the left margin. Do not use the label “Running head:” before the running head. | Prediction errors support children’s word learning |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
| {{item.snippet}} |
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
An academic title is probably the first thing your readers will experience about your paper. This handout will show you two approaches to creating paper titles, one that is more informative, and another that is more creative. The first is most often used for formal academic papers. The second is more likely to be used for narratives or personal essays, but it can sometimes be used for academic papers as well.
General Considerations
Before deciding on a title, be sure to think carefully about your audience. Who will be reading this paper and what are their motivations? Do they want to be entertained? Are they concerned with acquiring information as clearly and concisely as possible? How do you want your reader to feel about the content of your paper? Asking questions such as these will help you determine the appropriate tone for your title.
A great academic title should tell your readers as much as possible about your paper’s central claim and its significance. Good titles often include:
- A set of key terms
Approach #1: Titles for Academic Papers
Good academic titles reveal not only the topic of the paper but some idea of your specific approach, argument, and area of discussion. Here are some typical and useful academic titles:
- Good Bye Lenin!: Free Market Nostalgia for Socialist Consumerism
- The Artful Thunder as Dramatic Technique in Shakespeare’s The Tempest
The Effects of Light and Temperature on the Growth of Populations of the Bacterium, Escherichia coli
“The Machine-Language of the Muscles”: Reading, Sport and the Self in Infinite Jest
Though representing a range of disciplines, each of these titles is clear, independent and self-explanatory. Notice how each title is relatively long and contains multiple phrases. Academic writing is complex and demands equally complex and purposeful titles. If you look carefully at the sample titles, you will notice that each has three separate elements:
- The hook – This is a creative element that draws in the reader. Typically this is a catchy, readable phrase that advertises the paper’s specific subject. The hook is sometimes a direct quotation from a text or a sudden introduction of a new and exciting element of your topic.
- Key terms – These are crucial words or phrases that are indispensable to the topic at hand. In academic writing, scholars are often asked to identify a few select terms that will identify their paper in an index. Similarly, the use of key terms in a paper’s title will make the paper more searchable in a database. You want to load your title with important terminology as a way to orient the reader to the concepts under discussion in the paper to follow. The best titles are like very brief summaries of the paper itself.
- The source – Sometimes called a “location,” this is the place in the title where the concepts under discussion are to be found. Depending on the discipline, your source might be a piece of writing, the name of a text, a geographical place, a person, an existing debate, an organism, and so on.
Good titles never state the obvious nor do they apply a generic label to a paper. Titles like “Paper #1” or “Lab Report” are clearly too general and unhelpful. Similarly, titles that rely too much on large abstractions are not welcome: “Society and its Many Problems.” In this title the reader has no idea which society is under discussion, what the particular problems may be, or why this is at all current and significant. Avoid clichés at all costs as well: “A Picture is Worth a Thousand Words”. This title is virtually meaningless. If it feels like a common title to you, it will likely seem as common to another reader. Remember, the assignment may be given by the instructor, but the title is your first chance to make the paper your own. Remember also to center your title at the top of your first page of your text. Use the same font and size as the rest of your paper.
Analyzing an Example of an Academic Paper Title
Consider this title from above:
This title’s parts are all clearly visible. The hook is a direct quotation from the novel under discussion, a well-chosen particular that advances an important theme in the novel. The next part: “Reading, Sport and the Self” contains the title’s key terms. The title is making a promise here to the reader that the paper will engage these three critical concepts. Finally we see the source of the title, prompted by the preposition “in”. Someone reading this title or searching for it in a database would easily identify it as a study of a particular book, in this case, a novel by David Foster Wallace, which is concerned with the ideas of reading, sport and the self. In the humanities, you will often see writers divide their titles into two distinct parts, as in this example, marked by a colon that allows the hook to introduce the rest of the title.
Here is another example, this time from the sciences:
Science writing rarely uses a hook in the same way as papers in the humanities. The hook in a science paper is often simply a highly relevant but exciting and direct introduction of a new approach or discovery. What you mostly find in science writing titles is a catalog of key terms that corresponds directly to the paper’s thesis, significance and methods. Here we see a number of key terms: light, temperature, growth, and the bacterium itself. This title would be highly searchable and is very informative. The final part is the source which simply and clearly identifies the bacterium under discussion.
Approach #2: Titles for Narrative and Personal Papers
Being simple and clear can be very useful in a formal academic essay, but what if you aren’t writing an analytical paper? How do you write a title for a personal essay or statement? How about a title for that English paper that asks you to write a narrative or share an observation? These types of papers might well demand titles that simply sound interesting and creative rather than strictly academic.
In these cases you may want to use an interesting phrase from your paper. Perhaps there is a humorous or dramatic anecdote you offer in your creative paper that sums it all up. Perhaps there is a quotation or phrase that could serve as the title. In these cases you simply want to interest the reader by making the paper seem unique. Here is your opportunity to really put your stamp on the paper and to intrigue the reader. Here are some interesting and intriguing titles for creative essays:
“Why I Screen My Calls” “The Week of Rental Car Disasters” “My Son, the Burglar, Revisited” “What’s So Wrong with the Brady Bunch?”
Each of these titles is provocative. The first two offer the agenda for the paper; presumably you will learn the hilarious and awful history behind each title by reading the paper. The final two titles depend on humorous and contrary bits of information: a father writing about his burglar son, which seems at odds with what we might expect a father to write about his son (and in this case “revisited” is a provocative word since perhaps the son has burgled again). The Brady Bunch title is also funny because it promises a defense of an unexpected position or at least an eminently arguable one, which makes it an intriguing paper title.
In Practice
Imagine you are a student writing a paper for a class on animal behavior. You have a particular species to study, you have done the field work, and you have some conclusions to offer. Here is your first attempt: “Monkey Behavior”.
This is very general and tells us nothing about the kind of monkey or a particular behavior. It does little to attract the reader.
Your second attempt is a little better: “The Effects of Sugar on Monkey Behavior”.
This title is a little clearer and even mildly amusing. Now, at least we have some idea of a cause and an understanding of some important concepts. But can you be more specific? Wouldn’t it make sense to add more key terms from the paper itself? Readers already can conjecture that sugar would have some effect on monkey behavior, so this title needs to be less mysterious and more precise. Here is a better academic title:
“Sugar Stimulates Intensity of Tail-Twitch Social Behavior in Panamanian Monkeys”
Now you have a title that is full of specific key terms, includes a clear location, and provides a bold and specific claim before the text of the paper begins. This is incredibly helpful to your readers.
Try your hand at creating an academic title for a paper with the following topic:
“Write a 5-7 page paper analyzing any work of the author and illustrator Dr. Seuss. You may make reference to one or more of his books, but you must analyze the text(s) based on at least one of the following: Seuss’s use of metaphor, imagery, symbolism, or rhyme. You must also make a connection between this device and his drawing technique or subject matter. Use quotes to support your argument.”
HINT: This is a tough (though potentially interesting) assignment prompt, but remember the three parts of the academic title: hook, key terms, and source. Your hook could be a quote, perhaps a direct quote that shows either metaphor, imagery, symbolism or rhyme. This would be a smart move because you would reveal in the title which of the four options you chose for the paper topic. In other words, by quoting, you would already have an example before you introduce your argument. Your key terms would likely be lifted from the assignment prompt itself (metaphor, imagery, etc. . .). The source would be just that: the name of the book you chose to explore.
Now challenge yourself to make a creative title for this paper. The possibilities are endless here. Think in terms of being clever and witty and actually making use of the terms and techniques the assignment asks you to consider.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback
APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
In APA Style (7th edition), the cover page, or title page, should include:
- A running head (professional papers only) and page number
- The title of the paper
- The name of the author(s)
- The institutional affiliation
- An author note; optional (professional papers only)
- A student paper should also include course information
Note : APA 7 provides slightly different directions for formatting the title pages of professional papers (e.g., those intended for scholarly publication) and student papers (e.g., those turned in for credit in a high school or college course).
Professional paper APA title page
Student paper APA title page
Formatting an APA title page
Note : All text on the title page should be double-spaced and typed in either 12-point, Times New Roman font. In the 7th edition, APA increaded the flexibility regarding font options: which now include Calibri 11, Arial 11, Lucida Sans Unicode 10, Times New Roman 12, or Georgia 11. All words should be centered, and capitalize the first letter of important words.
Running Head
In the 7th edition of the APA style manual, running heads are only required for professional papers that are being submitted for publication (student papers do not require a running head, but still need a page number).
Your title page should contain a running head that is flush left at the top of the page and a page number that is flush right at the top of the page.
Place the running head in the page’s header:
- The running head is the abbreviated title of the paper (IN UPPERCASE LETTERS) aligned left on the page header of all pages, including the title page. APA (7th edition) guidelines require that running heads be a maximum of 50 characters (spaces count as characters).
- The “Running head:” label used in the APA sixth edition is no longer used.
- Place the page number in this same header, but align right, beginning with page number 1 on the title page.
- This header should be 1 inch from the top. Some instructors allow for 1/2 inch, too, but the default is 1 inch.
Paper Title
Position the title of the paper in the upper half of the page. The title should be centered and written in boldface, and important words should be capitalized.
The APA recommends that your title should be a maximum of 12 words and should not contain abbreviations or words that serve no purpose.
Author Name(s)
Institutional affiliation.
Position the school or university’s name below the author(s) name, centered.
A student paper should also include the course number and name, instructor name, and assignment due date.
Further Information
- APA Student Title Page Guide
- APA Referencing
- How to Write a Lab Report
- Essay Writing Guide for Psychology Students
- APA Style Citations & References
- Example of an APA Formatted Paper
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
| Essay type | Skills tested | Example prompt |
|---|---|---|
| Has the rise of the internet had a positive or negative impact on education? | ||
| Explain how the invention of the printing press changed European society in the 15th century. | ||
| Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself. | ||
| Describe an object that has sentimental value for you. |
In high school and college, you will also often have to write textual analysis essays, which test your skills in close reading and interpretation.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, textual analysis essays, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of essays.
An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement —a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations ) and analysis.
Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic. This is the most common type of essay at college level—most papers you write will involve some kind of argumentation.
The essay is divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion:
- The introduction provides your topic and thesis statement
- The body presents your evidence and arguments
- The conclusion summarizes your argument and emphasizes its importance
The example below is a paragraph from the body of an argumentative essay about the effects of the internet on education. Mouse over it to learn more.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a topic. It doesn’t require an original argument, just a balanced and well-organized view of the topic.
Expository essays test your familiarity with a topic and your ability to organize and convey information. They are commonly assigned at high school or in exam questions at college level.
The introduction of an expository essay states your topic and provides some general background, the body presents the details, and the conclusion summarizes the information presented.
A typical body paragraph from an expository essay about the invention of the printing press is shown below. Mouse over it to learn more.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
A narrative essay is one that tells a story. This is usually a story about a personal experience you had, but it may also be an imaginative exploration of something you have not experienced.
Narrative essays test your ability to build up a narrative in an engaging, well-structured way. They are much more personal and creative than other kinds of academic writing . Writing a personal statement for an application requires the same skills as a narrative essay.
A narrative essay isn’t strictly divided into introduction, body, and conclusion, but it should still begin by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the point of the story—what you learned from your experience, or why it made an impression on you.
Mouse over the example below, a short narrative essay responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” to explore its structure.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
A descriptive essay provides a detailed sensory description of something. Like narrative essays, they allow you to be more creative than most academic writing, but they are more tightly focused than narrative essays. You might describe a specific place or object, rather than telling a whole story.
Descriptive essays test your ability to use language creatively, making striking word choices to convey a memorable picture of what you’re describing.
A descriptive essay can be quite loosely structured, though it should usually begin by introducing the object of your description and end by drawing an overall picture of it. The important thing is to use careful word choices and figurative language to create an original description of your object.
Mouse over the example below, a response to the prompt “Describe a place you love to spend time in,” to learn more about descriptive essays.
On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green extending from the back of the house, and I sit on a lawn chair at the far end to read and relax. I am in my small peaceful paradise: the shade of the tree, the feel of the grass on my feet, the gentle activity of the fish in the pond beside me.
My cat crosses the garden nimbly and leaps onto the fence to survey it from above. From his perch he can watch over his little kingdom and keep an eye on the neighbours. He does this until the barking of next door’s dog scares him from his post and he bolts for the cat flap to govern from the safety of the kitchen.
With that, I am left alone with the fish, whose whole world is the pond by my feet. The fish explore the pond every day as if for the first time, prodding and inspecting every stone. I sometimes feel the same about sitting here in the garden; I know the place better than anyone, but whenever I return I still feel compelled to pay attention to all its details and novelties—a new bird perched in the tree, the growth of the grass, and the movement of the insects it shelters…
Sitting out in the garden, I feel serene. I feel at home. And yet I always feel there is more to discover. The bounds of my garden may be small, but there is a whole world contained within it, and it is one I will never get tired of inhabiting.
Though every essay type tests your writing skills, some essays also test your ability to read carefully and critically. In a textual analysis essay, you don’t just present information on a topic, but closely analyze a text to explain how it achieves certain effects.
Rhetorical analysis
A rhetorical analysis looks at a persuasive text (e.g. a speech, an essay, a political cartoon) in terms of the rhetorical devices it uses, and evaluates their effectiveness.
The goal is not to state whether you agree with the author’s argument but to look at how they have constructed it.
The introduction of a rhetorical analysis presents the text, some background information, and your thesis statement; the body comprises the analysis itself; and the conclusion wraps up your analysis of the text, emphasizing its relevance to broader concerns.
The example below is from a rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . Mouse over it to learn more.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Literary analysis
A literary analysis essay presents a close reading of a work of literature—e.g. a poem or novel—to explore the choices made by the author and how they help to convey the text’s theme. It is not simply a book report or a review, but an in-depth interpretation of the text.
Literary analysis looks at things like setting, characters, themes, and figurative language. The goal is to closely analyze what the author conveys and how.
The introduction of a literary analysis essay presents the text and background, and provides your thesis statement; the body consists of close readings of the text with quotations and analysis in support of your argument; and the conclusion emphasizes what your approach tells us about the text.
Mouse over the example below, the introduction to a literary analysis essay on Frankenstein , to learn more.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-types/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write an expository essay, how to write an essay outline | guidelines & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
The Economic Times daily newspaper is available online now.
Want a promotion 5 tips to strategically ask for a better job title.
A job title significantly impacts career growth, as it influences how hiring managers perceive your experience and skills. If responsibilities or pay change without a title update, valuable opportunities may be missed. Timing is crucial when requesting a title change.

Artificial Intelligence(AI)
Java Programming with ChatGPT: Learn using Generative AI
By - Metla Sudha Sekhar, Developer and Lead Instructor

Basics of Generative AI : Unveiling Tomorrow's Innovations

Generative AI for Dynamic Java Web Applications with ChatGPT

Mastering C++ Fundamentals with Generative AI: A Hands-On

Master in Python Language Quickly Using the ChatGPT Open AI

Office Productivity
Zero to Hero in Microsoft Excel: Complete Excel guide 2024

Vastu Shastra Course
By - Sachenkumar Rai, Vastu Shashtri

Data Science
SQL for Data Science along with Data Analytics and Data Visualization

Web Development
A Comprehensive ASP.NET Core MVC 6 Project Guide for 2024

Mastering Microsoft Office: Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and 365

Digital marketing - Wordpress Website Development
By - Shraddha Somani, Digital Marketing Trainer, Consultant, Strategiest and Subject Matter expert
Mastering Full Stack Development: From Frontend to Backend Excellence

Financial Literacy - TDS, Budget, Income Tax Act, GST, Indirect tax
By - CA Rahul Gupta, CA with 10+ years of domain experience, trainer

Business Storytelling Masterclass
By - Ameen Haque, Founder of Storywallahs
Future of Marketing & Branding Masterclass
By - Dr. David Aaker, Professor at Haas School of Business

HR & People Management
Human Potential and the Future of Employment
By - Lynda Gratton, Co-chair of the World Economic Forum Council on Work, Wages and Job Creation, Professor of Management Practice

ESG and Business Sustainability Strategy
By - Vipul Arora, Partner, ESG & Climate Solutions at Sattva Consulting Author I Speaker I Thought Leader

Financial Reporting and Analytics
By - Dr. C.P. Gupta, Professor: Department of Finance and Business Economics, University of Delhi

Performance Marketing for eCommerce Brands
By - Zafer Mukeri, Founder- Inara Marketers

Applying for jobs? Avoid these 5 mistakes while searching for openings

What companies want and students think companies want are vastly different, shows report

Surviving first day at work: A quick guide for freshers
Read More News on

How these paints, FMCG, and IT stocks can save your portfolio in a bear market

After a stellar stock market debut, what Bajaj Housing Finance has for long-term investors

Why fake satellite signals are a real threat to navigation systems in aviation, defence ops

Decoding Isha Ambani’s game plan for Reliance’s FMCG brands

Bajaj Housing may be the next HDFC, can investor returns match?

Stock Radar: Oberoi Realty breaks out of Symmetrical Triangle pattern; time to buy?
Find this comment offensive?
Choose your reason below and click on the Report button. This will alert our moderators to take action
Reason for reporting:
Your Reason has been Reported to the admin.

To post this comment you must
Log In/Connect with:
Fill in your details:
Will be displayed
Will not be displayed
Share this Comment:
Uh-oh this is an exclusive story available for selected readers only..
Worry not. You’re just a step away.

Prime Account Detected!
It seems like you're already an ETPrime member with
Login using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits
Log out of your current logged-in account and log in again using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits.
To read full story, subscribe to ET Prime
₹34 per week
Billed annually at ₹2499 ₹1749
Super Saver Sale - Flat 30% Off
On ET Prime Membership
Unlock this story and enjoy all members-only benefits.
Offer Exclusively For You
Save up to Rs. 700/-
ON ET PRIME MEMBERSHIP
Get 1 Year Free
With 1 and 2-Year ET prime membership
Get Flat 40% Off
Then ₹ 1749 for 1 year
ET Prime at ₹ 49 for 1 month
Market Savvy Offer
Get flat 20% off on ETPrime
90 Days Prime access worth Rs999 unlocked for you

Exclusive Economic Times Stories, Editorials & Expert opinion across 20+ sectors
Stock analysis. Market Research. Industry Trends on 4000+ Stocks
Get 1 Year Complimentary Subscription of TOI+ worth Rs.799/-
Stories you might be interested in
The Official Careers Website of the City of New York
D.A.T. Clerk
- Agency: DISTRICT ATTORNEY KINGS COUNTY
- Job type: Full-time
- Title Classification: No exam required
Job Description
The Kings County District Attorney's Office, located in the Metrotech area of Brooklyn, New York, is accepting applications for a Clerk position in its Early Case Assessment Bureau (ECAB). The Early Case Assessment Bureau (ECAB) screens all arrests that occur in Brooklyn, determining whether a prosecution will be declined or will go forward and if the latter, what charges will be brought. ECAB staff members interview police officers and, in some instances, victims and witnesses. The bureau drafts the charging document (i.e., the complaint) upon which the defendant will initially be arraigned, and prepares supporting documents and notices to be submitted in court. Duties: Prepare case folders for forwarding to court in accordance with established Unit schedule and guidelines Organize and maintain DA Office files, court papers and police records Assist D.A.T. Unit supervisor with the completion of paper work essential to closing out outstanding D.A.T. cases Answer, screen and route telephone calls Maintain supply of case files Provide general assistance and support services as required within the Unit
1. There are no formal education or experience requirements for this position. However, the ability to understand and carry out simple instructions is required. 2. Candidates must be able to understand and be understood in English.
The City of New York is an inclusive equal opportunity employer committed to recruiting and retaining a diverse workforce and providing a work environment that is free from discrimination and harassment based upon any legally protected status or protected characteristic, including but not limited to an individual's sex, race, color, ethnicity, national origin, age, religion, disability, sexual orientation, veteran status, gender identity, or pregnancy.
Civil service title
COMMUNITY ASSISTANT
Title classification
Non-Competitive-5
Business title
Posted until
- Experience level: Entry-Level
Number of positions
Work location
120 Schermerhorn St Bklyn Ny
- Category: Legal Affairs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Position Paper Topics. The argument or position essay is a standard type of writing exercise that almost everyone encounters at the high school or college level. This essay has two primary defining components: It has to be about an issue that people don't agree on. It focuses on disagreements about facts, definitions, causes, values, or solutions.
A position paper states a position and supports it through references to credible sources. An argumentative essay is similar, but it generally presents its position as an argument or question rather than as a statement. Here are a few examples of titles for both: Position paper: A Car-Free Campus Is Healthier for Everyone
A position paper is a kind of essay that clearly focuses on one side of an arguable point about an issue. It is similar to a debate and can also be identified as an argumentative paper. The main aim of the position paper is to persuade the audience that your argument or opinion is valid. Convincing the audience is not a piece of cake.
Position Paper. Definition: Position paper is a written document that presents an argument or stance on a particular issue or topic. It outlines the author's position on the issue and provides support for that position with evidence and reasoning. Position papers are commonly used in academic settings, such as in Model United Nations conferences or debates, but they can also be used in ...
4. Create an Outline. Once you have decided about the direction you're taking with your essay, proceed with the position essay outline. This step is often overlooked, but it will be much easier to find and correct mistakes and gaps at this early stage. So, writing a position paper outline actually saves you time.
A position paper requires three basic parts: an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Follow these seven steps to help write a position paper on any topic: 1. Choose a topic. In some classes or jobs, you can choose the topic of a position paper. If you're choosing your topic, consider ones relevant to your industry or academic interests.
Position Paper Outline Example. Every good position paper outline should start with writing a title for a research paper.Having done that, you can proceed with the outline. Notably, this kind of paper resembles an opinion essay, though, in the latter, you had to present two opposing opinions without necessarily sharing one of them.
Express your position idea. Focus on one specific aspect of the topic in order to express it in a one-sentence opinion. Make sure you have found a really arguable idea. If the topic cannot be debated, then it can hardly be used for writing a good position paper. Be precise in your statement.
5. Summarize your argument and restate your position. End your paper focusing on your argument and avoid the counter-arguments. You want your audience to walk away with your view on the topic being one that resonates with them. When you write a position paper, write with confidence and state your opinion with authority.
If you do this part correctly, the rest should simply be a process of filling in the blanks. Below is a basic framework for how you might structure a position paper: Introduction. Setting up the subject. Thesis Statement. Basic Argument. Identification of Supporting Evidence. Supporting Evidence 1.
End your introduction with your thesis. 3. Include at least 2 body paragraphs. A short position paper may only contain 2 body paragraphs - one for the counter-argument and one for the supportive points. However, most position papers will have 3 or 4 body paragraphs, with 2 dedicated to supportive evidence.
It would help if you organized you articulated your thoughts in a logical and transitional flow to ensure your readers follow through with the entire text. Below is a guideline to use as an example when composing a position paper. 1. Introduction. Topic introduction. Background information. Thesis statement. 2.
Position Paper Topics About Government, Law, and War. 5. Use of torture during war. Some people believe that using torture to elicit information from prisoners is cruel and inhumane. The opposition states that torture of prisoners of war is necessary in order to protect citizens.
Guidelines for essay titles in Chicago Manual of Style format. Chicago style also requires that essay titles be in title case. Other than that, Chicago style doesn't have specific guidelines for what a title should or shouldn't include. Here is an example of an essay title in Chicago style: 2021 Returns: What We Projected vs. Actual Returns
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
An effective research paper title will. identify the limited subject of the essay, and; the position the paper takes on the subject.; It may also be useful to grab the reader's interest with a brief quote or detail, but if your goal is to persuade your reader, your title will also need to inform.
A position paper (sometimes position piece for brief items) is an essay that presents an arguable opinion about an issue - typically that of the author or some specified entity. Position papers are published in academia, in politics, in law and other domains. The goal of a position paper is to convince the audience that the opinion presented is valid and worth listening to.
Writing effective headings. Although similar, headings are not the same as titles. Headings head paragraphs and help structure a document. Effective headings make your paper easily scannable. Common high level headings in dissertations and research papers are "Methods", "Research results", and "Discussion". Lower level headings are ...
In an argumentative essay, your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning. In an expository essay, you'll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn't have to include a strong opinion in this case ...
Paper title. Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize major words of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms.
Depending on the discipline, your source might be a piece of writing, the name of a text, a geographical place, a person, an existing debate, an organism, and so on. Good titles never state the obvious nor do they apply a generic label to a paper. Titles like "Paper #1" or "Lab Report" are clearly too general and unhelpful.
Formatting Rules. In APA Style (7th edition), the cover page, or title page, should include: A running head (professional papers only) and page number. The title of the paper. The name of the author (s) The institutional affiliation. An author note; optional (professional papers only) A student paper should also include course information.
Argumentative essays. An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement—a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations) and analysis.. Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic.
A job title significantly impacts career growth, as it influences how hiring managers perceive your experience and skills. If responsibilities or pay change without a title update, valuable opportunities may be missed. Timing is crucial when requesting a title change.
Organize and maintain DA Office files, court papers and police records Assist D.A.T. Unit supervisor with the completion of paper work essential to closing out outstanding D.A.T. cases Answer, screen and route telephone calls Maintain supply of case files Provide general assistance and support services as required within the Unit