- Bankruptcy Basics
- Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
- Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- Debt Collectors and Consumer Rights
- Divorce and Bankruptcy
- Going to Court
- Property & Exemptions
- Student Loans
- Taxes and Bankruptcy
- Wage Garnishment

Understanding the Assignment of Mortgages: What You Need To Know
3 minute read • Upsolve is a nonprofit that helps you get out of debt with education and free debt relief tools, like our bankruptcy filing tool. Think TurboTax for bankruptcy. Get free education, customer support, and community. Featured in Forbes 4x and funded by institutions like Harvard University so we'll never ask you for a credit card. Explore our free tool
A mortgage is a legally binding agreement between a home buyer and a lender that dictates a borrower's ability to pay off a loan. Every mortgage has an interest rate, a term length, and specific fees attached to it.

Written by Attorney Todd Carney . Updated November 26, 2021
If you’re like most people who want to purchase a home, you’ll start by going to a bank or other lender to get a mortgage loan. Though you can choose your lender, after the mortgage loan is processed, your mortgage may be transferred to a different mortgage servicer . A transfer is also called an assignment of the mortgage.
No matter what it’s called, this change of hands may also change who you’re supposed to make your house payments to and how the foreclosure process works if you default on your loan. That’s why if you’re a homeowner, it’s important to know how this process works. This article will provide an in-depth look at what an assignment of a mortgage entails and what impact it can have on homeownership.
Assignment of Mortgage – The Basics
When your original lender transfers your mortgage account and their interests in it to a new lender, that’s called an assignment of mortgage. To do this, your lender must use an assignment of mortgage document. This document ensures the loan is legally transferred to the new owner. It’s common for mortgage lenders to sell the mortgages to other lenders. Most lenders assign the mortgages they originate to other lenders or mortgage buyers.
Home Loan Documents
When you get a loan for a home or real estate, there will usually be two mortgage documents. The first is a mortgage or, less commonly, a deed of trust . The other is a promissory note. The mortgage or deed of trust will state that the mortgaged property provides the security interest for the loan. This basically means that your home is serving as collateral for the loan. It also gives the loan servicer the right to foreclose if you don’t make your monthly payments. The promissory note provides proof of the debt and your promise to pay it.
When a lender assigns your mortgage, your interests as the mortgagor are given to another mortgagee or servicer. Mortgages and deeds of trust are usually recorded in the county recorder’s office. This office also keeps a record of any transfers. When a mortgage is transferred so is the promissory note. The note will be endorsed or signed over to the loan’s new owner. In some situations, a note will be endorsed in blank, which turns it into a bearer instrument. This means whoever holds the note is the presumed owner.
Using MERS To Track Transfers
Banks have collectively established the Mortgage Electronic Registration System , Inc. (MERS), which keeps track of who owns which loans. With MERS, lenders are no longer required to do a separate assignment every time a loan is transferred. That’s because MERS keeps track of the transfers. It’s crucial for MERS to maintain a record of assignments and endorsements because these land records can tell who actually owns the debt and has a legal right to start the foreclosure process.
Upsolve Member Experiences
Assignment of Mortgage Requirements and Effects
The assignment of mortgage needs to include the following:
The original information regarding the mortgage. Alternatively, it can include the county recorder office’s identification numbers.
The borrower’s name.
The mortgage loan’s original amount.
The date of the mortgage and when it was recorded.
Usually, there will also need to be a legal description of the real property the mortgage secures, but this is determined by state law and differs by state.
Notice Requirements
The original lender doesn’t need to provide notice to or get permission from the homeowner prior to assigning the mortgage. But the new lender (sometimes called the assignee) has to send the homeowner some form of notice of the loan assignment. The document will typically provide a disclaimer about who the new lender is, the lender’s contact information, and information about how to make your mortgage payment. You should make sure you have this information so you can avoid foreclosure.
Mortgage Terms
When an assignment occurs your loan is transferred, but the initial terms of your mortgage will stay the same. This means you’ll have the same interest rate, overall loan amount, monthly payment, and payment due date. If there are changes or adjustments to the escrow account, the new lender must do them under the terms of the original escrow agreement. The new lender can make some changes if you request them and the lender approves. For example, you may request your new lender to provide more payment methods.
Taxes and Insurance
If you have an escrow account and your mortgage is transferred, you may be worried about making sure your property taxes and homeowners insurance get paid. Though you can always verify the information, the original loan servicer is responsible for giving your local tax authority the new loan servicer’s address for tax billing purposes. The original lender is required to do this after the assignment is recorded. The servicer will also reach out to your property insurance company for this reason.
If you’ve received notice that your mortgage loan has been assigned, it’s a good idea to reach out to your loan servicer and verify this information. Verifying that all your mortgage information is correct, that you know who to contact if you have questions about your mortgage, and that you know how to make payments to the new servicer will help you avoid being scammed or making payments incorrectly.
Let's Summarize…
In a mortgage assignment, your original lender or servicer transfers your mortgage account to another loan servicer. When this occurs, the original mortgagee or lender’s interests go to the next lender. Even if your mortgage gets transferred or assigned, your mortgage’s terms should remain the same. Your interest rate, loan amount, monthly payment, and payment schedule shouldn’t change.
Your original lender isn’t required to notify you or get your permission prior to assigning your mortgage. But you should receive correspondence from the new lender after the assignment. It’s important to verify any change in assignment with your original loan servicer before you make your next mortgage payment, so you don’t fall victim to a scam.
Attorney Todd Carney
Attorney Todd Carney is a writer and graduate of Harvard Law School. While in law school, Todd worked in a clinic that helped pro-bono clients file for bankruptcy. Todd also studied several aspects of how the law impacts consumers. Todd has written over 40 articles for sites such... read more about Attorney Todd Carney
Continue reading and learning!

It's easy to get debt help
Choose one of the options below to get assistance with your debt:
Considering Bankruptcy?
Our free tool has helped 14,529+ families file bankruptcy on their own. We're funded by Harvard University and will never ask you for a credit card or payment.
Private Attorney
Get a free evaluation from an independent law firm.
Learning Center
Research and understand your options with our articles and guides.
Already an Upsolve user?
Bankruptcy Basics ➜
- What Is Bankruptcy?
- Every Type of Bankruptcy Explained
- How To File Bankruptcy for Free: A 10-Step Guide
- Can I File for Bankruptcy Online?
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy ➜
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Filing Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
- What Is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy & When Should I File?
- Chapter 7 Means Test Calculator
Wage Garnishment ➜
- How To Stop Wage Garnishment Immediately
Property & Exemptions ➜
- What Are Bankruptcy Exemptions?
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy: What Can You Keep?
- Yes! You Can Get a Mortgage After Bankruptcy
- How Long After Filing Bankruptcy Can I Buy a House?
- Can I Keep My Car If I File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
- Can I Buy a Car After Bankruptcy?
- Should I File for Bankruptcy for Credit Card Debt?
- How Much Debt Do I Need To File for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
- Can I Get Rid of my Medical Bills in Bankruptcy?
Student Loans ➜
- Can You File Bankruptcy on Student Loans?
- Can I Discharge Private Student Loans in Bankruptcy?
- Navigating Financial Aid During and After Bankruptcy: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Filing Bankruptcy to Deal With Your Student Loan Debt? Here Are 3 Things You Should Know!
Debt Collectors and Consumer Rights ➜
- 3 Steps To Take if a Debt Collector Sues You
- How To Deal With Debt Collectors (When You Can’t Pay)
Taxes and Bankruptcy ➜
- What Happens to My IRS Tax Debt if I File Bankruptcy?
- What Happens to Your Tax Refund in Bankruptcy
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy ➜
- Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 13 Bankruptcy: What’s the Difference?
- Why is Chapter 13 Probably A Bad Idea?
- How To File Chapter 13 Bankruptcy: A Step-by-Step Guide
- What Happens When a Chapter 13 Case Is Dismissed?
Going to Court ➜
- Do You Have to Go To Court to File Bankruptcy?
- Telephonic Hearings in Bankruptcy Court
Divorce and Bankruptcy ➜
- How to File Bankruptcy After a Divorce
- Chapter 13 and Divorce
Chapter 11 Bankruptcy ➜
- Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
- Reorganizing Your Debt? Chapter 11 or Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Can Help!
State Guides ➜
- Connecticut
- District Of Columbia
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia

Upsolve is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit that started in 2016. Our mission is to help low-income families resolve their debt and fix their credit using free software tools. Our team includes debt experts and engineers who care deeply about making the financial system accessible to everyone. We have world-class funders that include the U.S. government, former Google CEO Eric Schmidt, and leading foundations.
To learn more, read why we started Upsolve in 2016, our reviews from past users, and our press coverage from places like the New York Times and Wall Street Journal.
Choose Your Legal Category:
- Online Law Library
- Bankruptcy Law
- Business Law
- Civil Law
- Criminal Law
- Employment Law
- Family Law
- Finance Law
- Government Law
- Immigration Law
- Insurance Law
- Intellectual Property Law
- Personal Injury Law
- Products & Services Law
- Real Estate Law
- Wills, Trusts & Estates Law
- Attorney Referral Services
- Top 10 Most Popular Articles
- Legal Dictionary
- How It Works - Clients
- Legal Center
- About LegalMatch
- Consumer Satisfaction
- Editorial Policy
- Attorneys Market Your Law Practice Attorney Login Schedule a Demo Now Did LegalMatch Call You Recently? How It Works - Attorneys Attorney Resources Attorney Success Stories Attorney Success Story Videos Compare Legal Marketing Services Cases Heatmap View Cases
- Find a Lawyer
- Legal Topics
- Real Estate Law
Mortgage Assignment Laws and Definition
(This may not be the same place you live)
What is a Mortgage Assignment?
A mortgage is a legal agreement. Under this agreement, a bank or other lending institution provides a loan to an individual seeking to finance a home purchase. The lender is referred to as a creditor. The person who finances the home owes money to the bank, and is referred to as the debtor.
To make money, the bank charges interest on the loan. To ensure the debtor pays the loan, the bank takes a security interest in what the loan is financing — the home itself. If the buyer fails to pay the loan, the bank can take the property through a foreclosure proceeding.
There are two main documents involved in a mortgage agreement. The document setting the financial terms and conditions of repayment is known as the mortgage note. The bank is the owner of the note. The note is secured by the mortgage. This means if the debtor does not make payment on the note, the bank may foreclose on the home.
The document describing the mortgaged property is called the mortgage agreement. In the mortgage agreement, the debtor agrees to make payments under the note, and agrees that if payment is not made, the bank may institute foreclosure proceedings and take the home as collateral .
An assignment of a mortgage refers to an assignment of the note and assignment of the mortgage agreement. Both the note and the mortgage can be assigned. To assign the note and mortgage is to transfer ownership of the note and mortgage. Once the note is assigned, the person to whom it is assigned, the assignee, can collect payment under the note.
Assignment of the mortgage agreement occurs when the mortgagee (the bank or lender) transfers its rights under the agreement to another party. That party is referred to as the assignee, and receives the right to enforce the agreement’s terms against the assignor, or debtor (also called the “mortgagor”).
What are the Requirements for Executing a Mortgage Assignment?
What are some of the benefits and drawbacks of mortgage assignments, are there any defenses to mortgage assignments, do i need to hire an attorney for help with a mortgage assignment.
For a mortgage to be validly assigned, the assignment document (the document formally assigning ownership from one person to another) must contain:
- The current assignor name.
- The name of the assignee.
- The current borrower or borrowers’ names.
- A description of the mortgage, including date of execution of the mortgage agreement, the amount of the loan that remains, and a reference to where the mortgage was initially recorded. A mortgage is recorded in the office of a county clerk, in an index, typically bearing a volume or page number. The reference to where the mortgage was recorded should include the date of recording, volume, page number, and county of recording.
- A description of the property. The description must be a legal description that unambiguously and completely describes the boundaries of the property.
There are several types of assignments of mortgage. These include a corrective assignment of mortgage, a corporate assignment of mortgage, and a mers assignment of mortgage. A corrective assignment corrects or amends a defect or mistake in the original assignment. A corporate assignment is an assignment of the mortgage from one corporation to another.
A mers assignment involves the Mortgage Electronic Registration System (MERS). Mortgages often designate MERS as a nominee (agent for) the lender. When the lender assigns a mortgage to MERS, MERS does not actually receive ownership of the note or mortgage agreement. Instead, MERS tracks the mortgage as the mortgage is assigned from bank to bank.
An advantage of a mortgage assignment is that the assignment permits buyers interested in purchasing a home, to do so without having to obtain a loan from a financial institution. The buyer, through an assignment from the current homeowner, assumes the rights and responsibilities under the mortgage.
A disadvantage of a mortgage assignment is the consequences of failing to record it. Under most state laws, an entity seeking to institute foreclosure proceedings must record the assignment before it can do so. If a mortgage is not recorded, the judge will dismiss the foreclosure proceeding.
Failure to observe mortgage assignment procedure can be used as a defense by a homeowner in a foreclosure proceeding. Before a bank can institute a foreclosure proceeding, the bank must record the assignment of the note. The bank must also be in actual possession of the note.
If the bank fails to “produce the note,” that is, cannot demonstrate that the note was assigned to it, the bank cannot demonstrate it owns the note. Therefore, it lacks legal standing to commence a foreclosure proceeding.
If you need help with preparing an assignment of mortgage, you should contact a mortgage lawyer . An experienced mortgage lawyer near you can assist you with preparing and recording the document.
Save Time and Money - Speak With a Lawyer Right Away
- Buy one 30-minute consultation call or subscribe for unlimited calls
- Subscription includes access to unlimited consultation calls at a reduced price
- Receive quick expert feedback or review your DIY legal documents
- Have peace of mind without a long wait or industry standard retainer
- Get the right guidance - Schedule a call with a lawyer today!
Need a Mortgage Lawyer in your Area?
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia

Daniel Lebovic
LegalMatch Legal Writer
Original Author
Prior to joining LegalMatch, Daniel worked as a legal editor for a large HR Compliance firm, focusing on employer compliance in numerous areas of the law including workplace safety law, health care law, wage and hour law, and cybersecurity. Prior to that, Daniel served as a litigator for several small law firms, handling a diverse caseload that included cases in Real Estate Law (property ownership rights, residential landlord/tenant disputes, foreclosures), Employment Law (minimum wage and overtime claims, discrimination, workers’ compensation, labor-management relations), Construction Law, and Commercial Law (consumer protection law and contracts). Daniel holds a J.D. from the Emory University School of Law and a B.S. in Biological Sciences from Cornell University. He is admitted to practice law in the State of New York and before the State Bar of Georgia. Daniel is also admitted to practice before the United States Courts of Appeals for both the 2nd and 11th Circuits. You can learn more about Daniel by checking out his Linkedin profile and his personal page. Read More

Jose Rivera, J.D.
Managing Editor
Preparing for Your Case
- What to Do to Have a Strong Mortgage Law Case
- Top 5 Types of Documents/Evidence to Gather for Your Mortgages Case
Related Articles
- Assumable Mortgages
- Loan Modification Laws
- Behind on Mortgage Payments Lawyers
- Home Improvement Loan Disputes
- Reverse Mortgages for Senior Citizens
- Mortgage Settlement Scams
- Short Sale Fraud Schemes
- Deed of Trust or a Mortgage, What's the Difference?
- Owner Carryback Mortgages
- Contract for Deed Lawyers Near Me
- Mortgage Subrogation
- Property Lien Waivers and Releases
- Different Types of Promissory Notes
- Repayment Schedules for Promissory Notes
- Ft. Lauderdale Condos and Special Approval Loans
- Special Approval Loans for Miami Condos
- Removing a Lien on Property
- Mortgage Loan Fraud
- Subprime Mortgage Lawsuits
- Property Flipping and Mortgage Loan Fraud
- Avoid Being a Victim of Mortgage Fraud
- Second Mortgage Lawyers
- Settlement Statement Lawyers
- Loan Approval / Commitment Lawyers
- Broker Agreement Lawyers
- Truth in Lending Disclosure Statement (TILA)
- Housing and Urban Development (HUD) Info Lawyers
- Good Faith Estimate Lawyers
- Mortgage Loan Documents
Discover the Trustworthy LegalMatch Advantage
- No fee to present your case
- Choose from lawyers in your area
- A 100% confidential service
How does LegalMatch work?
Law Library Disclaimer

16 people have successfully posted their cases

What Is Assignment of Mortgage: What You Need to Know

We will explore the idea of mortgage assignment in this thorough guide, going over its definition, steps involved, potential consequences, and more. So read on to learn more about this important facet of the real estate market, whether you’re a homeowner, a prospective buyer, or just inquisitive about mortgages.
What is Assignment of Mortgage?
The assignment of mortgage, often simply referred to as mortgage assignment , is a legal process that involves the transfer of a mortgage loan from one party to another. This transfer typically occurs between mortgage lenders or financial institutions and is a common practice within the mortgage industry.
The Key Parties Involved
- Assignor: The person transferring the mortgage is known as the assignor. The initial lender or financial organization that gave the borrower the mortgage loan is often the assignor.
- Assignee: The assignee is the party receiving the mortgage assignment. This could be another lender or financial institution that is buying the mortgage, often as part of a financial transaction.
- Borrower: The borrower is the individual or entity that initially took out the mortgage loan to finance the purchase of a property.
Why is Assignment of Mortgage Necessary?
Assignment of mortgage occurs for various reasons, and it serves specific purposes for all parties involved.
1. Loan Portfolio Management
Mortgage assignment is a common practice used by lenders to better manage their loan portfolios. Lenders might raise funds to offer more loans or issue new mortgages by selling or transferring mortgage loans to other financial organizations. This procedure aids in keeping their portfolios risk-balanced and liquid.
2. Risk Mitigation
Lenders may also assign mortgages to mitigate risk. When they transfer a mortgage to another entity, they are essentially transferring the associated risk as well. This can be a strategic move to reduce their exposure to potential defaults or financial instability.
3. Secondary Mortgage Market
The secondary mortgage market plays a significant role in the assignment of mortgages. Many mortgages are bundled together into mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and sold to investors. Assignment of mortgages allows lenders to participate in this market, which provides additional funding for new mortgage loans.
The Assignment of Mortgage Process
The process of assigning a mortgage, or deciding to sell your mortgage , involves several steps and legal requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the typical process:
1. Agreement between Parties
The assignor (original lender) and assignee (new lender or investor) must enter into a formal agreement outlining the terms and conditions of the new mortgage assignment. This agreement includes details such as the transfer price, terms of the loan, and any specific warranties or representations.
2. Notice to the Borrower
Once the agreement is in place, the borrower is typically notified of the assignment. This notice informs them that the servicing of their mortgage, including collecting monthly mortgage payments, will now be handled by the assignee. The borrower is advised to send future payments to the assignee.
3. Recordation
In many jurisdictions, mortgage assignments must be recorded with the appropriate government office, such as the county recorder’s office. This recordation provides public notice of the transfer and ensures that the assignee has a legal claim on the property.
4. Continuation of Monthly Mortgage Payments
For the borrower, the most noticeable change is the address where monthly payments are sent. Instead of sending payment to the original lender, the borrower will send them to the assignee. It is crucial for borrowers to keep records of these changes to avoid any confusion or missed payments.
Implications of Mortgage Assignment for Borrowers
While the assignment of mortgage primarily involves lenders and investors, it can have implications for borrowers as well. Here are some important considerations for borrowers:
1. No Change in Loan Terms
Borrowers should be aware that the assignment of mortgage does not change the terms of their loan. The interest rate, monthly payments, and other loan terms remain the same. The only change is the entity to which payments are made.
2. Proper Record-Keeping
Borrowers must maintain accurate records of their mortgage payments and correspondence related to the assignment. This helps ensure that payments are correctly credited and can be vital in case of any disputes or issues.
3. Communication with the New Lender
If borrowers have questions or concerns about their mortgage after the assignment, they should reach out to the new lender or servicer. Open and clear communication can help address any issues that may arise during the transition.
4. Property Taxes and Insurance
Borrowers are still responsible for property taxes and homeowner’s insurance, even after the assignment of mortgage. These payments are typically not affected by the transfer of the loan.
The Role of Mortgage Servicers
Mortgage servicers play a crucial role in the assignment of mortgage process. This section will explore the responsibilities of mortgage servicers, their relationship with borrowers, and how they manage mortgage loans on behalf of investors or lenders.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Assignment is subject to various legal mortgage requirements and regulations that vary by jurisdiction. Discussing these legal aspects will help readers understand the legal framework governing the assignment of mortgages in their region and how it impacts the process.
Impact on Credit and Credit Reporting
The assignment of mortgage can have implications for borrowers’ credit reports and scores. Explore how mortgage assignment can affect credit histories, reporting by credit bureaus, and what borrowers can do to protect their credit during and after the assignment.
Assignment of Mortgage vs. Assumption of Mortgage
Differentiating between assignment of mortgage and assumption of mortgage is important. This section will explain the key differences, where one party takes over the mortgage and liability, while the other party merely transfers the loan to a new lender.
Impact on Property Taxes and Insurance
Taxes and insurance are essential components of homeownership. Explain how the assignment of mortgage may affect property tax payments and the homeowner’s insurance policy, as these are often escrowed into the monthly mortgage payment.
Potential Challenges and Disputes
Discuss common challenges or disputes that can arise during or after the assignment of mortgage, such as miscommunication, incorrect payment processing, or disputes over ownership rights. Offer advice on how to handle and resolve these issues.
Foreclosure and Default Scenarios
In the unfortunate event of mortgage default, understanding how the assignment of mortgage affects foreclosure proceedings is crucial. Explain how the assignee handles foreclosures and what options are available to borrowers facing financial difficulties.
Future Trends and Innovations
Explore emerging trends and innovations in the mortgage industry related to the assignment of mortgages. This could include the use of blockchain technology, digital mortgages, or other advancements that may impact the process.
In the complex world of real estate and mortgage financing , the assignment of mortgage plays a pivotal role in the movement of funds and management of risk. It allows lenders to efficiently manage their portfolios, mitigate risk, and participate in the secondary mortgage market. For borrowers, understanding the process and implications of mortgage assignment is essential to ensure the smooth continuation of their monthly mortgage payments.
As you navigate the world of homeownership or consider entering it, remember that the assignment of mortgage is a routine occurrence designed to benefit all parties involved. By staying informed and maintaining open communication with your lender or servicer, you can ensure that your mortgage loan remains a manageable and secure financial commitment.
In summary, purchase of mortgage is a vital mechanism within the mortgage industry that facilitates the transfer of mortgage loans from one party to another. This process helps lenders manage their portfolios, mitigate risk, and participate in the secondary mortgage market.
For borrowers, it means a change in the entity collecting their monthly mortgage payments but typically does not alter the terms of the original loan. Keeping accurate records and staying informed about the transition are crucial steps to ensure a smooth experience for homeowners. So, whether you’re a homeowner, lender, or investor, understanding assignment of mortgage is key to navigating the real estate landscape effectively.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, tax, or accounting advice.

Written by Alan Noblitt
Leave a comment.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Have a question?
Click the button below, and we will get back to you quickly

What Is Mortgage Assignment vs. Mortgage Assumption?

Mortgage assumption is now rare, while mortgage assignment is quite common.
Photodisc/Photodisc/Getty Images
More Articles
- 1. How to Invest in Property With No Money Down
- 2. What Does It Mean When a Mortgage Matures?
- 3. How to Assume a Promissory Note
Mortgage assignment, usually involving a mortgage lender, is very different from mortgage assumption, involving a homebuyer. Mortgage assignments occur when the original lender transfers the mortgage loan to a third party. Lenders who sell mortgages, which is most of them, assign their mortgages to others, who become the owners of the loans. Mortgage assumption occurs when a homebuyer assumes the home seller's existing loan, making all future payments. Buyers become the new mortgage borrowers.
Due on Sale Clauses
Most contemporary mortgages include due on sale clauses. This means that if a transfer of ownership occurs in the form of a home sale, the current mortgage must be paid off, as the balance becomes due. Due on sale language eliminates the option for a buyer to assume the mortgage on the home she's buying. Due on sale clauses have little effect on mortgage assignments to buyers or other third parties. Due on sale language helps make mortgage assignments easier, as the loan buyer knows the mortgage will be paid off when the property is sold.
Government Loans
While most mortgage loans are sold and assigned to others, few mortgages are assumable. Federal Housing Administration and Veterans Administration mortgages, commonly called government loans, are the only legally assumable home loans left in the mortgage market. Government loans also may be assigned to third party buyers, as other mortgage loans are. Assuming government loans is not automatic, as the homebuyers must qualify for these mortgages, meeting FHA and VA income and credit guidelines.
Third Parties
While most contemporary mortgage assignments involve lenders selling their loans, borrowers may assign their mortgages, if their loan note language permits, to third parties. Although this is technically a form of mortgage assumption, it differs from traditional legal assumption in that the original borrower who assigned the mortgage remains responsible for the loan balance if the assignee does not make scheduled monthly payments. While both mortgage assignment and assumption involve third parties, the position of mortgage loan buyers and mortgage assignees is legally different.
While rare, novation is more of a hybrid of mortgage assumption and mortgage assignment. When permitted, the mortgage loan is both assumed by and assigned to another borrower. However, the original borrower is no longer responsible for monthly payments or personally liable for the balance of the loan. Legally, novation equals a new obligation, but with the same terms, including interest rate, of the former mortgage loan. Few contemporary mortgage loan notes permit this form of assumption and assignment.
Significance
Until the 1970s, mortgage assumptions were common, while mortgage assignments were rare. After the federal government created mortgage companies Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac and after due on sale clauses became popular, the roles reversed. For the past four decades, few mortgage loans were assumable, while most mortgage loans were sold and assigned to third parties. The contemporary practices benefit lenders but do not help borrowers, particularly when interest rates rise. Lenders reduce their rate risk, shifting most of the risk to mortgage borrowers, since homebuyers cannot assume lower interest rate mortgage loans.
- Financial Web: Understanding Assumptions
- Lender 411: Transferring a Mortgage
Related Articles
How to invest in property with no money down, what does it mean when a mortgage matures, how to assume a promissory note, does it make a difference who is the buyer or co-buyer for financing, what is a subordinate clause in a mortgage, do mortgage borrowers have to be on the title deed, what is an assignment of trust deed, what is a loan maturity date for a mortgage, what is the difference between the deed of absolute sale and the deed of assignment, the disadvantages of owner-carried mortgages, refinance vs. restructure mortgage, warranty deed vs. deed of trust.
Zacks Research is Reported On:
Zacks Investment Research
is an A+ Rated BBB
Accredited Business.
Copyright © 2024 Zacks Investment Research
At the center of everything we do is a strong commitment to independent research and sharing its profitable discoveries with investors. This dedication to giving investors a trading advantage led to the creation of our proven Zacks Rank stock-rating system. Since 1986 it has nearly tripled the S&P 500 with an average gain of +26% per year. These returns cover a period from 1986-2011 and were examined and attested by Baker Tilly, an independent accounting firm.
Visit performance for information about the performance numbers displayed above.
NYSE and AMEX data is at least 20 minutes delayed. NASDAQ data is at least 15 minutes delayed.
- Personal Loans
- Buying a Home
- Home Improvements

Daniel Moore
Demystifying mortgage assignment: what it means for borrowers and lenders, demystifying mortgage assignment: what it means for borrowers and lenders. explore the process, benefits, and risks in our comprehensive guide..

A mortgage assignment is a financial process in which an existing mortgage is transferred from the current holder to another party. It can occur for various reasons, such as a lender selling the mortgage to another bank or financial institution.
Understanding mortgage assignment is essential for both borrowers and lenders, as it impacts the terms and the handling of the loan.
This brief introduction lays the groundwork for a deeper understanding of what mortgage assignment entails and its significance in the mortgage industry.
Understanding Mortgage Assignment
Mortgage assignment is when the original lender transfers the mortgage to another lender or financial institution. This can occur for various reasons, including the original lender wanting to liquidate assets or reduce risk exposure.
Steps in the Mortgage Assignment Process
Discover the critical steps in the mortgage assignment process, from initiation to completion, ensuring a smooth transfer between lenders and maintaining clarity for borrowers.
The process begins when the original lender assigns the mortgage to another party. This decision can be driven by a strategic need to manage financial resources more effectively.
The original and the new lender agree on the terms of the assignment. This agreement includes details about the transfer of rights and the responsibilities each party will hold.
Notification
The borrower is informed about the mortgage assignment. Borrowers must receive clear and concise information about what this change means for their mortgage terms.
Legal Documentation
The transfer of a mortgage is formalized through legal documents. These documents are critical as they protect the rights of all parties involved, ensuring the assignment adheres to financial regulations.
The mortgage assignment is complete once all parties have signed the legal documents and all conditions are met. The new lender now holds the rights and duties originally held by the original lender.
Critical Points for Borrowers and Lenders
Borrowers should pay attention to any changes in the terms of their mortgage, and both lenders need to handle the legal aspects carefully to prevent future disputes. Proper communication between all parties can smooth the transition and maintain trust.
Mortgage assignment doesn't have to be a complicated affair. Clear communication and adherence to legal procedures can be a straightforward process beneficial to all involved.

Advantages of Mortgage Assignment for Lenders and Borrowers
Mortgage assignment offers significant benefits for both lenders and borrowers, each finding unique advantages in the process. Understanding these benefits can help parties make informed decisions about their mortgage management strategies.
For Lenders
Mortgage assignment allows lenders to free up capital and reduce risk by transferring the mortgage to another party, optimizing their financial assets efficiently.
Freeing Up Capital
One of the primary advantages for lenders in the process of mortgage assignment is the ability to free up capital.
By transferring the rights of a mortgage to another financial institution or entity, the original lender can redeploy resources into new lending opportunities or other investments. This can improve the lender's liquidity and enhance its financial flexibility.
Reducing Risk
Mortgage assignment also allows lenders to reduce their risk exposure. When a mortgage is transferred, the associated risks, such as the possibility of default, are also transferred to the acquiring party.
This shift can help the original lender manage its risk portfolio more effectively, allowing for a more stable financial position.
For Borrowers
For borrowers, mortgage assignment can lead to better loan terms and ensure the continuity of their mortgage agreement with a new lender.
Potential for Better Terms
For borrowers, one of the critical advantages of mortgage assignment is the potential to secure better terms from a new lender. This new lender may offer lower interest rates, better repayment conditions, or more favorable terms to attract and maintain clients.
As a result, borrowers can enjoy cost savings and a loan structure more aligned with their current financial situation.
Continuity of Agreement
Despite the change in the lender, mortgage assignment ensures that the continuity of the mortgage agreement is maintained. This means that borrowers do not have to renegotiate the fundamental terms of their mortgage.
Their payment schedule, interest rate, and loan duration remain the same, providing them stability and predictability in their financial planning.
Potential Risks and Disadvantages of Mortgage Assignment
Mortgage assignment can be a valuable tool for managing financial portfolios for borrowers and lenders.
However, it comes with certain risks and disadvantages that must be considered. This section outlines some challenges, helping both parties make informed decisions.
In the mortgage assignment process, lenders face significant challenges, including legal complexities and managing borrower expectations, which require careful navigation to avoid disputes and dissatisfaction.
Legal Complexities and Potential Disputes
One of the primary concerns for lenders in the process of mortgage assignment is the array of legal complexities that can arise.
Transferring a mortgage from one lender to another involves meticulous documentation and strict adherence to legal standards, which, if not properly managed, can lead to disputes with borrowers. These disputes may revolve around misunderstandings about the mortgage terms or the new lender's responsibilities.
Challenges in Managing Borrower Expectations
Lenders may also face challenges in managing borrower expectations during a mortgage assignment. Borrowers might not fully understand the implications of their mortgage being assigned to another lender, which can lead to dissatisfaction or conflict.
Lenders must clearly and effectively communicate what a mortgage assignment means and how it will affect the borrower's loan terms and conditions.
This section examines borrowers' challenges during mortgage assignments, focusing on potential changes regarding the risks of engaging with a new lending institution.
Possible Changes in Mortgage Terms
For borrowers, one of the significant risks associated with mortgage assignment is the potential for changes in the terms of their mortgage.
When a new lender takes over a mortgage, they might adjust the interest rates, payment schedules, or other terms to align with their lending policies. Such changes can sometimes be unfavorable to borrowers, increasing their financial burden.
Risks of Dealing with a New Lending Institution
Additionally, borrowers face risks related to the reputation and stability of the new lending institution. If the new lender has less favorable customer service or a weaker financial position, it could impact the borrower's experience and mortgage security.
Borrowers must thoroughly research the new lender and ensure they are comfortable with their practices and stability.
Considering Mortgage Assignment? Fetch Your Rate Today
As we conclude our discussion on mortgage assignment, it's clear that borrowers and lenders can benefit from this process when managed effectively.
Whether you're a lender looking to reorganize your portfolio or a borrower facing a change in the lender, understanding the terms and conditions of mortgage assignment is critical.
If you're contemplating a mortgage assignment, now is the time to contact Fetch arate and see how this option might work.

Pledge vs Hypothecation vs Lien vs Mortgage vs Assignment
The difference between pledge, hypothecation, lien, mortgage, and assignment lies in the security charge that can be created on any asset held by a lender against the money lent (usually called the collateral). The type of asset charge defines whether the agreement can be classified as a pledge, lien, or mortgage. Let us see in detail the difference between pledge vs hypothecation vs lien vs mortgage vs assignment.
There are several types of security interests that can be adopted by banks or lenders depending upon the collateral involved and the circumstances. Different forms of creating charges on assets are as follows:
Hypothecation
Short summary table.
Pledge is commonly used for goods or securities such as gold, stocks, certificates, etc. The lender (pledgee) holds the actual possession of such securities until the borrower (pledger) has the borrowed amount with him. Once the borrowed amount has been returned, the securities are returned as well. If the pledger defaults on the loan amount, the pledgee can sell off the goods pledged to him as security in order to recover the principal and the interest amount. In this case risk of lending comparatively reduces because possession of assets is with the lender.
Hypothecation is usually when the charge is on movable assets rather than having a charge on fixed assets. However, hypothecation is different from pledges in the sense that the possession of such movable security stays with the borrower. Hence, in the event of default, the lender is first required to take possession / seize such property or asset in order to recover the principal and interest. An example of hypothecation is vehicle financing, where the lender has the asset that has been hypothecated against the loan with a bank. If the borrower defaults, the bank then takes possession of the vehicle after sufficient notice to recover the money.
Also Read: Hypothecation
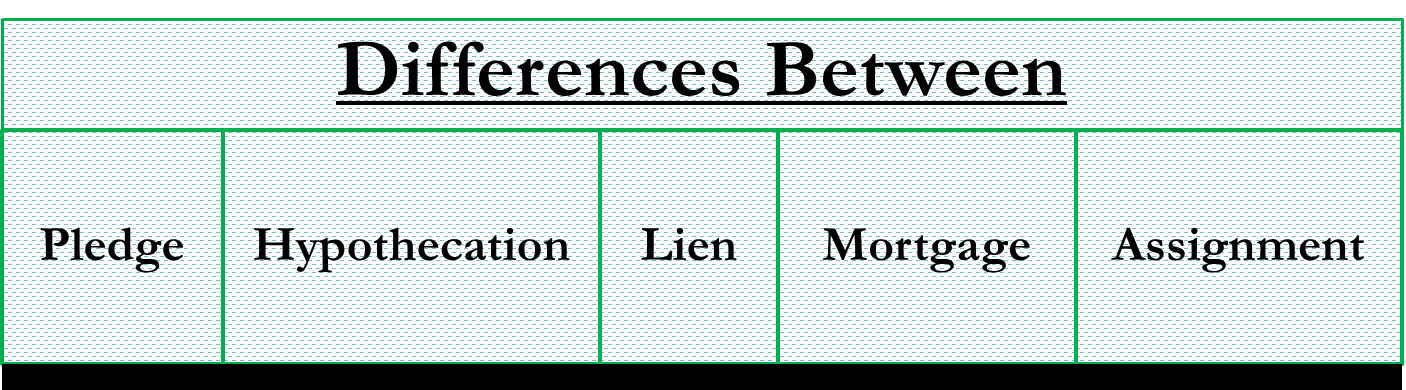
Under a lien, the lender gets the right to hold up a property or machinery used as collateral against funds borrowed. However, unless the contract states otherwise, the lender doesn’t have the right to sell the property or the asset if the borrower defaults on the loan. Examples of lien include rent receivable, unpaid fees, etc. It is a right given to the creditor to retain/possess the security until the loan amount g. Since possession is with the creditor, it is the strongest form of security. Lien can be on both movable and immovable property. But generally, lending companies choose to have mortgages on immovable property and lien on movable security like shares, gold, deposits, etc.
Under a mortgage , the legal ownership of the asset can be transferred to the lender if the borrower defaults on the loan amount. However, the borrower continues to remain in possession of the property. A mortgage is usually used for immovable assets (example: house, land, building, or any property which is permanently fixed to the earth or attached to the land). Home loans classify as mortgages.
An assignment is another type of charge on current assets or fixed assets. Under assignment, the charge is created on the assets held in the books. It is another mode of providing security against borrowing. Examples of assignments include life insurance policies, books of debts, receivables, etc., which the bank can finance. For example – A bank can finance against the book debts. The borrower assigns the book debts to the bank in such a case.
To get an idea about the difference between pledge vs hypothecation vs lien vs mortgage vs assignment, refer to the table below.
| Basis | Pledge | Hypothecation | Lien | Mortgage | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collateral | Goods or securities such as gold, stocks, certificates, etc | Movable assets | Property or machinery | Immovable assets | Current assets or fixed assets |
| Examples | Gold, stocks, certificates, etc. | Vehicle financing | Rent receivable, unpaid fees, etc | House, land, building, | Life insurance policies, books of debts, receivables, etc. |
Quiz on Pledge vs Hypothecation vs Lien vs Mortgage vs Assignment
Let’s take a quick test on the topic you have read here.
Your answer:
Correct answer:
SHARE YOUR RESULTS
Your Answers
RELATED POSTS
- Mortgage Vs. Hypothecation – Similarities and Differences
- Secured Loans
- Secured Personal Loans – Meaning, Features, Benefits and Drawbacks
- Recourse vs Non-Recourse Loan/Debt
- Floating Lien – Meaning, Importance and More
- Restrictive Debt Covenants on Term Loan Agreement

Sanjay Bulaki Borad
MBA-Finance, CMA, CS, Insolvency Professional, B'Com
Sanjay Borad, Founder of eFinanceManagement, is a Management Consultant with 7 years of MNC experience and 11 years in Consultancy. He caters to clients with turnovers from 200 Million to 12,000 Million, including listed entities, and has vast industry experience in over 20 sectors. Additionally, he serves as a visiting faculty for Finance and Costing in MBA Colleges and CA, CMA Coaching Classes.
5 thoughts on “Pledge vs Hypothecation vs Lien vs Mortgage vs Assignment”
Really simple and so easy to refer .Especially good for nonfinance people who aims to move to general top management .
Thanks for sharing. I really like your explanations.
Tysm sir it helps me easily to understand n differentiate between all type of securities
Really great way illustration. It helped me a lot.
I love the concept; so very easy to understand.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Lien Assignment Process and Procedure
The lien assignment process almost always begins with the owner’s mortgage lender (i.e. bank) commencing a foreclosure on its first deed of trust. Prior to the bank proceeding to foreclosure sale, it must submit a bid to the Public Trustee’s office. At that time, investors review the bank’s bid and determine if they would be interested in paying off the bank in exchange for acquiring the property. This is usually about the same time that investors obtain title work on the property and contact the association, its management company or our office to inquire about the potential purchase of the association’s lien. Most investors realize that even if no recorded lien exists, the association still may have an assignable lien by operation of Colorado Common Interest Ownership Act.
Assuming the investor gets in touch with our office (whether directly or following a referral from the manager or association), our firm will contact the board or management company for an updated ledger on the property. We then review the ledger and add in any time that may have been written off because of a bankruptcy and additional attorney fees that are not yet reflected on the ledger. We use this information to formulate a lien sale price. In some instances we will attempt to sell the lien for more than the total amount owed, but we always assign the lien for at least payment in full through the current month. Following an agreement with an investor to purchase the lien, our office processes the lien sale through the execution of a lien assignment document. This document sets forth the legal rights and obligations between the investor and the association and allows the investor to acquire property through a redemption process.
If the lien is sold, the association receives payment in full (or occasionally, more than payment in full) and the investor receives all rights associated with the association’s lien. The investor takes the completed lien assignment to the Public Trustee and files what is known as an Intent to Redeem. This document tells the Public Trustee that the investor has purchased the association’s lien and corresponding right to redeem at the Public Trustee’s sale. The investor then tenders payment to the Public Trustee for all amounts owed to the foreclosing lender. This process is known as redemption.
Following a successful redemption, the investor will take title to the property and will be issued a Public Trustee’s Deed. This Deed confirms that the investor now owns the property. It is important to remember that the Public Trustee’s Deed is sometimes issued several weeks after the investor actually takes legal title to a property. Technically, legal title transfers once all applicable redemption periods expire. Associations should contact our office if there are any questions about the actual date that a title transferred to an investor.
Usually, investors that acquire association liens through the lien assignment process are interested in rehabilitating the property and reselling it relatively quickly. However, during the time the investor owns the property, he or she is subject to all the same covenants as any other owner, including the obligation to pay assessments.
Keep In Touch
Sign up for our Newsletter and Blog today.
I'm Ready to Gain Some Altitude
Schedule a Consultation
If you’re looking for legal consultation, schedule one today .
F-1-17, Processing a Transfer of Ownership (04/13/2022)
Obtaining mi approval for a conventional mortgage loan, responding to a title transferred via grant deed, completing a transfer of ownership.
The servicer must process a transfer of ownership in accordance with Chapter D1-4, Transfers of Ownership .
When a transfer of ownership occurs for a mortgage loan, obtaining the mortgage insurer’s approval is either
part of the credit review process, or
not required unless the borrower requests a release of liability.
The servicer must review the MI policy for the specific provision regarding transfers of ownership, assumptions and releases of liability.
The servicer must evaluate all transfers of ownership as required in Chapter D1-4, Transfers of Ownership. When the servicer becomes aware of a property transfer through Grant Deed, it must complete the actions shown in the following table.
| ✓ | The servicer must… |
|---|---|
| Continue to report credit information related to a mortgage loan delinquency (including the acceptance of a Mortgage Release or the initiation of foreclosure proceedings) to credit bureaus in the borrower’s name. | |
| Determine that the title to the property is clear and marketable (by obtaining a title bring-down). | |
| File an (IRS Form 1099-A) if it accepts a Mortgage Release or acquires title to the property through foreclosure, using the borrower’s name and Social Security number (rather than a third-party company’s name and Tax Identification Number). The servicer should not file a |
The servicer must process any transfer of ownership in accordance with Chapter D1-4, Transfers of Ownership. The servicer must complete the applicable procedure in the following table depending on the type of transaction.
| Type of Transaction | Servicer Action | |
|---|---|---|
| An Exempt Transaction | The servicer must process the transfer of ownership as described in the following table. : Fannie Mae does not require an exempt transferee to assume the mortgage loan except in connection with a release of liability or in conjunction with a mortgage loan modification. | |
| Fannie Mae is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ) for execution.
: Once Fannie Mae returns the executed assignment of mortgage to the servicer, the servicer is authorized to execute the assumption or assumption and release agreement, as applicable, must record the agreement if required by applicable law, and must send a copy of the executed agreement (original recorded, if applicable) to its document custodian. | |
| the servicer is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ||
| A Transfer Subject to State Law Restrictions | The servicer must process the transfer of ownership as described in the following table. The servicer must include a release of liability provision in the transfer instruments if the borrower requested a release of liability and the mortgage insurer agreed to it. | |
| Fannie Mae is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | the servicer must either ) for execution.
: Once Fannie Mae returns the executed assignment of mortgage to the servicer, the servicer is authorized to execute the appropriate documents, as applicable, must record the document(s) if required by applicable law, and must send a copy of the executed document(s) (original recorded, as applicable) to its document custodian. | |
| the servicer is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | the servicer | |
| Regardless of the owner of record for the mortgage loan, if the servicer is required by applicable law to record the executed transfer documents, the servicer should request a title bring-down from the title insurer. The bring-down must | ||
| A Conventional Mortgage Loan With No Due-on-Sale Provision | The servicer must process the transfer of ownership as described in the following table, if the release of liability is approved. | |
| Fannie Mae is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ) for execution.
: Once Fannie Mae returns the executed assignment of mortgage to the servicer, the servicer is authorized to execute the assumption or assumption and release agreement, as applicable, must record the agreement if required by applicable law, and must send a copy of the executed agreement (original recorded, as applicable) to its document custodian. | |
| the servicer is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ||
| A Non-Exempt Transaction With an Exception due to the Loan Type and Creditworthy Purchaser | The servicer must process the transfer of ownership as described in the following table. The servicer must include a release of liability provision in the agreement if the borrower requested a release of liability and the mortgage insurer agreed to it. | |
| Fannie Mae is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ) for execution.
: Once Fannie Mae returns the executed assignment of mortgage to the servicer, the servicer is authorized to execute the agreement, must record the agreement if required by applicable law, and must send a copy of the executed agreement (original recorded, as applicable) to its document custodian. | |
| the servicer is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ||
| : When the transfer of ownership involves an ARM that does not include a lifetime interest rate change limitation in its terms, the servicer must include the following language in the assumption or assumption and release agreement, as applicable:
In addition, if the mortgage loan is convertible to a fixed-rate mortgage loan, the servicer also must include the following sentence:
To determine the appropriate interest rate to insert in this provision, the servicer should add 6% to the sum of the mortgage margin and the index that is in effect on the date that the assumption statement is prepared. If the transaction has not closed within 30 days, the servicer should establish a new rate based on the latest available index. | ||
| An Assumption of a Delinquent Mortgage Loan | The servicer must process the transfer of ownership as described in the following table. | |
| Fannie Mae is the mortgagee of record and the servicer does not have an assignment of mortgage | ) for execution. : Once Fannie Mae returns the executed assignment of mortgage to the servicer, the servicer is authorized to execute the assumption or assumption and release agreement, as applicable, must record the agreement if required by applicable law, and must send a copy of the executed agreement (original recorded, if applicable) to its document custodian. | |
| the servicer (or MERS) is the mortgagee of record, or if Fannie Mae is the mortgagee of record and the servicer has an assignment of mortgage | ||
| Regardless of the owner of record for the mortgage loan, if the servicer is required by applicable law to record the executed transfer documents, the servicer should request a title bring-down from the title insurer. The bring-down must | ||
| An FHA or VA Mortgage Loan | The servicer must process the transfer of ownership as described in the following table. | |
| Fannie Mae is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ) for execution.
Once Fannie Mae returns the executed assignment of mortgage to the servicer, the servicer is authorized to execute the assumption or assumption and release agreement, as applicable, must record the agreement if required by applicable law or applicable FHA/VA program requirements, and must send a copy of the executed agreement (original recorded, if applicable) to its document custodian. | |
| the servicer is the owner of record for the mortgage loan | ||
The table below provides references to recently issued Announcements that are related to this topic.
| Announcements | Issue Date |
|---|---|
| April 13, 2022 | |
| May 15, 2019 |

Have questions?
Get answers to your policy and guide questions, straight from the source.
Work with Fannie Mae
- Customer Login
- Password Reset
- Not a customer? Get Started
Products & Solutions
- Mortgage Products & Options
- Technology Apps & Solutions
Support & Resources
- Customer Service
- News & Events
- Learning Center
- Guide Forms
Other Sites
- The Marketing Center
- Fannie Mae's Consumer Website
- Duty to Serve
Servicing Guide

Download PDF Guide
(Published: July 10 2024 )
Servicing Questions? Ask Poli
Get answers to your Guide & policy questions with Fannie Mae's AI-powered search tool.
Guide Resources
Forms, announcements, lender letters, notices, and more.
Browse the Guide
- Copyright and Preface
- A1-1-01, Application and Approval of Seller/Servicer
- A1-1-02, Representation and Warranty Requirements
- A1-1-03, Evaluating a Servicer’s Performance
- A1-2-01, Servicer’s Termination of the Lender Contract
- A1-2-02, Fannie Mae’s Termination of the Lender Contract without Cause
- A1-3-01, Requirements for Voluntary Repurchase
- A1-3-02, Fannie Mae-Initiated Repurchases, Indemnifications, Make Whole Payment Requests and Deferred Payment Obligations
- A1-3-03, Repurchase Obligations Related to Bifurcated Mortgage Loans
- A1-3-04, Reporting the Repurchase
- A1-3-05, Redelivering a Mortgage Loan
- A1-3-06, Automatic Reclassification of MBS Mortgage Loans
- A1-4.1-01, Defining a Breach of Contract
- A1-4.1-02, Fannie Mae’s Remedies
- A1-4.2-01, Compensatory Fees Other Than Delays in the Liquidation Process
- A1-4.2-02, Compensatory Fees for Delays in the Liquidation Process
- A2-1-01, General Servicer Duties and Responsibilities
- A2-1-02, Servicer’s Duties and Responsibilities Related to MBS Mortgage Loans
- A2-1-03, Servicer's Duties and Responsibilities Related to Mortgage Loans with Resale Restrictions or Shared Equity Transactions
- A2-1-04, Execution of Legal Documents
- A2-1-05, Note Holder Status for Legal Proceedings Conducted in the Servicer’s Name
- A2-1-06, Use of Fannie Mae Trademarks
- A2-1-07, Subservicing
- A2-1-08, First Lien Mortgage Loan Requirements
- A2-1-09, Compliance with Requirements and Laws
- A2-2-01, Refinance and Lending Practices
- A2-3-01, Servicer Compensation
- A2-3-02, Servicing Fees for Portfolio and MBS Mortgage Loans
- A2-3-03, Yield Differential Adjustments
- A2-3-04, Late Charges as Compensation
- A2-3-05, Fees for Certain Servicing Activities
- A2-3-06, Prepayment Premiums
- A2-4-01, Quality Control Reviews
- A2-5-01, Ownership and Retention of Individual Mortgage Loan Files and Records
- A2-6-01, Custodial Documents
- A2-7-01, Concurrent Servicing Transfers
- A2-7-02, Pledge of Servicing Rights and Transfer of Interest in Servicing Income
- A2-7-03, Post-Delivery Servicing Transfers
- A2-8-01, Mortgage Electronic Registration System
- A2-9-01, General Requirements
- A2-9-02, Special Provision for Puerto Rico
- A3-1-01, Maintaining Fannie Mae Seller/Servicer Status
- A4-1-01, Staffing, Training, Procedures, and Quality Control Requirements
- A4-1-02, Establishing Custodial Bank Accounts
- A4-1-03, Addressing Borrower Inquiries and Disputes
- A4-2.1-01, Preventing Defaults and Managing Delinquencies
- A4-2.1-02, Property Inspection Vendor Management and Oversight
- A4-2.1-03, Managing Short Sales
- A4-2.1-04, Establishing Contact with the Borrower
- A4-2.1-05, Requirements for Collection and Foreclosure Prevention Strategies Unique to Second Lien Mortgage Loans
- A4-2.1-06, Adverse Action Notification Certification
- A4-2.1-07, Servicer's Duties and Responsibilities Related to Mortgage Loans with an Outstanding Non-Interest-Bearing Balance
- A4-2.2-01, Selecting and Retaining Law Firms
- A4-2.2-02, Law Firm Management and Oversight
- A4-2.2-03, Prohibition Against Servicer-Specified Vendors for Fannie Mae Referrals, Use of Vendors, and Outsourcing Companies
- A4-2.2-04, Law Firm Suspensions, Matter Transfers, and Terminations
- B-1-01, Administering an Escrow Account and Paying Expenses
- B-2-01, Property Insurance Requirements Applicable to All Property Types
- B-2-02, Property Insurance Requirements for One- to Four-Unit Properties
- B-2-03, Master Property Insurance Requirements for Project Developments
- B-2-04, Individual Property Insurance Requirements for Units in Project Developments
- B-3-01, Flood Insurance Requirements Applicable to All Property Types
- B-4-01, Additional Insurance Requirements
- B-5-01, Insured Loss Events
- B-5-02, Uninsured Loss Events
- B-6-01, Lender-Placed Insurance Requirements
- B-7-01, General Liability Insurance Requirements for Project Developments
- B-7-02, Fidelity/Crime Insurance Requirements for Project Developments
- B-8.1-01, Conventional Mortgage Insurance Servicer Responsibilities
- B-8.1-02, Paying Conventional Mortgage Insurance Premiums
- B-8.1-03, Replacing Conventional Mortgage Insurance Policies
- B-8.1-04, Termination of Conventional Mortgage Insurance
- B-8.2-01, FHA Mortgage Insurance Coverage Requirements
- B-8.2-02, Conversion of FHA Coinsured Mortgage Loans to Full Insurance
- B-8.2-03, Termination or Cancellation of FHA Mortgage Insurance and FHA Mortgage Insurance Premium
- C-1.1-01, Servicer Responsibilities for Processing Mortgage Loan Payments
- C-1.1-02, Processing Payment Shortages or Funds Received When a Mortgage Loan Modification Is Pending
- C-1.1-03, Automatically Drafting Payments from the Borrower’s Bank Account
- C-1.1-04, Accepting Biweekly Payments from Third-Party Payment Contractors
- C-1.2-01, Processing Additional Principal Payments
- C-1.2-02, Processing Short Sale Proceeds
- C-1.2-03, Processing Payments in Full
- C-1.2-04, Satisfying the Mortgage Loan and Releasing the Lien
- C-1.2-05, Charging for a Release of Lien
- C-2.1-01, Responsibilities for ARM Loan Servicing
- C-2.1-02, Notifying the Borrower Regarding Interest Rate and/or Payment Changes
- C-2.2-01, Identifying and Disclosing Adjustment Errors
- C-2.2-02, Assuming Responsibility for Conversion Notice Errors
- C-2.2-03, Determining Whether to Provide a Refund or Credit for Overcharges
- C-2.3-01, Processing ARM Conversions to Fixed Rate Mortgage Loans
- C-2.3-02, Notifying Fannie Mae of Conversions for Portfolio Mortgage Loans
- C-2.3-03, Repurchasing Converted MBS Mortgage Loans and Redelivering Them to Fannie Mae
- C-3-01, Responsibilities Related to Remitting P&I Funds to Fannie Mae
- C-3-02, Remitting Payoff Proceeds
- C-4.1-01, Notifying Credit Repositories
- C-4.2-01, Filing IRS Forms
- C-4.3-01, Servicer Responsibilities Related to Investor Reporting
- D1-1-01, Evaluating a Request for the Release, or Partial Release, of Property Securing a Mortgage Loan
- D1-1-02, Evaluating a First Lien Mortgage Loan for Charge-Off and Release of Lien
- D1-1-03, Evaluating a Second Lien Mortgage Charge-Off
- D1-2-01, Renovation Mortgage Loans
- D1-3-01, Evaluating the Impact of a Disaster Event and Assisting a Borrower
- D1-4.1-01, Determining Whether a Transfer of Ownership Is Permitted
- D1-4.1-02, Allowable Exemptions Due to the Type of Transfer
- D1-4.1-03, Allowable Exceptions Due to State Law Restrictions (“Window-Period” Mortgage Loans)
- D1-4.1-04, Transfers of Ownership by Grant Deed
- D1-4.1-05, Enforcing the Due-on-Sale (or Due-on-Transfer) Provision
- D1-4.2-01, Conventional Mortgage Loans that Do Not Include a Due-on-Sale (or Due-on-Transfer) Provision
- D1-4.2-02, Conventional Mortgage Loans That Include a Due- on-Sale (or Due-on-Transfer) Provision
- D1-4.3-01, Transfers of Ownership on FHA and VA Mortgage Loans
- D1-4.3-02, Transfers of Ownership on RD Mortgage Loans
- D1-5-01, Call Options and Cross-Default Provisions
- D1-6-01, Requesting to Waive Certain Rights under the Mortgage Loan
- D1-6-02, Handling Notices of Liens, Legal Action, Other Actions Impacting Fannie Mae’s Interest
- D1-6-03, Handling Property Forfeitures and Seizures
- D2-1-01, Determining if the Borrower’s Mortgage Payment is in Imminent Default
- D2-2-01, Achieving Quality Right Party Contact with a Borrower
- D2-2-02, Outbound Contact Attempt Requirements
- D2-2-03, Sending a Payment Reminder Notice
- D2-2-04, Sending a Borrower a Solicitation Package for a Workout Option
- D2-2-05, Receiving a Borrower Response Package
- D2-2-06, Sending a Breach or Acceleration Letter
- D2-2-07, Resolving an Appeal of a Mortgage Loan Modification Trial Period Plan Denial for a Principal Residence
- D2-2-08, Interviewing Face-to-Face with a Borrower for Certain FHA and HUD Mortgage Loans
- D2-2-09, Additional Borrower Contact Requirements for the Servicer of a Second Lien Mortgage Loan
- D2-2-10, Requirements for Performing Property Inspections
- D2-3.1-01, Determining the Appropriate Workout Option
- D2-3.1-02, Conditions of a First and Second Lien Mortgage Loan Modification for an MBS Mortgage Loan
- D2-3.1-03, Working with a Borrower that has a Group Home Mortgage Loan
- D2-3.1-04, Offering a Workout Option When Also Servicing a Subordinate Lien Mortgage Loan
- D2-3.1-05, Interacting with Mortgage Assistance Fund Program Providers
- D2-3.1-06, Notifying Fannie Mae of Lead-Based Paint Citations
- D2-3.2-01, Forbearance Plan
- D2-3.2-02, Repayment Plan
- D2-3.2-03, Government Mortgage Loan Modifications
- D2-3.2-04, Payment Deferral
- D2-3.2-05, Disaster Payment Deferral
- D2-3.2-06, Fannie Mae Flex Modification
- D2-3.3-01, Fannie Mae Short Sale
- D2-3.3-02, Fannie Mae Mortgage Release (Deed-in-Lieu of Foreclosure)
- D2-3.4-01, Military Indulgence
- D2-3.4-02, Offering a Mortgage Release (Deed-in-Lieu of Foreclosure) for a Second Lien Mortgage Loan
- D2-3.4-03, Assignment of a Mortgage Loan to the Insurer or Guarantor
- D2-3.4-04, Qualifying Mortgage Assumption Workout Option
- D2-4-01, Reporting a Delinquent Mortgage Loan to Fannie Mae
- D2-4-02, Reporting a Workout Option to Fannie Mae
- D2-4-03, Reporting Certain Workout Options to Treasury
- E-1.1-01, General Requirements for Referring a Mortgage Loan to a Law Firm
- E-1.1-02, Required Referral Documents
- E-1.1-03, Required Referral Data
- E-1.2-01, Timing of the Bankruptcy Referral
- E-1.2-02, Timing of the Foreclosure Referral for Mortgage Loans Generally
- E-1.2-03, Timing of the Foreclosure Referral for Second Lien Conventional Mortgage Loans Not Secured by a Principal Residence
- E-1.2-04, Timing of the Foreclosure Referral for Government Mortgage Loans
- E-1.3-01, General Servicer Responsibilities for Non-Routine Matters
- E-1.3-02, Reporting Non-Routine Litigation to Fannie Mae
- E-1.3-03, Reporting “Legal Filings” to MERS
- E-2.1-01, General Servicing Requirements for Mortgage Loans Under Bankruptcy Protection
- E-2.1-02, Confirming Bankruptcy Information
- E-2.1-03, Suspending Debt Collection Efforts
- E-2.1-04, Expected Servicer/Attorney Interaction During Bankruptcy Proceedings
- E-2.1-05, Filing a Notice of Appearance and Sending Proper Notices
- E-2.1-06, Reviewing Bankruptcy Reorganization Plans
- E-2.1-07, Preparing and Filing a Proof of Claim
- E-2.1-08, Monitoring Borrower Payments and Critical Dates
- E-2.1-09, Identifying Workout Opportunities
- E-2.1-10, Dealing with Delays in the Bankruptcy Process
- E-2.1-11, Remitting P&I for MBS Mortgage Loans That Are Part of a Bankruptcy
- E-2.2-01, Managing Chapter 7 Bankruptcies
- E-2.2-02, Managing Chapter 11 Bankruptcies
- E-2.2-03, Managing Chapter 12 Bankruptcies
- E-2.2-04, Managing Chapter 13 Bankruptcies
- E-2.3-01, Identifying Abusive Filers
- E-2.3-02, Addressing Individuals with Fractional Interests in a Security Property
- E-2.3-03, Handling Cramdowns of the Mortgage Debt
- E-2.3-04, Bankruptcies Involving Mortgage Loans Secured by Investment Properties
- E-2.3-05, Bankruptcies Involving Multiple Fannie Mae Mortgage Loans
- E-2.3-06, Responding to Bankruptcies Identified After Foreclosure Sale
- E-2.3-07, Cross-Border Insolvency Proceedings
- E-3.1-01, General Servicing Requirements Related to Foreclosure Proceedings
- E-3.1-02, Performing Due Diligence Prior to Considering Foreclosure
- E-3.1-03, Fannie Mae Address for Instruments of Record
- E-3.1-04, Addressing a Bankruptcy Filed During Active Foreclosure
- E-3.2-01, Conducting Prereferral Review
- E-3.2-02, Initiating Foreclosure Proceedings on a First Lien Conventional Mortgage Loan
- E-3.2-03, Initiating Foreclosure Proceedings on a Second Lien Conventional Mortgage Loan
- E-3.2-04, Postponing Foreclosure Referral for Mortgage Loans Not Secured by a Principal Residence
- E-3.2-05, Expected Servicer/Attorney Interaction During Foreclosure Proceedings
- E-3.2-06, Conducting Borrower Outreach During Foreclosure
- E-3.2-07, Impact of Engagement with a Mortgage Assistance Fund Program Provider
- E-3.2-08, Processing Reinstatements During Foreclosure
- E-3.2-09, Conducting Foreclosure Proceedings
- E-3.2-10, Paying Certain Expenses During the Foreclosure Process
- E-3.2-11, Collecting Under an Assignment of Rents
- E-3.2-12, Performing Property Preservation During Foreclosure Proceedings
- E-3.2-13, Addressing Title Defects Generally
- E-3.2-14, Addressing Title Defects for Bifurcated Mortgage Loans
- E-3.2-15, Allowable Time Frames for Completing Foreclosure
- E-3.3-01, Completing Preforeclosure Sale Review
- E-3.3-02, Certifying the Status of Workout Negotiations Prior to Foreclosure Sale
- E-3.3-03, Inspecting Properties Prior to Foreclosure Sale
- E-3.3-04, Marketing the Foreclosure Sale and Using Foreclosure Auction Services
- E-3.3-05, Issuing Bidding Instructions
- E-3.3-06, Handling a Suspension or Reduction of the Redemption Period
- E-3.3-07, Pursuing a Deficiency Judgment
- E-3.4-01, Suspending Foreclosure Proceedings for Workout Negotiations
- E-3.4-02, Canceling the Foreclosure Sale for a Completed Workout
- E-3.5-01, Foreclosure of a Property Securing an MBS Mortgage Loan
- E-3.5-02, Handling Third-Party Sales
- E-3.5-03, Providing Evidence of Title
- E-4.1-01, Notifying Fannie Mae of an Acquired Property
- E-4.1-02, Eliminations and Rescissions of Foreclosure Sales
- E-4.2-01, Completing Conveyance Documents
- E-4.2-02, Handling Reconveyance to the Insurer or Guarantor
- E-4.3-01, Managing the Property Post-Foreclosure Sale
- E-4.3-02, Inspecting Properties Post-Foreclosure Sale
- E-4.3-03, The Broker's, Agent's, or Property Management Company's Responsibilities
- E-4.3-04, Handling Eviction Proceedings
- E-4.4-01, Continuing or Canceling Property Insurance Coverage
- E-4.4-02, Remitting Property Insurance Settlement Proceeds or Unearned Premium Refunds
- E-4.4-03, Canceling Flood Insurance Coverage for Acquired Properties
- E-4.4-04, Remitting Flood Insurance Settlement Proceeds or Unearned Premium Refunds
- E-4.5-01, Filing MI Claims for Conventional Mortgage Loans or for Other Mortgage Loans for which Fannie Mae Bears the Risk of Loss
- E-4.5-02, Filing MI Claims for FHA Mortgage Loans
- E-4.5-03, Filing MI Claims for FHA Coinsured Mortgage Loans
- E-4.5-04, Filing MI Claims for FHA Title I Loans
- E-4.5-05, Filing MI Claims for HUD Section 184 Mortgage Loans
- E-4.5-06, Filing MI Claims for VA Mortgage Loans
- E-4.5-07, Filing MI Claims for RD Mortgage Loans
- E-5-01, Requesting Reimbursement for Expenses
- E-5-02, Servicer Responsibilities Prior to Requesting Reimbursement of Attorney Fees and Costs
- E-5-03, Allowable Bankruptcy Fees
- E-5-04, Allowable Foreclosure Fees
- E-5-05, Reimbursing Law Firms/Reimbursement of Uncollected Fees, Costs or Advances
- E-5-06, Technology Fees and Electronic Invoicing
- E-5-07, Other Reimbursable Default-Related Legal Expenses
- F-1-01, Servicing ARM Loans
- F-1-02, Escrow, Taxes, Assessments, and Insurance
- F-1-03, Establishing and Implementing Custodial Accounts
- F-1-04, Evaluating a Request for the Release, or Partial Release, of Property Securing a Mortgage Loan
- F-1-05, Expense Reimbursement
- F-1-06, Filing an MI Claim for a Liquidated Mortgage Loan or Acquired Property
- F-1-07, Handling Property Forfeitures and Seizures
- F-1-08, Managing Foreclosure Proceedings
- F-1-09, Processing Mortgage Loan Payments and Payoffs
- F-1-10, Obtaining and Executing Legal Documents
- F-1-11, Post-Delivery Servicing Transfers
- F-1-12, Preparing to Implement a Workout Option
- F-1-13, Processing a Fannie Mae Mortgage Release (Deed-In-Lieu of Foreclosure)
- F-1-14, Processing a Fannie Mae Short Sale
- F-1-15, Processing a Government Mortgage Loan Modification
- F-1-16, Processing a Repayment Plan
- F-1-17, Processing a Transfer of Ownership
- F-1-18, Processing a Workout Incentive Fee
- F-1-19, Processing a Military Indulgence
- F-1-20, Remitting and Accounting to Fannie Mae
- F-1-21, Reporting a Delinquent Mortgage Loan via Fannie Mae’s Servicing Solutions System
- F-1-22, Reporting a Workout Option via Fannie Mae’s Servicing Solutions System
- F-1-23, Reporting to Third Parties
- F-1-24, Requesting Fannie Mae’s Approval via Fannie Mae’s Servicing Solutions System
- F-1-25, Reclassifying or Voluntary Repurchasing an MBS Mortgage Loan
- F-1-26, Servicing eMortgages
- F-1-27, Processing a Fannie Mae Flex Modification
- F-1-28, Reviewing a Transfer of Ownership for Credit and Financial Capacity
- F-2-01, Bankruptcy Referral and Completion Timelines
- F-2-02, Incentive Fees for Workout Options
- F-2-03, Compensatory Fee Calculation Examples
- F-2-04, Firm Minimum Requirements
- F-2-05, Historical Yield Differential Adjustment Provisions
- F-2-06, Mortgage Insurer Delegations for Workout Options
- F-2-07, Reporting the Principal Amount for Mortgage Loans with Principal Forbearance
- F-2-08, Servicing Fees for MBS Mortgage Loans
- F-2-09, Servicing Fees for Portfolio Mortgage Loans
- F-2-10, Fannie Mae’s Workout Hierarchy
- F-3-01, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: A
- F-3-02, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: B
- F-3-03, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: C
- F-3-04, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: D
- F-3-05, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: E
- F-3-06, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: F
- F-3-07, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: G
- F-3-08, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: H
- F-3-09, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: I
- F-3-10, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: J
- F-3-11, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: K
- F-3-12, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: L
- F-3-13, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: M
- F-3-14, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: N
- F-3-15, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: O
- F-3-16, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: P
- F-3-17, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: Q
- F-3-18, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: R
- F-3-19, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: S
- F-3-20, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: T
- F-3-21, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: U
- F-3-22, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: V
- F-3-23, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: W
- F-3-24, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: X
- F-3-25, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: Y
- F-3-26, Acronyms and Glossary of Defined Terms: Z
- F-4-01, References to Fannie Mae's Website
- F-4-02, List of Contacts
- F-4-03, List of Lender Contracts
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Personal Finance
Satisfaction of Mortgage: What it is, How it Works
Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Julia_Kagan_BW_web_ready-4-4e918378cc90496d84ee23642957234b.jpg)
Lea Uradu, J.D. is a Maryland State Registered Tax Preparer, State Certified Notary Public, Certified VITA Tax Preparer, IRS Annual Filing Season Program Participant, and Tax Writer.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/lea_uradu_updated_hs_121119-LeaUradu-7c54e49efe814a048e41278182ba02f8.jpg)
What Is a Satisfaction of Mortgage?
A satisfaction of mortgage is a document that confirms a mortgage has been paid off and details the provisions for the transfer of collateral title rights. Mortgage lenders are required to prepare satisfaction of mortgage documents that must be signed by all parties associated with the mortgage loan and collateral title.
Key Takeaways
- A satisfaction of mortgage is a signed document confirming that the borrower has paid off the mortgage in full and that the mortgage is no longer a lien on the property.
- Lending institutions are responsible for preparing and filing the satisfaction of mortgage with the appropriate county recorder, land registry office, city registrar, or recorder of deeds.
- Some borrowers prepay their mortgages by making extra mortgage payments in an effort to pay off their mortgages faster.
- A satisfaction of mortgage document includes details of the mortgage loan, provisions releasing the lender from a lien against the property, and the steps taken to transfer the property title.
How a Satisfaction of Mortgage Works
Lending institutions are responsible for preparing and filing the satisfaction of mortgage documents. Procedures surrounding satisfaction of mortgage documents and their filing are governed by individual states.
Many financial planners recommend accelerating mortgage payments in order to pay off a mortgage faster . Making the occasional extra mortgage payment—assuming the lender allows it without penalty—can slash months off the mortgage term and save thousands in interest costs. A viable strategy to expedite paying off a mortgage will help homeowners get the coveted satisfaction of mortgage document even sooner.
The satisfaction of mortgage is also useful if the owner wants to pledge the property as collateral for a business or personal loan. Of course, the merits of taking out a loan using the house as collateral, after spending decades paying off the mortgage, should be thoroughly considered before being done.
The Satisfaction of Mortgage Documentation Process
When a borrower prepays their mortgage or makes the final mortgage payment, a satisfaction of mortgage document must be prepared, signed, and filed by the financial institution in ownership of the mortgage. The satisfaction of mortgage document is created by a lending institution and their legal counsel.
Oftentimes the original mortgage lender will be responsible for the mortgage throughout its life. In some cases, a mortgage may have been sold by the mortgage lender to another financial institution. If sold, the owner of the mortgage at the time of the final payment is responsible for completing the satisfaction of mortgage documentation. If multiple parties have been involved in the loan, then it may take a few weeks for the final satisfaction of mortgage document to be prepared.
A satisfaction of mortgage document will include the names of all parties associated with the mortgage. Other basic information will include the details of the mortgage loan and its payments, an acknowledgment that all payments have been made in full, details on the mortgage loan’s collateral property, provisions releasing the lender from a lien against the property, and the steps taken to transfer the property title .
A satisfaction of mortgage document must be signed by all parties to be valid. Once signed it must be filed according to the procedures mandated by the state. Usually, the documentation will be filed with the county recorder, land registry office, city registrar, or recorder of deeds .
Once the satisfaction of mortgage is recorded with the appropriate agency, the mortgagor (the individual or entity that borrowed the money to buy the property) will have a clear title to the property.
Special Considerations
While the borrower is not directly responsible for creating the satisfaction of mortgage document and filing it with the appropriate agency, they should still follow the process closely to ensure that all steps have been completed. Some states will provide a specific timeframe for the completion of the satisfaction of mortgage documents. This can work to the advantage of the borrower in ensuring that the process occurs in a timely manner.
Once the process for the satisfaction of mortgage document has been completed, the borrower should also receive filing confirmation from the appropriate filing agency. In the event that a satisfaction of mortgage is not filed and recorded with the appropriate agency , the property could continue to show a lien against it despite repayment.
Cornell Law School Legal Information Institute. " 46 CFR § 67.265 - Requirements for Instruments Evidencing Satisfaction or Release ."
South Carolina Legislature. " Title 29 - Mortgages and Other Liens ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-670982192-dff89be201f8448dad0333580f1bdf77.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Difference Between Assignment and Transfer
The difference between assignment and transfer is that assign means it's legal to transfer property or a legal right from one person to another. 3 min read
The difference between assignment and transfer is that assign means it's legal to transfer property or a legal right from one person to another, while transfer means it's legal to arrange for something to be controlled by or officially belong to another person.
When used as verbs, assign means to set apart or designate something for a purpose while transfer means to pass or move from one person, place, or thing to someone or someplace else. When used as nouns, assign means the assignee and transfer is the act of removing or conveying something from one person, thing, or place to another. Transfer generally refers to titles whereas assignment is used with obligations and rights.
Definitions of Assignment and Transfer
- Assignment: Assignment is used in real estate law and contracts law. It covers the transfer of rights held by the assignor to the assignee.
- Transfer: To remove or convey from one person or place to someone or somewhere else.
Distinction Between Assignment and Transfer
When distinguishing between assignment and transfer, take licenses, for example. Licenses are contracts that don't allow legal action for infringement. They fall under state law. Therefore, state law will decide whether the license is an obligation or right that can be transferred or assigned legally.
One way to distinguish this example is that an individual contract under an agreement cannot be assigned, like entitlement to grant back royalties . In addition, the contract cannot be transferred. You need to break it down and figure out what the actual issue is — the parties' intent. An additional distinction is when the contract holder is an entity and the business owners want to transfer a portion or all of their stock. This can be seen as an implied transfer of the whole contract. However, it would not likely be an assignment of the rights covered under this agreement.
Difference Between Assign and License
The key difference between assign and license is that with a license, the person who grants permission, known as the licensor, keeps an interest in the product being licensed . In an assignment, the assignor will transfer his or her rights to the product or property being assigned.
Another difference is that assignments must be in writing and a license can be executed without being written. Consider, for example, intellectual property such as patents. Patents can be licensed verbally in some instances, but assignments for patents must be in writing and filed with the United States Patent and Trademark Office .
Assignments grant the assignee full ownership of a product or property. Therefore, an assignment will typically cost more to acquire than a license.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there ever situations in which a license can be transferred but is not assignable?
- Yes, in the case of allowing an assignment to one of your affiliates, the assignor would still be liable for the performance of the agreement under general assignment law. In this situation, you would not typically permit a transfer, because in a transfer, the person transferring would not maintain any obligations related to performance. Don't rely solely on this general understanding, but still expressly detail your agreement on what a licensee can legally do.
How will transfer and assignment rights affect someone's ability to sublicense?
- In theory, if a licensee has the authority to assign license rights to someone else, you could argue that it also provides the right to sublicense it. The issue here is that with a sublicense, the person sublicensing it keeps a license right, therefore effectively creating two licensees. With an assignment, only one right is assigned, and the assignee is the one who has possession of the license. With well-drafted licenses, the right to sublicense is not typically implied, as the licensor is the one who reserves all rights that are not expressly granted.
What is the effect of poorly drafted licenses?
- A poorly drafted license could result in giving someone implied rights to also sublicense. An example is a software license that allows a licensee to access the software without clarifying any restrictions or clearly defining the word “use.” This means that, depending on what this software is supposed to do, someone could think the term “use” means the licensee has permission to grant a sublicense as part of their usage rights.
If you need help understanding the difference between assignment and transfer, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel only accepts the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Assignment Law
- Assignment and Novation Agreement: What You Need to Know
- Legal Assignment
- Assignment Legal Definition
- Assignment Of Contracts
- Assignment of Rights and Obligations Under a Contract
- Partial Assignment of Contract
- Assignment of Rights Example
- What Is the Definition of Assigns
- Transfer of Intellectual Property
Pledge Vs Hypothecation Vs Mortgage Vs Assignment

Sooner or later, majority of people require loan in order to meet their financial requirement to purchase any asset or good. There are many financial institutions like banks, NBFCs, etc. which offer loans to the customers. From the point of view of the lender, it is always good to keep a security against given loan in order to safeguard it in case of any default by the borrower.

Whenever an Individual or a Non-Individual applies for a loan, the bank or the lender asks for any security for this purpose. Pledge, Hypothecation and Mortgage are different terms that are used to create a charge on the assets which is given by the borrower to the lender.
When an applicant wants to avail any loan, the bank or the lender always keeps a security in the form of some assets. The purpose behind keeping a security by the bank is that it has the right to sell that asset, in case the borrower defaults in repayment of the loan and realise the amount.
Pledge is used when the lender (Pledgee) takes actual possession of the asset pledged. In case of Hypothecation, possession of the asset remains with the borrower. Loan is given on security of immovable property, in case of Mortgage. Assignment is used when the owner of a contract (Assignor) handovers a contract to another party (Assignee). Assignment gives the assignee, right of all the responsibilities and all the benefits of the contract assigned.
What is Pledge?
Definition: As per Section 172 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, Pledge is the bailment of goods as a security for the payment of a debt or performance of a promise. The bailor in case of Pledge is known as Pawnor and the bailee is known as Pawnee.
Borrower needs to provide the bank any asset or good that is worth the same amount or more than the loan which he is taking from the bank.
All about Pledge
- Pledge is a kind of Special Contract
- Pledge is a part of Bailment
- Pledge is a contract by which possession of goods or assets is transferred as a security
- Pledger or Pawnor is the person who gives goods as a security. He is the borrower
- Pledgee or Pawnee is the person who receives goods as a security. He is the lender
- Pledgee is bound to return pledged goods on the successful repayment of loan
- A pledgee has no right to use the goods pledged
- A Pledgee has the right to sell the goods pledged, on default after giving a notice to the Pledger
Essentials of Contract of Pledge
- There must be a Lawful Purpose
- The pledged goods must be long lasting
- Delivery of Goods/ Security
- Return of Goods
Duties of Pawnor (Pledger)
- Duty to repay the loan
- Duty to pay expenses in case of default
Right of Pawnor (Pledger)
- Right to redeem the goods pledged
- Right to receive the increase
Duties of Pawnee (Pledgee)
- Duty not to use pledged goods
- Duty to return the goods on the successful repayment of loan
Right of Pawnee (Pledgee)
- Right to retain the pledged goods
- Right to extraordinary expenses
- Right to sell the goods in case of default by the Pawnor
Interested to know Reasons to use Debit Card
What is Hypothecation?
Definition: As per Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, hypothecation is defined as "a charge in or upon any movable property, existing or future, created by a borrower in favour of a secured creditor without delivery of possession of the movable property to such creditor, as a security for financial assistance, and includes floating charge and crystallization into fixed charge on movable property".
Hypothecation is used as a security of movable assets while taking a loan from the bank. Here the possession of the security remains with the borrower instead of the lender. When the borrower is not able to repay the loan and its interest, then the bank has the right to sell the hypothecated asset such as car, two wheeler, etc. and recover the outstanding loan amount along with accrued interest.
All about Hypothecation
- Hypothecation is a charge created on movable assets
- Under Hypothecation, possession of the asset remain with the borrower
- Loan Period is smaller
- Loan amount is comparatively lesser
- The bank should verify that the party has a good reputation. It can check the property regularly. It can even ask the hypothecator to submit periodic report of the property
- There may be some incidents wherein the borrowers may cheat the banker by either partly selling goods hypothecated to the bank or not keeping the required stock of goods. Here, if bank finds that borrower is trying to mischief, it can insist upon or can convert hypothecation to pledge and takes over possession of the goods and keeps the same under its own custody
Interested to know Small Finance Bank Vs Payments Bank Vs Commercial Bank
What is Mortgage?
Definition: As per Section 58 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882, Mortgage is the transfer of an interest in specific immovable property for the purpose of securing payment of money advanced by way of loan, existing or future debt, or the performance of an engagement which may give rise to a pecuniary liability.
All about Mortgage
- Mortgage is a charge created on immovable assets
- Immovable Assets include land, building, or anything attached to earth
- The transferor is called a mortgagor
- The transferee a mortgagee
- The principal money and interest of which payment is secured for the time being is called the Mortgage Money
- The instrument (if any) by which the transfer is effected is called a Mortgage Deed
- Possession of the asset remain with the borrower
- Loan Period is longer
- Loan amount is comparatively higher
Essentials of Mortgage
- Transfer of Interest
- Specific Immovable Property
- To Secure the Payment of a Loan
- Return of interest of Property
Types of Mortgage
- Simple Mortgage
- English Mortgage
- Anomalous Mortgage
- Usufructuary Mortgage
- Mortgage by Conditional Sale
- Mortgage by deposit of title of deeds
Interested to know You can invest as low as Rs. 100 in a Mutual Fund
What is Assignment?
Assignment is an agreement between two parties wherein one party transfers some or all his ownership rights on a particular property owned by him to the other party. After Assignment, the property is transferred to the person receiving the property rights.
All about Assignment
- Assignment is an agreement between two parties
- The property owner transferring the ownership right is called Assignor
- The person receiving the property right is called Assignee
- Assignor can transfer the rights either partly or fully
- Assignment is irrevocable
- Assignment is used generally in case of insurance policy or annuity
- Assignment can either be made by endorsement on the insurance policy or by some separate instrument
- After Assignment, the property is transferred to the Assignee
- Assignee gets all the rights of the assigned item
- Assignee can deal with the assigned item in any manner as per his wish
- If the insured person dies, the insurance company pays the outstanding amount of debt of the insured person (assignor) to the assignee and then pays the rest of the amount to the beneficiaries of the insurance policy
Types of Assignment
- Absolute Assignment: In it, Assignor transfer all ownership rights to the Assignee
- Collateral Assignment: In it, Assignor transfers a part of his ownership rights to the assignee which is limited upto to outstanding loan value and the remaining ownership rights with the assignor (insured person)
Benefits of Assignment
- Assignor gets loan more easily
- Assignee is more secured in case of demise of the borrower or default by the borrower
Find below major differences among Pledge, Hypothecation, Mortgage and Assignment:
| Basis of Difference | Pledge | Hypothecation | Mortgage | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To avail secured loan easily | Getting smaller amount of loan in an easy way alongwith possession of the asset | Availing higher amount of loan for immovable assets in a simple way at comparitively lower interest rates | To cover outstanding amount of debt |
| Act under which it is defined | Section 172 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 | Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act | Section 58 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882 | N.A. |
| Definition | Pledge is the bailment of goods as a security for the payment of a debt or performance of a promise. | Hypothecation is a charge in or upon any movable property, existing or future, created by a borrower in favour of a secured creditor without delivery of possession of the movable property to such creditor, as a security for financial assistance, and includes floating charge and crystallization into fixed charge on movable property | Mortgage is the transfer of an interest in specific immovable property for the purpose of securing payment of money advanced by way of loan, existing or future debt, or the performance of an engagement which may give rise to a pecuniary liability | An agreement between two parties wherein one party transfers some or all his ownership rights on a particular property owned by him to the other party |
| Type of Assets/ Goods | May be Movable or Immovable but must be long lasting | Movable | Immovable | Movable |
| Loan Period | Average | Smaller | Larger | Larger |
| Loan Amount | Moderate | Lesser | Higher | Higher |
| Possession of Asset | Pledgee | Hypothecator (Borrower) | Borrower | Assignee |
| Owenership of Asset | Pledger | Hypothecator (Borrower) | Borrower | Assignee |
| Rights to sell the Asset | A Pledgee has the right to sell the goods pledged, on default after giving a notice to the Pledger | Lender | If the mortgagor fails to repay the loan, the mortgagee has the right to sell the property and recover the loan from the sale amount | N.A. |
| Right to use the assets or goods | A pledgee has no right to use the goods pledged | Hypothecator (Borrower) | Borrower | N.A. |
| Others | Borrower can not use pledged asset during the term of loan | N.A. | Generally, policy of borrower is also assigned with mortgage | N.A. |
| Example | Gold Loan, Loan against NSCs, etc. | Vehicle Loan, Loan against Securities, etc. | Housing Loans | Assignment of Insurance Policy while taking home loan |
Important Points to note
- Term "Mortgage" must only be used in connection with immovable assets.
- Terms "Pledge" and "Hypothecation" may generally be used in case of movable assets.
- Where a mortgage of movable is created by delivery of possession of goods, it is known as Pledge.
- Where a mortgage of movable is created without delivery of possession, it is called Hypothecation.
- Loans given under hypothecation are not so secured from point of view of lender's safety.

Personal Finance Blogs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An assignment transfers all the original mortgagee's interest under the mortgage or deed of trust to the new bank. Generally, the mortgage or deed of trust is recorded shortly after the mortgagors sign it, and, if the mortgage is subsequently transferred, each assignment is recorded in the county land records.
The assignment of mortgage needs to include the following: The original information regarding the mortgage. Alternatively, it can include the county recorder office's identification numbers. The borrower's name. The mortgage loan's original amount. The date of the mortgage and when it was recorded.
Mortgages are assigned using a document called an assignment of mortgage. This legally transfers the original lender's interest in the loan to the new company. After doing this, the original lender will no longer receive the payments of principal and interest. However, by assigning the loan the mortgage company will free up capital.
An assignment of a mortgage refers to an assignment of the note and assignment of the mortgage agreement. Both the note and the mortgage can be assigned. To assign the note and mortgage is to transfer ownership of the note and mortgage. Once the note is assigned, the person to whom it is assigned, the assignee, can collect payment under the ...
Mortgage assignment is a common practice used by lenders to better manage their loan portfolios. Lenders might raise funds to offer more loans or issue new mortgages by selling or transferring mortgage loans to other financial organizations. This procedure aids in keeping their portfolios risk-balanced and liquid. 2.
A transfer of mortgage is the reassignment of an existing mortgage from the current holder to another person or entity. Not all mortgages can be transferred to another person. If a mortgage can be ...
Mortgage assignment, usually involving a mortgage lender, is very different from mortgage assumption, involving a homebuyer. ... This means that if a transfer of ownership occurs in the form of a ...
An assignment of mortgage is a legal term that refers to the transfer of the security instrument that underlies your mortgage loan − aka your home. When a lender sells the mortgage on, an investor effectively buys the note, and the mortgage is assigned to them at this time. The assignment of mortgage occurs because without a security ...
Every transfer of a mortgage loan, whether an "absolute" transfer or a limited assignment as "collateral" for another loan, starts with the transfer of the borrower's promissory note from the existing lender to an assignee. Some ancient cases suggest that the holder of a promissory note can . in . some circumstances transfer it with
A mortgage assignment is a financial process in which an existing mortgage is transferred from the current holder to another party. It can occur for various reasons, such as a lender selling the mortgage to another bank or financial institution. Understanding mortgage assignment is essential for both borrowers and lenders, as it impacts the ...
While a mortgage (or deed of trust) is a vital document in taking out a home loan, a promissory note defines the terms and details of the loan and creates the obligation for the homeowner to repay the loan. A mortgage, on the other hand, is a type of security instrument and is discussed in more detail below. When an investor purchases a loan ...
The difference between pledge, hypothecation, lien, mortgage, and assignment lies in the security charge that can be created on any asset held by a lender against the money lent (usually called the collateral). The type of asset charge defines whether the agreement can be classified as a pledge, lien, or mortgage.
What does Assignment of Mortgage mean: The most common example of an Assignment of Mortgage is when a mortgage lender transfers/sells the mortgage to another lender. This can be done more than once until the balance is paid. The lender does not have to inform the borrower that the mortgage is being assigned to another party.
If the assignment to the foreclosing party is not valid, this may be a viable defense to a foreclosure. In some states, you can demand that the foreclosing party produce a written assignment of the mortgage. If it does not have an assignment or failed to record it as required by state law, this may result in the dismissal of the foreclosure ...
An "assignment" is the document that's the legal record of the mortgage transfer from one entity to another. If you're a homeowner facing foreclosure and the lender sold your loan to a new owner but didn't complete a proper assignment of mortgage, you might be able to challenge the foreclosure in court. In This Article.
The mortgage, on the other hand, is transferred by an assignment. Most mortgages have a provision that permits the mortgagor (the person who holds the mortgage) to assign it to another.
Define Transfer of Lien. means an absolute assignment of note and liens (including, without limitation, all mortgages and any other security for each of the Assigned Loans) or other similar document transferring a lien or security interest, executed by Borrower or any Guarantor to Administrative Agent, for the benefit of the Lenders, in form agreed to by Borrower and Administrative Agent ...
Posted September 17, 2011. Tweet. The lien assignment process almost always begins with the owner's mortgage lender (i.e. bank) commencing a foreclosure on its first deed of trust. Prior to the bank proceeding to foreclosure sale, it must submit a bid to the Public Trustee's office. At that time, investors review the bank's bid and ...
The servicer must process a transfer of ownership in accordance with Chapter D1-4, Transfers of Ownership. When a transfer of ownership occurs for a mortgage loan, obtaining the mortgage insurer's approval is either. part of the credit review process, or. not required unless the borrower requests a release of liability.
A satisfaction of mortgage document includes details of the mortgage loan, provisions releasing the lender from a lien against the property, and the steps taken to transfer the property title. How ...
Assignment: Assignment is used in real estate law and contracts law. It covers the transfer of rights held by the assignor to the assignee. Transfer: To remove or convey from one person or place to someone or somewhere else. Distinction Between Assignment and Transfer. When distinguishing between assignment and transfer, take licenses, for example.
Pledge, Hypothecation and Mortgage are different terms that are used to create a charge on the assets which is given by the borrower to the lender. When an applicant wants to avail any loan, the bank or the lender always keeps a security in the form of some assets. The purpose behind keeping a security by the bank is that it has the right to ...