Density and Specific Gravity - Practice Problems
Jump to: Rock and Mineral density | Rock and mineral specific gravity You can download the questions (Acrobat (PDF) 25kB Jul24 09) if you would like to work them on a separate sheet of paper.

Calculating Densities of Rocks and Minerals

`Volume\times Density=Mass` You can then divide both sides by density to get volume alone: `Volume=\frac{Mass}{Density}` By substituting in the values listed above, `Volume=\frac{2000\ kg}{3200\ \frac{kg}{m^{3}}}`
so the volume will be 0.625 m 3 Note that the above problem shows that densities can be in units other than grams and cubic centimeters. To avoid the potential problems of different units, many geologists use specific gravity (SG), explored in problems 8 and 9, below.

`text{volume}=text{length}\times text{width}\times text{height}` .
The volume of the cube is
`2cm\times2cm\times2cm=8cm^{3}` . The density then is the mass divided by the volume: `Density=\frac{Mass}{Volume}` `Density=\frac{40g}{8cm^{3}}=5.0\frac{g}{cm^{3}}` Thus the cube is NOT gold , since the density (5.0 g/cm 3 ) is not the same as gold (19.3 g/cm 3 ). You tell the seller to take a hike . You might even notice that the density of pyrite (a.k.a. fool's gold) is 5.0 g/cm 3 . Luckily you are no fool and know about density!
Calculating Specific Gravity of Rocks and Minerals
Take the quiz .
If this is not how you feel, you can go back to the explanations .
« Previous Page Next Page »

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Density Calculations – Worked Example Problem

Density is the measurement of the amount of mass per unit volume. Density calculations are done using the formula:
Example Problems: 1. Calculate the density in g/mL of 30 mL of solution that weighs 120 grams. 2. Calculate the density in g/mL of 0.4 L of solution weighing 150 grams. 3. Calculate the density in g/mL of 3000 mL of solution weighing 6 kg.
Example 2 We want to know the density in g/mL, but our volume is in liters. First, convert the volume to mL.
Example 3 Again, we want g/mL, and our mass is in kg. Convert the mass to grams.
Related Posts
About me and why I created this physics website.
Density Problems
- Search Website
Real World Applications — for high school level and above
- Amusement Parks
- Battle & Weapons
- Engineering
- Miscellaneous
Education & Theory — for high school level and above
- Useful Formulas
- Physics Questions
- Example Mechanics Problems
- Learn Physics Compendium
Kids Section
- Physics For Kids
- Science Experiments
- Science Fair Ideas
- Science Quiz
- Science Toys
- Teacher Resources
- Commercial Disclosure
- Privacy Policy
© Copyright 2009-2024 real-world-physics-problems.com
M D = –––– V 25.1 g 13.6 g/cm 3 = –––––– V V = 1.845588 cm 3
M D = –––– V M 11.4 g/cm 3 = –––––––––––– 1.845588 cm 3 V = 21.0 g
V Pb = V Hg
M Pb V Pb = –––– D Pb and M Hg V Hg = –––– D Hg
M Pb M Hg –––– = –––– D Pb D Hg
M Pb 25.1 –––– = –––– 11.4 13.6 M Pb = 21.0 g
Density = mass / volume rearrange to: Volume = mass / density V = 2.25 g / 2.70 g/cm 3 = 0.83 cm 3 Note: since 1 mL = 1 cm 3 , this is 0.83 mL
11.20 mL + 0.83 mL = 12.03 mL
(a) Calculate the volume (density of Al = 2.70 g cm¯ 3 (b) Calculate the thickness of the piece of Al in mm
1.50 g / 2.70 g/cm 3 = 0.555555 cm 3 (answer to a) 0.555555 cm 3 = (x) (24.0 cm) (30.0 cm) x = 0.000772 cm (to 3 sig figs) There are 10 mm in one cm, so divide the cm answer by 10 to get the thickness in mm. 0.0000772 mm (answer to b)
That means 92.276 cm 3 is Zn and 7.724 cm 3 is Cu.
(92.276 cm 3 ) (7.14 g/cm 3 ) = 658.85064 g (7.724 cm 3 ) (8.96 g/cm 3 ) = 69.20704 g
728.05768 g / 100. cm 3 = 7.28 g/cm 3 (that's the answer to three sig figs)
1.00 x 10 5 kg = 1.00 x 10 8 g 1.00 x 10 8 g / 6.62 g cm¯ 3 = 1.51 x 10 7 cm 3 1.51 x 10 7 cm 3 3 = 247 cm = 2.47 m
D = m / V V = m / D V = 71.7 g / 7.87 g/cm 3 V = 9.11 cm 3
63.0 mL + 9.11 mL = 72.1 mL (rounded off to the proper number of sig figs)
V = 71.7 g Fe x (1 cm 3 / 7.87 g Fe) = 9.11 cm 3
Let us assume 1.00 cm 3 of Al is present. That means 2.70 g of Al is present. In the rod of tin that is hollow, the mass of tin present weighs 2.70 g. We know this because the average densities of the two rods are equal. Remember, the average density of the tin rod includes the empty space. What volume of solid tin is required to provide 2.70 g? The answer is 0.370 cm 3 (from 2.70 g divided by 7.31 g/cm 3 ). The rest of the tin rod must be hollow. This is 0.670 cm 3 . Since the overall volume was 1.00 cm 3 , the fraction of the tin rod that is hollow is 0.670
Identical external dimensions means overall volume is the same for both rods. Let's call that V. It must be that mass Al = mass Sn. So, let's convert from volume Al to volume Sn with equivalent mass: 2.70 g Al 1 g Sn 1 cm 3 V x ––––––– x ––––––– x ––––––– = 0.370V 1 cm 3 1 g Al 7.31 g Sn
(V − 0.370V) / V 1 − 0.370 = 0.630
Kilograms will be changed to grams by multiplying the numerator by 1000. Liters will be changed to mL by multiplying the denominator by 1000. Those two multiplications cancel each other out. And one mL equals one cm 3 . The answer is 22.59 g/cm 3 . Here's a dimensional analysis set up showing the solution: 22.59 kg 1000 g 1 L 1 mL ––––––– x –––––– x ––––––– x ––––– = 22.59 g/cm 3 1 L 1 kg 1000 mL 1 cm 3
One mole of gold weighs 196.9665 g. V = mass / density = 196.9665 g / 19.32 g cm¯ 3 = 10.195 cm 3 The formula for volume of a cylinder is V = πr 2 L The length (L) of the wire is therefore: L = 10.195 cm 3 / [(3.14159) (0.05000 cm) 2 ] = 1298 cm By the way, note the 0.05 cm for the radius. The wire was 1 mm in diameter, which is 0.1 cm. And then half of that for the radius is 0.05 cm.
0.050 L = 50. mL = 50. cm 3 (11.34 g/cm 3 ) (50. cm 3 ) = 567 g 0.50 kg = 500 g The 0.050 L contains more mass.
0.50 kg = 500 g 500 g / 11.34 g/cm 3 = 44.1 cm 3 44.1 cm 3 = 44.1 mL = 0.0441 L The larger volume has the greater mass since both samples are lead. The answer to the problem is 0.050 L.
0.500 lb / 0.4098 lb/in 3 = 1.22 in 3
1 inch = 2.54 cm (1.00 in) 3 = (2.54 cm) 3 1.00 in 3 = 16.387 cm 3
11.34 g 16.387 cm 3 –––––– x –––––––– = 185.828 g/in 3 cm 3 in 3
0.500 lb = 226.796 g
1 in 3 226.796 g x –––––––– = 1.22 in 3 185.828 g
Chemistry Steps
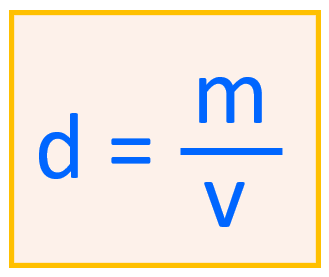
General Chemistry
Chemistry and math.
In these practice problems, we will work on determining the density, volume, and the mass of different objects. First, density is calculated by the ratio of the mass and the volume of the object:
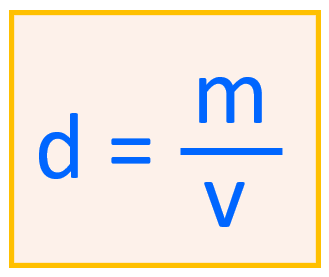
For example , what is the density of a metal if its 2.35 g sample has a volume of 0.654 g/mL?
\[{\rm{d}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,\,\frac{{\rm{m}}}{{\rm{v}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\frac{{{\rm{2}}{\rm{.35}}\,{\rm{g}}}}{{{\rm{0}}{\rm{.654}}\,{\rm{mL}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{3}}{\rm{.59}}\,{\rm{g/mL}}\]
Sometimes the volume may not be given and there are two main scenarios here depending on if the object has a regular or irregular shape . So, let’s discuss them one by one.
The density of Objects with Regular Shapes
The first example here would be the density of an object with a cubic shape. For example , a wood block with a length of 11 in, 7.5 in width and 1.95 in thickness weighs 4.93 lb. Calculate density of the block in lb/in 3 .
The mass is given and therefore, the only thing missing is the volume of the block which we find by multiplying all the sides:
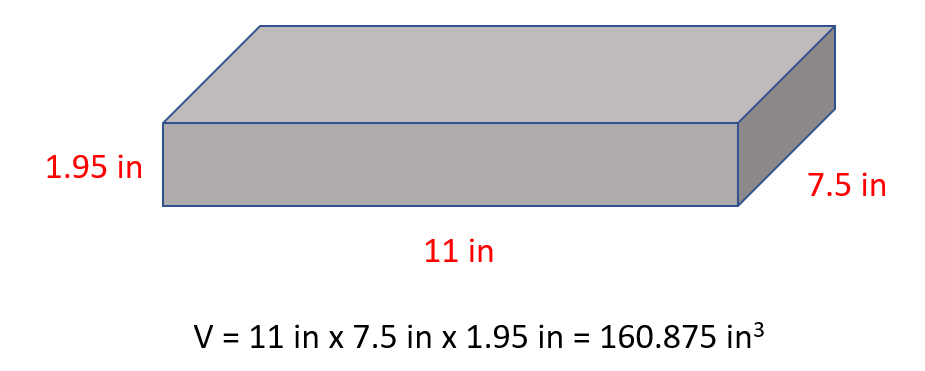
And now, we can determine the density:
\[{\rm{d}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,\,\frac{{\rm{m}}}{{\rm{v}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\frac{{{\rm{4}}{\rm{.93}}\,{\rm{lb}}}}{{{\rm{160}}{\rm{.875}}\,{\rm{i}}{{\rm{n}}^{\rm{3}}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{0}}{\rm{.031}}\,{\rm{lb/i}}{{\rm{n}}^{\rm{3}}}\]
The density of Objects with Irregular Shapes
The most common example here is the one where the density of metal pellets needs to be determined. For example , a sample containing 15.4 g of metal pellets is poured into a graduated cylinder initially containing 12.0 mL of water, causing the water level in the cylinder to rise to 16.2 mL. Calculate the density of the metal.
What you need to visualize in these problems, is that the volume of pellets or anything else that was added to water, is equal to the volume of the water displaced :
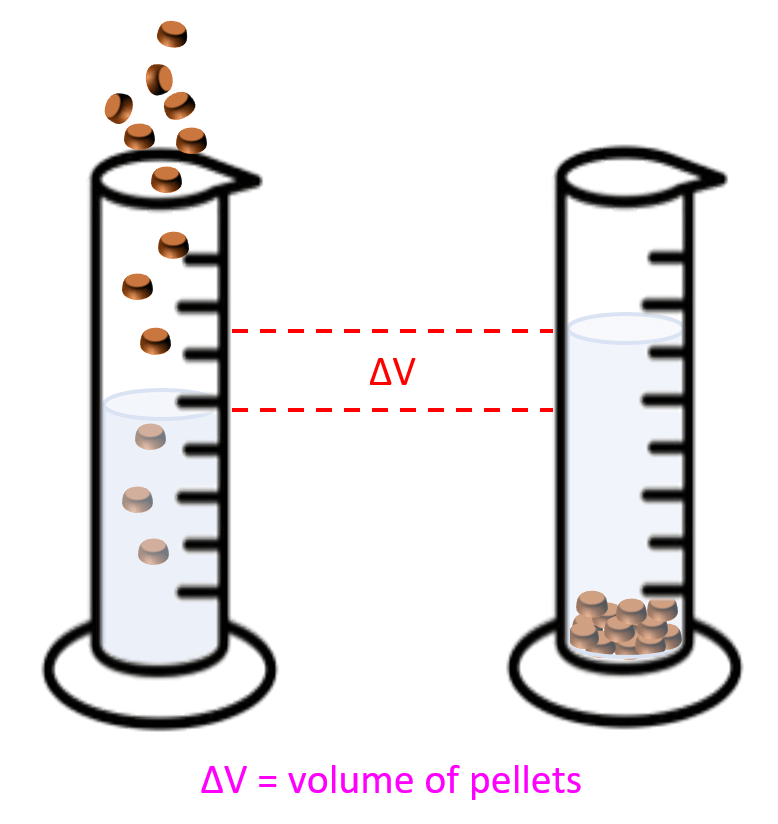
So, in this case, the volume of the pellets would be:
16.2 – 12.0 = 4.20 mL
Therefore, the density is the ratio of the mass and this difference in initial and final volumes:
\[{\rm{d}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,\,\frac{{\rm{m}}}{{\rm{v}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\frac{{{\rm{15}}{\rm{.4}}\,{\rm{g}}}}{{{\rm{4}}{\rm{.20}}\,{\rm{mL}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{3}}{\rm{.67}}\,{\rm{g/mL}}\]
Density When the Units are Different
Another type of problem is when the initial units are different than what they are asked to be in the answer. For example , determine the density of a plastic in g/cm 3 if a 1.39-lb piece occupies 6.48 in 3 volume.
First, we can calculate the density in lb/in 3 and then convert the units to g/cm 3 .
\[{\rm{d}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,\,\frac{{\rm{m}}}{{\rm{v}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\frac{{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.39}}\,{\rm{lb}}}}{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.48}}\,{\rm{i}}{{\rm{n}}^{\rm{3}}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{0}}{\rm{.2145}}\,{\rm{lb/i}}{{\rm{n}}^{\rm{3}}}\]
Now, remember, for converting two units, we treat them like separate units and do the conversions one by one. Check the “Multi-Step Unit Conversion” section here for more details.
\[{\rm{0}}{\rm{.2145}}\;\frac{{\cancel{{{\rm{lb}}}}}}{{\cancel{{{\rm{i}}{{\rm{n}}^{\rm{3}}}}}}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{453}}{\rm{.6}}\,{\rm{g}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{lb}}}}}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{(1}}\,\cancel{{{\rm{in}}{{\rm{)}}^{\rm{3}}}}}}}{{{{{\rm{(2}}{\rm{.54}}\,{\rm{cm)}}}^{\rm{3}}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{5}}{\rm{.94}}\,{\rm{g/c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{3}}}\,\,\]
So, in the first part, we converted pounds to grams, and the second multiplication was to convert in 3 to cm 3 . Remember, you need to apply the exponent to both the number and the unit when converting units raised to a power ( Converting Units Raised to Power ).
The density of a Cylinder
Another common question is determining the density of a cylinder. What you need to remember here is the formula that may not be given:
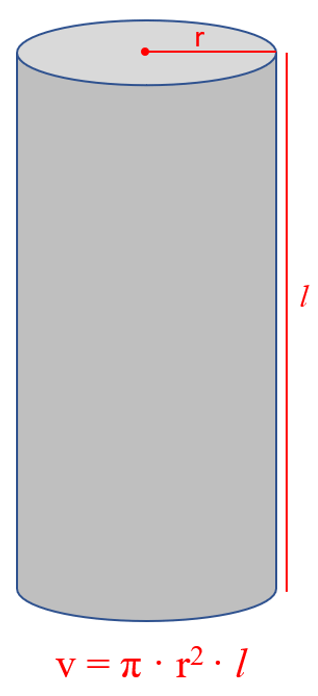
If you forget it, try to remember the formula for the surface of circle:
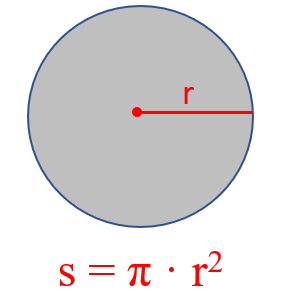
Now you can visualize the cylinder as a stack of multiple circles and therefore, its volume is the product of the circle’s surface and the height of the cylinder.
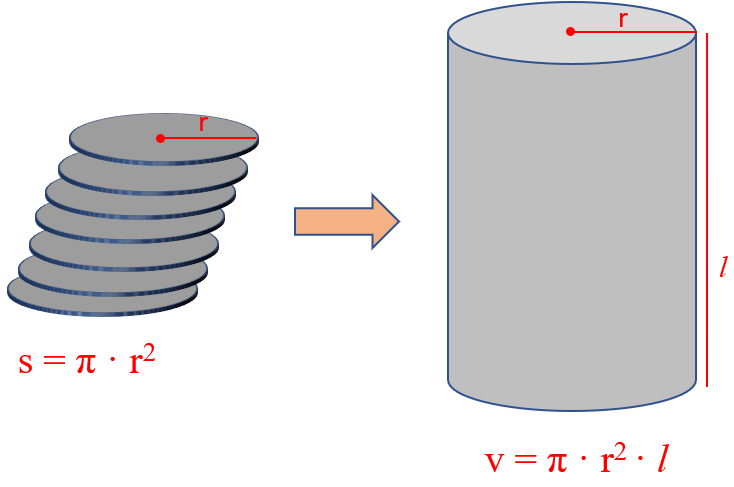
For example , a plastic cylinder has a length of 8.52 in, a radius of 2.34 in, and a mass of 5.60 lb. What is the density of the plastic in lb/in 3 ?
The volume of a cylinder is calculated by the formula v = π · r 2 · l, and therefore,
v = π · r 2 · l = 3.14 x (2.34) 2 in x 8.52 in = 146.488 in 3
The density is the ratio of the mass and the calculated volume:
\[{\rm{d}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,\,\frac{{\rm{m}}}{{\rm{v}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\frac{{{\rm{5}}{\rm{.60}}\,{\rm{lb}}}}{{{\rm{146}}{\rm{.488}}\,{\rm{i}}{{\rm{n}}^{\rm{3}}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{0}}{\rm{.0382}}\,{\rm{lb/i}}{{\rm{n}}^{\rm{3}}}\]
Mass and Volume from Density
The formula for the density can be rearranged to get an expression for the mass or the volume. For example , what is the mass of a metal block with a density of 9.25 g/ml if it occupies 14.6 cm 3 volume?
Rearranging the formula for density, we ger that the mass if the product of the volume and density:
\[{\rm{m}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,{\rm{d}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{v}}\,{\rm{ = }}\,{\rm{9}}{\rm{.25}}\,\frac{{\rm{g}}}{{\cancel{{{\rm{mL}}}}}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{14}}{\rm{.6}}\,\cancel{{{\rm{mL}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{135}}\;{\rm{g}}\]
Notice that 1 mL = 1cm 3 that is why we replaced cm 3 by ml for the volume and canceled them with the density units.
The volume is the ratio of the mass and density . For example, what is the volume of 154 g bromine in milliliters if it has a density of 3.10 g/cm 3 ?
\[{\rm{v}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,\frac{{\rm{m}}}{{\rm{d}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\,\frac{{{\rm{154}}\,{\rm{g}}}}{{{\rm{3}}{\rm{.10}}\,{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{3}}}}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{49}}{\rm{.7}}\,{\rm{g/c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{3}}}\]
- Significant Figures
- Significant Figures in Addition, Subtraction Multiplication, and Division
- Significant Figures Practice Problems
- Converting Units With Conversion Factors Dimensional Analysis
- Conversion Factors and Dimensional Analysis Practice Problems
How many dozen eggs are in 15,652 eggs?
How many years are in 5,489 days?
How many weeks are in 2.5 centuries? (1 yr. = 52 weeks)
Would 550 m 2 of fabric be enough to upholster 200 chairs if each requires 35.4 ft 2 fabric?
A 20.0-mL sample of a liquid has a mass of 17.8 g. What is the liquid’s density in grams per milliliter?
A sample containing 31.25 g of metal pellets is poured into a graduated cylinder initially containing 11.9 mL of water, causing the water level in the cylinder to rise to 18.7 mL. Calculate the density of the metal.
What is the mass of a 2.85 L sample of a liquid that has a density of 0.954 g/mL?
What is the volume of 100. g bromine in milliliters if it has a density of 3.10 g/cm 3 ?
Complete the missing data for the density, mass, and volume in the following table:
| Mass | Volume | Density |
| 2.35 g | 0.035 L | |
| 356 mL | 1.56 g/cm | |
| 14.6 kg | 4.81 g/mL |
How many kilograms of honey with a density of 1.40 kg/L are there in a gallon container?
The density of iron is 8.96 g/cm 3 . What is its density in pounds per cubic inch (lb/in 3 )?
The density of iron is 7.86 g/cm 3 . What is the volume of 5.24 lb of iron expressed in cubic inches?
A plastic cylinder has a length of 7.25 in, a radius of 1.26 in, and a mass of 841 g. What is the density of the plastic in g/cm 3 ?
What is the radius of a steel sphere that has a mass of 65.0 g and a density of 7.86 g/cm 3 ?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail. You can also subscribe without commenting.
- Which is more massive on the surface of the Earth ?
- Which is more massive on the surface of the Moon ?
- Which is heavier on the surface of the Earth ?
- Which is heavier on the surface of the Moon ?
- The phrase "more massive" should be read literally as "has more mass" not "fills more space".
- The phrase "heavier" should be read as "is pulled down more strongly by gravity" not "is more dense".
| layer | depth range (km) | mean density (kg/m ) | consistency |
|---|---|---|---|
| crust | 0–20 | 2700 | solid |
| mantle | 20–2890 | 4500 | plastic |
| outer core | 2890–5160 | ? | liquid |
| inner core | 5160–6370 | ? | solid |
- the average density of the entire Earth
- the percent of the Earth's mass located in the mantle, and
- the average density of the core.
- Write something completely different.
- Mayonnaise is essentially a mixture of vegetable oil and water with a bit of egg yolk added as an emulsifier (a substance that keeps the oil and water from separating). Traditional mayonnaise has a density of about 910 kg/m 3 while reduced fat, low calorie, or "light" mayonnaise has a density of about 1,000 kg/m 3 . Why is "light" (low calorie) mayonnaise "heavier" (more dense) than traditional mayonnaise?
- Why does "heavy cream" have a lower density than "light cream"? Explain this apparent contradiction.
- Find the mass of the air contained in a room that is 16.40 m long by 4.5 m wide by 3.26 m high.

| characteristic | value |
|---|---|
| side length | 50 cm (20 in) |
| thickness | 0.63 cm (0.248 in) |
| mass | 186 kg (410 lbs) |
| material | 24 karat gold |
| value in 2022 |
- Compute the density of gold using only the values in the table above.
- What would be the length of a side of the Castello Cube if it was crushed into a cube that was no longer hollow?
- What would be the mass of the Castello Cube if it was entirely filled with gold?
| shape | height | diameter | mass | composition* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| right circular cylinder | 39 mm, approximately | 39 mm, approximately | 1 kg, exactly | 90% platinum 10% iridium |
- cubic millimeters
- cubic centimeters (milliliters)
- cubic decimeters (liters)
- cubic meters
- the density of the IPK in kg/m 3
| material | density (kg/m ) |
|---|---|
| iridium | 22,400 |
| platinum | 21,450 |
- the volume of the IPK that is platinum
- the volume of the IPK that is iridium
- the volume of the IPK as a whole given the results of your two previous calculations
- the height and diameter of the IPK in millimeters using the results of your previous calculation and assuming that both measurements were meant to be the same, which was the intention of the designers
statistical
| object | mass | radius | density (kg/m ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | |||
| Moon | |||
| Sun |
| object | mass | radius | density (kg/m ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| the Sun | 1.99 kg | 696,000 km | |
| white dwarf star | 0.5 to 1.4 solar masses | 5,000 km | |
| neutron star | 1.4 to 3 solar masses | 10 km | |
| stellar black hole | more than 3 solar masses | 2 / (event horizon) | |
| supermassive black hole | >10 solar masses | 2 / (event horizon) | |
| the known universe | 10 kg | 13.8 × 10 light years | |
| particle (atom, molecule, ion) | partial density | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | symbol | mass (u) | (particles/cm ) | (u/cm ) |
| helium | He | 4 | 40,000 | |
| hydrogen | H | 2 | 35,000 | |
| argon 40 | Ar | 40 | 30,000 | |
| neon | Ne | 22 | 05,000 | |
| argon 36 | Ar | 36 | 02,000 | |
| methane | CH | 16 | 01,000 | |
| ammonia | NH | 18 | 01,000 | |
| carbon dioxide | CO | 44 | 01,000 | |
| oxygen | O+ | 16 | trace | n/a |
| aluminum | Al+ | 27 | trace | n/a |
| silicon | Si+ | 28 | trace | n/a |
| phosphorous | P+ | 31 | possible | n/a |
| sodium | Na+ | 23 | possible | n/a |
| magnesium | Mg+ | 24 | possible | n/a |
| total density → | ||||
- Complete the table above.
- Determine the density of the moon's atmosphere in kg/m 3 .
| object | mass (kg) | radius (m) | density (kg/m ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| iron shot put | 7.26 (16 lbs) | ||
| iron atom | (55.847 u) | ||
| iron atom's electron cloud | (26 m ) | ||
| iron nucleus | (55.847 u) | (~4 fm) |
Density – problems and solutions
Wanted : density (ρ)
Density (ρ) = 250 g/cm 3
m = ρ V = (250 g/cm 3 )(5 cm 3 ) = 1250 gram
3. Volume of water is 35 cm 3 and mass of water is 60 gram, what is the density of the water.
4. Mass of an metal is 120 gram and volume of an metal is 60 cm 3 . What is the density of the metal?
ρ = density, m = mass, V = volume
Wanted : density
Volume (V) = volume of spilled water = 40 ml
0.04 liters = (0.04)(0.001) m 3 = 0.00004 m 3
Mass (m) = 100 gram + 20 gram = 120 gram = 120 / 1000 kilogram = 0.120 kilogram
Share this:
Density Example Problem: Calculate Mass From Density
SDI Productions / Getty Images
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
Density is the amount of matter, or mass, per unit volume. This example problem shows how to calculate the mass of an object from a known density and volume.
Simple Example (Metric Units)
As an example of a simple problem, find the mass of a piece of metal that has a volume of 1.25 m 3 and a density of 3.2 kg/m 3 .
First, you should notice both the volume and the density use the volume of cubic meters. That makes the calculation easy. If the two units were not the same, you'd need to convert one so they would be in agreement.
Next, rearrange the formula for density to solve for mass.
Density = Mass ÷ Volume
Multiply both sides of the equation by volume to get:
Density x Volume = Mass
- Mass = Density x Volume
Now, plug in the numbers to solve the problem:
Mass = 3.2 kg/m 3 x 1.25 m 3
If you see the units won't cancel out, then you know you did something wrong. If that happens, rearrange the terms until the problem works. In this example, cubic meters cancels out, leaving kilograms, which is a mass unit.
Mass = 4 kg
Simple Example (English Units)
Find the mass of a blob of water with a volume of 3 gallons. It seems easy enough. Most people memorize the density of water as 1. But that's in grams per cubic centimeters. Fortunately, it's easy to look up the density of water in any unit.
Density of Water = 8.34 lb/gal
So, the problem becomes:
Mass = 8.34 lb/gal x 3 gal
Mass = 25 lb
The density of gold is 19.3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of a bar of gold in kilograms that measures 6 inches x 4 inches x 2 inches?
Density is equal to the mass divided by the volume. D = m/V where D = density m = mass V = volume We have the density and enough information to find the volume in the problem. All that remains is to find the mass. Multiply both sides of this equation by the volume, V and get: m = DV Now we need to find the volume of the gold bar. The density we have been given is in grams per cubic centimeter but the bar is measured in inches. First, we must convert the inch measurements to centimeters. Use the conversion factor of 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters. 6 inches = 6 inches x 2.54 cm/1 inch = 15.24 cm. 4 inches = 4 inches x 2.54 cm/1 inch = 10.16 cm. 2 inches = 2 inches x 2.54 cm/1 inch = 5.08 cm. Multiply all three of these numbers together to get the volume of the gold bar. V = 15.24 cm x 10.16 cm x 5.08 cm V = 786.58 cm 3 Place this into the formula above: m = DV m = 19.3 g/cm 3 x 786.58 cm 3 m = 14833.59 grams The answer we want is the mass of the gold bar in kilograms. There are 1000 grams in 1 kilogram, so: mass in kg = mass in g x 1 kg/1000 g mass in kg = 14833.59 g x 1 kg/1000 g mass in kg = 14.83 kg.
The mass of the gold bar in kilograms measuring 6 inches x 4 inches x 2 inches is 14.83 kilograms.
Tips for Success
- The biggest problem students make when solving for mass is not setting up the equation correctly. Remember, mass equals density multiplied by volume. This way, the units for volume cancel out, leaving the units for mass.
- Be sure the units used for volume and density work together. In this example, the mixed metric and English units were intentionally used to show how to convert between units.
- Volume units, in particular, can be tricky. Remember, when you determine volume, you need to apply the correct formula .
Summary of Density Formulas
Remember, you can arrange one formula to solve for mass, density, or volume. Here are the three equations to use:
- Density = Mass ÷ Volume
- Volume = Mass ÷ Density
For more example problems, use the Worked Chemistry Problems . It contains over 100 different worked example problems useful for chemistry students.
- This density example problem shows how to calculate the density of a material when the mass and volume are known.
- This example problem shows how to find the density of an ideal gas when given the molecular mass, pressure, and temperature.
- This example problem shows the steps necessary to convert inches to centimeters .
- "CRC Handbook of Tables for Applied Engineering Science," 2nd Edition. CRC Press, 1976, Boca Raton, Fla.
- How to Calculate Density - Worked Example Problem
- Density Worked Example Problem
- How to Find Mass of a Liquid From Density
- Percent Composition by Mass Example
- How to Calculate Density of a Gas
- How to Measure Volume and Density
- Freezing Point Depression Example Problem
- Molecular Mass Calculations
- Boiling Point Elevation Example Problem
- Calculating the Concentration of a Chemical Solution
- Mass Percent Composition Problem
- How to Find the Volume in a Test Tube
- What Is the Density of Air at STP?
- How to Calculate Mass Percent Composition
- Example Problem of Mass Relations in Balanced Equations
- How to Convert Grams to Moles and Moles to Grams
Density Calculations Quiz
This online quiz is intended to give you extra practice in calculating density, mass or volume of over 150 different materials in g/cm 3 , g/mL or kg/m 3 .
Select your preferences below and click 'Start' to give it a try!
| Number of problems: | |
| Density units to use: | ) and grams per milliliter (g/mL) ) |
| Display density as: | |
| Display problems as: | |
| Question format: | |
| Given values are: | |
| Show solutions: | |
| Display quiz as: | • • • |
Density, Area and Volume
Related Topics: Common Core (Geometry) Common Core for Mathematics
Examples, solutions, videos, and lessons to help High School students learn how to apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot).
Common Core: HSG-MG.A.2
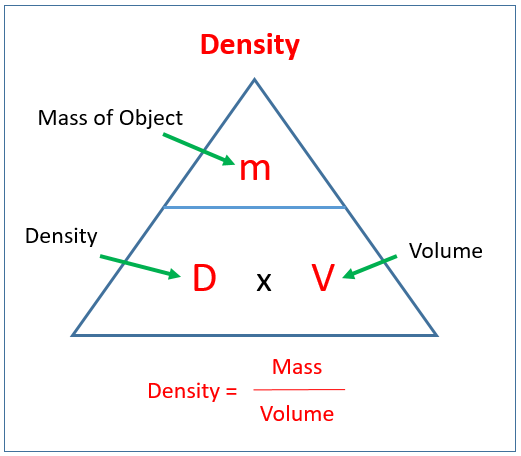
Density, Mass and Volume How to use the Density Mass Volume formula triangle and find volume of shapes. It goes through a couple of examples of finding mass. Example:
- The density of this metal block is 5 g/cm 3 . Find the mass of the block.
- The density of this prism is 4 g/cm 3 . Find the mass of the prism.
Density Word Problems Simple problems dealing with density formula (D = m / v). Example:
- What is the density of an aluminum metal block that has a mass of 27.0 g and a volume of 10.0 cm 3 ?
- What is the density of a steel block that has a mass of 7.8 g and a volume of 1.0 cm 3 ?
- What is the density of a nail that has a mass of 12.5 g and a volume of 1.6 cm 3 ?
- On Great Skies Airlines a carry-on suitcase can be no more than 12 kg and 30,000 cm 3 . Does the following suitcase qualify as a carry-on.
Density Calculations Solving density word problems using the formula triangle. Example:
- A loaf of bread has a volume of 2,270 cm 3 and a mass of 454 g. Whas the density of the bread?
- What is the volume of a tank that can hold 18.754 g of methanol whose density is 0.788 g/cm 3 ?
- A bottle has a capacity of 1.2 liters. If the density of ether is 0.74 g/ml., what mass of ether can the bottle hold?
Density Facts and Practice Problems Learn more about density and practice calculating using word problems. Density is how much mass is contained in a given volume? Example:
- What is the density of carbon dioxide gas if 0.196 g occupies a volume of 100 mL?
- A block of wood 3 cm on each side has a mass of 27 g. What is the density of the block?
- A 10.0 cm 3 sample of copper has a mass of 89.6 g. What is the density of copper?
Density Practice Problems This video shows the equation for Density and gives 2 example problems. Example:
- What is the density of a bolt that has a mass of 14 g and a volume of 2 ml?
- What is the volume of a liquid silver sample that has a density of 0.125 g/ml and a mass of 1.2g?
What is BTU (British Thermal Unit)? A short explanation of how to calculate water temperature rise in ц, given certain BTUs per hour.
Understanding the BTU - Energy produced

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

Explore Insights, Tips and Articles with HeyCoach Blogs
HeyCoach's easy-to-follow blogs, packed with tips and tricks to help you excel in the tech industry.
Top 50 DSA Practice Problems to Sharpen Your Skills
Mastering Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) is crucial for every software developer, not just for cracking coding interviews but also for solving real-world problems efficiently. Practicing DSA problems regularly enhances problem-solving skills and prepares you for various scenarios. This article presents the top 50 DSA practice problems that cover a broad spectrum of essential data structures and algorithms. These problems are tailored to improve your analytical thinking and provide a deep understanding of fundamental concepts. Let’s dive into these challenges to boost your skills in DSA.
1. Find the Maximum Subarray Sum (Kadane’s Algorithm)
Given an array of integers, find the contiguous subarray with the maximum sum.
2. Two Sum Problem
Find two numbers in a given array that add up to a specific target number.
3. Merge Two Sorted Arrays
Given two sorted arrays, merge them into a single sorted array.
4. Rotate Array
Rotate an array to the right by a given number of steps.
5. Find the Duplicate Number in an Array
Identify the duplicate number in an array containing multiple elements where one number is repeated.
6. Find the Missing Number in an Array
Given an array of integers containing numbers from 1 to n, find the one missing number.
7. Longest Palindromic Substring
Find the longest substring in a given string that reads the same forwards and backwards.
8. Reverse a String
Reverse a given string using iterative and recursive methods.
9. Check if Two Strings are Anagrams
Determine if two strings are anagrams of each other by checking character frequencies.
10. Valid Parentheses Checker
Check if a given string containing only parentheses is valid by ensuring proper opening and closing.
11. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Implement an inorder traversal of a binary tree both recursively and iteratively.
12. Find the Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree and two nodes, find their lowest common ancestor.

13. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Traverse a binary tree level by level from top to bottom.
14. Depth-First Search (DFS) on a Graph
Implement DFS to explore all nodes in a graph.
15. Breadth-First Search (BFS) on a Graph
Use BFS to traverse a graph starting from a specific node.
16. Find the Shortest Path in a Binary Maze
Determine the shortest path in a binary maze from a starting point to an endpoint using BFS.
17. Detect a Cycle in a Directed Graph (Kahn’s Algorithm)
Use Kahn’s Algorithm to detect cycles in a directed graph.
18. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Find the longest increasing subsequence in a given array of integers.
19. 0/1 Knapsack Problem
Solve the classic 0/1 knapsack problem using dynamic programming.
20. Fibonacci Sequence using Dynamic Programming
Implement the Fibonacci sequence calculation using dynamic programming for efficiency.
21. Minimum Coin Change Problem
Find the minimum number of coins required to make a given amount using a set of denominations.
22. Edit Distance Between Two Strings
Calculate the minimum number of edits (insertions, deletions, or substitutions) required to transform one string into another.
23. Reverse a Linked List
Reverse a singly linked list using iterative and recursive methods.
24. Detect a Cycle in a Linked List (Floyd’s Cycle Detection Algorithm)
Identify if a linked list has a cycle using the Tortoise and Hare method.
25. Merge Two Sorted Linked Lists
Merge two sorted linked lists into one sorted linked list.
26. Find the Intersection Point of Two Linked Lists
Find the node where two singly linked lists intersect.
27. Find the Middle of a Linked List
Locate the middle node of a linked list in one pass using the slow and fast pointer technique.
28. Implement a Stack using Queues
Use two queues to implement a stack data structure.
29. Implement a Queue using Stacks
Use two stacks to implement a queue data structure.
30. Design a Min Stack
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
31. Find the Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
Given a histogram, find the largest rectangle that can be formed with consecutive bars.
32. Implement Binary Search
Implement binary search on a sorted array to find a target value.
33. Find a Peak Element in an Array
Identify a peak element in an array where the element is greater than its neighbors.
34. Implement Quick Sort
Sort an array using the quick sort algorithm.
35. Implement Merge Sort
Implement merge sort to sort an array efficiently.
36. Heap Sort Algorithm
Use heap data structure to sort an array using heap sort.
37. Find the Kth Largest Element in an Array
Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array using a heap.
38. Solve the N-Queens Problem
Place N queens on an N×N chessboard such that no two queens threaten each other.
39. Sudoku Solver using Backtracking
Solve a Sudoku puzzle using backtracking.
40. Generate Valid Parentheses Combinations
Generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses given a number of pairs.
41. Find All Permutations of a String
Generate all possible permutations of a given string.
42. Combination Sum Problem
Find all unique combinations in a set of candidate numbers where the chosen numbers sum to a target.
43. Word Search in a 2D Grid
Given a 2D grid of letters, check if a given word exists in the grid.
44. Topological Sort in a Directed Graph
Perform a topological sort on a directed acyclic graph (DAG).
45. Find the Diameter of a Binary Tree
Calculate the longest path between any two nodes in a binary tree.
46. Check if a Binary Tree is a Valid Binary Search Tree
Verify if a binary tree meets the conditions of a binary search tree (BST).
47. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Convert a sorted array into a balanced binary search tree.
48. Design a LRU Cache
Implement an LRU (Least Recently Used) cache data structure with O(1) operations.
49. Find the Median of Two Sorted Arrays
Find the median value of two sorted arrays combined.
50. Longest Common Subsequence
Find the longest subsequence common to two given strings.
Solving these DSA problems will make you prepared for interviews and will also help in improving your coding skills. The goals of some of the problems are as follows, every problem is a chance to develop problem-solving skills and learn more about various sorts of data structures and algorithms. Solving the following DSA practice problems are significant as they prepare a candidate to solve similar problems without stress.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

COMMENTS
Problem 7: A golden-colored cube is handed to you. The person wants you to buy it for $100, saying that is a gold nugget. You pull out your old geology text and look up gold in the mineral table, and read that its density is 19.3 g/cm 3. You measure the cube and find that it is 2 cm on each side, and weighs 40 g.
m = mass. V = volume. Example Problems: 1. Calculate the density in g/mL of 30 mL of solution that weighs 120 grams. 2. Calculate the density in g/mL of 0.4 L of solution weighing 150 grams. 3. Calculate the density in g/mL of 3000 mL of solution weighing 6 kg.
Density Problems. On this page I put together a collection of density problems to help you better understand calculations involving density. Problem # 1. A solid ball has a mass of 50 grams and a volume of 20 cm 3. What is the density? (Answer: 2.5 g/cm 3) Problem # 2. A solid ball has a mass of 100 grams and a radius of 2 cm.
Short Solution: 1) Look up the density of lead in pounds per cubic inch to find a value of 0.4098 lb/in 3. 2) Divide 0.500 lb by density: 0.500 lb / 0.4098 lb/in 3 = 1.22 in 3. Long Solution, deliberately starting with metric density: 1) Look up the density of lead to find a value of 11.34 g/cm 3.
Density = Mass/Volume. Step 1: Calculate Volume. In this example, you are given the dimensions of the object, so you have to calculate the volume. The formula for volume depends on the shape of the object, but it's a simple calculation for a box: Volume = length x width x thickness. Volume = 10.0 cm x 10.0 cm x 2.0 cm.
Step 2: Plug your variables into the density formula. density = mass/volume. density = 11.2 grams/8 cm 3. density = 1.4 grams/cm 3. Answer 1: The sugar cube has a density of 1.4 grams/cm 3. Question 2: A solution of water and salt contains 25 grams of salt in 250 mL of water.
To see all my Chemistry videos, check outhttp://socratic.org/chemistryWe'll practice solving density example problems. We'll look at how to use the density n...
This chemistry video tutorial explains how to solve density problems. It provides all of the formulas and equations you need such as finding the volume of a...
For example, a wood block with a length of 11 in, 7.5 in width and 1.95 in thickness weighs 4.93 lb. Calculate density of the block in lb/in 3. The mass is given and therefore, the only thing missing is the volume of the block which we find by multiplying all the sides: And now, we can determine the density:
For each problem below, write the equation and show your work. Always use units and box in your final answer. The density of silver (Ag) is 10.5 g/cm3. Find the mass of Ag that occupies 965 cm3 of space. A 2.75 kg sample of a substance occupies a volume of 250.0 cm3. Find its density in g/cm3.
Show your work! - Sample A has a mass of 24.0 g and a volume of 6.0 ml. - Sample B has a mass of 12.0 g and a volume of 6.0 ml. - Sample C has a mass of 12.0 g and a volume of 3.0 ml. 10. A graduated cylinder contains 17.5 ml of water. When a metal cube is placed onto the cylinder, its water level rises to 20.3 ml. Calculate the following:
conceptual. Mayonnaise is essentially a mixture of vegetable oil and water with a bit of egg yolk added as an emulsifier (a substance that keeps the oil and water from separating). Traditional mayonnaise has a density of about 910 kg/m 3 while reduced fat, low calorie, or "light" mayonnaise has a density of about 1,000 kg/m 3.
Calculate density, and identify substances using a density chart. Density is a measure of the amount of mass in a certain volume. This physical property is often used to identify and classify substances. It is usually expressed in grams per cubic centimeters, or g/cm3. The chart on the right lists the densities of some common materials.
ρ = m / V = 0.120 kg / 0.00002 m 3 = 120 kg / 0.02 m 3 = 6000 kg/m 3. What is density? Answer: Density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume.It is calculated by dividing the mass of an object by its volume: Density=MassVolume Density = Volume Mass . How does the density of an object relate to its ability to float or sink in a fluid?
Next, rearrange the formula for density to solve for mass. Density = Mass ÷ Volume. Multiply both sides of the equation by volume to get: Density x Volume = Mass. or. Mass = Density x Volume. Now, plug in the numbers to solve the problem: Mass = 3.2 kg/m 3 x 1.25 m 3.
What is density? We take a look at how the math in the density equation works. We use a simple chemistry experiment to find the density of peanut oil, water ...
This online quiz is intended to give you extra practice in calculating density, mass or volume of over 150 different materials in g/cm 3, g/mL or kg/m 3. Select your preferences below and click 'Start' to give it a try! Number of problems: 1. 5. 10. 25.
Density, Mass and Volume. How to use the Density Mass Volume formula triangle and find volume of shapes. It goes through a couple of examples of finding mass. Example: The density of this metal block is 5 g/cm 3. Find the mass of the block. The density of this prism is 4 g/cm 3. Find the mass of the prism. Show Video.
Example 1. A piece of gold has a mass of 115.92 grams and a volume of 6 cm 3.What is its density? d = m/v. d = 115.92 g/6cm 3. d = 19.32 g/cm 3. Note that the density of a substance stays the same ...
Conclusion. Solving these DSA problems will make you prepared for interviews and will also help in improving your coding skills. The goals of some of the problems are as follows, every problem is a chance to develop problem-solving skills and learn more about various sorts of data structures and algorithms.