Home ➔ Citation Questions ➔ Citing a Website in an Essay — APA and MLA Reference Guide

Citing a Website in an Essay — APA and MLA Reference Guide
Building a strong house starts with a sturdy foundation. Similarly, writing a good essay requires reliable information. Your citations and references prove to your reader that your ideas are based on facts. Searching for solid information can take time, but the Internet makes it easier by offering a wide range of sources.
You’ll find not only digital versions of print materials but also lots of content that’s only online, like blogs or research reports. To use this information in your essay, you need to know how to cite a website in an essay properly. This article will show you how to do that. We’ll focus on how to cite in two common styles, APA and MLA.
Note: Examples below are for the reference list entry only. For in-text citation guidelines, check — How to Cite a Source in an Essay .

Understanding the Essential Elements
When citing websites in your essay, it’s important to grasp the key components of a proper citation. So, what are these essential elements? Let’s break it down.
- Author: The first piece of the puzzle is the author’s name. If available, this typically includes the last name and initials of the author. Sometimes, you might have an organization or a company as the author. Remember, proper citation respects the hard work of the original creator.
- Date: The next element is the publication date. This is the year, and often the month and day, when the content was published or last updated. Dates are crucial as they allow readers to determine the timeliness and relevance of the source.
- Site Name: The name of the website where the content is published.
- Title: Here, we’re talking about the title of the web page or article. Be accurate and copy the article title exactly as it appears on the website. Remember, it’s a direct reflection of the content.
- Source: Finally, where did you find the information? This could be the website’s URL. This helps readers trace back to the original source if they wish.
- Page Number: If the source includes numbered pages, paragraphs, or sections, these details are included, particularly in direct quotations.
- Retrieval Date: For online sources that are likely to change over time (like a Wiki page), APA style recommends adding a retrieval date.
The order and format of these elements may vary between APA and MLA styles, but their inclusion remains a constant across both. Understanding these components is the first step in mastering the art of proper citation. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the specific rules of each style in the following sections.
How to Cite a Website in APA
Citing a website in APA (American Psychological Association) style involves several key steps. Let’s walk through them.
- Example: Johnson, A. B., & Smith, C. D.
- Example: (2023, January 1)
- Example: How to bake bread at home
- Example: Baking 101
- Example: https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
The final website citation would look like this:
Johnson, A. B., & Smith, C. D. (2023, January 1). How to bake bread at home. Baking 101. https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
Remember to adhere to your institution’s guidelines for font and line spacing. Most often, APA citations are double-spaced and use a standard font, like 12-point Times New Roman.
That’s the basics of citing web pages in APA style. But remember, more complex situations will require additional rules. For example, multiple authors, no author, or no date all have their own guidelines.
- Example: How to bake bread at home. (2023, January 1). Baking 101. https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
- Example: Johnson, A. B., & Smith, C. D. (n.d.). How to bake bread at home. Baking 101. https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
- Example: Johnson, A. B., Smith, C. D., & Lee, E. F. (2023, January 1). How to bake bread at home. Baking 101. https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
- Example: American Baking Association. (2023, January 1). How to bake bread at home. Baking 101. https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
- Example: American Baking Association. (2023, January 1). How to bake bread at home. Baking 101. Retrieved June 24, 2023, from https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
These are just common exceptions. Always refer to an APA style guide or manual for the most accurate and up-to-date website citation rules.
How to Cite a Website in MLA
The Modern Language Association (MLA) format for citing websites involves several key steps, with variations for certain exceptions. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Example: Johnson, Amy B., and Charles D. Smith.
- Example: “How to Bake Bread at Home.”
- Example: Baking 101,
- Example: Johnson Publishing,
- Example: 1 Jan. 2023,
- Example: www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home
Johnson, Amy B., and Charles D. Smith. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, Johnson Publishing, 1 Jan. 2023, www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
Remember to follow the formatting guidelines provided by your institution, but generally, MLA citations are double-spaced and use a legible font like Times New Roman.
Now, let’s go over the exceptions:
- “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, Johnson Publishing, 1 Jan. 2023, www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
- Johnson, Amy B., et al. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, Johnson Publishing, 1 Jan. 2023, www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
- American Baking Association. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, Johnson Publishing, 1 Jan. 2023, www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
- Johnson, Amy B., and Charles D. Smith. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home . Accessed 25 June 2023.
Although it’s not required in every website citation, the accessed date can be a helpful piece of information to include, providing additional context about the currency of your information.
Always refer to an MLA guide or publication manual for the most accurate and up-to-date rules for citing a website. This is just a general guide and may not cover all possible scenarios you may encounter.
Bonus: How to Cite a Website in Chicago Style
Citing a website in the Chicago Manual of Style involves certain key steps. Here’s a straightforward guide to assist you, along with examples of common exceptions.
- Example: Amy B. Johnson and Charles D. Smith
- Example: “How to Bake Bread at Home”
- Example: (2023),
- DOI example: https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ajae/aaq063
The final citation would look like this:
Johnson, Amy B., and Charles D. Smith. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, (2023), https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
Now let’s consider the exceptions:
- “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, (2023), https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
- Amy B. Johnson, Charles D. Smith, and Elizabeth F. Lee. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, (2023), https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
- American Baking Association. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, (2023), https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
- Amy B. Johnson and Charles D. Smith. “How to Bake Bread at Home.” Baking 101, Accessed June 26, 2023, https://www.baking101.com/bake-bread-at-home .
Please note that the above examples are for the bibliography. Footnotes or endnotes in Chicago style may differ slightly, so always be sure to check with your instructor or refer to the Chicago Manual of Style.
The list of references
- Citation Guide: How to cite Websites — Dixie State University Library
- APA Quick Citation Guide — PennState University Libraries
- Citing Internet Sources — Yale Poorvu Center of Teaching and Learning
Was this article helpful?

Webpage on a Website References
This page contains reference examples for webpages, including the following:
- Webpage on a news website
- Comment on a webpage on a news website
- Webpage on a website with a government agency group author
- Webpage on a website with an organizational group author
- Webpage on a website with an individual author
- Webpage on a website with a retrieval date
1. Webpage on a news website
Bologna, C. (2019, October 31). Why some people with anxiety love watching horror movies . HuffPost. https://www.huffpost.com/entry/anxiety-love-watching-horror-movies_l_5d277587e4b02a5a5d57b59e
Roberts, N. (2020, June 10). Trayvon Martin’s mother, Sybrina Fulton, qualifies to run for elected office . BET News. https://www.bet.com/news/national/2020/06/10/trayvon-martin-mother-sybrina-fulton-qualifies-for-office-florid.html
Toner, K. (2020, September 24). When Covid-19 hit, he turned his newspaper route into a lifeline for senior citizens . CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2020/06/04/us/coronavirus-newspaper-deliveryman-groceries-senior-citizens-cnnheroes-trnd/index.html
- Parenthetical citations : (Bologna, 2019; Roberts, 2020; Toner, 2020)
- Narrative citations : Bologna (2019), Roberts (2020), and Toner (2020)
- Use this format for articles from news websites. Common examples are BBC News, BET News, Bloomberg, CNN, HuffPost, MSNBC, Reuters, Salon, and Vox. These sites do not have associated daily or weekly newspapers.
- Use the newspaper article category for articles from newspaper websites such as The New York Times or The Washington Post .
- Provide the writer as the author.
- Provide the specific date the story was published.
- Provide the title of the news story in italic sentence case.
- List the name of the news website in the source element of the reference.
- End the reference with the URL.
2. Comment on a webpage on a news website
Owens, L. (2020, October 7). I propose a bicycle race between Biden and Trump [Comment on the webpage Here’s what voters make of President Trump’s COVID-19 diagnosis ]. HuffPost. https://www.spot.im/s/00QeiyApEIFa
- Parenthetical citation : (Owens, 2020)
- Narrative citation : Owens (2020)
- Credit the person who left the comment as the author using the format that appears with the comment (i.e., a real name and/or a username). The example shows a real name.
- Provide the specific date the comment was published.
- Provide the comment title or up to the first 20 words of the comment in standard font. Then in square brackets write “Comment on the webpage” and the title of the webpage on which the comment appeared in sentence case and italics.
- Provide the name of the news website in the source element of the reference.
- Link to the comment itself if possible. Otherwise, link to the webpage on which the comment appears. Either a full URL or a short URL is acceptable.
3. Webpage on a website with a government agency group author
National Institute of Mental Health. (2018, July). Anxiety disorders . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders/index.shtml
- Parenthetical citation : (National Institute of Mental Health, 2018)
- Narrative citation : National Institute of Mental Health (2018)
- For a page on a government website without individual authors, use the specific agency responsible for the webpage as the author.
- The names of parent agencies not present in the author element appear in the source element (in the example, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health). This creates concise in-text citations and complete reference list entries.
- Provide as specific a date as possible for the webpage.
- Some online works note when the work was last updated. If this date is clearly attributable to the specific content you are citing rather than the overall website, use the updated date in the reference.
- Do not include a date of last review in a reference because content that has been reviewed has not necessarily been changed. If a date of last review is noted on a work, ignore it for the purposes of the reference.
- Italicize the title of the webpage.
4. Webpage on a website with an organizational group author
World Health Organization. (2018, May 24) . The top 10 causes of death . https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death
- Parenthetical citation : (World Health Organization, 2018)
- Narrative citation : World Health Organization (2018)
- For a page from an organization’s website without individual authors, use the name of the organization as the author.
- Because the author of the webpage and the site name are the same, omit the site name from the source element to avoid repetition.
5. Webpage on a website with an individual author
Horovitz, B. (2021, October 19). Are you ready to move your aging parent into your home? AARP. https://www.aarp.org/caregiving/home-care/info-2021/caregiving-questions.html
Schaeffer, K. (2021, October 1). What we know about online learning and the homework gap amid the pandemic. Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2021/10/01/what-we-know-about-online-learning-and-the-homework-gap-amid-the-pandemic/
- Parenthetical citations : (Horovitz, 2021; Schaeffer, 2021)
- Narrative citations : Horovitz (2021) and Schaeffer (2021)
- When individual author(s) are credited on the webpage, list them as the author in the reference.
- Provide the site name in the source element of the reference.
6. Webpage on a website with a retrieval date
U.S. Census Bureau. (n.d.). U.S. and world population clock . U.S. Department of Commerce. Retrieved January 9, 2020, from https://www.census.gov/popclock/
- Parenthetical citation : (U.S. Census Bureau, n.d.)
- Narrative citation : U.S. Census Bureau (n.d.)
- When contents of a page are designed to change over time but are not archived, include a retrieval date in the reference.
Webpage references are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 10.16 and the Concise Guide Section 10.14
- Bibliography Answers
How to cite a website in APA, MLA, or Harvard style

There are many different ways to cite a website, depending on which citation style you need to format it in.
The easy way to cite a website in any citation style
Use our citation generator below to automatically cite a website in any style, including APA, MLA 7 and 8, and Harvard. Just select the style you need, copy the URL into the search box, and press search. We’ll do the rest.
The manual way to cite a website
To cite a website by hand just follow the instructions below. For the 3 most popular styles–APA, MLA 8, and Harvard–this is as follows:
In APA style
You need to locate these details for the website: page or article author, page or article title, website name, published date, access date, page URL (web address) .
- The author can typically be found on the page, but if there isn’t one listed you can use the website name in its place.
- The page title can be found near the top of the page, and you can also find it by hovering your mouse over the browser tab.
- The website name can usually be found in the web address or by looking for a logo or similar at the very top of the page.
- There often isn’t a publish date , but if there is it’ll be very close to the page title.
- The access date is the date you took information from the article (usually today).
- The page URL can be copied straight from the address bar of your browser and will start with either http:// or https://.
Then use this template, replacing the colored placeholders with the information you found on the page:
Author last name , author first name initial . ( published year , published month and day ). Page title . Retrieved accessed month and day , accessed year , from article URL .
The final formatted citation should look like this:
Ingle, S. (2018, February 11). Winter Olympics was hit by cyber-attack, officials confirm. Retrieved July 24, 2018, from https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2018/feb/11/winter-olympics-was-hit-by-cyber-attack-officials-confirm.
For a more comprehensive guide, including what to do when you can’t find certain details, have a look at our more in-depth guide to citing a website in APA format .
In MLA 8 style
Here are the specific details you need to find on the page: page or article author, page or article title, website name, published date, access date, page URL (web address) .
Then use this template:
Author last name , author first name . “ Page title .” website name , published date day, month, year , page URL . Accessed accessed date day, month, year .
Ingle, Sean. “Winter Olympics Was Hit by Cyber-Attack, Officials Confirm.” The Guardian , 11 Feb. 2018, https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2018/feb/11/winter-olympics-was-hit-by-cyber-attack-officials-confirm. Accessed 13 July 2018.
For a more comprehensive guide, including what to do when you can’t find certain details, have a look at our more in-depth guide to citing a website in MLA 8 format .
In Harvard style
First, find these details for the website: page or article author, page or article title, website name, published date, access date, page URL (web address) .
Author last name , author firstname initial ( published date year ). Page title . [online] website name . Available at: page URL [Accessed accessed date day, month, year ].
Ingle, S. (2018). Winter Olympics was hit by cyber-attack, officials confirm . [online] The Guardian. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2018/feb/11/winter-olympics-was-hit-by-cyber-attack-officials-confirm [Accessed 13 Jul. 2018].
Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

Thursday, February 23: The Clark Library is closed today.
APA Style (7th Edition) Citation Guide: Websites
- Introduction
- Journal Articles
- Magazine/Newspaper Articles
- Books & Ebooks
- Government & Legal Documents
- Biblical Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Films/Videos/TV Shows
- How to Cite: Other
- Additional Help
Table of Contents
Entire Website - No Separate Pages or Sections
Page or Section from a Website
Note: All citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent in a Reference List.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
This Microsoft support page contains instructions about how to format a hanging indent in a paper.
It can sometimes be difficult to find out who the author of a website is. Remember that an author can be a corporation or group, not only a specific person. Author information can sometimes be found under an "About" section on a website.
If there is no known author, start the citation with the title of the website instead.
The best date to use for a website is the date that the content was last updated. Otherwise look for a copyright or original publication date. Unfortunately this information may not be provided or may be hard to find. Often date information is put on the bottom of the pages of a website.
If you do not know the complete date, put as much information as you can find. For example you may have a year but no month or day.
If an original publication date and a last updated date are provided, use the last updated date. If the more current date is "last reviewed" instead of "last updated," use the original publication date (since the review may not have changed the content).
If there is no date provided, put the letters (n.d.) in round brackets where you'd normally put the date.
Titles should be italicized when the document stands alone (e.g. books, reports, websites, etc.), but not when it is part of a greater whole (e.g. chapters, articles, webpages, etc.).
Website Name
Provide website names in title case without italics after titles of work. Include a period after the website name, followed by the URL. When the author of the work is the same as the website name, omit the site name from the reference.
Retrieval Date
If the content of a website is likely to change over time (e.g. Wikis), you must provide the date you last visited the website.
If a URL is too long to fit onto one line, try to break it at a slash (/).
Entire Website
Note: If you are quoting or paraphrasing part of a website, you should create a reference for a Page or Section. If you mention a website in general, do not create a reference list entry or an in-text citation. Instead, include the name of the website in the text and provide the URL in parentheses.
The Department of Justice has a site called ReportCrime.gov (https://www.reportcrime.gov/) to help people identify and report crimes in their area.
Note : If you cite multiple webpages from a website, create a reference for each. Include the date you retrieved the information if the content is likely to change over time.
Created by a Corporate or Group Author
Corporation/Group/Organization's Name. (Year website was last updated/published, Month Day if given). Title of page: Subtitle (if any). Website Name. URL
Example in which the content is unlikely to change over time:
American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. (2019, November 21). Justice served: Case closed for over 40 dogfighting victims . https://www.aspca.org/news/justice-served-case-closed-over-40-dogfighting-victims
Example in which the content is likely to change over time:
Adidas. (2020). Sustainability . Retrieved January 23, 2020, from https://www.adidas.com/us/sustainability
Note: When the author and site name are the same, omit the site name in the reference.
In-Text Paraphrase:
(Corporation/Group's Name, Year)
Example: (Adidas, 2020)
In-Text Quote:
(Corporation/Group's Name, year, Section Name section, para. Paragraph Number if more than one paragraph in section)
Example: (Adidas, 2020, Sustainability section, para. 1)
Note: When there are no visible page numbers or paragraph numbers, you may cite the section heading and the number of the paragraph in that section to identify where your quote came from.
Abbreviating Corporation/Group Author Name in In-Text citations:
Author names for corporations/groups can often be abbreviated. The first time you refer to the author, provide the full name, along with the abbreviation.
If the group name appears in the text of your paper, include the abbreviation in the in-text parenthetical citation:
Example: The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA, 2019) assisted in the rescue of 40 dogs.
If the group name first appears within a parenthetical citation, include the full group name as well as the abbreviation in square brackets:
Example: Forty dogs were rescued in Bendena, Kansas (American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals [ASPCA], 2019).
Provide the full group name (without an abbreviation) in the reference list entry:
Created by an Individual Author
Author's Last Name, First Initial. Second Initial if Given. (Year website was last updated/published, Month Day if given). Title of page: Subtitle (if any). Website Name. URL
Price, D. (2018, March 23). Laziness does not exist . Medium. https://humanparts.medium.com/laziness-does-not-exist-3af27e312d01
Shillam, S. (2018). Message from the Dean . University of Portland. Retrieved October 1, 2018, from https://nursing.up.edu/about/index.html
(Author Last Name, Year)
Example: (Shillam, 2018)
(Author Last Name, Year, Section Name section, para. Paragraph Number if more than one paragraph in section)
Example: (Shillam, 2018, Message from the dean section, para. 2)
Created by an Unknown Author
Title of page: Subtitle (if any). (Year website was last updated/published, Month Day if given). Website Name. URL
Example in which the content is unlikely to change over time (because the restaurant has closed) :
Jarra's Ethiopian Restaurant [Reviews]. (2012, November 9). Yelp. https://www.yelp.com/biz/jarras-ethiopian-restaurant-portland
Powell's City of Books [Reviews]. (2020, February 25). Yelp. Retrieved February 28, 2020, from https://www.yelp.com/biz/powells-city-of-books-portland-4
("Title," Year)
Example: ("Powell's City of Books," 2020)
("Title," Year, Section Name section, para. Paragraph Number if more than one paragraph in section)
Example: ("Powell's City of Books," 2020, Review Highlights)
Note: When there are no visible page numbers or paragraph numbers, you may cite the section heading and the number of the paragraph in that section to identify where your quote came from. In this example, there is only one paragraph under the specific heading, so no paragraph number is needed.
- << Previous: Government & Legal Documents
- Next: Biblical Sources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 25, 2024 9:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.up.edu/apa
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Cite a Website
Last Updated: February 9, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Michelle Golden, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Michelle Golden is an English teacher in Athens, Georgia. She received her MA in Language Arts Teacher Education in 2008 and received her PhD in English from Georgia State University in 2015. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,566,693 times.
If you're writing a research paper, you'll likely do quite a bit of research online. If you have websites that you want to use as sources for your paper, an entry for the website must appear in the reference list (also called the bibliography or Works Cited) at the end of your paper. You'll also include a citation in-text at the end of any sentence in which you've paraphrased or quoted information that appeared on that website. While the information you need to provide is generally the same across all methods, the way you format that information may vary depending on whether you're using the Modern Language Association (MLA), American Psychological Association (APA), or Chicago style of citation.
Sample Citation Templates

- Example: Claymore, Crystal.
- If no individual author is listed, but the website is produced by a government agency, organization, or business, use that name as the author. For example, if you're using a CDC web page as a source, you would list the author as "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention."
Tip: For your entire Works Cited entry, if an element doesn't exist or isn't provided, simply skip that part of the citation and move on to the next part.

- Example: Claymore, Crystal. "Best-Kept Secrets for Amazing Cupcake Frosting."

- Example: Claymore, Crystal. "Best-Kept Secrets for Amazing Cupcake Frosting." Crystal's Cupcakes , 24 Sept. 2018,

- Example: Claymore, Crystal. "Best-Kept Secrets for Amazing Cupcake Frosting." Crystal's Cupcakes , 24 Sept. 2018, www.crystalscupcakes.com/amazing-frosting.

- Example: Claymore, Crystal. "Best-Kept Secrets for Amazing Cupcake Frosting." Crystal's Cupcakes , www.crystalscupcakes.com/amazing-frosting. Accessed 14 Feb. 2019.
MLA Works Cited Format:
Author Last Name, First Name. "Title of Web Page in Title Case." Name of Website , Day Month Year of publication, URL. Accessed Day Month Year.

- For example, you might write: "The best cupcake frosting techniques are often the least intuitive (Claymore)."
- If you include the author's name in your text, there's no need for a parenthetical citation. For example, you might write: "Award-winning baker Crystal Claymore wasn't afraid to give away all her secrets, sharing her favorite frosting techniques on her website."

- Example: Canadian Cancer Society.

- Example: Canadian Cancer Society. (2017).
- If you're citing several pages from the same website that were published in the same year, add a lower-case letter to the end of the year so you can differentiate them in your in-text citations. For example, you might have "2017a" and "2017b."

- Example: Canadian Cancer Society. (2017). Cancer research.
- If the content you're citing is a stand-alone document, the title should be italicized. This will usually be the case if you're citing a PDF document that appears on a website. If you're not sure, use your best judgment in deciding whether to italicize it or not.

- Example: Canadian Cancer Society. (2017). Cancer research. Retrieved from http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-101/cancer-research/?region=on
APA Reference List Format:
Author Last Name, A. A. (Year). Title of web page in sentence case. Retrieved from URL

- For example, you might write: "Clinical trials are used to test new cancer treatments (Canadian Cancer Society, 2017)."
- If you include the author's name in your text, place the year in parentheses immediately after the author's name. For example, you might write: "The Canadian Cancer Society (2017) noted that Canada is a global leader in clinical trials of cancer treatments."

- Example: UN Women.

- Example: UN Women. "Commission on the Status of Women."

- Example: UN Women. "Commission on the Status of Women." UN Women .

- Example: UN Women. "Commission on the Status of Women." UN Women . Accessed February 14, 2019.

- Example: UN Women. "Commission on the Status of Women." UN Women . Accessed February 14, 2019. http://www.unwomen.org/en/csw.
Chicago Bibliography Format:
Author Last Name, First Name. "Title of Web Page in Title Case." Name of Website or Publishing Organization . Accessed Month Day, Year. URL.

- Example: UN Women, "Commission on the Status of Women," UN Women , accessed February 14, 2019, http://www.unwomen.org/en/csw.
Community Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://libguides.up.edu/mla/common/websites
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing/7Webpages
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/webpage-website-references
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/web_sources.html
- ↑ http://libanswers.snhu.edu/faq/48009
About This Article

To cite a website in text using MLA formatting, include the author's last name in parentheses at the end of the sentence you're using the source in. If there is no author, include the title of the web page instead. If you're using APA formatting, include the author's last name followed by a comma and the year of publication in parentheses at the end of the sentence. If you don't know the author's name, use the name of the web page instead. For more tips from our English co-author, like how to cite a website in Chicago style, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 28, 2016
Did this article help you?
Oct 2, 2017
Oct 5, 2018
Abraham Mathews
Nov 28, 2018
Apr 19, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / How to Cite Sources
How to Cite Sources
Here is a complete list for how to cite sources. Most of these guides present citation guidance and examples in MLA, APA, and Chicago.
If you’re looking for general information on MLA or APA citations , the EasyBib Writing Center was designed for you! It has articles on what’s needed in an MLA in-text citation , how to format an APA paper, what an MLA annotated bibliography is, making an MLA works cited page, and much more!
MLA Format Citation Examples
The Modern Language Association created the MLA Style, currently in its 9th edition, to provide researchers with guidelines for writing and documenting scholarly borrowings. Most often used in the humanities, MLA style (or MLA format ) has been adopted and used by numerous other disciplines, in multiple parts of the world.
MLA provides standard rules to follow so that most research papers are formatted in a similar manner. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the information. The MLA in-text citation guidelines, MLA works cited standards, and MLA annotated bibliography instructions provide scholars with the information they need to properly cite sources in their research papers, articles, and assignments.
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Documentary
- Encyclopedia
- Google Images
- Kindle Book
- Memorial Inscription
- Museum Exhibit
- Painting or Artwork
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Sheet Music
- Thesis or Dissertation
- YouTube Video
APA Format Citation Examples
The American Psychological Association created the APA citation style in 1929 as a way to help psychologists, anthropologists, and even business managers establish one common way to cite sources and present content.
APA is used when citing sources for academic articles such as journals, and is intended to help readers better comprehend content, and to avoid language bias wherever possible. The APA style (or APA format ) is now in its 7th edition, and provides citation style guides for virtually any type of resource.
Chicago Style Citation Examples
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes ) or at the end of a paper (endnotes).
The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but the Turabian style is geared towards student published papers such as theses and dissertations, while the Chicago style provides guidelines for all types of publications. This is why you’ll commonly see Chicago style and Turabian style presented together. The Chicago Manual of Style is currently in its 17th edition, and Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations is in its 8th edition.
Citing Specific Sources or Events
- Declaration of Independence
- Gettysburg Address
- Martin Luther King Jr. Speech
- President Obama’s Farewell Address
- President Trump’s Inauguration Speech
- White House Press Briefing
Additional FAQs
- Citing Archived Contributors
- Citing a Blog
- Citing a Book Chapter
- Citing a Source in a Foreign Language
- Citing an Image
- Citing a Song
- Citing Special Contributors
- Citing a Translated Article
- Citing a Tweet
6 Interesting Citation Facts
The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there’s more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations , and other formatting specifications. Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
Ever wonder what sets all the different styles apart, or how they came to be in the first place? Read on for some interesting facts about citations!
1. There are Over 7,000 Different Citation Styles
You may be familiar with MLA and APA citation styles, but there are actually thousands of citation styles used for all different academic disciplines all across the world. Deciding which one to use can be difficult, so be sure to ask you instructor which one you should be using for your next paper.
2. Some Citation Styles are Named After People
While a majority of citation styles are named for the specific organizations that publish them (i.e. APA is published by the American Psychological Association, and MLA format is named for the Modern Language Association), some are actually named after individuals. The most well-known example of this is perhaps Turabian style, named for Kate L. Turabian, an American educator and writer. She developed this style as a condensed version of the Chicago Manual of Style in order to present a more concise set of rules to students.
3. There are Some Really Specific and Uniquely Named Citation Styles
How specific can citation styles get? The answer is very. For example, the “Flavour and Fragrance Journal” style is based on a bimonthly, peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1985 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original research articles, reviews and special reports on all aspects of flavor and fragrance. Another example is “Nordic Pulp and Paper Research,” a style used by an international scientific magazine covering science and technology for the areas of wood or bio-mass constituents.
4. More citations were created on EasyBib.com in the first quarter of 2018 than there are people in California.
The US Census Bureau estimates that approximately 39.5 million people live in the state of California. Meanwhile, about 43 million citations were made on EasyBib from January to March of 2018. That’s a lot of citations.
5. “Citations” is a Word With a Long History
The word “citations” can be traced back literally thousands of years to the Latin word “citare” meaning “to summon, urge, call; put in sudden motion, call forward; rouse, excite.” The word then took on its more modern meaning and relevance to writing papers in the 1600s, where it became known as the “act of citing or quoting a passage from a book, etc.”
6. Citation Styles are Always Changing
The concept of citations always stays the same. It is a means of preventing plagiarism and demonstrating where you relied on outside sources. The specific style rules, however, can and do change regularly. For example, in 2018 alone, 46 new citation styles were introduced , and 106 updates were made to exiting styles. At EasyBib, we are always on the lookout for ways to improve our styles and opportunities to add new ones to our list.
Why Citations Matter
Here are the ways accurate citations can help your students achieve academic success, and how you can answer the dreaded question, “why should I cite my sources?”
They Give Credit to the Right People
Citing their sources makes sure that the reader can differentiate the student’s original thoughts from those of other researchers. Not only does this make sure that the sources they use receive proper credit for their work, it ensures that the student receives deserved recognition for their unique contributions to the topic. Whether the student is citing in MLA format , APA format , or any other style, citations serve as a natural way to place a student’s work in the broader context of the subject area, and serve as an easy way to gauge their commitment to the project.
They Provide Hard Evidence of Ideas
Having many citations from a wide variety of sources related to their idea means that the student is working on a well-researched and respected subject. Citing sources that back up their claim creates room for fact-checking and further research . And, if they can cite a few sources that have the converse opinion or idea, and then demonstrate to the reader why they believe that that viewpoint is wrong by again citing credible sources, the student is well on their way to winning over the reader and cementing their point of view.
They Promote Originality and Prevent Plagiarism
The point of research projects is not to regurgitate information that can already be found elsewhere. We have Google for that! What the student’s project should aim to do is promote an original idea or a spin on an existing idea, and use reliable sources to promote that idea. Copying or directly referencing a source without proper citation can lead to not only a poor grade, but accusations of academic dishonesty. By citing their sources regularly and accurately, students can easily avoid the trap of plagiarism , and promote further research on their topic.
They Create Better Researchers
By researching sources to back up and promote their ideas, students are becoming better researchers without even knowing it! Each time a new source is read or researched, the student is becoming more engaged with the project and is developing a deeper understanding of the subject area. Proper citations demonstrate a breadth of the student’s reading and dedication to the project itself. By creating citations, students are compelled to make connections between their sources and discern research patterns. Each time they complete this process, they are helping themselves become better researchers and writers overall.
When is the Right Time to Start Making Citations?
Make in-text/parenthetical citations as you need them.
As you are writing your paper, be sure to include references within the text that correspond with references in a works cited or bibliography. These are usually called in-text citations or parenthetical citations in MLA and APA formats. The most effective time to complete these is directly after you have made your reference to another source. For instance, after writing the line from Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times…,” you would include a citation like this (depending on your chosen citation style):
(Dickens 11).
This signals to the reader that you have referenced an outside source. What’s great about this system is that the in-text citations serve as a natural list for all of the citations you have made in your paper, which will make completing the works cited page a whole lot easier. After you are done writing, all that will be left for you to do is scan your paper for these references, and then build a works cited page that includes a citation for each one.
Need help creating an MLA works cited page ? Try the MLA format generator on EasyBib.com! We also have a guide on how to format an APA reference page .
2. Understand the General Formatting Rules of Your Citation Style Before You Start Writing
While reading up on paper formatting may not sound exciting, being aware of how your paper should look early on in the paper writing process is super important. Citation styles can dictate more than just the appearance of the citations themselves, but rather can impact the layout of your paper as a whole, with specific guidelines concerning margin width, title treatment, and even font size and spacing. Knowing how to organize your paper before you start writing will ensure that you do not receive a low grade for something as trivial as forgetting a hanging indent.
Don’t know where to start? Here’s a formatting guide on APA format .
3. Double-check All of Your Outside Sources for Relevance and Trustworthiness First
Collecting outside sources that support your research and specific topic is a critical step in writing an effective paper. But before you run to the library and grab the first 20 books you can lay your hands on, keep in mind that selecting a source to include in your paper should not be taken lightly. Before you proceed with using it to backup your ideas, run a quick Internet search for it and see if other scholars in your field have written about it as well. Check to see if there are book reviews about it or peer accolades. If you spot something that seems off to you, you may want to consider leaving it out of your work. Doing this before your start making citations can save you a ton of time in the long run.
Finished with your paper? It may be time to run it through a grammar and plagiarism checker , like the one offered by EasyBib Plus. If you’re just looking to brush up on the basics, our grammar guides are ready anytime you are.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
A Quick Guide to Referencing | Cite Your Sources Correctly
Referencing means acknowledging the sources you have used in your writing. Including references helps you support your claims and ensures that you avoid plagiarism .
There are many referencing styles, but they usually consist of two things:
- A citation wherever you refer to a source in your text.
- A reference list or bibliography at the end listing full details of all your sources.
The most common method of referencing in UK universities is Harvard style , which uses author-date citations in the text. Our free Harvard Reference Generator automatically creates accurate references in this style.
| (Smith, 2013) | |
| Smith, J. (2013) . 2nd ed. London: Penguin. |
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Referencing styles, citing your sources with in-text citations, creating your reference list or bibliography, harvard referencing examples, frequently asked questions about referencing.
Each referencing style has different rules for presenting source information. For in-text citations, some use footnotes or endnotes , while others include the author’s surname and date of publication in brackets in the text.
The reference list or bibliography is presented differently in each style, with different rules for things like capitalisation, italics, and quotation marks in references.
Your university will usually tell you which referencing style to use; they may even have their own unique style. Always follow your university’s guidelines, and ask your tutor if you are unsure. The most common styles are summarised below.
Harvard referencing, the most commonly used style at UK universities, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical bibliography or reference list at the end.
| In-text citation | Sources should always be cited properly (Pears and Shields, 2019). |
|---|---|
| Reference list | Pears, R. and Shields, G. (2019) . 11th edn. London: MacMillan. |
Harvard Referencing Guide
Vancouver referencing, used in biomedicine and other sciences, uses reference numbers in the text corresponding to a numbered reference list at the end.
| In-text citation | Sources should always be cited properly (1). |
|---|---|
| Reference list | 1. Pears R, Shields G. Cite them right: The essential referencing guide. 11th ed. London: MacMillan; 2019. |
Vancouver Referencing Guide
APA referencing, used in the social and behavioural sciences, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical reference list at the end.
| In-text citation | Sources should always be cited properly (Pears & Shields, 2019). |
|---|---|
| Reference list | Pears, R., & Shields, G. (2019). (11th ed.). London, England: MacMillan. |
APA Referencing Guide APA Reference Generator
MHRA referencing, used in the humanities, uses footnotes in the text with source information, in addition to an alphabetised bibliography at the end.
| In-text citation | Sources should always be cited properly. |
|---|---|
| Footnote | 1. Richard Pears and Graham Shields, , 11th edn (London: MacMillan, 2019). |
| Bibliography | Pears, Richard and Graham Shields, , 11th edn (London: MacMillan, 2019). |
MHRA Referencing Guide
OSCOLA referencing, used in law, uses footnotes in the text with source information, and an alphabetical bibliography at the end in longer texts.
| In-text citation | Sources should always be cited properly. |
|---|---|
| Footnote | 1. Richard Pears and Graham Shields, (11th edn, MacMillan 2019). |
| Bibliography | Pears R and Shields G, (11th edn, MacMillan 2019). |
OSCOLA Referencing Guide
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
In-text citations should be used whenever you quote, paraphrase, or refer to information from a source (e.g. a book, article, image, website, or video).
Quoting and paraphrasing
Quoting is when you directly copy some text from a source and enclose it in quotation marks to indicate that it is not your own writing.
Paraphrasing is when you rephrase the original source into your own words. In this case, you don’t use quotation marks, but you still need to include a citation.
In most referencing styles, page numbers are included when you’re quoting or paraphrasing a particular passage. If you are referring to the text as a whole, no page number is needed.
In-text citations
In-text citations are quick references to your sources. In Harvard referencing, you use the author’s surname and the date of publication in brackets.
Up to three authors are included in a Harvard in-text citation. If the source has more than three authors, include the first author followed by ‘ et al. ‘
| Number of authors | Harvard in-text citation example |
|---|---|
| 1 author | (Jones, 2017) |
| 2 authors | (Jones and Singh, 2017) |
| 3 authors | (Jones, Singh and Smith, 2017) |
| 4+ authors | (Jones et al., 2017) |
The point of these citations is to direct your reader to the alphabetised reference list, where you give full information about each source. For example, to find the source cited above, the reader would look under ‘J’ in your reference list to find the title and publication details of the source.
Placement of in-text citations
In-text citations should be placed directly after the quotation or information they refer to, usually before a comma or full stop. If a sentence is supported by multiple sources, you can combine them in one set of brackets, separated by a semicolon.
If you mention the author’s name in the text already, you don’t include it in the citation, and you can place the citation immediately after the name.
- Another researcher warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’ (Singh, 2018, p. 13) .
- Previous research has frequently illustrated the pitfalls of this method (Singh, 2018; Jones, 2016) .
- Singh (2018, p. 13) warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’.
The terms ‘bibliography’ and ‘reference list’ are sometimes used interchangeably. Both refer to a list that contains full information on all the sources cited in your text. Sometimes ‘bibliography’ is used to mean a more extensive list, also containing sources that you consulted but did not cite in the text.
A reference list or bibliography is usually mandatory, since in-text citations typically don’t provide full source information. For styles that already include full source information in footnotes (e.g. OSCOLA and Chicago Style ), the bibliography is optional, although your university may still require you to include one.
Format of the reference list
Reference lists are usually alphabetised by authors’ last names. Each entry in the list appears on a new line, and a hanging indent is applied if an entry extends onto multiple lines.

Different source information is included for different source types. Each style provides detailed guidelines for exactly what information should be included and how it should be presented.
Below are some examples of reference list entries for common source types in Harvard style.
- Chapter of a book
- Journal article
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . City: Publisher. |
| Example | Saunders, G. (2017) . New York: Random House. |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Chapter title’, in Editor name (ed(s).) . City: Publisher, page range. |
| Example | Berman, R. A. (2004) ‘Modernism and the bildungsroman: Thomas Mann’s Magic Mountain’, in Bartram, G. (ed.) . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 77–92. |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), page range. |
| Example | Adair, W. (1989) ‘ and : Hemingway’s debt to Thomas Mann’, , 35(4), pp. 429–444. |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Google (2019) . Available at: https://policies.google.com/terms?hl=en-US (Accessed: 2 April 2020). |
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Your university should tell you which referencing style to follow. If you’re unsure, check with a supervisor. Commonly used styles include:
- Harvard referencing , the most commonly used style in UK universities.
- MHRA , used in humanities subjects.
- APA , used in the social sciences.
- Vancouver , used in biomedicine.
- OSCOLA , used in law.
Your university may have its own referencing style guide.
If you are allowed to choose which style to follow, we recommend Harvard referencing, as it is a straightforward and widely used style.
References should be included in your text whenever you use words, ideas, or information from a source. A source can be anything from a book or journal article to a website or YouTube video.
If you don’t acknowledge your sources, you can get in trouble for plagiarism .
To avoid plagiarism , always include a reference when you use words, ideas or information from a source. This shows that you are not trying to pass the work of others off as your own.
You must also properly quote or paraphrase the source. If you’re not sure whether you’ve done this correctly, you can use the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker to find and correct any mistakes.
Harvard referencing uses an author–date system. Sources are cited by the author’s last name and the publication year in brackets. Each Harvard in-text citation corresponds to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end of the paper.
Vancouver referencing uses a numerical system. Sources are cited by a number in parentheses or superscript. Each number corresponds to a full reference at the end of the paper.
| Harvard style | Vancouver style | |
|---|---|---|
| In-text citation | Each referencing style has different rules (Pears and Shields, 2019). | Each referencing style has different rules (1). |
| Reference list | Pears, R. and Shields, G. (2019). . 11th edn. London: MacMillan. | 1. Pears R, Shields G. Cite them right: The essential referencing guide. 11th ed. London: MacMillan; 2019. |
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- A Quick Guide to Harvard Referencing | Citation Examples
- APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
How to Avoid Plagiarism | Tips on Citing Sources
More interesting articles.
- A Quick Guide to OSCOLA Referencing | Rules & Examples
- Harvard In-Text Citation | A Complete Guide & Examples
- Harvard Referencing for Journal Articles | Templates & Examples
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
- MHRA Referencing | A Quick Guide & Citation Examples
- Reference a Website in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Referencing Books in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Vancouver Referencing | A Quick Guide & Reference Examples
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual . Both books provide extensive examples, so it's a good idea to consult them if you want to become even more familiar with MLA guidelines or if you have a particular reference question.
Basic in-text citation rules
In MLA Style, referring to the works of others in your text is done using parenthetical citations . This method involves providing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way to do this is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as the examples below will illustrate, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- The source information required in a parenthetical citation depends (1) upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD) and (2) upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page.
In-text citations: Author-page style
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
In-text citations for print sources by a corporate author
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
In-text citations for sources with non-standard labeling systems
If a source uses a labeling or numbering system other than page numbers, such as a script or poetry, precede the citation with said label. When citing a poem, for instance, the parenthetical would begin with the word “line”, and then the line number or range. For example, the examination of William Blake’s poem “The Tyger” would be cited as such:
The speaker makes an ardent call for the exploration of the connection between the violence of nature and the divinity of creation. “In what distant deeps or skies. / Burnt the fire of thine eyes," they ask in reference to the tiger as they attempt to reconcile their intimidation with their relationship to creationism (lines 5-6).
Longer labels, such as chapters (ch.) and scenes (sc.), should be abbreviated.
In-text citations for print sources with no known author
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article) or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
"The Impact of Global Warming in North America." Global Warming: Early Signs . 1999. www.climatehotmap.org/. Accessed 23 Mar. 2009.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Parenthetical citations and Works Cited pages, used in conjunction, allow readers to know which sources you consulted in writing your essay, so that they can either verify your interpretation of the sources or use them in their own scholarly work.
Author-page citation for classic and literary works with multiple editions
Page numbers are always required, but additional citation information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto . In such cases, give the page number of your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:
Author-page citation for works in an anthology, periodical, or collection
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
See also our page on documenting periodicals in the Works Cited .
Citing authors with same last names
Sometimes more information is necessary to identify the source from which a quotation is taken. For instance, if two or more authors have the same last name, provide both authors' first initials (or even the authors' full name if different authors share initials) in your citation. For example:
Citing a work by multiple authors
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
Corresponding Works Cited entry:
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR, doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al.
Franck, Caroline, et al. “Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic.” American Journal of Preventative Medicine , vol. 45, no. 3, Sept. 2013, pp. 327-333.
Citing multiple works by the same author
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author :
Citing two books by the same author :
Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
Citing multivolume works
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
Citing the Bible
In your first parenthetical citation, you want to make clear which Bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
If future references employ the same edition of the Bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
Citing indirect sources
Sometimes you may have to use an indirect source. An indirect source is a source cited within another source. For such indirect quotations, use "qtd. in" to indicate the source you actually consulted. For example:
Note that, in most cases, a responsible researcher will attempt to find the original source, rather than citing an indirect source.
Citing transcripts, plays, or screenplays
Sources that take the form of a dialogue involving two or more participants have special guidelines for their quotation and citation. Each line of dialogue should begin with the speaker's name written in all capitals and indented half an inch. A period follows the name (e.g., JAMES.) . After the period, write the dialogue. Each successive line after the first should receive an additional indentation. When another person begins speaking, start a new line with that person's name indented only half an inch. Repeat this pattern each time the speaker changes. You can include stage directions in the quote if they appear in the original source.
Conclude with a parenthetical that explains where to find the excerpt in the source. Usually, the author and title of the source can be given in a signal phrase before quoting the excerpt, so the concluding parenthetical will often just contain location information like page numbers or act/scene indicators.
Here is an example from O'Neill's The Iceman Cometh.
WILLIE. (Pleadingly) Give me a drink, Rocky. Harry said it was all right. God, I need a drink.
ROCKY. Den grab it. It's right under your nose.
WILLIE. (Avidly) Thanks. (He takes the bottle with both twitching hands and tilts it to his lips and gulps down the whiskey in big swallows.) (1.1)
Citing non-print or sources from the Internet
With more and more scholarly work published on the Internet, you may have to cite sources you found in digital environments. While many sources on the Internet should not be used for scholarly work (reference the OWL's Evaluating Sources of Information resource), some Web sources are perfectly acceptable for research. When creating in-text citations for electronic, film, or Internet sources, remember that your citation must reference the source on your Works Cited page.
Sometimes writers are confused with how to craft parenthetical citations for electronic sources because of the absence of page numbers. However, these sorts of entries often do not require a page number in the parenthetical citation. For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
Miscellaneous non-print sources
Two types of non-print sources you may encounter are films and lectures/presentations:
In the two examples above “Herzog” (a film’s director) and “Yates” (a presentor) lead the reader to the first item in each citation’s respective entry on the Works Cited page:
Herzog, Werner, dir. Fitzcarraldo . Perf. Klaus Kinski. Filmverlag der Autoren, 1982.
Yates, Jane. "Invention in Rhetoric and Composition." Gaps Addressed: Future Work in Rhetoric and Composition, CCCC, Palmer House Hilton, 2002. Address.
Electronic sources
Electronic sources may include web pages and online news or magazine articles:
In the first example (an online magazine article), the writer has chosen not to include the author name in-text; however, two entries from the same author appear in the Works Cited. Thus, the writer includes both the author’s last name and the article title in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader to the appropriate entry on the Works Cited page (see below).
In the second example (a web page), a parenthetical citation is not necessary because the page does not list an author, and the title of the article, “MLA Formatting and Style Guide,” is used as a signal phrase within the sentence. If the title of the article was not named in the sentence, an abbreviated version would appear in a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence. Both corresponding Works Cited entries are as follows:
Taylor, Rumsey. "Fitzcarraldo." Slant , 13 Jun. 2003, www.slantmagazine.com/film/review/fitzcarraldo/. Accessed 29 Sep. 2009.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL , 2 Aug. 2016, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Multiple citations
To cite multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the citations by a semi-colon:
Time-based media sources
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
When a citation is not needed
Common sense and ethics should determine your need for documenting sources. You do not need to give sources for familiar proverbs, well-known quotations, or common knowledge (For example, it is expected that U.S. citizens know that George Washington was the first President.). Remember that citing sources is a rhetorical task, and, as such, can vary based on your audience. If you’re writing for an expert audience of a scholarly journal, for example, you may need to deal with expectations of what constitutes “common knowledge” that differ from common norms.
Other Sources
The MLA Handbook describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the handbook does not describe, making the best way to proceed can be unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of MLA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard MLA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source. For example, Norquest College provides guidelines for citing Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers —an author category that does not appear in the MLA Handbook . In cases like this, however, it's a good idea to ask your instructor or supervisor whether using third-party citation guidelines might present problems.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Website
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, citing a website in apa.
Once you’ve identified a credible website to use, create a citation and begin building your reference list. Citation Machine citing tools can help you create references for online news articles, government websites, blogs, and many other website! Keeping track of sources as you research and write can help you stay organized and ethical. If you end up not using a source, you can easily delete it from your bibliography. Ready to create a citation? Enter the website’s URL into the search box above. You’ll get a list of results, so you can identify and choose the correct source you want to cite. It’s that easy to begin!
If you’re wondering how to cite a website in APA, use the structure below.
Author Last Name, First initial. (Year, Month Date Published). Title of web page . Name of Website. URL
Example of an APA format website:
Austerlitz, S. (2015, March 3). How long can a spinoff like ‘Better Call Saul’ last? FiveThirtyEight. http://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-long-can-a-spinoff-like-better-call-saul-last/
Keep in mind that not all information found on a website follows the structure above. Only use the Website format above if your online source does not fit another source category. For example, if you’re looking at a video on YouTube, refer to the ‘YouTube Video’ section. If you’re citing a newspaper article found online, refer to ‘Newspapers Found Online’ section. Again, an APA website citation is strictly for web pages that do not fit better with one of the other categories on this page.
Social media:
When adding the text of a post, keep the original capitalization, spelling, hashtags, emojis (if possible), and links within the text.
Facebook posts:
Structure: Facebook user’s Last name, F. M. (Year, Monday Day of Post). Up to the first 20 words of Facebook post [Source type if attached] [Post type]. Facebook. URL
Source type examples: [Video attached], [Image attached]
Post type examples: [Status update], [Video], [Image], [Infographic]
Gomez, S. (2020, February 4). Guys, I’ve been working on this special project for two years and can officially say Rare Beauty is launching in [Video]. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/Selena/videos/1340031502835436/
Life at Chegg. (2020, February 7) It breaks our heart that 50% of college students right here in Silicon Valley are hungry. That’s why Chegg has [Images attached] [Status update]. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/LifeAtChegg/posts/1076718522691591
Twitter posts:
Structure: Account holder’s Last name, F. M. [Twitter Handle]. (Year, Month Day of Post). Up to the first 20 words of tweet [source type if attached] [Tweet]. Twitter. URL
Source type examples: [Video attached], [Image attached], [Poll attached]
Example: Edelman, J. [Edelman11]. (2018, April 26). Nine years ago today my life changed forever. New England took a chance on a long shot and I’ve worked [Video attached] [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/Edelman11/status/989652345922473985
Instagram posts:
APA citation format: Account holder’s Last name, F. M. [@Instagram handle]. (Year, Month Day). Up to the first 20 words of caption [Photograph(s) and/or Video(s)]. Instagram. URL
Example: Portman, N. [@natalieportman]. (2019, January 5). Many of my best experiences last year were getting to listen to and learn from so many incredible people through [Videos]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/p/BsRD-FBB8HI/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link
If this guide hasn’t helped solve all of your referencing questions, or if you’re still feeling the need to type “how to cite a website APA” into Google, then check out our APA citation generator on CitationMachine.com, which can build your references for you!
Featured links:
APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDF
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What a Thesis Paper is and How to Write One

From choosing a topic and conducting research to crafting a strong argument, writing a thesis paper can be a rewarding experience.
It can also be a challenging experience. If you've never written a thesis paper before, you may not know where to start. You may not even be sure exactly what a thesis paper is. But don't worry; the right support and resources can help you navigate this writing process.
What is a Thesis Paper?

A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a graduation requirement for certain bachelor's, master's or honors programs. Thesis papers present your own original research or analysis on a specific topic related to your field.
“In some ways, a thesis paper can look a lot like a novella,” said Shana Chartier , director of information literacy at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU). “It’s too short to be a full-length novel, but with the standard size of 40-60 pages (for a bachelor’s) and 60-100 pages (for a master’s), it is a robust exploration of a topic, explaining one’s understanding of a topic based on personal research.”
Chartier has worked in academia for over 13 years and at SNHU for nearly eight. In her role as an instructor and director, Chartier has helped to guide students through the writing process, like editing and providing resources.
Chartier has written and published academic papers such as "Augmented Reality Gamifies the Library: A Ride Through the Technological Frontier" and "Going Beyond the One-Shot: Spiraling Information Literacy Across Four Years." Both of these academic papers required Chartier to have hands-on experience with the subject matter. Like a thesis paper, they also involved hypothesizing and doing original research to come to a conclusion.
“When writing a thesis paper, the importance of staying organized cannot be overstated,” said Chartier. “Mapping out each step of the way, making firm and soft deadlines... and having other pairs of eyes on your work to ensure academic accuracy and clean editing are crucial to writing a successful paper.”
How Do I Choose a Topic For My Thesis Paper?

What your thesis paper is for will determine some of the specific requirements and steps you might take, but the first step is usually the same: Choosing a topic.
“Choosing a topic can be daunting," said Rochelle Attari , a peer tutor at SNHU. "But if (you) stick with a subject (you're) interested in... choosing a topic is much more manageable.”
Similar to a thesis, Attari recently finished the capstone for her bachelor’s in psychology . Her bachelor’s concentration is in forensics, and her capstone focused on the topic of using a combined therapy model for inmates who experience substance abuse issues to reduce recidivism.
“The hardest part was deciding what I wanted to focus on,” Attari said. “But once I nailed down my topic, each milestone was more straightforward.”
In her own writing experience, Attari said brainstorming was an important step when choosing her topic. She recommends writing down different ideas on a piece of paper and doing some preliminary research on what’s already been written on your topic.
By doing this exercise, you can narrow or broaden your ideas until you’ve found a topic you’re excited about. " Brainstorming is essential when writing a paper and is not a last-minute activity,” Attari said.
How Do I Structure My Thesis Paper?
Thesis papers tend to have a standard format with common sections as the building blocks.
While the structure Attari describes below will work for many theses, it’s important to double-check with your program to see if there are any specific requirements. Writing a thesis for a Master of Fine Arts, for example, might actually look more like a fiction novel.
According to Attari, a thesis paper is often structured with the following major sections:
Introduction
- Literature review
- Methods, results
Now, let’s take a closer look at what each different section should include.
Your introduction is your opportunity to present the topic of your thesis paper. In this section, you can explain why that topic is important. The introduction is also the place to include your thesis statement, which shows your stance in the paper.
Attari said that writing an introduction can be tricky, especially when you're trying to capture your reader’s attention and state your argument.
“I have found that starting with a statement of truth about a topic that pertains to an issue I am writing about typically does the trick,” Attari said. She demonstrated this advice in an example introduction she wrote for a paper on the effects of daylight in Alaska:
In the continental United States, we can always count on the sun rising and setting around the same time each day, but in Alaska, during certain times of the year, the sun rises and does not set for weeks. Research has shown that the sun provides vitamin D and is an essential part of our health, but little is known about how daylight twenty-four hours a day affects the circadian rhythm and sleep.
In the example Attari wrote, she introduces the topic and informs the reader what the paper will cover. Somewhere in her intro, she said she would also include her thesis statement, which might be:
Twenty-four hours of daylight over an extended period does not affect sleep patterns in humans and is not the cause of daytime fatigue in northern Alaska .
Literature Review
In the literature review, you'll look at what information is already out there about your topic. “This is where scholarly articles about your topic are essential,” said Attari. “These articles will help you find the gap in research that you have identified and will also support your thesis statement."
Telling your reader what research has already been done will help them see how your research fits into the larger conversation. Most university libraries offer databases of scholarly/peer-reviewed articles that can be helpful in your search.
In the methods section of your thesis paper, you get to explain how you learned what you learned. This might include what experiment you conducted as a part of your independent research.
“For instance,” Attari said, “if you are a psychology major and have identified a gap in research on which therapies are effective for anxiety, your methods section would consist of the number of participants, the type of experiment and any other particulars you would use for that experiment.”
In this section, you'll explain the results of your study. For example, building on the psychology example Attari outlined, you might share self-reported anxiety levels for participants trying different kinds of therapies. To help you communicate your results clearly, you might include data, charts, tables or other visualizations.
The discussion section of your thesis paper is where you will analyze and interpret the results you presented in the previous section. This is where you can discuss what your findings really mean or compare them to the research you found in your literature review.
The discussion section is your chance to show why the data you collected matters and how it fits into bigger conversations in your field.
The conclusion of your thesis paper is your opportunity to sum up your argument and leave your reader thinking about why your research matters.
Attari breaks the conclusion down into simple parts. “You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and discuss possible next steps for further research,” she said.
Find Your Program
Resources to help write your thesis paper.
While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn’t have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier.
If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
- Citation Handbooks: An online citation guide or handbook can help you ensure your citations are correct. APA , MLA and Chicago styles have all published their own guides.
- Citation Generators: There are many citation generator tools that help you to create citations. Some — like RefWorks — even let you directly import citations from library databases as you research.
- Your Library's Website: Many academic and public libraries allow patrons to access resources like databases or FAQs. Some FAQs at the SNHU library that might be helpful in your thesis writing process include “ How do I read a scholarly article? ” or “ What is a research question and how do I develop one? ”
It can also be helpful to check out what coaching or tutoring options are available through your school. At SNHU, for example, the Academic Support Center offers writing and grammar workshops , and students can access 24/7 tutoring and 1:1 sessions with peer tutors, like Attari.
"Students can even submit their papers and receive written feedback... like revisions and editing suggestions," she said.
If you are writing a thesis paper, there are many resources available to you. It's a long paper, but with the right mindset and support, you can successfully navigate the process.
“Pace yourself,” said Chartier. “This is a marathon, not a sprint. Setting smaller goals to get to the big finish line can make the process seem less daunting, and remember to be proud of yourself and celebrate your accomplishment once you’re done. Writing a thesis is no small task, and it’s important work for the scholarly community.”
A degree can change your life. Choose your program from 200+ SNHU degrees that can take you where you want to go.
Meg Palmer ’18 is a writer and scholar by trade who loves reading, riding her bike and singing in a barbershop quartet. She earned her bachelor’s degree in English, language and literature at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) and her master’s degree in writing, rhetoric and discourse at DePaul University (’20). While attending SNHU, she served as the editor-in-chief of the campus student newspaper, The Penmen Press, where she deepened her passion for writing. Meg is an adjunct professor at Johnson and Wales University, where she teaches first year writing, honors composition, and public speaking. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is the Difference Between Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees?

Academic Referencing: How to Cite a Research Paper

What is Considered Plagiarism And How to Avoid It
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
Astronomers discover oldest known eclipse reference in 6,000-year-old Hindu text
The passages are flowery but fitting for an eclipse, describing the sun as being "pierced" with darkness and gloom and proposing that evil beings had caused the sun's "magic arts to vanish."

When astronomers combed through an ancient Hindu text known as the Rig Veda, they discovered that it referenced a total solar eclipse that occurred roughly 6,000 years ago — making it the oldest known mention of an eclipse.
The Rig Veda, a collection of sayings and hymns from various religious and philosophical schools, was compiled around 1500 B.C. Like nearly all religious texts, it mentions historical events. Most are contemporary to when it was written, but some stretch back much further. For example, various passages in the Rig Veda mention the location of the rising sun during the vernal equinox. One reference describes the vernal equinox as occurring in Orion , and another has it occurring in the Pleiades .
These descriptions allow astronomers to date those references, because as Earth spins on its axis, it wobbles like a spinning top, changing the relative position of important astronomical events. Currently, the vernal equinox is in the constellation Pisces . It was in Orion around 4500 B.C. and in the Pleiades around 2230 B.C., meaning the Rig Veda recorded some memories of events far earlier than its compilation.
Related: 'Zeus made night from mid-day:' Terror and wonder in ancient accounts of solar eclipses
The Rig Veda's language is highly symbolic and allegorical, making it difficult to discern which stories are myths and which are historical. But two astronomers — Mayank Vahia of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in Mumbai and Mitsuru Soma of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan — think they've found references to an ancient eclipse. They reported their findings in the Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage .
The passages are flowery but fitting for an eclipse, describing the sun as being "pierced" with darkness and gloom and proposing that evil beings had caused the sun's "magic arts to vanish." The astronomers noted that these passages do not reference the story of Rahu and Ketu, which is a more recent Hindu mythology surrounding the eclipse, indicating that these passages were described before those stories were created.
Further passages helped the astronomers narrow down the time frame of the solar eclipse . It occurred when the vernal equinox was in Orion, and it also happened just three days prior to an autumnal equinox. It was also a total solar eclipse, and it must have happened over the area where the eventual writers of the Rig Veda lived.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
— 'Zeus made night from mid-day:' Terror and wonder in ancient accounts of solar eclipses
— What the Aztecs thought about solar eclipses
— What did ancient humans know about astronomy?
The astronomers found that only two possible dates fit these criteria: Oct. 22, 4202 B.C., and Oct. 19, 3811 B.C. Both of these dates are earlier than the current record holders for the oldest mention of an eclipse — a clay tablet, unearthed in Syria, that recorded an eclipse in either 1375 B.C. or 1223 B.C., and a rock carving in Ireland that might reference an eclipse in 3340 B.C.
The newfound reference in the Rig Veda highlights how total solar eclipses captivated people in antiquity and how ancient texts can contribute to our present-day knowledge of celestial events.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Paul M. Sutter is an astrophysicist at SUNY Stony Brook and the Flatiron Institute in New York City. Paul received his PhD in Physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2011, and spent three years at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, followed by a research fellowship in Trieste, Italy, His research focuses on many diverse topics, from the emptiest regions of the universe to the earliest moments of the Big Bang to the hunt for the first stars. As an "Agent to the Stars," Paul has passionately engaged the public in science outreach for several years. He is the host of the popular "Ask a Spaceman!" podcast, author of "Your Place in the Universe" and "How to Die in Space" and he frequently appears on TV — including on The Weather Channel, for which he serves as Official Space Specialist.
1 month until the annular solar eclipse 2024: Here's what you need to know
Where can I see the total solar eclipse on Aug. 12, 2026?
NASA astronaut Butch Wilmore reports 'strange noise' coming from Boeing's Starliner spacecraft, 'I don't know what's making it'
Most Popular
- 2 1 month until the annular solar eclipse 2024: Here's what you need to know
- 3 Best Alien comic books of all time
- 4 Weird mystery waves that baffle scientists may be 'everywhere' inside Earth's mantle
- 5 Astrophotographer captures Comet 13P/Olbers and the Black Eye Galaxy M64 in stunning detail (photo)
Blog The Education Hub
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2024/09/02/how-to-claim-15-hours-free-childcare-code/
Hundreds of thousands of parents can now access 15 hours free childcare for 9-month-olds – how to apply

Hundreds of thousands of eligible working parents can now access 15 hours government-funded early education for children aged 9-months-old and older after new rules kicked in from 1 September 2024.
Those who are eligible to take advantage of the scheme this term should have already received their code and secured a childcare place.
Also, from today, eligible working parents who plan to take up a funded place from January 2025 can now apply for a code. If they’re starting a new job or returning from parental leave this may affect when they’re eligible - more information on this below.
It's worth noting that some providers may charge for extra services, such as providing lunch and nappies, or optional extras such as trips, in addition to the government funded childcare . Visit childcarechoices.gov.uk for further information.
When can I apply and how do I get my code?
Applications are open for eligible working parents whose children will be aged at least 9-months-old on or before 31 December 2024.
This can be combined with the universal 15 hours to make 30 hours childcare when your child turns 3 or 4.
When you apply, you’ll receive a code to give to your childcare provider.
It’s important to remember that codes need to be renewed every three months . To do this, you’ll need to remember to login to your childcare account to check when your reconfirmation dates are, so that you can renew your code on time. If you don’t renew it on time, you will need to reapply.
You can claim your place the term after your child turns the relevant age. This gives local authorities and childcare providers enough time to prepare.
There is no limit on the number of codes available. However, if you’re applying for childcare to start in January 2025, we recommend that you reach out to your preferred provider as soon as possible to check when they will need your code.
We know that it may be difficult at this stage to secure your first-place provider. If you are struggling to find a place you should contact your local authority, who will be able to help source a local provider offering the entitlements.
How do I apply?
You apply online here on gov.uk once you have checked our eligibility criteria .
You’ll need to make sure you have the following information to hand before starting the application:
- your national insurance number (or unique taxpayer reference if you are self-employed)
- the date you started or are due to start work
- details of any government support or benefits you receive
- the UK birth certificate reference number (if you have one) for your child.
You may find out if you’re eligible straight away, but it can take up to 7 days.
Once your application has been approved, you’ll get a code to give to your childcare provider.
Eligible parents are also able to access tax-free childcare through the same application system. You can apply for tax-free childcare at any time.
However, you don't need to apply for tax-free childcare to be eligible to apply for the 15 hours childcare scheme.
Can I apply for government-funded childcare if I’m on parental leave?
Yes, you can.
If you’re applying for childcare for an older child, who is not the reason for your parental leave, you can continue to apply in the usual way.
For parents applying for funded childcare for the child who is the reason for your parental leave, you can apply for a childcare code at the same time as everyone else as long as you plan to return to work from parental leave or start a new job by the end of January 2024.
Parents on parental leave will need to apply online. They may be told their application is ‘pending’ if it is more than 31 days before they return to work, but they will still receive a letter in the post within 1 to 2 weeks so they can access their childcare entitlement.
Parents starting new work before 31 January can call HMRC on 0300 123 4097 to receive a code.
What if I’m on parental leave and returning to work after 1 February 2025?
Parents who plan to start or return to work on or before 31 January 2025 can apply for a code from 1 September 2024 to use from 1 January 2025.
For parents starting or returning to work on or after 1 February 2025, the following dates will apply:
| 1 October 2024 to 31 January 2025 | 1 September 2024 to 31 December 2025 | 1 January 2025 |
| 1 February 2025 to 30 April 2025 | 1 January 2025 to 31 March 2025 | 1 April 2025 |
| 1 May 2025 to 30 September 2025 | 1 April 2025 to 31 August 2025 | 1 September 2025 |
For the purposes of accessing the entitlement, taking annual leave after the end of your parental leave counts as having returned to work.
It is important to remember that if you are applying for childcare for an older child who is not the reason for your parental leave, you can apply regardless of your return-to-work date.
What happens once I receive my code?
Once you receive your code, you’ll need to take it to your childcare provider, along with your National Insurance number and your child’s date of birth.
Your childcare provider will process the code to provide your place.
Your local authority can provide support for finding a government-funded place in your area. You can find out who your local authority is here .
If I receive a code in a letter from HMRC, does this make my code on my Childcare Account invalid?
No. Both codes will be valid.
If you have two codes, one from your letter beginning with 11 and one from the website beginning with 50, please give your provider the code from the website, as this is the permanent digital code for your child.
If you only have one code (beginning with 11) then you can use this code to start using your government-funded hours.
Please remember that once your reconfirmation window opens, you will still need to reconfirm your eligibility through your Childcare Account and share the digital code you receive with your provider.
Do I need to wait for my reconfirmation window to add another child to my account?
A parent who is already using the childcare service for another child can add a new child to their account at any time.
Your reconfirmation cycle for your current Tax-Free Childcare won’t affect this.
What happens if I’m using an entitlement for my 2-year-old when they become 3?
Parents are able to access the universal 15 hours childcare support from the term after the child’s third birthday through to when they start school.
If your child is accessing the 15 hours entitlement for 2-year-olds and you remain eligible, your child will automatically be moved onto 30 hours (universal 15 hours + 15 hours for working parents) from the term after your child turns 3.
You will just need to keep reconfirming your code as normal, and it will become usable to claim 30 hours.
You should also speak to your provider to let them know you intend to take up 30 hours.
If you are accessing disadvantaged entitlement childcare for, you will also able to access the universal entitlement from the term after your child turns 3.
You may also be interested in:
- Free Speech Act: what you need to know
- What is the national curriculum and why is it being reviewed?
- The King’s Speech 2024: What does it mean for education?
Tags: 15 hours free childcare , Applying for 15 hours free childcare , Childcare , Free childcare 2024 , Free childcare eligibility , tax-free childcare , When to apply for 15 hour free childcare
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | ||||||
Comments and moderation policy
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- Setting Up the APA Reference Page | Formatting & References (Examples)
Setting Up the APA Reference Page | Formatting & References (Examples)
Published on November 4, 2020 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on January 17, 2024.
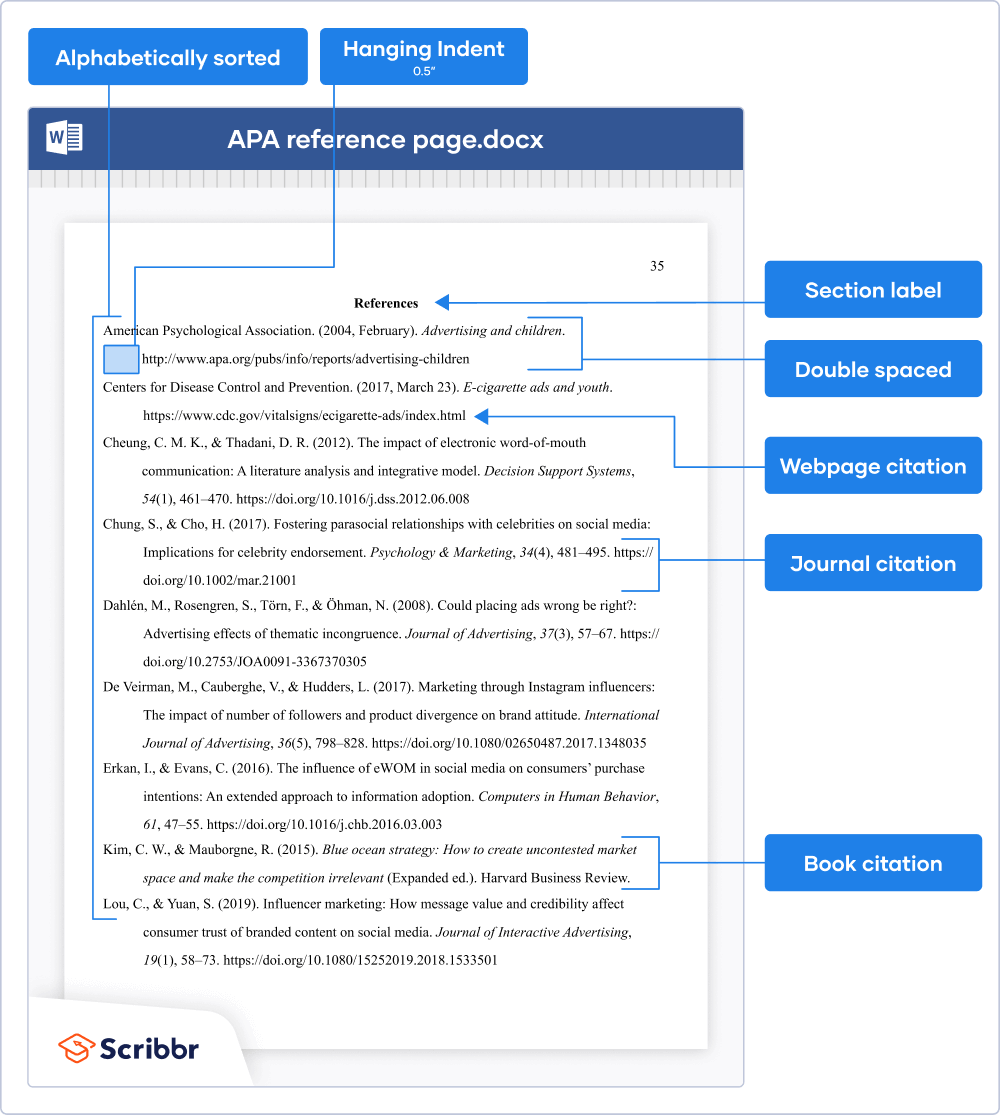
On the APA reference page, you list all the sources that you’ve cited in your paper. The list starts on a new page right after the body text.
Follow these instructions to set up your APA reference page:
- Place the section label “References” in bold at the top of the page (centered).
- Order the references alphabetically .
- Double-space all text.
- Apply a hanging indent of 0.5 inches.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Setting up the apa reference page, apa alphabetization guidelines, which sources to include on the reference page, annotated bibliography, creating apa references.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
References are ordered alphabetically by the first author’s last name. If the author is unknown, order the reference entry by the first meaningful word of the title (ignoring articles: “the”, “a”, or “an”).
Word processors like Word or Google Docs and citation generators can usually order the reference list automatically. However, ordering becomes challenging when citing multiple works by the same author or works by authors with the same last name.
Our in-depth article on ordering references in APA Style explains what to do in these situations.
Only include references for sources cited in the body text (with an APA in-text citation ). Don’t include references for:
- Sources that you only consulted;
- Personal communications (e.g., emails or phone calls);
- General mentions of websites or periodicals ;
- Common knowledge .
For some student papers, it’s common to describe or evaluate the source in an annotation . These annotations are placed on a new line below the corresponding reference entry. The entire annotation is indented 0.5 inches.
If an annotation consists of multiple paragraphs, the first line of the second and any subsequent paragraphs is indented an additional 0.5 inches.

The format of an APA reference differs depending on the source type. Play around with the options in the Scribbr Example Generator to get familiar with APA Style.
Scribbr Citation Generator
With Scribbr’s free APA citation generator you can easily cite your sources according to the new 7th edition guidelines. It’s accurate, fast, and easy to use. Give it a try!
APA Citation Generator
APA citation examples
Check out Scribbr’s citation examples to learn more about citing each type of source, ranging from books and journals to podcasts and tweets !
Periodicals
- Journal article
- Newspaper article
Reports and gray literature
- Press release
- Dissertation or thesis
- Conference paper
Books and reference works
- Dictionary entry
- Encyclopedia entry
Audiovisual works
- Movie or documentary
- YouTube video
Online media
- Personal communication
- Tables and figures
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, January 17). Setting Up the APA Reference Page | Formatting & References (Examples). Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/apa-reference-page/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, ordering works on the apa reference page, apa title page (7th edition) | template for students & professionals, apa format for academic papers and essays, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples Published on March 5, 2021 by Jack Caulfield. Revised on January 17, 2024. To cite a page from a website, you need a short in-text citation and a corresponding reference stating the author's name, the date of publication, the title of the page, the website name, and the URL.
To cite a website or online article in APA Style, you need the author, title, date, website name, and URL.
An MLA website citation includes author, page title, website name, date and URL. The in-text citation is just the author's last name.
To provide readers with credible sources, learn how to cite a website in an essay. Quick guide for APA or MLA reference page entries for your paper.
MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) The MLA Handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it's included in this list.
This page contains reference examples for webpages such as news website; comments on news website pages; webpages with government, organizational, or individual authors; and when to include retrieval dates.
To reference a website in Harvard style, include the name of the author or organization, the year of publication, the title of the page, the URL, and the date on which you accessed the website. In-text citation example. (Google, 2020) Reference template. Author surname, initial. (Year) Page Title.
The easy way to cite a website in any citation style Use our citation generator below to automatically cite a website in any style, including APA, MLA 7 and 8, and Harvard. Just select the style you need, copy the URL into the search box, and press search. We'll do the rest.
Citing a website on the reference page In the next section of this APA citation website guide, we're going to focus on how to format an APA website citation. If you're wondering how to create an APA citation of a web page, the majority of web references use the structure shown below.
How to Cite a Website in MLA: Your questions about creating an MLA citation for a website are answered in our free resource. Get it here.
Entire Website Note: If you are quoting or paraphrasing part of a website, you should create a reference for a Page or Section. If you mention a website in general, do not create a reference list entry or an in-text citation. Instead, include the name of the website in the text and provide the URL in parentheses.
To cite a website in APA format, you must include the author's name, the publication date, the page or article title, the website's name, and the URL, in that order. This is the basic information you use whether you're citing a web page, blog post, online article, online video, or even a social media post; however, the format changes slightly for each, which we explain below. To cite ...
In text, you can cite these references separately as usual (e.g., American Nurses Association, 1991b), or you can combine citations with the same author if desired. Simply state the author once and then provide the years of the applicable references in chronological order, separated by commas. Combined in-text citations:
If you're writing a research paper, you'll likely do quite a bit of research online. If you have websites that you want to use as sources for your paper, an entry for the website must appear in the reference list (also called the...
In-Text Citations Resources on using in-text citations in APA style The Basics General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Author/Authors How to refer to authors in-text, including single and multiple authors, unknown authors, organizations, etc.
Here is a complete list for how to cite sources. Most of these guides present citation guidance and examples in MLA, APA, and Chicago.
How to Cite Sources | Citation Generator & Quick Guide Citing your sources is essential in academic writing. Whenever you quote or paraphrase a source (such as a book, article, or webpage), you have to include a citation crediting the original author.
Referencing is how you acknowledge your sources to avoid plagiarism. Most referencing styles require in-text citations and a reference list.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Citing a website in APA Once you've identified a credible website to use, create a citation and begin building your reference list. Citation Machine citing tools can help you create references for online news articles, government websites, blogs, and many other website! Keeping track of sources as you research and write can help you stay organized and ethical. If you end up not using a ...
A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a college graduation requirement. The 5 components to a standard thesis typically include an introduction, literature review, methods and results, discussion and conclusion. ... Citation Handbooks: An online citation guide or handbook can help you ensure your citations are ...
Learn how to set up APA format for your paper. From the title page and headings to references and citations.
Astronomers combed through an ancient Hindu text and discovered that it referenced a total solar eclipse that occurred roughly 6,000 years ago, making it the oldest known mention of an eclipse.
A Dark Web Market Worth $1.7Bn By 2030. The global market for dark web threat intelligence is surging. A report from Data Intelligence estimated that the sector will reach $1.7 billion by 2030.. Driven by the rising recurrence of digital threats, companies like ZeroFox, CrowdStrike, Digital Shadows, Flare, IBMX-force, and other leading players are investing in innovation and AI to build the ...
Learn how to cite sources in your text with APA and MLA styles, including examples and tips for different types of sources.
your national insurance number (or unique taxpayer reference if you are self-employed) the date you started or are due to start work; details of any government support or benefits you receive; the UK birth certificate reference number (if you have one) for your child. You may find out if you're eligible straight away, but it can take up to 7 ...
On the APA reference page, you list all the sources that you've cited in your paper. The list starts on a new page right after the body text. Follow these instructions to set up your APA reference page: Place the section label "References" in bold at the top of the page (centered). Order the references alphabetically. Double-space all text.