How to write a process essay
- August 25, 2023
Process essays are one of the most common types of essays . It’s simply explaining a process of how to do something.
In this article, we’ll show you how to write a process essay in steps with interactive examples.
Process essay definition
Let’s take a look at the steps outlined below to write a clear and effective process essay.

Choose a topic
You should start by choosing a topic that not only interests you but also attracts your target audience.
Whether it’s brewing the perfect cup of coffee or conquering the art of origami, your topic should be engaging and well-defined. Let’s have a look at topic examples:
- Crafting Exquisite Miniature Bookbindings
- Building a Sustainable Vertical Garden
- Making the Perfect Cup of Coffee
So for this guide, I’ve chosen “Making the Perfect Cup of Coffee”. Now let’s continue with the next steps.
Create a process essay outline
Now that you’ve your topic at hand, it’s time to create an outline to present the steps chronologically. Outline will also help you organize your thoughts and ideas so you won’t get lost during the writing process.
Let’s examine this step with an example of a process essay explaining “Making the Perfect Cup of Coffee”.
Process essay outline example
- Thesis statement
- Provide safety precautions if necessary.
- Address to the reader
- Provide any variations or customization options if applicable.
- End with a memorable concluding thought or call to action.
By presenting the steps in chronological order, your readers can follow the process smoothly.
During this step, just make sure to:
- Expand on each step you outlined earlier.
- Use clear and concise language.
- Make use of bullet points or numbered lists to make the process visually appealing.
After completing the outline, it’s time to write an interesting introduction.
Write an introduction
- Hook the reader's interest with a hook sentence
- Offer a brief overview of the topic and its significance
- Introduce and explain the process with a thesis statement at the end of introduction
Process essay introduction example
Introduction
Now that we have an intro on our hand, you need to tell what materials you need to finish the process.
Write the materials needed for the process
Listing the necessary materials for the process is a best practice for process essays. Typically found just after the introduction, this paragraph is devoted to outlining the necessary materials.
Here, p rioritizing the list is important; the more influential a component is, the higher its position on the list should be.
Example material list for process essay
Body paragraphs
Materials needed
- High-quality coffee beans that align with your flavor preference.
- A grinder for optimal flavor extraction.
- Equipment for brewing methods, such as a pour-over apparatus, a drip coffee maker, a French press, or an espresso machine.
- Fresh and clean water for brewing.
- Optional additives like milk, cream, sugar, flavored syrups, or other preferred elements.
Start writing the process
Right after listing the materials needed, it’s time to start writing the process itself.
When describing your process, be careful not to make it too complicated. To keep your readers on track, use transitional words like “after,” “eventually,” “first,” “then,” and others help you maintain an understandable tone.
Or simply use a 1,2,3, bullet point structure as seen in example below to remind readers of their step during the process.
Body paragraphs - Process writing example
Materials needed ...
- Grind the beans just before brewing for optimal freshness. Use a burr grinder and adjust the coarseness to match your brewing method (coarse for French press, fine for espresso).
- Weigh your coffee grounds using a scale. A standard ratio is 1 to 2 tablespoons of coffee per 6 ounces of water, but adjust to your taste.
- Ensure the water is heated to the ideal temperature, typically between 195-205°F (90-96°C). Water that's too hot or too cold can affect the taste.
- Pay attention to the brewing time. Generally, 4-5 minutes is suitable for most methods, but again, adjust based on your preference.
- After finishing, regularly clean your coffee maker or French press to prevent rancid oils and residue from affecting your coffee's taste.
As seen from the example above, using an imperative language structure is generally preferable. It makes total sense as you’re describing a process in steps and usually don’t need a full sentence structure.
Give tips and supporting details
After explaining the process above, it’s now time to provide tips and supporting details. Here, make use examples, tips, and even warnings if necessary.
In other words, anticipate the questions your readers might have and address them as you go along.
Body paragraphs - Supporting details
Supporting details & tips
- Ensure safe handling of hot water and coffee-making equipment.
- Water that's too hot can result in over-extraction, while water that's too cold won't extract enough flavor.
Write a conclusion
At this step, you simply need to write a conclusion paragraph to end your process essay. First summarize the key points, and restate the process in a concise and short sentence. And finally, finish your process essay by a memorable sentence or a call-to-action.
Process essay conclusion example
Revise and polish your essay.
Now that you’ve written your essay, take a breath, and then come back for some editing. Check for consistency, correct sentence structure, efficient transitions , tense selection , and other linguistic issues that may arise.
If possible, make use of proofreading tools like QuillBot or Grammarly .
- Think about potential reader misunderstandings and address them. If needed, explain what should be avoided.
- Offer explanations for steps that might seem unusual or complicated.
- Define any unfamiliar terms or materials that the reader might not understand. This ensures clarity in your essay.
So you’ve successfully learned how to write a captivating process essay. Remember, practice makes perfect. The more you write, the better you’ll become.
Recently on Tamara Blog
How to write a discussion essay (with steps & examples), writing a great poetry essay (steps & examples), how to write a process essay (steps & examples), writing a common app essay (steps & examples), how to write a synthesis essay (steps & examples), how to write a horror story.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Learning Objectives
- Determine the purpose and structure of the process analysis essay
- Understand how to write a process analysis essay
The Purpose of Process Analysis in Writing
The purpose of a process analysis essay is to explain how to do something or how something works. In either case, the formula for a process analysis essay is the same. The process is articulated into clear, definitive steps.
Almost everything we do involves following a step-by-step process. From riding a bike as children to learning various jobs as adults, we initially need instructions to effectively execute the task. Likewise, we have likely had to instruct others, so we know how important good directions are—and how frustrating it is when they are poorly put together.
Writing at Work
The next time you have to explain a process to someone at work, be mindful of how clearly you articulate each step. Strong communication skills are critical for workplace satisfaction and advancement. Effective process analysis plays a critical role in developing that skill set.
The Structure of a Process Analysis Essay
The process analysis essay opens with a discussion of the process and a thesis statement that states the goal of the process. The organization of a process analysis essay is typically chronological. That is, the steps of the process are conveyed in the order in which they usually occur. Body paragraphs will be constructed based on these steps. If a particular step is complicated and needs a lot of explaining, then it will likely take up a paragraph on its own. But if a series of simple steps is easier to understand, then the steps can be grouped into a single paragraph.
The time transitional phrases provided earlier are also helpful in organizing process analysis essays (see in 4.2 Narration, Transitional Words and Phrases for Expressing Time and in 4.3 Illustration, Phrases of Illustration ). Words such as first , second , third , next , and finally are helpful cues to orient reader and organize the content of essay.
Self-Practice Exercise 4.5
H5P: Process Analysis Practice
Exercise Preamble
Choose a process to write about. Remember that you will need to clearly articulate all the necessary steps, so it should be a process you know really well. If you’re feeling stuck, here are some ideas:
- Tying a shoelace
- Parallel parking
- Planning a successful first date
- Being an effective communicator
Begin by listing all the steps you need to undertake to achieve this process. Be as detailed as possible and include everything at this stage. Point form is fine. Just get everything out — you can edit and revise at the next step.
Now, revise your list to put the points you have already articulate above in the order that makes the most sense for your process analysis
Thesis Statement
- What will the thesis statement of your process analysis be? Remember that it should articulate the goal of the process.
- Decide how many paragraphs you will need. Remember that the steps should be articulated in order, and that you can combine smaller steps, but more complex ones may need their own paragraphs. Make a note of what will be covered in each paragraph.
- What transition words will you use to show the connections between your ideas?
Writing a Process Analysis Essay
Choose a topic that is interesting, is relatively complex, and can be explained in a series of steps. As with other rhetorical writing modes, you should choose something you know well so that you can more easily describe the finer details about each step in the process. Your thesis statement should come at the end of your introduction, and it should state the final outcome of the process you are describing.
Body paragraphs are composed of the steps in the process. Each step should be expressed using strong details and clear examples. Use time transitional phrases to help organize steps in the process and to orient readers. The conclusion should thoroughly describe the result of the process described in the body paragraphs. See Appendix 1: Readings: Examples of Essays to read an example of a process analysis essay.
Key Takeaways
- A process analysis essay explains how to do something, how something works, or both.
- The process analysis essay opens with a discussion of the process and a thesis statement that states the outcome of the process.
- The organization of a process analysis essay typically follows a chronological sequence.
- Time transitional phrases are particularly helpful in process analysis essays to organize steps and orient reader.
ENGL Resources Copyright © by Tara Horkoff. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Encyclopedia for Writers
Writing with ai, the ultimate blueprint: a research-driven deep dive into the 13 steps of the writing process.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - Founder, Writing Commons
This article provides a comprehensive, research-based introduction to the major steps , or strategies , that writers work through as they endeavor to communicate with audiences . Since the 1960s, the writing process has been defined to be a series of steps , stages, or strategies. Most simply, the writing process is conceptualized as four major steps: prewriting , drafting , revising , editing . That model works really well for many occasions. Yet sometimes you'll face really challenging writing tasks that will force you to engage in additional steps, including, prewriting , inventing , drafting , collaborating , researching , planning , organizing , designing , rereading , revising , editing , proofreading , sharing or publishing . Expand your composing repertoire -- your ability to respond with authority , clarity , and persuasiveness -- by learning about the dispositions and strategies of successful, professional writers.

Table of Contents
Like water cascading to the sea, flow feels inevitable, natural, purposeful. Yet achieving flow is a state of mind that can be difficult to achieve. It requires full commitment to the believing gam e (as opposed to the doubting game ).
What are the Steps of the Writing Process?
Since the 1960s, it has been popular to describe the writing process as a series of steps or stages . For simple projects, the writing process is typically defined as four major steps:
- drafting
This simplified approach to writing is quite appropriate for many exigencies–many calls to write . Often, e.g., we might read an email quickly, write a response, and then send it: write, revise, send.
However, in the real world, for more demanding projects — especially in high-stakes workplace writing or academic writing at the high school and college level — the writing process involve additional steps, or strategies , such as
- collaboration
- researching
- proofreading
- sharing or publishing.
Related Concepts: Mindset ; Self Regulation
Summary – Writing Process Steps
The summary below outlines the major steps writers work through as they endeavor to develop an idea for an audience .
1. Prewriting
Prewriting refers to all the work a writer does on a writing project before they actually begin writing .
Acts of prewriting include
- Prior to writing a first draft, analyze the context for the work. For instance, in school settings students may analyze how much of their grade will be determined by a particular assignment. They may question how many and what sources are required and what the grading criteria will be used for critiquing the work.
- To further their understanding of the assignment, writers will question who the audience is for their work, what their purpose is for writing, what style of writing their audience expects them to employ, and what rhetorical stance is appropriate for them to develop given the rhetorical situation they are addressing. (See the document planner heuristic for more on this)
- consider employing rhetorical appeals ( ethos , pathos , and logos ), rhetorical devices , and rhetorical modes they want to develop once they begin writing
- reflect on the voice , tone , and persona they want to develop
- Following rhetorical analysis and rhetorical reasoning , writers decide on the persona ; point of view ; tone , voice and style of writing they hope to develop, such as an academic writing prose style or a professional writing prose style
- making a plan, an outline, for what to do next.
2. Invention
Invention is traditionally defined as an initial stage of the writing process when writers are more focused on discovery and creative play. During the early stages of a project, writers brainstorm; they explore various topics and perspectives before committing to a specific direction for their discourse .
In practice, invention can be an ongoing concern throughout the writing process. People who are focused on solving problems and developing original ideas, arguments , artifacts, products, services, applications, and texts are open to acts of invention at any time during the writing process.
Writers have many different ways to engage in acts of invention, including
- What is the exigency, the call to write ?
- What are the ongoing scholarly debates in the peer-review literature?
- What is the problem ?
- What do they read? watch? say? What do they know about the topic? Why do they believe what they do? What are their beliefs, values, and expectations ?
- What rhetorical appeals — ethos (credibility) , pathos (emotion) , and logos (logic) — should I explore to develop the best response to this exigency , this call to write?
- What does peer-reviewed research say about the subject?
- What are the current debates about the subject?
- Embrace multiple viewpoints and consider various approaches to encourage the generation of original ideas.
- How can I experiment with different media , genres , writing styles , personas , voices , tone
- Experiment with new research methods
- Write whatever ideas occur to you. Focus on generating ideas as opposed to writing grammatically correct sentences. Get your thoughts down as fully and quickly as you can without critiquing them.
- Use heuristics to inspire discovery and creative thinking: Burke’s Pentad ; Document Planner , Journalistic Questions , The Business Model Canvas
- Embrace the uncertainty that comes with creative exploration.
- Listen to your intuition — your felt sense — when composing
- Experiment with different writing styles , genres , writing tools, and rhetorical stances
- Play the believing game early in the writing process
3. Researching
Research refers to systematic investigations that investigators carry out to discover new knowledge , test knowledge claims , solve problems , or develop new texts , products, apps, and services.
During the research stage of the writing process, writers may engage in
- Engage in customer discovery interviews and survey research in order to better understand the problem space . Use surveys , interviews, focus groups, etc., to understand the stakeholder’s s (e.g., clients, suppliers, partners) problems and needs
- What can you recall from your memory about the subject?
- What can you learn from informal observation?
- What can you learn from strategic searching of the archive on the topic that interests you?
- Who are the thought leaders?
- What were the major turns to the conversation ?
- What are the current debates on the topic ?
- Mixed research methods , qualitative research methods , quantitative research methods , usability and user experience research ?
- What citation style is required by the audience and discourse community you’re addressing? APA | MLA .
4. Collaboration
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others to exchange ideas, solve problems, investigate subjects , coauthor texts , and develop products and services.
Collaboration can play a major role in the writing process, especially when authors coauthor documents with peers and teams , or critique the works of others .
Acts of collaboration include
- Paying close attention to what others are saying, acknowledging their input, and asking clarifying questions to ensure understanding.
- Expressing ideas, thoughts, and opinions in a concise and understandable manner, both verbally and in writing.
- Being receptive to new ideas and perspectives, and considering alternative approaches to problem-solving.
- Adapting to changes in project goals, timelines, or team dynamics, and being willing to modify plans when needed.
- Distributing tasks and responsibilities fairly among team members, and holding oneself accountable for assigned work.
- valuing and appreciating the unique backgrounds, skills, and perspectives of all team members, and leveraging this diversity to enhance collaboration.
- Addressing disagreements or conflicts constructively and diplomatically, working towards mutually beneficial solutions.
- Providing constructive feedback to help others improve their work, and being open to receiving feedback to refine one’s own ideas and contributions.
- Understanding and responding to the emotions, needs, and concerns of team members, and fostering a supportive and inclusive environment .
- Acknowledging and appreciating the achievements of the team and individual members, and using successes as a foundation for continued collaboration and growth.
5. Planning
Planning refers to
- the process of planning how to organize a document
- the process of managing your writing processes
6. Organizing
Following rhetorical analysis , following prewriting , writers question how they should organize their texts. For instance, should they adopt the organizational strategies of academic discourse or workplace-writing discourse ?
Writing-Process Plans
- What is your Purpose? – Aims of Discourse
- What steps, or strategies, need to be completed next?
- set a schedule to complete goals
Planning Exercises
- Document Planner
- Team Charter
7. Designing
Designing refers to efforts on the part of the writer
- to leverage the power of visual language to convey meaning
- to create a visually appealing text
During the designing stage of the writing process, writers explore how they can use the elements of design and visual language to signify , clarify , and simplify the message.
Examples of the designing step of the writing process:
- Establishing a clear hierarchy of visual elements, such as headings, subheadings, and bullet points, to guide the reader’s attention and facilitate understanding.
- Selecting appropriate fonts, sizes, and styles to ensure readability and convey the intended tone and emphasis.
- Organizing text and visual elements on the page or screen in a manner that is visually appealing, easy to navigate, and supports the intended message.
- Using color schemes and contrasts effectively to create a visually engaging experience, while also ensuring readability and accessibility for all readers.
- Incorporating images, illustrations, charts, graphs, and videos to support and enrich the written content, and to convey complex ideas in a more accessible format.
- Designing content that is easily accessible to a wide range of readers, including those with visual impairments, by adhering to accessibility guidelines and best practices.
- Maintaining a consistent style and design throughout the text, which includes the use of visuals, formatting, and typography, to create a cohesive and professional appearance.
- Integrating interactive elements, such as hyperlinks, buttons, and multimedia, to encourage reader engagement and foster deeper understanding of the content.
8. Drafting
Drafting refers to the act of writing a preliminary version of a document — a sloppy first draft. Writers engage in exploratory writing early in the writing process. During drafting, writers focus on freewriting: they write in short bursts of writing without stopping and without concern for grammatical correctness or stylistic matters.
When composing, writers move back and forth between drafting new material, revising drafts, and other steps in the writing process.
9. Rereading
Rereading refers to the process of carefully reviewing a written text. When writers reread texts, they look in between each word, phrase, sentence, paragraph. They look for gaps in content, reasoning, organization, design, diction, style–and more.
When engaged in the physical act of writing — during moments of composing — writers will often pause from drafting to reread what they wrote or to reread some other text they are referencing.
10. Revising
Revision — the process of revisiting, rethinking, and refining written work to improve its content , clarity and overall effectiveness — is such an important part of the writing process that experienced writers often say “writing is revision” or “all writing is revision.”
For many writers, revision processes are deeply intertwined with writing, invention, and reasoning strategies:
- “Writing and rewriting are a constant search for what one is saying.” — John Updike
- “How do I know what I think until I see what I say.” — E.M. Forster
Acts of revision include
- Pivoting: trashing earlier work and moving in a new direction
- Identifying Rhetorical Problems
- Identifying Structural Problems
- Identifying Language Problems
- Identifying Critical & Analytical Thinking Problems
11. Editing
Editing refers to the act of critically reviewing a text with the goal of identifying and rectifying sentence and word-level problems.
When editing , writers tend to focus on local concerns as opposed to global concerns . For instance, they may look for
- problems weaving sources into your argument or analysis
- problems establishing the authority of sources
- problems using the required citation style
- mechanical errors ( capitalization , punctuation , spelling )
- sentence errors , sentence structure errors
- problems with diction , brevity , clarity , flow , inclusivity , register, and simplicity
12. Proofreading
Proofreading refers to last time you’ll look at a document before sharing or publishing the work with its intended audience(s). At this point in the writing process, it’s too late to add in some new evidence you’ve found to support your position. Now you don’t want to add any new content. Instead, your goal during proofreading is to do a final check on word-level errors, problems with diction , punctuation , or syntax.
13. Sharing or Publishing
Sharing refers to the last step in the writing process: the moment when the writer delivers the message — the text — to the target audience .
Writers may think it makes sense to wait to share their work later in the process, after the project is fairly complete. However, that’s not always the case. Sometimes you can save yourself a lot of trouble by bringing in collaborators and critics earlier in the writing process.
Doherty, M. (2016, September 4). 10 things you need to know about banyan trees. Under the Banyan. https://underthebanyan.blog/2016/09/04/10-things-you-need-to-know-about-banyan-trees/
Emig, J. (1967). On teaching composition: Some hypotheses as definitions. Research in The Teaching of English, 1(2), 127-135. Retrieved from http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED022783.pdf
Emig, J. (1971). The composing processes of twelfth graders (Research Report No. 13). Urbana, IL: National Council of Teachers of English.
Emig, J. (1983). The web of meaning: Essays on writing, teaching, learning and thinking. Upper Montclair, NJ: Boynton/Cook Publishers, Inc.
Ghiselin, B. (Ed.). (1985). The Creative Process: Reflections on the Invention in the Arts and Sciences . University of California Press.
Hayes, J. R., & Flower, L. (1980). Identifying the Organization of Writing Processes. In L. W. Gregg, & E. R. Steinberg (Eds.), Cognitive Processes in Writing: An Interdisciplinary Approach (pp. 3-30). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Hayes, J. R. (2012). Modeling and remodeling writing. Written Communication, 29(3), 369-388. https://doi: 10.1177/0741088312451260
Hayes, J. R., & Flower, L. S. (1986). Writing research and the writer. American Psychologist, 41(10), 1106-1113. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.41.10.1106
Leijten, Van Waes, L., Schriver, K., & Hayes, J. R. (2014). Writing in the workplace: Constructing documents using multiple digital sources. Journal of Writing Research, 5(3), 285–337. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2014.05.03.3
Lundstrom, K., Babcock, R. D., & McAlister, K. (2023). Collaboration in writing: Examining the role of experience in successful team writing projects. Journal of Writing Research, 15(1), 89-115. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2023.15.01.05
National Research Council. (2012). Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.https://doi.org/10.17226/13398.
North, S. M. (1987). The making of knowledge in composition: Portrait of an emerging field. Boynton/Cook Publishers.
Murray, Donald M. (1980). Writing as process: How writing finds its own meaning. In Timothy R. Donovan & Ben McClelland (Eds.), Eight approaches to teaching composition (pp. 3–20). National Council of Teachers of English.
Murray, Donald M. (1972). “Teach Writing as a Process Not Product.” The Leaflet, 11-14
Perry, S. K. (1996). When time stops: How creative writers experience entry into the flow state (Order No. 9805789). Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses A&I; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (304288035). https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/when-time-stops-how-creative-writers-experience/docview/304288035/se-2
Rohman, D.G., & Wlecke, A. O. (1964). Pre-writing: The construction and application of models for concept formation in writing (Cooperative Research Project No. 2174). East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University.
Rohman, D. G., & Wlecke, A. O. (1975). Pre-writing: The construction and application of models for concept formation in writing (Cooperative Research Project No. 2174). U.S. Office of Education, Department of Health, Education, and Welfare.
Sommers, N. (1980). Revision Strategies of Student Writers and Experienced Adult Writers. College Composition and Communication, 31(4), 378-388. doi: 10.2307/356600
The Elements of Style

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority & Credibility – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - How to Differentiate Quality Information from Misinformation & Rhetrickery
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. You need to be strategic about how you consume and use information in order to thrive,...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

How to Write a Process Essay?
18 June, 2020
14 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
What is a “process essay”? What makes it different from dozens of other papers you create on a daily basis? What are its main components and what the main goal of this type of writing you need to bear in mind? If you're looking for answers to these questions, you're in luck! You can get them all from our academic guide on how to write a process essay.

Composing a process essay can be rather complicated especially if you are not familiar with this type of writing and do not know what pitfalls and specifications to pay attention to.
That is why our custom essay writing service has created this guide to help you tackle this task. We will answer all these questions in our article below and even provide you with great process essay examples and topics you can write on to stand out. So, if that sounds like something you need right now, read on: we are here to help and equip you with knowledge!
But first things first. Since it is impossible to create an excellent process essay without crystal clear understanding of the term, we will start with the definition. So, let’s dive in!
What is a process essay?
A process essay is commonly written either to explain how something works or to guide a reader through the process of completing a particular task, states the process essay definition.
Process essays also go under the “How-to articles” title and aim to teach the target audience how to achieve certain goals or complete specific assignments.
So, look at it like this. In case of “How to quit smoking” process essay, your primary goal is to provide several helpful ways of quitting this habit. These might be evidence-based recommendations if you have experience in this area, or simply common sense ideas you found while conducting your research.
Now that you realize what you will be working with, let’s look into different types of process essays and practical ways to compose them. Our essay writing guide will walk you through the process essay writing step by step.
Types of process essays
There are two main types of such papers: the ones that explain how something works , and those that show you how to complete a particular task .
1. How to do something.
Though it sounds quite self-explanatory, we’d like to emphasize the importance of clear instructions in case you are writing a process essay.
Your readers must be able to follow your guidance and complete each step successfully. So, split the process into small steps, keep it short and to the point at each stage of crafting a process essay.
For instance, in a “How to quit smoking” process essay , you can split the whole process into seven steps:
- Choose a date for a quit day;
- Imagine life without cigarettes and expect it;
- Have one last cigarette as a “Goodbye!”;
- Be among people to support you;
- Keep your goal in perspective not to give up;
- Don’t fall for substitutes;
- Be accountable.
2. How something works.
By contrast, this is an informative type of writing that aims to achieve one goal – explain the principle of work behind some process. Unlike the mentioned above type, this process essay type does not encourage a reader to take an action and do something step by step.
However, you must make sure that by the end of your essay, the audience will know for sure how something functions.
As an example of this type of a process essay, let’s see how an earthquake happens .
- First, the energy within the earth core builds up due to various moves in the earth crust;
- The energy level grows up and causes tension in the tectonic plates;
- After some time, the pressure radiates outwards by moving the plates from each other;
- The seismic waves shake the earth as they get from the core of the earth to the surface;
- That is when the earthquake takes place.
Before we go any further, let’s look at another example. In case of “How to prepare for a vacation” process essay, your task is to compose a few steps that your readers can take when getting ready for their vacation. In other words, you are describing how to do something.
Meanwhile, “What happens to your brain when you sleep” process essay is merely an explanation of the principle. In it, you are not encouraging readers to take any actions whatsoever. So, here is the fundamental difference.
How to write a process essay?
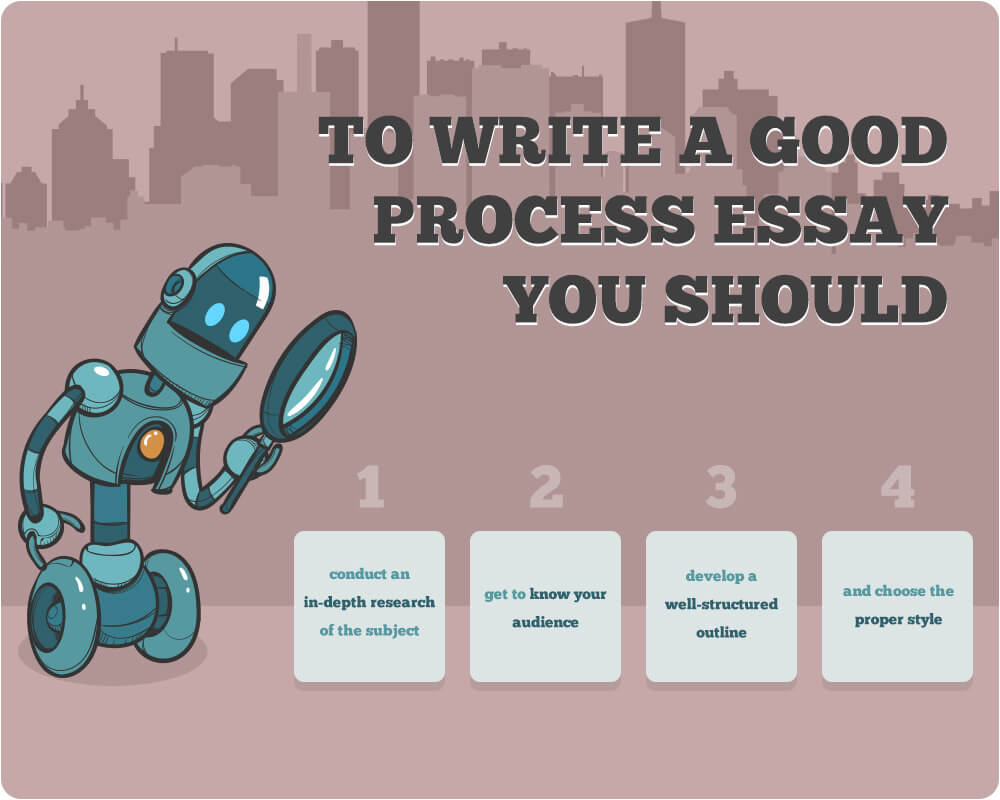
Getting started with process essay writing
When developing a process essay outline, take some time to answer the following questions:
- Who is your target audience? How deep is their knowledge of the subject? The complexity of your essay depends on their skills level. Thus, for instance, when explaining to your peers how to stretch a dollar to see the world, you can use basic terminology and examples they can relate to. However, your vocabulary should be way more sophisticated if you are writing a process essay on how to improve the overall quality of higher education in your state to the City Council.
- How can you divide the process into small steps? You do not want to bore your audience to death with unnecessary details in a process essay. Yet, you cannot afford to skip valuable steps if they are crucial to the overall understanding of the subject of your process essay. So, try to find the golden cut and figure out the most suitable amount of steps.
- What sources will you use for the task? It goes without saying that you can only use reliable sources to support your argument in a process essay. These sources should be all mentioned in the end of your essay. And remember about proper in-text citation styles. Read the materials carefully and take only the information that will add value to your essay and helps make it shine.
How to write a process essay outline
Finally, let’s look into the process essay structure. Needless to say that you must start with something that will grab readers’ attention, or in other words, “a hook.”
It is true for any essay, and process essay writing is not an exception.
The structure of your essay regardless of the process essay topics should consist of:
- A powerful introduction.
- Main body paragraphs.
- An interesting conclusion.
Related Post: Essay outline | Research Paper outline
Sounds simple, yet there are several things you should not forget about process essay writing.
How to write an introduction to a process essay
Once you compose a hook, mention why you believe that readers should use your approach to solve a problem even though there are dozens of other ones. We know two effective ways to achieve this in your process essay:
- Show how much time this task will take . People don’t have all the time in the world to tackle just this one task. So, you’ll really help them by stating how much time completing something using your approach will take and underline that with your approach described in a process essay it will take less time than if they opt for a different one. “Writing can be tough, especially if you always felt that it is not exactly your suit. However, Michael D. Pollock, a credible expert in this area, has recently presented 10 effective tips that will help you learn writing fast and make you able to craft a 1000-word article in 30 minutes. So, keep reading to find out how you can write this fast too.”
- Introduce your audience to the historical background of the approach (if any) you’re using in a process essay. Let them see the roots of your solution. Here is what a good introduction of a process essay should look like: “Giving a speech with lots of eyes concentrated on you is not an easy task. No wonder so many students dread this task. However, speech can be a powerful tool, and we can teach you how to give them right. Steve Jobs is known as one of the best public speakers of our time. People were sitting on the edge of their seats when he spoke. And we’ll teach you how to grab attention like he did using just five simple tricks he applied.”
At last, compose an engaging thesis of a process essay. Many students consider it a scary part. But it all goes down to this.
Your thesis statement should reason why your way is the best and why readers looking for answers should search no more and give your solution a chance.
It’s easier than you think. Here is a good thesis statement example:
“With more than 580 million tons of household waste produced all over the world, Every tiny effort you make to become eco-friendly counts. And if you don’t want to spend extra money on sustainable products but want to save the environment, use our guide on ten simple eco-friendly steps you can do daily without even noticing it!”
This is what a thesis statement for a process essay on how to be eco-friendly would look like. Yours can be different, but you get the idea!
How to plan main body paragraphs
- Dedicate one body paragraph to one point you want to bring to light.
- Provide enough details on each step including the ultimate goal of this step and reasons why this method was chosen for its achievement.
- Keep it short and to the point.
How to write a conclusion
Now is that time you reminded the readers about the purpose of a process essay, reasons why you chose this particular approach, and briefly mentioned steps needed to accomplish the task.
Besides, you can call your audience to action but only in case you are writing an essay that shows how to do something. Otherwise, it will be inapplicable.
Finally, help them set their expectations right: what results can they count on in the end? How long will it take them to achieve those results after reading your process essay and applying its tips?
How to use transition words in a process essay
Transition words can help you create a seamless reading experience. You can take readers smoothly from one step to another. And what is more you can help them immerse into the process!
Therefore, begin each new paragraph with a transition word, add one in between examples you provide, and summarize your instructions with them, too.

Think of transition words as of bridges that connect paragraphs and sentences. They make smooth communication between the two possible. And with them in your process essay, no reader feels irritated or frustrated with your writing style, as they have to stumble upon every other sentence in your piece.
Good process essay topics
It is not enough to just know the theory to create a good process essay. One should also come up with a topic that will be both interesting and useful to his readers. Here’s a list of our suggestions on process essay ideas:
- How to choose a perfect future career.
- How to survive college and stay sane.
- How to eat healthy on campus.
- How to balance your social and academic life.
- How to pay out a student loan while still at college.
- How to improve your public speaking skills.
- How to see the world with only $100 in your pocket.
- How to learn a foreign language.
- How to renovate your apartment and not go bankrupt.
- How to start your own business.
- How to prepare for your first interview.
- How to get volunteers to help you clean the neighborhood.
- How to write a life list.
- How to set boundaries in the relationship.
- How to study overseas for free.
Related Posts: Argumentative essay topics | Compare&Contrast essay topics
Process essay writing tips
Wrapping up, we would like to introduce you to a couple of vital recommendations on process essay writing:
- Your process essay subject cannot be too broad or too narrow. Look out for the golden cut!
- Introduce your readers to possible complications of the process. After all, forewarned is forearmed.
- Create a short vocabulary your audience can use in case they are not familiar with the terminology essential to the general understanding of the process essay in question.
- Develop a list of resources your readers will need as they deal with certain tasks. This way you will have them prepared to put your recommendations to action right away.
- Always write a process essay using Active Voice!
Need help with your process essay writing? Handmadewriting is here for you to help. Drop us a line to get our professional essay writers to develop an excellent piece for you!

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
13 Ways to Quickly Improve Your Academic Essay Writing Skills
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Anyone can learn to produce an academic essay if they begin with a few basic essay-writing rules.
An academic essay must be based upon a solid but debatable thesis, supported by relevant and credible evidence, and closed with a succinct and thorough conclusion.
By adhering to the best way to write an essay, you can create valuable, persuasive papers even when you're under a time crunch!
What Makes a Good Essay?
As previously noted, the foundation of any good academic essay is its thesis statement.
Do not confuse your thesis with your opening sentence. There are many good ways to start an essay , but few essays immediately present their main ideas.
After you draft your thesis, you can begin to develop your essay around it. This development will include the main supporting points of your essay, which will scaffold its main body.
Essays also typically include a relevant and compelling introduction and conclusion.
Learn How to Write a Great Thesis Statement .

Understanding How to Write a Good Essay
When writing an academic essay, you must take a number of qualities and characteristics into careful consideration. Focus, development, unity, coherence, and correctness all play critical roles when it comes to distinguishing an exceptional essay from one that is less than perfect.
The following essay-writing tips can help writers organize, format, and support their essays in ways that fit their intended purpose and optimize their overall persuasiveness. Here are 13 essay tips for developing and writing your next academic paper.
1. Know What You Are Going to Write About Before You Start Writing
While untrained writers might just sit down and start typing, educated and experienced writers know that there are many steps to writing an essay.
In short, you should know what you want to say before you type a single word. The easiest way to narrow down a thesis and create a proper argument is to make a basic outline before you begin composing your essay.
Your outline should consist of rough notes that sketch out your introduction (including your thesis), the body of your essay (which should include separate paragraphs that present your main supporting points with plenty of evidence and examples), and your conclusion (which ties everything together and connects the argument back to your thesis).
2. Acquire a Solid Understanding of Basic Grammar, Punctuation, and Style
Before getting into more refined essay-writing techniques, you must have a solid grasp of grammar, punctuation, and style. Without these writing fundamentals, it will be difficult to communicate your ideas effectively and ensure that they are taken seriously.
Grammar basics include subject and verb agreement, correct article and pronoun use, and well-formed sentence structures. Make sure you know the proper uses for the most common forms of punctuation. Be mindful of your comma usage and know when a period is needed.
Finally, voice is tremendously important in academic essay writing. Employ language that is as concise as possible. Avoid transition words that don't add anything to the sentence and unnecessary wordiness that detracts from your argument.
Furthermore, use the active voice instead of the passive whenever possible (e.g., "this study found" instead of "it was found by this study"). This will make your essay's tone clear and direct.
3. Use the Right Vocabulary and Know What the Words You Are Using Actually Mean
How you use language is important, especially in academic essay writing. When writing an academic essay, remember that you are persuading others that you are an expert who argues intelligently about your topic.
Using big words just to sound smart often results in the opposite effect—it is easy to detect when someone is overcompensating in their writing.
If you aren't sure of the exact meaning of a word, you risk using it incorrectly. There's no shame in checking, and it might save you from an embarrassing word misuse later!
Using obscure language can also detract from the clarity of your argument—you should consider this before pulling out a thesaurus to change a perfectly appropriate word to something completely different.
4. Understand the Argument and Critically Analyze the Evidence
While writing a good essay, your main argument should always be at the front of your mind. While it's tempting to go off on a tangent about an interesting side note, doing so makes your writing less concise.
Always question the evidence you include in your essay; ask yourself, "Does this directly support my thesis?" If the answer is "no," then that evidence should probably be excluded.
When you are evaluating evidence, be critical and thorough. You want to use the strongest research to back up your thesis. It is not enough to simply present evidence in support of an argument. A good writer must also explain why the evidence is relevant and supportive.
Everything you include should clearly connect to your topic and argument.

5. Know How to Write a Conclusion That Supports Your Research
One of the most overlooked steps to writing an essay is the conclusion. Your conclusion ties all your research together and proves your thesis. It should not be a restatement of your introduction or a copy-and-paste of your thesis.
A strong conclusion briefly outlines the key evidence discussed in the body of an essay and directly ties it to the thesis to show how the evidence proves or disproves the main argument of your research.
Countless great essays have been written only to be derailed by vague, weakly worded conclusions. Don't let your next essay become one of those.
6. Build a Solid Thesis to Support Your Arguments
A thesis is the main pillar of an essay. By selecting a specific thesis, you'll be able to develop arguments to support your central opinion. Consider writing about a unique experience or your own particular view of a topic .
Your thesis should be clear and logical, but it should also be debatable. Otherwise, it might be difficult to support it with compelling arguments.
7. Develop an Interesting Opening Paragraph to Hook In Readers from the Get-Go
No matter how you begin your essay, you must strive to capture the reader's interest immediately. If your opening paragraph doesn't catch the eye and engage the brain, any attempt at persuasion may end before the essay even starts.
The beginning of your essay is crucial for setting the stage for your thesis.
8. Always Remember to Edit and Proofread Your Essay
Any decent writer will tell you that writing is really rewriting. A good academic essay will inevitably go through multiple drafts as it slowly takes shape. When you arrive at a final draft, you must make sure that it is as close to perfect as possible.
This means subjecting your essay to close and comprehensive editing and proofreading processes. In other words, you must read your paper as many times as necessary to eliminate all grammar/punctuation mistakes and typos.
It is helpful to have a third party review your work. Consider consulting a peer or professional editing service. Keep in mind that professional editors are able to help you identify underdeveloped arguments and unnecessarily wordy language, and provide other feedback.
Get Critical Feedback on Your Writing
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, 9. when developing your essay's main body, build strong and relevant arguments.
Every sentence in the main body of your paper should explain and support your thesis. When deciding how much evidence to include in an academic essay, a good guideline is to include at least three main supporting arguments.
Those main supporting arguments, in turn, require support in the form of relevant facts, figures, examples, analogies, and observations.
You will need to engage in appropriate research to accomplish this. To organize your research efforts, you may want to develop a list of good research questions .
10. Choose the Format of Your Essay before Writing It
The final shape that your essay takes depends a great deal on what kind of format you use. Popular college essay format types include the Modern Language Association of America ( MLA ), American Psychological Association ( APA ), and Chicago Manual of Style ( Chicago style).
These formats govern everything from capitalization rules to source citation. Often, professors dictate a specific format for your essay. If they do not, you should choose the format that best suits your field.
11. Create Clear Transitions between Your Ideas
Although unnecessary transition words are the enemy of clarity and concision, they can be invaluable tools when it comes to separating and connecting the different sections of your essay.
Not only do they help you express your ideas but they also bring a cohesive structure to your sentences and a pleasant flow to your writing. Just be sure that you are using the right transition words for the right purpose and to the proper effect.
12. Always Include an Organized Reference Page at the End of Your Essay
As a key component of MLA, APA, and Chicago Style formatting, the reference or Works Cited page is an essential part of any academic essay.
Regardless of the format used, the reference page must be well organized and easy to read so that your audience can see exactly where your outside information came from.
To produce a properly formatted reference page, you may have to familiarize yourself with specialized phrases and abbreviations, such as " et al ."

13. Use Inclusive Language
Incorporating inclusive language in your academic writing ensures that your work is respectful and accessible to all readers. Use gender-neutral pronouns like "they/them" and replace gender-specific terms with inclusive alternatives, such as "firefighter" instead of "fireman."
You can also respect cultural diversity by avoiding stereotypes and generalizations, specifying details like "Japanese, Thai, and Indian cuisine" rather than "Asian cuisine." Engaging with diverse audiences for feedback and staying updated on inclusive language practices will help you continuously improve your writing.
How to Write a Good Hook for an Essay
The key to a good hook is to introduce an unexplored or absorbing line of inquiry in your introduction that addresses the main point of your thesis.
By carefully choosing your language and slowly revealing details, you can build reader anticipation for what follows.
Much like an actual worm-baited fishing hook, a successful hook will lure and capture readers, allowing the writer to "reel them in."
How to Get Better at Writing Essays
You can get better at writing essays the same way that you improve at anything else: practice, practice, practice! However, there are a few ways that you can improve your writing quickly so you can turn in a quality academic essay on time.
In addition to following the 13 essay tips and guidelines above, you can familiarize yourself with a few common practices and structures for essay development.
Great writing techniques for essays include brainstorming and tree diagrams, especially when coming up with a topic for your thesis statement. Becoming familiar with different structures for organizing your essay (order of importance, chronological, etc.) is also extremely helpful.
How to Write a Good Introduction for an Essay
To learn how to write a good essay, you must also learn how to write a good introduction.
Most effective essay introductions begin with relatively broad and general subject matter and then gradually narrow in focus and scope until they arrive at something extremely specific: the thesis. This is why writers tend to place their thesis statements at the very end of their introductory paragraph(s).
Because they are generally broad and often relate only tangentially to an essay's main point, there is virtually no limit on what the beginning of a good introduction can look like. However, writers still tend to rely on somewhat cliché opening sentences, such as quotations and rhetorical questions.
How to Write a Good Conclusion for an Essay
Briefly put, a good conclusion does two things. It wraps up any loose ends and drives home the main point of your essay.
To learn how to write a good conclusion, you will want to ensure that no unanswered questions remain in the reader's mind. A good conclusion will restate the thesis and reinforce the essay's main supporting points.
Take Your Essay from Good to Great
About the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing turn into a great one after the editing process. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained nearly 20 degrees collectively. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How Academic Writing Differs from Other Forms of Writing

How to Master the 4 Types of Academic Writing

The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
5 Tips for Improving Your Essay Writing Skills

5-minute read
- 5th November 2021
As a student , essay writing is an integral part of your education. So, how can you improve your essay writing skills? We’ve got five top tips that may help:
- Analyse the essay question so you understand the assignment.
- Write an outline to organize your ideas and prepare your essay.
- Do research to find evidence and sources to support your ideas.
- Use the drafting process to refine your essay before submitting it.
- Get your essay proofread to make sure it is clear and error free.
Read on to learn more about how to improve your essay writing skills.
1. Analyze the Essay Question
The most important step in writing an essay is understanding the assignment. As soon as you have your essay question, then, try to identify the following key words:
- Content words – Content words will tell you what the topic of your essay should be. For instance, in “Discuss the causes of World War II,” the key content words are “causes” and “World War II.”
- Instructional verbs – Instructional verbs will give you a sense of how to approach your essay. There is a big difference, for example, between explaining an idea and analyzing it. Look for what you’re being asked to do in the question, then let this guide your essay writing.
- Limiting words – Limiting words will tell you what to focus on. For example, “In discuss the consequences of the Brexit for trade in the EU,” the phrase “for trade in the EU” limits the scope of the essay question (i.e., while Brexit may have many consequences, the focus here should be trade in the EU).
Try underlining or highlighting these types of words in your essay question.
2. Create an Outline
Another great essay writing skill is to outline your work before you start writing. Most essays will follow a basic format, which you can use to structure an outline:
- An introductory section or paragraph that presents the topic, your thesis statement , and any important background information the reader will need.
- The body paragraphs (or sections), each of which should discuss a single point, example, or idea that supports your main argument.
- A conclusion , where you summarize how your argument supports your thesis.
When planning an essay, then, you can break it down in the way shown above and make notes about what each part will say. Once you are happy with your outline, you can then use this to guide the essay writing process.
3. Use Evidence and Sources Effectively
Having a point you want to argue for or a claim you want to make is fine, but a good essay will also use evidence and sources to support the points it makes.
Once you have worked out a position to argue for, then, do some research to find evidence that supports it. This can include quotations, statistics, and illustrations.
As well as including this evidence in your essay, though, you’ll need to analyze it and show how it support your arguments. Whatever you use, make sure there’s a clear connection between the evidence and the point you’re trying to make.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
In addition, remember to cite your sources properly! You need to show where you’ve found your evidence. This will usually include citing sources in the text of your essay and adding a reference list or bibliography at the end of your document, where you should provide full details of the sources you cited. If you’re not sure how to approach referencing sources, check your style guide or ask your professor.
4. Use the Drafting Process
The biggest mistake people make when writing an essay is to only write it once! Rather, you should always redraft at least once to polish your initial version.
Once you’ve written a draft, then, take a break from it (ideally at least overnight). Then, when you’re ready, go back over your essay and look for ways to improve it. This might be simply checking that you express yourself clearly. But you might also spot ways to strengthen your arguments, such as by adding more evidence.
If you do this at least once, your essay will be far stronger. And there’s always room for further redrafting if you want to be certain your writing is perfect.
5. Have Your Essays Proofread
Okay, strictly speaking this doesn’t quite fall under the category of “essay writing skills” in the same way as the other points here. But one of the smartest things you can do before submitting an essay is have it proofread by an expert.
At Proofed, for example, our academic proofreaders can check your writing to make sure it reads clearly and smoothly, correcting any spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors that slipped through the drafting process. We can even provide feedback on how to improve your academic writing.
If you need help polishing an essay, then, submit it for proofreading today.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
Free email newsletter template.
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read

How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt
- Asking Analytical Questions
- Introductions
- What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common?
- Anatomy of a Body Paragraph
- Transitions
- Tips for Organizing Your Essay
- Counterargument
- Conclusions
- Strategies for Essay Writing: Downloadable PDFs
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines

- Subject Guides
Academic writing: a practical guide
The writing process.
- Academic writing
- Academic writing style
- Structure & cohesion
- Criticality in academic writing
- Working with evidence
- Referencing
- Assessment & feedback
- Dissertations
- Reflective writing
- Examination writing
- Academic posters
- Feedback on Structure and Organisation
- Feedback on Argument, Analysis, and Critical Thinking
- Feedback on Writing Style and Clarity
- Feedback on Referencing and Research
- Feedback on Presentation and Proofreading
Approaching the stages in effective academic writing: before, during and after.
Stages in assignment writing
Writing is a process, not the end product!
There's a lot more to a successful assignment than writing out the words. Reading, thinking, planning, and editing are also vital parts of the process.

These steps take you through the whole writing process: before, during and after:
1. Read the assignment instructions thoroughly. What exactly do you need to do?

2. Read, make notes, think critically , repeat. This is a crucial step!
3. Make a general plan with the main points.
4. Make a detailed plan, focusing on creating a clear structure.
5. Check the plan. Is the task addressed fully? Are you being critical?
6. Write the first draft. Read and think more as needed.
7. Edit and redraft as needed.
8. Proofread carefully. Focus on referencing, spelling and grammar.
9. Submit the assignment. Give yourself time before the deadline in case of problems.
10. Read feedback carefully to help improve your next assignments.
11. Start the process again for your next assignment!
This process is applicable to various writing projects, including essays, reports, and dissertations. Modifications can be made to suit specific requirements of those assignments.
View in a new window: The writing process [Google Doc]
Planning tips
Doing any project takes time, and academic writing projects are no exception. Planning takes time, and there's lots to consider before starting the planning process.
Here are ten tips on just that...
| • • • • • • • • • • • |

Have you read the assessment guidelines / criteria for the task?
These may be issued with the assessment and are usually found on the VLE or department web pages or printed in a hard copy from the department. If available, these will provide clearer instructions for approaching the assignment. Assessment criteria outline the knowledge, skills and understanding you will need to demonstrate to pass the assessment. Be sure that you understand what's being asked of you. Take a look at our tips on understanding assessment criteria .
| • • • • • • • • • • • |

What are the guidelines on the presentation of your work?
Is a font style and font size specified? Is line spacing and margin width specified? Does your assignment need to follow a particular structure? Is a cover sheet required?
If you want to set your document up properly, look at our guidance on using text processing software .

What kind of writing is specified in the task?
Is it an essay, report, case study, reflection...? The type or genre of writing will determine the style, organisation and conventions you should use. Take a look at examples of that type of work to gain an understanding of form.

Does your assessment specify a specific audience?
Is it for an academic or specialist audience; a professional or business audience; a lay audience? You will need to adapt your style and language to suit your target audience.

What are the expectations in terms of the inclusion of information?
What range of evidence, sources, data, etc., is required? Is there a specific context identified in the assignment title? Where will you source this information (e.g. lecture notes, seminar/tutorial notes, prior reading, information on the VLE)? What additional reading will you need to do?
Take a look at our guidance on choosing the right information sources .

Which referencing style is required?
Have you checked the referencing guidelines for your department? Have you completed the online integrity tutorial ? Do you intend to use reference management software ?

Have you checked the module learning outcomes and grade descriptors?
Module learning outcomes outline the knowledge, skills and understanding you will gain by completing the module. Grade descriptors identify what you must do to achieve a specific grade (1st, 2:1, 2:2 etc.). Taking note of these will help you determine the level you need to write at. Take a look at our tips on understanding module learning outcomes .

What is the word limit?
What is included in the word limit? What are the penalties if you are over or under word count? If there are separate tasks, is there a word count for each one?

What is the deadline for the assessment?
Is there a specified time by which you have to submit your assignment on the deadline date? What are the penalties if you go over this deadline? Do you know what the regulations are if you are unable to submit (e.g. because of exceptional circumstances)?

How will you submit?
Where do you need to submit to? If this is an office, what are the office hours? Are you required to submit more than one copy? If you're submitting electronically, do you know where to upload the work? Do you know how to upload it?
Ensure you allow enough time in case you have problems with printers or electronic submissions.
| • • • • • • • • • • • |
Before you start: understanding task requirements
Meeting task requirements.
To get a good mark, you must complete the set assignment! This means answering all parts of the task, staying relevant throughout and using an appropriate structure and style.
For example, if the task is to write an essay critiquing the cultural influence of Star Wars, but instead, you write a reflective piece on your own opinion of Star Trek, you won't get a very good grade as you've not completed the set assignment.
To make sure your work meets the task requirements:
- Read the assessment brief carefully! If you have any questions, ask your tutor to clarify.
- Break down the title/question - see the advice below.
- Plan your points before you start writing. Have you covered everything? Are all the points relevant?
- Use the style and structure expected for that type of writing.
- Identify where you need to be descriptive and where you need to be critical:

Breaking down your title
You've been given an assignment title, but what is it actually asking? This activity takes you through the stages of analysing a question, breaking down an assignment title to clearly identify the task.
Choose an assignment title:
Analysing the question - Arts & Humanities
Below is an example question from the Faculty of Arts and Humanities to show you how to analyse a question to ensure that all elements of the task are addressed:
Describe how the presentation of gender in children's literature from the 1950s to the present has changed and critically evaluate how the development of feminist criticism has contributed to this change. Illustrate your answer with examples from the module material and wider reading .
In the above text, select the words or phrases that identify the two broad topics
That's not the right answer
You still need to identify the topics.
Have another go or reveal the answer .
Yes, that's the right answer!
The broad topics of this question are gender in children's literature in literature, and feminist criticism .
| • • • • • |
In the essay question, click on the specific context you will need to look at.
The specific context you need to look at is children's literature , specifically, children's literature from the 1950s to the present .
| • • • • • |
Now click on the instructional words or phrases that indicate the tasks which need to be completed - there are three to identify.
You still need to identify some of the instructions. Have another go or reveal the answers .
You're being instructed to describe , critically evaluate , and illustrate .
Describe how the presentation of gender in children's literature from the 1950s to the present has changed and critically evaluate how the development of feminist criticism has contributed to this change . Illustrate your answer with examples from the module material and wider reading .
Click on the part of the question which will get you the most marks and therefore should get the most attention .
The part of the question that will get you the most marks and therefore should get the most attention is critically evaluate how feminist criticism has contributed to this change .
You got correct.
Hopefully you got some ideas from those exercises about how to analyse and break down your questions. Now take a look at some of the other advice on these pages.
| • • • • • |
Analysing the question - Sciences
Below is an example question from the Faculty of Sciences to show you how to analyse a question to ensure that all elements of the task are addressed:
To what extent have approaches to environmental management contributed to our current position on energy production and use ? Evaluate the ways in which these approaches may help to shape our energy strategy for the future .
In the essay question, click on the words or phrases that identify the broad topic you will need to discuss in your answer
The broad topic of this question is environmental management .
In the essay question, click on the two words which specify the contexts you will need to look at.
You still need to identify the contexts.
The words that specify the specific contexts you will need to look at are current and future .
Now click on the phrases or instructional words that indicate the tasks which need to be completed - there are two to identify.
You're being instructed to consider to what extent and to evaluate .
Click on the part of the question which will get you the most marks and therefore should get the most attention
The part of the question that will get you the most marks and therefore should get the most attention is evaluate the ways in which these approaches may help to shape our energy strategy for the future .
Analysing the question - Social Sciences
Below is an example question from the Faculty of Social Sciences to show you how to analyse a question to ensure that all elements of the task are addressed:
Outline the ways in which young people criminally offend in society and how restorative justice seeks to modify such behaviour . Critically evaluate the effectiveness of restorative justice in terms of rehabilitating young offenders and also protecting the public .
In the essay question, click on the words or phrases that identify the broad topics you will need to discuss in your answer
The broad topics of this question are people criminally offend and restorative justice .
In the essay question, click on the phrase which specifies the context you will need to look at.
The specific context you need to look at is young people .
Now select the phrases or instructional words that indicate the tasks which need to be completed - there are two to identify
You're being instructed to outline and critically evaluate .
The part of the question that will get you the most marks and therefore should get the most attention is critically evaluate the effectiveness of restorative justice in terms of rehabilitating young offenders and also protecting the public .
Planning assignment structure
Once you've understood the task requirements, done some reading and come up with some ideas for what to include, you can start mapping out your assignment structure.
A good plan is key for a well-structured assignment - don't just launch into writing with no idea of where you're going!
This planning stage can also be a useful opportunity to think more deeply about the assignment and consider how the different ideas fit together, so it can help you develop your argument.
It's ok to make changes to your plan later - you might come up with more ideas, or another line of argumentation while writing. Make sure that you check the structure is still logical though!

Find out more about planning the general structure of an assignment:

Proofreading & checking
Everyone makes small mistakes and typos when they write; things like spelling mistakes, grammar or punctuation errors, incorrect referencing format or using the wrong word.
When you've spent a long time working on an assignment, you may not notice these small errors, so make sure to proofread (or check ) your work carefully before you submit it. You don't want these mistakes to make it into your final assignment, as they can make it harder for the reader to understand your points and could affect your grade.
Our top proofreading tips:
- use a spellchecker - but remember this won't pick up everything!
- put your assignment away for a little while, then come back later and read through it carefully. Focus on spelling, grammar and punctuation.
- it can be easier to notice mistakes if you read your assignment out loud or use a tool like Read&Write to read it to you.
- check that each of your citations and references is correctly formatted
Here are some specific things you can look out for in proofreading:
close all accordion sections
Language & formatting checks
Spelling and grammar.
- Check for spelling errors using a spellchecker and reading through the work.
- Check for double spaces and repeated words.
- Check for homophones - words that sound the same but look different (eg, to/too/two, right/write)
- Check that verbs and nouns match (eg, These results suggest.., NOT These results suggests...)
- Have any personal or informal words/phrases been used?
Punctuation
- General guide to correct punctuation use [Web]
- Full stops (.) and commas (,) come immediately after the word and need a space after them.
- Brackets () go inside a sentence (ie, before the full stop).
- Have you followed your department's formatting guidelines?
- Is the same font and text size used for all body text?
- Have you double spaced the writing? Is this required?
- Have you used the correct method of linking to appendices?
Referencing style checks
It's very important that your citations and references are correct - this is something that markers will definitely be looking for!
Before you submit, check your referencing is correct:
- Are author names correct? Especially pay attention to which name is the surname.
- Have all authors been included? Check your referencing style's format for dealing with multiple authors.
- Do references include all of the required information?
- Is the correct punctuation and text formatting used, especially full stops, commas, ampersand (&) and italics ?
- Are in-text citations inside the sentence (ie., before the full stop)?
- Are all sources cited in the text included in the reference list (or vice versa)?
- Do you have to include a reference list (which includes only sources directly cited in the text), or a bibliography (which includes all sources used to produce the writing and not all have to be cited in the text).
More detailed advice:

Submitting assignments on Yorkshare VLE
Most assignments will be submitted through the Yorkshare VLE (Blackboard). You'll receive information on how to do this from your department.
For advice on using the submission points, see our dedicated guide:

Use feedback to improve your next assignments
Feedback on your work can show what you're doing well and identify areas that you need to work on. For example, if you receive feedback that your work isn't clearly organised, you could focus on planning carefully and using a logical structure in your next assignments.
Find out how to use your feedback to improve and advice in dealing with common issues in our assessment and feedback guide:
- << Previous: General writing skills
- Next: Academic writing style >>
- Last Updated: Sep 16, 2024 3:31 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/academic-writing
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A (Very) Simple Way to Improve Your Writing
- Mark Rennella

It’s called the “one-idea rule” — and any level of writer can use it.
The “one idea” rule is a simple concept that can help you sharpen your writing, persuade others by presenting your argument in a clear, concise, and engaging way. What exactly does the rule say?
- Every component of a successful piece of writing should express only one idea.
- In persuasive writing, your “one idea” is often the argument or belief you are presenting to the reader. Once you identify what that argument is, the “one-idea rule” can help you develop, revise, and connect the various components of your writing.
- For instance, let’s say you’re writing an essay. There are three components you will be working with throughout your piece: the title, the paragraphs, and the sentences.
- Each of these parts should be dedicated to just one idea. The ideas are not identical, of course, but they’re all related. If done correctly, the smaller ideas (in sentences) all build (in paragraphs) to support the main point (suggested in the title).
Most advice about writing looks like a long laundry list of “do’s and don’ts.” These lists can be helpful from time to time, but they’re hard to remember … and, therefore, hard to depend on when you’re having trouble putting your thoughts to paper. During my time in academia, teaching composition at the undergraduate and graduate levels, I saw many people struggle with this.
- MR Mark Rennella is Associate Editor at HBP and has published two books, Entrepreneurs, Managers, and Leaders and The Boston Cosmopolitans .
Partner Center
Essay Papers Writing Online
Tips and tricks for crafting engaging and effective essays.

Writing essays can be a challenging task, but with the right approach and strategies, you can create compelling and impactful pieces that captivate your audience. Whether you’re a student working on an academic paper or a professional honing your writing skills, these tips will help you craft essays that stand out.
Effective essays are not just about conveying information; they are about persuading, engaging, and inspiring readers. To achieve this, it’s essential to pay attention to various elements of the essay-writing process, from brainstorming ideas to polishing your final draft. By following these tips, you can elevate your writing and produce essays that leave a lasting impression.
Understanding the Essay Prompt
Before you start writing your essay, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the essay prompt or question provided by your instructor. The essay prompt serves as a roadmap for your essay and outlines the specific requirements or expectations.
Here are a few key things to consider when analyzing the essay prompt:
- Read the prompt carefully and identify the main topic or question being asked.
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or guidelines provided, such as word count, formatting requirements, or sources to be used.
- Identify key terms or phrases in the prompt that can help you determine the focus of your essay.
By understanding the essay prompt thoroughly, you can ensure that your essay addresses the topic effectively and meets the requirements set forth by your instructor.
Researching Your Topic Thoroughly

One of the key elements of writing an effective essay is conducting thorough research on your chosen topic. Research helps you gather the necessary information, facts, and examples to support your arguments and make your essay more convincing.
Here are some tips for researching your topic thoroughly:
| Don’t rely on a single source for your research. Use a variety of sources such as books, academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources to gather different perspectives and valuable information. | |
| While conducting research, make sure to take detailed notes of important information, quotes, and references. This will help you keep track of your sources and easily refer back to them when writing your essay. | |
| Before using any information in your essay, evaluate the credibility of the sources. Make sure they are reliable, up-to-date, and authoritative to strengthen the validity of your arguments. | |
| Organize your research materials in a systematic way to make it easier to access and refer to them while writing. Create an outline or a research plan to structure your essay effectively. |
By following these tips and conducting thorough research on your topic, you will be able to write a well-informed and persuasive essay that effectively communicates your ideas and arguments.
Creating a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a crucial element of any well-crafted essay. It serves as the main point or idea that you will be discussing and supporting throughout your paper. A strong thesis statement should be clear, specific, and arguable.
To create a strong thesis statement, follow these tips:
- Be specific: Your thesis statement should clearly state the main idea of your essay. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Be concise: Keep your thesis statement concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
- Be argumentative: Your thesis statement should present an argument or perspective that can be debated or discussed in your essay.
- Be relevant: Make sure your thesis statement is relevant to the topic of your essay and reflects the main point you want to make.
- Revise as needed: Don’t be afraid to revise your thesis statement as you work on your essay. It may change as you develop your ideas.
Remember, a strong thesis statement sets the tone for your entire essay and provides a roadmap for your readers to follow. Put time and effort into crafting a clear and compelling thesis statement to ensure your essay is effective and persuasive.
Developing a Clear Essay Structure
One of the key elements of writing an effective essay is developing a clear and logical structure. A well-structured essay helps the reader follow your argument and enhances the overall readability of your work. Here are some tips to help you develop a clear essay structure:
1. Start with a strong introduction: Begin your essay with an engaging introduction that introduces the topic and clearly states your thesis or main argument.
2. Organize your ideas: Before you start writing, outline the main points you want to cover in your essay. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas.
3. Use topic sentences: Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. This helps the reader understand the purpose of each paragraph.
4. Provide evidence and analysis: Support your arguments with evidence and analysis to back up your main points. Make sure your evidence is relevant and directly supports your thesis.
5. Transition between paragraphs: Use transitional words and phrases to create flow between paragraphs and help the reader move smoothly from one idea to the next.
6. Conclude effectively: End your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your thesis. Avoid introducing new ideas in the conclusion.
By following these tips, you can develop a clear essay structure that will help you effectively communicate your ideas and engage your reader from start to finish.
Using Relevant Examples and Evidence
When writing an essay, it’s crucial to support your arguments and assertions with relevant examples and evidence. This not only adds credibility to your writing but also helps your readers better understand your points. Here are some tips on how to effectively use examples and evidence in your essays:
- Choose examples that are specific and relevant to the topic you’re discussing. Avoid using generic examples that may not directly support your argument.
- Provide concrete evidence to back up your claims. This could include statistics, research findings, or quotes from reliable sources.
- Interpret the examples and evidence you provide, explaining how they support your thesis or main argument. Don’t assume that the connection is obvious to your readers.
- Use a variety of examples to make your points more persuasive. Mixing personal anecdotes with scholarly evidence can make your essay more engaging and convincing.
- Cite your sources properly to give credit to the original authors and avoid plagiarism. Follow the citation style required by your instructor or the publication you’re submitting to.
By integrating relevant examples and evidence into your essays, you can craft a more convincing and well-rounded piece of writing that resonates with your audience.
Editing and Proofreading Your Essay Carefully
Once you have finished writing your essay, the next crucial step is to edit and proofread it carefully. Editing and proofreading are essential parts of the writing process that help ensure your essay is polished and error-free. Here are some tips to help you effectively edit and proofread your essay:
1. Take a Break: Before you start editing, take a short break from your essay. This will help you approach the editing process with a fresh perspective.
2. Read Aloud: Reading your essay aloud can help you catch any awkward phrasing or grammatical errors that you may have missed while writing. It also helps you check the flow of your essay.
3. Check for Consistency: Make sure that your essay has a consistent style, tone, and voice throughout. Check for inconsistencies in formatting, punctuation, and language usage.
4. Remove Unnecessary Words: Look for any unnecessary words or phrases in your essay and remove them to make your writing more concise and clear.
5. Proofread for Errors: Carefully proofread your essay for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Pay attention to commonly misused words and homophones.
6. Get Feedback: It’s always a good idea to get feedback from someone else. Ask a friend, classmate, or teacher to review your essay and provide constructive feedback.
By following these tips and taking the time to edit and proofread your essay carefully, you can improve the overall quality of your writing and make sure your ideas are effectively communicated to your readers.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.

Writing for Success
(52 reviews)
Copyright Year: 2015
ISBN 13: 9781946135285
Publisher: University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Tracy Peterson, Adjunct Writing Instructor, Southwestern Oregon Community College on 8/16/23
Index is highly comprehensive. It includes the title of chapters as well as each subsection that can be linked directly from the index to the page within the document itself. Chapters include all major areas of study within my WR90 course. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
Index is highly comprehensive. It includes the title of chapters as well as each subsection that can be linked directly from the index to the page within the document itself. Chapters include all major areas of study within my WR90 course.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
Information is accurate and well thought out. It would be great to have PDFs of exercises given in the book. As it is, I’m not sure how usable the exercises are in the digital only format. I do, however, appreciate the focus on sentence skills. These are greatly needed among my Wr 090 students.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Content is pretty timeless, and I don’t believe updates will need to be made often.
Clarity rating: 4
Text is clear, though perhaps a bit hard to access for many of my Writing 090 students. Terms such as “Rhetorical Modes”, for example, would not be understood. Simpler language would be more useful in a lower-level course. The occasional flowchart is useful; I would love to see more diagrams and/or images and less heavy text. While examples are given (generally one or two per concept), more would always be helpful.
Consistency rating: 5
The text is very consistent with the way ideas are presented, giving tips and highlights, key factors, examples, exercises, learning objectives, etc. All of these things are reproduced in each section and within each chapter in the same way, making them easy to find and identify.
Modularity rating: 5
Chapters may be easily separated and rearranged according to the needs of the instructor. Subsections within each chapter are able to be completed independently.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The organization of the text is logical and rational. It begins with an introduction to writing, moves on to sentence skills, refining writing technique, the writing process, writing an essay, different rhetorical modes of essay writing, research and citations, presentations, and example essays.
Interface rating: 3
Title page could be a little more appealing. There are quite a lot of formatting issues, large oversized text boxes with writing in bottom quarter only throughout the entire text (Ex: pg 5), strange front sizes, and too much space on page (Ex: pg 72).
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text contains no grammatical errors. It was well worded and well written.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
The text is pretty neutral. I would appreciate bringing in a little more cultural relevance into the text: images of multi-racial students, etc. However, the text does includes a section for English Language Learners which I greatly appreciate. These subsections could be added throughout the course, or done as a single unit.
Overall it is a well-made text. I personally would rather see a more project based textbook, but not finding any like that, I think this text creates a good jumping off point, from which the instructor can create and deliver more project based assignments.
Reviewed by Tonya Rickman, Adjunct Instructor English Department, Old Dominion University on 7/25/23
The content presented in this book is quite appropriate for college students, especially those students who are new to college and/or struggling with the rigors of reading and writing assignments required at the post-secondary level. The text is... read more
The content presented in this book is quite appropriate for college students, especially those students who are new to college and/or struggling with the rigors of reading and writing assignments required at the post-secondary level. The text is comprehensive as it encompasses a wide range of topics and strategies related to reading, writing, and academic work at the post-secondary level, making it a valuable resource for students and instructors alike. There is a glossary that includes key terminology – much of the language included in the book is straightforward (one does not need an extensive knowledge of English terminology to understand this book).
The text appears to be error free. There were a few examples provided in the grammar section (beginning on page 51), where the author discusses editing fragments that begin with prepositions. In those examples there appears to be a word repeated (e.g., when, When). However, it quickly becomes apparent to the reader that the repeated word “when” is not a typo, but it’s the format used to demonstrate a common error.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Even though the text was published in 2015 the information is still relevant and aligned with most of the reading and writing learning outcomes expected in a freshman and/or sophomore English course as well as other disciplines. Based on the current cultural climate in academia and shifting cultural norms in the broader society, the author might update examples in the book to convey a bit more of a feel of cultural inclusivity as well as a broader sense of technological advances (AI). That said, the systematic academic styles and simplistic tone certainly puts the reader at ease, especially when reading grammar rules that students might find confusing when presented in a more complex resource. Additionally, the exercises used to provide the reader with practice (i.e., Writing at Work) are not only a thoughtful way to help the reader make connections with the content of the text, but also useful in expanding the reader’s thinking beyond the use of a particular skill for academic purpose to a real-world application (i.e., the workplace).
Clarity rating: 5
Readers of this book have likely encountered the vast majority of terms used in the book at other times throughout their time in academia. The author actually described grammar and punctuation in a way that is understandable (i.e., short descriptions, rudimentary examples).
The format pretty much remains the same throughout the text – the author consistently articulates learning objectives, concepts, strategies, practice, and key takeaways. Additionally, visuals and links to external resources are regularly available to aid readers in gaining a deeper understanding of ideas. There is a logical progression of ideas as the reader moves forward in the text. For example, the reader is introduced to strategies for time management and study skills before learning strategies for conducting research.
Absolutely, this text can be read in sequential order (i.e., chapter one, two, three…), or the reader could refer to any chapter of interest based on his/her learning needs. As an English instructor, who has directed students to a variety of grammar resources online, I could see the benefit of directing students to a page in this text instead of several different online resources. Based on the quality of content in this text, it’s an efficient and effective way put a useful resource in the hands of students.
The sequential order of topics in the text is sensible – the structure enables the reader to know what’s coming next. The concepts in the text become increasingly complex as the reader progresses through each section of the text. The end of the text gives the reader the opportunity to apply understanding of concepts discussed earlier in the text. The progression in the complexity of skills is most notable in the steps for completion of a research paper – here the reader is challenged to apply several skills discussed earlier in the text (e.g., identifying the scope and sequence, considering steps in writing process, managing time).
Interface rating: 4
The majority of hypertext links are useful in navigating to other sections of the text and many of the links to external sources are still active (e.g., Library of Congress Subject Headings link). After visiting the external website, the reader is able to easily navigate back to the original text. The actual images (e.g., charts and tables) in the text are appropriately displayed – the color, spacing, and fonts are visually pleasing.
A huge part of the text is dedicated to the use of grammar – there don’t seem to be issues with grammar.
The text feels a bit culturally neutral - most of the examples are pretty generic. The reader likely feels the author is most concerned with providing examples for the purpose of highlighting development of essential skills that are part of the reading and writing process. For example, while there are multiple examples that spotlight contemporary issues (e.g., mortgage crisis, low-carb diets), the style and tone of writing feel appropriate for an academic text – you feel the examples are provide for academic purposes not to convey any views or positions on any of the issues.
I would recommend this book to English teachers for use with secondary and post-secondary students.
Reviewed by Alicia Andre, Faculty, Century College on 3/8/23
Writing for Success is a good text for an intro-college writing and grammar text. There are 15 chapters, and each chapter is well-organized and includes some sample essays and grammar exercises. What I like about this text, is that you can pick... read more
Writing for Success is a good text for an intro-college writing and grammar text. There are 15 chapters, and each chapter is well-organized and includes some sample essays and grammar exercises. What I like about this text, is that you can pick which topics will fit your course design. The beginning of the book has a comparison/contrast on the expectations of high school and college. This is a good way to start a college composition course because students often do not understand the demands of college writing. It also starts with reading strategies, and this is also helpful because many students today do not read carefully, and this can be a problem when they start to write a paper that asks them to analyze a reading. There is a lot to pick and choose from in this 600-page book.
The authors did an excellent job in this area as there were not any errors that I could see.
The chapters are relevant for any college composition course. The only concern is that the MLA/APA chapter may need to be updated. It might be a good idea to have a link to the Purdue Owl English web page in this chapter as the rules of MLA and APA often change over the years. Some of the readings and links might need to be updated as well.
I thought the organization and content were clear and easy to follow. I like that the “objectives” are included at the top of each chapter as this can be a nice way to see how course objectives link to the textbook chapters. Also, there are “tips” to help learners along the way.
There is clear consistency and it is easy to follow. The terminology seems accurate as well.
The modules are comprehensive and topics that I use in my college composition courses. The writing text that I am using now, has these topics embedded in units, but this text has similar topics in separate chapters which can be easy for the instructor and the student to locate. For instance, if I want to go over “understanding purpose in writing”, I can find information in the introduction. If I want to go over sentence boundaries, I can go to Chapter 2 or Chapter 6 depending on which one is a better way to explain the importance of using cohesive devices in writing. There is also a chapter on study skills that I would use at the start of the semester.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
I suppose it isn’t easy to decide which chapter should go first to last. I looked at the organization of chapters and I would say Chapter 8 on “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin” should be after “Chapter 1: Introduction to Writing”, but since many teachers will simply assign certain chapters at different times, this isn’t a big problem. I like that the textbook included a chapter specifically designed for English Language Learners (ELL) since that is my subject area.
I think it is good, but I would like to see more visuals like graphs, pictures, and sample essays with edits. There are some good aspects though as the text has boxed information with samples. For instance, in the chapter on punctuation, the boxed information shows how the punctuation is used in the sentence. The text also includes some practice exercises in “blue” boxes. This is helpful because I can scan for those exercises and have students do those as homework. One concern I have is that some of the sample essays (i.e., Page 235) have small print and is difficult to read.
No errors that I can tell.
I think for the most part it is good in terms of being inclusive. The readings in the unit on narration included readings from Sandra Cisneros and Sherman Alexie. Some of the readings might include some sensitive topics related to race and abortion that could be problematic. However, I think that if I use this textbook, I can just pick and choose which topic best fits my students' needs.
I think this is an excellent book for a college composition course.
Reviewed by Jiale Hu, Assistant Professor|Director of Research and Global Outreach, Virginia Commonwealth University on 8/10/22
It is a comprehensive book introducing writing skills. This book covers all the necessary writing basics, from words, sentences, and paragraphs to the whole essay. The authors also provide detailed instructions on the steps of writing. read more
It is a comprehensive book introducing writing skills. This book covers all the necessary writing basics, from words, sentences, and paragraphs to the whole essay. The authors also provide detailed instructions on the steps of writing.
Although some references need to be updated, the contents are accurate. The book provides error-free and unbiased content on writing.
This book is very helpful for students or even junior faculty who want to improve their writing skills.
As it is a book introducing academic writing skills, the authors did a fantastic job of writing this book in a clear way.
I appreciate that the authors structure all the chapters and sections in a consistent way. It makes reading and navigation more efficiently.
The book uses multiple strategies to break the contents into smaller reading sections. There are no enormous blocks of text without subheadings.
The contents of this book are well organized. Each chapter has multiple subchapters. Each subchapter has multiple sections to present the contents and topics in a logical, clear fashion. The authors have learning objectives at the beginning of each subchapter and key takeaways at the end of each subchapter. Major headings and subheadings are clear. All the further explanations or clarifications and examples or exercises have been put in the boxes for easy navigation.
Interface rating: 5
This book provides five formats, including online, pdf, ebook, XML, and ODF. Each format looks great! I did not experience any interface issues. I did not find any navigation problems, distortion of images/charts, and any other display features that may distract or confuse readers.
After I read the book thoroughly, I did not notice any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The book has a chapter for English language learners. This is greatly appreciated. I did not see any text culturally insensitive or offensive. The essays in the final chapter also include a variety of examples.
My favorite chapter is Chapter 8: The Writing Process: How Do I Begin? This chapter provides detailed steps of the writing process: Prewriting, Outlining the structure of ideas, Writing a rough draft, Revising, and Editing. Especially in the chapter on outlining, the authors provide great examples showing different ways of organizing ideas and constructing outlines.
Reviewed by Seo Lee, Assistant Professor, University of Wisconsin - Superior on 8/21/21
comprehensive book to adopt effective writing strategies for college students read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
comprehensive book to adopt effective writing strategies for college students
it was very accurate and clear, such as the basics of vocabulary, paragraph development, and introduction of essay paper.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
since I do not have a lot of writing assignments for the class, this book is not relevant to my course work
this book is very easy to follow through the context of book, very organized that need to college students
Consistency rating: 4
very structured and well-organized content
Modularity rating: 4
Yes. it help to write essay paper, the learn the process of writing
well-organized content
easy to follow, introduce the basic elements of writing for college students
Grammatical Errors rating: 3
I do not see grammatical errors
Cultural Relevance rating: 2
did not involve the cultural contexts.
Reviewed by Pam Whitfield, English faculty, Rochester Community & Technical College on 12/21/20
Pretty accessible for students. Maybe a bit simple for freshman writing, but I would consider using it in a comp 101 course and supplementing with my own materials. I am most likely to use it for a “higher level” developmental writing... read more
Pretty accessible for students. Maybe a bit simple for freshman writing, but I would consider using it in a comp 101 course and supplementing with my own materials. I am most likely to use it for a “higher level” developmental writing course. Grammar comes first in the table of contents. That’s fine with me as it makes accessing those sections easy, but I would not teach these chapters chronologically. I would pick and choose, reordering chapters for my students to teach more holistically, so comp methodology has grammar embedded in it.
No glossary or index. This is a large omission and could be easily corrected: hire a grad student to do it as a summer project.
The content and examples are accurate overall. Ch 6 replaces persona/speaker/writer with tone in the rhetorical triangle. I find that reductionist or overly simplistic. But the chapter as a whole is superbly geared toward the dev ed writers I typically teach. I would use it in a class for students who missed the testing placement cut off for freshman composition.
I'd call its approach pretty classic in terms of comp pedagogy. It will not become obsolete in the near future. Updates should focus on new media and digital sources/examples.
Highly readable for students.
Yes, it's a text that provides a great overview but does not go deep into any one area or skill set. For ex, Chapter 5 for ELL students is just a start. Or perhaps it’s a jumping off place for teacher’s own pedagogy and materials. The slang and idioms lists are very short, for instance. They are just a starting point. This chapter could be an effective review for a competent ELL student or allow the instructor to assign one section/topic as needed to individual students.
I like the amount of sectioning; it reads in bite sized pieces for students. This is a long book—over 600 pages. It could be intimidating to dev ed and ELL students.
What helps make this text more organized and user friendly: key takeaways list at end of each chapter. charts and lists for quick reference by students. quick tips in text boxes. “writing at work” tips that help students connect the usefulness of what they’re learning in the classroom to the workplace.
There are a few poor design choices. For ex, student examples are displayed in italic font (as if the student were writing cursive). Italic font slows reading speed on the page and increases eye fatigue. Never put more than one sentence total into italics. The PDF version really needs a way to "tag" or jump to each chapter directly. Better yet, to jump to each section in the chapter by using a hyperlink or similar tool in the table of contents.
Everything I read was clean.
There is some variety. I would not term this a standout or obvious strength of the text.
I would test drive it for one semester in dev ed first, then consider adapting and supplementing it for my first year comp students.
Reviewed by Christian Aguiar, Asst Professor of English, The University of the District of Columbia on 12/21/20
This text provides extensive coverage of all of the content areas typically covered in first-year composition courses at community colleges. It includes chapters on paragraph structure, the writing process, rhetorical modes, research, MLA and APA... read more
This text provides extensive coverage of all of the content areas typically covered in first-year composition courses at community colleges. It includes chapters on paragraph structure, the writing process, rhetorical modes, research, MLA and APA documentation, sentence structure, punctuation, mechanics, revision, and even designing presentations. Individual chapters include check-in questions and, in most cases, suggested activities for students to complete as they read. There is also a selection of sample essays that follow the rhetorical modes. Finally, hyperlinks have been strategically placed to help students review important concepts by referring them back directly to the chapter where that concept was first introduced. This makes for a richly layered reading experience while also facilitating modular usage of the text.
The text generally follows the established approach to teaching writing, so its discussion of research writing, for example, includes sections on topic selection, planning, conducting research, organizing ideas, drafting and revising.
Wisely, the authors have avoided over-embellishing their work with examples that might become dated. Those examples critical to student learning tend to focus on general, enduring topics. Some of the suggested topics and activities may not age quite as well - for example, one activity asks students to complete an idea map to analyze the impact of “social networking,” which may already be a somewhat dated concept for students. Since the activities are clearly set apart in lightly-shaded boxes, it’s easy for users to update these activities as needed. It must be said that the included student examples are pretty generic; I’ve never used them.
In a nod to digital reading habits, the authors have kept paragraphs mercifully short - typically 2-3 sentences, rarely any more. Sub-headings are used judiciously. Each chapter section introduces learning objectives at the top of the page and “takeaways” at the bottom. The authors don’t attempt to over-simplify the writing styles, so the readability score is relatively high, in the 10th-12th grade or college range. This makes the text ideal for a first-year writing course, though it may prove somewhat challenging when used as part of development coursework, such as in a corequisite course.
The design of the text is clear and lucid. There are fifteen chapters, each divided into several sections covering individual topics. Each topic begins with clear learning objectives and concludes with one or more key points. All chapters feature built-in comprehension questions, short writing activities, and/or writing tips. The visual design is crisp; it makes use of white space and a consistent color palette to improve readability.
The organization of the text makes it very easy to assign a single chapter, or section of a chapter, at a time. Each section has its own URL that can be embedded in an LMS to bring students directly to the desired reading. The use of hyperlinks to refer back to ideas covered in “previous” chapters makes it easier to take the text out of order, as students are able to readily access concepts.
See consistency
The digital interface is clean, consistent, and easy to navigate. The text does not generally make use of images, though there are frequent tables, charts and organizers that read clearly on Chrome and Firefox.
In two years of teaching with the text, I have found no grammatical errors.
The text is culturally competent in the sense of being quite generic and inoffensive; it does not necessarily engage a range of experiences or voices. I haven't found this a problem because the text does not include any embedded readings - it is strictly focused on writing content, so I supplement it with short stories, essays, and films that I have selected. This makes the text readily adaptable to varied cultural contexts. The student sample essays included at the end of the text do embody a white, middle-class aesthetic, though: one describes baseball, “America’ pastime,” while another compares London and Washington, D.C.
I’ve used this book as a core text for my first-year writing course for two years, and I find it generally does everything the standard first-year writing textbook does with the added benefits of being clearer, more concise, editable and, of course, free. It is designed to support process- or modes-based courses, but it can also be easily used in smaller chunks to support other approaches to first-year writing.
Reviewed by Holly Armstrong, Instructor, Middlesex Community College on 6/30/20
Writing for Success thoroughly covers all aspects of writing. Beginning with the basics of vocabulary, the text progresses through word order, paragraph development, sentence variety and clarity, then moves on to beginning an essay through to... read more
Writing for Success thoroughly covers all aspects of writing. Beginning with the basics of vocabulary, the text progresses through word order, paragraph development, sentence variety and clarity, then moves on to beginning an essay through to research writing. For first year students, including English language learners, the textbook provides clear and thorough descriptions of the writing process and provides examples of completed essays for review as well.
The content of the text is accurate and error-free. While the text covers more topics than I would use in my Reading, Writing, and Reasoning course, the review of vocabulary development, word order, sentence variety, grammar, and paragraph writing are crucial for my students.
Instructional material in Writing for Success is up-to-date and not likely to go out of date since the focus is on the very basics of introductory writing through to essay formats.
Writing for Success is easy to read and appropriate for first year students. While lengthy, the overall review of vocabulary, word order, sentence writing, paragraph development, including help for English learners especially regarding word choice and sentence order, provide clear and concise information.
Tone used is consistent throughout the text. Examples and exercises for each covered topic are easily found and clearly labeled.
Writing for Success covers all aspects of reading and writing, while also incorporating grammar review, and providing help for English learners. While the text is long, instructors can pick relevant material to use and students have a resource that can be used as a reference tool for later courses as well.
Writing for Success follows a logical flow for introducing writing to first year students. The text has a detailed table of contents and each section is clearly labeled and easy to follow. However, there is no index or glossary as part of the text, and this feature is one that could be added for greater ease of use.
I read Writing for Success online and did not have any issues. I was able to navigate the text easily.
The text contained no grammatical errors.
The text was not culturally insensitive. Perhaps the readings included can be updated to include more relevant and timely topics.
Writing for Success is a thorough text encompassing all aspects of the writing process. For first year students, it provides a complete grammar review as well as clearly organized and detailed instruction for essay writing, including model essays. Throughout the text, clear and thorough explanations of concepts are given. Although the text contains limited images, it is well organized and easy to follow. While some students may not need such a thorough review before beginning essay writing, a text that can meet the needs of all learners in my introductory course is welcome.
Reviewed by Brenda Williams, Faculty, Lane Community College on 6/23/20
It is complete and accurate. It covers a lot of material. read more
It is complete and accurate. It covers a lot of material.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
No errors and it is unbiased.
It is very relevant. It will help college students adjust to the college environment and expectations.
The text is direct and clear. An easy read.
It is consistent throughout each chapter and easy to navigate.
It does cover alot of material but that could make it easier to break up into smaller assignments.
It flows and is organized. It can be taught in a different order though which can be helpful.
I had no issues. Things were easy to find and navigate.
I didn't find anything insensitive or offensive.
It was written well.
Reviewed by Dr. Deborah Bradford, Part-time Professor, Bridgewater State University on 6/11/20
This book is very complete, but does not have an index or glossary. It does have a Table of Contents. It might be the most extensive book I have encountered for the topics that are covered. read more
This book is very complete, but does not have an index or glossary. It does have a Table of Contents. It might be the most extensive book I have encountered for the topics that are covered.
This book is accurate and unbiased with no errors.
Writing for Success is timeless in its content. I don't see anything that would make it obsolete. If any updates were needed, I'm sure they could be made easily.
Writing for Success is very clearly written which is especially helpful for beginning writers. The examples given are also very clear followed by exercises that reinforce the material. I did not find any outstanding (in a negative way) technical terminology.
The text is very consistent regarding terminology and framework. One can expect to always find the same headings/subheadings in each chapter such as Learning Objectives, Exercises, Tips, Writing at Work, Key Takeaways, etc. My additional comments about organization (which is very close to the meaning of framework) are below.
Writing for Success is a huge book that covers just about everything a professor would want for any level writer. There really is no way the book could or should be used in its entirety during one semester. It definitely can be easily broken up and reorganized into smaller sections according to what is needed at different points in the semester.
This book is very well-organized. When one becomes familiar with how the material is presented after the first chapter or so, it is comforting to see this same format followed throughout, making the information easier to read and comprehend. The headings and subheadings are clearly marked and bolded and the information that is in a box (Learning Objectives, Tips, etc.) in one chapter is consistently in a box in the other chapters. However, chapters 2-5 (or at least chapters 2-3) might be better placed nearer the end of the book, after the rhetorical mode essay examples or in an appendix. After reading chapter 1, I was surprised to suddenly be thrust into chapters on grammar and punctuation when I would have preferred continuing to read about the elements of writing that are discussed after chapter 5. However, the sequence of chapters can be changed according to the needs of the particular class (as noted in the Modularity section above).
I did not encounter any interface issues.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
I did not find the book to be culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
This book is great and I would recommend it to any professor who is teaching a beginning or even intermediate writing course. I especially like the sections entitled Tips and Key Takeaways which serve as very helpful and concise information/reminders of what to keep in mind for good writing. I was so happy to also see the section entitled Writing at Work included, as I have not seen similar content in many writing books. It is so important to include, as I always want to have my students make a connection between their school work and the outside world, i.e. their real world professional work -- a connection that is sometimes difficult for them to make, especially for the traditional college-aged students.
Reviewed by Eileen Feldman, Instructor, Bunker Hill Community College on 6/4/20
This book presents traditional aspect of writing: grammar, sentence construction, paragraph development, essays, research. It raises the bar by adding chapters directed to novices transitioning into college, to English Language Learners, and to... read more
This book presents traditional aspect of writing: grammar, sentence construction, paragraph development, essays, research. It raises the bar by adding chapters directed to novices transitioning into college, to English Language Learners, and to making oral presentations. There is a Table of Contents but no index
The material and grammar/spelling showed no errors
The relevance is written for longevity. Contemporary technology is referred to and can be added to by interested readers. The topics suggested for writing exercises are timeless but could also be expanded by the Creative Commons agreement.
The text is clear in language, font, and format. There are so graphics , but charts and blue shading for tips help focus attention.
The framework of this book is consistent. Each chapter contains purpose statements, tips to help students, workplace writing situations, key takeaway summaries, and end of chapter quizzes. There are student paragraphs and essay to demonstrate each concept.
Each section can be separated and used as students' needs are assessed. The order of chapters can be changed at teacher's discretion.
The text is clear and logical. The entire Appendix of student sample essays of each rhetorical style appeared rather surprisingly and could be incorporated with those preceding sections.
There are no interface problems, but neither are there many charts or images.
THere are no glaring grammatical errors.
The topics suggested are of American interest and might not resonate with a variety of cultures in the class. Likewise the sample student essay might be intimidating or irrelevant to some readers.
The two outstanding contributions added to this rhetoric are1) the lengthy socioemotional introduction to college level work and challenges and 2)the concern with incorporation of these wkills into workplace environment.
Reviewed by Christy Moore, Associate Professor, Marian University on 3/27/20
The text is VERY comprehensive. I believe it would be difficult to get all the way through the text in one semester. It covers the most basic writing processes early and then eases the student into a more complex understanding of what he/she needs... read more
The text is VERY comprehensive. I believe it would be difficult to get all the way through the text in one semester. It covers the most basic writing processes early and then eases the student into a more complex understanding of what he/she needs to know to write effectively for the assignments normally given at the college level. The Key Takeaways sections and End of the Chapter exercises really provide teachers a way to continuously assess student understanding throughout the semester.
The content is accurate and all of the exercises that I tried, that are provided to test student understanding, were written correctly as well. Each section is very specific and accurately instructs on certain skills and topics essential for quality writing.
Based on the fact that this text covers English grammar and writing at an acceptable level for a college student, the material is very relevant and should remain that way quite easily. Any student that did not have the opportunity to have a strong grammar/writing class in high school will learn so much from the material provided in the text. As technology grows and changes, there may be a place for additions to different formats for student writing.
I believe the text to be clear, concise and to the point. All of the exercises provided throughout the text allow for students to check their own clarity and understanding of the material as well. The writing and grammar terminology used in the text is clear and specific in both definition and organization.
The consistency of the terminology and framework is more than adequate. One thing that this text provides that I think is essential for the student just entering college is predictability. All of the chapters follow a similar framework that can really provide much needed continuity for a student just getting started a college level reader and writer.
Depending on pre-assessment of students in the course, I believe that this text is set up for easy reorganization of material. There will be some sections that students should be able to test out of due to more than adequate prior knowledge. For those though that need a more step by step approach to topics, the content is divided into very manageable sections that will not be overwhelming to a novice to the writing process.
The structure of the text is logical and clear. The text is formatted in a way where an instructor can jump back and forth to meet the needs of specific students for the writing assignment at hand. I would like to see some writing assignments earlier in the text which could help incorporate a student's understanding of the grammar and mechanics that he/she just learned.
The book's interface had no issues. I navigated the chapters and sub-sections very easily and viewed many of the quality charts, graphs and examples provided throughout the text. I liked the bolded vocabulary terms and links provided that take you back and forth to chapters that supplement one another.
I found no grammatical errors.
I did not find the text to be culturally insensitive or offensive.
I wish all of the students that I have in my Reading and Writing in the Content Areas course would have the opportunity to utilize this book in an entry level writing class on campus. It would give me the peace of mind that they have all been introduced to the material that is essential to develop good writers and that they can move on to teach writing appropriately in their future secondary classrooms.
Reviewed by Joseph Amdahl, Adjunct, Chemeketa Community College on 5/21/19
This category might indicate one of the downsides of this particular textbook -- the text covers quite a bit of ground, coming in at a mere 645 pages. Having said that, a lot of the page includes examples, exercises, and their "Key Takeaways"... read more
This category might indicate one of the downsides of this particular textbook -- the text covers quite a bit of ground, coming in at a mere 645 pages. Having said that, a lot of the page includes examples, exercises, and their "Key Takeaways" section -- so the page count doesn't come across as overwhelming as it might seem. Overall, thorough/useful text that would work well for a composition course.
There were no glaring issues with the book regarding accuracy. Writing comes across as objective. A few minor aspects -- for example, the author writes: "A good paragraph contains three distinct components: a topic sentence, body, and concluding sentence." Would have liked more regarding paragraph transitions and implementation of both topic sentence and paragraph transition sentences for students. Overall, book seems accurate and with low bias.
The first half of the text will hold up well, -given that it covers less malleable material like grammar/usage/etc. The essay/writing exercises could be useful in the second half - though not totally inspiring. Given that MLA/APA format evolves/changes, the last section of the textbook will probably go out of date within the next few years.
The material in the textbook is fairly clear. One of the downsides of this text is how much ground is covered. Would probably be more clear if the book was split into two books -- one on grammar/usage and one on the writing process and the elements of an essay.
The text seems consistent regarding both terminology and framework.
Given the page count of this textbook, it might be difficult to cover this much material in a 10-week term. The "Key Takeaways" sections of the chapters were useful and a neat way to add clarity to the intention of each section. Again, given the white space on the page, the text doesn't come across as overwhelming -- though it could have been split into two books in order to add clarity. Would be easy for an instructor to assign sections here (one per week might be manageable).
The layout of the textbook makes sense. From the building blocks of language/grammar/usage to the writing process, essay assignments, editing, and finally formatting. Again, could probably split into two textbooks -- one that covers grammar/usage/format and one that covers the writing process & essay assignments.
The text has no glaring interface issues; however, a few of the pages had quite a bit of white space. For example, page 460 ends after a short paragraph, followed by mostly white space, and then some boxes containing information on pg. 461. Organization like this was probably an attempt to make the content as clear as possible.
There were no glaring grammatical errors.
I didn't notice anything offensive or culturally insensitive within the textbook.
This textbook would be useful to a range of students. The exercises, on a variety of grammar/usage topics, are clear and thorough. The one downside is just that this textbook covers quite a bit of ground.
Reviewed by Candace Hoes, Adjunct Lecturer, LAGCC on 5/17/19
The textbook begins at the basics of writing, such as grammar, word choice, and constructing sentences, and then builds to more complex concepts such as creating a thesis in a research paper. There are adequate stepping stones along the way, with... read more
The textbook begins at the basics of writing, such as grammar, word choice, and constructing sentences, and then builds to more complex concepts such as creating a thesis in a research paper. There are adequate stepping stones along the way, with examples of strong and weak theses that gradually build upon each other. I could see using this textbook for both an intro composition course and several building levels. There are examples of several types of essays both within the text itself and hyperlinked to outside websites.
The instructional matter of this textbook seems consistent with basic composition courses.
I wish that instead of links, the textbook provided a few examples of parenthetical citations of commonly used types of sources. I can see the advantage to providing links is that it more or less places the burden on those websites to stay up to date with the MLA's stipulations instead of updating the textbook itself. However, in my experience, students don't always follow links and would probably ask the professor directly instead. The websites that are linked, such as Purdue Owl, are very robust, but beginning composition students have difficulty navigating those websites to find their answers.
This textbook avoids jargon when explaining concepts and breaks down concepts that can easily confuse a beginning composition student, such as the main idea versus a controlling idea.
This textbook uses the same terminology throughout.
The textbook is highly modular. For example, in my composition course, I would assign brief, five-minute presentations to the students on grammar and punctuation as a review. The sections on word choice and additional help for English language learners would be good as individual readings or to refer students to on a case by case basis if I noticed errors in their essays. The sections that discuss essay types are very in-depth, so I would use them as the backbone for a lesson delivered during the class and assign them as reading as reinforcement. They could be used to open up a unit that culminates in that type of essay. I would focus on one skill in particular in each unit, such as a strong thesis, body paragraphs, introductions and conclusions, etc.
However, the example I gave drew from several different areas of the textbook. It's designed in such a way that it's easy to pick and choose what you need. You wouldn't have to adhere to their organization or go "straight down the list" in order to make sense and use of the textbook.
I appreciate that the learning objectives are separated out into boxes at the beginning of each sub-unit to make it easier for the instructor to scan for individual lessons. The organization of subjects are designed build upon each other from the smallest building blocks of writing to more complex assignments. Key takeaways and exercises are included at the close of each section as well.
The text itself is well formatted in an easy to read typeface and font.
The table of contents on the PDF is easy to use and has internal links to pages, which eliminates the need for searching for page numbers. Each subsection is also linked, which comes in hand because the chapters themselves have been broken down into such discreet sections that it's easy to find just the lesson that's needed rather than search an entire chapter.
Some of the external hyperlinks are no longer working.
I wish that some of the images and charts were easier to read in the PDF, but they can be clicked on and printed for handouts.
I did not find any glaring grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
In the lesson on developing a thesis, the textbook asks students to write a thesis on, "Texting while driving; The legal drinking age in the United States; Steroid use among professional athletes; Abortion; Racism." While these are topics that students are likely to have strong opinions on and therefore it's easy for them to create an "argument," I do not find that beginning compositions students have the finesse to address abortion and racism delicately. That could easily spiral into a hurtful and insensitive writing exercise. The examples of essays included in the textbook themselves seem pretty homogeneous from a cultural perspective. There are external links to essays from more culturally diverse perspectives, but unfortunately some of them are no longer active.
Overall this is a very robust and useful textbook.
Reviewed by Bradley Hartsell, Adjunct English Instructor, Emory & Henry College on 3/13/19
With 600+ pages, this textbook really builds college writing from the ground up, starting with 'sentence writing' and 'subject-verb agreement' all the way up to writing a research paper and examples of 10 different kinds of essay. In between, the... read more
With 600+ pages, this textbook really builds college writing from the ground up, starting with 'sentence writing' and 'subject-verb agreement' all the way up to writing a research paper and examples of 10 different kinds of essay. In between, the textbook is thorough in its explanations and rife with exercises concerning grammar-related instruction and essay construction. I'm not left feeling an aspect I teach in my courses is ignored or goes underserved.
Content Accuracy rating: 3
The textbook's explanation of grammar and sentence construction certainly seem correct, as does their advanced lessons such as developing and revising a thesis statement. However, I did errors on pg. 44 and pg. 49 ("Computers are tool" has a missing word; "The entire family overslept Because because we lost power" and "He has been seeing a physical therapist Since since his accident" seem indicate that those are correct sentences as written, failing to account for the repeated and incorrectly capitalized word). Regarding biases, on pg. 359, in strengthening a working thesis about teenage girls becoming too sexualized, the authors take some editorial liberties asserting that "It is true that some young women in today's society are more sexualized..."; it seems distracting for them to comment on this topic at all, at least without any providing any couched language, like "While the writer of this thesis may feel this way, he or she should also consider X, Y, and Z..."; for example, the authors suggest this 'student' should ask themselves the following questions, including "What constitutes 'too sexualized?'" which is an instructive question for the 'student' to ask themselves but the authors should also be operating within those same parameters, or better yet, abstaining from any comment on female sexuality at all. Also, their example sentences/questions seem conspicuously politically-charged (e.g. "The welfare system is a joke" pg. 358; "Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation." pg. 357; "Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration." pg. 355). And lastly, there are unnecessary editorial uses (i.e. not instruction sentences, examples, etc.) of gendered pronouns ('He' being a bad storyteller, pg. 353).
English grammar and college writing have the convenience of not really going out of date; APA/MLA formatting can easily be updated accordingly.
This textbook does a good job of putting grammatical jargon, like independent clauses, in plain terms so that anyone can understand it. Even as an English instructor, I don't always readily recall the correct terms and exact definitions, even if I know how to use them in practice, so Writing for Success does a nice job of stripping away heightened language and providing plenty of right/wrong examples, therefore making something otherwise pedantic fairly accessible.
Throughout the comprehensive span of the textbook, I see no departure in the terminology or the fairly conversational style of communicating information.
This textbook is formatted and coherently layered in a way that is easy to visualize and process, with properly sectioned-off section introductions, lesson 'tips,' examples, and exercises.
The textbook flows in a logical, linear fashion, beginning with simple 'subject-verb agreement' and each section linearly building from the one that came before it, until now-grammatically correct sentence structure can be built into more complex sentences, and thus drafting a college essay (and so on).
The interface is fluid; it's convenient that it goes to desired page upon click in the table of contents; places to enter answers prompt a text bar to allow you to write into.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
See above--there are no major errors that I can tell, but I did see careless mistakes on pg. 44 and pg. 49.
I find this textbook greatly lacking here. Exercise 1 on pg. 355 asks students to make a student for, in part, 'abortion' and 'racism.' Why? The former is especially charged. Elsewhere, the authors can be clumsy when addressing femininity, race, and politics. Again, why include charged examples? Yes, most language is mostly inoffensive (e.g. "My mother freezed the remaining tomatoes from her garden so that she could use them during the winter), but be it editorial or 'student' examples, they needlessly make allusions to divisive topics. Allow me to restate from above: on pg. 359, in strengthening a working thesis about teenage girls becoming too sexualized, the authors take some editorial liberties asserting that "It is true that some young women in today's society are more sexualized..."; it seems distracting for them to comment on this topic at all, at least without any providing any couched language, like "While the writer of this thesis may feel this way, he or she should also consider X, Y, and Z..."; for example, the authors suggest this 'student' should ask themselves the following questions, including "What constitutes 'too sexualized?'" which is an instructive question for the 'student' to ask themselves but the authors should also be operating within those same parameters, or better yet, abstaining from any comment on female sexuality at all. Also, their example sentences/questions seem conspicuously politically-charged (e.g. "The welfare system is a joke" pg. 358; "Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation." pg. 357; "Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration." pg. 355). And lastly, there are unnecessary editorial uses (i.e. not instruction sentences, examples, etc.) of gendered pronouns ('He' being a bad storyteller, pg. 353). Regardless of the authors' politics, left or right, it seems relatively easy to use language and examples without allusions to politics--socially, bodily, or otherwise.
The idea and general execution of this textbook is everything I want in an English textbook--free for my students to use and comprehensive enough to cover any reasonable topic to expect in my composition classes. For me, the variety in my class calls for some students needing very basic attention paid to grammar (check), while others ace grammar and need thesis strengthening or outlining of research topics (check). There are a couple of grammar mistakes I've noted (which suggests there could be more that I've missed), and I strongly believe some (many?) editorial decisions need to be shelved, namely that of the authors' inclusion of politically-adjacent (or even politically-charged) language and examples. Students in a first-year writing course shouldn't be asked to develop a thesis statement about abortion, or read the authors imply something of a referendum on an assassinated president.
Reviewed by James Gapinski, Instructional Specialist, Chemeketa Community College on 3/8/19
WRITING FOR SUCCESS has extensive depth and breadth. It is over 600 pages in the PDF format, but it doesn’t contain much redundant or extraneous information. The book starts with some discussion of how college writing is different from other forms... read more
WRITING FOR SUCCESS has extensive depth and breadth. It is over 600 pages in the PDF format, but it doesn’t contain much redundant or extraneous information. The book starts with some discussion of how college writing is different from other forms of writing—setting up that distinction provides realistic expectations and contextualization for beginning college-level writers. The book moves into a discussion of reading strategies, emphasizing the importance of comprehending and exploring college readings before diving into writing assignments. I like how these pre-writing discussions frame the entire book, moving naturally toward more technical chapters on grammar and usage, revision, research, and documentation styles. This book is a beast, containing just about anything a writing teacher might need for introductory composition students.
This book is accurate and thorough. I do not notice errors in fact.
WRITING FOR SUCCESS contains useful information that is likely relevant on many college campuses. It is current, but it is not necessarily forward-thinking in its scope. Within the state of Oregon—and more broadly on the national stage—college-level writing is moving toward multimodal composition. This book covers the classic writing assignments found in a typical college classroom, but it does not dive as explicitly into emerging forms of writing. In coming years, outcomes and assessments will likely focus on multiple expressive modes within the composition process. Shifts toward new modes of writing will render the book obsolete if it is not amended or updated. Moreover, there are some missed opportunities in this book for embedding more URLs that prompt additional research and intertextual learning. There are some chapters that incorporate links to online writings by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., links to online library resources, and so on, but these are few and far between in WRITING FOR SUCCESS. A broader focus on new media could greatly improve this book’s long-term relevance.
This textbook is clear and accessible. Whenever new terminology is introduced, definitions are readily provided and explained. It scaffolds information meaningfully and thoughtfully.
This book features consistent formatting and organization. After students have read one or two chapters, they will expect some charts and tables that help define concepts, quick tips in each chapter, and regular exercises to practice what they’ve learned. These learning tools are provided in predictable ways, so students are not caught off-guard by new content.
WRITING FOR SUCCESS breaks information into recognizable modules. Chapters are clearly organized around core themes, and they could be easily assigned piecemeal or out-of-sequence. Additionally, within each chapter, information is presented in bite-sized pieces, with clear headings for navigation and reference. Overall, navigation is clear, and this textbook’s format allows instructors to pick and choose which topics they want students to read.
Topics follow a logical order. The book starts with an introduction to college writing, moves into writing basics, and ends with discussion of formal research writing. The section on English Language Learners felt out of sequence, as if it were placed into the book at random. The ELL chapter is extremely valuable and should remain in the book, but on a macro level, it does not flow with the surrounding chapters. Still, that is only one hiccup in an otherwise well-organized book.
The interface is clean, and this book is offered in multiple formats for ease of access. I personally read the PDF format, and it was easy to navigate. The informational boxes with tips and exercises were eye-catching, and the text itself is formatted well.
I did not notice any glaring grammatical problems.
WRITING FOR SUCCESS draws from examples and recommends additional readings across several cultural contexts, so it earns some kudos for that. Moreover, the book is aware of its own textual inferences; when the book presents students with hypothetical examples, the fictitious students are not exclusively given Indo-European names. However, some problems arise elsewhere in the text. For example, there is a sample exercise that talks about “gay marriage” being legal in six states. Not only is “marriage equality” a more inclusive term, but the exercise itself is outdated and does not reflect the fact that marriage equality is now recognized on the federal level. In another example, the narrative essay section directs students to several pieces written by Sherman Alexie. While its important to include native authors in textbooks, Sherman Alexie has been publicly accused of sexual misconduct. In the #MeToo era, perhaps Natalie Diaz or Louise Erdrich are more appropriate native writers to highlight. While these are just two isolated examples, I found several other microaggressions and culturally insensitive missteps in this book. It feels out-of-touch in key moments. These problems could be addressed through some surgical revisions, but this aspect of the text is problematic in its current form.
Overall, this is a comprehensive book with many valuable chapters. It has some shortcomings, and I would be hesitant to adopt the book in its entirety. However, its incredible breadth and thoughtful modularity allows instructors to pick and choose which chapters best fit their learning goals.
Reviewed by Dhipinder Walia, Lecturer, Lehman College on 5/21/18
This text covers all structural and technical concepts in Standard American English using succinct tutorials and relevant examples. Additionally, there are several sections that may guide student writers towards major writing assignments like the... read more
This text covers all structural and technical concepts in Standard American English using succinct tutorials and relevant examples. Additionally, there are several sections that may guide student writers towards major writing assignments like the research paper, the narrative essay, and the expository essay.
The content is accurate and error-free.
The instructional material is up to date and will not easily become out of date. The only portion that I found less than timely is the APA/MLA portion as well as the visual chapter. The aesthetics of charting and presentations has already changed since this publication.
There is no jargon here. Everything is intended for a beginner writer. It is also easy for instructors to layer on difficult concepts during lecture if students are up for it.
The tone is consistent as is the emphasis on the writer and their process.
Modularity rating: 3
I didn't find the organization to be effective. Traditionally, in a composition course, I am not going to assign a student to read chapters on mechanics. Rather, I would assign a type of writing alongside a reading alongside a particular concept. It might be interesting to readjust the organization to show the way grammar, structure, and content work together rather than apart.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
As mentioned above, I don't think the flow works as an instructional tool for a first year writing course. I think it works better as a supplementary resource for a student writer.
There were no interface issues.
This text contained no grammatical errors
The text is not insensitive though the readings are political in nature.
This is a useful text for composition instructors to have, particularly when teaching an online course. I could easily copy and paste tutorials into my feedback for students. Should the structure of this text change, I may consider using it as a text.
Reviewed by Catherine Batsche, Associate Dean, University of South Florida on 3/27/18
This text provides a comprehensive overview of writing. The text covers basic writing skills, organizational skills, and the writing process. There are even chapters on writing research papers and various types of essays. It could be used as a... read more
This text provides a comprehensive overview of writing. The text covers basic writing skills, organizational skills, and the writing process. There are even chapters on writing research papers and various types of essays. It could be used as a text for a writing course or as a reference book for students who need to work on selected problem areas to improve their writing.
The text provided accurate information, good examples, and several activities to reinforce the major points in each chapter.
The book contains basic information about writing that should continue to be relevant over time.
Clarity rating: 3
The writing style of the book is extremely clear and easy to follow.
The framework for this book is applied consistently across chapters and sections. Each chapter begins with clearly stated learning objectives, exercises, learning tips, and key takeaways.
The book can easily be used as stand-alone chapters, entire sections, or the book as a whole. I plan to use several chapters in workshops to train teaching assistants who will grade assignments in writing-intensive courses. The teaching assistants will then use the entire book as a reference book when providing feedback to students.
The text is well organized and flows in a clear, logical fashion. Some chapters may be less useful for some classes depending on the purpose of the class. For example, the first few chapters on study skills seems out of place in relation to the remainder of the text. Likewise, the chapters on APA and MLA style are too condensed to provide more than an overview and will need to be supplemented with other material. However, these chapters do not detract from the overall quality of the book.
The presentation of the book does not have as much visual appeal as some other online books. It is text-heavy but well organized. I had no problem navigating the book.
I have not found any grammatical errors.
I have not found any examples that might be offensive. However, I have not yet used the book in its entirety so I will learn more about this aspect as I begin to use it with students.
Many undergraduate students need to improve their writing skills but don't know how to get the help they need. This book provides a valuable resource for students who need to learn more about the writing process as well as those who need to improve in specific areas such as grammar and punctuation. I plan to use the text to train teaching assistants how to provide feedback to students who are taking courses that have major writing assignments. This is an excellent book that can be used as a stand-alone text or as a supplemental reference in any course that has major writing assignments.
Reviewed by Davida Jordan, Adjunct Instructor, Portland Community College on 8/15/17
Extremely comprehensive, clocking in at over 600 pages, this book is an excellent grammar reference for writing students. It includes practical exercises that can be used to strengthen work writing or academic writing. It would appeal to a wide... read more
Extremely comprehensive, clocking in at over 600 pages, this book is an excellent grammar reference for writing students. It includes practical exercises that can be used to strengthen work writing or academic writing. It would appeal to a wide variety of students, from beginning to advanced and is arranged in order of increasing difficulty. Besides giving practical information about grammar and writing, the text includes helpful suggestions on organization, time management, and study skills.
There are some small typos such as missing letters or words. Overall, the book is mainly error-free, but for a good grammar and writing textbook, it really should be 100% accurate. The tone is unbiased and in fact is encouraging and fair.
The book addresses the complexities of writing in the twenty-first century and guides students through carefully choosing their online resources and verifying their validity.
I appreciated the additional examples of different rhetorical styles at the very end of the book; however, many of the links were broken. This is an easy-to-remedy problem, though.
The text uses encouraging languages and easy-to-understand metaphors to illustrate abstract concepts.
The text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework from chapter to chapter. There is a reliable pattern that each chapter follows.
Most of the time, it's easy to pick out the different sections of the book because they are color-coded or similarly marked. For example, nearly all of the Key Takeaways are in a green box. All of the Tips for Writing at Work are in a grey box. All of the Learning Objectives are in a black box.
It's possible to click on writing examples and view them in a larger version in a new window.
Although the book builds in terms of levels of difficulty, it would be very easy to use a chapter out of order to suit the instructor's needs. Each chapter can stand alone even though some pieces of writing are carried through as examples from chapter to chapter. This gives the book cohesiveness but doesn't impede its modularity.
The text is logical and clear. Grammatical concepts are explained thoroughly, and the writing process is taken apart step-by-step for the students.
There are several parts where an underlined sentence is referred to, but it's not actually underlined in the text. It's possible this is only a problem in the PDF version. Overall, the formatting is clear and easy to follow.
Seeing as it's a grammar and writing textbook, the grammatical errors are minimal.
The text includes great excerpts from diverse authors such as Amy Tan, Sherman Alexie, Sandra Cisneros, Gary Shteyngart, and MLK.
In the opening chapters, some grammatical concepts were addressed superficially but then were returned to in more detail in later chapters, which was reassuring. Chapter 5 focuses on English language learners, the students I teach. However, the entire book could be useful to both native and non-native English speakers.
Reviewed by Rachel Wilson, Adult Education Instructor, Bossier Parish Community College on 6/20/17
The text covers all its bases, from success and study skills for new college students to draft, revising, writing, and presenting a research paper. Chapters 1 through 5 cover the basics of grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and word choice,... read more
The text covers all its bases, from success and study skills for new college students to draft, revising, writing, and presenting a research paper. Chapters 1 through 5 cover the basics of grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and word choice, and these chapters cover only that which is most important to writing without getting into unnecessary grammar review. The text provides relevant exercises to go along with each chapter and its individual sections. In chapter 6, the author discusses paragraphing, while in chapter 7, he provides the student tips on improving writing at a sentence level. Chapter 8 covers the writing process, providing ample information on pre-writing strategies and revision and editing techniques. The text also effectively walks the student through the process of writing an essay in chapter 9 and discusses the rhetorical modes in depth in chapter 10. The last chapters (11-15) are dedicated to researching, writing research papers, presenting those papers,0 documenting sources, and providing sample essays in the different rhetorical modes. While the author does a good job covering the basics of documenting sources, I would still have to send my students to their writing handbook or the OWL at Purdue for comprehensive coverage of the source citation formats.
This text is, as far as I can see, both accurate and error-free, though, as stated above, there are a few sections (mostly with documentation) where outside sources would have to be consulted for in depth discussions of the topics.
The only area I feel could use a little updating would be the documentation chapter, though for just an overview, it does its job adequately. The text is set up in a way that seems to allow for easy updates as necessary, and the information contained within is timeless enough to withstand possible changes in writing instruction.
The text is written in easily understandable prose and defines its particular terms in an accessible way for students.
Consistency rating: 2
The text maintains consistency and follows a well-organized framework.
This text is organized in such a way that makes it easy to assign small readings to students without having to jump back and forth between chapters or different parts of the book in general.
The text builds on itself, from having the necessary study skills to understanding basic grammar and sentence structure to navigating the writing process. It then transitions from the writing process to the essay, the types of essays, and research papers. It ends with documentation and presentation of research. I would suggest, though, including chapter 15 (readings on the rhetorical modes) in the chapter on rhetorical modes (chapter 10) or distinguishing it as an appendix rather than a chapter of its own at the end.
The features of the textbook within the text itself are easily navigated, especially with hyperlinks to jump to specific parts of the book. However, while the book does have a short section index at the beginning of each chapter, a comprehensive table of contents at the beginning, or even an index at the end, of the book would go a long way in making this work more easily accessible to the everyday user. As it currently stands, a user must scroll through the entire document to find what the book covers. While an instructor can direct his or her students to specific sections with the appropriate PDF page number, the student user would not be able to discover specific information in the text efficiently right off hand.
With having read through the text, and to the best of my grammar knowledge, I see no major errors or typos.
The text is appropriately inclusive and culturally sensitive.
As an Adult Education Instructor without access to textbooks in the classroom for my students, it is especially helpful to have access to a college level textbook that discusses the basics of grammar and writing my students will need very soon. Instead of having to make copies that will get thrown away or lost, I can give my students the link to this text and assign them specific sections to read before each lesson. As I will soon be teaching a college-level English 101 as well, I am excited to have this text as a supplement to the department-required text.
Reviewed by R.A.Q. Jenkins, Assistant Professor, Southern University and A&M College on 6/20/17
One of this text's advantages is its comprehensiveness. However, I find that too much emphasis was placed on writing basics, which in fact, comprises the bulk of the text. While this portion is extensive, I found the chapter on rhetorical modes... read more
One of this text's advantages is its comprehensiveness. However, I find that too much emphasis was placed on writing basics, which in fact, comprises the bulk of the text. While this portion is extensive, I found the chapter on rhetorical modes lacking. For example, Narration was covered in four pages. I would have preferred more emphasis on basic features of each mode, guided writing practice, and illustrations/visuals (annotated sample essays). The text does not include a glossary or index, which are additional disadvantages. Overall, however, I find this text effective.
The content appears accurate and error-free.
The overall content is foundational, so relevance is not an issue. Formatting and style guides, URLs, and sample essays can be readily updated as needed.
Besides its comprehensiveness, a highlight of the text is its clarity. The writing directly addresses the student much more so than other texts I have used. The conversational tone, especially in the early chapters, should engage even the most reluctant writer. Many of the tips and advice provided serve to assist students beyond the composition course into the whole of their academic career and the workplace. This is definitely a student-friendly text.
Chapters are consistently organized throughout and feature learning objectives, exercises, collaborative activities, and key takeaways, which should be particularly helpful for students. Several of the exercises require students to revisit and revise a previous exercise, as new skills and knowledge are acquired.
This text is suitable for modules, which would allow instructors to organize chapters according to the demands of the course and student's needs. Much of this text's early chapters would serve as much needed review and guided practice for students, since more so than other texts I have used, this one provides in-depth coverage of basic writing skills. Chapters 10-15 should meet the needs of most first year writing programs.
The text is well-organized. However, the sample essays (ch. 15) would have been better placed after the rhetorical modes chapter (ch. 10). The strength of the text's organization are the chapters on writing a research paper and visual presentations.
I downloaded the PDF version and had no significant problems with the interface. The only issue I did have was after clicking a hyperlink then attempting to return to the text, I was redirected to the beginning. This may be an inconvenience for some.
I did not notice any grammatical errors.
The text refrains from cultural insensitivity. Several of the examples, grammar exercises, and sample readings were inclusive of various kinds of diversity. In particular, a text's sample essays plays a crucial role in my overall satisfaction, as I expect to see culturally relevant essays that may resonate with my students. This text included commonly used standbys, such as King's "Letter from Birmingham Jail and Alexie's Indian Education.
Reviewed by William Broussard, Assistant Professor, English, Southern University on 6/20/17
The book covers the writing process, several essay styles, as well as grammar and syntax exercises thoroughly without being intimidating, and is excellently paced. Particularly impressive is the amount of detail given to the sentence, paragraph,... read more
The book covers the writing process, several essay styles, as well as grammar and syntax exercises thoroughly without being intimidating, and is excellently paced. Particularly impressive is the amount of detail given to the sentence, paragraph, punctuation, and the particulars of the writing process.
The book accurately describes, in great detail, all elements of the writing process. Combines all elements of a traditional handbook with specific reference to the rhetorics of several essay styles, and does so in an encouraging manner. Aim is clearly to encourage non-English/Writing majors.
Content appears up-to-date, and of note is a section on presentations and visual rhetorics which will be useful and likely interesting to contemporary students. Book is light on visual imagery, making it less appealing to contemporary/millennial students, but its structure seems amenable to relatively easy updating, and all links were accurate.
The book is clear and provides many examples of student writing to explain the application of material discussed in each chapter.
The book moves along at a predictable pace and begins with building blocks of writing (sentence and paragraph style, punctuation, process) before moving on to more complex assignments. By Chapter 15, which focuses on a number of essay styles, the student has had individual chapters to prepare each step of building an essay, ensuring mastery before taking on more complex projects.
It is simple to imagine this textbook divided into two parts so as to encompass an English 1 and English 2 textbook, and to imagine teaching the introductory elements while interspersing major assignments from Chapter 15 alternatingly.
Well-organized, and as mentioned previously, it is excellently paced with each ensuing chapter building logically upon the previous one.
The book is lacking only in this area. The pdf version features noticeably few visual images and pictures, and very few links for students to interact with supplementary materials to the text. However, the author provides a link for the submission materials which shows an openness to addressing it. However, what is included is accurate and appropriate.
No perceived grammatical or spelling errors. Simple and clear writing style.
Text is inoffensive, but lack of visual texts or discussion of more challenging contemporary topics (the book does not include any sample texts by contemporary authors on challenging issues).
An excellent choice for introductory writing courses.
Reviewed by Emily Aucoin, Assistant Professor, River Parishes Community College on 6/20/17
The textbook effectively covers the writing process and addresses mechanical and grammatical concerns. While the chapter devoted to rhetorical modes is not terribly in depth, it does an adequate job of introducing and explaining each type of... read more
The textbook effectively covers the writing process and addresses mechanical and grammatical concerns. While the chapter devoted to rhetorical modes is not terribly in depth, it does an adequate job of introducing and explaining each type of writing assignment. The research section of the text is effective, but the MLA references are dated. There also is a detailed table of contents but no glossary.
The textbook's content seems accurate, error-free, and unbiased.
For the most part, the content seems relevant and long-standing. The main area in need of updating is MLA, but linking to an outside website could quickly remedy this problem.
The book is written in a straight-forward, clear manner that should be readily understood by most freshmen-level students. The embedded exercises and tips also are accessible.
The included terminology is clear and consistent, as well as appropriate for the subject matter. The chapters also follow a logical framework and reinforce material through exercises and relevant examples.
The textbook easily can be divided into smaller, stand-alone reading sections. Instructors should be able to readily assign portions of the text to meet their course learning outcomes and objectives.
Overall, the textbook is well organized; it effectively addresses key elements of grammar and mechanics, walks students through the writing process, and details various types of writing. While I would like to see Chapter 10 (Rhetorical Modes) divided into separate, better detailed chapters, on the whole, the textbook's organization is logical.
The textbook was easy to follow, particularly because of the detailed table of contents and chapter outlines. Some links also were included throughout to help readers more easily navigate the text.
The text seems free of grammatical errors.
The text does not seem culturally insensitive or offensive. Some of the linked essays in Chapter 15, for example, provide students with readings that are culturally diverse.
On the whole, this is an effective, comprehensive resource that could be of use in any freshman-level composition course.
Reviewed by Genevieve Halkett, Instructor, Chemeketa Community College on 4/11/17
The book is extremely comprehensive, beginning with the concept of college writing, moving on to writing basics such as sentence structure, punctuation, and paragraph structure. it provides a good guide to essays; it includes basic structure,... read more
The book is extremely comprehensive, beginning with the concept of college writing, moving on to writing basics such as sentence structure, punctuation, and paragraph structure. it provides a good guide to essays; it includes basic structure, rhetorical modes, research and documentation and ten different types of model essays.
The index is complete and easy to follow.
There are a few typographical errors but the majority of the 607-page resource was accurate.
There was no real bias though I would like to see more cultural variety in the literary excerpts and situations used in the exercises.
Most of the resource focuses on writing and grammatical structure; there may be small changes that need to be made as the use of the English language evolves; however, this will be negligible. I anticipate this text requiring very few changes in years to come.
it is well laid-out and easy to follow. The explanations, examples, and directions are clear and concise. It is also written with both native and English as a Second or Other Language (ESOL) speakers in mind; the word choice and structure reflect this.
The text's framework and terminology are consistent; I did not see any examples of inconsistency.
This resource lends itself to a modular approach; it would be easy for an instructor to relevant chapters that reflect student needs, course time constraints, or changes within a curriculum.
The resource's is consistent overall; each chapter begins with learning objectives, explanation, examples, exercises, and key takeaways. It is a good resource for students since they are quickly able to anticipate and follow each chapter.
This resource was quite simply designed; there are no charts or images that would lead to confusion. Enough space is given so that blocks of text are read without difficulty and it is free of distraction.
Since it is a writing textbook, I was gratified to find that the grammatical structure and use was very accurate.
I would definitely have like to have seen more examples of the races, ethnicities, and backgrounds I encounter in class; most of the examples used were extremely neutral and reflected a very narrow strata of society. For me, this was the weakest part of the text.
This is an excellent resource-well structured, user friendly and easily adaptable. My main concern-the lack of cultural relevance- can be balanced by providing supplementary materials reflective of the learners' cultures and backgrounds.
Reviewed by Elizabeth Sandell, Professor, Minnesota State University, Mankato on 4/11/17
Provides instruction in steps and sections; builds writing, reading, and critical thinking; and combines comprehensive grammar review with paragraph writing and composition. Provides a range of discussion ideas, examples, and exercises. Serves... read more
Provides instruction in steps and sections; builds writing, reading, and critical thinking; and combines comprehensive grammar review with paragraph writing and composition. Provides a range of discussion ideas, examples, and exercises. Serves both students and instructors. 600+ pages -- very comprehensive.
Quite accurate in terms of the information provided. Uses sources that we use in my writing-intensive classes, so the book is addressing real needs in the classroom. Suggestions reinforce the concepts and practices that our librarians share with students and instructors.
Thought-provoking scenarios provides opportunities for collaboration and interaction. The exercises are especially useful for working with groups of students, which is how I organize workshops and discussions in my classes. Tips for effective writing are included in every chapter. It's nice to have positive examples of how to write, rather than dwelling on negative examples of how not to write. Addresses each concept with clear, concise,and effective examples that are reinforced with opportunities to demonstrate learning. This textbook will be useful for students throughout their academic studies.
Very clear. Clear exercises teach sentence and paragraph writing skills that I already try to emphasize in my classes. I will use many of the exercises, but base them on the content of my course curriculum, instead of generic assignments.
Provides consistent and constant reinforcement through examples and exercises about writing. Involves students in the learning process through reading, problem-solving, practicing, and experiences in the processes of writing.
Modularity rating: 2
Each chapter is stand-alone and easy to read on-line or to print and read off-line. Each chapter has examples that organize the discussion and form a common basis for learning.
Overall, the organization, structure, and flow is fine. Textbook is more than 600 pages, which makes it more of a reference / resource book. I will pull materials that I need for my specific writing-intensive course.
Presents comfortable, easy-to-read material with simple graphics and helpful charts. The Table of Contents does not allow the reader to jump directly to the chapter or section.
The text contains no grammatical errors that I found... If there had been a few mistakes, I would still use the text as a resource.
I am starting to use the idea of the academy as a culture. So, in the writing-intensive course I teach about human relations in a multicultural society, I emphasize how student writing in college must be qualitatively different than writing in secondary schools. I am delighted that this text begins with an introduction to that very idea. Word choices in the text imply inclusion of a variety of ethnic groups and audience backgrounds (e.g., Malik, Miguel, Elizabeth).
I will use this book in a second-year general education writing-intensive course. This resource is useful and friendly, although it is very long. With its incremental approach, the text addresses a wide range of writing levels and abilities. I think students will appreciate it as a resource that they can use throughout their academic life.
The text would also be valuable in a first-year intro-to-college course (we call it First Year Experience), because it teaches many useful academic study practices. For first-generation college students, this text introduces many strategies about how to "do college" with which their families may not be familiar.
Reviewed by Leann Gertsma, Adjunct English Instructor, Minnesota West Community & Technical College on 2/8/17
I was surprised to find this textbook to be a very comprehensive writing handbook. It not only covers grammar and sentence structure, but also devotes a lot of time to the topics of college writing, the writing process, writing techniques, and... read more
I was surprised to find this textbook to be a very comprehensive writing handbook. It not only covers grammar and sentence structure, but also devotes a lot of time to the topics of college writing, the writing process, writing techniques, and essay types. All the sections are clearly labeled with useful exercises to guide students through the material. I appreciated the hyperlinks throughout to navigate to other related sections. One area that seemed to be lacking was the table of contents in each new chapter. These pages were not enabled with hyperlinks and failed to have page numbers associated with them.
I felt this text was accurate. It contains good information for first year writing students. I did not see any bias or errors throughout.
While I did find most of the information current and very relevant to writing students, some of the links in the last chapter did not work. As websites continually change, these would need to be updated on a regular basis. The research chapters would also need to be updated on a regular basis as these materials change frequently.
I found the textbook to be clear. The prose was adequate for first year composition students. There are many examples in the chapters that are relevant to the readers and help put the concepts into practical application.
This textbook is consistent in language, tone, and structure.
The textbook is arranged in an easy to use fashion. The chapters have easy to follow headings, and the key concepts are highlighted. All the chapters are arranged in a similar manner with objectives, lessons, examples, exercises, and key takeaways. Instructors can easily assign specific sections or chapters, while skipping others without confusion. I think the APA and MLA chapter should be split into two chapters to avoid confusion.
The topics are arranged in a clear structure throughout the text. I would have liked to see the chapters arranged in a different format, but this is a minor problem as the instructor can assign the chapters in a different order than they are presented.
This textbook was easy to navigate. The only concern I saw with this was the several of hyperlinks in the final chapter did not work anymore.
I did not find any errors in the text.
I did not see any insensitive or offensive language in the text.
I liked the example papers in the text. However, I wish there were more of them. I also found the chapter on APA and MLA a bit confusing. Students often struggle with these concepts so I think they should have been presented differently. The two styles should not be lumped together in one chapter. They should be separated.
Reviewed by Timothy VanSlyke, Instructor, Chemeketa Community College on 2/8/17
Although there is no index or glossary, I feel that the text is very comprehensive in its coverage of developmental writing. The text clearly walks the student through the writing process and introduces the major rhetorical styles students will... read more
Although there is no index or glossary, I feel that the text is very comprehensive in its coverage of developmental writing. The text clearly walks the student through the writing process and introduces the major rhetorical styles students will face in college. It is clear that the author has worked extensively with the population(s) likely to have need of this course and has planned a comprehensive curriculum to serve them. Having worked extensively with students needing to develop their academic writing skills, I found it very straightforward to adopt the text and align it with my course outcomes.
Content is definitely error free and unbiased. I haven't found any errors or content that struck me as biased or inaccurate.
I think this book will be relevant for quite some time as the need for students to communicate effectively in writing is not going to change. The organization of the text lends itself to updating quite well. For example, the sections devoted to grammar and mechanics, the writing process, and rhetorical styles may need little or no updating, while over time, the sections devoted to research writing (e.g. MLA style) might need more revision.
Given that this book is intended for developing writers, I feel clarity is essential. Too much jargon would scare away students who may already feel overwhelmed. This book strikes an excellent balance between communicating important concepts and terms without being overly technical. Good examples of this can be found in the sections on grammar and mechanics as well as in the rhetorical modes section.
The organization of the book easily lends itself to easy navigation, chapters are divided into logical sections (e.g. 1.1, 1.2, 1.3) and each section follows a consistent format. There are recurring sections that are color coded (exercises in blue boxes, "key takeaways" in green boxes) and the numbering system is clear and logical. The only downside is that the downloadable PDF version of the book doesn't have a table of contents, but I found that if your pdf reader can show bookmarks, there are bookmarks to each of the sections.
This book is very modular. Each chapter is divided into sub-sections (chapter 1.1, 1.2, etc) and the sections are logically divided and lend themselves to easy be assigned as separate readings.
The structure of the text is logical and clear, but what I like most is that the chapters are not overly dependent on a linear flow, which allows me to assign chapters out of sequence without worrying that it will be disruptive to students.
I would describe the interface as quite user friendly. A quick skim of the online Table of Contents is all that is needed to understand the organization of the text and its major sections. Accessing each section is quite easy with the links provided.
One standout in this area is a complete chapter devoted to second language learners, which is quite useful for this population. Otherwise, I have found this to be an excellent resource that introduced students to the academic culture.
Overall I am very pleased with this text, and excited that I can offer my students a book of this quality completely for free!
Reviewed by Jennie Harrop, Chair, Department of Professional Studies, George Fox University on 2/8/17
Writing for Success is admirably comprehensive, but maybe a little too much so. While some professors will find the one-source stop helpful in reducing textbook costs, many students will be overwhelmed by the sheer breadth of information. Because... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
Writing for Success is admirably comprehensive, but maybe a little too much so. While some professors will find the one-source stop helpful in reducing textbook costs, many students will be overwhelmed by the sheer breadth of information. Because the text attempts to cover so much in a single volume, much of the information is offered at a surface level without the depth necessary for the content to become memorable and meaningful. Two key components that are missing in this text because of its surface-level scope are the WHY (why is this information relevant?) and the HOW (how do I apply this?).
Most information is accurate, although some is not thorough enough. When explaining the dash or parentheses, for example, it might be helpful for students to hear when and why these punctuation marks are most effectively used. If a student masters the use of parentheses as described in section 3.6, should he or she pepper an essay with lots of parenthetical asides? If not, why not?
In the section on APA formatting, the title page running heads are not correct.
The key information in the text will not become outdated, although the examples and the sample texts will. The book would benefit from consistent updates to ensure that the examples are culturally sensitive and generationally appropriate. The APA and MLA sections will also need consistent updates.
The prose is clear, but the information covered is not always. In section 5.2 titled "Negative Statements," for example, students are told that negative statements are the opposite of positive statements, but the text does not explain why this information is worth considering. In section 5.6 titled "Modal Auxiliaries," the text moves immediately to examples and exercises without an explanation of why this information might be pertinent or useful.
The terminology and framework presented are consistent throughout.
The text is consistently broken into individual chunks of information rather than meandering prose, which can be enormously helpful for students. Some sections jump directly into the modular chunks of examples and exercises without bothering with any explanatory sections at all, however. In those cases, students need some kind of explanation of why the information presented is important and relevant.
The text's organization is consistent and easy to navigate. The information is presented in divisions familiar to most writing texts: (1) mechanics, (2) writing process, and (3) sample essays.
The Table of Contents is a helpful feature, allowing one to skip through topics easily. I was unable to download this text in a way that would allow me to highlight or make notes.
The grammar is correct throughout.
The examples used are culturally sensitive but mostly bland in a way that makes them forgettable and unimpactful. If cultural relevance means that we whitewash, this text is successful; if it means that we step into the controversy, then the examples in this book need to be more forthright and genuine.
I have used this book in a basic writing course, and I found the students informed but uninspired. I will continue to require this text as a reference books for all students in our program, but I will seek a more lively text for future writing courses in order to keep students engaged, enthusiastic, and forward-thinking.
Reviewed by Sherri Kurczewski, Instructor , Portland Community College on 12/5/16
This book has sections that I would cover in my class. It is a basic writing tool for beginner writers in college. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 1 see less
This book has sections that I would cover in my class. It is a basic writing tool for beginner writers in college.
Overall the book is accurate. It goes over the basic differences of high school vs. college writing with additional grammar explanations and exercises.
This book is for a basic writing class for students who are underprepared for college level writing.
The book was written very direct to the beginning college writer. The tables help explain the differences in high school vs. college writing.
The consistency of the book was good. There was not a lot of terminology that would be over the students understanding.
The book is good at putting each section together. There are small, yet informative grammar sections. An instructor may skip over some chapters without confusing the student.
The organization of the book seems fine. It has the basic ideas of writing and then leads to grammar.
There were no issues with navigation of this file.
I did not see any errors in grammar.
This is a straightforward book without many examples. I did not see any issues.
I would definitely use this book in my basic writing class. It is a quick read and I could easily pull out sections to use and compare.
Reviewed by Anna Erwert, Adjunct faculty, Portland Community College on 8/21/16
The book is extremely comprehensive. If a college works on a 10-week quarter, it's unlikely a student would use the whole book. However, I personally like this completeness because it allows flexibility. Whole class, we could use the chapter on... read more
The book is extremely comprehensive. If a college works on a 10-week quarter, it's unlikely a student would use the whole book. However, I personally like this completeness because it allows flexibility. Whole class, we could use the chapter on the writing process, and then after essay 1, I could assess writers and assign them portions of the sentence level and grammar sections as needed. Also the most common writing errors, like comma splices and frags, are covered and include exercises.
With a decade plus teaching college Writing and Reading, I feel the book is accurate in the sense that it covers what students actually need. I did not see bias. It is very concise and matter-of-fact.
It's relevant eternally, but one caveat: most colleges are moving toward supporting Reading and Writing in one class. Integration of reading skills would be a way to keep this book fresh.
Very little jargon. Everything is well defined, though I do think more examples and samples would be nice. However: this is an easy section for the individual instructor to augment.
Very consistent.
This is my favorite part of the book. It is way more inclusive than we could use in one quarter, but I could assign grammar or sentence level stuff with flexibility, as needed. I could also do the whole book in reverse (sometimes I like to start big, then move to smaller concerns)or present only the Research section for a Reading class.
Very logical but also easy to manipulate logically
There isn't anything confusing about it. I don't think it is the most engaging, exciting design in the world, but perhaps that is not the goal here. More pictures though, sorry- it is a visual age- would be welcome. Still, instructors could add in pics, slides, video, etc.
I saw no errors
The book is geared more to the college student, not the particular culture or gender. In some ways this is a relief to me, as I am trying to work with topics that bring us together, like say, the cost of college, as opposed to those that fragment us, like racial profiling. In a ten week course in one of the most diverse campuses in the PCC system, this is becoming very important. In this sense, the book fits.
Super useful framework. Teachers will augment with samples, interactive activities, visual aids, etc., but that makes it better for your specific audience anyway.
Reviewed by Olga Filatova, Visiting Assistant Professor, Miami University on 8/21/16
I was surprised by how much useful content the book has. It covers everything I would need to teach in a first year college composition writing class. The text gives overview of reading and writing strategies, and covers everything from grammar,... read more
I was surprised by how much useful content the book has. It covers everything I would need to teach in a first year college composition writing class. The text gives overview of reading and writing strategies, and covers everything from grammar, vocabulary, punctuation, sentence structure, elements of composition and writing process, to rhetorical modes and elements of research. It has so much material, that it can be adjusted to a wide range of students' needs and writing abilities. Parts of the book can be used as a reference. The book is very much in line with my course goals, and is particularly effective in helping students with writing in a variety of genres, introducing a clear thesis statement and sustaining it throughout the paper with support and evidence. It also has good tips for reading, writing and editing. However, I didn't find the section for language learners helpful. I teach composition to international students, and would definitely skip the chapter. The concepts in the chapter are not well-explained and application exercises are insufficient. This chapter can be used as a reference for instructors who don't usually work with LLs.
The content is accurate. I didn't find the readings particularly engaging, but they are good for structure analysis. The links to additional essays provide opportunities to choose more engaging reading material.
Writing foundation principles are solid. MLA and APA citation and formatting would need most often updates. The link to Purdue OWL solves this problem.
The book is written in a very clear manner. However, some of the explanation might be too long and lack sufficient examples.
The book is very consistent. I would rearrange the chapters and start with the writing process. Grammar, vocabulary and punctuation can be in a reference section of the book.
The text is divided into chapters and sections. Each of the chapters follows the same structure. The chapters have clear learning objectives, subtitles and exercises for practical application. The main points are summarized at the end. Students would have no trouble navigating the content.
The topics are presented in a logical way. As I mentioned above, I would rearrange the chapters in the book. The way the chapters are arranged now puts the emphasis on developmental writing vs rhetorical practices.
The books interface is very good.
The book is excellently written. I didn't see any grammar errors.
The book is culturally relevant. It focuses on American culture. It lacks elements of global cultural awareness, but it is good enough for the purposes.
Thank you for the book. It is very good. I will use it with my students next semester!
Reviewed by Laura Funke, Instructor, Inver Hills Community College on 8/21/16
The text is almost too comprehensive—trying to cover writing, reading, and study skills strategies. Within writing, it covers grammar, mechanics, paragraph writing, essay writing, ELL troublespots, and even documentation. Although an instructor... read more
The text is almost too comprehensive—trying to cover writing, reading, and study skills strategies. Within writing, it covers grammar, mechanics, paragraph writing, essay writing, ELL troublespots, and even documentation. Although an instructor could easily focus on specific chapters based on the level of the class and needs of the students, the effort to be comprehensive led some areas to be overly simplistic and basic. For example, in the section on writing introductions, there is a list of strategies for starting the essay (the hook or attention grabber) but not much direct instruction or modeling. In other words, quality was sometimes sacrificed for quantity.
From my experience, the content of the book was accurate in most areas, but some advice was simplistic. For example, telling English language learners to avoid slang and idioms is wrong. What often makes ELLs’ writing awkward is the lack of idioms. The advice to avoid slang might be better for a chapter for native English speakers. In the same ELL section, the author stated that simple present is used “when actions take place now” but that is not the case. Present progressive verbs are used for the current moment (“Right now, I am writing a review.”) These inaccuracies happened on occasion, but in general, the advice and information given by the writer was accurate.
The text can be easily updated because of the modular organization. The topics used for examples or exercises would benefit from regular updating. Some topics are engaging for students, but others would not be for most students (such as ‘the hardiness of the kangaroo rat’).
The text is written in using clear, accessible language that is appropriate to first year college students. New terms are explained clearly and put in bold letters. It might be helpful to put key terms and definitions in margins, as many textbooks do, or at least consider an index and glossary at the end of the book.
I didn’t notice any inconsistencies in framework or terminology.
The text is structured in such a way that instructors and students can pick and choose among relevant chapters. There are references to prior chapters, but the text doesn't assume that students have read the text from front to back. Students can easily refer back to prior chapters when more background is needed or if additional follow-up instruction is needed. One recommendation would be to include the chapter and section number on each page in a footer or header.
The information flows logically for the most part. The book begins with a broad overview of writing and student success strategies. Then it moves from sentences, to paragraphs, to essays, to research papers. One section that seemed out of place was to include 'purpose, audience, and tone' in the chapter on paragraph writing. It would seem to be a topic that could use its own chapter. I also felt that chapter 7 on sentence variety was misplaced after paragraph writing. Still, I appreciated that the author circled back to some topics briefly even if they were covered in more detail in another chapter. For example, the author discusses wordiness and word choice in the chapter on revision even though those topics were discussed in an earlier chapter. Imbedding some sentence-level concerns into the chapters on paragraph or essay writing helps students to see the relevance of the sentence-level instruction.
Occasionally an informal font is used to show student examples of writing. This playful font is difficult to read (see p. 233). It would be better to use a standard font like Times New Roman to make the text easier to read. Also, the book is very text-heavy. There are few to no engaging photographs or images for readers. Even though it is clearly organized with headings, subheadings, bold words, and other organizational devices which are very helpful, it is not visually engaging. There is a nice use of internal links. In one section, chapter 6.2 p. 247-248), the directions prior to three model paragraphs said “The topic sentence is underlined for you” but I didn’t see any underlining. I don’t know if that is an error in the text or a problem with my own computer.
I noticed no grammatical errors when reviewing the text.
The text is not culturally insensitive. However, I wouldn’t say that the writing samples are particularly engaging or daring in terms of challenging the status quo. Most of the topics are standard examples: “How to grow tomatoes from a Seedling,” “Effects of Video Game Addiction” and “Comparing and Contrasting London and Washington D.C.” I would like to see more creative and engaging course readings in the text, readings that address the interests and backgrounds of culturally- and linguistically-diverse students.
The practice exercises are often very engaging and creative. For example, p. 287 the author explains an exercise in which students rewrite children stories (written using simple prose) with more complex syntactical structures to practice sentence complexity and variety. Most all exercises are practical and student-friendly. The text doesn’t get bogged down with excessive use of exercises; instead, students’ own writing is often the basis of the exercises, making them relevant to developing their own writing skills.
Though I appreciate the author’s efforts at comprehensiveness and detail, I found the text quite dry. With more visuals, updated course readings, and perhaps an updated format that isn’t so text-heavy, the text would be more engaging for students.
Reviewed by Jennifer von Ammon, Full-time faculty, Lane Community College on 8/21/16
The text is primarily focused on grammar review and would be an appropriate text for a development writing course. Although there are several chapters dedicated to mechanics, there are limited essay assignment options, so an instructor would need... read more
The text is primarily focused on grammar review and would be an appropriate text for a development writing course. Although there are several chapters dedicated to mechanics, there are limited essay assignment options, so an instructor would need to craft engaging essay assignments to supplement the lessons.
The book appears accurate and unbiased.
Content seems fairly up-to-date though some of the suggested topics were somewhat overused (abortion, legal drinking age). Inclusion of different learning styles (visual, verbal, auditory, kinesthetic) is relevant.
The text is written clearly and has helpful headings/subheadings to organize material. Incorporating more images/illustrations could have enhanced the text.
The book is consistent in tone and structure.
The text could be assigned into smaller reading sections. I appreciated the "key takeaways" at the close of each chapter.
Though I appreciated the comprehensive coverage of grammar/sentence structure/mechanics, I would have liked to have seen the text incorporate writing assignments earlier in the text.
The text is clearly presented with headings/subheadings, but including more images may make the text more engaging for students.
The text appears to have no grammatical errors.
I did not find the text insensitive or offensive though some of the topics and references seemed somewhat outdated (MTV).
Reviewed by Paul Carney, English Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 8/21/16
The text covers all the essentials of college composition, from the writing process and mechanics to rhetorical modes and the research paper. The material devoted to grammar, punctuation and usage is well organized and fairly thorough. While very... read more
The text covers all the essentials of college composition, from the writing process and mechanics to rhetorical modes and the research paper. The material devoted to grammar, punctuation and usage is well organized and fairly thorough. While very brief, the sub-divided units on punctuation could be more developed. That said, too much textual explanation and not enough modeling can be a real turn off for students struggling with these mechanical issues. One cannot defer to the text for teaching. The rhetorical modes are equitably covered, though persuasion might welcome more attention and development. For a basic college composition text, this text certainly suffices.
The information is accurate and consistent with language arts standards for bias and equity. However, the example essays in the back could be more reflective of cultural and class diversity.
The writer does a fine job of using examples (exercises, models, examples, etc.) relevant to students in the near future. With supplemental readings and other OERs, this text will withstand expiration of content for at least three years.
The book's clarity is, perhaps, its greatest strength. The writer is keenly aware of his/her audience, college students who approach writing with an array of aptitudes and attitudes. Chapter 1, for instance, "Introduction to Writing," begins a foundational conversation with the reader, a conversation suitable to and supportive of most college students. The sentence complexity is appropriate for the audience. Also, student readers will appreciate the inclusion of "Tips" for building clarity.
The text is consistent in terms of utilizing and referencing terminology and other sections of the book.. The writer consistently uses and revisits key concepts and terminology (grammar, sentence structure, paragraph development, unity, etc.), reminding the reader that writing is a recursive process involving strategic "layering" of ideas and skills.
Each chapter in Writing for Success can "stand alone" if necessary. Oftentimes, in the interest of responding to differentiated learning styles, instructors must isolate and prescribe content for students' individual writing challenges. This text lends itself to easy access to subheadings for particular reference and reinforcement.
I do appreciate the inclusion of exercises at the end of chapters 2, 3, 4 and 5.
The text's organizational format may be its greatest and only notable weakness. The book begins with a thorough, thoughtful introduction to the writing process by citing fears and misconceptions commonly held by college students. This section of the book is critical to establishing a casual but accurate understanding of the writing process. Then, rather abruptly, succeeding chapters shift to local writing issues relating to writing basics - fragments, punctuation, sentence fluency. Typically, and I would argue more logically and appropriately, these localized writing matters should appear in the back of the text for easy access and reference. Logically, the chapter(s) following the discussion of the writing process should launch the student into the writing process itself.
I had initially downloaded the pdf version of the text, thinking that was the one and only interface for accessing, reading and utilizing the text. However, in a later attempt I was able to access a digital version that is quite easy to navigate. I like the ever-present position of the table of contents for easy point-and-click navigation. The chapters line up sequentially and the display is reader-friendly.
The style and mechanics reflect mastery of grammar and usage.
Again, I would point to the example essays as evidence of shallow (not necessarily insensitive) attention to cultural and class diversity. Were I to use this text, I would supplement the example essays with models reflective of wider cultural experiences (class, gender, race, LGBT).
Writing for Success is what it says it is, a book that provides essential instruction in how to approach and embark on the writing process. It provides a basic review of grammar and usage that probably would require additional instruction and opportunities for practice. A college writing instructor who usually defaults to his or her favorite and reliable "bag of tricks" would find this open text very useful for foundational instruction.
Thanks for this opportunity to review an open text in the Creative Commons.
Paul Carney
Reviewed by William Wells, Instructor, Metropolitan State University on 8/21/16
This book covers all the topics I would normally cover in a first year composition course and more. I would like to see an effective, preferably interactive, Table of Contents and a glossary. read more
This book covers all the topics I would normally cover in a first year composition course and more. I would like to see an effective, preferably interactive, Table of Contents and a glossary.
The content is extremely accurate and well-articulated.
This book will likely be useful until we communicate exclusively with emoticons. Necessary updates should be fairly easy to integrate.
Clear and well-written for its audience.
The text is generally consistent in tone and framework and uniformly consistent in terminology.
The text appears as of it would be easily adaptable as modules.
Some of the topics seem slightly out of place, but it has a clear structure.
The text appears to have several broken links, particularly in the beginning, in the .pdf version.
I had some questions about word usage--particularly the heading of "Dos" and "Don'ts" which, to my eye, looks funny. I would probably go with "Do's and Dont's."
The text does not seem culturally insensitive and makes an overt attempt to accommodate those students with differences in learning styles.
I will be giving it a try in my next class.
Reviewed by Michelle Robbins, Instructor, Portland Community College on 1/7/16
Writing for Success includes all the topics I cover in a developmental writing class, plus a large chunk on research papers. It covers grammar and constructing paragraphs and essays in a comprehensive manner. For developmental writing, I did... read more
Writing for Success includes all the topics I cover in a developmental writing class, plus a large chunk on research papers. It covers grammar and constructing paragraphs and essays in a comprehensive manner.
For developmental writing, I did find that Chapter 2 was a bit light on the parts of speech. For instance, in one exercise students must identify adverbs and adjectives, but there is no real explanation of them first. However, the sentence practice in regard to subjects, verbs, and independent clauses was solid.
Chapter 6 on purpose, tone, audience, and content was excellent. I haven't seen those elements addressed in quite the same way (sometimes barely at all) in other textbooks I have used.
I was also pleased with the links to articles and essays. (More on this in relevance and cultural relevance.)
Content is accurate, error-free, and unbiased. The author includes a variety of links to additional readings and does an excellent job of covering different sides of an issue. For instance, he is sure to link to articles arguing both for and against the use of torture.
Because grammar, language, and writing change fairly slowly, the content here is relevant and lasting. Some articles may become dated, but those are easy to change. Many of them won't need to be replaced anyway because, regardless of their dates, they are still good examples (and, obviously, in writing and literature older works are critical to examine). One of the sample essays was written in 1994. Certainly our outlooks on the material has changed (the role of wives), but the piece is still a good (and creative) example of a definition essay--and fodder for discussion.
The text is clear and accessible for upper-level remedial students and still works for 100-level courses. The student examples are useful, but a few of them were not especially compelling or strong examples and could be replaced.
It is consistent. I thought the repetition of sections such as "writing at work" and "key takeaways" were helpful for students absorbing a lot of information.
The organization of sections made the text easy to follow. At first I thought it would be better organized by integrating the writing samples in the last chapter into the instructional chapters, but ultimately, I found that grouping the types of content (grammar in one area, writing instruction in one, samples in another, and so on) made accessing content easier--especially because they are also cross-referenced within the chapters.
Much of the time, I want my students to access different topics simultaneously, so I found the organization here to work fine. The chapters and sub-sections are clear, so it is easy to move between them.
I found the cross-referencing of sub-sections to be particularly helpful, as in the chapter on coordination: it refers back to the section on semi-colons and vice versa.
All worked well for me. All graphics were clear, and it was key to be able to magnify the student samples for better readability.
One significant issue is that many of the links to essay examples in Chapter 15 are dead.
I found no errors.
The links to outside sources included cultural variety (and were quite interesting!). Perhaps the examples within the text itself might show more variety.
I was especially impressed by the links to Chapter 15 examples (those that worked); there were blogs, poems, and magazine articles. The variety of source types and authors was excellent, and the pieces themselves were compelling.
Overall, Writing for Success was clearly written, useful, and fairly comprehensive. I would definitely use it in my developmental Writing 90 course. I can also envision using many sections for Writing 80.
Reviewed by Kelsea Jones, Adjunct Instructor, Treasure Valley Community College on 1/7/16
McLean's text is surprisingly comprehensive, covering topics from reading and study strategies, to grammar, to writing paragraphs and essays, to research. While some of this material would be spot-on for first year composition, I feel as though... read more
McLean's text is surprisingly comprehensive, covering topics from reading and study strategies, to grammar, to writing paragraphs and essays, to research. While some of this material would be spot-on for first year composition, I feel as though most of the strategies are more appropriate for developmental composition courses (like WR 115: Intro to College Writing in the Oregon system).
The major downside of this text is that there is no Table of Contents or index for this 600+ page book.
The information in the text appears to accurate, unbiased, and very detailed.
The text makes use of sentence and essay examples that are relevant and that will not have to be constantly updated. The main pieces of information in this text that would need to be updated are the APA and MLA style guides; however, both guides follow the most recent editions. Otherwise, the links provided in the text, such as those to the Purdue OWL, may need the most monitoring and updating.
The writing style of this text is accessible and conversational. Terms are introduced with examples, including some excellent graphic organizers, before they are used in the text, and the terminology is consistent throughout.
There is a consistent framework in each chapter: learning objectives are listed, information is presented with tips and examples, and the information is summarized in a "Key Takeaways" box.
The text is divided into chapters and sub-sections that could be divided into smaller reading sections or reorganized to fit individual course needs. Instructors could take or leave any of the content without confusing their students.
The text is organized so that students can build upon their skills, from reading and studying all the way to researching and making presentations; in that way, it is a clearly organized and structured text. However, this organization is what makes the text more appropriate for developmental writing courses than first year composition courses. The reading, studying, and grammar sections of the text could easily be organized into appendices at the back of the book to act as supplemental material rather than the meat of the text.
Interface rating: 2
There are a few confusing interface issues with this version of the text: 1) None of the paragraphs are indented, which makes skimming the text difficult. 2) The learning objectives and tips in the text are set off in a light gray color that is easy to miss while scrolling through the pages; the blue and green colors chosen for the exercises and key takeaways are much easier to see and read. 3) Several headings for sections, tables, and figures are cut off from the information they introduce. 4) There are no clickable links in the text, table of contents, or index to aid navigation. 5) There is no title page for the text!
The text contains no apparent grammatical errors.
There was no content that was culturally offensive, but I also did not find the text to be particularly inclusive.
Overall, I found this text to be a good Open Educational Resource that offers a real wealth of information about college writing. For all of its interface problems, the text would be easy enough to adapt to either developmental composition courses or first year comp courses. I would recommend this text to instructors interested in using OERs in their classes.
Reviewed by Shawn Osborne, Instructor, Portland Community College on 1/7/16
The text clearly covers all areas and ideas of the subject at this level and is well organized. A nice addition is that each chapter opens with Learning Objectives and closes with Key Takeaways. read more
The text clearly covers all areas and ideas of the subject at this level and is well organized. A nice addition is that each chapter opens with Learning Objectives and closes with Key Takeaways.
I found the content to be accurate, error-free, and unbiased.
The content is up-to-date and relevant. It is arranged in such a way that any necessary updates should be quite easy to implement.
The text is straight forward and clear.
The terminology and framework of the text is consistent.
The text can be divided into smaller reading sections easily.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear way.
There are no interface issues. The images/charts and other display features are well placed and bring clarity to the learning point.
There are no grammatical errors in the text.
The text is culturally relevant.
Chapter 5: Help for English Language Learners and Chapter 14: Creating Presentations are useful additions to the text. I also appreciate the links to further readings in Chapter 15 and believe this will be very beneficial for students.
Reviewed by Fran Bozarth, Adjunct Professor, Portland Community College on 1/7/16
This book really covers it all so long as there is no need to address reading fiction - in fact, it has way more than I would be able to use in a term! However, it appears to be appropriate for a semester course, or for two terms of... read more
This book really covers it all so long as there is no need to address reading fiction - in fact, it has way more than I would be able to use in a term! However, it appears to be appropriate for a semester course, or for two terms of quarter-length courses.
Subjects are covered appropriately, although I don't know that students would find all of it particularly engaging - use of this material would be VERY reliant upon an effective, engaging instructor.
At our college we have the additional course goal of requiring some understanding of reading fiction, and an instructor utilizing this book would need to supplement for it.
While the Table of Contents is very clear, there is no index or glossary.
The content in this book is consistent with the goals of most Reading/Writing/Study Skills/College Success courses I have encountered. It seems to be error-free, and the author did a particularly good job of projecting no biases that I could detect.
The content related to this text has remained fairly static for decades, though there have been some developments in the past few decades regarding holding students more accountable for knowing their learning styles, and for constructing meaning with connections to their own experiences. This book addresses the basic, standard content, and nicely brings in opportunities for students to better understand themselves as learners. Again, this will depend heavily upon the instructor and their ability to engage students.
Some of the exercises and examples may become obsolete if there are any major technological changes in our society (for example, if email is suddenly abandoned in favor of something else.) However, I believe that such updates would be quite easy to implement given the use of a simple "Find & Replace" feature.
Clarity is a strong suit for this text. I did not locate any portion of the book that lacked clarity. Context was provided for examples of poor writing as well as for strong writing. Context was also provided for any specialized language.
The book is extremely consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
The framework utilizes a "here is what you will learn" type of bulleted list, followed by sections that match the bulleted list, with examples where appropriate, and exercises at the end of the chapter. The end of the book includes not only a full-text example of each type of essay, but also provides links to additional examples written by often well-known and well-regarded authors.
The structure of the overall text is appropriate, and logical. I really appreciate that exercises aren't just randomly thrown in, as many published textbooks often do.
The text is easily readable, but I find that the layout of the pages can cause the text and sections to run together. More effective use of headings and subheadings would make this easier for students to follow. Additionally, there isn't an easily discernible break between chapters/sections. I would very much like to see more solid page breaks (title pages perhaps?) at the beginning of each chapter/section. Given the learning styles assessment at the beginning of the book, it would be appropriate to at least include some icons that match each section - for example the "Key Take Aways " could have a key icon. Some suggestions for students regarding how they can apply this using their unique learning styles might be helpful as well. Otherwise, that learning style information seems to be unrelated from the students' point of view.
The links in the PDF did not seem to work. I don't know if I need to consider looking at this material in a different format in order to use the in-text links. (In other words, I don't know if it's me or if it's the text or the technology or what....)
The topics in the text are presented in a very appropriate fashion, with concepts building in a logical way, one upon the next. Very nicely scaffolded!
The interface seemed to be working correctly. I was able to read everything, and things seemed to be correctly placed. I was not sure if the blue text was supposed to be linked. I was unable to click it and go to any links (which were typically references to other chapters within the text, so it wouldn't be impossible to locate those items - just tedious.)
The text appears to have been impeccably edited. All of the writing lesson content was modeled within the text. Items that were incorrect were clearly labeled as being examples of poor writing, or were clearly used for the purpose of applying identification and editing skills.
This text appears to be quite sterile when it comes to cultural sensitivity. Given the audience, the examples are typically American with some culturally diverse names thrown in. The examples given weren't particularly indicative of one race, ethnicity or background or another. In some ways, I am thankful for the lack of contrived cultural sensitivity. I didn't note anything that would create a barrier to culturally diverse populations, other than the assumptions that are made based upon american culture (such as the notion that we have all had a job at one time or another, or at least have some understanding of the concept of employment.)
This book has much to offer. The authors did an excellent job of including the content that is consistent with standard reading/writing/study skill content. I think it will be very workable and pliable for use by instructors who chose it.
Reviewed by Kimberly Gutierrez, Assistant Professor of English, Bismarck State College on 1/7/16
One of the classes I teach is a freshman composition writing lab that focuses on sentence level errors and sentence clarity. This is a super resource for that type of class. The book contains all sentence, grammar and mechanics concepts that are... read more
One of the classes I teach is a freshman composition writing lab that focuses on sentence level errors and sentence clarity. This is a super resource for that type of class. The book contains all sentence, grammar and mechanics concepts that are essential to teaching students to recognize and repair sentence-level errors. The Table of Contents clearly outlines all of the all of the component of the book. As far as being the main source for a first semester freshman composition class, if I used it, I would certainly supplement it with more readings, but for freshman composition sentence level instruction, this book is very thorough. My comprehensive rating reflects that particular focus.
The descriptions of the concepts are very detailed, and these descriptions are very accurate, explaining the concept with correct sample sentences.
Since the primary focus of this book is the grammatical concepts that impact sentence issues, the text will not necessarily need updating. Of course, MLA formatting guidelines do change, so these changes will will need to be updated within the book, but the general sentence concepts presented in the majority of the book will not soon become obsolete.
All portions of the book are very clearly presented. Grammar can be confusing to first semester freshman composition students, but the explanations are clearly presented. Examples are clearly connected to the grammar explanations.
Terminology is consistent within the text. Within the framework of a composition lab class, this text is consistent, covering all essential components covered in the course scope.
The clarity with how the concepts are presented in the Table of Contents allows instructors to pick and choose which the concepts will be presented and the order of presentation.
The book has a clear organizational flow (considering that I would use this book for a composition lab that has a sentence practice focus). The sentence concepts build logically on each other.
No interface issues occur when accessing the chapters, and there are no display features that distract the reader. The lessons are presented very clearly, and the practice exercises are easy to follow.
The grammar lessons are error free.
The practice sentences do not contain an culturally biased material.
This is a text that I would consider using for a composition lab course (sentence practice focus). I would also consider using the text for first semester freshman composition, but using the text for that type of course would require finding supplemental readings.
Reviewed by Brandy Hoffmann, English Instructor, Central Lakes College on 1/7/16
Writing for Success offers a variety of sections that could be extracted as resources/readings for a first year writing course. In other words, despite some weaknesses, this text serves the function of an OER, and parts of it could be utilized... read more
Writing for Success offers a variety of sections that could be extracted as resources/readings for a first year writing course. In other words, despite some weaknesses, this text serves the function of an OER, and parts of it could be utilized widely. Overall, I would not feel comfortable using this as a primary text to teach rhetorical modes, including argumentative research writing, but I would use it as a supplementary text.
Strengths: I found the coverage of the following subjects to be generally effective: the overall writing process; the revision process (with exercises, p. 470); the editing process (with exercises, p. 476); thesis development (with samples of weak/strong, Chapter 9); paragraphing and topic sentences (with models of different types of paragraphs--summary/analysis/synthesis/evaluation, Chapter 6); sentence fluency and variety (with exercises throughout Chapters 2 and 7); preliminary research and research proposals (Chapter 11); outlining (with samples, Chapter 8), and basic MLA and APA documentation, including an effective discussion of in-text citations on pp. 501-503.
I want to point out the overall usefulness of the exercises offered throughout this text (adding value to the text, since practical exercises for college writing instruction can be hard to come by). I also appreciated the beginnings of chapters, which effectively addressed the questioning student and established the context.
Weaknesses: Viewed as a whole, the text struggles in terms of audience and purpose, organization of content, and content selection and emphasis. The text emphasizes some extraneous subjects while understating other topics that would be important to many composition courses. For example, for a composition course built on rhetorical modes—narration, description, illustration, argumentation, etc.--this textbook offers only a short overview of each. It also offers a few models and links to outside readings, but it doesn't include anything on composing annotated bibliographies, rhetorical analysis essays, critical reviews, or literature reviews. There is an overview on how to write a research paper, but the discussion on how to integrate sources effectively - quoting, paraphrasing, summarizing - is somewhat weak, and the discussion of plagiarism is limited.
The text offers an extensive section on study skills (in chapter 1), which seemed misplaced in this text - unless it was modified to address study strategies for a writing course, specifically (for example, rather than models of lecture "note taking," how about models of research note-taking in chapter 11; and instead of comparing general high school and college assignments, compare writing assignments specifically). I would recommend an overall reorganization of the text, moving chapter 8 (writing process) toward the front, for example, while moving chapters 2 (sentences), 3 (punctuation), 4 (words), and 5 (ELL) toward the end--to emphasize higher order concerns, first; lower order concerns, second.
I appreciate the attempt to address workplace writing as well as academic or in-school writing, but I found the brief "Writing at Work" sidebars a bit forced, possibly distracting, and unnecessary (e.g. pp. 224-225; p. 348). The attempt to include a pseudo student to shed light on the subject is sometimes helpful (Mariah, Chapter 8) but sometimes forced and not developed enough to be useful (Crystal, Chapter 1). The brief bits on "collaboration" throughout the text could be deleted- not developed enough to be useful. There is no index or glossary, and in the PDF I was using there was no table of contents, though this is available elsewhere. Despite these weaknesses, there are many reasons to use this text, as outlined under "Strengths" above.
Overall, this is an accurate and unbiased text. There will always be subjectivity in the delivery of academic writing advice because of varying preferences and changing ideas about what is appropriate or inappropriate. I tend to disagree with the following suggestions or omissions offered in this text: suggestion (through models that indicate 3 points to support a thesis) that a 5-paragraph essay is still the go-to formula for college writing in (Chapter 9); suggestion that a thesis is always one sentence; suggestion that it's a good idea to search for a random quote for your introduction online (p. 361); omitting any reference to intentional sentence fragments; omitting idea that contractions can be used in academic writing (in certain instances); omitting clear attribution and documentation in the summary on p. 220 apart from the opening signal phrase--not the best summary sample; the suggestion that a topic sentence begins an essay or article (p. 233), which seems misleading.
Writing advice tends to be timeless, to an extent, so there aren't big concerns that the content will become outdated. The author avoided pop culture and current event references, which was smart. The only suggestion would be to modify the text to better address new challenges and innovations in writing genres/writing instruction - perhaps including a chapter on multimodal writing and online writing toward the end of the text. (The use of "trade books" in Chapter 1 seems outdated, not fully defined.)
Overall, I found the writing to be very effective - definitely student-friendly yet not patronizing and still sophisticated. The writer avoided convoluted, wordy prose, and wrote in a tone appropriately formal yet conversational and relatable.
Yes, despite the overall issues with content organization and selection, which I address elsewhere, I found the text to be internally conistent with terminology and framework.
Yes, this text is easily divisible into smaller reading assignment, given the breakdown of subsectios within each chapter and the inclusion of exercise sections, etc. There are some issues with headers/interface, depending on the version of the text used, addressed in interface section.The text did not seem self-referential.
As stated above, I would recommend an overall reorganization of the text, moving chapter 8 (writing process) toward the front, for example, while moving chapters 2 (sentences), 3 (punctuation), 4 (words), and 5 (ELL) toward the end--to emphasize higher order concerns, first; lower order concerns, second.
Including Learning Objectives at the beginning of each chapter is helpful, allowing easy alignment with course objectives; the "key takeaways" at the end of each chapter are also helpful.
Please note: I was evaluating a downloaded PDF version of the text, so experience may be different in a different mode. Throughout the text, headings/labels can be difficult to distinguish from one another, making it challenging to follow the hierarchy/logic of the text. The organization of the "Reading Strategies" section in Chapter 1 was a bit confusing, listing the "three broad categories" of strategies but then failing to organize section headings that aligned. On p. 10, I would recommend moving "Ask and answer questions" before "Summarize."
For the "tips" offered throughout the text, it would be helpful if they were labeled in some way (e.g. "Tips: Succeeding in Timed Writings," p. 34). I would suggest eliminating the "Writing at Work" sidebars but turning some of these into tips (e.g. "Tips: Emailing Your Professor," p. 17). The paragraph on p. 38 that lists all chapters seems unnecessary and overwhelming. In the discussion of the SQ3R Strategy on p. 12, it seems like these steps should be handled separately with headings. The four academic purposes in Chapter 6 should be obviously highlighted at the beginning of the section rather than listed in the middle of the paragraph without emphasis (p. 217). On p. 230, "6.12" is referenced but does not exist? Use of "for this assignment" on p. 461 seems misleading.
Also, the font size, heading placement, spacing, indenting, and bullet formatting are all a bit awkward throughout; the text could be cleaned up for improved design and readability, though these issues do not detract largely from the text's usability.
Please note: I was evaluating a downloaded PDF version of the text, so experience may be different in a different mode. I located a few interface issues in my reading of the text: On p. 238+ the text keeps referring to underlined topic sentences, but they are not underlined. On p. 244 the text refers to underlined transitional words, but they are also not underlined.
Certain references to other sections in the text are colored in a way that makes them seem as if you could click on a link and be carried to a different section of the text, but this didn’t function, at least not in the PDF that I had downloaded (such as “see Chapter 12 ‘Writing a Research Paper’” on p. 10).
It would be helpful if there was a repeat of the chapter title on the top of each page of the text.
I located the following dead links in the PDF that I downloaded:
http://www.sunywcc.edu/LIBRARY/research/MLA_APA_08.03.10.pdf http://www.writing.ku.edu/guides p. 546
http://www.forsyth.k12.ga.us/132320728102659810/lib/132320728102659810/_files/Alexie,_Sherman_-_Indian_Education_TEXT.rtf http://www.pfeonyx.com/alliance/IndianCollection/Alexie2.pdf p. 596
http://teachers.sduhsd.k12.ca.us/mcunningham/grapes/mother%20tounge.pdf http://learning.swc.hccs.edu/members/donna.gordon/sum-2010-engl-1301-5-wk-crn-33454/1301-reading-block-crn-33454/Tan_Mother%20Tongue.pdf http://www.newamerica.net/publications/articles/2000/on_the_internet_theres_no_place_to_hide p. 602
http://api.ning.com/files/-3HiJ651xE-rSj4Q4WeH-*f0NQJGyoXgI8AR*3Rat-AyxVuVAgEE bfbuyGbTu9gpi7z3gT4jqd52W3fBsDRfFGgEgLxB5wO4/GetItRight.PrivatizeExecutionsArthurMiller.pdf p. 605
http://bcs.bedfordstmartins.com/everythingsanargument4e/content/cat_020/Brady_I_Want_a_Wife.pdf http://www.usd305.com/212720101692451310/lib/212720101692451310/20100429123836146.pdf p. 607
http://eec.edc.org/cwis_docs/NEWS_ARTICLES_JOURNALS/Laird_Ellen.pdf http://depedia.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=I%27m_your_teacher%2C_not_your_Internet-Service_Provider p. 609
http://depedia.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=I%27m_your_teacher%2C_not_your_Internet-Service_Provider http://www.alandershowitz.com/publications/docs/torturewarrants.html p. 613
The title and link has changed for article p. 598: should be http://www.newsweek.com/dark-side-web-fame-93505 List of "Sources" on p. 568 awkward too... not sure links are directing to intended spot.
I located a few mechanical/sentence-level errors: p. 2 in Preface, 2nd paragraph, the list with "instruction in steps, builds writing, reading, and critical..." could use semicolons for clearer listing/separation of items. p. 166 wording issue: "jargon a type" p. 202, 213, 275, 340, 366 spacing errors: "errors within, at and on"; "butit"; "thanswimming"; "Fencessymoblize"; "Writingis"; p. 208 lack of consistent periods at end of phrases in Table 5.16 p. 300 words/punctuation missing: "For example, for every Roman numeral I, there must be a For every A, there must be a B."
The text did not seem culturally insensitive or offensive and seemed usable by a wide audience of students.
I plan on using segments of this text in future writing courses, and I am grateful for the availability of OER texts like this one. So, despite any weaknesses addressed, this is still a valuable resource for faculty who are trying to lower the barriers to student success in their classrooms through the adoption of OER resources. I recommend the text, but study it carefully to determine how it will be used in your specific writing courses. It is probably best used as a supplementary text.
Reviewed by Michelle Cristiani, Instructor, Portland Community College on 1/7/16
What I look for in a writing text at this level is flow from simple to complex: word placement and part of speech up through essays. This text follows that format beautifully. One glaring omission is fragment and run-on work. This is such a... read more
What I look for in a writing text at this level is flow from simple to complex: word placement and part of speech up through essays. This text follows that format beautifully. One glaring omission is fragment and run-on work. This is such a common issue at this level. I would also want to see more transition from sentence to paragraph, not just paragraph to essay. There are a couple of underdeveloped sections as the topics grow in detail: for example, nine rhetorical modes are discussed, which is a wide array, but within each section there is not much elaboration or examples. But overall, there are appropriate exercises after concepts are introduced. The text provides a solid framework for instructors to build upon as they see fit. The table of contents are easy to navigate and generally well-organized. I do find chapter 8 misplaced, though – it is titled ‘how do I begin.’ Because it describes the writing process from prewrite to edit it seems sensible to place it closer to the beginning. I especially appreciate the inclusion of research and citation – it is well-done.
The lessons and examples are true to the field. The structure mirrors most other texts in organization and usage. The research and citation sections are more-or-less current.
Longevity is easy to attain with this discipline because grammar/writing rules are tried and true...but the organization of this text makes it a true 'open' resource. One could update or mold portions into a larger discussion on grammar concepts like punctuation, or writing for description. The APA and MLA sections are vague enough as to not need much updates as the rules change. The links work. I see at least one MLA rule that has changed since 2009, but it's relatively minor, and easily updated.
Grammar-heavy texts can be tricky for students because there are so many labels, like 'rhetorical mode,' that they know the definitions of, but have not heard the terms themselves. This text keeps that jargon to a minimum, so that students can focus on the concept and not the vocabulary. Subject-verb agreement is the least accessible, but that is often difficult to explain for any text, and the exercises support the instruction. Parallelism could be defined more cleanly. The research section is quite clear. The learning objectives are clear enough as to be useful tools themselves.
Exercises are often post-concept and always post-chapter. Learning objectives are defined at the beginning of each section. Each section resembles the others, and for that reason can be easily modulated - but there are no clear cumulative assignments.
These chapters can stand alone quite easily. This works especially well for instructors like myself who teach grammar concepts side-by-side with writing concepts - they will pair closely in this model. The end-of-chapter exercises could easily be used as pretests as well as post-tests. Chapter 13 on research documentation is slightly self-referential, but the sections are unlikely to be taught separately and it doesn't feel overdone.
As previously mentioned, chapter 8 on getting started might be moved forward. Ideally the text would pair the writing process stages directly with modes, as they do change given the purpose...but since this might made the text less modular I understand the vision behind its generality. The reading examples might be closer to the chapter on modes, instead of at the end after research. Within chapters, flow is sensible and straightforward.
The layout and structure is simple and clean. Charts keep their shape even when window size is minimized. The clear table of contents is navigable by both scroll and click.
Grammar texts especially need to be spotless; I spotted no errors. Most importantly, there is consistency in structure and punctuation, for example in learning objectives from chapter to chapter.
Most important in this volume are the sample essay readings. Linked and cited authors include various time periods and controversial yet not sensitive topics. The text is to be commended for inclusion of essays from at least five different races and a variety of worldviews.
A solid framework and foundation for essay writing. The book could be used for a class specifically about writing, or as a companion to another course. Modules on research and citation are of specific relevance to a variety of content areas, and the extra essays in the final chapter can inspire debate and argument both in writing and verbal discussion.
Reviewed by Mary Sylwester, Instructor, Portland Community College on 1/7/16
This textbook is amazingly comprehensive--probably more than any teacher actually wants. It covers strategies for success in college, reading, grammar, spelling, drafting, revising, thesis statements, and various rhetorical modes. Unfortunately,... read more
This textbook is amazingly comprehensive--probably more than any teacher actually wants. It covers strategies for success in college, reading, grammar, spelling, drafting, revising, thesis statements, and various rhetorical modes. Unfortunately, it does not include an index. The table of contents is fairly detailed, however.
The content is accurate: rules for spelling and punctuation and general rhetorical content are presented as any writing instructor would expect. More explanation about rules for grammar and punctuation would be nice: for example, the explanation of the dash is "to set off information in a sentence for emphasis." This is accurate, but not the whole story.
The main portions of this text will not become outdated. The section on readings, however, is already problematic. The book offers one reading example per mode, and then others as links. Just in a quick survey of links in two of the rhetorical modes, I found five that were no longer operational. To be fair, the book does try to get around that problem with multiple link sources for the same essay, but I found this strategy confusing, as it tends to look as if there are more readings available than actually are present. In the future, as with any textbook including readings, there will be a need to provide up-to-date topics.
I found the book very readable. There is little or no jargon. This book would be appropriate for a freshman in college.
The page design is consistent: examples and exercises are similarly formatted and easy to locate. The author uses fictional student names to illustrate how some principles might be applied in real life.
In the "Exercise" sections, the book does refer the studen to other parts of the chapters. All the examples I found, however, referred the student to sections within the same chapter and not out to other chapters of the book. For example, in the Exercises for Ch. 8, the instructions say: "Working in a peer-review group of four, go to Section 8.3 “Drafting” and reread the draft of the first two body paragraphs . . . ."
This book starts with strategies for success, which seems reasonable, but then has a giant section about sentence grammar & spelling before even getting to writing paragraphs. "Refining Your Writing" comes before "How Do I Begin?" which seems backwards. The topic of thesis statements does not come up until Chapter 9, which seems terribly late. If I were teaching from this text, I would probably skip from Chapter 1 to Chapter 6, and use Chapters 2-5 (grammar and spelling) as references.
The display seems fine: I read it online rather than downloading. One benefit to the online format is the search window at the top, which offers a kind of substitute for indexing.
The only problem I ran into was that several links to the readings in Chapter 15 were nonfunctional.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
Student example names used seem to cover a variety of ethnic backgrounds, but most are women's names. Readings cover a wide spectrum of ethnicities. For example, links to readings in the "Narrative Essay" section include Chicano, Russian Jewish, and Native American.
This is generally a well written textbook. However, there are two problems that instructors will encounter in using it: (1) it is not organized pedagogically, so instructors will need to consider the order of readings carefully, and not just move chapter by chapter through the book. (2) many links to readings are not functional, so instructors will need to be aware of that and either find new links or provide their own readings.
Finally, I have grave reservations about the ethics of using weblinks for essentially all the current readings in a textbook. I understand that using links in an online class for one-time readings is fine, but many of these links (especially those that remain functional) are to publications that have paying subscribers, such as The New Yorker. I would feel better about using a textbook that actually had permission to use other writers' work as a permanent fixture of the book.
Reviewed by Laura Sanders, Instructor, Portland Community College on 1/7/16
This text covers a range of topics students might need while building reading, critical thinking, research, and writing skills in developmental to upper division courses. read more
This text covers a range of topics students might need while building reading, critical thinking, research, and writing skills in developmental to upper division courses.
I see no evidence of inaccurate, erroneous, or biased content.
I believe it is safe to say that this book will be useful for a long time. While APA and MLA style may change and grammar rules may soften or transform, this book would be easy to update.
The book is accessible to students entering a course with various levels of academic preparation and experience.
Each chapter begins with learning objectives and ends with takeaways. Throughout each chapter, there are charts and exercises to clarify and emphasize key content.
Clearly marked sections focus on student success strategies, grammar and punctuation, and approaches to composition. Instructors could easily select the chapters most relevant to individual reading and writing courses at all levels.
The book is structured very well. It begins with reading strategies and helping students transition from a high school to college learning environment. It moves into sentence-level techniques, including specific areas for English language learners. The text also includes sections on the writing process, rhetoric, research, documentation, and presentation.
The text is easy to navigate.
I do not see any grammatical errors.
While I do not see anything I consider offensive, I do believe few of my students would "see themselves" in this text. The sample names (like "Steve" and "Jones") and sample essay topics (baseball, video game addiction) do not suggest a recognition of the broad cultural diversity instructors encounter in college classrooms today. For me, this lack of inclusiveness marks the main weakness of this text.
I enjoyed reviewing the text and plan to assign a few chapters to my online writing students.
Reviewed by Amy Forester, Instructor, Clackamas Community College and Portland Community College on 1/7/16
The text is very comprehensive. There are sections that are useful for many different writing levels, from students in need of grammar and punctuation instruction to research writing. Also, each section is nicely developed with examples,... read more
The text is very comprehensive. There are sections that are useful for many different writing levels, from students in need of grammar and punctuation instruction to research writing. Also, each section is nicely developed with examples, explanations, and exercises.
The text is very accurate. It gives clear and easy-to-read instruction on many topics.
This text has great longevity. I can imagine using it for many years because the examples are not time-sensitive. This is a great book to accompany a reading list or anthology.
This is one of the first things I noticed about the text. I really like the tone and style of the writing. It is clear and does not over-complicate ideas. The author clearly has experience with first-year writing students because it is written in a clear, accessible way.
I appreciate the consistency of this text. The terminology is direct and logical, and students will find it easy to get a broader understanding of a topic because the text provides links to other parts of the text where the term is mentioned. Also, the chapter organization is perfect for first-year students who do not want long, meandering chapters.
I will be using this book in modules for different writing classes. For example, it is easy to teach the grammar and punctuation sections in a remedial course and leave them out in research writing courses. Each section is very well developed.
The topics are nicely organized in this text. Each chapter has the same features, so students know what to expect. I am particularly impressed with the section Writing at Work, which gives students a sense for how each strategy is used in the workplace.
Overall, the interface is very easy to read. The one improvement that should be made is, at least in my screen view, the student writing samples are hard to read because they are small and in a difficult font.
It is grammatically correct.
The text is not culturally insensitive. It seems inclusive in its examples.
I am particularly impressed with the grammar and punctuation chapters. I have used many different books to teach these topics, and have found that they are often explained in complicated, technical language. I will definitely use these chapters in my classes.
Reviewed by Katie McCurdie, Instructor, Portland State University on 1/7/16
The comprehensiveness of this text is very impressive. At 600 pages, it covers so many aspects of college writing, from grammar to essay writing to creating presentations, that pieces of this text would surely be useful for a wide variety of... read more
The comprehensiveness of this text is very impressive. At 600 pages, it covers so many aspects of college writing, from grammar to essay writing to creating presentations, that pieces of this text would surely be useful for a wide variety of courses, but it is probably best suited to a first-year composition course. The first chapter provides a good introduction to writing in college, which includes a comparison to writing assignments in high school, along with more general advice on succeeding in college. This would be useful for just about any student entering an American university. It would also aid international students in understanding the expectations surrounding reading and writing as they transition from schools in their home country, where expectations, amount of coursework, and types of assessments can be drastically different. The next four chapters focus on sentence-level language issues: sentence structure, punctuation, vocabulary, and a whole grammar chapter for English language learners. These chapters could provide a great introduction to or review of the basics of English grammar, as well as the metalanguage needed to talk about grammar. In fact, I could see all four of the chapters begin useful for English language learners at intermediate and advanced levels. Chapters six through thirteen cover writing, from paragraphs to research papers, and fourteen focuses on presentations. Short exercises immediately reinforce the content in a variety of ways, such as by editing, completing sentences, and identifying and labeling grammar items. The amount of exercises might be enough for relatively advanced users of English, but those at a lower level would likely need additional exercises from another source. The “Writing Application” exercises at the end of most chapter sections provide opportunities for students to use what they’ve learned in short writing activities. In addition, there are end-of-chapter exercises for more practice.
Throughout the text, there is a combined focus on writing for academic purposes and writing in the real world. Examples and exercises reinforce this with work emails, business letters, job descriptions, cover letters, advertisements, and personal narratives and essays. This should send the message to students that the skills they are learning will be applied to all areas of their lives.
Although this text hasn’t reinvented the wheel in terms of writing instruction, it does present some novel ways to approach certain topics. For instance, there is a section in Chapter 2 on identifying and correcting fragments and run-ons that would potentially be very helpful for both native and non-native writers. It includes flow charts that students could use on their own to aid them in finding and fixing these all too common sentence structure errors in their own writing – an excellent tool to help students move towards becoming independent writers.
The table of contents is detailed and descriptive, but is not included in the pdf version.
I found the content to be mostly accurate. However, there are a couple places where the labeling of grammar items seemed incorrect or inconsistent to me. For instance, in Chapter 2, the text introduces some sentence structure basics including prepositional phrases (“At night,” “In the beginning,” etc.). However, when discussing how to fix fragments that begin with prepositional phrases a few pages later, the example sentences do not actually contain them; instead, they begin with adverb clauses or phrases (“After walking all day…”). For a native writer, distinguishing between these two different structures might not be crucial since the point here is fixing the fragment error. If using this text with English language learners, however, the discrepancy could cause confusion.
Information and example essays seem relevant and up-to-date although the chapter on MLA and APA documentation will have to be updated in the future. Updates should be easy to perform due to the text’s modularity.
The language used in the text is very easy to understand and approachable. Examples mostly consist of everyday language and situations or general academic vocabulary.
The text seems consistent to me except for the grammar terminology error I mentioned above.
This text seems made to be divided into smaller parts to be covered individually or even in a different order. Although the text does refer to itself at times, it does not rely on these references to convey information clearly and completely. Therefore, I noticed some sections of the text that necessarily repeat information from previous sections so as to stand alone as an independent lesson.
I appreciate how the book is organized, beginning with the introduction to college writing, which orients students to what they’ll be doing and why. I think it was a good choice to then put the grammar chapters next, before getting into the writing chapters. Writing books I’ve used tend to stick the grammar instruction at the end of the text or even hide it away in an appendix, but this text encourages students to become proficient writers from the sentence level up. The only part that seems oddly placed to me is Chapter 7, “Refining Your Writing,” which covers sentence variety, coordination and subordination, and parallelism. Also, I agree with another reviewer who said that it would be better if each rhetorical mode were given its own chapter. I never teach nine different modes in one course (maybe two or three), so the modularity would be better if each mode could be separate. On the other hand, I like how research writing is divided into two chapters and covered in detail. This type of writing is so difficult for most students, so it’s nice to have that comprehensive instruction. It’s also great to have the additional chapter at the end with example essays.
The interface is user-friendly with clear headings and sub-headings, logical use of bold text, numbered and bulleted lists, and blocks of subtle color to set off certain pieces of text from the main text. When suitable, information is presented in chart form or inside boxes. The font is highly readable and not distracting. Each chapter has a few main sections that are consistent throughout the text: “Learning Objectives” at the beginning, “Exercises” sprinkled throughout the chapter, and “Key Takeaways” at the end. There are also small boxes labeled “Tips,” which give advice on succeeding academically, and “Writing at Work,” which offers suggestions on how to use writing in real communication situations. As a result, the set-up of each chapter is predictable, which would theoretically allow teachers and students to fall into a comfortable routine.
One problem I found with the interface is that sometimes the margin sizes are not consistent from one page to the next. For instance, an indented list that begins on one page and continues on the next may not be indented on the second page. This is a small issue and may just be in the pdf version of the text.
I also noticed some navigation mistakes, when the text refers the reader to another part of the text, but it’s not the intended part. For example, in the section on fixing run-ons, it says, “For more information on semicolons, see Section 2.4.2 ‘Capitalize Proper Nouns’. However, there is nothing about semicolons in this section; this would most likely be in Chapter 3, which covers punctuation.
I did not see any errors.
I did not notice anything culturally insensitive, and there are some inclusive examples.
Overall, I find this text to be thoughtfully written, and I’d definitely consider using it for upper level writing & grammar-focused courses in the Intensive English Program.
Reviewed by Kirk Perry, Adjunct Instructor, Portland Community College - Cascade on 1/7/16
This textbook aspires to be a combined grammar book and reader. It covers all the appropriate areas, but the coverage is a bit thin when it comes to examples. read more
This textbook aspires to be a combined grammar book and reader. It covers all the appropriate areas, but the coverage is a bit thin when it comes to examples.
As far as I can tell.
The instructional content is very plain and basic; it will be sure to bore students for decades to come.
The readings (links) are good quality and likely to be useful for a decade or so.
Very clear and plain language--but again, not enough examples.
If anything, this text could be more technical. I think it is unhelpful to describe subordinating conjunctions as "dependent words." This strikes me as vague and misleading.
Yes, quite consistent.
Yes, it is effectively modular. Helpful subheadings and sections. There are lists and diagrams, but some sections can be a bit too text-y (dense paragraphs).
Yes: overview > grammar > process > writing modes > research > citation.
However, the example essays for the modes come in the final chapter. There is no good reason why "Chapter 10: Modes" could not be merged with "Chapter 15: Readings: Examples of Essays"--particularly because most of the examples are links.
Appears good.
Didn't notice any problems.
The example essay links provide a variety of ethnic/cultural perspectives.
This book is helpful but tries to do a bit too much--being both a grammar and a reader. It needs more examples of everything: run-on sentences, sense details, example essays, etc.
To adopt this for a course such as WR 115 or WR 121, I would have to provide many supplemental readings.
Reviewed by Annie Knepler, University Studies Writing Coordinator, Portland State University on 1/7/16
Writing for Success is quite thorough. It covers everything from sentence structure to the writing process. It has additional sections on creating effective presentations and concludes with sample essays. I could see how instructors could use... read more
Writing for Success is quite thorough. It covers everything from sentence structure to the writing process. It has additional sections on creating effective presentations and concludes with sample essays. I could see how instructors could use various elements of the text and adapt it to their course.
At the same time, it often felt a little too comprehensive, and sometimes seemed to aim for breadth over depth. For example, not much space is devoted to integrating sources and ideas. Learning how to apply sources, and develop your own ideas based on research, is such an important element of college writing. Paraphrasing and integrating source material is complex, and takes a lot of practice. Otherwise, students tend to let the sources speak for them instead of truly conversing with the sources (which is what I would begin to expect of college level students). The text leaves the impression that integrating sources is a straightforward task as opposed to one that involves critical thinking and analytic skills. Overall, I found the research section fairly weak.
I have looked at and worked with several writing texts, and I’m used to ones that either focus on a specific aspect of writing (such as research writing) or have a specific approach. This text tries to be a more general writing text, and it, perhaps, tries to cover too much.
The book strikes me as accurate, thorough, and generally without bias. At the same time, I don’t fully agree with the approach it takes to writing and grammar. The text does a really nice job of explaining certain grammatical elements and providing several examples to demonstrate the idea. However, the text generally treats grammar as rules rather than conventions. These conventions often change or shift over time, just as writing conventions change over time.
Similarly, whereas I appreciated the texts emphasis on writing as a process, Writing for Success does not really highlight the idea that writing can also be a process of discovery for the student. To me, this is an important concept for both learning and writing, and it helps get students excited about the possibilities for college writing. For example, when discussing thesis statements, the book indicates that a writer might end up revising a working thesis to broaden or narrow down their thesis. However, it does not present the possibility that students’ ideas may shift in significant ways as they write, research, and discover ideas. I allow my students to leave themselves open to the idea that their working thesis could change in significant ways as they write.
Overall, for me, it does not adequately emphasize the idea that writing should be both dynamic and purposeful.
The book is designed in a way that makes it easy to update specific details and examples. In general, many of the concepts it covers, such as specific issues students should pay attention to as they edit and revise (such as wordiness, transitions, etc.), will likely remain consistent.
However, I would not characterize the text as particularly relevant given the current conversations in the field of composition and composition pedagogy. In recent years, there has been a much stronger focus on purpose, audience, and genre in relation to writing, and although these concepts are addressed, they are not really emphasized or approached with the degree of complexity I would expect out of a college-level writing course. Writing for Success seems to encourage an expanded version of the five paragraph essay rather than providing students with the tools to recognize multiple approaches to writing. It approaches writing with a step-by-step approach, rather than as a complex task that involves continual critical thinking and problem solving.
Although the text encourages students to apply these ideas to other writing tasks (something I really appreciated about the text), it often implies that the writing they will do in their writing class may not have a clear context or purpose. It even states that students’ “college composition courses will focus on writing for its own sake.”
The writing in the text is very clear and straightforward. It would be helpful for the authors to more clearly define the audience for the book. It strikes me as a text that would be too basic for many first-year college writing courses.
I also found some of the organizational decisions confusing (I address this below under organization/flow).
Consistency rating: 3
The chapters follow a fairly consistent structure in terms of content. They all start by stating objectives, explain the main concepts, review the concepts, and provide exercises. The text also fairly consistently encourages active learning by posing questions for students/readers to consider as they delve into a topic.
To my eyes, there are some inconsistencies in terms of the framework and the message of the text. For example, it opens by framing writing as a challenge, and I was prepared for it to address several of the complexities of college writing. Instead, it goes on to take a fairly formulaic approach to writing, and even implies at times that the five-paragraph essay is a common form for college writing.
The text is broken into clear sections. I’m not sure how well the text would work if assigned from start to finish, but I can see how instructors might select specific chapters for a specific purpose. I usually have a select group of students that might struggle with a certain issue and I would, for example, direct a student that is struggling with commas to that specific section.
I also appreciate the way the is designed to work with other classes that a student might be taking. The exercises often direct students to apply the ideas they’re learning to a piece of writing that they are already working on for another class or to a task they have been assigned in their job.
The structure of the text was, at times, a little confusing. For example, the fact that tone, audience, and purpose are first discussed under a chapter on paragraphs was a little disorienting. Though these elements clearly relate to paragraphs and paragraph structure, they are really a central element of the larger structure and purpose of an essay or paper. Beyond that, in this section the author clearly explains different types of paragraphs, and provides a clear and detailed description of concepts such as analysis and evaluation.
There were a few other choices that did not make sense to me. For example, why are signal phrases and verbs discussed in the section on formatting as opposed to the section on integrating material into texts? That doesn’t really make sense.
My main concern is with the larger structure of the book. It starts by breaking down sentences structure and explaining the parts of the sentence. It seems like these chapters would make more sense in connection to editing since these are issues students should explore as they are editing their work. Most research shows that students more successfully learn grammar and sentence structure when it’s addressed in a specific context (such as their own work). The structure of the book implies that students can “learn” elements of a sentence and then easily apply that to their work.
I read the text in iBook, and the formatting did not always functioned properly. Some of the tables/columns were hard to read, and there were instances where the text referred to underlined sections of the examples, but there was no underline in my version.
I did look at the PDF version, and this did not seem to be an issue.
The book is generally free of errors. I looked at some of the previous reviews, and it seems as though some of the specific errors people noted have already been edited out of the text. I did find one clear typo on page 408 where the word “Thesis” in a title is written “ThesIs.”
The book did not make any statements that were insensitive or inoffensive. At the same time, it also did not address issues of language that relate to culture or gender. So it essentially avoids the topic, which is insensitive in its own way. For instance, it does not deal with issues of language and gender, and in the chapter on pronouns it does not examine the increasingly common use of the singular “they.” I appreciated the section for English language learners, but was a little confused about it’s overall purpose. It did not in any ways address some of the rhetorical issues that multilingual and international students often struggle with, and instead seemed to want to take the place of an English language course. In other words, it seemed as though it was well meant, but not sufficient or clear.
I appreciate that the text encourages students to be not only active readers and writers, but also active students. It emphasizes that they should seek help if they need it, and demonstrates ways to engage with reading.
The lists of words, such as transitional words, were very helpful. My experience is that students benefit greatly from these types of examples. The section on presentation skills was also useful and provided some good tips concerning tone, voice, and connecting with your audience.
I also appreciate the use of examples in the text, and these were generally very helpful. The sample essays at the end were helpful, and I really appreciated all the links to model readings available on the web. Despite the examples, while reading the text, it often feels like there’s a little too much telling students how to write rather than showing.
My main concern is that it wouldn’t work well for a more theme or genre-based writing course, one that worked to place student writing in a specific context. At our university, writing instruction is integrated into yearlong, theme-based courses for first-year students. When I taught composition at a university with a more traditional first-year writing sequence, the courses were theme-based, and students were encouraged to think of their writing as contextualized and purposeful. Writing for Success often seems to assume that writing courses function more as isolated courses where students focus on the structures and processes of putting together expository writing.
As I note above, I think it would be helpful to better define the specific audience for this textbook. It’s certainly not appropriate for the college writing classes I’ve taught or worked with, and it could be that it has a different purpose. A college writing course should introduce students to more complex ways to approach their writing, and get them excited about the possibilities for communicating their ideas. I’m not sure that this text would achieve that goal.
Reviewed by Sara Crickenberger, Instructor, Virginia Tech on 6/10/15
The pdf of the textbook does not provide a table of contents or an index/glossary. It opens with a Preface then jumps right into Chapter 1. These omissions are inconvenient for planning and for both students and instructors trying to locate... read more
The pdf of the textbook does not provide a table of contents or an index/glossary. It opens with a Preface then jumps right into Chapter 1. These omissions are inconvenient for planning and for both students and instructors trying to locate specific material in the 613-page book. However, the textbook covers a wide breadth of material relevant to a first-year writing class, ranging from basic discussion and tips to help students succeed as college-level readers and writers to sample essays employing a variety of rhetorical modes. I likely would not use everything in this textbook, but it contains a great deal of material that I would find useful.
The content appears to be accurate and unbiased. I did not find any factual errors or inconsistencies.
The material in the textbook is up-to-date and relevant. Some examples use historical references, which are essentially timeless. A couple of the sample essays discuss topics such as universal health care and low-carbohydrate diets that may be front page news one day and off the public radar the next, but the material was not dated in a way that made it less valuable as a resource for students. The sample essays are in the last chapter in the book, which could easily be updated with newer essays.
The book is easy to read and clearly speaks to college writing students. The language is accessible, explanations are clear, and instructions are easy to follow. The author defines terms that are specific to the study of language and writing and gives examples illustrating how they are used. After each section students are asked to demonstrate their understanding of the material by completing exercises based on their reading.
The book uses a consistent framework that includes learning objectives for each section, discussion/explanation of the material, exercises that allow students to practice what they have been reading/learning, tips to make difficult ideas more accessible or reinforce messages, key takeaways to reinforce the learning objectives for each section, and a writing application.
The book is divided nicely into numbered chapters and sections that work well as self-contained units. Each section has clear learning objects, examples, exercises, and a writing application. It would be easy to assign a chapter or section within a chapter with the accompanying examples and exercises for students to compete.
The chapter on Writing for English Language Learners seems a bit oddly placed. Since that material is relevant for only a segment of the student population, I probably would have moved that chapter toward the back of the book with the more specialized content on documentation and presentations rather than between the chapters on word choice and shaping content. However, the content in the ELL chapter does relate closely to word choice and sentence structure, so another instructor might think this is the perfect place for this material.
The biggest problem with navigation in this textbook is the lack of a table of contents and index is. However, I had one other problem with the formatting. The text is double spaced, but paragraphs are not indented and there are no blank lines between paragraphs, so it is difficult to tell where paragraphs break. This is an issue in terms of ease of reading, and it sets a poor example for students who are learning the conventions of mechanics and formatting.
There are a few spacing issues. In some places subheads butt directly against body copy or tables, for instance. And some page breaks cause awkward breaks in exercises, tables, and charts. These are small issues that don't significantly affect the readability or usability.
I found few errors in the book. One issue that I did notice is a problem that is common among my students, so I was especially disappointed to see the error in the text. The author uses "where" in reference to something other than place: "...establish a buddy system where you check in with a friend about school projects" (25).
The text has a few other issues, such as bullet points that don't use parallel verb structures, some use of "to be" constructions that could easily be revised to more active/vivid sentence structures, and some typographical errors, such as "accuratelydid" (92) and "ascrawny" (149). These errors are relatively rare but start to get annoying after a couple of hundred pages.
The book does not contain references that are culturally insensitive or offensive. The author switches between male and female names in examples/exercises and uses names that are reflective of a diverse population.
I am planning to use this book as one of my texts in a first-year writing class next fall. I likely will adapt it a bit by adding a table of contents, indenting paragraphs, correcting mechanical errors, etc. so that it is more functional and serves as a model of the writing and formatting I expect from students. I actually like the double spacing, which most publishers don't use because of space/cost issues. It provides plenty of room for students to annotate the text electronically or on print copies. I am not sure I am up for undertaking indexing.
Reviewed by Kari Steinbach, Instructor, University of Northwestern - St. Paul on 7/15/14
The text covers some helpful elements of a first college writing course, such as an overview of several genres of writing assignments, some grammar and usage issues, use of peer review and collaboration in writing, and research strategies. Some... read more
The text covers some helpful elements of a first college writing course, such as an overview of several genres of writing assignments, some grammar and usage issues, use of peer review and collaboration in writing, and research strategies. Some may consider the addition of the study strategy and reading strategy material to be too basic--even for a first year writing course. Without a clear table of contents or index, the organization was difficult to decipher and required paging back and forth throughout the book.
The book appears to be free from any obvious errors. Because of the rapid changes in databases, electronic research strategies, and documentation styles, it is likely that updates will need to be made--but this is the case for any text dealing with research and documentation.
Aside from requiring updates due to documentation and research changes, there may need to be an update of sample essays that have subject matter that may become outdated. Examples of cited sources may become outdated--especially in fields that change quickly.
The use of flow charts to help students understand grammar concepts is helpful. A better use of white space, illustration, font changes, bullets, and color in the design would make the text more visually fluid and more readable. The addition of full text student sample papers to show formatting is very helpful. I also appreciated the list of objectives at the beginning of each chapter.
The text appears to be consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
It would be helpful for the rhetorical mode section to be split into separate chapters, with each genre given more individual emphasis and examples of the strategies required for that genre.
My preference would be to teach grammatical concepts as they come up within the course of writing assignments. I would prefer a text that had grammar covered in an appendix that could be referred to throughout the course and as the issues came up during the writing assignments. I would not teach grammar independent of the writing assignment.
There is a need for a clear table of contents and index.
There are no obvious issues with the book's grammar.
There are no obvious issues of cultural insensitivity in the text.
Reviewed by Jonathan Carlson, Instructor, Composition, University of Northwestern - St. Paul on 7/15/14
The first chapter covers many "first year" or "freshmen" tips, best practices ideas and how-to info. Probably good material for the group using this book, but not essential. Table 1.2 is valuable to a student's overall understanding of writing.... read more
The first chapter covers many "first year" or "freshmen" tips, best practices ideas and how-to info. Probably good material for the group using this book, but not essential. Table 1.2 is valuable to a student's overall understanding of writing. Table 8.1 is great! The outline checklist on 301 and 302 is good info. I like the discussion of thesis statements on page 341. It points out significant errors. I appreciate the section on plagiarism. This is such a key issue today, with so much research done online with text that is so easy to copy and paste. I like that the book notes that there is intentional and unintentional plagiarism. I think the reading examples in chapter 15 could be stronger. The compare and contrast essay is quite brief, and it is not organized for easy reading (one massive paragraph and one short paragraph). The cause and effect essay is rather short. I would like to see 3 to 5 page examples - approximations of what I will be expecting my Comp 1 students to write. I feel the persuasive essay is much too brief to be persuasive. Universal health care coverage is a massive and nuanced topic, and to serve it up in two pages seems almost offensive. By the by, the linked essays seems very good. I just think the book needs better, stronger examples of student essays. Overall, I think this is perhaps the most comprehensive writing textbook I've seen. However, the sample writings included in the text need to be expanded and off "better quality"--closer to what a student would turn in for a Comp I course.
Pg 319: "Generally speaking, write your introduction and conclusion last, after you have fleshed out the body paragraphs." This is dangerous advice. While I don't think it means to, I feel it downplays the importance of a thesis and/or mapping statement/plan of coherence. Without such a guide directly in front of them, many students will go off course. I feel the discussion/instruction of the thesis statement should occur in the outlining and drafting segment. It can and should be revisited later, but to wait to this point could be detrimental to the paper. Section 11.4: Accurate and essential. Students really need to know how to evaluate source material. From page 435: Questionable sources: free online encyclopedias. Thank you! From page 438: "Think ahead to a moment a few weeks from now, when you've written your research paper and are almost ready to submit it for a grade. There is just one task left - writing your list of sources." I've always thought it wise to have students created their references page as they write the paper. They can delete a source they don't end up including, and if they wait to the end, they are more likely to forget a source. Page 570: The chart should probably be labeled "Winter Olympic Medal Standings since 1924." If the combined total is calculated, the US has more than double our closest competitor, the Soviet Union. Also, the URL included in the text does not work. On the whole, the info is accurate and will be very helpful to students.
Not much in the book seems dated. Not much background is given for the fictional students in the book, and no pictures of them are provided. While this does increase the longevity of the book, it also decreases the chances of a real student identifying with the students in the textbook. The sample student writing on 361 is or will be dated, but if you're writing about tech, it's going to be. Beyond the Hype: Evaluating Low-Carb Diets from page 455. This is quite dated. After the myth that Atkins died from heart issues circulated, the low carb movement died with him. The process that this paper goes through is structured well. And I think that the teaching done by it is very relevant. So...I don't think that it's relevance as a fad should necessarily be considered. But if the book gets updated in 5 to 10 years, I'd recommend a different topic. The annotated essay portion on page 470 looks like it was created on an old-school typewriter. Ding! Page 531: The discussion of the URL vs. DOI is timely but may become irrelevant. I'm glad to see it's in here, but it may become irrelevant in the future.
All the language seems clear to me. However, I have a Master's in Writing. It's difficult to take that filter off and think as a college freshman would. For example, page 327 uses the phrase "formal English." I have a strong context for that, but would most college freshman. I honestly am not sure. It might be helpful to have a few early college students review the textbook.
Yes, it is internally consistent. The book uses similar language throughout and references previous and upcoming chapters frequently.
The textbook seems appropriately modular. An instructor could use portions he/she wanted or needed and leave out non-applicable content such as the "freshman seminar" type sections. Nearly half the book is grammar, punctuation and "college wisdom" content, which makes modularity especially important if the book is being exclusively used a Composition I textbook. And I do think its modularity is designed well and designed well enough to function in that way. The text does references previous and upcoming chapters frequently, but I think this still works fine.
There is no table of contents at the front. The portions about Crystal, while they are related thematically to the text, still seem out of place. I've used another textbook with a similar element (a group of first-year students who share their struggles and successes). In the textbook I used, there were pictures of the students, and their comments and insight were set off in colorful textbooks. While it seemed a bit cheesy, as does this, the concept is helpful to students, I think. Setting off this element in sidebar allows the text to flow more smoothly and helps to identify the comments as such. Some of the tables are broken at the page breaks in segments that make them hard to follow. For example, if they were broken between rows instead of in the middle of them, that would make them easier to follow. Exercise 2 on page 544/545 is an example of a terrible table break. The overview of sections on page 38 is very confusing. This info should be included mainly in a table of contents or a chapter introduction. The Choosing Specific, Appropriate Words section on page 327-328 could be set off with a different color or the like. It seems odd simply being part of the flow of text. Something to consider: This textbook is set up in something of a narrative structure. It might be more effective if set up as an owner's manual, considering our current generation of learners' aversion to lengthy text. 9.1 Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement Chapter 9 is covering developing a thesis, but chapter 8 looks at writing the draft. The instructions on the thesis need to come before instructions on writing the draft. Consider adding table 8.1 to page 354. Finally, there is no index, glossary or works cited sections at the end. The overall organization is good, quite functional, but some of the "accessories" are missing.
The color scheme is too muted. Various sections are "highlighted" in light gray. More distinct colors would give the reader clearer clues about how the text is organized. Also, some sort of picture or icon would help to recognize certain segments. For example, the "Writing at Work" segments could have a small picture of a person at an office desk (preferably Dwight Schrute). I really like the charts on page 49 and 51, 54.
I found a few punctuation errors, but they're all essentially the same: missing spaces. This may have happened when the document was converted to PDF. Orunless on page 52. "athesis" on page 338. Fencessymbolize on page 340. seeChapter 6 on page 368. From page 392: "Writers are particularly prone to such trappings in cause-and-effect arguments "Shouldn't it be "traps" instead of "trapping"? Manual published from page 424 Table 11.1 on 423 and 424 uses two fonts inconsistently. asSmithsonian Magazine orNature from page 434 athttp://www.apa.org and athttp://owl.english.purdue.edu on page 492. From page 521: "byperiods." From page 516: "inand"
I didn't find much that was necessarily inclusive, other than the names of the fictional students. There were some sample essays (linked) that included non-white authors, which is certainly inclusive. However, I don't think any of the examples or articles were exclusive. Being a "white" male myself, I have a filter that is difficult to remove. I would hope that you could find some non-white reviewers to give you their opinion of this element.
Very, very comprehensive. I actually felt all the grammar and "freshmen seminar" elements took up too much of the textbook, but since it's free and the modularity works well, that's fine. Please add stronger student sample essays, a table of contents, glossary, index and works cited sections. And make the color scheme bolder. Thanks for the opportunity to review this textbook!
Reviewed by Tanya Grosz, Assistant Professor of English & Director of Undergraduate Pathways, University of Northwestern - St. Paul on 7/15/14
I was surprised at just how comprehensive this book was. It covers everything from study strategies to prewriting to editing and punctuation and research writing. Also, it includes writing strategies for ELL students which is very helpful. While I... read more
I was surprised at just how comprehensive this book was. It covers everything from study strategies to prewriting to editing and punctuation and research writing. Also, it includes writing strategies for ELL students which is very helpful. While I would have liked to have seen more full-text essays woven throughout the text, there are several in the final chapter, there are links to others, and there are a few throughout the book.
I have taught writing for 20 years, and I find this text to be both accurate and helpful. I find that students, regardless of age, struggle most with essay organization, and this text devotes the appropriate amount of time to organizing a paragraph and essay.
Updates could be made in a straightforward and easy fashion; many of the principles are solid and timeless. The MLA/APA part can be easily updated as can the essay examples.
The tone is extremely accessible. As I read through chapters 1 - 3, I was concerned that the text was almost too basic to be used with college freshmen, but as I reflected upon this, it dawned upon me that I cover some of the same concepts in the first week of class based on a writing and editing assessment. A teacher could easily extract those components that aren't necessary. Ultimately, this book is clear and readable.
Each chapter has a framework that is consistent; there is review at the end that is helpful and exercises for the student who wishes to practice what has been covered in the chapter.
I could easily see myself extracting certain elements of various chapters and using some chapters but not others. The book lends itself to easily using some chapters and not others and certain parts of a chapter without the entirety.
This is a difficult question because no one would likely organize a textbook the same way as someone else. I found the Refining Writing chapter (Chapter 7) a little oddly placed, but it certainly was not a deal-breaker, and because of its excellent modularity, one could easily organize the presentation differently. The topics are definitely presented clearly and logically.
The charts and graphs did not present very clearly on my screen, but I'm not sure if that's the text or my computer. While it wasn't distracting, the graphs were a bit pixelated and fuzzy. The essay samples were clear. Navigation was easy.
I thought the grammar, sentence flow, punctuation, etc. was excellent.
I wish I had access to the chapter for ELL students 20 years ago! I found nothing offensive in the text and found helpful chapters for college-bound high school students, freshmen or sophomore college students, and adult learners.
I find this book to be pragmatic, helpful, clear, straightforward, and well done. I am going to recommend it to my department for review. I think there should be a Learning Style quiz embedded or linked to when discussing learning styles for students. The writing tips and advice given were accurate and relevant. Literally, the only piece I would have liked to have seen addressed but did not was how to be an effective peer editor, but the tips for editing one's own paper could easily be applied to editing a peer's essay. While I would likely not use the chapter on presenting with my own class, I found it to be helpful. I do have one question about the formatting of the essays in chapter 12 at the end of the book: Why were the paragraphs not indented? I know of no composition instructors who allow block formatting for submitted essays. I recommend reviewing this book!
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Writing
- Chapter 2: Writing Basics: What Makes a Good Sentence?
- Chapter 3: Punctuation
- Chapter 4: Working with Words: Which Word Is Right?
- Chapter 5: Help for English Language Learners
- Chapter 6: Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content
- Chapter 7: Refining Your Writing: How Do I Improve My Writing Technique?
- Chapter 8: The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?
- Chapter 9: Writing Essays: From Start to Finish
- Chapter 10: Rhetorical Modes
- Chapter 11: Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?
- Chapter 12: Writing a Research Paper
- Chapter 13: APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting
- Chapter 14: Creating Presentations: Sharing Your Ideas
- Chapter 15: Readings: Examples of Essays
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Writing for Success is a text that provides instruction in steps, builds writing, reading, and critical thinking, and combines comprehensive grammar review with an introduction to paragraph writing and composition.
Beginning with the sentence and its essential elements, this book addresses each concept with clear, concise and effective examples that are immediately reinforced with exercises and opportunities to demonstrate, and reinforce, learning.
Each chapter allows your students to demonstrate mastery of the principles of quality writing. With its incremental approach, it can address a range of writing levels and abilities, helping each student in your course prepare for their next writing or university course. Constant reinforcement is provided through examples and exercises, and the text involves students in the learning process through reading, problem-solving, practicing, listening, and experiencing the writing process.
Each chapter also has integrated examples that unify the discussion and form a common, easy-to-understand basis for discussion and exploration. This will put your students at ease, and allow for greater absorption of the material.
Tips for effective writing are included in every chapter, as well. Thought-provoking scenarios provide challenges and opportunities for collaboration and interaction. These exercises are especially helpful if you incorporate group work in your course. Clear exercises teach sentence and paragraph writing skills that lead to common English composition and research essays.
Exercises are integrated in each segment. Each concept is immediately reinforced as soon as it is introduced to keep students on track.
Exercises are designed to facilitate interaction and collaboration. This allows for peer-peer engagement, development of interpersonal skills, and promotion of critical thinking skills.
Exercises that involve self-editing and collaborative writing are featured. This feature develops and promotes student interest in the areas and content.
There are clear internal summaries and effective displays of information. This contributes to ease of access to information and increases the ability of your students to locate desired content.
Rule explanations are simplified with clear, relevant, and theme-based examples. This feature provides context that will facilitate learning and increase knowledge retention.
There is an obvious structure to the chapter and segment level. This allows for easy adaptation to your existing and changing course needs or assessment outcomes.
Contribute to this Page

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principal tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question
Scaffolding the Writing Process: An Approach to Assignment Design in the SOSC Core
By Sarah Johnson, Assistant Senior Instructional Professor & Director of Undergraduate Studies in Laws, Letters, and Society and CCTL Associate Pedagogy Fellow
Every time I design a new course, I return to the most significant piece of advice that I received when I was getting ready to teach for the first time: that it is my job to prepare my students to succeed on the assignments I give them. When I first heard this, it struck me as an obvious responsibility but also one that I had hardly considered. I was a graduate student at the time who was about to teach a section of Classics of Social and Political Thought in the Social Sciences (SOSC) Core along with a political theory seminar of my own design. These were courses in which students would read books, talk about them, and then write about them. I realized, on reflection, that I had assumed that my students would simply learn by doing, or that with the opportunity to read, discuss, and write that I was giving them—and with some feedback from me along the way—they would leave my classes more adept at these tasks than they were when the classes began. I had thus intended to rely upon my students’ other teachers to shape them into the kinds of readers, interlocutors, and writers that I both needed and wanted them to be and had no concrete strategy for taking on that responsibility myself. What would effective teaching moments look like in the kinds of courses that I wanted to offer? I’ve spent the last fifteen years trying to answer this question, largely through experimentation in the classroom and by learning from my own teachers and colleagues.
Below I share an approach to designing writing assignments that came together when I was teaching full time in the SOSC Core as a Harper-Schmidt Fellow. It prepares students to succeed on their SOSC essays by breaking down the writing process into the essential steps that college-level writing demands and giving students time to attend to each one. The aim of scaffolding the writing process in this way is to help students not only to practice but also to learn the necessity and value of tasks such as exploratory writing, refining their ideas in conversation with others, and being mindful of their own development as writers (and thinkers). Using this assignment for the first essay of the quarter or year also helps me to clarify what I expect from my students each time they write a paper, even when some of the steps aren’t formally assigned. The ultimate goal of the assignment is to cultivate in my students a way of thinking about and approaching the writing process that will provide a foundation for further growth in other contexts.
Two Preparatory Assignments: Exploration and Framework
I give students their essay assignment about two and a half weeks before the deadline and structure this time to help them use it effectively. There are various ways of doing this. One approach that I learned from Kristen Brookes, a former colleague who teaches at the Amherst College Writing Center, is to give students an opportunity to use informal, exploratory writing to generate ideas for a paper immediately after receiving the assignment. Following Kristen’s model, I first ask my students to revisit the material they will be writing about and to copy down about five passages that they think can help them to answer the essay question. They bring these passages to our next class, where I give them time to hand-write in short bursts of three to five minutes in response to a series of prompts. After initially writing about their tentative argument for the paper, the students engage with each of their chosen passages in whatever way is most useful to them—for example, by explaining its meaning or why they think it will be useful, or by writing about any questions the passage inspires. As I learned from Kristen, what matters most in this exercise is that the students write constantly during their brief time with each prompt and resist the urge to criticize or edit what they have written. The point of an exercise like this is to get all their ideas onto the page without judgment. Once that is done, they can spend time reviewing what they have written to determine which ideas are more and less useful and revisit their plans for their paper.
My students then take advantage of the momentum generated by this initial exercise as they complete a second preparatory assignment that is due roughly twelve days before the essay deadline. The students’ task here is to transform their initial ideas into a framework for their paper. This framework includes a draft thesis-statement followed by a point-based outline, in which they write out the point of each paragraph in a complete sentence. As a final component of the framework assignment, I ask the students to provide a few pieces of textual evidence that can be analyzed to substantiate each point along with a brief discussion of why each passage will be helpful.
I saw Kristen make great use of pairing exploratory writing and point-based outline assignments at Amherst, but it was while training to be a lector for the Academic and Professional Writing course here at Chicago in graduate school that I first learned the value of teaching students to think about paragraphs in terms of points as opposed to topics or topic sentences. Whereas a topic sentence need only announce in broad terms what each paragraph will discuss, a paragraph’s point announces to the reader the reason why that paragraph exists at all. It is the specific step in the paper’s overarching argument that a given paragraph will develop and defend in order to develop and defend that larger argument successfully. Within a paragraph, then, the point carries the authority of a thesis: it governs everything that is written in it and helps the writer to determine what they must accomplish before moving on to the next paragraph. The framework assignment thus allows students to begin considering the moves they will need to make in their paper, the order in which those moves must be made, and the kinds of evidence and analysis that they might provide to execute those moves effectively. The assignment requires much of the reading and thinking effort that a full draft would require, but by producing just its essential components a student can more easily see the relationships among their thesis and their paragraphs and where things may have gone wrong as they worked up their argument.
Required Meeting: Feedback and Refining Ideas
I use these two preparatory assignments as the basis for a twenty-minute conversation with each student one week to ten days before the essay is due. The purpose of requiring students to meet with me at this stage is not only to provide verbal feedback on their framework assignment and to address questions and concerns about their developing paper. Its purpose is also to help students make the most of their discoveries from the preparatory assignments and to demonstrate the role of conversation in the refinement and generation of ideas.
For instance, when reviewing the framework assignment, I might see that a student’s points develop a different and stronger argument than is found in the thesis statement at the top of the page. In this case, I would use our conversation to explain the misalignment between the existing thesis and points, to show the student the insight that they reached through the process of working on their paper, and to brainstorm with the student what a thesis statement might look like that would do justice to their insight. Another student might plan to discuss an important concept in their paper without doing so in sufficient detail. Here I would ask the student to explain their understanding of the concept in order to draw out the knowledge they have about it that does not yet appear in their framework. We could then discuss how to incorporate that information into their paper.
Reflection: Opening a Conversation about Writing
Just as the required meeting offers students a chance to step back from their ideas in the middle of the writing process to reflect on the shape their paper is taking, I give students a way to take stock of their entire experience of writing the paper after they finish it. I want them to keep in mind that the paper they have written for me is part of their larger process of development as writers, a process that began long before they entered my classroom and one that will continue long after they leave. This means that when they write for me, they are drawing upon habits and skills that they learned by writing in other contexts while also cultivating new habits and skills that they can rely upon in future papers. Before submitting their final drafts, my students therefore prepare a 300- to 500-word reflection that helps them to understand their own writing process and to become more self-conscious about their development as writers. These reflections discuss 1) what they found most challenging about writing the essay; 2) something that they learned while writing it; 3) something that their essay does well; and 4) something that they could do to improve the essay. When they write their final paper of the quarter, I also ask them to discuss 5) how they have improved as a writer during the quarter; and 6) in what ways they would like to improve as a writer in future quarters.
Final Paper Comments: A Focus on Writing Development
The students’ reflections on their papers open a conversation about writing that I enter through my feedback. I typically begin my comments at the end of a paper by engaging with one of their own observations about their writing process. For example, students often report that their argument underwent significant changes between the time they began outlining and drafting their paper and when they submitted it. Some will take from this experience the insight that they need to try to give themselves more time than they typically do to write their papers as these transformations, although frustrating, ultimately made their final draft much better than it would have otherwise been. In response to an observation like this, I might explain that this is indeed an indispensable part of the writing process and that building in more time for these discoveries and revisions will help them to write at an even higher level. But some students will draw a different conclusion from the same experience, namely that they did something wrong because they did not begin writing with the best possible argument in mind. Their goal in future essays is usually to develop a better plan for their papers in advance so that they can avoid friction and uncertainty in the drafting process. In these cases, I would caution them against this aspiration by explaining that we typically only find the best arguments we can make through the process of writing itself, and that the evolution of their own argument demonstrates that they did exactly what they were supposed to do during the writing process.
In the rest of my comments, I discuss two or three writing issues that I want the student to try to address in their next paper. I number these discussions and place corresponding numbers in the margins of the essay to show the student where each problem occurred. Over the years, these numbers have become the only margin notes I make on essays, an approach that I remember one of my own professors, Aryeh Kosman, using when I was in college. I have discovered that providing feedback in this way allows me to focus the student’s attention on making the improvements that I think will have the greatest impact on the next paper they write, whether that paper is written for me or another instructor. And by addressing these at the end of the paper, I give myself the space both to explain why the issues I identified are indeed problems and to provide concrete suggestions for how to avoid them in the future. In doing so, I often draw upon my training for Academic and Professional Writing, where I was taught to rewrite sentences for my students in order to show them how the feedback I was offering could be put to use and the difference that it would make to their writing.
Although this kind of feedback necessarily emphasizes problems at the level of writing over problems at the level of textual interpretation, this does not mean that I ignore the claims my students make about the texts we are studying. Rather, it means that what I say about a student’s interpretation will be in the service of helping them to do a better job on their next paper, which is unlikely to be on the same text and will often be in another course altogether. For example, students often attribute ideas to an author that I don’t think can be supported by the text at all, and certainly not by the parts of it that they quoted or cited as evidence. When this happens, I might explain why I don’t think they can use a particular passage as evidence for their claim, offer a few examples of claims that the passage could in fact support, and explain the difference between these claims and the student’s. My aim in doing this would be to help the student to become a more careful reader by giving them tools that can help them to scrutinize their textual evidence during the drafting process.
Final Thoughts
While this specific approach to scaffolding writing assignments can help students to succeed on their SOSC essays, the principle that underlies it—breaking down a writing process into its essential components—can also guide the design of writing assignments in upper-level undergraduate courses. It has helped me, for example, when designing research assignments for my courses in the Law, Letters, and Society program. I ask myself what students would have to accomplish throughout the quarter to succeed on their projects and turn these expected milestones into guided assignments that provide an opportunity for feedback. No matter the level of the course, then, I aim to avoid assuming that my students already know the motions that I expect them to go through to complete an assignment and instead build those into the course itself.
Sarah Johnson is Assistant Senior Instructional Professor and Director of Undergraduate Studies in the Law, Letters, and Society (LLSO) Program. Her current research focuses on the coevolution of Karl Marx’s ideas about history, critique, and political economy in the 1840s. In addition to teaching courses on political economy in LLSO, she regularly teaches in the Classics of Social and Political Thought Core sequence.
- Accessibility Tools
- Current Students
- The University
- Student Services
- Centre for Academic Success
- The Academic Skills Lab
- Academic Writing
Essay Structure
- Swansea University DSA Assessment Centre
- Student Support Services
- Digital Skills
- Dissertation skills
- Why read your writing?
- Signposting
- Writing persuasively
How to structure your essay
Tricks for sentence writing.
- Common errors in structure and argument
- Grammar and Punctuation
- Academic Integrity
- Presentation Skills
- Study Skills
- Inclusive Student Support Services
- Reaching Wider
A well-structured essay is important as it enhances readability, ensures logical flow, and effectively communicates the main ideas. When your essay is clearly organised it helps the reader understand and retain the essay's key points.
A typical assignment has an introduction, a main body and a conclusion. The purpose of the introduction is to signpost everything that a reader can expect from the assignment. The main body is where this will be delivered, and the conclusion provides a summary of the main points, perhaps guiding us to further reading or investigation.
A high-quality essay is composed of high-quality sentences. This page focuses on rules for writing complete sentences that flow together to create a well written academic piece.
Common errors in structure
This guide highlights common errors in structure and argument, and gives you a short explanation of what you can do to avoid them.

- High-impact business writing
- Effective email writing
- Bid, tender and sales-proposal writing
- Technical writing
- Writing for customer service

- Customer-service writing
- Effective report writing
Blog
Why my messy writing process works
Why my messy writing process works

Author : Rob Ashton
Posted : 17 / 09 / 24
Share this:

But if we could see inside their heads, we’d probably find that their experience is much closer to ours than we thought.
Writing is not a natural process for the human brain. So when humans write, humans generally struggle.
Even I don’t find writing easy. But I’ve come to realise that this struggle can actually be a good thing.
Before I explain why, here’s a peek at my own all-too-human writing process.
Deadline first
Starting is the hardest part. I find it pretty much impossible without a deadline. In fact, I wouldn’t be writing this now if I hadn’t promised it to my editor by tomorrow morning (and if she hadn’t berated me for finishing late last week).
But until I start, I usually have no idea what I’m going to say. I struggle even to imagine myself writing, let alone to think of something worth sharing. Often I’ll look at a previous issue and feel like it was written by a stranger.
In some respects, it was.
Just like you, I have many responsibilities besides writing. I also have a life outside of work. So I’m constantly changing roles throughout the week.
When I’m in ‘dad mode’, for example, my writing skills aren’t usually in high demand. They’re sealed off, and trying to switch my brain to ‘writing mode’ becomes quite tricky.
As a result, I avoid touching my keyboard as if it were a hotplate.
It gets easier
As soon as that first sentence is down, though, things get easier.
It doesn’t really matter what it says – I usually change it later anyway. What matters is that, from that point onwards, my writer persona takes over.
As I type, new ideas start to materialise almost miraculously. I jot them down as placeholders in [square brackets], then reorder them into a logical and (hopefully) captivating structure.
By now, my head is usually spinning, such is the effort needed just to get this far. I don’t want that confusion leaching into my writing, so I take a quick break.
Once I’ve parked my bottom back on my seat, I rewrite my original (often terrible) intro, check the order of the other ideas in the list and flesh them out.
Two to three hours later, the first draft is done.
I put it to one side for at least a day, giving me some much-needed distance from it. And the next morning, I’m ready to do battle.
I edit it without mercy, often removing and reordering whole chunks of text. I trudge through a dense monologue of jumbled and ambiguous thoughts, wondering why it seemed so clear only yesterday.
Then I finally send it to my editor.
She spends several hours going through it again, tightening, clarifying and otherwise improving what I’ve written. Then I go through and review her changes.
She proofreads it, I take in her corrections. And finally – my fingers almost trembling over my mouse – I schedule it to go out at 7am the next morning.
The relief I feel at that point rarely lasts until the end of publication day, as it dawns on me that I’ll soon need to start the whole process over again.
Hard write …
This is just what I do. We all have to find what works for us, and your mileage will vary. I have the luxury of deciding what to write about (although that can be just another excuse to procrastinate).
I also tend to plan more thoroughly if I’m writing longer documents, such as a report.
But my point is that it doesn’t matter if it’s a messy process.
I’ve been writing for three decades, and I still don’t find it easy. We evolved to speak and listen, not to read and write. So producing any document is a real workout for the brain.
Yes, we get better at it over time. But if you still find it hard, that’s because it is.
At least, anything that’s worth writing is hard.
… easy read
But here’s the thing: it’s good that it’s hard.
This process of typing and ordering our ideas slows down our thinking enough for our brain to make sense of them. It makes it easier to draw on our personal knowledge bank and see where the gaps are.
It enables us to properly connect one idea to another and forces us to create a structure out of the jumble of thoughts in our head.
In short, it makes us do the work for the reader .
Whenever you find something incisive and easy to read, bear in mind that the author probably found it hard to write.
And if you’re struggling with writing a document, that could well be a sign that you’re on the right track.
The good news
There is some good news in all this. The human writing process, for all its difficulty, is the gateway to our best ideas. There’s often real gold in our brains if we’re prepared to use our keyboards to find it.
And because it’s hard, those who don’t already avoid it often aren’t that good at it. So if you can be just a little bit better, you’ll stand out immediately.
Don’t aim to be an amazing writer (yet). Just pick a couple of key areas and aim to get ten per cent better in those. Work on your readability , for example. Or start improving your introductions .
The crucial part is to get started.
The American author Louis L’Amour wrote more than 100 books, but he still observed that the water doesn’t flow until you turn on the tap.
So if you don’t have a deadline already, agree one with someone else. It could help you cross the chasm between your office door and your keyboard.
Image credit: Unsplash+ / Getty Images

The definitive guide to transforming the writing of individuals and teams
Author: rob ashton.
Rob Ashton is the founder of Emphasis and posts mainly about writing and the brain – a topic he's been researching for seven years. You can read more of his work in Writing Matters – our weekly bulletin of career-building writing advice backed by science.

Popular topics
Advice and tips (151)
Grammar (61)
Choose your words wisely (47)
Plain English (25)
Psychology and linguistics (24)
Uncategorised (21)
Language abuse (21)
60-second fix (21)
Reader-centred writing (16)
Punctuation (15)
Online and social media (15)
Technology (15)
News from Emphasis (13)
Spellings (13)
Jargon (12)
Presentations and speeches (11)
Report writing (10)
International issues (10)
Podcast (10)
Design and formatting (9)
Technical writing (9)
Courses for companies (8)
Letters and CVs (8)
Graduates (6)
Quizzes (6)
Proofreading (6)
Customer relations (6)
Numbers and finance (6)
Literacy and education (5)
Development of English (4)
Legal writing (4)
Twitter (4)
Writing news stories (4)
Style guide (4)
Wordplay (4)
Advertising (4)
Partners (3)
PDF downloads (2)
Pitches and proposals (2)
Team leaders and managers (2)
Conferences and exhibitions (2)
Editing (2)
Internal communication (1)
Artificial intelligence (1)
Policies and procedures (1)
Learning and development (1)
webinars (1)
Book reviews (1)
Writing for media (1)
Tutorial (1)
More topics
Writing argumentative essays with Kialo Edu

Your students may shine in verbal discussions, but it can be more challenging for them to translate their ideas into a coherent argumentative essay. Fortunately, you can use Kialo Edu’s free, adaptable written discussions to support students’ argumentative essay writing skills.
Kialo discussions guide students to clearly express viewpoints, address counterarguments, and provide compelling evidence. This sharpens students’ reasoning, argumentative, and critical thinking skills , empowering them to explore and defend complex issues through writing.
Let’s see how you can use Kialo discussions to enhance argumentative essay writing for your students!
How to choose a strong argumentative essay topic
Crafting a compelling argumentative essay begins with selecting the right topic. Follow the tips below to guide your students in making a strong selection.
1. Allow students to choose topics that interest them, especially topics relatable to their own experiences.
This will help boost students’ engagement with the essay, while their personal insights will add authenticity to their arguments.
2. Encourage students to select topics linked to current events or topical societal issues.
Such topics are more likely to capture interest, boosting audience engagement with the essay.
3. Remind students to select a topic with clear opposing viewpoints.
If viewpoints on a topic are already universally accepted, their essay may lack depth and purpose.
4. Give students time to conduct preliminary research .
This helps students find adequate evidence to support their arguments before finalizing their topic.
5. Help students choose strong argumentative essay topics with Kialo Edu’s Topic Library .
Our Topic Library is bursting with hundreds of relevant, engaging (and free!) argumentative essay ideas, organized by curriculum subject and age range.
How to write an argumentative essay on Kiao Edu
Students can practice writing their argumentative essays on Kialo. First, students should add a thesis statement. Then, students can write pro and con claims to develop lines of reasoning that act as supporting arguments while addressing counter arguments.
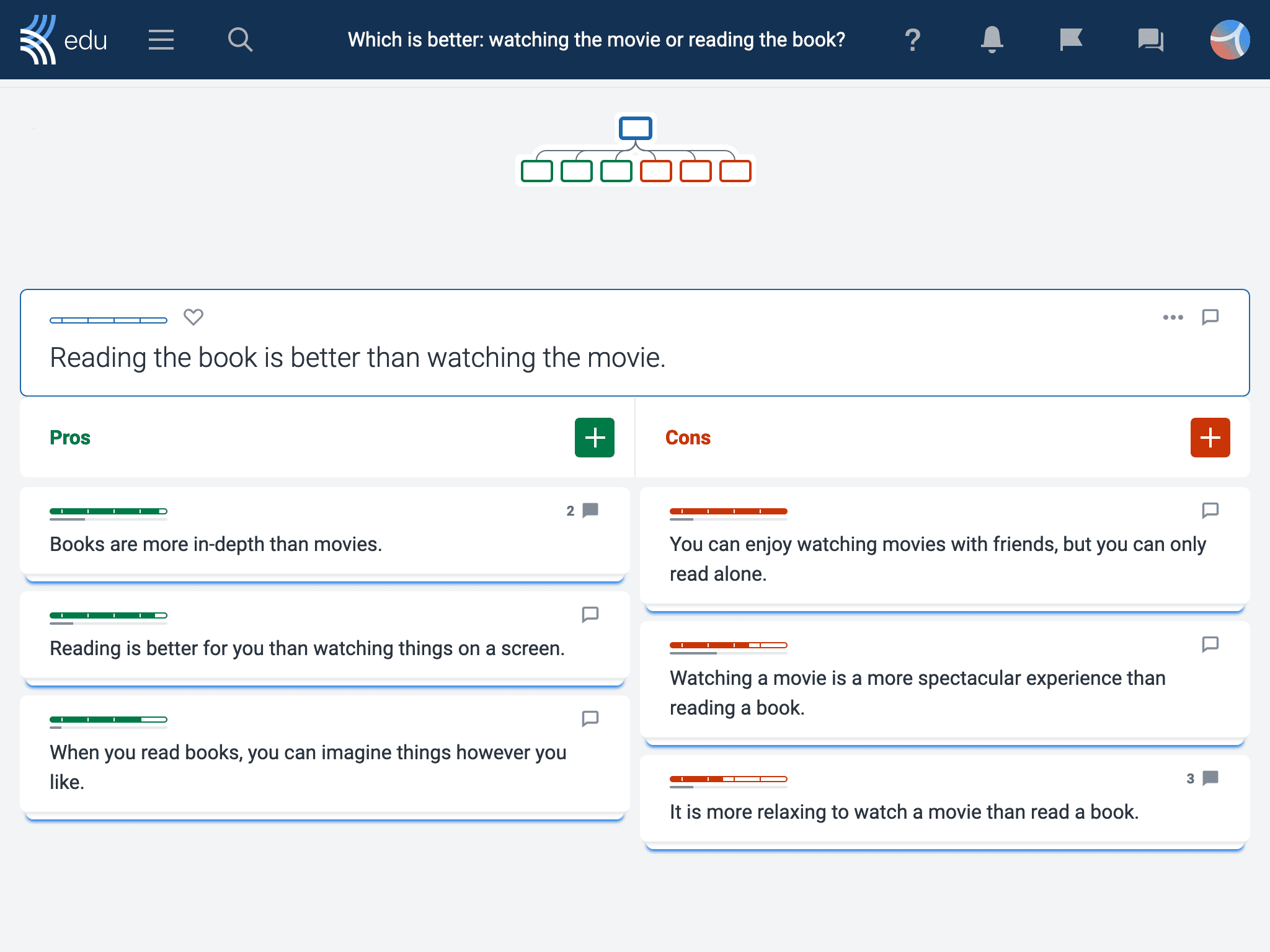
This mirrors a traditional essay format, where students present the thesis in the introduction and develop their arguments in the paragraphs of the body.
Let’s take a closer look at how each section in a traditional argumentative essay corresponds to parts of a Kialo discussion.
1. Traditional essay: Introduction
Kialo discussion: thesis and background information.
Students begin their argument by adding a thesis — a concise statement that articulates the main argument of the essay.
They can also provide context in the Background Information to give an overview or abstract of their essay.
2. Traditional essay: Body paragraphs
Kialo discussion: pro and con claims.
Students use Kialo’s branching discussion framework to present the main arguments in support of their thesis. The visual discussion format reduces the cognitive load for students, freeing them up to concentrate on structuring their argument.
Students begin each branch with a top-level pro claim — the equivalent of a topic sentence — and then support this with further pro claims. The branching structure encourages students to make one claim at a time, directly addressing the previous point.
For those students who tend to overlook opposing perspectives, they can easily see both the supporting and opposing viewpoints that appear side by side in a Kialo discussion. This helps prompt students to consider and come up with counterarguments, as well as rebuttals to these counterarguments to further strengthen their main argument.
As students build their arguments, connective lines illustrate the logical relationships between each claim. This approach helps students understand how broader arguments are built on detailed evidence, enabling them to construct clear and precise arguments that develop specific lines of reasoning.
Finally, to help students avoid gaps in their reasoning, they can choose to view their argument in a unique “sunburst” mini-map , helping them identify knowledge gaps and thereby strengthening their argument.
3. Traditional essay: Conclusion
Kialo discussion: collaborative evaluation.
When students’ arguments reach their conclusion, the collaborative nature of Kialo discussions means students can progress beyond simply summarizing their claims.
Instead, students can vote on the impact of each other’s claims and add evaluative comments, while educators can provide Grading and Feedback on individual claims and the overall discussion. With comments and feedback that target specific claims, students can easily improve their arguments without engaging in extensive rewrites.
4. Traditional essay: References or bibliography
Kialo discussion: linking sources to claims and using the sources sidebar.
Throughout the discussion, students can strengthen claims by adding links to supporting evidence , including statistics, expert opinions, and real-world examples. This boosts the credibility of their claims and enables readers to verify the information.
Encourage students to add sources by enabling Tasks . You can specify the number of sources students must link to, tailoring the lesson to your learning objectives to monitor students’ progress.
And once students have completed their argument, they’ll find all their sources compiled into a reference list in the Sources sidebar!
Whether it’s selecting topics , writing arguments, or organizing sources, Kialo Edu’s free written discussion format will empower your students to excel in their argumentative essays. Get started today by signing up at Kialo Edu !
We’d love to hear how using Kialo has helped your students improve their argumentative essays. Contact us at [email protected] or on social media.
Want to try Kialo Edu with your class?
Sign up for free and use Kialo Edu to have thoughtful classroom discussions and train students’ argumentation and critical thinking skills.
UChicago’s Study Abroad contest winners share the stories behind their art
Students discuss creative process behind winning photo, video and writing entries.
Editor’s note: This story is part of Dispatches from Abroad , a series highlighting UChicago community members who are researching, studying and working around the world.
The University of Chicago’s Office of Study Abroad has organized annual photo, video, and writing contests since 1997. The student entries illuminate their experiences working or studying abroad.
“Each year, the submissions practically shout about the spectrum of intellectual, emotional and environmental encounters inherent to inhabiting new places,” said Associate Director of Study Abroad Kylie Zahora.
We spoke to representatives from each contest, to provide a behind-the-scenes look at how each of their entries came to fruition.
Seraphina Halpern, AB’24, completed her thesis research in anthropology with field work on Prince Edward Island. She received third prize for her photo which depicted a lobster crew trawling for lost traps before dawn (above).
I went to Prince Edward Island to study the local lobster fishing industry, or, more specifically, how fishermen and their families make sense of the economic risk and occasional illicit activity that characterize their careers. My thesis in anthropology pulled evidence directly from the conversations I had, interactions I watched, and time I spent with the community. I am extremely grateful for the university's support for my research and the Islanders’ willingness to welcome me, without which my project wouldn't have been possible.
To me, this photo shows the grit and the beauty of fishermen’s life. Lost and unattended lobster traps continue trapping lobsters indefinitely, an environmental hazard known as “ghost fishing.” The fishermen's union hires crews to search the region for traps between fishing seasons. I was lucky enough to join this boat for a day on the hunt for ghost fishing traps. If you look closely, you can make out the fishermen's coffee cups and cigarettes, silhouetted by the sunrise as we left the harbor.
Sophia Rodriguez-Bell, AB’24, participated in a direct enrollment program at Trinity College Cambridge. She won first prize for her writing entry titled Fuera del hogar, ya estoy aquí (Away from home, I am already here), which explores how her Chicana identity influenced her daily experience at a British university.
Although I knew before going to the U.K. that I would almost always be the only Chicano or Chicana in the room, I didn’t quite grasp how isolating that would be. For the most part, it was fine. But every now and then, it would hit me. A holiday I celebrate would come and go, and there was no one else who celebrated. I would crave tamales, but the only place I trusted was 2.5 hours each way and double the price I was used to paying.
Being one of a few is normal, but being one of one was jarring. I would mull this over every now and then, but I couldn’t find an effective outlet for it. My writing entry was essentially a thought dump. It’s unpolished, but that’s authentic to how I was thinking at the time.
Below is the opening paragraph to her award-winning essay :
Two UK pints of whole milk is £1.20. A UK pint is 20oz. A pound is $1.25, give or take two pennies for market fluctuation. I do back-of-the-hand math in the Sainsbury’s refrigerated aisle, as the store worker next to me refills the student-ravaged shelves. It is 9:15 p.m. Wednesday. This milk means maybe two weeks worth of hot chocolate. How expensive does this make each cup? Crushed Ibarra tablets sit on my shelf in an empty, 10oz plastic container that used to house Parmesan. I don’t know how much the Ibarra weighs, how much of the 100lbs I stuffed between two suitcases was taken up by hot chocolate powder. Factor in my backpack and me, and I don’t know how much of the exorbitant United airfare here was spent on bringing Mexican hot chocolate to the UK. Whatever it was, it was more expensive than the milk. I get in the self-checkout queue.
Michael Ibrahim, AB’24, joined the Middle Eastern Civilizations program in Cairo. He won first prize for his video entry “Egyptian Adventure, 2024”, which presents a mosaic of Egypt shown through short video snippets of his many adventures.
It really started before I even got to Egypt, when I heard the song that I ended up using on TikTok. It’s a trap remix of the Egyptian song “Batwanes Beek” by Warda, and I thought it would be fun to make a video to the song. In a sense the whole video was really built around the song. I knew I wanted to have the transitions line up with the beat of the music, and there was a part of the song right before the beat drop where I knew I wanted to have a fast montage of short video clips and pictures. I'm always taking videos with my phone, so I had a lot of material to work with. Once I started to take videos, I had some ideas of where I wanted certain clips to go but I only really started editing the video when I got back. I made the whole thing on my phone using the video editing app CapCut.
Egypt is a beautiful country and I really wanted to showcase that in my video. A lot of the clips are from Cairo and Giza, where I tried to show a lot of beautiful mosques, buildings, and streets from Old Cairo as well as the better-known pyramids. Most of the clips, though, were not taken in Cairo but in Alexandria, Luxor, Aswan, and Siwa. I think Egypt’s natural beauty is underrated. Take for example Siwa, which is a palm-filled oasis in the middle of the desert surrounded by sweeping sand dunes, beautiful white rock formations, and pristine natural springs; or Luxor, where you can see the sun set over the mighty Nile, across which you can see lush green fields and the Theban mountains. Overall, I mostly just tried to have fun with it and make a cool video highlighting my experience.
Video by Michael Ibrahim, AB’24
Recommended Stories

At Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, UChicago student unravels…

UChicago students share “life-changing” experiences as Fulbright…
Top Stories
Ai is biased against speakers of african american english, study finds, ralph a. austen, historian of africa and a ‘scholar’s scholar,’ 1937-2024, collapse of bat populations increased infant mortality rate, study finds.
Get more with UChicago News delivered to your inbox.
Related Topics
Latest news, third annual south side science festival set to bring a day of discovery for all ages on oct. 5.

Inside the Lab
Education Lab: Using tutoring to reverse pandemic-era learning loss

AI Insights

Particle physics
Fermilab short-baseline detector detects its first neutrinos

Go 'Inside the Lab' at UChicago
Explore labs through videos and Q&As with UChicago faculty, staff and students

UChicago Medicine
UChicago scientists develop new nanomedicine approach to improve cancer treatment
Around uchicago.

In Memoriam
Artificial Intelligence
NSF awards $20 million to build AI models that predict scientific discoveries a…
New chicago booth course empowers student entrepreneurs to tackle global issues.
Campus News
Project to improve accessibility, sustainability of Main Quadrangles

UChicago President Paul Alivisatos accepts 2024 Kavli Prize in Nanoscience

Obama Foundation
University of Chicago Obama Foundation Scholars Program includes 18 emerging leaders for 2024-25
Meet A UChicagoan
“The trouble comes from using these immortal materials for disposable products.”

Patrick Jagoda to deliver Aims of Education address Sept. 26

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Hook sentence. Background information. Thesis statement. Step 1: Begin with the basics. Describe the initial steps or preparations required. Explain any tools, materials, or ingredients needed. Provide safety precautions if necessary. Step 2: Break Down the Process. Divide the process into clear, sequential steps.
10. Practice, Practice, Practice: The more you practice writing essays, the better you will get at it. Keep practicing and refining your writing skills. Tricks to Improve Your Writing Skills. Improving your writing skills can be a challenging but rewarding process. Here are some tricks to help you become a better writer: 1.
The Purpose of Process Analysis in Writing. The purpose of a process analysis essay is to explain how to do something or how something works. In either case, the formula for a process analysis essay is the same. The process is articulated into clear, definitive steps. Almost everything we do involves following a step-by-step process.
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Process writing involves taking students through a series of steps to produce a text. The same process can and should be use for every type of text students produce - for example, poems, letters, reports and blogs. During process writing, students think about what they are going to write, draft and revise, while they give and receive feedback ...
This article provides a comprehensive, research-based introduction to the major steps, or strategies, that writers work through as they endeavor to communicate with audiences.. Since the 1960s, the writing process has been defined to be a series of steps, stages, or strategies. Most simply, the writing process is conceptualized as four major steps: prewriting, drafting, revising, editing.
Be accountable. 2. How something works. By contrast, this is an informative type of writing that aims to achieve one goal - explain the principle of work behind some process. Unlike the mentioned above type, this process essay type does not encourage a reader to take an action and do something step by step. However, you must make sure that by ...
Avoid transition words that don't add anything to the sentence and unnecessary wordiness that detracts from your argument. Furthermore, use the active voice instead of the passive whenever possible (e.g., "this study found" instead of "it was found by this study"). This will make your essay's tone clear and direct. 3.
Although there are many ways of approaching process writing, it can be broken down into three stages: Pre-writing. The teacher needs to stimulate students' creativity, to get them thinking how to approach a writing topic. In this stage, the most important thing is the flow of ideas, and it is not always necessary that students actually produce ...
prompt on your own. You'd be surprised how often someone comes to the Writing Center to ask for help on a paper before reading the prompt. Once they do read the prompt, they often find that it answers many of their questions. When you read the assignment prompt, you should do the following: • Look for action verbs.
We've got five top tips that may help: Analyse the essay question so you understand the assignment. Write an outline to organize your ideas and prepare your essay. Do research to find evidence and sources to support your ideas. Use the drafting process to refine your essay before submitting it.
Strategies for Essay Writing; Strategies for Essay Writing. Strategies for Essay Writing. Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt; Asking Analytical Questions; Thesis; Introductions; What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common? Anatomy of a Body Paragraph; Transitions;
Writing is a process, not the end product! There's a lot more to a successful assignment than writing out the words. Reading, thinking, planning, and editing are also vital parts of the process. These steps take you through the whole writing process: before, during and after: 1. Read the assignment instructions thoroughly.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Every component of a successful piece of writing should express only one idea. In persuasive writing, your "one idea" is often the argument or belief you are presenting to the reader. Once you ...
This guide aims to describe the overall process of essay writing, however, to develop the individual skills you need, seek advice from the Skills for Academic Success Team (S.A.S.). The S.A.S. team provide workshops, study guides and one-to-one advice for students wishing to develop the skills they need to write good essays.
Step 1: Prewriting. Think and Decide. Make sure you understand your assignment. See Research Papers or Essays. Decide on a topic to write about. See Prewriting Strategies and Narrow your Topic. Consider who will read your work. See Audience and Voice. Brainstorm ideas about the subject and how those ideas can be organized.
A Complete Guide to the Writing Process: 6 Stages of Writing. Every writer works in a different way. Some writers work straight through from beginning to end. Others work in pieces they arrange later, while others work from sentence to sentence. Understanding how and why you write the way you do allows you to treat your writing like the job it ...
2. Organize your ideas: Before you start writing, outline the main points you want to cover in your essay. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas. 3. Use topic sentences: Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph.
2. Define your argument. As you plan and prepare to write the essay, you must consider what your argument is going to be. This means taking an informed position or point of view on the topic presented in the question, then defining and presenting a specific argument. Consider these two argument statements:
The organization of the text is logical and rational. It begins with an introduction to writing, moves on to sentence skills, refining writing technique, the writing process, writing an essay, different rhetorical modes of essay writing, research and citations, presentations, and example essays. Interface rating: 3
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
Below I share an approach to designing writing assignments that came together when I was teaching full time in the SOSC Core as a Harper-Schmidt Fellow. It prepares students to succeed on their SOSC essays by breaking down the writing process into the essential steps that college-level writing demands and giving students time to attend to each one.
Essay Structure. A well-structured essay is important as it enhances readability, ensures logical flow, and effectively communicates the main ideas. When your essay is clearly organised it helps the reader understand and retain the essay's key points.
Writing is not a natural process for the human brain. So when humans write, humans generally struggle. Even I don't find writing easy. But I've come to realise that this struggle can actually be a good thing. Before I explain why, here's a peek at my own all-too-human writing process. Deadline first. Starting is the hardest part.
Our Topic Library is bursting with hundreds of relevant, engaging (and free!) argumentative essay ideas, organized by curriculum subject and age range. How to write an argumentative essay on Kiao Edu. Students can practice writing their argumentative essays on Kialo. First, students should add a thesis statement.
Students discuss creative process behind winning photo, video and writing entries. Students discuss creative process behind winning photo, video and writing entries ... Below is the opening paragraph to her award-winning essay: Two UK pints of whole milk is £1.20. A UK pint is 20oz. A pound is $1.25, give or take two pennies for market ...